

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 26-35.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020517
收稿日期:2020-11-24
修回日期:2021-01-12
出版日期:2021-12-01
发布日期:2021-12-01
通讯作者:
许冬梅
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: nxxudongmei@163.com基金资助:
Xing WANG1( ), Shuang YU1, Dong-mei XU1,2(
), Shuang YU1, Dong-mei XU1,2( ), Ke-chen SONG1
), Ke-chen SONG1
Received:2020-11-24
Revised:2021-01-12
Online:2021-12-01
Published:2021-12-01
Contact:
Dong-mei XU
摘要:
以宁夏盐池县退化荒漠草原为对象,实施深翻耕+补播(SR)、浅翻耕+补播(QR)和禁牧封育(F)恢复措施,同时以传统放牧为对照(CK),研究不同恢复措施草地 0~10 cm、10~20 cm、20~30 cm和30~40 cm土层土壤总有机碳(SOC)、全氮(TN)及颗粒有机碳(POC)、易氧化有机碳(ROC)、微生物量碳(MBC)、硝态氮(NO3--N)、铵态氮(NH4+-N)和微生物量氮(MBN)的变化特征,以探讨不同恢复措施对荒漠草原土壤碳氮及其组分的影响。结果表明:与其他处理相比,QR处理草地的土壤SOC含量(5.50~9.93 g·kg-1)、土壤TN含量(0.17~0.23 g·kg-1)、土壤ROC含量(0.53~0.99 g·kg-1)及土壤MBN含量(62.82~73.20 mg·kg-1)总体较高;土壤MBC含量(386.00~481.80 mg·kg-1)及碳、氮各组分占SOC和TN的比例总体以F处理的草地较高;不同恢复措施草地各土层土壤POC、NH4+-N和NO3--N含量较CK均有所下降。相关分析表明:SOC含量分别与TN、ROC含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与MBC含量呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。基于土壤碳、氮固存,在所有的处理中,浅翻耕+补播是退化荒漠草原恢复较为有效的措施。
王星, 于双, 许冬梅, 宋珂辰. 不同恢复措施对退化荒漠草原土壤碳氮及其组分特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 26-35.
Xing WANG, Shuang YU, Dong-mei XU, Ke-chen SONG. Effects of different restorative measures on soil carbon and nitrogen and their component fractions in a degraded desert steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 26-35.
处理 Treatments | 土壤水稳性大团聚体含量 Content of soil wet aggregates (%) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content (%) | 植被盖度 Vegetation coverage (%) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | Shannon-Wiener指数Shannon-Wiener index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.37±0.04 | 1.13±0.02 | 3.65±0.07 | 42.00 | 55.50 | 1.43 |
| SR | 10.19±0.02 | 1.48±0.03 | 7.59±0.06 | 53.70 | 98.50 | 2.54 |
| QR | 22.41±0.02 | 1.41±0.02 | 7.89±0.04 | 69.00 | 82.40 | 2.61 |
| F | 11.21±0.04 | 1.47±0.02 | 2.97±0.03 | 59.30 | 87.20 | 1.56 |
表1 不同恢复措施下的荒漠草原基本情况
Table 1 Basic situation of desert steppes under different restoration measurements
处理 Treatments | 土壤水稳性大团聚体含量 Content of soil wet aggregates (%) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content (%) | 植被盖度 Vegetation coverage (%) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | Shannon-Wiener指数Shannon-Wiener index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.37±0.04 | 1.13±0.02 | 3.65±0.07 | 42.00 | 55.50 | 1.43 |
| SR | 10.19±0.02 | 1.48±0.03 | 7.59±0.06 | 53.70 | 98.50 | 2.54 |
| QR | 22.41±0.02 | 1.41±0.02 | 7.89±0.04 | 69.00 | 82.40 | 2.61 |
| F | 11.21±0.04 | 1.47±0.02 | 2.97±0.03 | 59.30 | 87.20 | 1.56 |
| 项目Items | 土层深度Soil depth (cm) | CK | SR | QR | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳含量Content of soil organic carbon (SOC) | 0~10 | 3.22±0.20b | 3.74±0.25b | 5.50±0.82a | 3.27±0.11b |
| 10~20 | 3.65±0.06b | 3.61±0.21b | 6.17±1.68a | 3.62±0.59b | |
| 20~30 | 8.45±0.65b | 5.75±0.97c | 9.93±2.73a | 3.75±0.55d | |
| 30~40 | 11.72±0.52a | 7.99±0.99a | 9.63±1.35a | 7.40±2.79a | |
| 全氮含量Content of total nitrogen (TN) | 0~10 | 0.09±0.00c | 0.14±0.02ab | 0.18±0.00a | 0.11±0.01bc |
| 10~20 | 0.10±0.01b | 0.11±0.00b | 0.23±0.02a | 0.10±0.00b | |
| 20~30 | 0.21±0.03a | 0.22±0.04a | 0.19±0.02ab | 0.11±0.01b | |
| 30~40 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.22±0.03a | 0.17±0.02b | 0.17±0.01b |
表2 不同恢复措施荒漠草原土壤有机碳和全氮含量
Table 2 Contents of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen of desert steppes under different restoration measurements (g·kg-1)
| 项目Items | 土层深度Soil depth (cm) | CK | SR | QR | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳含量Content of soil organic carbon (SOC) | 0~10 | 3.22±0.20b | 3.74±0.25b | 5.50±0.82a | 3.27±0.11b |
| 10~20 | 3.65±0.06b | 3.61±0.21b | 6.17±1.68a | 3.62±0.59b | |
| 20~30 | 8.45±0.65b | 5.75±0.97c | 9.93±2.73a | 3.75±0.55d | |
| 30~40 | 11.72±0.52a | 7.99±0.99a | 9.63±1.35a | 7.40±2.79a | |
| 全氮含量Content of total nitrogen (TN) | 0~10 | 0.09±0.00c | 0.14±0.02ab | 0.18±0.00a | 0.11±0.01bc |
| 10~20 | 0.10±0.01b | 0.11±0.00b | 0.23±0.02a | 0.10±0.00b | |
| 20~30 | 0.21±0.03a | 0.22±0.04a | 0.19±0.02ab | 0.11±0.01b | |
| 30~40 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.22±0.03a | 0.17±0.02b | 0.17±0.01b |
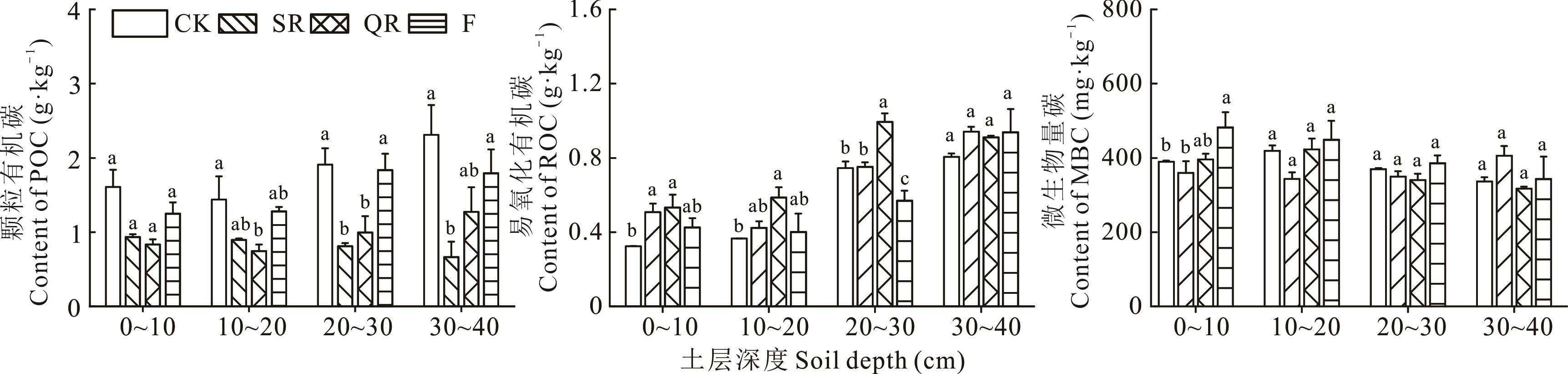
图1 不同恢复措施荒漠草原土壤活性有机碳含量不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among different restoration measurements at the same soil depth (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Soil active organic carbon content of desert steppes under different restoration measurements
处理 Treatments | 颗粒有机碳比例POC/SOC | 易氧化有机碳比例ROC/SOC | 微生物量碳比例MBC/SOC | 铵态氮比例 NH4+-N/TN | 硝态氮比例 NO3--N/TN | 微生物量氮比例MBN/TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 29.54±3.51b | 8.96±0.41b | 0.75±0.12b | 11.23±1.50a | 3.65±0.59a | 43.60±5.67ab |
| SR | 18.34±2.38c | 12.85±0.73a | 0.74±0.06b | 6.59±0.92b | 1.49±0.27b | 35.65±3.90b |
| QR | 12.54±1.53d | 9.44±0.77b | 0.51±0.07b | 5.50±0.48b | 1.48±0.24b | 36.75±2.20b |
| F | 38.65±4.52a | 14.64±1.55a | 1.14±0.13a | 7.14±0.48b | 1.34±0.20b | 48.08±3.28a |
表3 不同恢复措施荒漠草原土壤碳氮组分占总有机碳及全氮的比例
Table 3 Proportion of soil carbon and nitrogen components in total organic carbon and total nitrogen of desert steppes under different restoration measurements (%)
处理 Treatments | 颗粒有机碳比例POC/SOC | 易氧化有机碳比例ROC/SOC | 微生物量碳比例MBC/SOC | 铵态氮比例 NH4+-N/TN | 硝态氮比例 NO3--N/TN | 微生物量氮比例MBN/TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 29.54±3.51b | 8.96±0.41b | 0.75±0.12b | 11.23±1.50a | 3.65±0.59a | 43.60±5.67ab |
| SR | 18.34±2.38c | 12.85±0.73a | 0.74±0.06b | 6.59±0.92b | 1.49±0.27b | 35.65±3.90b |
| QR | 12.54±1.53d | 9.44±0.77b | 0.51±0.07b | 5.50±0.48b | 1.48±0.24b | 36.75±2.20b |
| F | 38.65±4.52a | 14.64±1.55a | 1.14±0.13a | 7.14±0.48b | 1.34±0.20b | 48.08±3.28a |
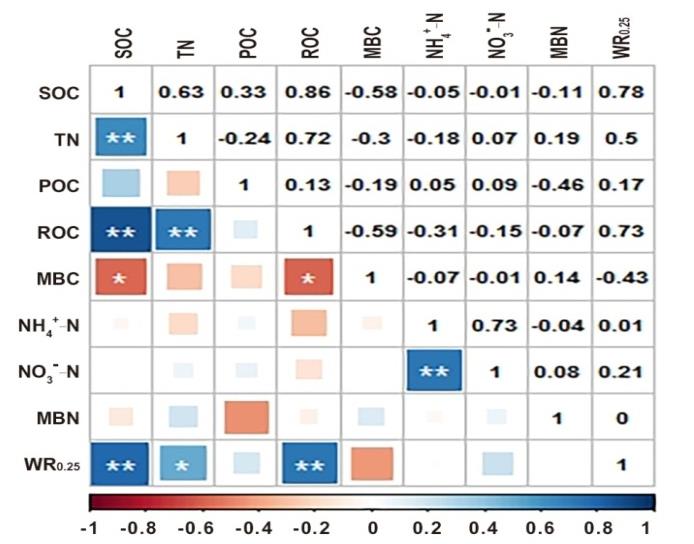
图3 不同恢复措施荒漠草原土壤水稳性团聚体及碳氮组分的相关性SOC为土壤有机碳; TN为土壤全氮; POC为颗粒有机碳; ROC为易氧化有机碳; MBC为微生物量碳; NH4+-N为铵态氮; NO3--N为硝态氮; MBN为微生物量氮; WR0.25为土壤水稳性团聚体。**表示极显著相关P<0.01, *表示显著相关P<0.05。SOC is soil organic carbon; TN is soil total nitrogen; POC is particulate organic carbon; ROC is readily oxidizable organic carbon; MBC is microbial biomass carbon; NH4+-N is ammonium nitrogen; NO3--N is nitrate nitrogen; MBN is microbial biomass nitrogen; WR0.25 is wet aggregate of soil water stability; ** means significant correlation at 0.01 level, * means significant correlation at 0.05 level.
Fig.3 Correlations between WR0.25, carbon and nitrogen components of desert steppes under different restoration measurements
| 1 | Elser J J, Fagan W F, Kerkhoff A J, et al. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytologist, 2010, 186: 593-608. |
| 2 | Li J P, Ma H B, Xie YZ, et al. Deep soil C and N pools in long-term fenced and overgrazed temperate grasslands in Northwest China. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 16088-16099. |
| 3 | Teague W R, Foy J K, Cross B T, et al. Soil carbon and nitrogen changes following root-plowing of rangeland. Journal of Range Management, 2020, 52(6): 666-670. |
| 4 | Dong Y Z, Wang Y L, Zhang J J, et al. Soil carbon and nitrogen storage of different land use types in northwestern Shanxi Loess Plateau. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(4): 955-960. |
| 董云中, 王永亮, 张建杰, 等. 晋西北黄土高原丘陵区不同土地利用方式下土壤碳氮储量. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(4): 955-960. | |
| 5 | Qi X, Jiang C S, Hao Q J, et al. Effects of different land uses on soil active organic carbon and nitrogen fractions in Jinyun Mountain. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(10): 3816-3824. |
| 祁心, 江长胜, 郝庆菊, 等. 缙云山不同土地利用方式对土壤活性有机碳、氮组分的影响. 环境科学, 2015, 36(10): 3816-3824. | |
| 6 | Halvorson A D, Jantalia C P. Nitrogen fertilization effects on irrigated no-till corn production and soil carbon and nitrogen. Agronomy Journal, 2011, 103(5): 1423-1433. |
| 7 | Chan K Y, Heenan D P, Oates A. Soil carbon fractions and relationship to soil quality under different tillage and stubble management. Soil and Tillage Research, 2002, 63(3/4): 133-139. |
| 8 | Giulia B, Else K B, Chidinma U O, et al. Sensitivity of labile carbon fractions to tillage and organic matter management and their potential as comprehensive soil quality indicators across pedoclimatic conditions in Europe. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 99: 38-50. |
| 9 | Hao S, Ping Z, Zhu Z Y, et al. Loss of labile organic carbon from subsoil due to land-use changes in subtropical China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 88: 148-157. |
| 10 | Cooper J, Baranski M, Stewart G, et al. Shallow non-inversion tillage in organic farming maintains crop yields and increases soil C stocks: A meta-analysis. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 94: 22-29. |
| 11 | Toenshoff T, Joergensen R G, Stuelpnagel R, et al. Dynamics of soil organic carbon fractions one year after the re-conversion of poplar and willow plantations to arable use and perennial grassland. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2013, 174: 21-27. |
| 12 | He M, Wang Y C, Wang L G, et al. Effects of subsoiling combined with fertilization on the fractions of soil active organic carbon and soil active nitrogen, and enzyme activities in black soil in Northeast China. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(2): 446-456. |
| 贺美, 王迎春, 王立刚, 等. 深松施肥对黑土活性有机碳氮组分及酶活性的影响. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(2): 446-456. | |
| 13 | Matias E D, Juan A G, Juan M M, et al. Sensitivity of different soil quality indicators to assess sustainable land management: Influence of site features and seasonality. Soil and Tillage Research, 2016, 159: 9-22. |
| 14 | Abid M, Lal R. Tillage and drainage impact on soil quality: Aggregate stability, carbon and nitrogen pools. Soil and Tillage Research, 2008, 100(1/2): 89-98. |
| 15 | Liu E, Teclemariam S G, Yan C R, et al. Long-term effects of no-tillage management practice on soil organic carbon and its fractions in the Northern China. Geoderma, 2014, 213: 379-384. |
| 16 | Wang W Y, Wang Q J, Wang C T, et al. The effect of land management on carbon and nitrogen status in plants and soil of alpine meadows on the Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation and Development, 2005, 16: 405-415. |
| 17 | Xu D M, Xu X Z, Wang G H, et al. Variations in soil organic carbon content and distribution during natural restoration succession on the desert steppe in Ningxia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(8): 35-42. |
| 许冬梅, 许新忠, 王国会, 等. 宁夏荒漠草原自然恢复演替过程中土壤有机碳及其分布的变化. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 35-42. | |
| 18 | Shen Y, Liu C F, Ma H B, et al. Response of a soil seed bank to modes of grassland management on a desert steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(14): 4725-4732. |
| 沈艳, 刘彩凤, 马红彬, 等. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对草地管理方式的响应. 生态学报, 2015, 35(14): 4725-4732. | |
| 19 | Guo Y J, Ma X J, Yu S, et al. Effects of reseeding on soil organic carbon content and its distribution in degraded desert steppes. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(2): 315-319. |
| 郭艳菊, 马晓静, 于双, 等. 补播对退化荒漠草原土壤有机碳及其分布的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(2): 315-319. | |
| 20 | Song N P, Yang X G, He X Z, et al. Soil nutrient effect of desert steppe reconstructed by artificial Caragana microphylla stand. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 32(4): 21-26. |
| 宋乃平, 杨新国, 何秀珍, 等. 荒漠草原人工柠条林重建的土壤养分效应. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(4): 21-26. | |
| 21 | Tao L B, Yu S, Wang G H, et al. Effects of enclosure on characteristics and stability of vegetation community of desert steppe in sandy area of Eastern Ningxia. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2018, 40(2): 67-74. |
| 陶利波, 于双, 王国会, 等. 封育对宁夏东部风沙区荒漠草原植物群落特征及其稳定性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2018, 40(2): 67-74. | |
| 22 | Wang X, Song N P, Yang X G, et al. Redundancy analysis of soil and vegetation of recovered grassland on abandoned land in the desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(2): 90-97. |
| 王兴, 宋乃平, 杨新国, 等. 荒漠草原弃耕恢复草地土壤与植被的RDA分析. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 90-97. | |
| 23 | Liu R T, Chai Y Q, Xu K, et al. Variations of ground vegetation and soil properties during the growth process of artificial sand-fixing Caragana intermedia plantations in desert steppe. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(11): 2955-2960. |
| 刘任涛, 柴永青, 徐坤, 等. 荒漠草原区柠条人工固沙林生长过程中地表植被-土壤的变化. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(11): 2955-2960. | |
| 24 | Wang G H, Wang J J, Tao L B, et al. Effects of enclosure on soil aggregate distribution and stability of desert steppe in Ningxia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(1): 76-81. |
| 王国会, 王建军, 陶利波, 等. 围封对宁夏荒漠草原土壤团聚体组成及其稳定性的影响. 草地学报, 2017, 25(1): 76-81. | |
| 25 | Wang K, Deng L, Ren Z P, et al. Grazing exclusion significantly improves grassland ecosystem C and N pools in a desert steppe of Northwest China. Catena, 2016, 137: 441-448. |
| 26 | Li G Q, Zhao P P, Shao W S, et al. Studies on the soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities of two fenced plant communities in desert steppe grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. |
| 李国旗, 赵盼盼, 邵文山, 等. 围封条件下荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤理化性状与酶活性的研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. | |
| 27 | Cambarrdella C A, Elliott E T. Carbon and nitrogen distribution in aggregates from cultivated and native grassland soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1993, 57(4): 1071-1076. |
| 28 | Yi Y L. Soil physical research. Beijing: Beijing University Press, 2009. |
| 依艳丽. 土壤物理研究法. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2009. | |
| 29 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2008. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008. | |
| 30 | Lu R K. Soil agricultural chemical analysis method. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 31 | Benbi D K, Brar K, Toor A S, et al. Total and labile pools of soil organic carbon in cultivated and undisturbed soils in Northern India. Geoderma, 2015, 237: 149-158. |
| 32 | Wu L G, Liu Z H, Zhang L, et al. Effects of artificial grassland establishment on soil nutrients and carbon properties in a black-soil-type degraded grassland. Plant and Soil, 2010, 33(1/2): 469-479. |
| 33 | Liu S, Wang Y, Liu B B, et al. Effects of different land management practices on soil carbon and nitrogen, enzyme activities, and microbial diversities Northwest of Shanxi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(12): 4376-4389. |
| 刘爽, 王雅, 刘兵兵, 等. 晋西北不同土地管理方式对土壤碳氮、酶活性及微生物的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(12): 4376-4389. | |
| 34 | Liang C, Schimel J P, Jastrow J D. The importance of anabolism in microbial control over soil carbon storage. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 64: 105-117. |
| 35 | Yang Y, Liu A J, Li L H, et al. Effects of different disturbance types on plant species composition and functional group characteristics of typical steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(3): 794-802. |
| 杨勇, 刘爱军, 李兰花, 等. 不同干扰方式对内蒙古典型草原植物种组成和功能群特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(3): 794-802. | |
| 36 | Liu B, Wu N, Luo P, et al. Characteristics of soil nutrient distribution in high-altitude meadow ecosystems with different management and degradation scenarios. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2007(4): 45-48. |
| 刘兵, 吴宁, 罗鹏, 等. 草场管理措施及退化程度对土壤养分含量变化的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2007(4): 45-48. | |
| 37 | Sun G, Wu N, Luo P. Effects of different management measures on soil nitrogen and carbon characteristics of grassland in Northwestern Sichuan. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2005(2): 304-310. |
| 孙庚, 吴宁, 罗鹏. 不同管理措施对川西北草地土壤氮和碳特征的影响. 植物生态学报, 2005(2): 304-310. | |
| 38 | Li Y Q, Huo Y S, Zhao Y A, et al. Effects of different measures for improving degraded grassland on the soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in steppe of Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2016, 38(5): 91-95. |
| 李雅琼, 霍艳双, 赵一安, 等. 不同改良措施对退化草原土壤碳、氮储量的影响. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(5): 91-95. | |
| 39 | Jiang D M, He S F, Cao C Y, et al. Effect of reseeding with rake on soil physical and chemical properties and biological activity of Alkalized grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2006(4): 18-23. |
| 蒋德明, 贺山峰, 曹成有, 等. 翻耙补播对科尔沁碱化草地土壤理化性质和生物活性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2006(4): 18-23. | |
| 40 | Xiao Y, Huang Z G, Wu H T, et al. Compositions and contents of active organic carbon in different wetland soils in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(23): 7625-7633. |
| 肖烨, 黄志刚, 武海涛, 等. 三江平原不同湿地类型土壤活性有机碳组分及含量差异. 生态学报, 2015, 35(23): 7625-7633. | |
| 41 | Yin Y L, Wang Y Q, Li S X, et al. Effects of enclosing on soil microbial community diversity and soil stoichiometric characteristics in a degraded alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(1): 127-136. |
| 尹亚丽, 王玉琴, 李世雄, 等. 围封对退化高寒草甸土壤微生物群落多样性及土壤化学计量特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(1): 127-136. | |
| 42 | Yang J, Sun Z J, Yang H L, et al. Effects of enclosure period on carbon and nitrogen characteristics and components of soil organic carbon in Artemisia desert. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(4): 564-572. |
| 杨静, 孙宗玖, 杨合龙, 等. 封育年限对蒿类荒漠土壤有机碳组分及其碳、氮特征的影响. 草业科学, 2016, 33(4): 564-572. | |
| 43 | Han C C, Yang Y, Liu B R, et al. The effect of enclosure years on soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, total phosphorus and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in desert steppe. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(16): 260-263. |
| 韩丛丛, 杨阳, 刘秉儒, 等. 围封年限对荒漠草原土壤有机碳、全氮、全磷与微生物量碳、氮等的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(16): 260-263. | |
| 44 | Johannes M, Knops H, Tilman D. Dynamics of soil nitrogen and carbon accumulation for 61 years after agricultural abandonment. Ecology, 2020, 81(1): 88-98. |
| 45 | Bai Y X, Sheng M Y, Hu Q J, et al. Effects of land use change on soil organic carbon and its components in Karst rocky desertification of Southwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(5): 1607-1616. |
| 白义鑫, 盛茂银, 胡琪娟, 等. 西南喀斯特石漠化环境下土地利用变化对土壤有机碳及其组分的影响. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(5): 1607-1616. | |
| 46 | Martinsen V, Mulder J, Austrheim G, et al. Carbon storage in low-alpine grassland soils: Effects of different grazing intensities of sheep. European Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 62: 822-833. |
| 47 | Liao S X, Ren Y T, Yuan X B, et al. Effect of enclosure on soil ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen of grassland in the Loess Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(6): 1044-1053. |
| 廖圣祥, 任运涛, 袁晓波, 等. 围封对黄土高原草地土壤铵态氮和硝态氮的影响. 草业科学, 2016, 33(6): 1044-1053. | |
| 48 | Wang F F, Xu H, Li T, et al. Effects and mechanisms of grazing on key processes of soil nitrogen cycling in grassland: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(10): 3277-3284. |
| 王芳芳, 徐欢, 李婷, 等. 放牧对草地土壤氮素循环关键过程的影响与机制研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(10): 3277-3284. |
| [1] | 韩小雨, 郭宁, 李冬冬, 谢明阳, 焦峰. 氮添加对内蒙古不同草原生物量及土壤碳氮变化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 13-25. |
| [2] | 刘慧霞, 董乙强, 崔雨萱, 刘星宏, 何盘星, 孙强, 孙宗玖. 新疆阿勒泰地区荒漠草地土壤有机碳特征及其环境影响因素分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 41-52. |
| [3] | 季波, 何建龙, 吴旭东, 王占军, 谢应忠, 蒋齐. 宁夏典型天然草地土壤有机碳及其活性组分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 24-35. |
| [4] | 王晓娇, 齐鹏, 蔡立群, 陈晓龙, 谢军红, 甘慧炯, 张仁陟. 培肥措施对旱地农田产量可持续性及土壤有机碳库稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 58-69. |
| [5] | 杨鑫光, 李希来, 金立群, 孙华方. 不同人工恢复措施下高寒矿区煤矸石山植被和土壤恢复效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 1-11. |
| [6] | 于双, 许冬梅, 许爱云, 刘金龙, 陶利波. 不同恢复措施对宁夏荒漠草原土壤碳氮储量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 12-19. |
| [7] | 张苗苗, 陈伟, 林丽, 张德罡, 吴玉鑫, 肖海龙. 青海省不同高寒草地土壤主要养分及可溶性有机碳特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 20-28. |
| [8] | 王旭洋, 李玉强, 连杰, 罗永清, 牛亚毅, 龚相文. CENTURY模型在不同生态系统的土壤有机碳动态预测研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 179-189. |
| [9] | 于双, 陶利波, 许冬梅, 许爱云, 刘金龙. 封育对荒漠草原土壤有机碳及其活性组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 190-196. |
| [10] | 王多斌, 籍常婷, 林慧龙. 基于DNDC模型的高寒草甸土壤有机碳含量动态研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 197-204. |
| [11] | 蒋腊梅, 杨晓东, 杨建军, 何学敏, 吕光辉. 不同管理模式对干旱区草地土壤有机碳氮库的影响及其影响因素探究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 22-33. |
| [12] | 汪雪琴, 刘廷玺, 张俊怡, 王冠丽, 段利民. 科尔沁草甸湿地土壤碳氮剖面分布及生长季动态特征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 34-44. |
| [13] | 刘栋, 崔政军, 高玉红, 剡斌, 张中凯, 吴兵, 谢亚萍, 牛俊义. 不同轮作序列对旱地胡麻土壤有机碳稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 45-57. |
| [14] | 王春燕, 燕霞, 顾梦鹤. 黄土高原弃耕地植被演替及其对土壤养分动态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 26-35. |
| [15] | 许冬梅, 许新忠, 王国会, 陶利波. 宁夏荒漠草原自然恢复演替过程中土壤有机碳及其分布的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 35-42. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||