

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 135-146.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023426
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王正( ), 李新, 张建贵, 柴继宽, 赵桂琴, 牛奎举(
), 李新, 张建贵, 柴继宽, 赵桂琴, 牛奎举( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-14
修回日期:2024-01-18
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-07-15
通讯作者:
牛奎举
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: niukj@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Zheng WANG( ), Xin LI, Jian-gui ZHANG, Ji-kuan CHAI, Gui-qin ZHAO, Kui-ju NIU(
), Xin LI, Jian-gui ZHANG, Ji-kuan CHAI, Gui-qin ZHAO, Kui-ju NIU( )
)
Received:2023-11-14
Revised:2024-01-18
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-07-15
Contact:
Kui-ju NIU
摘要:
为探究外源褪黑素对燕麦抗叶斑病的诱导效应及诱导抗病机理,本研究以‘牧乐思’燕麦品种为试验材料,叶面喷施不同浓度褪黑素(0、10、100、250、500和1000 μmol·L-1)后接种燕麦徳氏霉病原菌,以未接种病原菌为对照,接种病原菌9 d后统计病情指数和采集叶片测定抗氧化系统、苯丙烷代谢相关生理指标和相关酶基因相对表达量。结果表明,叶斑病明显抑制燕麦生长,喷施不同浓度褪黑素后叶斑病病情指数明显降低,其中100 μmol·L-1褪黑素处理下病原菌体外诱导效率、过氧化氢酶、苯丙氨酸解氨酶活性和抗坏血酸过氧化物酶基因表达量最高,分别高于只接种病原菌处理50.72%、80.32%、3.88%和148.00%;250 μmol·L-1褪黑素处理下超氧阴离子产生速率和丙二醛含量最低,分别低于只接种病原菌处理28.27%和86.62%,超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶、抗坏血酸过氧化物酶、肉桂酸-4-羟化酶、4-香豆酸∶辅酶A连接酶活性、木质素、总酚、类黄酮含量和超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶、苯丙氨酸解氨酶、4-香豆酸∶辅酶A连接酶、肉桂酸-4-羟化酶基因表达量最高,分别高于只接种病原菌处理128.23%、137.14%、74.00%、52.65%、26.73%、1.40%、10.33%、13.70%、352.56%、80.32%、65.71%、26.65%、52.65%和20.11%;500 μmol·L-1褪黑素处理下过氧化氢含量最低,低于只接种病原菌处理75.45%,叶绿素含量最高,高于只接种病原菌处理81.35%。综合各项指标结果,筛选出最适诱导浓度为250 μmol·L-1,试验结果可为燕麦防治叶斑病提供新途径。
王正, 李新, 张建贵, 柴继宽, 赵桂琴, 牛奎举. 外源褪黑素介导抗氧化和苯丙烷代谢提高燕麦叶斑病抗性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 135-146.
Zheng WANG, Xin LI, Jian-gui ZHANG, Ji-kuan CHAI, Gui-qin ZHAO, Kui-ju NIU. Exogenous melatonin mediates the antioxidant system and phenylpropanoid metabolism to induce resistance to leaf spot disease in oat[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 135-146.
| 引物Primer | 上游引物Upstream primer | 下游引物Downstream primer |
|---|---|---|
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | TGTCGATCGGGCAGATGATG | CCCCACCACCAGGTTTCATT |
| 过氧化物酶POD | AACGTGCAGAACCCGATCAT | AGCGGTAGTCCCTCTGATGT |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | CGGAGTCCCTCCACATGTTC | TTGACGTAGTGGGACTTGCC |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶APX | TTGTCGCTCTATCTGGTGGC | AGCCCCTCAGATTCTCCCTT |
| 苯丙氨酸解氨酶PAL | CTATCGATCTGCGCCACCTT | TGTGATTGGTGCTCAGGGTC |
| 4-香豆酸∶辅酶A连接酶4CL | AGGATGCTGCTGTCGTATCG | TGCGACGAACTGCTTGATCT |
| 肉桂酸-4-羟化酶C4H | AACTACGGCGACTTCATCCC | TCCTTGAAGAGCTTGAGGCG |
| 肌动蛋白基因The actin gene | GAGCGGGAAATTGTAAGGGAC | ATGGATGGCTGGAAGAGGAC |
表1 引物设计
Table 1 The qRT-PCR primer design
| 引物Primer | 上游引物Upstream primer | 下游引物Downstream primer |
|---|---|---|
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | TGTCGATCGGGCAGATGATG | CCCCACCACCAGGTTTCATT |
| 过氧化物酶POD | AACGTGCAGAACCCGATCAT | AGCGGTAGTCCCTCTGATGT |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | CGGAGTCCCTCCACATGTTC | TTGACGTAGTGGGACTTGCC |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶APX | TTGTCGCTCTATCTGGTGGC | AGCCCCTCAGATTCTCCCTT |
| 苯丙氨酸解氨酶PAL | CTATCGATCTGCGCCACCTT | TGTGATTGGTGCTCAGGGTC |
| 4-香豆酸∶辅酶A连接酶4CL | AGGATGCTGCTGTCGTATCG | TGCGACGAACTGCTTGATCT |
| 肉桂酸-4-羟化酶C4H | AACTACGGCGACTTCATCCC | TCCTTGAAGAGCTTGAGGCG |
| 肌动蛋白基因The actin gene | GAGCGGGAAATTGTAAGGGAC | ATGGATGGCTGGAAGAGGAC |
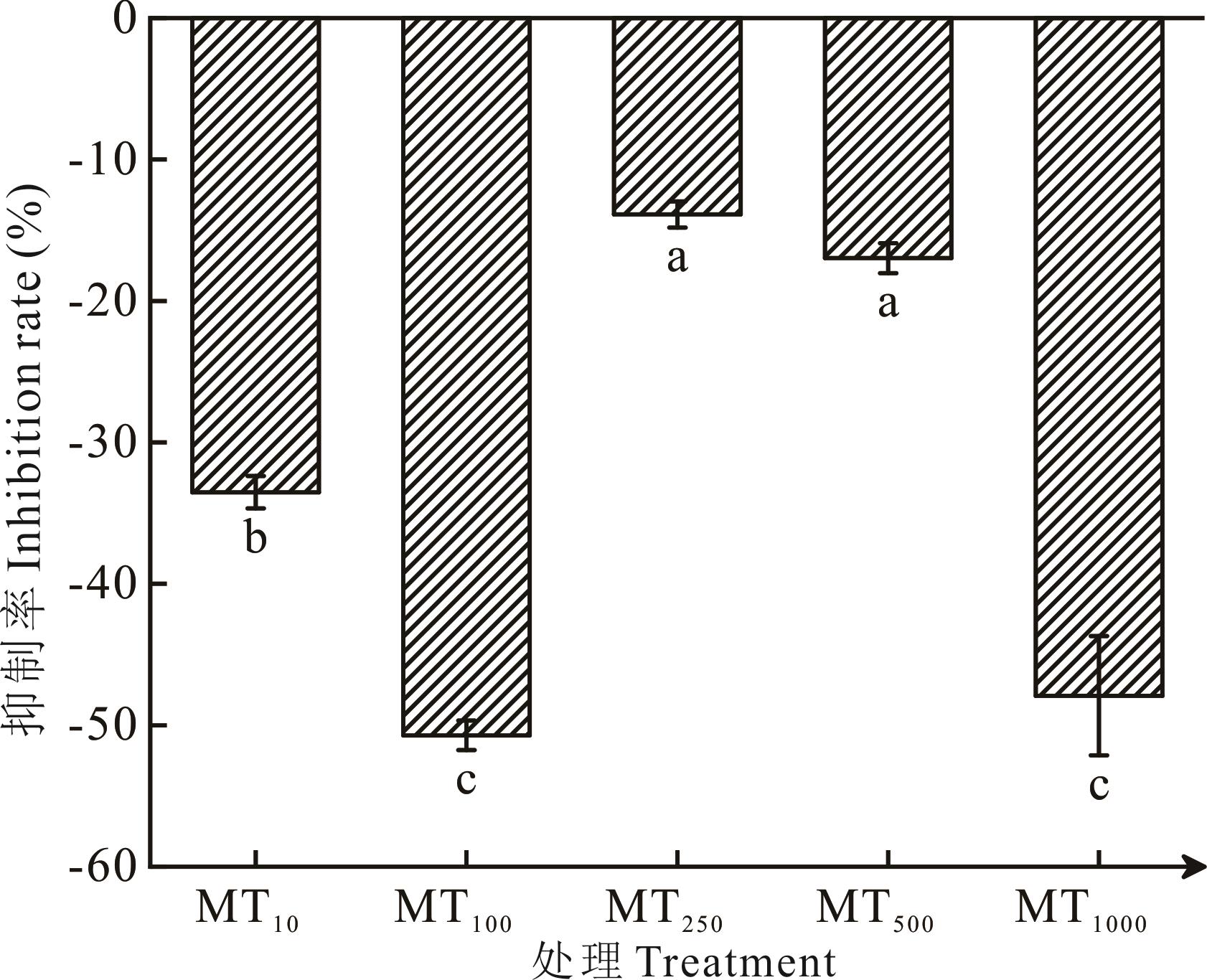
图1 外源褪黑素对病原菌生长的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。The different lowercase letters represent significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 The effect of exogenous melatonin on the growth of pathogenic bacteria
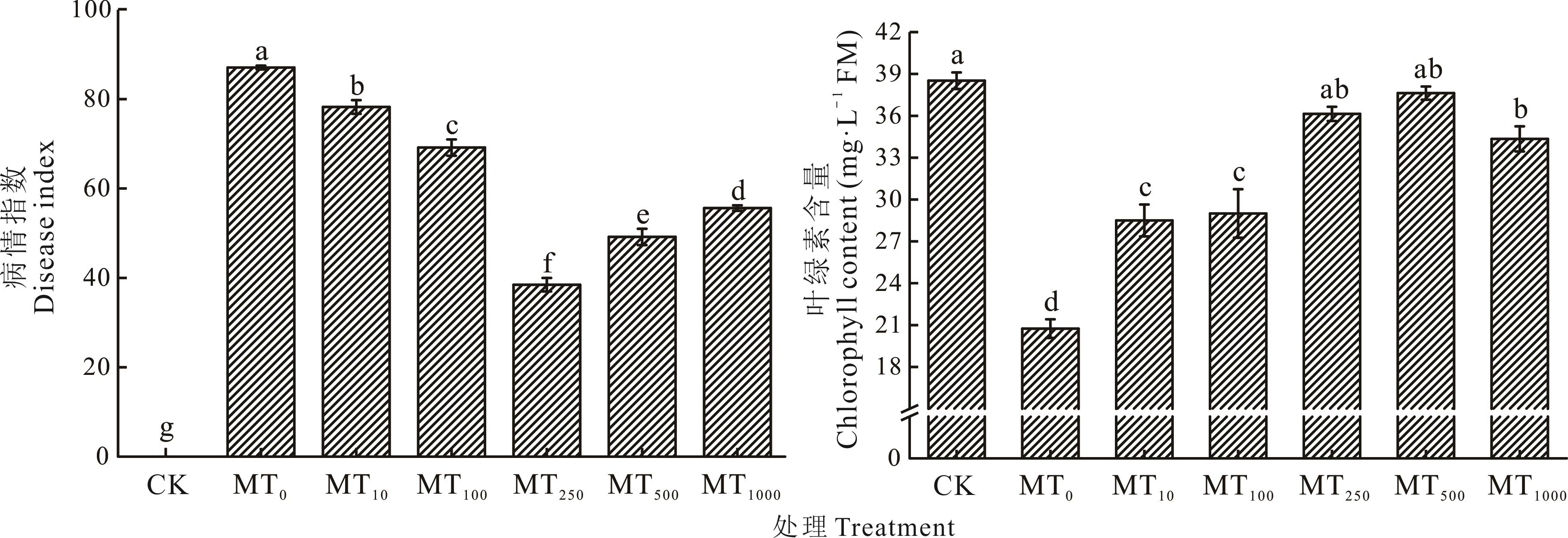
图4 外源褪黑素对燕麦苗期接种病原菌后叶片病情指数和叶绿素含量的影响
Fig.4 The effect of exogenous melatonin on the disease index and chlorophyll content of oat leaves after inoculation with pathogenic bacteria during the seedling stage

图5 外源褪黑素对燕麦幼苗接种病原菌后叶片H2O2含量、O2·-产生速率和丙二醛含量的影响
Fig.5 Effects of exogenous melatonin on H2O2 content, superoxide anion production rate, and malondialdehyde content in leaves of oat seedlings inoculated with pathogenic bacteria
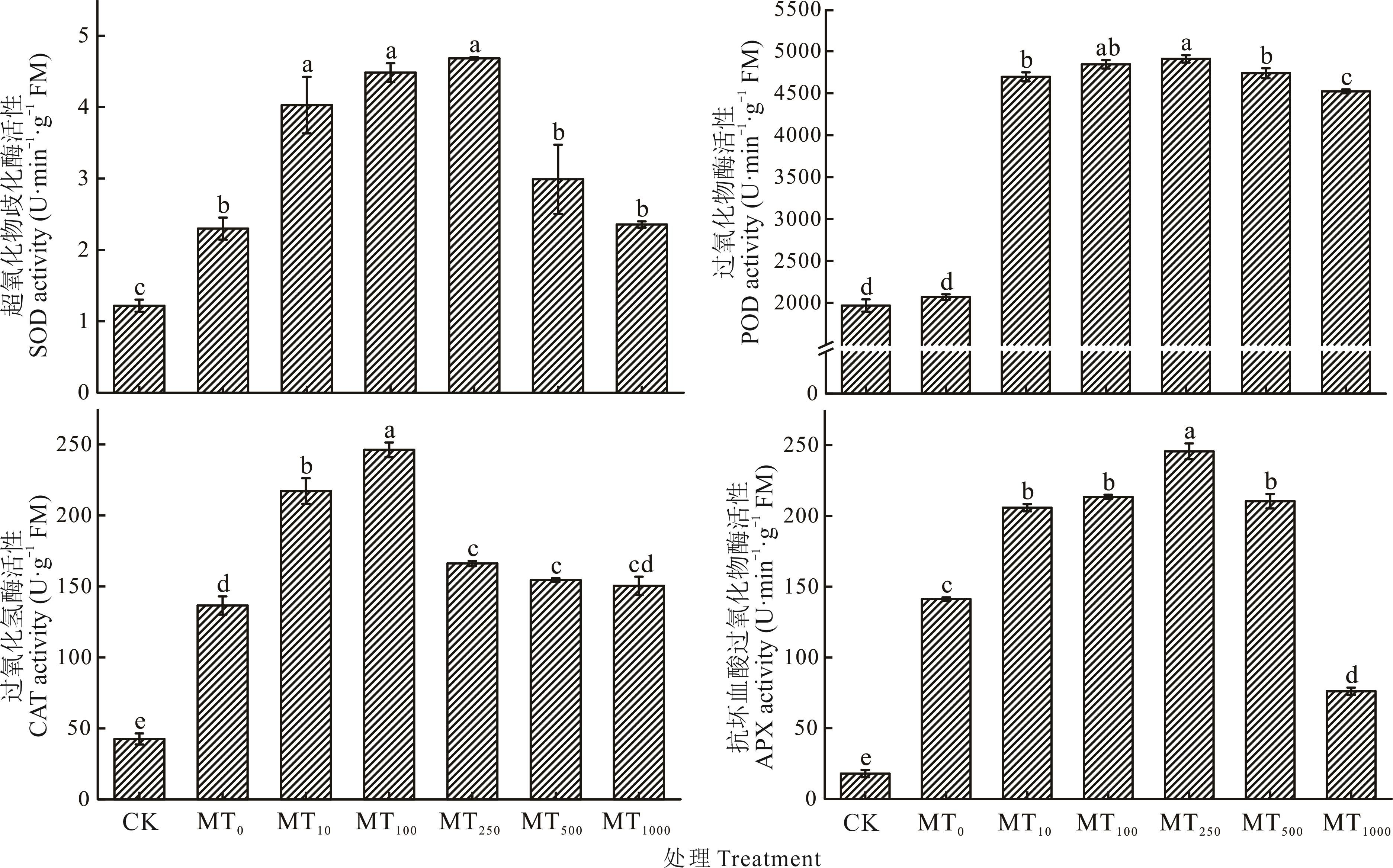
图6 外源褪黑素对燕麦幼苗接种病原菌后叶片抗氧化酶活性的影响SOD: superoxide dismutase; POD: peroxidase; CAT: catalase; APX: aseorbate peroxidase.
Fig.6 Effect of exogenous melatonin on antioxidant enzyme activity in oat seedlings after inoculation with pathogenic bacteria

图7 外源褪黑素对燕麦苗期接种病原菌后叶片苯丙烷代谢相关酶活性的影响PAL: phenylalnine ammonialyase; C4H: cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase; 4CL: 4-conumarate∶CoA ligase.
Fig.7 Effect of exogenous melatonin on the activity of phenylpropanoid metabolism related enzymes in oat leaves after inoculation with pathogenic bacteria during seedling stage
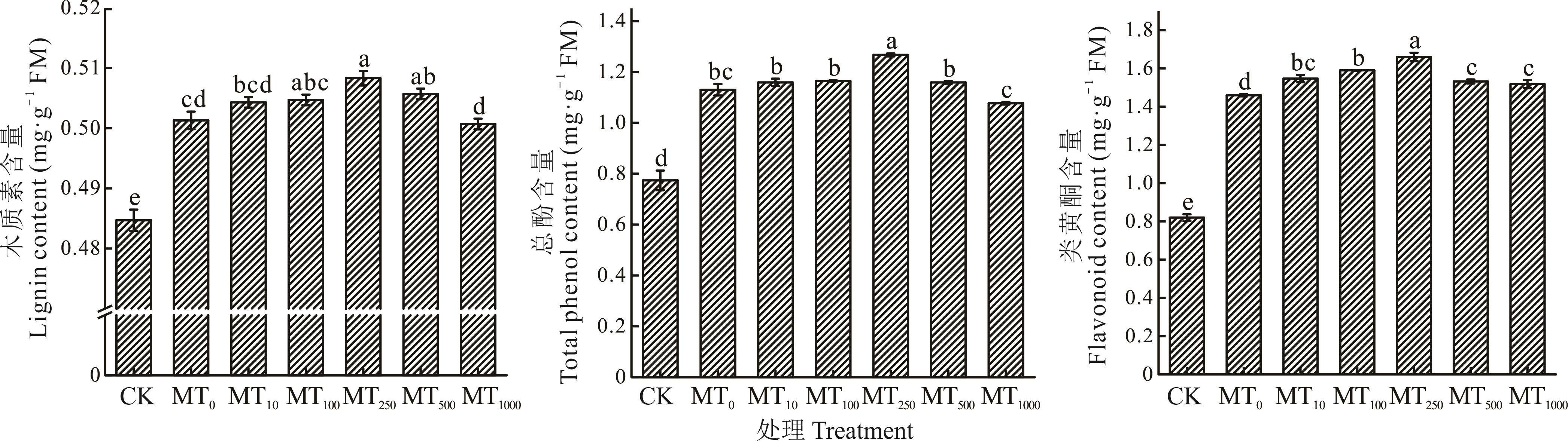
图8 外源褪黑素对燕麦苗期接种病原菌后叶片木质素、总酚和类黄酮含量的影响
Fig.8 The effect of exogenous melatonin on the lignin, total phenol, and flavonoid content of oat leaves after inoculation with pathogenic bacteria during the seedling stage

图9 外源褪黑素对燕麦苗期接种病原菌后叶片酶基因相对表达量的影响
Fig.9 The effect of exogenous melatonin on the relative expression of enzyme genes in oat leaves after inoculation with pathogenic bacteria during the seedling stage
| 1 | Ye X L, Gan Z, Wan Y, et al. Advances and perspectives in forage oat breeding. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. |
| 叶雪玲, 甘圳, 万燕, 等. 饲用燕麦育种研究进展与展望. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. | |
| 2 | Zhang M, Zhang M L, Guo J, et al. Summary of distribution, production, nutritional and physiological value of Avena sativa L. in China. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014(2): 116-118, 126. |
| 张曼, 张美莉, 郭军, 等. 中国燕麦分布、生产及营养价值与生理功能概述. 内蒙古农业科技, 2014(2): 116-118, 126. | |
| 3 | Nie X M, Zhao G Q, Sun H Y, et al. Incidence of oat leaf spot and pathogen identification in the main oat production areas of Gansu Province. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 157-167. |
| 聂秀美, 赵桂琴, 孙浩洋, 等. 甘肃省燕麦主产区叶斑病调查及病原鉴定. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 157-167. | |
| 4 | Dong B Z, Zhang X Y, Zhao G Q, et al. Evaluation of pesistance of oat varieties to leaf spot pathogens//Proceedings of the 2015 Academic Annual Meeting of the Chinese Society for Plant Pathology. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2015: 246. |
| 东保柱, 张笑宇, 赵桂琴, 等. 燕麦品种对叶斑病菌的抗性评价//中国植物病理学会2015年学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015: 246. | |
| 5 | Dong B Z, Zhang X Y, Zhao G Q, et al. Indoor toxicity and field control effect of different fungicides on oat leaf spot disease// Proceedings of the 2015 Academic Annual Meeting of the Chinese Society of Plant Pathology. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2015: 247. |
| 东保柱, 张笑宇, 赵桂琴, 等. 不同杀菌剂对燕麦叶斑病的室内毒力和田间防效//中国植物病理学会2015年学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015: 247. | |
| 6 | Song J L, Cheng X K, Liu P F, et al. Current situation of multidrug resistance of plant pathogens to fungicides. Plant Protection, 2021, 47(6): 28-33, 65. |
| 宋佳露, 程星凯, 刘鹏飞, 等. 植物病原菌对杀菌剂多药抗性的发生现状. 植物保护, 2021, 47(6): 28-33, 65. | |
| 7 | Dong L L. Study on plant induced disease resistance mechanism. Value Engineering, 2010, 29(24): 233. |
| 董玲玲. 关于植物诱导抗病机理的研究. 价值工程, 2010, 29(24): 233. | |
| 8 | Afreen F, Zobayed S M A, Kozai T. Melatonin in Glycyrrhiza uralensis: response of plant roots to spectral quality of light and UV-B radiation. Journal of Pineal Research, 2006, 41(2): 108-115. |
| 9 | Chen X, Latordap P, Liu F Q. Exogenous melatonin enhances rice plant resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Disease, 2020, 104(6): 1701-1708. |
| 10 | Li C, He Q L, Zhang F, et al. Melatonin enhances cotton immunity to Verticillium wilt via manipulating lignin and gossypol biosynthesis. The Plant Journal, 2019, 100(1): 784-800. |
| 11 | Liu Y P. Physiological mechanism of exogenous melation inducing resistance to clubroot in Chinese cabbage. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. |
| 刘亚萍. 外源褪黑素对大白菜根肿病抗性的生理机制研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. | |
| 12 | Yuan J H, Cao L X, Shi B H, et al. Evaluation of main oat cultivars or lines resistance against Drechslera leaf spot in northwest Hebei Province. China Plant Protection, 2014, 34(2): 31-34. |
| 袁军海, 曹丽霞, 石碧红, 等. 冀西北地区燕麦主栽品种(系)对叶斑病抗性鉴定. 中国植保导刊, 2014, 34(2): 31-34. | |
| 13 | Arnon D I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiology, 1949, 24(1): 1-15. |
| 14 | Chakrabarty D, Datta S K. Micropropagation of gerbera: Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities during acclimatization process. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2008, 30(1): 325-331. |
| 15 | Ke D, Sun G, Wang Z. Effects of superoxide radicals on ACC synthase activity in chilling-stressed etiolated mungbean seedlings. Plant Growth Regulation, 2007, 51(1): 83-91. |
| 16 | Kumar G, Knowles N R. Changes in lipid peroxidation and lipolytic and free-radical scavenging enzyme activities during aging and sprouting of potato (Solanum tuberosum) seed-tubers. Plant Physiology, 1993, 102(1): 115-124. |
| 17 | Beauchamp C, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry, 1971, 44(1): 276-287. |
| 18 | Munoz-Munoza J L, Garcia-Molina F, Garcia-Ruiz P A, et al. Enzymatic and chemical oxidation of trihydroxylated phenols. Food Chemistry, 2009, 113(1): 435-444. |
| 19 | Li L, Li N H, Jiang S M. Experimental guide of plant physiology module. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 37-103. |
| 李玲, 李娘辉, 蒋素梅. 植物生理学模块实验指导. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 37-103. | |
| 20 | Nakano Y, Asada K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1980, 22(1): 867-880. |
| 21 | Cao J K, Jiang W B, Zhao Y M. Guidance on postharvest physiological experiments of fruits and vegetables. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2017. |
| 曹建康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导. 北京: 中国轻工出版社, 2017. | |
| 22 | Xu J, Zhang Z, Li X, et al. Effect of nitrous oxide against Botrytis cinerea and phenylpropanoid pathway metabolism in table grapes. Scientia Horticulturae, 2019, 254: 99-105. |
| 23 | Bhaskara R M V, Arul J, Angers P, et al. Chitosan treatment of wheat seeds induces resistance to Fusarium graminearum and improves seed quality. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1999, 47(1): 1208-1216. |
| 24 | He J. Screening of inducing antibiotics and preliminary study on the mechanism of Taizi ginseng against leaf spot disease. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2022. |
| 何洁. 太子参抗叶斑病的诱抗剂筛选及机理初探. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2022. | |
| 25 | Li S E. Exogenous melatonin induces disease resistance against pathogen infection in cherry tomato fruit during postharvest storage. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2022. |
| 李生娥. 外源褪黑素诱导采后番茄果实抗病机制的研究. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2022. | |
| 26 | Deitz K J, Mittler R, Noctor G. Recent progress in understanding the role of reactive oxygen species in plant cell signaling. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171(3): 1535. |
| 27 | Zhu J C, Yang Y, Lou H, et al. Regulation of Fusarium wilt resistance in cotton by exogenous melatonin. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2023, 39(1): 243-252. |
| 朱金成, 杨洋, 娄慧, 等. 外源褪黑素调控棉花枯萎病抗性研究. 生物技术通报, 2023, 39(1): 243-252. | |
| 28 | Li Z Z, Zhang S J, Xue J X, et al. Exogenous melatonin treatment induces disease resistance against Botrytis cinerea on post-harvest grapes by activating defence responses. Foods, 2022, 11(1): 11-17. |
| 29 | Lin Y, Fan L, Xia X, et al. Melatonin decreases resistance to postharvest green mold on citrus fruit by scavenging defense-related reactive oxygen species. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2019, 153(1): 21-30. |
| 30 | Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55(2): 373-399. |
| 31 | Liang X, Lu F P, Lu H, et al. Preliminary study of the function of catalase in cassava resistance to mite. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2017, 38(2): 343-348. |
| 梁晓, 卢芙萍, 卢辉, 等. 保护酶CAT在木薯种质抗螨中的功能初步研究. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(2): 343-348. | |
| 32 | Guo Z G, Wang M X, Cui L, et al. Research progress on the underlying mechanisms of plant defense enzymes in response to pest stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(12): 4248-4258. |
| 郭祖国, 王梦馨, 崔林, 等. 6种防御酶调控植物体应答虫害胁迫机制的研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(12): 4248-4258. | |
| 33 | Yin L H. Mechanism and resistance induced on marssonina apple blotch. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014. |
| 殷丽华. 苹果属资源对苹果褐斑病的抗性机理及抗性诱导研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. | |
| 34 | Li C X, Chen L L, Zhao R R, et al. Melatonin induces disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato fruit by activating jasmonic acid signaling pathway. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(1): 6116-6124. |
| 35 | Sun Y K, Liu Z Y, Lan G P, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin on resistance of cucumber to downy mildew. Scientia Horticulturae, 2019, 255(1): 231-241. |
| 36 | Shang J, Wu W Z, Ma Y G. Phenylpropanoid metabolism pathway in plants. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2022, 38(11): 1467-1476. |
| 尚军, 吴旺泽, 马永贵. 植物苯丙烷代谢途径. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2022, 38(11): 1467-1476. | |
| 37 | Xie F, Hao L, Wang Z J, et al. Advances in understanding how branches of the phenylpropanoid pathway respond to biotic stress. China Plant Protection, 2023, 43(2): 23-30. |
| 谢凤, 郝乐, 王振杰, 等. 苯丙烷代谢途径分支对生物胁迫响应的研究进展. 中国植保导刊, 2023, 43(2): 23-30. | |
| 38 | Li S, Xu Y, Bi Y, et al. Melatonin treatment inhibits gray mold and induces disease resistance in cherry tomato fruit during postharvest. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2019, 157(1): 110962. |
| 39 | Qu G, Wu W, Ba L, et al. Melatonin enhances the postharvest disease resistance of blueberries fruit by modulating the jasmonic acid signaling pathway and phenylpropanoid metabolites. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10(1): 957581. |
| 40 | Zhang Z, Nie Y T, Cui K L, et al. Research progress on the function of melatonin in regulating growth, development and stress resistance in herbaceous species. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(9): 2571-2581. |
| 张昭, 聂宇婷, 崔凯伦, 等. 褪黑素调控草类植物生长发育及抗逆性功能研究进展. 草地学报, 2023, 31(9): 2571-2581. | |
| 41 | Xing X, Li L L, Yang H M, et al. Toxicity and control effects of fungicides in oat leaf spot by Drechslera avenae. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 48(4): 62-66. |
| 邢星, 李乐乐, 杨海明, 等. 不同杀菌剂对燕麦叶斑病菌的毒力和田间防效. 东北农业科学, 2023, 48(4): 62-66. |
| [1] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [2] | 关皓, 许多, 李海萍, 贾志锋, 马祥, 刘文辉, 陈有军, 李欣洋, 黄艳玲, 周青平, 陈仕勇. 高寒地区17个燕麦品种营养品质及瘤胃降解特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 185-198. |
| [3] | 米春娇, 洪流, 马馼, 毛培胜. 谷胱甘肽引发对老化燕麦种胚线粒体抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 51-59. |
| [4] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [5] | 杜文盼, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 杨莉, 张建贵, 史怡超, 张官禄. 根系分隔方式对燕麦/豌豆间作地上生物量、土壤养分及根系性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 25-36. |
| [6] | 桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85. |
| [7] | 张昭, 伏莹莹, 孙浩文, 孙逢雪, 闫慧芳. 不同品种燕麦种子活力鉴定与耐贮藏性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 165-174. |
| [8] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [9] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [10] | 慕平, 柴继宽, 苏玮娟, 章海龙, 赵桂琴. 燕麦不同组合正、反交杂种后代的表型及遗传参数分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 73-86. |
| [11] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [12] | 鲍根生, 李媛, 冯晓云, 张鹏, 孟思宇. 高寒区氮添加和间作种植互作对燕麦和豌豆根系构型影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 73-84. |
| [13] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| [14] | 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [15] | 李文龙, 李峰, 张仲鹃, 王殿清, 王欢, 靳慧卿, 特木热, 胡志玲, 陶雅. 鄂尔多斯高原北部一年两季燕麦种植模式生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 159-168. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||