

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 24-35.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020305
季波1,2,3( ), 何建龙2,3, 吴旭东2,3, 王占军2,3, 谢应忠1(
), 何建龙2,3, 吴旭东2,3, 王占军2,3, 谢应忠1( ), 蒋齐2,3(
), 蒋齐2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2020-06-30
修回日期:2020-09-08
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2021-01-08
通讯作者:
谢应忠,蒋齐
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: ycjqnx@163.com, Xieyz@nxu.edu.cn基金资助:
Bo JI1,2,3( ), Jian-long HE2,3, Xu-dong WU2,3, Zhan-jun WANG2,3, Ying-zhong XIE1(
), Jian-long HE2,3, Xu-dong WU2,3, Zhan-jun WANG2,3, Ying-zhong XIE1( ), Qi JIANG2,3(
), Qi JIANG2,3( )
)
Received:2020-06-30
Revised:2020-09-08
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2021-01-08
Contact:
Ying-zhong XIE,Qi JIANG
摘要:
为探寻宁夏典型温性天然草地土壤有机碳及活性组分变异及储量特征,以宁夏4种典型的天然草地(温性草甸草原、温性草原、温性草原化荒漠和温性荒漠草原)为研究对象,采用野外调查和室内分析相结合的方法,对宁夏全区49个固定监测点,土壤有机碳及其活性有机碳组分(易氧化有机碳、微生物生物量碳和水溶性有机碳)进行采样和室内分析。结果表明:1)宁夏草甸草原、温性草原、草原化荒漠和荒漠草原4种天然草地,0~40 cm土层深度土壤有机碳含量分别为34.23、12.84、5.76和3.82 g·kg-1;单位面积土壤有机碳储量分别为:13.43、5.75、2.58和2.29 kg·m-2,且均表现为:草甸草原>温性草原>草原化荒漠>荒漠草原。2)4种典型天然草地土样易氧化有机碳含量为0.75~7.43 g·kg-1,土壤微生物生物量碳含量为102.52~554.77 mg·kg-1,土壤水溶性有机碳含量为69.66~89.61 mg·kg-1,均表现为:草甸草原>温性草原>草原化荒漠>荒漠草原。4种草地类型土壤易氧化有机碳储量分别为2.56、1.44、0.62和0.48 kg·m-2;土壤微生物生物量碳储量分别为:218.31、170.50、81.99和68.26 g·m-2,均为草甸草原显著高于其他3种草地类型(P<0.05);水溶性有机碳储量分别为34.36、35.21、37.22和43.14 g·m-2,表现为荒漠草原显著大于其他3种草地类型(P<0.05)。3)4种典型天然草地易氧化有机碳分配比为18.42%~29.72%,温性草原最高;微生物生物量碳分配比为1.54%~3.83%,草甸草原最低;水溶性有机碳分配比为0.23%~2.01%,表现为:荒漠草原>草原化荒漠>温性草原>草甸草原,且均存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。4)土壤有机碳储量与土壤易氧化有机碳储量、微生物生物量碳储量、全氮、全磷和全钾含量呈显著(P<0.05)或极显著(P<0.01)正相关关系;与土壤水溶性有机碳储量、土壤容重及pH值呈显著(P<0.05)或极显著(P<0.01)的负相关关系。因此可见,宁夏荒漠草原土壤有机碳稳定性最差,温性草原土壤有机碳活性大,土壤有机碳碳库的生物可利用性最高,宁夏温性天然草地土壤有机碳储量大,不应被低估。
季波, 何建龙, 吴旭东, 王占军, 谢应忠, 蒋齐. 宁夏典型天然草地土壤有机碳及其活性组分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 24-35.
Bo JI, Jian-long HE, Xu-dong WU, Zhan-jun WANG, Ying-zhong XIE, Qi JIANG. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and active organic carbon in typical natural grassland in Ningxia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 24-35.
草地类型 Grassland type | 物种数 Species number | 群落盖度 Community coverage (%) | 丰富度指数 Richness index | 多样性指数 Diversity index | 均匀度指数 Evenness index | 优势度指数 Predominant index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 27±1 | 94.42±1.62a | 14.96±3.38a | 1.92±0.19a | 0.72±0.04a | 0.78±0.04a |
| WS | 22±3 | 83.94±9.90b | 13.67±3.26a | 1.79±0.22a | 0.70±0.05a | 0.75±0.05a |
| SD | 10±1 | 57.10±9.70c | 6.84±1.63b | 1.11±0.29b | 0.74±0.13a | 0.55±0.11b |
| DS | 12±0 | 56.85±11.64c | 8.19±2.35b | 1.27±0.27b | 0.61±0.10a | 0.59±0.12b |
表1 各草地类型群落基本特征
Table 1 Basic community characteristics of different grasslands (mean±SD)
草地类型 Grassland type | 物种数 Species number | 群落盖度 Community coverage (%) | 丰富度指数 Richness index | 多样性指数 Diversity index | 均匀度指数 Evenness index | 优势度指数 Predominant index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 27±1 | 94.42±1.62a | 14.96±3.38a | 1.92±0.19a | 0.72±0.04a | 0.78±0.04a |
| WS | 22±3 | 83.94±9.90b | 13.67±3.26a | 1.79±0.22a | 0.70±0.05a | 0.75±0.05a |
| SD | 10±1 | 57.10±9.70c | 6.84±1.63b | 1.11±0.29b | 0.74±0.13a | 0.55±0.11b |
| DS | 12±0 | 56.85±11.64c | 8.19±2.35b | 1.27±0.27b | 0.61±0.10a | 0.59±0.12b |
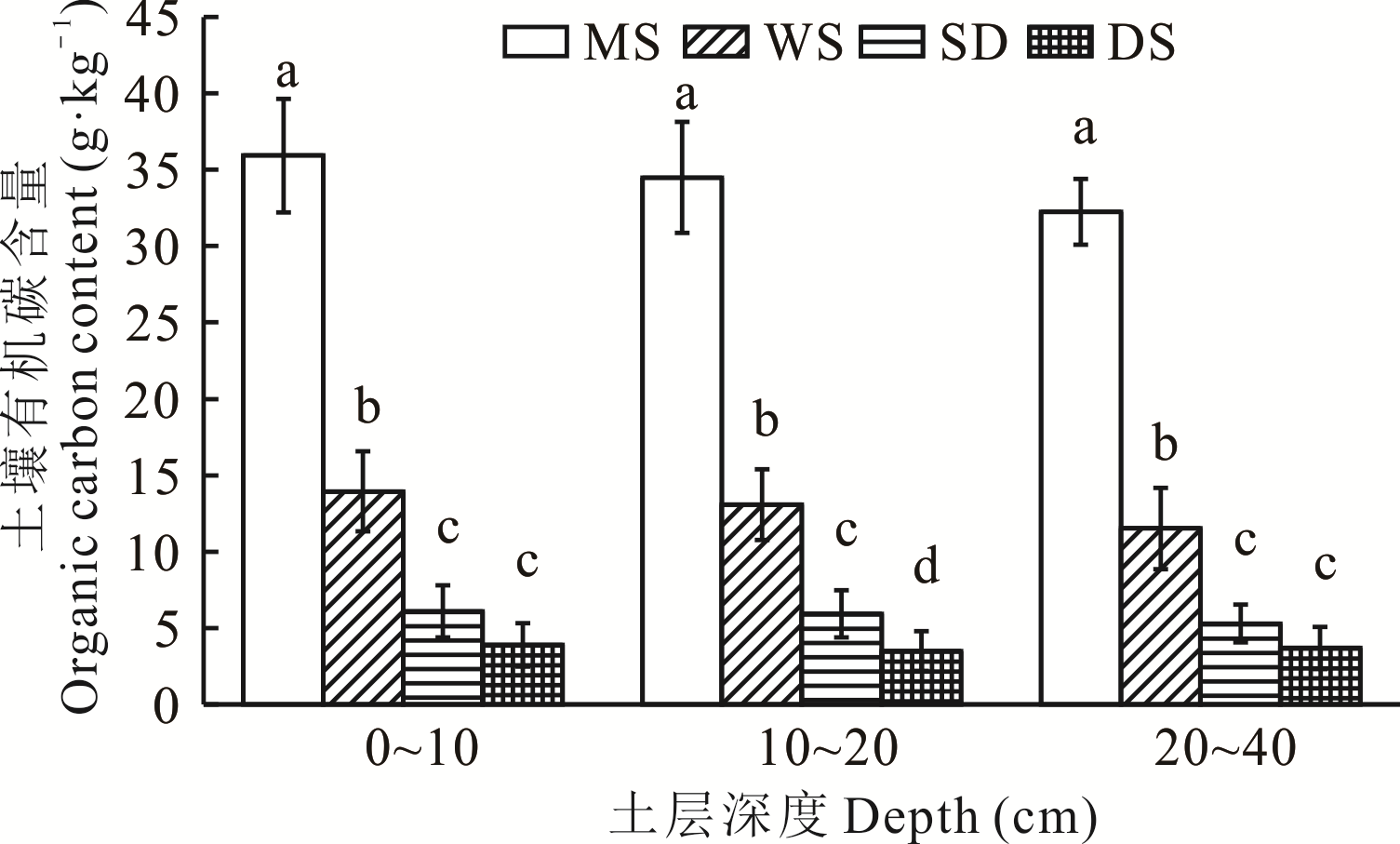
图2 典型天然草地土壤总有机碳含量差异不同小写字母表示不同草地类型相同土层深度在0.05水平上差异显著,下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different grassland types at the same soil layers (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.2 Soil organic carbon content in typical natural grassland
草地类型 Grassland type | 土层深度 Soil layer (cm) | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 0~10 | 0.94±0.08d | 3.45±0.50a | 0.77±0.08a | 20.21±0.97a | 7.92±0.34c |
| 10~20 | 0.97±0.07d | 3.50±0.38a | 0.76±0.07a | 20.10±0.53a | 7.98±0.31c | |
| 20~40 | 1.04±0.08d | 3.32±0.31a | 0.75±0.07a | 19.38±1.19a | 8.05±0.26c | |
| WS | 0~10 | 1.16±0.09c | 1.48±0.51b | 0.63±0.09b | 18.75±0.92b | 8.24±0.22b |
| 10~20 | 1.16±0.08c | 1.40±0.40b | 0.62±0.11b | 18.70±0.98b | 8.29±0.19b | |
| 20~40 | 1.29±0.05c | 1.37±0.47b | 0.62±0.09b | 18.35±0.81ab | 8.34±0.19b | |
| SD | 0~10 | 1.29±0.05b | 0.61±0.12c | 0.61±0.07b | 19.50±1.12ab | 8.68±0.32a |
| 10~20 | 1.32±0.12b | 0.59±0.17c | 0.62±0.10b | 19.42±1.40ab | 8.84±0.27a | |
| 20~40 | 1.31±0.08b | 0.58±0.19c | 0.60±0.09b | 19.30±1.59a | 8.88±0.34a | |
| DS | 0~10 | 1.49±0.12a | 0.40±0.21c | 0.38±0.07c | 17.81±0.86c | 8.70±0.27a |
| 10~20 | 1.49±0.12a | 0.41±0.24c | 0.38±0.04c | 17.46±1.11c | 8.76±0.26a | |
| 20~40 | 1.49±0.12a | 0.39±0.19c | 0.36±0.06c | 17.27±1.33c | 8.74±0.22a |
表2 宁夏典型天然草地土壤容重和养分特征
Table 2 Soil bulk density and soil nutrient of typical natural grassland in Ningxia
草地类型 Grassland type | 土层深度 Soil layer (cm) | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 0~10 | 0.94±0.08d | 3.45±0.50a | 0.77±0.08a | 20.21±0.97a | 7.92±0.34c |
| 10~20 | 0.97±0.07d | 3.50±0.38a | 0.76±0.07a | 20.10±0.53a | 7.98±0.31c | |
| 20~40 | 1.04±0.08d | 3.32±0.31a | 0.75±0.07a | 19.38±1.19a | 8.05±0.26c | |
| WS | 0~10 | 1.16±0.09c | 1.48±0.51b | 0.63±0.09b | 18.75±0.92b | 8.24±0.22b |
| 10~20 | 1.16±0.08c | 1.40±0.40b | 0.62±0.11b | 18.70±0.98b | 8.29±0.19b | |
| 20~40 | 1.29±0.05c | 1.37±0.47b | 0.62±0.09b | 18.35±0.81ab | 8.34±0.19b | |
| SD | 0~10 | 1.29±0.05b | 0.61±0.12c | 0.61±0.07b | 19.50±1.12ab | 8.68±0.32a |
| 10~20 | 1.32±0.12b | 0.59±0.17c | 0.62±0.10b | 19.42±1.40ab | 8.84±0.27a | |
| 20~40 | 1.31±0.08b | 0.58±0.19c | 0.60±0.09b | 19.30±1.59a | 8.88±0.34a | |
| DS | 0~10 | 1.49±0.12a | 0.40±0.21c | 0.38±0.07c | 17.81±0.86c | 8.70±0.27a |
| 10~20 | 1.49±0.12a | 0.41±0.24c | 0.38±0.04c | 17.46±1.11c | 8.76±0.26a | |
| 20~40 | 1.49±0.12a | 0.39±0.19c | 0.36±0.06c | 17.27±1.33c | 8.74±0.22a |

图8 土壤有机碳及其活性组分与土壤容重、养分及pH值相关性
Fig.8 Correlation coefficients between soil organic carbon and active organic carbon fractions and soil bulk density, nutrients and pH value
| 1 | Ji B, Li N, Ma F, et al. Effect of main re-vegetation patterns on soil organic carbon sequestration in southern Ningxia. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2017, 29(3): 483-488. |
| 季波, 李娜, 马璠, 等. 宁南典型退耕模式对土壤有机碳固存的影响.浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(3): 483-488. | |
| 2 | Li Y Y, Shao M A, Zheng J Y, et al. Impact of grassland recovery and reconstruction on soil organic carbon in the Northern Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(6): 2279-2287. |
| 李裕元, 邵明安, 郑纪勇, 等. 黄土高原北部草地的恢复与重建对土壤有机碳的影响. 生态学报, 2007, 27(6): 2279-2287. | |
| 3 | Huang Y Z, Xin Z B. Effects of different ecological restoration patterns on soil organic carbon in gullies of Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(3): 778-788. |
| 黄艳章, 信忠保. 不同生态恢复模式对黄土残塬沟壑区深层土壤有机碳的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(3): 778-788. | |
| 4 | Wu Y C, Li Z C, Cheng C F, et al. Effects of understory removal on soil labile organic carbon pool in a Cinnamomum camphora plantation. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(12): 3341-3346. |
| 吴亚丛, 李正才, 程彩芳, 等. 林下植被抚育对樟树人工林土壤活性有机碳库的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(12): 3341-3346. | |
| 5 | Yan L J, Li G, Wu J Q, et al. Effects of four typical vegetations on soil active organic carbon and soil carbon in Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(15): 5546-5554. |
| 闫丽娟, 李广, 吴江琪, 等. 黄土高原4种典型植被对土壤活性有机碳及土壤碳库的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(15): 5546-5554. | |
| 6 | Liu H M, Zhang H F, Zhao J N, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on labile soil organic carbon and carbon pool management index of Stipa baicalensis steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 18-26. |
| 刘红梅, 张海芳, 赵建宁, 等. 氮添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤活性有机碳和碳库管理指数的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 18-26. | |
| 7 | Xiong D P, Shi P L, Zhang X Z, et al. Effects of grazing exclusion on carbon sequestration and plant diversity in grasslands of China a meta-analysis. Ecological Cological Engineering, 2016, 94: 647-655. |
| 8 | Gao C P, Han G D, Wang Z W, et al. Carbon sequestration effect of different artificial grasslands in Inner Mongolia desert grassland area. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(4): 81-85. |
| 高翠萍, 韩国栋, 王忠武, 等. 内蒙古荒漠草原人工草地固碳效应分析. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(4): 81-85. | |
| 9 | Ni J. Carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems of China: Estimates at different resolutions and their responses to climate change. Climate Change, 2001, 49(3): 339-358. |
| 10 | Xie X L, Sun B, Zhou H Z, et al. Soil carbon storage and their influencing factors under native vegetations in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004(5): 687-699. |
| 解宪丽, 孙波, 周慧珍, 等. 不同植被下中国土壤有机碳的储量与影响因子. 土壤学报, 2004(5): 687-699. | |
| 11 | Xu H, Zhang Y R, Ji B, et al. Organic carbon of soil and roots for different woodland of Helanshan Mountain. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(2): 162-166. |
| 许浩, 张源润, 季波, 等. 贺兰山主要森林类型土壤和根系有机碳研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(2): 162-166. | |
| 12 | Gao Z Z, Dai F H, Shen Q L, et al. Ningxia vegetation. Yinchuan: Ningxia People’s Publishing House, 1988: 8. |
| 高正中, 戴法和, 沈庆录, 等. 宁夏植被. 银川: 宁夏人民出版社, 1988: 8. | |
| 13 | Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Analysis of soil physical and chemical properties. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1978. |
| 中国科学院南京土壤研究所. 土壤理化分析. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1978. | |
| 14 | Shen H, Cao Z H. Study on soil C pool management index of different farmland ecosystems. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2000(4): 663-668. |
| 沈宏, 曹志洪. 不同农田生态系统土壤碳库管理指数的研究.生态学报, 2000(4): 663-668. | |
| 15 | Wang Y, Ruan H H, Huang L L, et al. Soil labile organic carbon of different land use types in a reclaimed land area of Taihu Lake. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(4): 741-748. |
| 王莹, 阮宏华, 黄亮亮, 等. 围湖造田不同土地利用方式土壤活性有机碳的变化. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(4): 741-748. | |
| 16 | Li T K, Guo Z L, Kou C L, et al. Effects of extraction conditions on the test results of soil dissolved organic carbon. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(11): 1878-1883. |
| 李太魁, 郭战玲, 寇长林, 等. 提取方法对土壤可溶性有机碳测定结果的影响. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(11): 1878-1883. | |
| 17 | Dou Y X, Hou L, Ma H H, et al. Effects of forest thinning on soil labile organic carbon in a Pine-Oak mixed forest. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2015, 35(5): 64-69. |
| 窦艳星, 侯琳, 马红红, 等. 间伐对松栎混交林土壤活性有机碳的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2015, 35(5): 64-69. | |
| 18 | Ding Y G, Yang J, Song B Y, et al. Effect of different vegetation types on soil organic carbon in Mu Us desert. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(2): 18-25. |
| 丁越岿, 杨劼, 宋炳煜, 等. 不同植被类型对毛乌素沙地土壤有机碳的影响. 草业学报, 2012, 21(2): 18-25. | |
| 19 | Wang S Q, Zhou C H. Estimating soil carbon reservior of terrestrial ecosystem in China. Geographical Research, 1999(4): 349-356. |
| 王绍强, 周成虎. 中国陆地土壤有机碳库的估算. 地理研究, 1999(4): 349-356. | |
| 20 | Zhou L, Li B G, Zhou G S. Advances in controlling factors of soil organic carbon. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2005, 20(1): 99-105. |
| 周莉, 李保国, 周广胜. 土壤有机碳的主导影响因子及其研究进展. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(1): 99-105. | |
| 21 | Chen X T, Xu T L, Li X J, et al. Soil organic carbon concentrations and the influencing factors in natural ecosystems of northern China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(4): 1133-1140. |
| 陈心桐, 徐天乐, 李雪静, 等. 中国北方自然生态系统土壤有机碳含量及其影响因素. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(4): 1133-1140. | |
| 22 | Xie X L, Sun B, Zhou H Z, et al. Organic carbon density and storage in soil of China and spatial analysis. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004, 41(1): 35-43. |
| 解宪丽, 孙波, 周惠珍, 等. 中国土壤有机碳密度和储量的估算与空间分布分析. 土壤学报, 2004, 41(1): 35-43. | |
| 23 | Xu M G, Yu R, Wang B R. Progress on the study of soil active organic matter. Soils and Fertilizers, 2000(6): 3-7. |
| 徐明岗, 于荣, 王伯仁. 土壤活性有机质的研究进展. 土壤肥料, 2000(6): 3-7. | |
| 24 | Ma H P, Guo Q Q, Liu H M, et al. Soil organic carbon pool at the western side of the sygera mountains, Southeast Tibet, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(10): 3122-3128. |
| 马和平, 郭其强, 刘合满, 等. 藏东南色季拉山西坡土壤有机碳库研究. 生态学报, 2013, 33(10): 3122-3128. | |
| 25 | Liu Q, Tang J. Vertical distribution and correlation analysis of soil active organic carbon components in saline-alkali reed wetland. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(5): 1760-1766. |
| 刘骞, 汤洁. 盐碱芦苇湿地土壤活性有机碳组分垂直分布及相关性分析. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(5): 1760-1766. | |
| 26 | Zhang H Y, Wang K Q, Song Y L, et al. Distribution characteristics of soil active organic carbon in different land use types in Jianshan River watershed in Middle Yunnan Province. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(3): 16-21. |
| 张华渝, 王克勤, 宋娅丽, 等. 滇中尖山河小流域不同土地利用类型土壤活性有机碳分布特征. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(3): 16-21. | |
| 27 | Xu M L, Wu W, Yan Z M, et al. The content and vertical distribution of soil labile organic carbons in different land use types in the tidal flat area. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 44(4): 167-175. |
| 许梦璐, 吴炜, 颜铮明, 等.滨海滩涂不同土地利用类型土壤活性有机碳含量与垂直分布. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4): 167-175. | |
| 28 | Tang G Y, Huang D Y, Tong C L, et al. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon in hilly red soil region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(3): 3429-3433. |
| 唐国勇, 黄道友, 童成立, 等. 红壤丘陵景观单元土壤有机碳和微生物生物量碳含量特征. 应用生态学报, 2006, 17(3): 3429-3433. | |
| 29 | Jandl R, Sollins P. Water-extractable soil carbon in relation to the belowground carbon cycle. Biology Fertilizer Soils, 1997, 25(2): 196-201. |
| 30 | Zhang Q Q. The comparison of the different community types in mountain meadow steppe. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2015. |
| 张倩倩. 山地草甸草原不同群落类型碳储量比较研究. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2015. | |
| 31 | Li T J, Zhao Y, Zhang K L, et al. Soil geography. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2005. |
| 李天杰, 赵烨, 张科利, 等. 土壤地理学. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005. |
| [1] | 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 王芳, 李志刚. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| [2] | 高金龙, 刘洁, 殷建鹏, 葛静, 侯蒙京, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 天然草地牧草营养品质的高光谱遥感研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 172-185. |
| [3] | 王晓娇, 齐鹏, 蔡立群, 陈晓龙, 谢军红, 甘慧炯, 张仁陟. 培肥措施对旱地农田产量可持续性及土壤有机碳库稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 58-69. |
| [4] | 倪璐, 吴静, 李纯斌, 秦格霞, 李政, 孔婕. 近30年中国天然草地物候时空变化特征分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 1-12. |
| [5] | 林语梵, 朱鸿福, 王丽慧, 张桂杰. 宁夏黄灌区专用青贮玉米品种生产性能和营养价值研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 40-48. |
| [6] | 都帅, 刘昊, 尤思涵, 格根图, 贾玉山. 打捆密度和堆垛方式对天然草地青干草化学成分和真菌毒素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 143-150. |
| [7] | 于双, 许冬梅, 许爱云, 刘金龙, 陶利波. 不同恢复措施对宁夏荒漠草原土壤碳氮储量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 12-19. |
| [8] | 张苗苗, 陈伟, 林丽, 张德罡, 吴玉鑫, 肖海龙. 青海省不同高寒草地土壤主要养分及可溶性有机碳特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 20-28. |
| [9] | 李明雨, 黄文广, 杨君珑, 李小伟. 宁夏草原植物叶片氮磷化学计量特征及其驱动因素[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 23-32. |
| [10] | 王旭洋, 李玉强, 连杰, 罗永清, 牛亚毅, 龚相文. CENTURY模型在不同生态系统的土壤有机碳动态预测研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 179-189. |
| [11] | 于双, 陶利波, 许冬梅, 许爱云, 刘金龙. 封育对荒漠草原土壤有机碳及其活性组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 190-196. |
| [12] | 王多斌, 籍常婷, 林慧龙. 基于DNDC模型的高寒草甸土壤有机碳含量动态研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 197-204. |
| [13] | 聂明鹤, 沈艳, 饶丽仙. 宁夏典型草原区退耕草地群落演替序列与环境解释[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 11-20. |
| [14] | 黎嘉成, 高明, 田冬, 黄容, 徐国鑫. 秸秆及生物炭还田对土壤有机碳及其活性组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 39-50. |
| [15] | 蒋腊梅, 杨晓东, 杨建军, 何学敏, 吕光辉. 不同管理模式对干旱区草地土壤有机碳氮库的影响及其影响因素探究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 22-33. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||