

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 247-256.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022464
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-11-25
修回日期:2023-01-12
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
张吉宇
作者简介:E-mail: zhangjy@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Sheng-sheng WANG( ), Zhen DUAN, Pei ZHOU, Ji-yu ZHANG(
), Zhen DUAN, Pei ZHOU, Ji-yu ZHANG( )
)
Received:2022-11-25
Revised:2023-01-12
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-07-26
Contact:
Ji-yu ZHANG
摘要:
为研究草木樨共生固氮的形成机制,以白花草木樨野生型Ma389经甲基磺酸乙酯(EMS)诱变后的Ma58、Ma61和Ma62结瘤缺失型突变体为材料,接种苜蓿中华根瘤菌SM1021后对其结瘤表型和生物量进行了分析。结果表明:突变体Ma58、Ma61不形成侵染线和根瘤原基,突变体Ma62不形成侵染线,且只形成少数不固氮的白色小根瘤。3种突变体在低氮基质中生长30 d时,根鲜/干质量显著低于野生型(P<0.05),从40 d开始,地上部鲜/干质量、根鲜/干质量、株高和根长均显著低于野生型(P<0.05),在富氮基质中则无显著差异,表明这3种突变体的突变基因只与共生固氮相关,为草木樨共生固氮机制研究奠定了遗传材料基础。
王升升, 段珍, 周培, 张吉宇. 白花草木樨结瘤缺失型突变体的结瘤表型及生物量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 247-256.
Sheng-sheng WANG, Zhen DUAN, Pei ZHOU, Ji-yu ZHANG. Phenotype and biomass analysis of nodulation-deletion mutants in Melilotus albus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 247-256.
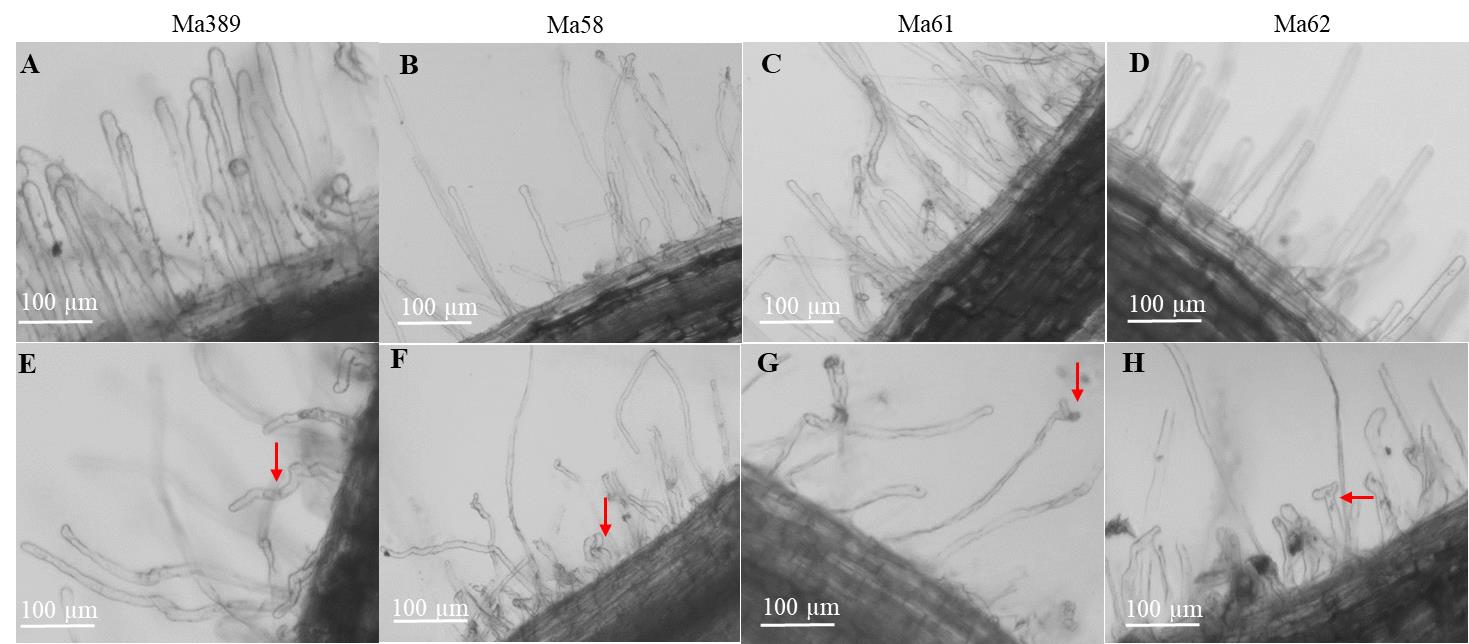
图1 野生型与3种突变体的根毛接种苜蓿中华根瘤菌后的变化A~D:未接种的根毛;E~H:接种后3 d的根毛;红色箭头指向代表性的变形根毛。A-D: Uninoculated root hairs; E-H: Root hairs after inoculation 3 days; The red arrow points to representative deformed root hairs.
Fig.1 Responses of root hairs from wild-type and three mutants inoculated with SM1021
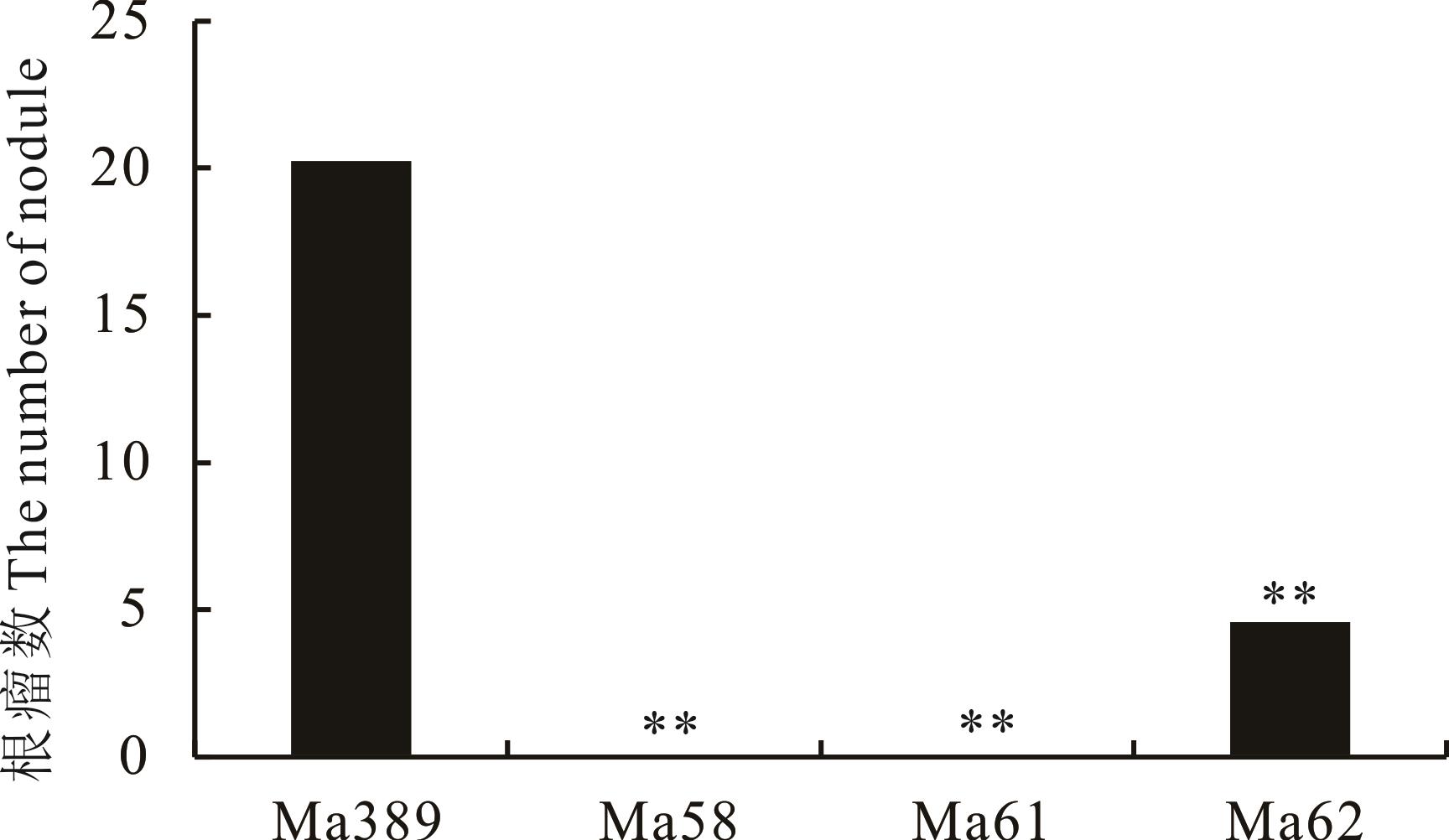
图3 野生型与3种突变体植株30 d时的根瘤数*表示野生型与非结瘤突变体在0.05水平上差异有统计学意义;**表示在0.01水平上差异有统计学意义。下同。* indicates statistically significant difference between wild-type and non-nodulation mutants at 0.05 level; ** indicates statistically significant difference at the 0.01 level. The same below.
Fig.3 Nodule number of wild-type and three mutants at 30 days
| 1 | Wang J Y. Screening and functional verification of genes related to symbiotic nitrogen fixation in mesorhizobium MAFF303099. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 王婧仪. 中慢生根瘤菌MAFF303099共生固氮相关基因筛选及功能验证. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. | |
| 2 | Zheng H L, Pang B P, Jin R S, et al. Primary identification of nitrogen fixation bacteria isolated from rhizosphere of 4 species of grasses in Xilingol grassland of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2011, 25(9): 106-109. |
| 郑红丽, 庞保平, 靳润岁, 等. 内蒙古锡林郭勒天然草原禾本科牧草根际18株固氮细菌的初步分类鉴定. 干旱区资源与环境, 2011, 25(9): 106-109. | |
| 3 | Huo H B. Responses of Robinia pseudoacacia to rhizobial nod factor and the mechanism of heme degrading enzyme HmuS in symbiosis. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2021. |
| 霍海波. 刺槐对根瘤菌结瘤因子的响应及血红素降解因子HmuS在共生中的作用机制研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. | |
| 4 | Zhang C. The phenotypic analysis and map-based cloning of nitrogen fixing deficient mutants in Medicago truncatula. Changsha: Hunan University, 2021. |
| 张超. 蒺藜苜蓿固氮缺失突变体的表型分析和图位克隆. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2021. | |
| 5 | Cui Z L, Zhang H Y, Chen X P, et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature, 2018, 555(7696): 363-380. |
| 6 | Zhang X, Eric A D, Denise L M, et al. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature, 2015, 528(5743): 51-59. |
| 7 | Xie K Y, Wang Y X, Wan J C, et al. Mechanisms and factors affecting nitrogen transfer in mixed legume/grass swards: A review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. |
| 谢开云, 王玉祥, 万江春, 等. 混播草地中豆科/禾本科牧草氮转移机理及其影响因素. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. | |
| 8 | Doyle J J, Luckow M A. The rest of the iceberg. Legume diversity and evolution in a phylogenetic context. Plant Physiology, 2003, 131(3): 900-910. |
| 9 | Li J H, Xi N, Man J, et al. Effects rhizobial population and inoculation method on the efficiency of alfalfa rhizobium inoculation. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(3): 743-749. |
| 李佳欢, 希娜, 漫静, 等. 苜蓿根瘤菌接种数量与方式对接种效果的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(3): 743-749. | |
| 10 | Sutton M A, Oenema O, Erisman J W, et al. Too much of a good thing. Nature, 2011, 472(7342): 159-161. |
| 11 | Peoples M B, Brockwell J, Herridge D F, et al. The contributions of nitrogen-fixing crop legumes to the productivity of agricultural systems. Symbiosis, 2009, 48(1/2/3): 1-17. |
| 12 | Roy S, Liu W, Nandety R S, et al. Celebrating 20 years of genetic discoveries in legume nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Plant Cell, 2020, 32(1): 15-41. |
| 13 | Saito K, Yoshikawa M, Yano K, et al. NUCLEOPORIN85 is required for calcium spiking, fungal and bacterial symbioses, and seed production in Lotus japonicus. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(2): 610-624. |
| 14 | Kiss E, Olah B, Kalo P, et al. LIN, a novel type of U-Box/WD40 protein, controls early infection by rhizobia in legumes. Plant Physiology, 2009, 151(3): 1239-1249. |
| 15 | Peters J L, Cnudde F, Gerats T. Forward genetics and map-based cloning approaches. Trends in Plant Science, 2003, 8(10): 484-491. |
| 16 | Stracke S, Kistner C, Yoshida S, et al. A plant receptor-like kinase required for both bacterial and fungal symbiosis. Nature, 2002, 417(6892): 959-962. |
| 17 | Wang D, Griffitts J, Starker C, et al. A nodule-specific protein secretory pathway required for nitrogen-fixing symbiosis. Science, 2010, 327(5969): 1126-1129. |
| 18 | Catoira R, Galera C, de Billy F, et al. Four genes of Medicago truncatula controlling components of a nod factor transduction pathway. Plant Cell, 2000, 12(9): 1647-1665. |
| 19 | Di H Y, Luo K, Zhang J Y, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Melilotus populations based on ITS and trnL-trnF sequences. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(2): 265-269. |
| 狄红艳, 骆凯, 张吉宇, 等. 基于ITS和trnL-trnF序列的草木樨种群遗传多样性研究. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(2): 265-269. | |
| 20 | Wu F, Luo K, Yan Z Z, et al. Analysis of miRNAs and their target genes in five Melilotus albus NILs with different coumarin content. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-13. |
| 21 | Wang P L, Yan Z Z, Gao L J, et al. Analysis of genetic variation in agronomic traits of half-sib families of Melilotus albus in the second generation of recurrent selection. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 238-245. |
| 王朋磊, 剡转转, 高莉娟, 等. 白花草木樨第二次轮回选择半同胞家系农艺性状的遗传变异分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 238-245. | |
| 22 | Wang S S, Duan Z, Zhang J Y. Establishment of hairy root transformation system of Melilotus albus induced by Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2591-2599. |
| 王升升, 段珍, 张吉宇. 发根农杆菌介导的白花草木樨毛状根转化体系的建立. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2591-2599. | |
| 23 | Luo K, Jahufer M Z Z, Zhao H, et al. Genetic improvement of key agronomic traits in Melilotus albus. Crop Science, 2018, 58(1): 285-294. |
| 24 | Chen L J, Wang P L, Chen X M, et al. Recurrent selection of new breeding lines and yield potential, nutrient profile and in vitro rumen characteristics of Melilotus officinalis. Field Crops Research, 2022, 287: 108657. |
| 25 | Utrup L J, Cary A J, Norris J H. Five nodulation mutants of white sweetclover (Melilotus-alba Dser) exhibit distinct phenotypes blocked at root hair curling, infection thread development, and nodule organogenesis. Plant Physiology, 1993, 103(3): 925-932. |
| 26 | Lum M R, Li Y, LaRue T A, et al. Investigation of four classes of non-nodulating white sweetclover (Melilotus alba annua Desr.) mutants and their responses to arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 2002, 42(2): 295-303. |
| 27 | Cooper J E. Early interactions between legumes and rhizobia: Disclosing complexity in a molecular dialogue. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2007, 103(5): 1355-1365. |
| 28 | Chaintreuil C, Rivallan R, Bertioli D J, et al. A gene-based map of the nod factor-independent Aeschynomene evenia sheds new light on the evolution of nodulation and legume genomes. DNA Research, 2016, 23(4): 365-376. |
| 29 | Saeki K. Rhizobial measures to evade host defense strategies and endogenous threats to persistent symbiotic nitrogen fixation: A focus on two legume-rhizobium model systems. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2011, 68(8): 1327-1339. |
| 30 | Ferguson B J, Indrasumunar A, Hayashi S, et al. Molecular analysis of legume nodule development and autoregulation. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2010, 52(1): 61-76. |
| 31 | Limpens E, Franken C, Smit P, et al. LysM domain receptor kinases regulating rhizobial nod factor-induced infection. Science, 2003, 302(5645): 630-633. |
| 32 | Ane J M, Kiss G B, Riely B K, et al. Medicago truncatula DMI1 required for bacterial and fungal symbioses in legumes. Science, 2004, 303(5662): 1364-1367. |
| 33 | Levy J, Bres C, Geurts R, et al. A putative Ca2+ and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase required for bacterial and fungal symbioses. Science, 2004, 303(5662): 1361-1364. |
| 34 | Hirsch S, Kim J, Munoz A, et al. GRAS proteins form a DNA binding complex to induce gene expression during nodulation signaling in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell, 2009, 21(2): 545-557. |
| 35 | Feng Y. Molecular mechanism of symbiosis receptor kinase regulating symbiosis nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 冯勇. 百脉根共生受体激酶SymRK 调控共生固氮的分子机制研究. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. | |
| 36 | Wu F, Duan Z, Xu P, et al. Genome and systems biology of Melilotus albus provides insights into coumarins biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(3): 592-609. |
| 37 | Borisov A Y, Madsen L H, Tsyganov V E, et al. The sym35 gene required for root nodule development in pea is an ortholog of Nin from Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiology, 2003, 131(3): 1009-1017. |
| [1] | 李思媛, 崔雨萱, 孙宗玖, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对蒿类荒漠草地土壤有机碳及土壤微生物生物量生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 58-70. |
| [2] | 许开宏, 施招, 马磊超, 王平, 陈昂, 王兴, 成明, 肖粤新, 王荣谭. 基于机载激光雷达与高景一号数据的草原地上生物量反演研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 40-49. |
| [3] | 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 李杭, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [4] | 郭芮, 伏帅, 侯蒙京, 刘洁, 苗春丽, 孟新月, 冯琦胜, 贺金生, 钱大文, 梁天刚. 基于Sentinel-2数据的青海门源县天然草地生物量遥感反演研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 15-29. |
| [5] | 郑甲成, 余婕, 李凡, 黄小奕, 李杰勤, 陈海州, 王歆, 詹秋文, 徐兆师. SbER10_X1调控饲用高粱光合作用和生物产量的功能特性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 91-100. |
| [6] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 马春晖, 张前兵. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| [7] | 苏乐乐, 秦燕, 王瞾敏, 张永超, 刘文辉. 氮磷添加对燕麦与箭筈豌豆不同种植方式草地土壤微生物-胞外酶化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 56-66. |
| [8] | 郭丽珠, 孟慧珍, 范希峰, 滕珂, 滕文军, 温海峰, 岳跃森, 张辉, 武菊英. 野牛草雌雄株对不同形态氮素的生理响应差异[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 65-74. |
| [9] | 许政勇, 孙斌, 张王菲, 李毅夫, 闫紫钰, 岳巍, 滕思翰. 基于优化三角形植被指数(TVI)的灌丛化草原植被地上生物量遥感估测方法研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 1-14. |
| [10] | 戎荣, 孙斌, 武志涛, 高志海, 杜自强, 滕思翰. 灌丛化草原小叶锦鸡儿灌丛地上生物量测量方法研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-47. |
| [11] | 厉方桢, 钟华平, 欧阳克蕙, 赵小敏, 李愈哲. 基于机器学习的阿勒泰地区草地地下生物量估测与数字制图[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 13-23. |
| [12] | 赵翊含, 侯蒙京, 冯琦胜, 高宏元, 梁天刚, 贺金生, 钱大文. 基于Landsat 8和随机森林的青海门源天然草地地上生物量遥感估算[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 1-14. |
| [13] | 游永亮, 赵海明, 李源, 武瑞鑫, 刘贵波, 周健东, 陈俊峰. 饲用麦类作物的生物量积累和营养品质动态变化规律[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 189-201. |
| [14] | 张玉琢, 杨志贵, 于红妍, 张强, 杨淑霞, 赵婷, 许画画, 孟宝平, 吕燕燕. 基于STARFM的草地地上生物量遥感估测研究——以甘肃省夏河县桑科草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 23-34. |
| [15] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||