
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 143-159.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022480
Ying JIANG1( ), Hui-hong ZHANG1(
), Hui-hong ZHANG1( ), Chang WEI1, Zheng-yang XU1, Ying ZHAO1, Fang LIU1, Ge-zi LI2, Xue-hai ZHANG2, Hai-tao LIU1(
), Chang WEI1, Zheng-yang XU1, Ying ZHAO1, Fang LIU1, Ge-zi LI2, Xue-hai ZHANG2, Hai-tao LIU1( )
)
Received:2022-12-07
Revised:2023-01-13
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-07-12
Contact:
Hai-tao LIU
Ying JIANG, Hui-hong ZHANG, Chang WEI, Zheng-yang XU, Ying ZHAO, Fang LIU, Ge-zi LI, Xue-hai ZHANG, Hai-tao LIU. Effects of exogenous melatonin on root development and physiological and biochemical characteristics of maize seedlings under drought stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 143-159.
| 生长指标Growth index | CK | MT0 | MT10 | MT50 | MT100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 40.90±0.50a | 31.07±0.83c | 29.83±1.68c | 36.70±1.25b | 31.00±1.25c |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 3.93±0.20a | 1.34±0.12d | 1.59±0.30cd | 2.24±0.20b | 1.73±0.13c |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight (mg·plant-1) | 286.33±14.03a | 123.23±15.46d | 156.67±23.79c | 264.20±6.41a | 197.57±4.00b |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 32.03±2.25a | 24.23±0.81bc | 22.50±2.26c | 25.70±1.18b | 25.13±0.90bc |
| 地下部鲜重Root fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 1.61±0.02a | 0.81±0.06c | 0.92±0.14c | 1.12±0.04b | 0.92±0.08c |
| 地下部干重Root dry weight (mg·plant-1) | 100.47±6.30a | 39.60±4.28d | 65.27±7.13c | 90.93±4.03ab | 81.77±6.71b |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.35±0.01b | 0.32±0.02b | 0.42±0.05a | 0.34±0.02b | 0.41±0.05a |
| 茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 0.43±0.05d | 0.55±0.08c | 0.92±0.02a | 0.69±0.01b |
| 根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 0.39±0.04c | 0.65±0.07b | 0.90±0.04a | 0.81±0.07a |
Table 1 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin treatments on the growth and tolerance index of maize seedlings under drought stress (mean±SD)
| 生长指标Growth index | CK | MT0 | MT10 | MT50 | MT100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 40.90±0.50a | 31.07±0.83c | 29.83±1.68c | 36.70±1.25b | 31.00±1.25c |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 3.93±0.20a | 1.34±0.12d | 1.59±0.30cd | 2.24±0.20b | 1.73±0.13c |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight (mg·plant-1) | 286.33±14.03a | 123.23±15.46d | 156.67±23.79c | 264.20±6.41a | 197.57±4.00b |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 32.03±2.25a | 24.23±0.81bc | 22.50±2.26c | 25.70±1.18b | 25.13±0.90bc |
| 地下部鲜重Root fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 1.61±0.02a | 0.81±0.06c | 0.92±0.14c | 1.12±0.04b | 0.92±0.08c |
| 地下部干重Root dry weight (mg·plant-1) | 100.47±6.30a | 39.60±4.28d | 65.27±7.13c | 90.93±4.03ab | 81.77±6.71b |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.35±0.01b | 0.32±0.02b | 0.42±0.05a | 0.34±0.02b | 0.41±0.05a |
| 茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 0.43±0.05d | 0.55±0.08c | 0.92±0.02a | 0.69±0.01b |
| 根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 0.39±0.04c | 0.65±0.07b | 0.90±0.04a | 0.81±0.07a |
| 项目Item | CK | MT0 | MT10 | MT50 | MT100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总根长Total root length (RL,cm) | |||||
| 总Total | 1078.57±25.11a | 350.76±21.23d | 413.58±4.26d | 643.92±63.89b | 492.62±25.79c |
| Ⅰ | 888.47±22.89a | 234.81±28.05e | 287.02±7.31d | 494.90±34.68b | 346.39±16.68c |
| Ⅱ | 159.23±7.12a | 98.03±11.25b | 102.63±11.85b | 118.21±27.44b | 117.03±16.48b |
| Ⅲ | 18.98±1.64a | 9.62±1.93b | 13.93±5.80ab | 17.63±5.11a | 16.69±1.29a |
| Ⅳ | 11.56±4.17a | 8.25±2.72a | 9.99±2.50a | 12.99±3.25a | 12.30±2.72a |
| 根表面积Root surface area (SA,cm2) | |||||
| 总Total | 111.70±2.09a | 49.61±1.12d | 59.08±3.99cd | 81.34±9.70b | 71.28±8.97bc |
| Ⅰ | 46.62±1.25a | 14.23±2.16d | 17.37±2.06d | 29.25±2.87b | 22.21±1.98c |
| Ⅱ | 35.19±2.72a | 20.63±2.19b | 22.49±2.44b | 26.72±5.90b | 25.71±3.50b |
| Ⅲ | 7.17±0.68a | 3.63±0.77b | 5.25±2.21ab | 6.62±1.92a | 6.29±0.53ab |
| Ⅳ | 9.51±2.48a | 6.38±1.73a | 8.15±2.47a | 10.00±2.83a | 9.86±2.55a |
| 根体积Root volume (RV,cm3) | |||||
| 总Total | 0.92±0.05a | 0.56±0.06c | 0.67±0.09bc | 0.82±0.12ab | 0.83±0.17ab |
| Ⅰ | 0.25±0.02a | 0.09±0.01c | 0.11±0.02c | 0.17±0.03b | 0.14±0.02b |
| Ⅱ | 0.64±0.07a | 0.36±0.04c | 0.40±0.04bc | 0.49±0.10b | 0.46±0.06bc |
| Ⅲ | 0.22±0.02a | 0.11±0.02b | 0.16±0.07ab | 0.20±0.06a | 0.19±0.02ab |
| Ⅳ | 0.83±0.02a | 0.47±0.10a | 0.68±0.28a | 0.72±0.20a | 0.76±0.28a |
| 根平均直径Root average diameter (RD, mm) | 0.33±0.01b | 0.45±0.04a | 0.45±0.03a | 0.40±0.01a | 0.46±0.04a |
| 根尖数Root tips (RT) | 2138.67±319.14a | 562.00±27.07c | 615.67±95.63bc | 1040.33±296.39b | 819.00±259.05bc |
Table 2 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on root structure and grading of maize seedlings under drought stress (mean±SD)
| 项目Item | CK | MT0 | MT10 | MT50 | MT100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总根长Total root length (RL,cm) | |||||
| 总Total | 1078.57±25.11a | 350.76±21.23d | 413.58±4.26d | 643.92±63.89b | 492.62±25.79c |
| Ⅰ | 888.47±22.89a | 234.81±28.05e | 287.02±7.31d | 494.90±34.68b | 346.39±16.68c |
| Ⅱ | 159.23±7.12a | 98.03±11.25b | 102.63±11.85b | 118.21±27.44b | 117.03±16.48b |
| Ⅲ | 18.98±1.64a | 9.62±1.93b | 13.93±5.80ab | 17.63±5.11a | 16.69±1.29a |
| Ⅳ | 11.56±4.17a | 8.25±2.72a | 9.99±2.50a | 12.99±3.25a | 12.30±2.72a |
| 根表面积Root surface area (SA,cm2) | |||||
| 总Total | 111.70±2.09a | 49.61±1.12d | 59.08±3.99cd | 81.34±9.70b | 71.28±8.97bc |
| Ⅰ | 46.62±1.25a | 14.23±2.16d | 17.37±2.06d | 29.25±2.87b | 22.21±1.98c |
| Ⅱ | 35.19±2.72a | 20.63±2.19b | 22.49±2.44b | 26.72±5.90b | 25.71±3.50b |
| Ⅲ | 7.17±0.68a | 3.63±0.77b | 5.25±2.21ab | 6.62±1.92a | 6.29±0.53ab |
| Ⅳ | 9.51±2.48a | 6.38±1.73a | 8.15±2.47a | 10.00±2.83a | 9.86±2.55a |
| 根体积Root volume (RV,cm3) | |||||
| 总Total | 0.92±0.05a | 0.56±0.06c | 0.67±0.09bc | 0.82±0.12ab | 0.83±0.17ab |
| Ⅰ | 0.25±0.02a | 0.09±0.01c | 0.11±0.02c | 0.17±0.03b | 0.14±0.02b |
| Ⅱ | 0.64±0.07a | 0.36±0.04c | 0.40±0.04bc | 0.49±0.10b | 0.46±0.06bc |
| Ⅲ | 0.22±0.02a | 0.11±0.02b | 0.16±0.07ab | 0.20±0.06a | 0.19±0.02ab |
| Ⅳ | 0.83±0.02a | 0.47±0.10a | 0.68±0.28a | 0.72±0.20a | 0.76±0.28a |
| 根平均直径Root average diameter (RD, mm) | 0.33±0.01b | 0.45±0.04a | 0.45±0.03a | 0.40±0.01a | 0.46±0.04a |
| 根尖数Root tips (RT) | 2138.67±319.14a | 562.00±27.07c | 615.67±95.63bc | 1040.33±296.39b | 819.00±259.05bc |
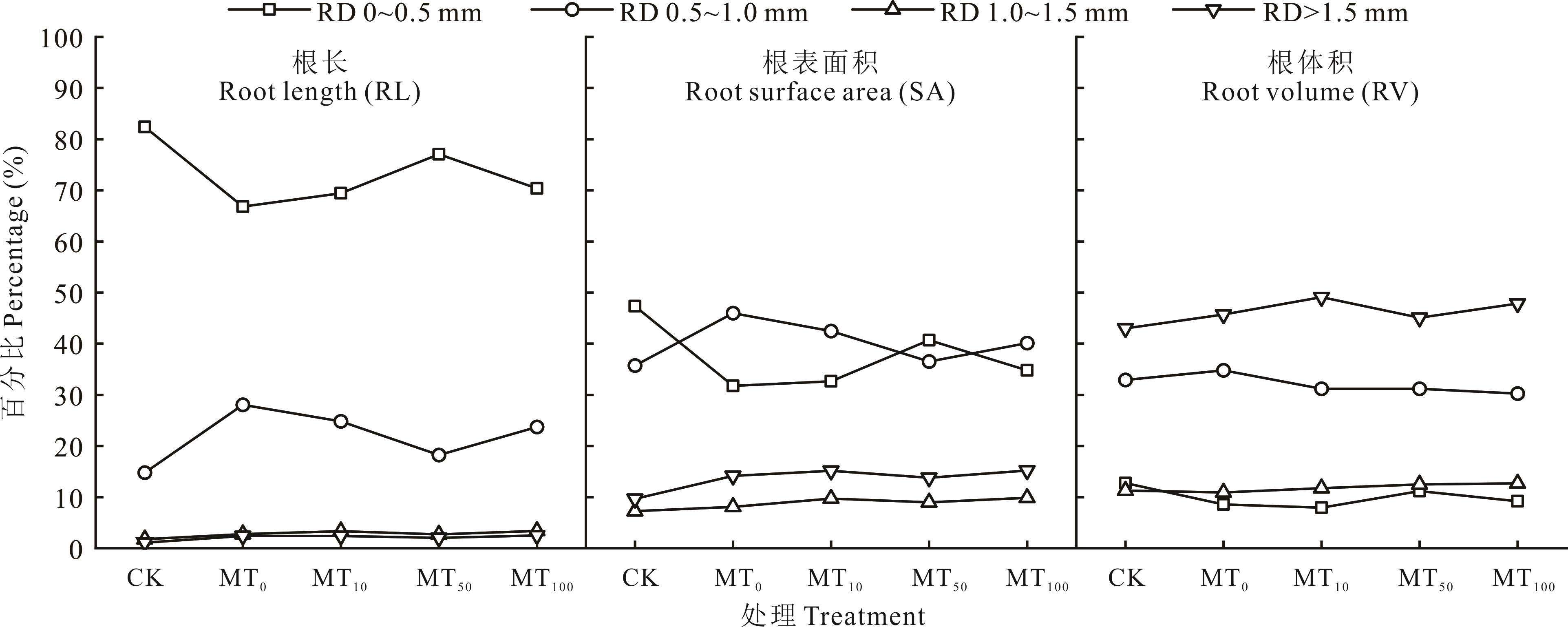
Fig.2 The percentage of different concentrations of melatonin on root length, root surface area and root volume in different diameters of maize seedlings under drought stress

Fig.8 Principal component analysis and random forest plot of maize seedling index changes induced by different concentrations of melatonin under drought stress
| 指标Indexes | RL | SA | RD | RV | RT | Ph | MRL | FW | DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pn | 0.840** | 0.813** | -0.776** | 0.710** | 0.783** | 0.832** | 0.725** | 0.820** | 0.849** |
| Gs | 0.512 | 0.521* | -0.501 | 0.553* | 0.437 | 0.595* | 0.316 | 0.498 | 0.599* |
| Ci | -0.176 | -0.242 | 0.093 | -0.286 | -0.131 | -0.165 | -0.086 | -0.164 | -0.376 |
| Tr | 0.493 | 0.487 | -0.449 | 0.461 | 0.467 | 0.493 | 0.246 | 0.499 | 0.433 |
| MDA | -0.858** | -0.833** | 0.779** | -0.713** | -0.782** | -0.792** | -0.627* | -0.871** | -0.818** |
| AsA | -0.815** | -0.775** | 0.770** | -0.642** | -0.782** | -0.728** | -0.646** | -0.809** | -0.718** |
| GSH | 0.002 | -0.062 | -0.067 | -0.177 | 0.110 | -0.157 | 0.157 | 0.021 | -0.363 |
| SPC | -0.259 | -0.178 | 0.202 | -0.082 | -0.288 | -0.172 | -0.369 | -0.299 | 0.117 |
| SOD | -0.161 | -0.075 | 0.105 | 0.037 | -0.252 | -0.037 | -0.364 | -0.184 | 0.231 |
| POD | -0.758** | -0.701** | 0.675** | -0.634* | -0.729** | -0.659** | -0.701** | -0.770** | -0.452 |
| CAT | -0.231 | -0.155 | 0.159 | -0.003 | -0.335 | -0.060 | -0.392 | -0.209 | 0.116 |
| APX | -0.239 | -0.072 | 0.503 | -0.160 | -0.255 | -0.461 | -0.336 | -0.272 | -0.023 |
Table 3 Correlation analysis of growth indexes and physiological indexes of maize seedlings treated with different concentrations of melatonin under drought stress
| 指标Indexes | RL | SA | RD | RV | RT | Ph | MRL | FW | DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pn | 0.840** | 0.813** | -0.776** | 0.710** | 0.783** | 0.832** | 0.725** | 0.820** | 0.849** |
| Gs | 0.512 | 0.521* | -0.501 | 0.553* | 0.437 | 0.595* | 0.316 | 0.498 | 0.599* |
| Ci | -0.176 | -0.242 | 0.093 | -0.286 | -0.131 | -0.165 | -0.086 | -0.164 | -0.376 |
| Tr | 0.493 | 0.487 | -0.449 | 0.461 | 0.467 | 0.493 | 0.246 | 0.499 | 0.433 |
| MDA | -0.858** | -0.833** | 0.779** | -0.713** | -0.782** | -0.792** | -0.627* | -0.871** | -0.818** |
| AsA | -0.815** | -0.775** | 0.770** | -0.642** | -0.782** | -0.728** | -0.646** | -0.809** | -0.718** |
| GSH | 0.002 | -0.062 | -0.067 | -0.177 | 0.110 | -0.157 | 0.157 | 0.021 | -0.363 |
| SPC | -0.259 | -0.178 | 0.202 | -0.082 | -0.288 | -0.172 | -0.369 | -0.299 | 0.117 |
| SOD | -0.161 | -0.075 | 0.105 | 0.037 | -0.252 | -0.037 | -0.364 | -0.184 | 0.231 |
| POD | -0.758** | -0.701** | 0.675** | -0.634* | -0.729** | -0.659** | -0.701** | -0.770** | -0.452 |
| CAT | -0.231 | -0.155 | 0.159 | -0.003 | -0.335 | -0.060 | -0.392 | -0.209 | 0.116 |
| APX | -0.239 | -0.072 | 0.503 | -0.160 | -0.255 | -0.461 | -0.336 | -0.272 | -0.023 |
处理 Treatment | MDA | AsA | GSH | SPC | SOD | POD | CAT | APX | 平均值 Average value | 排序Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT0 | 0.0366 | 0.8515 | 0.9185 | 0.3789 | 0.0426 | 0.6793 | 0.4053 | 0.1850 | 0.4372 | 4 |
| MT10 | 0.5375 | 0.3776 | 0.5756 | 0.7247 | 0.6555 | 0.8790 | 0.6472 | 0.7478 | 0.6431 | 2 |
| MT50 | 0.6105 | 0.3971 | 0.0808 | 0.9283 | 0.9917 | 0.8375 | 0.8764 | 0.4300 | 0.6440 | 1 |
| MT100 | 0.2036 | 0.6722 | 0.8218 | 0.5995 | 0.2570 | 0.7584 | 0.4429 | 0.9002 | 0.5820 | 3 |
Table 4 Average membership function values of physiological indexes of maize seedlings treated with different concentrations of melatonin under drought stress
处理 Treatment | MDA | AsA | GSH | SPC | SOD | POD | CAT | APX | 平均值 Average value | 排序Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT0 | 0.0366 | 0.8515 | 0.9185 | 0.3789 | 0.0426 | 0.6793 | 0.4053 | 0.1850 | 0.4372 | 4 |
| MT10 | 0.5375 | 0.3776 | 0.5756 | 0.7247 | 0.6555 | 0.8790 | 0.6472 | 0.7478 | 0.6431 | 2 |
| MT50 | 0.6105 | 0.3971 | 0.0808 | 0.9283 | 0.9917 | 0.8375 | 0.8764 | 0.4300 | 0.6440 | 1 |
| MT100 | 0.2036 | 0.6722 | 0.8218 | 0.5995 | 0.2570 | 0.7584 | 0.4429 | 0.9002 | 0.5820 | 3 |
| 1 | Li W. Research progress in understanding the effects of drought on growth of the soybean root system and the efficiency of irrigation. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(4): 192-202. |
| 李琬. 干旱对大豆根系生育的影响及灌溉缓解效应研究进展. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 192-202. | |
| 2 | Guo Y Y. Effects of exogenous melatonin on photosynthesis and physiological characteristics in maize under drought stress. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2020. |
| 郭艳阳. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米光合及生理特性的影响. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2020. | |
| 3 | Wen Q, Zhao W B, Zhang Y J, et al. Research progress of plant response to drought stress. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2020, 48(12): 11-15. |
| 温琦, 赵文博, 张幽静, 等. 植物干旱胁迫响应的研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(12): 11-15. | |
| 4 | Li P H, Xiang J Y, Wang L, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on physiological characteristics of tobacco seedlings under drought stress. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(5): 41-48. |
| 李鹏辉, 向金友, 王林, 等. 干旱胁迫下外源褪黑素对烟草幼苗生理特性的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(5): 41-48. | |
| 5 | Zhao N, Yu Z, Ma Y H, et al. Study on difference of drought resistance and salt tolerance among pacetter varieties at seedling stage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2007(3): 39-44. |
| 赵娜, 于卓, 马艳红, 等. 高丹草幼苗抗旱和耐盐性的品种间差异. 中国草地学报, 2007(3): 39-44. | |
| 6 | Song J X, Li J H, Liu M R, et al. Effects of brassinosteroid application on osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzymes in Leymus chinensis under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(8): 93-102. |
| 宋吉轩, 李金还, 刘美茹, 等. 油菜素内酯对干旱胁迫下羊草渗透调节及抗氧化酶的影响研究. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8): 93-102. | |
| 7 | Mittler R, Zilinskas B A. Regulation of pea cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase and other antioxidant enzymes during the progression of drought stress and following recovery from drought. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 1994, 5(3): 397-405. |
| 8 | Mustapha E, Hmadou M V, Hahib K. Osmoregulation and osmoprotection in the leaf cells of two olive cultivars subjected to severe water deficit. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2009, 31: 711-721. |
| 9 | Wang K Y, Chen F Q, Huang W X. Research advance on drought stress response mechanism in plants. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(2): 19-25. |
| 王凯悦, 陈芳泉, 黄五星. 植物干旱胁迫响应机制研究进展. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(2): 19-25. | |
| 10 | Ding Y F, Liang Y C, Zhu J, et al. Effects of silicon on plant growth, photosynthetic parameters and soluble sugar content in leaves of wheat under drought stress. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2007(3): 471-478. |
| 丁燕芳, 梁永超, 朱佳, 等. 硅对干旱胁迫下小麦幼苗生长及光合参数的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007(3): 471-478. | |
| 11 | Sairam R K, Vasanthan B, Ajay A. Calcium regulates Gladiolus flower senescence by influencing antioxidative enzymes activity. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2011, 33: 1897-1904. |
| 12 | Liu L, Li D, Ma Y L, et al. Alleviation of drought stress and the physiological mechanisms in tobacco seedlings treated with exogenous melatonin. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(8): 95-105. |
| 刘领, 李冬, 马宜林, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烤烟幼苗生长的缓解效应与生理机制研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 95-105. | |
| 13 | Chen Z F, Song S H, Zhang X N, et al. Effects of gibberellin on seed germination and seedling growth of tall fescue under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(6): 51-61. |
| 陈志飞, 宋书红, 张晓娜, 等. 赤霉素对干旱胁迫下高羊茅萌发及幼苗生长的缓解效应. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 51-61. | |
| 14 | Cui G B, Zhao X X, Liu S D, et al. Beneficial effects of melatonin in overcoming drought stress in wheat seedlings. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 118: 138-149. |
| 15 | Muhammad K, Su W N, Irshad A, et al. Application of paclobutrazol affect maize grain yield by regulating root orphological and physiological characteristics under a semi-arid region. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-15. |
| 16 | Zhang M C, He S Y, Qin B, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on morphology, photosynthetic physiology, and yield of spring soybean variety Suinong 26 under drought stress. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(9): 1791-1805. |
| 张明聪, 何松榆, 秦彬, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下春大豆品种绥农26形态、光合生理及产量的影响. 作物学报, 2021, 47(9): 1791-1805. | |
| 17 | Meng X P. Effects of melatonin priming seedlings treatment on growth and physiology of wheat under water stress. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2016. |
| 孟祥萍. 褪黑素引发种子对冬小麦水分胁迫下生长及生理的影响. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. | |
| 18 | Gong B, Shi Q H. Review of melatonin in horticultural crops. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50: 2326-2337. |
| 巩彪, 史庆华. 园艺作物褪黑素的研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50: 2326-2337. | |
| 19 | Wu Y, Lian H Y, Mu X J, et al. Effects of foliar spraying exogenous melatonin on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Dendranthema morifolium ‘Chuju’ seedlings under drought stress. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(11): 2241-2246. |
| 吴燕, 连洪燕, 牟雪姣, 等. 干旱胁迫下叶面喷施褪黑素对滁菊幼苗生理生化特性的影响. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(11): 2241-2246. | |
| 20 | Wang P, Sun X, Li C, et al. Long-term exogenous application of melatonin delays drought-induced leaf senescence in apple. Journal of Pineal Research, 2013, 54(3): 292-302. |
| 21 | Du X, Li B, Mao L X, et al. Effects of melatonin on yield and AsA-GSH cycle in soybean under drought stress. Crops, 2022(1): 174-178. |
| 杜昕, 李博, 毛鲁枭, 等. 褪黑素对干旱胁迫下大豆产量及AsA-GSH循环的影响. 作物杂志, 2022(1): 174-178. | |
| 22 | Yang X L, Xu H, Li T L, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on photosynthesis of tomato leaves under drought stress. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(16): 3186-3195. |
| 杨小龙, 须晖, 李天来, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下番茄叶片光合作用的影响. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(16): 3186-3195. | |
| 23 | Deng W, Zhang Z X, Cao Y H, et al. Effects of trichoderma viride alleviating drought stress on root growth of maize seedlings. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 54(2): 40-45. |
| 邓薇, 张祖衔, 曹宇航, 等. 绿色木霉缓解干旱胁迫对玉米幼苗根系生长的影响. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(2): 40-45. | |
| 24 | Shan L. To cope rationally with agricultural drought. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2011, 29(2): 1-5. |
| 山仑. 科学应对农业干旱. 干旱地区农业研究, 2011, 29(2): 1-5. | |
| 25 | Dai J Y, E Y J, Gu W L. Studies on the relationship between root growth and yield in maize (Zea mays)Ⅱ. The interaction of root system and leaves of maize and its relation with yield. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1988(4): 310-314. |
| 戴俊英, 鄂玉江, 顾慰连. 玉米根系的生长规律及其与产量关系的研究Ⅱ. 玉米根系与叶的相互作用及其与产量的关系. 作物学报, 1988(4): 310-314. | |
| 26 | Yang J, Jiang Y M, Zhou F, et al. Effects of PEG simulated drought stress on seedling morphology and physiological characteristics of different drought-resistance maize varieties. Crops, 2021(1): 82-89. |
| 杨娟, 姜阳明, 周芳, 等. PEG模拟干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性玉米品种苗期形态与生理特性的影响. 作物杂志, 2021(1): 82-89. | |
| 27 | Han X Y, Song F B. Effect of drought stress on root growth and rhizosphere nutrients of maize (Zea mays L.). Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006(3): 170-172. |
| 韩希英, 宋凤斌. 干旱胁迫对玉米根系生长及根际养分的影响. 水土保持学报, 2006(3): 170-172. | |
| 28 | Ma X H, Chen R M, Liu X Q, et al. Effects of melatonin on root growth and drought tolerance of maize seedlings. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(2): 1-14. |
| 马旭辉, 陈茹梅, 柳小庆, 等. 褪黑素对玉米幼苗根系发育和抗旱性的影响. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(2): 1-14. | |
| 29 | Sun Y R, Shi Y, Chen G J, et al. Evaluation of the germination characteristics and drought resistance of green manure crops under PEG stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(3): 89-98. |
| 孙艳茹, 石屹, 陈国军, 等. PEG模拟干旱胁迫下8种绿肥作物萌发特性与抗旱性评价. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 89-98. | |
| 30 | Gao J F. Experimental guidance on plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 31 | Zhang Z L, Qu W J, Li X F. Experimental guidance on plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009. |
| 张志良, 瞿伟菁, 李小方. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009. | |
| 32 | Zhang J, Kirkham M B. Antioxidant responses to drought in sunflower and sorghum seedlings. New Phytologist, 1996, 132(3): 361-373. |
| 33 | Guri A. Variation in glutathione and ascorbic acid content among selected cultivars of Phaseolus vulgaris prior to and after exposure to ozone. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 1983, 63(3): 733-737. |
| 34 | Wang X K, Huang J L. Experimental principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015. |
| 王学奎, 黄见良. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015. | |
| 35 | Wang P, Sun X, Chang C, et al. Delay in leaf senescence of Malus hupehensis by long-term melatonin application is associated with its regulation of metabolic status and protein degradation. Journal of Pineal Research, 2013, 55(4): 424-434. |
| 36 | Wang C, Zhu Y L, Yang L F, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on ascorbate glutathione cycle in vegetable soybean seeds. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2010, 16(5): 1209-1216. |
| 王聪, 朱月林, 杨立飞, 等. NaCl胁迫对菜用大豆种子抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(5): 1209-1216. | |
| 37 | Li L J, Gu W R, Li J, et al. Exogenously applied spermidine alleviates photosynthetic inhibition under drought stress in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings associated with changes in endogenous polyamines and phytohormones. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 129: 35-55. |
| 38 | Li D, Shen H T, Wang Y F, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on photosynthetic carbon assimilation and endogenous hormones in tobacco seedlings under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. |
| 李冬, 申洪涛, 王艳芳, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗光合碳同化和内源激素的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. | |
| 39 | Ye J, Deng X P, Wang S W, et al. Effects of melatonin on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant system in seedling of wheat under drought stress. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2015, 35(9): 1275-1283. |
| 叶君, 邓西平, 王仕稳, 等. 干旱胁迫下褪黑素对小麦幼苗生长、光合和抗氧化特性的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2015, 35(9): 1275-1283. | |
| 40 | Yu Q, Cao L, Jin X J, et al. Effects of melatonin on seed germination of soybean under low temperature stress. Soybean Science, 2019, 38: 56-62. |
| 于奇, 曹亮, 金喜军, 等. 低温胁迫下褪黑素对大豆种子萌发的影响. 大豆科学, 2019, 38: 56-62. | |
| 41 | He C J. Alleviating effect of exogenous melatonin on Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica under drought stress. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020, 51(3): 279-286. |
| 赫传杰. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下樟子松的缓解效应. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2020, 51(3): 279-286. | |
| 42 | Liu J, Wang W, Wang L. Exogenous melatonin improves seedling health index and drought tolerance in tomato. Plant Growth Regulation, 2015, 77(3): 317-326. |
| 43 | Wei W, Li Q T, Chu Y N, et al. Melatonin enhances plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance in soybean plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(3): 695-707. |
| 44 | Huang W, Tikkanen M, Zhang S B. Photoinhibition of photosystem I in Nephrolepis falciformis depends on reactive oxygen species generated in the chloroplast stroma. Photosynthesis Research, 2018, 137(1): 1-12. |
| 45 | Mao W J, Zhang H H, Jin W W, et al. Effects of drought stress on photosynthetic characteristics of tobacco seedlings at transplanting stage. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(2): 68-70. |
| 毛卫佳, 张会慧, 金微微, 等. 干旱胁迫对移栽期烟草幼苗光合特性的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2012, 40(2): 68-70. | |
| 46 | Yang X Y. Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant system of sunflower seedling under drought stress. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(4): 113-121. |
| 杨新元. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下向日葵幼苗生长、光合及抗氧化系统的影响. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(4): 113-121. | |
| 47 | Li C, Tan D X, Liang D, et al. Melatonin mediates the regulation of ABA metabolism, free-radical scavenging, and stomatal behaviour in two Malus species under drought stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66: 669-680. |
| 48 | Li H, Chang J J, Chen H J, et al. Exogenous melatonin confers salt stress tolerance to watermelon by improving photosynthesis and redox homeostasis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1-9. |
| 49 | Ye J, Wang S W, Deng X P, et al. Melatonin increased maize (Zea mays L.) seedling drought tolerance by alleviating drought-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative damage. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38(2): 1-13. |
| 50 | Zhang J K, Ma L, Wu S Q, et al. Alleviation effect of exogenous melatonin on low temperature injury of Actinidia arguta. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(5): 1081-1087. |
| 张俊康, 马丽, 吴姝青, 等. 外源褪黑素对软枣猕猴桃低温伤害的缓解效应. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(5): 1081-1087. | |
| 51 | Zhao Y C, Song W J, Dong J X, et al. Effects of fulvic acid potassium on reactive oxygen metabolism of fluecured tobacco seedlings grown under drought stress. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2017, 38(4): 29-36. |
| 赵永长, 宋文静, 董建新, 等. 黄腐酸钾对干旱胁迫下烤烟幼苗活性氧代谢的影响. 中国烟草科学, 2017, 38(4): 29-36. | |
| 52 | He J H, Chen J Z, Xu J Q, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on physiological mechanism of drought resistance of tobacco seedlings. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(2): 50-57. |
| 贺嘉豪, 陈建中, 徐坚强, 等. 外源褪黑素对烟草幼苗抗旱性生理机制的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 50-57. | |
| 53 | Liu N, Jin Z Y, Wang S S, et al. Sodic alkaline stress mitigation with exogenous melatonin involves reactive oxygen metabolism and ion homeostasis in tomato. Scientia Horticulturae, 2015, 181: 18-25. |
| 54 | Fleta-Soriano E, Díaz L, Bonet E, et al. Melatonin may exert a protective role against drought stress in maize. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2017, 203(4): 286-294. |
| [1] | Bao-qiang WANG, Wen-jing MA, Xian WANG, Xiao-lin ZHU, Ying ZHAO, Xiao-hong WEI. Nitric oxide regulation of secondary metabolite accumulation in Medicago sativa seedlings under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 141-151. |
| [2] | Yi-long ZHANG, Wen LI, Qi-kun YU, Pei-ying LI, Zong-jiu SUN. Nitrogen metabolism response mechanism to different drought stresses in leaves and roots of Cynodon dactylon [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [3] | Hao ZHANG, Hai-ying HU, Hui-xia LI, Hai-ming HE, Shuang MA, Feng-hua MA, Ke-chen SONG. Physiological response and transcriptome analysis of the desert steppe dominant plant Lespedeza potaninii to drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| [4] | Jia LIANG, Zhao-yang HU, Zhi-ming XIE, Liu-feng MA, Yun CHEN, Zhi-gang FANG. Exogenous melatonin alleviates the physiological effects of drought stress in sweet sorghum seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 206-215. |
| [5] | Cong-ze JIANG, Na SHOU, Wei GAO, Ren-shi MA, Yu-ying SHEN, Xian-long YANG. A multivariate evaluation of production performance and nutritional quality of different varieties of silage maize in the dry plateau area of Longdong [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 216-228. |
| [6] | Yan-peng LI, Na WEI, Qing-yan ZHAI, Hang LI, Ji-yu ZHANG, Wen-xian LIU. Genome-wide identification of members of the TCP gene family in Melilotus albus and their expression patterns under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [7] | Li-li ZHU, Ye-meng ZHANG, Wan-cai LI, Ya-li ZHAO, Xiang LI, Zhi-guo CHEN. Adaption to the Plateau climate in Qinghai of 39 silage maize varieties cultivated in different ecological regions of China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 68-78. |
| [8] | Mao-jian WANG, Wei SHI, Sheng-hua CHANG, Cheng ZHANG, Qian-min JIA, Fu-jiang HOU. Effects of irrigation modes on forage yield, quality and water use of corn-legume intercropping systems in the Hexi irrigation area [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 13-29. |
| [9] | Yi-long ZHANG, Qi-kun YU, Wen LI, Pei-ying LI, Zong-jiu SUN. Aboveground and belowground phenotypic characteristics of Cynodon dactylon lines differing in drought resistance and endogenous hormone response to drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 163-178. |
| [10] | Fu LIU, Cheng CHEN, Kai-xuan ZHANG, Mei-liang ZHOU, Xin-quan ZHANG. Cloning and identification of drought tolerance function of the LjbHLH34 gene in Lotus japonicus [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| [11] | Ying JIANG, Chang WEI, Qiu-juan JIAO, Feng-min SHEN, Ge-zi LI, Xue-hai ZHANG, Fang YANG, Hai-tao LIU. Effects of exogenous silicon application on physiological parameters, root architecture and diameter distribution of maize under cadmium stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 139-154. |
| [12] | Ying-zheng LI, Yu-lin CHENG, Lu-lu XU, Wan-song LI, Xu YAN, Xiao-feng LI, Ru-yu HE, Yang ZHOU, Jun-jun ZHENG, Xing-yu WANG, De-long ZHANG, Ming-jun CHENG, Yun-hong XIA, Jian-mei HE, Qi-lin TANG. A comparative study of silage quality characteristics of whole-plant, whole-ear and whole-straw silage of different maize varieties (lines) [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [13] | Ji-peng TIAN, Bei-yi LIU, Hong-ru GU, Cheng-long DING, Yun-hui CHENG, Zhu YU. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and calcium propionate on fermentation quality and mycotoxin contents of whole plant maize and oat silages [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 157-166. |
| [14] | Ling-shuang ZENG, Pei-ying LI, Zong-jiu SUN, Xiao-fan SUN. Analysis of antioxidant enzyme protection systems and gene expression differences in two Xinjiang bermudagrass genotypes with contrasting drought resistance [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. |
| [15] | Yi-ting JIN, Wen-hui LIU, Kai-qiang LIU, Guo-ling LIANG, Zhi-feng JIA. Effect of water deficit stress on the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Avena sativa ‘Qingyan No.1’ over the whole crop growth period [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 112-126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||