

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 82-90.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022392
魏艳1( ), 刘有斌1, 刘枭宏2, 谌芸1(
), 刘有斌1, 刘枭宏2, 谌芸1( ), 颜哲豪1, 都艺芝1
), 颜哲豪1, 都艺芝1
收稿日期:2022-10-06
修回日期:2022-12-05
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-06-16
通讯作者:
谌芸
作者简介:E-mail: sy22478@126.com基金资助:
Yan WEI1( ), You-bin LIU1, Xiao-hong LIU2, Yun CHEN1(
), You-bin LIU1, Xiao-hong LIU2, Yun CHEN1( ), Zhe-hao YAN1, Yi-zhi DU1
), Zhe-hao YAN1, Yi-zhi DU1
Received:2022-10-06
Revised:2022-12-05
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-06-16
Contact:
Yun CHEN
摘要:
为探究紫色土区草类根系对土壤抗剪性能的影响,以单播的拉巴豆、紫花苜蓿和裸地(CK)为对象,分析根系形态、纤维含量和抗拉力学性能,构建根-土复合体抗剪性能估算模型。结果表明:1)2种草根-土复合体黏聚力及不同荷载下的抗剪强度均高于CK,分别增强了141.30%~189.74%和1.18%~63.81%;2)2种草优势直径(d,mm)为0<d≤0.5径级,而在0.5<d≤1.0径级则表现为拉巴豆的根长密度、根表面积密度和根体积比均显著高于紫花苜蓿,分别高63.16%、62.50%和53.30%;3)黏聚力与根长密度呈显著正相关(R2>0.710,P<0.01),与根长密度、极限延伸率拟合效果较好(R2>0.900,P<0.01),模型预测值精度较高。总体上,紫色土坡地拉巴豆根系增强土壤抗剪性能效果优于紫花苜蓿根系。
魏艳, 刘有斌, 刘枭宏, 谌芸, 颜哲豪, 都艺芝. 紫色土区拉巴豆和紫花苜蓿根-土复合体抗剪性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 82-90.
Yan WEI, You-bin LIU, Xiao-hong LIU, Yun CHEN, Zhe-hao YAN, Yi-zhi DU. Study on shear strength of root-soil composite of Dolichos lablab and Medicago sativa in purple soil region[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 82-90.
处理 Treatment | 土壤容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity (%) | 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity (%) | 非毛管孔隙度 Non-capillary porosity (%) | 自然含水率 Soil moisture (%) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 裸地CK | 1.34±0.09 | 47.23±0.02 | 34.70±0.03 | 12.54±0.06 | 13.36±0.03 | 21.69±5.05 |
| 拉巴豆D. lablab | 1.21±0.02 | 54.36±0.15 | 32.30±1.18 | 22.26±1.23 | 15.36±0.28 | 28.58±5.42 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 1.27±0.05 | 51.32±0.02 | 32.74±1.98 | 18.58±1.31 | 15.49±0.02 | 30.23±7.52 |
表1 研究区土壤理化性质
Table 1 Soil physical and chemical properties in the study area
处理 Treatment | 土壤容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity (%) | 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity (%) | 非毛管孔隙度 Non-capillary porosity (%) | 自然含水率 Soil moisture (%) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 裸地CK | 1.34±0.09 | 47.23±0.02 | 34.70±0.03 | 12.54±0.06 | 13.36±0.03 | 21.69±5.05 |
| 拉巴豆D. lablab | 1.21±0.02 | 54.36±0.15 | 32.30±1.18 | 22.26±1.23 | 15.36±0.28 | 28.58±5.42 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 1.27±0.05 | 51.32±0.02 | 32.74±1.98 | 18.58±1.31 | 15.49±0.02 | 30.23±7.52 |
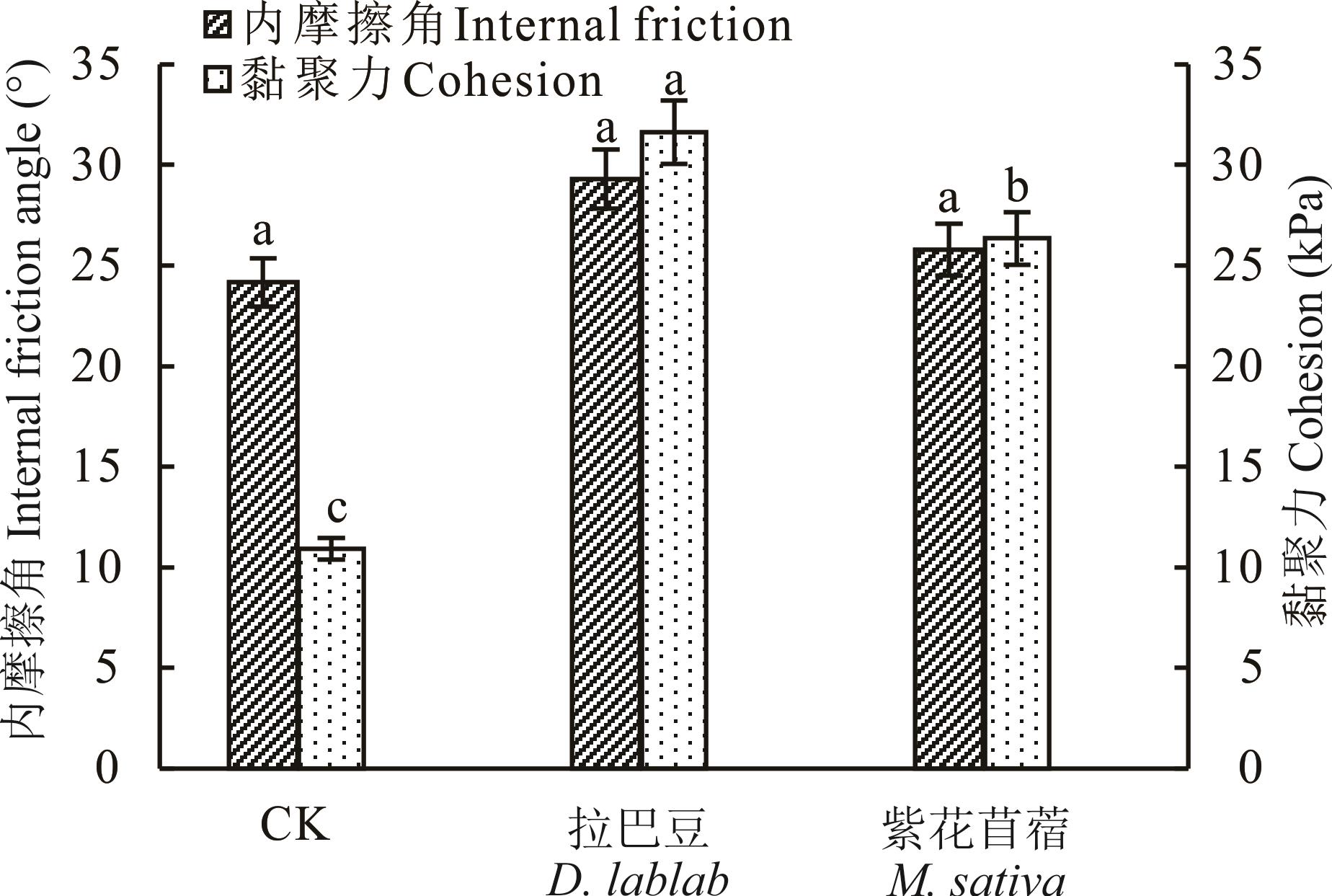
图2 根-土复合体及CK的黏聚力和内摩擦角不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.2 Cohesion and internal friction angle of root-soil complex and CK
根径 Root diameter | 植物种类 Plant species | 根长密度 Root length density (cm·cm-3) | 根表面积密度 Root surface density (cm2·cm-3) | 根体积比 Root volume ratio (cm3·cm-3) | 根尖数 Root tips | 纤维素 Cellulose (%) | 半纤维素 Lignin (%) | 木质素 Hemicellulose (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 2.74±1.30Aa | 0.17±0.07Aa | 0.11±0.04Ab | 1055±723Aa | 36.81±0.85Aa | 26.61±1.84Aa | 21.36±0.10Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 2.84±2.83Aa | 0.15±0.14Aa | 0.09±0.08Aa | 1523±469Aa | 31.69±0.49Aa | 24.06±0.08Aa | 21.15±0.25Aa | |
| Ⅱ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 0.62±0.30Ab | 0.13±0.07Aa | 0.23±0.12Aa | 21±8Ab | 35.05±2.01Aab | 24.64±1.44Aa | 22.11±2.59Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.38±0.29Bb | 0.08±0.06Bab | 0.15±0.11Ba | 17±5Ab | 34.17±2.48Aa | 25.29±1.03Aa | 23.35±2.86Aa | |
| Ⅲ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 0.11±0.07Ab | 0.04±0.02Ab | 0.13±0.07Ab | 4±2Ab | 32.46±0.36Bb | 24.50±0.93Aa | 21.53±1.56Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.11±0.07Ab | 0.04±0.03Ab | 0.13±0.09Aa | 3±1Ab | 37.03±1.35Aa | 26.12±0.15Aa | 21.58±0.28Aa | |
| Ⅳ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 0.04±0.02Ab | 0.02±0.01Ab | 0.09±0.06Ab | 1±1Ab | 35.08±0.26Aa | 27.37±1.07Aa | 24.37±3.02Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.06±0.06Ab | 0.04±0.03Ab | 0.15±0.14Aa | 1±1Ab | 35.58±1.66Aa | 25.06±0.72Aa | 23.26±1.02Aa |
表2 根-土复合体中根系形态特征和纤维含量
Table 2 Morphological traits and fiber contents of roots in the root-soil complexes
根径 Root diameter | 植物种类 Plant species | 根长密度 Root length density (cm·cm-3) | 根表面积密度 Root surface density (cm2·cm-3) | 根体积比 Root volume ratio (cm3·cm-3) | 根尖数 Root tips | 纤维素 Cellulose (%) | 半纤维素 Lignin (%) | 木质素 Hemicellulose (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 2.74±1.30Aa | 0.17±0.07Aa | 0.11±0.04Ab | 1055±723Aa | 36.81±0.85Aa | 26.61±1.84Aa | 21.36±0.10Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 2.84±2.83Aa | 0.15±0.14Aa | 0.09±0.08Aa | 1523±469Aa | 31.69±0.49Aa | 24.06±0.08Aa | 21.15±0.25Aa | |
| Ⅱ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 0.62±0.30Ab | 0.13±0.07Aa | 0.23±0.12Aa | 21±8Ab | 35.05±2.01Aab | 24.64±1.44Aa | 22.11±2.59Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.38±0.29Bb | 0.08±0.06Bab | 0.15±0.11Ba | 17±5Ab | 34.17±2.48Aa | 25.29±1.03Aa | 23.35±2.86Aa | |
| Ⅲ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 0.11±0.07Ab | 0.04±0.02Ab | 0.13±0.07Ab | 4±2Ab | 32.46±0.36Bb | 24.50±0.93Aa | 21.53±1.56Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.11±0.07Ab | 0.04±0.03Ab | 0.13±0.09Aa | 3±1Ab | 37.03±1.35Aa | 26.12±0.15Aa | 21.58±0.28Aa | |
| Ⅳ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 0.04±0.02Ab | 0.02±0.01Ab | 0.09±0.06Ab | 1±1Ab | 35.08±0.26Aa | 27.37±1.07Aa | 24.37±3.02Aa |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.06±0.06Ab | 0.04±0.03Ab | 0.15±0.14Aa | 1±1Ab | 35.58±1.66Aa | 25.06±0.72Aa | 23.26±1.02Aa |
根径级别 Root diameter class | 植物种类 Plant species | 抗拉强度 Tensile strength (MPa) | 极限延伸率 Ultimate elongation (%) | 弹性模量 Elastic modulus (MPa) | 平均根直径 Mean root diameter (mm) | 样本数 Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 52.07±7.52Aa | 6.24±1.41Aab | 864.68±153.45Ba | 0.26 | 14 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 47.69±16.38Aa | 3.67±1.50Ab | 1538.11±740.75Aa | 0.39 | 10 | |
| Ⅱ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 38.88±6.85Ab | 5.31±1.84Ab | 839.82±325.14Aa | 0.67 | 17 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 36.86±3.83Ab | 7.13±2.55Aab | 607.52±271.76Bb | 0.87 | 19 | |
| Ⅲ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 24.60±7.57Ac | 9.61±2.56Aa | 289.75±152.79Ab | 1.36 | 20 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 20.41±4.02Bc | 11.09±3.67Aa | 195.03±43.06Bb | 1.22 | 20 | |
| Ⅳ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 13.94±5.37Ad | 9.22±2.29Aa | 170.38±89.79Ab | 1.62 | 14 |
| 紫花苜蓿M.sativa | 12.07±3.02Ac | 11.52±3.85Aa | 123.57±64.04Bb | 1.79 | 17 |
表3 单根抗拉力学性能指标
Table 3 Root tensile properties of different root diameter classes
根径级别 Root diameter class | 植物种类 Plant species | 抗拉强度 Tensile strength (MPa) | 极限延伸率 Ultimate elongation (%) | 弹性模量 Elastic modulus (MPa) | 平均根直径 Mean root diameter (mm) | 样本数 Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 52.07±7.52Aa | 6.24±1.41Aab | 864.68±153.45Ba | 0.26 | 14 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 47.69±16.38Aa | 3.67±1.50Ab | 1538.11±740.75Aa | 0.39 | 10 | |
| Ⅱ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 38.88±6.85Ab | 5.31±1.84Ab | 839.82±325.14Aa | 0.67 | 17 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 36.86±3.83Ab | 7.13±2.55Aab | 607.52±271.76Bb | 0.87 | 19 | |
| Ⅲ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 24.60±7.57Ac | 9.61±2.56Aa | 289.75±152.79Ab | 1.36 | 20 |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 20.41±4.02Bc | 11.09±3.67Aa | 195.03±43.06Bb | 1.22 | 20 | |
| Ⅳ | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 13.94±5.37Ad | 9.22±2.29Aa | 170.38±89.79Ab | 1.62 | 14 |
| 紫花苜蓿M.sativa | 12.07±3.02Ac | 11.52±3.85Aa | 123.57±64.04Bb | 1.79 | 17 |
指标 Indicators | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
黏聚力 Cohesion | 内摩擦角 Internal friction angle | 黏聚力 Cohesion | 内摩擦角 Internal friction angle | |
| 根长密度Root length density | 0.715** | -0.025 | 0.949** | -0.579* |
| 根表面积密度Root surface density | 0.729** | -0.037 | 0.575 | -0.563 |
| 根体积比Root volume ratio | 0.400 | -0.034 | -0.174 | -0.031 |
| 根尖数Root tips | 0.651* | 0.228 | 0.590* | -0.276 |
| 纤维素Cellulose | -0.424 | 0.116 | 0.120 | -0.046 |
| 半纤维素Hemicellulose | 0.066 | 0.420 | 0.723* | -0.476 |
| 木质素Lignin | 0.720* | 0.292 | 0.390 | -0.353 |
| 抗拉强度Tensile strength | 0.381 | -0.327 | -0.183 | 0.200 |
| 极限延伸率Ultimate elongation | -0.673* | 0.562 | -0.878** | 0.529 |
表4 相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis
指标 Indicators | 拉巴豆D. lablab | 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
黏聚力 Cohesion | 内摩擦角 Internal friction angle | 黏聚力 Cohesion | 内摩擦角 Internal friction angle | |
| 根长密度Root length density | 0.715** | -0.025 | 0.949** | -0.579* |
| 根表面积密度Root surface density | 0.729** | -0.037 | 0.575 | -0.563 |
| 根体积比Root volume ratio | 0.400 | -0.034 | -0.174 | -0.031 |
| 根尖数Root tips | 0.651* | 0.228 | 0.590* | -0.276 |
| 纤维素Cellulose | -0.424 | 0.116 | 0.120 | -0.046 |
| 半纤维素Hemicellulose | 0.066 | 0.420 | 0.723* | -0.476 |
| 木质素Lignin | 0.720* | 0.292 | 0.390 | -0.353 |
| 抗拉强度Tensile strength | 0.381 | -0.327 | -0.183 | 0.200 |
| 极限延伸率Ultimate elongation | -0.673* | 0.562 | -0.878** | 0.529 |
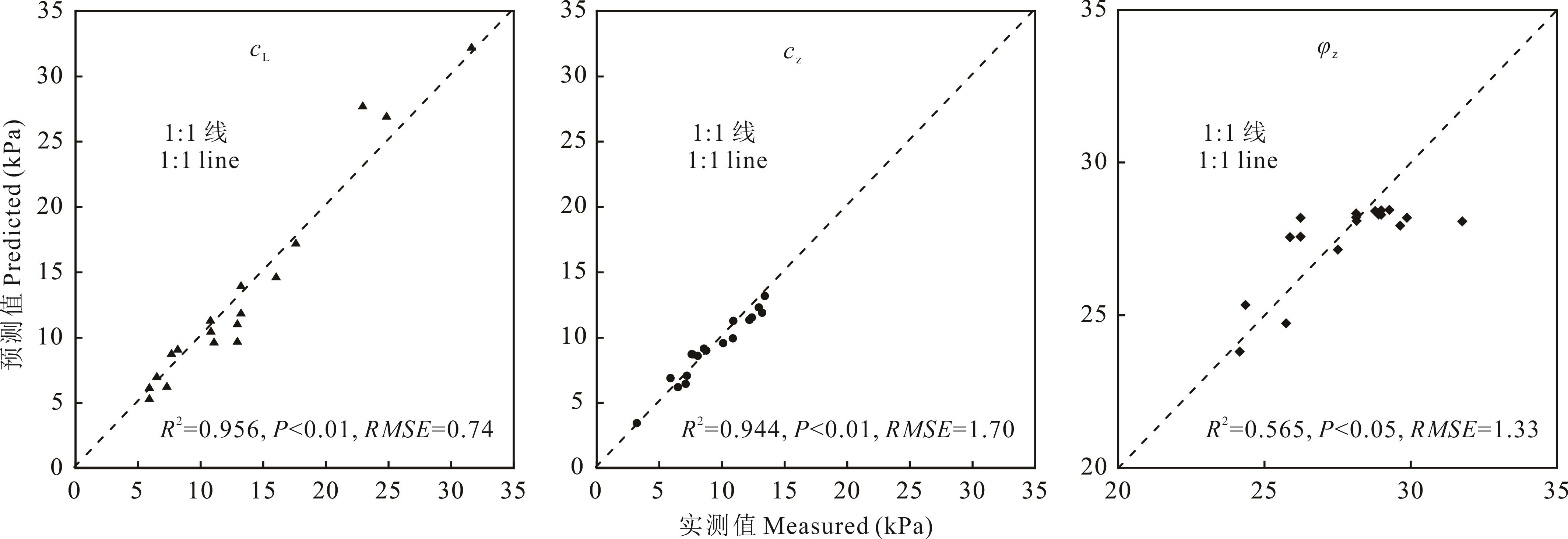
图4 拟合方程预测值与实测值对比cL:?拉巴豆根-土复合体黏聚力Cohesion of D. lablab root-soil composite; cZ: 紫花苜蓿根-土复合体黏聚力Cohesion of M. sativa root-soil composite; φZ: 紫花苜蓿根-土复合体内摩擦角Internal friction angle of M. sativa root-soil composite.
Fig.4 Measured cohesion and internal friction angle versus predicted values
| 1 | Chen Y, He B H, Lian C X, et al. Root system distribution characteristics of three herbs and their effects on soil composition and nutrients in the ‘Purple Soil’ region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(10): 99-107. |
| 谌芸, 何丙辉, 练彩霞, 等. 紫色土区3种草本植物根系特征及改土培肥效应. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 99-107. | |
| 2 | Ding W B, He W J, Shi D M, et al. Effect of drying-wetting condition on attenuation-recovery of soil shear strength of bio-embankment on sloping farmland comprising purple soil. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(6): 56-67. |
| 丁文斌, 何文健, 史东梅, 等. 干湿作用对紫色土坡耕地生物埂土壤抗剪强度衰减-恢复效应. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 56-67. | |
| 3 | Lin C, Tu S, Huang J, et al. The effect of plant hedgerows on the spatial distribution of soil erosion and soil fertility on sloping farmland in the purple-soil area of China. Soil & Tillage Research, 2009, 105(2): 307-312. |
| 4 | Li J, Wang X, Jia H X, et al. Ecological restoration with shrub roots for slope reinforcement in a shallow landslide-prone region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(14): 5117-5126. |
| 李佳, 汪霞, 贾海霞, 等. 浅层滑坡多发区典型灌木根系对边坡土体抗剪强度的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(14): 5117-5126. | |
| 5 | Fan C C, Tsai M H. Spatial distribution of plant root forces in root-permeated soils subject to shear. Soil & Tillage Research, 2016, 156: 1-15. |
| 6 | Xia Z Y, Liu Q, Xu W N, et al. Characteristics of interface friction between Indigofera amblyantha root system and soil. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(1): 128-134. |
| 夏振尧, 刘琦, 许文年, 等. 多花木蓝根系与土体界面摩阻特征. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(1): 128-134. | |
| 7 | Wang R Z, Chen Y, Li T, et al. Root distribution characteristics of Vetiveria zizanioides and Digitaria sanguinalis and their effects on the anti-erodibility of purple soil in slopelands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(7): 45-54. |
| 王润泽, 谌芸, 李铁, 等. 香根草和马唐的根系特征及对坡地紫色土抗侵蚀性的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 45-54. | |
| 8 | Liu Y B, Hu X S, Yu D M, et al. Distribution characteristics of combined herb and shrub roots in loess area of Xining basin and their effect on enhancing soil shear strength. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(3): 471-481. |
| 刘亚斌, 胡夏嵩, 余冬梅, 等. 西宁盆地黄土区草本和灌木组合根系分布特征及其增强土体抗剪强度效应. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(3): 471-481. | |
| 9 | Pollen N. Temporal and spatial variability in root reinforcement of streambanks: Accounting for soil shear strength and moisture. Catena, 2007, 69(3): 197-205. |
| 10 | Zhao J L, Li G F, Hu W, et al. Experiment research on rainforest trees tap root resistance slide effect in the shallow landslide. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(S1): 3663-3669. |
| 赵记领, 李光范, 胡伟, 等. 雨林乔木直根根土复合体的抗剪强度试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(S1): 3663-3669. | |
| 11 | Zhang C B, Zhou X, Jiang J, et al. Root moisture content influence on root tensile tests of herbaceous plants. Catena, 2019, 172: 140-147. |
| 12 | Li Z Y, Ouyang M, Xiao H B, et al. Improvement of slope soil consolidation capacity of plant root system based on regulation of root architecture. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(12): 3271-3280, 3290. |
| 李珍玉, 欧阳淼, 肖宏彬, 等. 基于根系构型的调控提高植物边坡根系固土能力. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(12): 3271-3280, 3290. | |
| 13 | Li Y P, Wang Y Q, Wang Y J, et al. Effects of Vitex negundo root properties on soil resistance caused by pull-out forces at different positions around the stem. Catena, 2017, 158: 148-160. |
| 14 | Zhang C B, Chen L H, Jiang J. Why fine tree roots are stronger than thicker roots: The role of cellulose and lignin in relation to slope stability. Geomorphology, 2014, 206(206): 196-202. |
| 15 | Tang H, Chen Y, Liu X H, et al. Study on the mechanic features of root and root-soil matrix of Dolichos lablab L.hedgerows on the slopes of the karst area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(16): 6114-6125. |
| 唐菡, 谌芸, 刘枭宏, 等. 喀斯特坡地拉巴豆地埂篱根及根-土复合体力学特性. 生态学报, 2019, 39(16): 6114-6125. | |
| 16 | Ghestem M, Ceylon G, Bernard A, et al. Influence of plant root system morphology and architectural traits on soil shear resistance. Plant & Soil, 2014, 377(1/2): 43-61. |
| 17 | Li J X, He B H, Chen Y, et al. Root characteristics of Cynodon dactylis and Trifolium repens and their effect on shear performance of purple soil in barren hillside. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 29(10): 144-152. |
| 李建兴, 何丙辉, 谌芸, 等. 不同护坡草本植物的根系分布特征及其对土壤抗剪强度的影响. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(10): 144-152. | |
| 18 | Su X, Zhou Z, Liu J, et al. The role of root traits of climax community species to shear strength in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Soil & Tillage Research, 2022, 221: 105417. |
| 19 | Zhang C B, Chen L H, Liu Y P, et al. Triaxial compression test of soil-root composites to evaluate influence of roots on soil shear strength. Ecological Engineering, 2010, 36(1): 19-26. |
| 20 | Liu X H. The effects of terrace hedgerows roots on the erodibility of the root-soil complex in the purple soil area. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021. |
| 刘枭宏. 紫色土区地埂篱根系对根-土复合体抗侵蚀性能的影响. 重庆: 西南大学, 2021. | |
| 21 | Lateh H, Avani N, Bibalani G H. Tensile strength and root distribution of Acacia mangium and Macaranga tanarius at spatial variation (Case study: East-West highway, Malaysia). International Journal of Biosciences, 2015, 6(7): 18-28. |
| 22 | Institute of Soil Physics, Nanjing Soil Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Physical properties of soil. Beijing: Beijing Science Press, 1978. |
| 中国科学院南京土壤研究所土壤物理研究室. 土壤物理性质测定法. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978. | |
| 23 | Qiang J J, Yan Z H, Chen Y, et al. Factors affecting the shear strength of root-soil complexes from three types of grass hedgerows in a karst area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 27-37. |
| 强娇娇, 颜哲豪, 谌芸, 等. 喀斯特区3种草篱根-土复合体抗剪性能及其影响因素. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 27-37. | |
| 24 | Li H S. Experimental principle and techniques for plant physiology and biochemistry. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. | |
| 25 | Baets S D, Poesen J, Reubens B, et al. Root tensile strength and root distribution of typical Mediterranean plant species and their contribution to soil shear strength. Plant and Soil, 2008, 305(1/2): 207-226. |
| 26 | Liu Y B, Hu X S, Yu D M, et al. Influence of the roots of mixed-planting species on the shear strength of saline loess soil. Journal of Mountain Science, 2021, 18(3): 806-818. |
| 27 | Liu X H, Chen Y, Yan Z H, et al. The effects of grass hedgerow roots on shear strength and scouring resistance of root-soil complexes in the purple soil region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 98-107. |
| 刘枭宏, 谌芸, 颜哲豪, 等. 紫色土区草篱根系对其根-土复合体抗剪和抗冲性能的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 98-107. | |
| 28 | Mao Z J, Zhang J G, Bi Y L, et al. Numerical analysis of protection time effect on planting alfalfa in loess slope with shallow failure. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(15): 72-83. |
| 毛正君, 张瑾鸽, 毕银丽, 等. 紫花苜蓿对黄土边坡浅层破坏防护时间效应的数值分析. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(15): 72-83. | |
| 29 | Li Q, Liu G B, Zhang Z, et al. Effect of root architecture on structural stability and erodibility of topsoils during concentrated flow in hilly Loess Plateau. Chinese Geographical Science, 2015, 25: 757-764. |
| 30 | Matti C, Bischetti G B, Gentile F. Biotechnical characteristics of root systems of typical Mediterranean species. Plant and Soil, 2005, 278(1/2): 23-32. |
| 31 | Feng S Y, Wang J G, Wen H, et al. Soil shear strength of collapsing erosion area in south Jiangxi of China relative to position of the soil and its influencing factors. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(1): 71-83. |
| 冯舒悦, 王军光, 文慧, 等. 赣南崩岗侵蚀区不同部位土壤抗剪强度及影响因素研究. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(1): 71-83. | |
| 32 | Gonzalez-Ollauri A, Mickovski S B. Plant-soil reinforcement response under different soil hydrological regimes. Geoderma, 2017, 285: 141-150. |
| [1] | 杨瑞杰, 何淑勤, 周树峰, 杨晶月, 金钰宪, 郑子成. 杂交粱草生长期土壤抗冲性变化特征及其根系调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 149-159. |
| [2] | 廖小琴, 王长庭, 刘丹, 唐国, 毛军. 氮磷配施对高寒草甸植物根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 160-174. |
| [3] | 陈晓明, 韩东英, 宋桂龙. 砷(As)胁迫对海滨雀稗As吸收特征及根系形态影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 112-119. |
| [4] | 何伟鹏, 胡夏嵩, 刘昌义, 李璇, 李希来, 付江涛, 卢海静, 杨馥铖, 李国荣. 黄河源区不同禁牧年限对垂穗披碱草单根及其根-土复合体力学强度特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 106-117. |
| [5] | 曹玉莹, 苏雪萌, 周正朝, 郑群威, 岳佳辉. 黄土高原典型草本植物根-土复合体抗剪性能的空间差异性及其影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 94-105. |
| [6] | 金媛媛, 陈振江, 王添, 李春杰. 内生真菌和田间管理措施对土壤真菌群落丰度和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 142-152. |
| [7] | 许爱云, 张丽华, 王晓佳, 马冲, 李元景, 曹兵. 蒙古冰草非结构性碳水化合物及碳氮磷化学计量特征对氮添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 35-43. |
| [8] | 王晓龙, 杨曌, 来永才, 李红, 钟鹏, 徐艳霞, 柴华, 李莎莎, 吴玥, 宋敏超, 周景明. 不同秋眠等级苜蓿根系性状对越冬的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 144-153. |
| [9] | 姜瑛, 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 申凤敏, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 杨芳, 柳海涛. 外源硅对镉胁迫下玉米生理参数及根系构型分级的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 139-154. |
| [10] | 杨志新, 郑旭, 陈来宝, 于泳鑫, 张凤华, 李鲁华, 王家平. 干旱区盐碱地食叶草根系形态分布适应策略研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 15-27. |
| [11] | 甘凤玲, 韦杰, 李沙沙. 紫色土埂坎典型草本根系摩阻特性对土壤含水率的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 28-37. |
| [12] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. |
| [13] | 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 柳海涛, 张静静, 申凤敏, 姜瑛, 张雪海, 孙娈姿, 杨芳, 刘振. 镉暴露条件下玉米生长及根系构型分级特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. |
| [14] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [15] | 白婕, 臧真凤, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 王可珍, 屈洋, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿叶片和根系膜脂过氧化及C、N特征对水分和N添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 213-220. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||