
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 112-119.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022266
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiao-ming CHEN( ), Dong-ying HAN, Gui-long SONG(
), Dong-ying HAN, Gui-long SONG( )
)
Received:2022-06-28
Revised:2022-07-29
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-04-21
Contact:
Gui-long SONG
Xiao-ming CHEN, Dong-ying HAN, Gui-long SONG. Effect of arsenic stress on arsenic uptake and root morphological changes in seashore paspalum[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 112-119.
处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length (cm) | 总根表面积 Total root surface area (cm2) | 平均直径 Average diameter (mm) | 总根体积 Total root volume(cm3) | 根尖数 Number of root tips (No.) | 分枝数 Number of branches (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 737.657±32.453a | 54.953±2.321a | 0.234±0.041b | 0.328±0.071a | 3812±164c | 2921±113a |
| As10 | 695.321±25.282b | 48.866±3.118b | 0.233±0.052b | 0.276±0.052b | 5551±103a | 2725±184ab |
| As100 | 558.665±22.310c | 46.327±3.225c | 0.262±0.013a | 0.307±0.093ab | 5033±76b | 2559±96b |
Table 1 Changes of root morphological of seashore paspalum under arsenic treatment
处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length (cm) | 总根表面积 Total root surface area (cm2) | 平均直径 Average diameter (mm) | 总根体积 Total root volume(cm3) | 根尖数 Number of root tips (No.) | 分枝数 Number of branches (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 737.657±32.453a | 54.953±2.321a | 0.234±0.041b | 0.328±0.071a | 3812±164c | 2921±113a |
| As10 | 695.321±25.282b | 48.866±3.118b | 0.233±0.052b | 0.276±0.052b | 5551±103a | 2725±184ab |
| As100 | 558.665±22.310c | 46.327±3.225c | 0.262±0.013a | 0.307±0.093ab | 5033±76b | 2559±96b |
处理 Treatment | 根长Root length (cm) | 根表面积Root surface-area (cm2) | 根体积Root volume (cm3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D: 0~0.5 mm | D>0.5 mm | D: 0~0.5 mm | D>0.5 mm | D: 0~0.5 mm | D>0.5 mm | |
| CK | 636.112±20.192a | 101.141±9.255b | 25.890±2.262a | 21.964±4.226b | 0.185±0.029a | 0.224±0.048c |
| As10 | 599.313±22.274a | 95.567±9.189b | 23.477±3.611a | 19.384±1.194b | 0.114±0.031b | 0.296±0.087b |
| As100 | 438.809±17.341b | 119.148±7.224a | 16.300±1.807b | 25.737±0.970a | 0.080±0.017c | 0.359±0.031a |
Table 2 Root length, root surface area and root volume with different diameter of seashore paspalum under arsenic treatment
处理 Treatment | 根长Root length (cm) | 根表面积Root surface-area (cm2) | 根体积Root volume (cm3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D: 0~0.5 mm | D>0.5 mm | D: 0~0.5 mm | D>0.5 mm | D: 0~0.5 mm | D>0.5 mm | |
| CK | 636.112±20.192a | 101.141±9.255b | 25.890±2.262a | 21.964±4.226b | 0.185±0.029a | 0.224±0.048c |
| As10 | 599.313±22.274a | 95.567±9.189b | 23.477±3.611a | 19.384±1.194b | 0.114±0.031b | 0.296±0.087b |
| As100 | 438.809±17.341b | 119.148±7.224a | 16.300±1.807b | 25.737±0.970a | 0.080±0.017c | 0.359±0.031a |
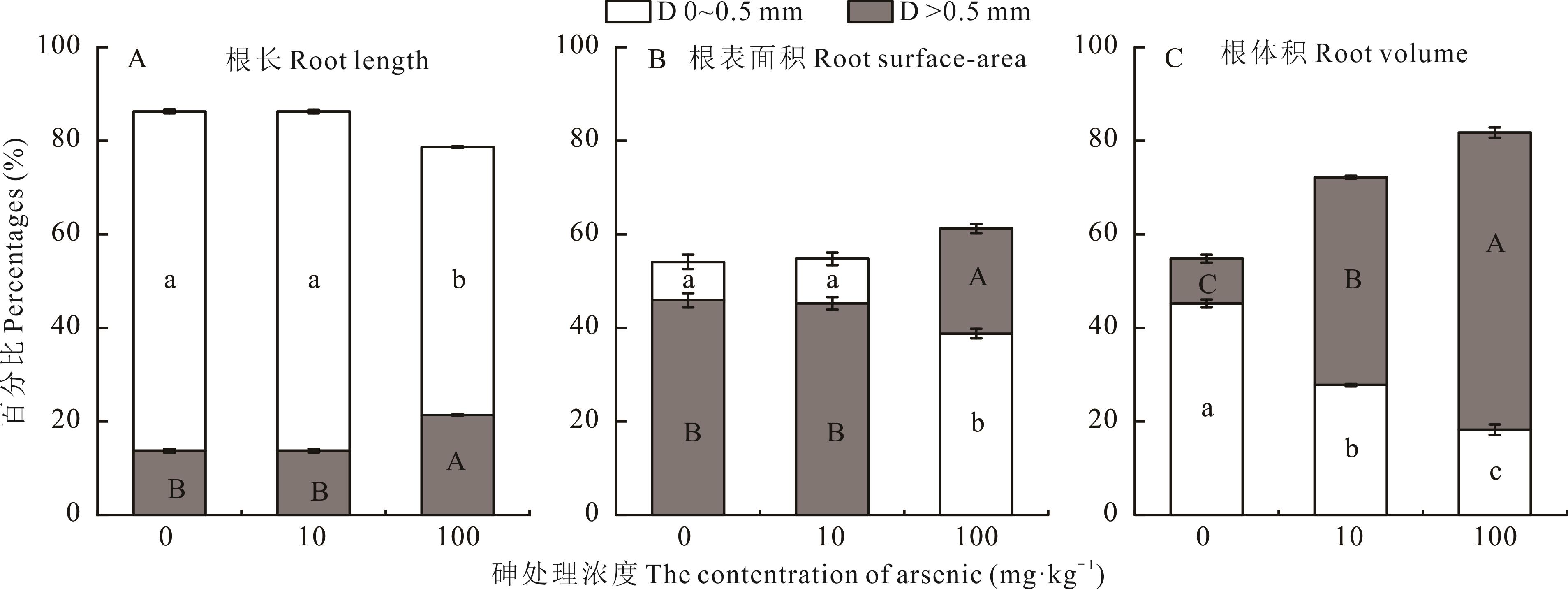
Fig.5 Root length, root surface area and root volume of different root diameter classes expressed as percentages for seashore paspalum under arsenic treatment
| 1 | Rahaman M S, Rahman M M, Mise N, et al. Environmental arsenic exposure and its contribution to human diseases, toxicity mechanism and management. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 289: 117940. |
| 2 | Yang Q Q, Li Z Y, Lu X N, et al. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642: 690-700. |
| 3 | Hao J, Zhang J, Zhang P P, et al. A study on the herbs at the initial natural reclamation stage of plants in gangue fields. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(4): 51-60. |
| 郝婧, 张婕, 张沛沛, 等. 煤矸石场植被自然恢复初期草本植物生物量研究. 草业学报, 2013, 22(4): 51-60. | |
| 4 | Chen T, Liu Y G, Wang Y, et al. Effects of exogenous phosphorus on antioxidant enzyme system of emergent plants under arsenic stress. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 35(5): 1040-1046. |
| 陈天, 刘云根, 王妍, 等. 外源磷对砷胁迫下挺水植物抗氧化酶系统的影响. 江苏农业学报, 2019, 35(5): 1040-1046. | |
| 5 | Kofroňová M, Hrdinová A, Mašková P, et al. Strong antioxidant capacity of horseradish hairy root cultures under arsenic stress indicates the possible use of Armoracia rusticana plants for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 174: 295-304. |
| 6 | Miteva E. Accumulation and effect of arsenic on tomatoes. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2002, 33(11/12): 1917-1926. |
| 7 | Zhang J L, Huang Y, Wu L F, et al. As subcellular distribution and physiological response of Typha angustifolia L. to as exposure. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(5): 1042-1050. |
| 张晋龙, 黄颖, 吴丽芳, 等. 砷胁迫对狭叶香蒲生理生态及砷亚细胞分布的影响. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1042-1050. | |
| 8 | Lou L Q, Shi G L, Wu J H, et al. The influence of phosphorus on arsenic uptake/efflux and as toxicity to wheat roots in comparison with sulfur and silicon. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2015, 34(2): 242-250. |
| 9 | Li J S, Huang N, Ma J X, et al. Comparison of physiological response and resistances of four Paspalum vaginatum to low temperature stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(6): 1444-1448. |
| 李静思, 黄宁, 麻加欣, 等. 4个海滨雀稗对低温胁迫的生理响应及抗寒性比较. 草地学报, 2018, 26(6): 1444-1448. | |
| 10 | Wu X L, Guo Z F, Chen S M, et al. Advances in research on the tolerance of seashore paspalum (Paspalums vaginatium). Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(5): 1117-1125. |
| 吴雪莉, 郭振飞, 陈申秒, 等. 海滨雀稗耐逆性研究进展. 草地学报, 2019, 27(5): 1117-1125. | |
| 11 | Moreno B, Cañizares R, Macci C, et al. Molecular tools to understand the bioremediation effect of plants and earthworms on contaminated marine sediments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 300: 398-405. |
| 12 | Wang K. The stress responses and tolerance thresholds to soil lead, cadmium and zinc contamination in centipedegrass and seashore paspalum. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2010. |
| 王恺. 假俭草和海滨雀稗对土壤Pb、Cd、Zn污染胁迫的响应及耐受阈值研究. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2010. | |
| 13 | Green J J, Baddeley J A, Cortina J, et al. Root development in the Mediterranean shrub Pistacia lentiscus as affected by nursery treatments. Journal of Arid Environments, 2004, 61(1): 1-12. |
| 14 | Xu P X. Studies on cadmium tolerance and detoxification in tall fescue and kentucky bluegrass. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2014. |
| 徐佩贤. 高羊茅和草地早熟禾对镉的耐受能力和解毒机制研究. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014. | |
| 15 | Johnson L D, Marquez-Ortiz J J, Lamb J F S, et al. Root morphology of alfalfa plant introductions and cultivars. Crop Science, 1998, 38(2): 497-502. |
| 16 | Li X M, Song G L. Cadmium uptake and root morphological changes in Medicago sativa under cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. |
| 李希铭, 宋桂龙. 镉胁迫对紫花苜蓿镉吸收特征及根系形态影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. | |
| 17 | Liu W, Pan Q S, Zhang P, et al. Determination of total arsenic in Chinese traditional herbs by high pressure digestion-hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Advanced Materials Research, 2012(554/555/556):1967-1970. |
| 18 | Liu W Q, Zhong X Y, Xue W T. Effects of heavy metal pollution on roots. Science & Technology Vision, 2014(5): 282-283. |
| 刘伟强, 钟小玉, 薛文涛. 重金属污染对根系的影响. 科技视界, 2014(5): 282-283. | |
| 19 | Kubo K, Watanabe Y, Matsunaka H, et al. Differences in cadmium accumulation and root morphology in seedlings of Japanese wheat varieties with distinctive grain cadmium concentration. Plant Production Science, 2011, 14(2): 148-155. |
| 20 | Arduini I, Masoni A, Mariotti M, et al. Low cadmium application increase Miscanthus growth and cadmium translocation. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 2004, 52(2): 89-100. |
| 21 | Wang S F, Shi X, Sun H J, et al. Metal uptake and root morphological changes for two varieties of Salix integra under cadmium stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(19): 6065-6073. |
| 王树凤, 施翔, 孙海菁, 等. 镉胁迫下杞柳对金属元素的吸收及其根系形态构型特征. 生态学报, 2013, 33(19): 6065-6073. | |
| 22 | Liu D T, Jing Y P, Chen J J, et al. Rice lateral root development and its impact factors. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(8): 1403-1411. |
| 刘大同, 荆彦平, 陈晶晶, 等. 水稻的侧根发育及其影响因素. 作物学报, 2014, 40(8): 1403-1411. | |
| 23 | Li J X, He B H, Chen Y. Root features of typical herb plants for hillslope protection and their effects on soil infiltration. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(5), 1535-1544. |
| 李建兴, 何丙辉, 谌芸. 不同护坡草本植物的根系特征及对土壤渗透性的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(5): 1535-1544. | |
| 24 | Kong L S. Absorption, accumulation, tolerance and variation of heavy metal elements in plants. Environmental Science, 1983(1): 65-69. |
| 孔令韶. 植物对重金属元素的吸收积累及忍耐、变异. 环境科学, 1983(1): 65-69. | |
| 25 | Conesa H M, Evangelou M W H, Robinson B H, et al. A critical view of current state of phytotechnologies to remediate soils: Still a promising tool? The Scientific World Journal, 2012(5): 173829. |
| 26 | Meharg A A, Zhao F J. Arsenic & rice. Dordrecht: Springer, 2012: 1-6. |
| 27 | Song W Y, Park J Y, Mendozacózatl D G, et al. Arsenic tolerance in Arabidopsis is mediated by two ABCC-type phytochelatin transporters. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(49): 21187-21192. |
| 28 | Song W Y, Yamaki T, Yamaji N, et al. A rice ABC transporter, OsABCC1, reduces arsenic accumulation in the grain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(44): 15699-15704. |
| 29 | Bao T, Lian M H, Sun L N, et al. Research progress on the phytoremediation of soils contaminated by heavy metals. Ecology and Environment, 2008(2): 858-865. |
| 鲍桐, 廉梅花, 孙丽娜, 等. 重金属污染土壤植物修复研究进展. 生态环境, 2008(2): 858-865. | |
| 30 | Chen W, Zhang M M, Song Y Y, et al. Impacts of heavy metals on the fluorescence characteristics and root morphology of 2 turfgrass species. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 333-342. |
| 陈伟, 张苗苗, 宋阳阳, 等. 重金属离子对2种草坪草荧光特性及根系形态的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 333-342. |
| [1] | Kai JIANG, Xue-li WU, Yi-jun LIU, Yue MA, Yang SONG, Wen-jie LU, Zeng-yu WANG. Comparative study on transformation systems of seashore paspalum using hpt and bar genes as selection markers [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 165-177. |
| [2] | Zhi-xin YANG, Xu ZHENG, Lai-bao CHEN, Yong-xin YU, Feng-hua ZHANG, Lu-hua LI, Jia-ping WANG. Morphological adaptation strategies of Rumex hanus planted in saline-alkali land of arid areas [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 15-27. |
| [3] | Cheng-zhen ZHAO, Qiang LI, Rong-zhen ZHONG. Effect of mowing in different phenological growth stages on shoot regrowth, root morphology and forage yield of Leymus chinensis [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 92-100. |
| [4] | SUN Xiao-fu, HUANG Li-juan, WANG Pu-chang, ZHAO Li-li, LIU Fang. Effects of different phosphorus supply levels on morphology and physiology of Paspalum wettsteinii [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 58-69. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xiang, YANG Yong, LIU Xue-yong, XIANG Zuo-xiang. Effect of exogenous salicylic acid on the antioxidant enzyme activities and fatty acid profiles in seashore paspalum under low temperature stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1): 117-124. |
| [6] | QING Yue, LI Ting-xuan, YE Dai-hua. Effects of inorganic N on the N accumulation and root morphology of a mining ecotype of Polygonum hydropiper [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1): 203-210. |
| [7] | QIAN Chen, LIU Zhi-wei, ZHONG Xiao-xian, WU Juan-zi, ZHANG Jian-li, PAN Yu-mei. Transcriptomic analysis of the self-incompatibility mechansim in Paspalum vaginatum by comparison with an artificial self-compatible mutant [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(5): 132-142. |
| [8] | GUO Xiong-fei. Effects of biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on soil nutrients and growth of Cassia occidentalis under heavy metal contamination [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(11): 150-161. |
| [9] | LIU Tian-Zeng, XIE Xin-Chun, ZHANG Ju-Ming. Mutagenic effect of 60Co-γ irradiation on turf characteristics of Paspalum vaginatum [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(7): 62-70. |
| [10] | LI Shuai, ZHAO Guo-Jing, XU Wei-Zhou, GAO Zhi-Juan, WU Ai-Jiao, XU Bing-Cheng. Responses of old world bluestem root systems to changes in soil water conditions [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 169-177. |
| [11] | LI Xi-Ming, SONG Gui-Long. Cadmium uptake and root morphological changes in Medicago sativa under cadmium stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. |
| [12] | YU Jing-Jin, LI Ran, LIU Meng-Xian, YANG Zhi-Min. Ecophysiological mechanisms associated with drought tolerance and post-drought recovery in warm- and cool-season turfgrasses [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(11): 86-93. |
| [13] | LIU Wan-Gou, LI Liang-Xian, XIE Hai-Rong, HE Yong-Yi, LIU Jin-Xiang. Effect of soil bulk density on root morphology and biomass of vetiver grass seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(4): 214-220. |
| [14] | CHEN Wei,ZHANG Miao-miao,SONG Yang-yang,CHEN Jian-gang,ZHANG De-gang. Impacts of heavy metals on the fluorescence characteristics and root morphology of 2 turfgrass species [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 333-342. |
| [15] | ZHONG Xiao-xian, LIU Zhi-wei, CHANG Pan-pan, WU Juan-zhi, ZHANG Jian-li. Acquirement of self-compatible somatic mutants induced by colchicine in Paspalum vaginatum [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(6): 205-212. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||