

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 71-81.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022489
马仁诗1,2( ), 蒋丛泽1,2, 高玮1,2, 李中利1,2, 沈禹颖1,2, 杨宪龙1,2(
), 蒋丛泽1,2, 高玮1,2, 李中利1,2, 沈禹颖1,2, 杨宪龙1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-14
修回日期:2023-02-27
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
杨宪龙
作者简介:E-mail: yangxianl@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Ren-shi MA1,2( ), Cong-ze JIANG1,2, Wei GAO1,2, Zhong-li LI1,2, Yu-ying SHEN1,2, Xian-long YANG1,2(
), Cong-ze JIANG1,2, Wei GAO1,2, Zhong-li LI1,2, Yu-ying SHEN1,2, Xian-long YANG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-12-14
Revised:2023-02-27
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-07-26
Contact:
Xian-long YANG
摘要:
为探究饲用甜高粱节水丰产的灌溉与施氮栽培模式,采用温室自动称重式蒸渗仪研究了3个灌溉量[灌溉保持土壤水分为田间持水量的30%~50%(I1)、50%~70%(I2)、70%~90%(I3)]和3个施氮模式[常规尿素施氮(以纯N计,下同)200 kg·hm-2(U200)、包膜尿素施氮160 kg·hm-2(CU160)、包膜尿素施氮120 kg·hm-2(CU120)]对饲用甜高粱生长、干物质产量、耗水规律及水氮利用效率的影响。结果表明,增加灌溉量显著促进了饲用甜高粱株高、茎粗的生长和单株总叶面积的增加,与I1相比,I2、I3下株高平均值分别提高了9.5%、15.4%,茎粗分别提高了2.4%、27.6%,单株总叶面积分别提高了32.0%、76.0%。同一施氮模式下,饲用甜高粱茎、叶、地上部整株的鲜质量、干质量及茎叶比均随灌水量的增加而显著增大。与I1相比,I2、I3下整株鲜质量平均值分别显著提高了61.7%、187.4%,整株干质量分别显著提高了55.7%、129.8%。施氮模式显著影响茎、叶、地上部整株的鲜质量和干质量。与U200相比,CU160下整株鲜重、干重平均值分别提高了13.9%、22.8%。随着灌溉量的增加,饲用甜高粱单株耗水量及水氮利用效率显著增加。与I1相比,I2、I3下累积耗水量平均值分别显著提高了52.1%、108.4%,干物质水分利用效率分别提高了2.6%、11.3%,氮肥偏生产力分别提高了51.9%、128.3%。施氮模式显著影响水氮利用效率,与U200相比,CU160下干物质水分利用效率提高了22.4%,CU160、CU120下氮肥偏生产力分别提高了53.5%、80.0%。因此,适度灌溉并采用缓释肥减施氮素显著促进了甜高粱植株干物质量的积累和水氮利用效率的提升。
马仁诗, 蒋丛泽, 高玮, 李中利, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 不同水分条件下缓释氮肥对饲用甜高粱生长和水氮利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 71-81.
Ren-shi MA, Cong-ze JIANG, Wei GAO, Zhong-li LI, Yu-ying SHEN, Xian-long YANG. Effects of slow-release N fertilizer on growth and water- and N- use efficiencies of forage sweet sorghum under three different irrigation regimes[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 71-81.
土壤容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate N (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 田间持水量 Field capacity (%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.26 | 12.2 | 0.9 | 15.9 | 7.3 | 110.0 | 25.9 | 8.1 |
表1 试验土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of the soil in the experiment
土壤容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate N (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 田间持水量 Field capacity (%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.26 | 12.2 | 0.9 | 15.9 | 7.3 | 110.0 | 25.9 | 8.1 |
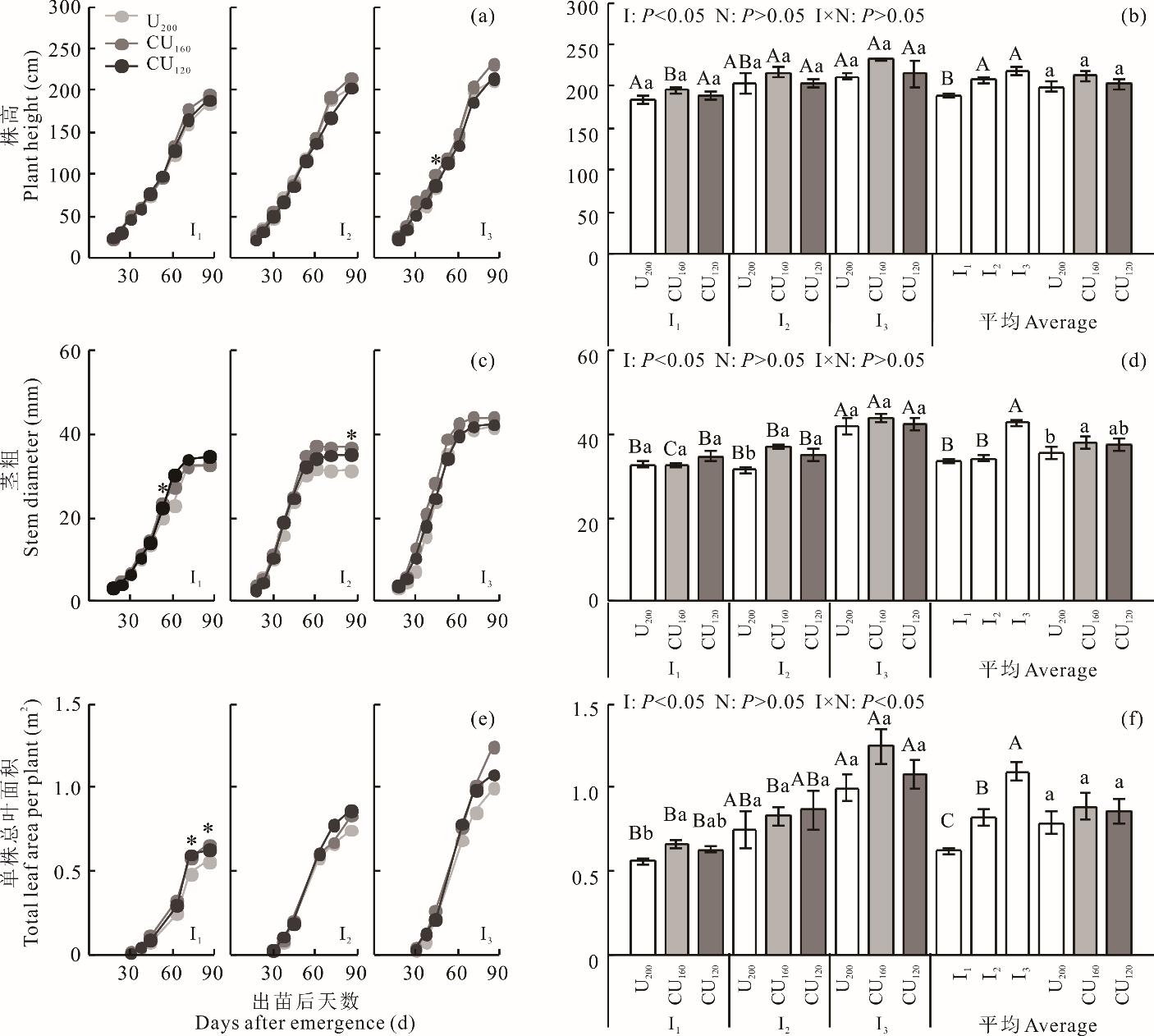
图2 不同处理下饲用甜高粱株高(a)、茎粗(c)、单株总叶面积(e)动态及收获期株高(b)、茎粗(d)、单株总叶面积(f)数据为4次重复平均值±标准误;不同小写字母表示相同灌溉量下不同施氮模式之间差异显著,不同大写字母表示相同施氮模式下灌溉量之间差异显著(P<0.05);I,N和I×N分别表示灌溉量,施氮模式以及灌溉量与施氮模式的交互作用;下同。动态图中,*表示处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。The data are the mean±standard error; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among nitrogen fertilization methods at the same irrigation amount, and different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among irrigation amounts at the same nitrogen fertilization method (P<0.05); I, N and I×N represent irrigation amount, nitrogen fertilization methods and the interaction between irrigation amount and nitrogen fertilization methods, respectively; The same below. In the dynamic charts (2a, c, e), * indicates significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.2 Dynamics in plant height (a), stem diameter (c), total leaf area per plant (e) and plant height (b), stem diameter (d), total leaf area per plant (f) at harvest of forage sweet sorghum under different treatments
灌溉量 Irrigation amount | 施氮模式 N fertilization methods | 鲜质量 Fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 干质量 Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 茎叶比 Stem-leaf ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 地上部 Aboveground | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 地上部 Aboveground | |||
| I1 | U200 | 193.6±1.3Ba | 294.5±22.6Ca | 488.1±22.4Ca | 50.6±0.7Ba | 46.5±2.7Ba | 97.1±2.0Cb | 0.9±0.1Ca |
| CU160 | 190.7±8.7Ca | 321.2±8.4Ca | 511.8±15.3Ca | 52.1±1.4Ca | 53.9±1.5Ca | 106.0±2.8Cab | 1.0±0.0Ba | |
| CU120 | 209.9±12.1Ba | 326.9±28.3Ca | 536.7±33.6Ca | 55.5±2.0Ba | 54.3±3.3Ca | 109.8±4.1Ca | 1.0±0.1Ba | |
| I2 | U200 | 209.8±17.2Bc | 607.1±41.6Ba | 817.0±58.1Ba | 55.0±7.1Bb | 94.0±12.2Aa | 148.9±19.0Ba | 1.7±0.1Aa |
| CU160 | 316.8±5.0Ba | 606.0±66.5Ba | 922.9±69.0Ba | 82.5±2.4Ba | 97.0±6.4Ba | 179.6±8.2Ba | 1.2±0.1Bb | |
| CU120 | 261.9±13.6Bb | 493.8±29.9Ba | 755.7±41.3Ba | 68.5±1.8Bab | 93.7±8.9Ba | 162.2±7.7Ba | 1.4±0.2Aab | |
| I3 | U200 | 395.6±15.9Aab | 939.8±37.0Ab | 1335.5±52.9Ab | 92.4±4.8Aa | 117.3±6.0Ab | 209.7±10.8Ab | 1.3±0.0Ba |
| CU160 | 467.9±14.6Aa | 1267.8±21.6Aa | 1735.8±36.1Aa | 104.3±6.7Aa | 197.7±6.7Aa | 302.0±13.5Aa | 1.9±0.1Aa | |
| CU120 | 365.7±26.2Ab | 1026.3±56.9Ab | 1392.0±81.5Ab | 85.4±8.3Aa | 133.9±14.9Ab | 219.3±15.5Ab | 1.6±0.3Aa | |
灌溉量平均 Average over irrigation amount | I1 | 198.4±5.4C | 316.0±11.7C | 514.4±14.3C | 52.9±1.0C | 52.0±1.7C | 105.0±2.3C | 1.0±0.0B |
| I2 | 262.8±14.8B | 569.0±30.0B | 831.8±36.4B | 68.6±4.1B | 94.9±5.0B | 163.5±7.6B | 1.4±0.1A | |
| I3 | 405.4±16.7A | 1072.8±46.1A | 1478.2±61.0A | 93.2±4.3A | 148.1±11.5A | 241.3±14.0A | 1.6±0.1A | |
施氮模式平均 Average over N fertilization methods | U200 | 260.7±27.9b | 613.2±78.2a | 873.9±103.9b | 64.9±6.1b | 86.7±9.6b | 151.6±15.0b | 1.3±0.1a |
| CU160 | 312.2±33.5a | 682.9±116.6a | 995.1±149.2a | 77.4±6.6a | 108.8±17.6a | 186.2±23.9a | 1.3±0.1a | |
| CU120 | 279.2±21.8b | 615.6±92.4a | 894.8±113.2b | 69.8±4.5ab | 94.0±11.1b | 163.8±14.5b | 1.3±0.1a | |
| I | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | |
| N | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P>0.05 | |
| I×N | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | |
表2 不同处理下饲用甜高粱地上部鲜质量、干质量与茎叶比
Table 2 Aboveground fresh weight, dry weight and stem-leaf ratio of forage sweet sorghum under different treatments
灌溉量 Irrigation amount | 施氮模式 N fertilization methods | 鲜质量 Fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 干质量 Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 茎叶比 Stem-leaf ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 地上部 Aboveground | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 地上部 Aboveground | |||
| I1 | U200 | 193.6±1.3Ba | 294.5±22.6Ca | 488.1±22.4Ca | 50.6±0.7Ba | 46.5±2.7Ba | 97.1±2.0Cb | 0.9±0.1Ca |
| CU160 | 190.7±8.7Ca | 321.2±8.4Ca | 511.8±15.3Ca | 52.1±1.4Ca | 53.9±1.5Ca | 106.0±2.8Cab | 1.0±0.0Ba | |
| CU120 | 209.9±12.1Ba | 326.9±28.3Ca | 536.7±33.6Ca | 55.5±2.0Ba | 54.3±3.3Ca | 109.8±4.1Ca | 1.0±0.1Ba | |
| I2 | U200 | 209.8±17.2Bc | 607.1±41.6Ba | 817.0±58.1Ba | 55.0±7.1Bb | 94.0±12.2Aa | 148.9±19.0Ba | 1.7±0.1Aa |
| CU160 | 316.8±5.0Ba | 606.0±66.5Ba | 922.9±69.0Ba | 82.5±2.4Ba | 97.0±6.4Ba | 179.6±8.2Ba | 1.2±0.1Bb | |
| CU120 | 261.9±13.6Bb | 493.8±29.9Ba | 755.7±41.3Ba | 68.5±1.8Bab | 93.7±8.9Ba | 162.2±7.7Ba | 1.4±0.2Aab | |
| I3 | U200 | 395.6±15.9Aab | 939.8±37.0Ab | 1335.5±52.9Ab | 92.4±4.8Aa | 117.3±6.0Ab | 209.7±10.8Ab | 1.3±0.0Ba |
| CU160 | 467.9±14.6Aa | 1267.8±21.6Aa | 1735.8±36.1Aa | 104.3±6.7Aa | 197.7±6.7Aa | 302.0±13.5Aa | 1.9±0.1Aa | |
| CU120 | 365.7±26.2Ab | 1026.3±56.9Ab | 1392.0±81.5Ab | 85.4±8.3Aa | 133.9±14.9Ab | 219.3±15.5Ab | 1.6±0.3Aa | |
灌溉量平均 Average over irrigation amount | I1 | 198.4±5.4C | 316.0±11.7C | 514.4±14.3C | 52.9±1.0C | 52.0±1.7C | 105.0±2.3C | 1.0±0.0B |
| I2 | 262.8±14.8B | 569.0±30.0B | 831.8±36.4B | 68.6±4.1B | 94.9±5.0B | 163.5±7.6B | 1.4±0.1A | |
| I3 | 405.4±16.7A | 1072.8±46.1A | 1478.2±61.0A | 93.2±4.3A | 148.1±11.5A | 241.3±14.0A | 1.6±0.1A | |
施氮模式平均 Average over N fertilization methods | U200 | 260.7±27.9b | 613.2±78.2a | 873.9±103.9b | 64.9±6.1b | 86.7±9.6b | 151.6±15.0b | 1.3±0.1a |
| CU160 | 312.2±33.5a | 682.9±116.6a | 995.1±149.2a | 77.4±6.6a | 108.8±17.6a | 186.2±23.9a | 1.3±0.1a | |
| CU120 | 279.2±21.8b | 615.6±92.4a | 894.8±113.2b | 69.8±4.5ab | 94.0±11.1b | 163.8±14.5b | 1.3±0.1a | |
| I | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | |
| N | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P>0.05 | |
| I×N | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 | |

图3 监测期内不同处理下饲用甜高粱单株日蒸腾速率
Fig.3 Daily transpiration rate of forage sweet sorghum on individual scale under different treatments during the monitoring period
| 1 | Liliane T N, Charles M S. Factors affecting yield of crops. London: Agronomy-climate Change & Food Security, 2020. |
| 2 | Ma R S, Jiang C Z, Shou N, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen gradients on growth and water use efficiency of forage sweet sorghum. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(12): 2334-2346. |
| 马仁诗, 蒋丛泽, 受娜, 等. 水氮梯度对饲用甜高粱生长和水分利用效率的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(12): 2334-2346. | |
| 3 | Li X F, Shao J Y, Yu W Z, et al. Combined effects of high temperature and drought on yield and photosynthetic characteristics of summer maize. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(18): 3516-3529. |
| 李小凡, 邵靖宜, 于维祯, 等. 高温干旱复合胁迫对夏玉米产量及光合特性的影响. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(18): 3516-3529. | |
| 4 | Meng Z J, Bian X M, Liu A N, et al. Effect of regulated deficit irrigation on physiological and photosynthetic characteristics of summer maize and its optimized combination of agronomic techniques. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 20(3): 182-186. |
| 孟兆江, 卞新民, 刘安能, 等. 调亏灌溉对夏玉米光合生理特性的影响. 水土保持学报, 2006, 20(3): 182-186. | |
| 5 | Xie T T, Su P X. Effect of drought stress on yield, quality and water use efficiency of sweet sorghum in marginal oasis of Hexi Corridor. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2011, 19(2): 300-304. |
| 解婷婷, 苏培玺. 干旱胁迫对河西走廊边缘绿洲甜高粱产量、品质和水分利用效率的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(2): 300-304. | |
| 6 | Li G, Zhao B, Dong S, et al. Controlled-release urea combining with optimal irrigation improved grain yield, nitrogen uptake, and growth of maize. Agricultural Water Management, 2020, 227: 105834. |
| 7 | Kang C R, Xie J H, Li L L, et al. Effects of planting density and nitrogen fertilizer rate on maize yield and photosynthetic characteristics in arid areas of central Gansu, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 141-149. |
| 康彩睿, 谢军红, 李玲玲, 等. 种植密度与施氮量对陇中旱农区玉米产量及光合特性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 141-149. | |
| 8 | Gao L M, Tian Q, Su J, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on dry matter yield and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency in sweet sorghum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 192-198. |
| 高丽敏, 田倩, 苏晶, 等. 施氮水平对甜高粱干物质产量及氮肥利用率的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 192-198. | |
| 9 | Li T, Wang Z, Wang C, et al. Ammonia volatilization mitigation in crop farming: A review of fertilizer amendment technologies and mechanisms. Chemosphere, 2022, 303: 134944. |
| 10 | Cheng Q, Li G H, Lu W P, et al. Increasing planting density and decreasing nitrogen rate increase yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(6): 1035-1046. |
| 程前, 李广浩, 陆卫平, 等. 增密减氮提高夏玉米产量和氮素利用效率. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(6): 1035-1046. | |
| 11 | Gao W, Shou N, Jiang C Z, et al. Effect of nitrogen application rate on dry matter accumulation, allocation and water use efficiency of forage sorghum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 26-35. |
| 高玮, 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 等. 施氮量对饲用高粱干物质积累、分配及水分利用效率的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 26-35. | |
| 12 | Fan X L, Liu F, Liao Z Y, et al. The status and outlook for the study of controlled-release fertilizers in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2009, 15(2): 463-473. |
| 樊小林, 刘芳, 廖照源, 等. 我国控释肥料研究的现状和展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(2): 463-473. | |
| 13 | Tian H, Liu Z, Zhang M, et al. Biobased polyurethane, epoxy resin, and polyolefin wax composite coating for controlled-release fertilizer. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(5): 5380-5392. |
| 14 | Zhou L P, Yang L P, Bai Y L, et al. Comparison of several slow-released nitrogen fertilizers in ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization in summer maize field. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2016, 22(6): 1449-1457. |
| 周丽平, 杨俐苹, 白由路, 等. 不同氮肥缓释化处理对夏玉米田间氨挥发和氮素利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(6): 1449-1457. | |
| 15 | Zhou B Y, Wang X B, Wang Z M, et al. Effect of slow-release fertilizer and tillage practice on grain yield and nitrogen efficiency of summer maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2016, 22(3): 821-829. |
| 周宝元, 王新兵, 王志敏, 等. 不同耕作方式下缓释肥对夏玉米产量及氮素利用效率的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(3): 821-829. | |
| 16 | Li S G, Liu M, Liu F, et al. Current status and future prospective of sorghum production and seed industry in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(3): 471-482. |
| 李顺国, 刘猛, 刘斐, 等. 中国高粱产业和种业发展现状与未来展望. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(3): 471-482. | |
| 17 | Chen Y P, Xiao Y, Kong L J, et al. Effects of slow-release fertilizer treatments on nitrogen accumulation and distribution of super-high yield summer maize. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(27): 34-40. |
| 陈艳萍, 肖尧, 孔令杰, 等. 缓释肥施用量对超高产夏玉米氮素积累分配的影响. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(27): 34-40. | |
| 18 | Wang L, Li X M, Ni S L, et al. Winter wheat traits, water use efficiency and cost-effectiveness under SODm slow release nitrogen fertilizer on the semi-humid arid areas. Crops, 2013, 154(3): 71-74. |
| 王磊, 李兴茂, 倪胜利, 等. SODm缓释氮肥对半湿润偏旱区冬小麦性状、水分利用效率及经济效益的影响. 作物杂志, 2013, 154(3): 71-74. | |
| 19 | Fang L N. ‘Hunnigreen’ forage sorghum quality forage for animal production. Pratacultural Science, 2003, 20(12): 56-57. |
| 房丽宁. 饲用甜高粱新品种“大力士”. 草业科学, 2003, 20(12): 56-57. | |
| 20 | Fang Q X, Yu Q, Wang E L, et al. Soil nitrate accumulation, leaching and crop nitrogen use as influenced by fertilization and irrigation in an intensive wheat-maize double cropping system in the North China Plain. Plant and Soil, 2006, 284(4): 335-355. |
| 21 | Xu J, Tao H B, Song Q F, et al. The effect of water-nitrogen regimes on the nitrogen utilization and soil NO3 --N residue of winter wheat-summer maize system in the North China Plain. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2011, 26(4): 153-158. |
| 徐杰, 陶洪斌, 宋庆芳, 等. 水氮配置对华北冬小麦-夏玉米种植体系氮素利用及土壤硝态氮残留的影响. 华北农学报, 2011, 26(4): 153-158. | |
| 22 | Du H X, Feng H, Wu P T, et al. Influence of water and N fertilizer regulation on root growth characteristics of summer maize. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2013, 31(1): 89-94, 100. |
| 杜红霞, 冯浩, 吴普特, 等. 水、氮调控对夏玉米根系特性的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2013, 31(1): 89-94, 100. | |
| 23 | Zhao B, Dong S T, Wang K J, et al. Effects of controlled-release on summer maize grain yield ammonia volatilization and fertilizer nitrogen use efficiency. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(11): 2678-2684. |
| 赵斌, 董树亭, 王空军, 等. 控释肥对夏玉米产量及田间氨挥发和氮素利用率的影响. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(11): 2678-2684. | |
| 24 | Li S X, Wang Z H, Malhi S S, et al. Nutrient and water management effects on crop production, and nutrient and water use efficiency in dryland areas of China. Advances in Agronomy, 2009, 102: 223-265. |
| 25 | Meng F C, Zhang J H, Hao C, et al. Effects of elevated CO2 and different irrigation on photosynthetic parameters and yield of maize in Northeast China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(7): 2126-2135. |
| 孟凡超, 张佳华, 郝翠, 等. CO2浓度升高和不同灌溉量对东北玉米光合特性及产量的影响. 生态学报, 2015, 35(7): 2126-2135. | |
| 26 | Guo J J, Zhang F C, Wang H D, et al. Effects of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer and urea blending on maize growth and nitrogen uptake under different nitrogen application rates. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(20): 3930-3943. |
| 郭金金, 张富仓, 王海东, 等. 不同施氮量下缓释氮肥与尿素掺混对玉米生长与氮素吸收利用的影响. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(20): 3930-3943. | |
| 27 | Kimball B A, LaMorte R L, Pinter Jr P J, et al. Free-air CO2 enrichment and soil nitrogen effects on energy balance and evapotranspiration of wheat. Water Resources Research, 1999, 35(4): 1179-1190. |
| 28 | Li L, Hong J P, Wang H T, et al. Effects of watering and nitrogen fertilization on the growth, grain yield and water- and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(5): 1367-1373. |
| 栗丽, 洪坚平, 王宏庭, 等. 水氮处理对冬小麦生长、产量和水氮利用效率的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(5): 1367-1373. | |
| 29 | Wang J, Liu W Z, Dang T H, et al. Nitrogen fertilization effect on soil water and wheat yield in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agronomy Journal, 2013, 105(1): 143-149. |
| 30 | Liang Y J, Yi Y L, Xu G B, et al. Progress on coupling effects between water and fertilizers. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2006, 45(3): 385-388. |
| 梁运江, 依艳丽, 许广波, 等. 水肥耦合效应的研究进展与展望. 湖北农业科学, 2006, 45(3): 385-388. | |
| 31 | Zhang M W, Liu J B, Qiao J F, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization of summer maize with different planting densities. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 49(5): 55-62. |
| 张美微, 刘京宝, 乔江方, 等. 施氮量对不同种植密度夏玉米产量和氮素吸收利用的影响. 河南农业科学, 2020, 49(5): 55-62. | |
| 32 | Zhang N N, Zhao D Q, Han Y L, et al. Effect of combined application of urea and slow-release fertilizer under same nitrogen level on growth of spring maize in Loess tableland area. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 1642-1650. |
| 张宁宁, 赵德强, 韩云良, 等. 尿素与缓释肥同一氮素水平下配施对黄土台塬区春玉米生长的影响. 西北农业学报, 2020, 29(11): 1642-1650. |
| [1] | 高玮, 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 施氮量对饲用高粱干物质积累、分配及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 26-35. |
| [2] | 曲婷, 周立业. 入侵植物少花蒺藜草异型种子萌发策略及其幼苗生长特性[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 91-100. |
| [3] | 张桐瑞, 李富翠, 韩烈保, 陈雨峰, 宋桂龙, 张亚楠, 陈佳宝, 唐斌, 窦玮豪. 践踏对草垫式人造-天然混合草坪质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 26-40. |
| [4] | 胡伟, 张亚红, 李鹏, 王小菊, 张鹏, 何毅, 康馨匀. 水氮供应对地下滴灌紫花苜蓿生产性能及水氮利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 41-50. |
| [5] | 赵刚, 李尚中, 张建军, 王磊, 党翼, 樊廷录, 王淑英, 程万莉. 不同播种方式对陇东旱塬区全膜双垄沟玉米播种质量和生长发育的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 145-155. |
| [6] | 汪毅, 郭海林, 陈静波, 宗俊勤, 李丹丹, 姜亦巍, 刘建秀. 国审品种‘苏植1号’杂交结缕草抗旱性初步评价与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 30-39. |
| [7] | 杨彬, 吕世奇, 寇一翾, 孙杉, 赵长明. 半干旱地区不同生育期菊芋生长特性与气体交换特征[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10): 77-85. |
| [8] | 鱼小军, 景媛媛, 徐长林, 师尚礼, 张建文, 陈陆军, 杨海磊, 肖红. 高寒区垄沟覆膜方式对苜蓿生长、根颈及根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(6): 43-52. |
| [9] | 张前兵,艾尼娃尔·艾合买提,于磊,鲁为华,常青. 绿洲区不同灌溉方式及灌溉量对苜蓿田土壤盐分运移的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(6): 69-77. |
| [10] | 杨海霞,刘润进,郭绍霞. AM真菌摩西球囊霉对盐胁迫条件下高羊茅生长特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 195-203. |
| [11] | 黄彩变,曾凡江,雷加强. 塔克拉玛干沙漠南缘3个沙拐枣种的抗旱特性比较[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 136-143. |
| [12] | 何春雨,杜久元,刘广才,柴强,张礼军,申三宝,鲁清林,黄高宝. 全膜覆土穴播冬小麦农田土壤含水率与耗水量时空动态[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(1): 131-141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||