

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 122-134.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023208
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
常单娜1( ), 陈子英2, 韩梅2, 李正鹏2, 严清彪2, 吕帅磊1, 周国朋1, 孙小凤2, 曹卫东1(
), 陈子英2, 韩梅2, 李正鹏2, 严清彪2, 吕帅磊1, 周国朋1, 孙小凤2, 曹卫东1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-23
修回日期:2023-09-07
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-01-15
通讯作者:
曹卫东
作者简介:E-mail: caoweidong@caas.cn基金资助:
Dan-na CHANG1( ), Zi-ying CHEN2, Mei HAN2, Zheng-peng LI2, Qing-biao YAN2, Shuai-lei LV1, Guo-peng ZHOU1, Xiao-feng SUN2, Wei-dong CAO1(
), Zi-ying CHEN2, Mei HAN2, Zheng-peng LI2, Qing-biao YAN2, Shuai-lei LV1, Guo-peng ZHOU1, Xiao-feng SUN2, Wei-dong CAO1( )
)
Received:2023-06-23
Revised:2023-09-07
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-01-15
Contact:
Wei-dong CAO
摘要:
毛叶苕子是我国重要的肥饲兼用绿肥作物,研究毛叶苕子磷获取特征及根际特性的基因型差异,为毛叶苕子磷高效利用提供理论支撑。在青海西宁开展盆栽试验,设置毛叶苕子品种和磷肥种类双因素,毛叶苕子品种为大田试验筛选的磷高效及磷低效品种(系)各2个,磷肥种类为过磷酸钙和磷矿粉,设置不施磷肥对照,共12个处理。盛花期测定分析毛叶苕子磷素积累量、土壤磷组分、土壤有机酸、根系酸性磷酸酶(RACP)、土壤酸性及碱性磷酸酶活性(ACP、ALP)、土壤酸性及碱性磷酸酶(phoC、phoD)基因丰度。结果显示,不同磷效率毛叶苕子品种(系)总磷吸收量和磷肥利用率分别为7.45~46.07 mg·盆-1和7.12%~22.49%;磷高效品种(系)总磷吸收量和磷肥利用率均显著高于磷低效品种(系),增幅分别为0.91%~61.20%和12.52%~60.25%。相比磷低效品种(系),磷高效品种(系)提高了活性磷(labile P)和中等活性磷(moderately labile P)的比例,降低了稳定性磷(stable P)的比例,后者的活性磷和中等活性磷的比例分别是前者的6.14~26.14倍和1.04~1.54倍,前者的稳定性磷库比例是后者的2.92~7.91倍。磷高效品种(系)土壤总有机酸(TOA)、草酸(OXA)含量、RACP、ACP、ALP活性均显著高于磷低效品种(系),分别提高117.45%~254.60%、19.40%~50.75%、16.37%~146.40%、6.19%~104.19%和6.16%~35.06%。磷高效品种(系)phoC 和 phoD丰度分别是磷低效品种(系)的1.07~2.58倍和1.46~3.64倍。线性回归分析表明,土壤TOA、OXA、RACP、ACP与活性磷均呈显著或极显著正相关,决定系数分别为0.40、0.46、0.13、0.19;与stable P均呈显著或极显著负相关,决定系数分别为0.75、0.58、0.41和0.49。综上,磷高效毛叶苕子品种(系)活化难溶性磷的能力较强,具有更高的磷素积累量和磷肥利用率。其主要通过增加有机酸(主要是草酸)含量、磷酸酶活性、phoC和phoD基因丰度活化难溶性磷,提高土壤中活性磷和中等活性磷的比例,促进对磷的吸收利用。
常单娜, 陈子英, 韩梅, 李正鹏, 严清彪, 吕帅磊, 周国朋, 孙小凤, 曹卫东. 毛叶苕子磷获取特征及根际特性的基因型差异[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 122-134.
Dan-na CHANG, Zi-ying CHEN, Mei HAN, Zheng-peng LI, Qing-biao YAN, Shuai-lei LV, Guo-peng ZHOU, Xiao-feng SUN, Wei-dong CAO. Differences in phosphorus acquisition characteristics and rhizosphere properties among different hairy vetch genotypes[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 122-134.
处理 Treatment | 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙Calcium superphosphate | 磷矿粉 Rock phosphate | KCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施磷肥CK | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.67 |
| 过磷酸钙SP | 0.84 | 3.59 | 0.00 | 0.67 |
| 磷矿粉RP | 0.84 | 0.00 | 17.24 | 0.67 |
表1 不同处理肥料用量
Table 1 Fertilizer application in each treatment (g·pot-1)
处理 Treatment | 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙Calcium superphosphate | 磷矿粉 Rock phosphate | KCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施磷肥CK | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.67 |
| 过磷酸钙SP | 0.84 | 3.59 | 0.00 | 0.67 |
| 磷矿粉RP | 0.84 | 0.00 | 17.24 | 0.67 |
处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 干重Dry weight (g·pot-1) | 根冠比 Root/shoot (%) | 磷吸收量P uptake (mg·pot-1) | 利用率 Utilization rate (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部 Shoot | 地下部 Root | 总计 Total | 地上部 Shoot | 地下部 Root | 总计 Total | ||||
| CK | HV1 | 8.88±0.04gh | 0.48±0.01c | 9.36±0.05hi | 5.44±0.20a | 9.19±0.10fgh | 0.50±0.01b | 9.70±0.10ef | - |
| HV2 | 9.25±0.08g | 0.46±0.02c | 9.71±0.08h | 5.04±0.29a | 12.25±0.66ef | 0.51±0.06b | 12.01±0.14e | - | |
| HV3 | 8.63±0.05h | 0.29±0.01ef | 8.92±0.04i | 3.44±0.17d | 10.72±0.15efgh | 0.18±0.02c | 7.45±0.31f | - | |
| HV4 | 7.30±0.02i | 0.27±0.02ef | 7.58±0.03j | 3.78±0.27cd | 8.15±0.27gh | 0.24±0.03c | 8.39±0.27f | - | |
| SP | HV1 | 25.53±0.19b | 0.72±0.03a | 26.25±0.22b | 2.83±0.11e | 40.96±4.22b | 0.99±0.09a | 39.45±1.98b | 21.91±0.11e |
| HV2 | 26.21±0.37a | 0.67±0.01a | 26.88±0.35a | 2.58±0.08e | 45.21±1.59a | 0.86±0.08a | 46.07±1.67a | 22.49±0.08e | |
| HV3 | 24.40±0.05c | 0.38±0.02d | 24.79±0.05c | 1.59±0.10f | 38.29±0.35bc | 0.80±0.08ab | 39.15±0.31b | 19.47±0.10f | |
| HV4 | 21.55±0.10d | 0.55±0.03b | 22.10±0.11d | 2.06±0.14f | 36.32±0.85c | 0.63±0.03b | 36.96±0.86b | 18.20±0.14f | |
| RP | HV1 | 11.67±0.13e | 0.48±0.01c | 18.24±0.22e | 4.18±0.11bc | 16.69±0.62d | 0.53±0.03b | 25.85±0.98c | 11.41±0.11bc |
| HV2 | 10.33±0.16f | 0.45±0.02c | 16.17±0.26f | 4.36±0.14b | 14.19±0.24de | 0.60±0.12b | 24.08±0.37c | 10.27±0.14b | |
| HV3 | 9.27±0.04g | 0.25±0.00f | 14.29±0.07g | 2.75±0.09e | 7.27±0.33h | 0.09±0.00c | 16.22±0.23d | 7.12±0.09e | |
| HV4 | 9.11±0.02g | 0.31±0.00e | 14.14±0.03g | 3.50±0.09d | 12.07±0.36efg | 0.11±0.00c | 16.78±0.37d | 7.25±0.09d | |
| 磷P | 14769.73*** | 120.56*** | 9292.87*** | 103.45*** | 595.91*** | 80.69*** | 1298.73*** | 423.13*** | |
| 品种HV | 230.20*** | 92.13*** | 252.82*** | 37.56*** | 10.44*** | 25.64*** | 41.77*** | 13.33*** | |
| 磷P×品种HV | 37.18*** | 3.60*** | 35.08*** | 63.92*** | 3.84** | 3.24* | 8.01*** | 0.67ns | |
表2 不同磷效率毛叶苕子品种(系)的干重、磷吸收量和磷肥利用率
Table 2 Dry weight, phosphorus uptake, and phosphorus fertilizer utilization rate of different phosphorus efficiency hairy vetch cultivars (lines)
处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 干重Dry weight (g·pot-1) | 根冠比 Root/shoot (%) | 磷吸收量P uptake (mg·pot-1) | 利用率 Utilization rate (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部 Shoot | 地下部 Root | 总计 Total | 地上部 Shoot | 地下部 Root | 总计 Total | ||||
| CK | HV1 | 8.88±0.04gh | 0.48±0.01c | 9.36±0.05hi | 5.44±0.20a | 9.19±0.10fgh | 0.50±0.01b | 9.70±0.10ef | - |
| HV2 | 9.25±0.08g | 0.46±0.02c | 9.71±0.08h | 5.04±0.29a | 12.25±0.66ef | 0.51±0.06b | 12.01±0.14e | - | |
| HV3 | 8.63±0.05h | 0.29±0.01ef | 8.92±0.04i | 3.44±0.17d | 10.72±0.15efgh | 0.18±0.02c | 7.45±0.31f | - | |
| HV4 | 7.30±0.02i | 0.27±0.02ef | 7.58±0.03j | 3.78±0.27cd | 8.15±0.27gh | 0.24±0.03c | 8.39±0.27f | - | |
| SP | HV1 | 25.53±0.19b | 0.72±0.03a | 26.25±0.22b | 2.83±0.11e | 40.96±4.22b | 0.99±0.09a | 39.45±1.98b | 21.91±0.11e |
| HV2 | 26.21±0.37a | 0.67±0.01a | 26.88±0.35a | 2.58±0.08e | 45.21±1.59a | 0.86±0.08a | 46.07±1.67a | 22.49±0.08e | |
| HV3 | 24.40±0.05c | 0.38±0.02d | 24.79±0.05c | 1.59±0.10f | 38.29±0.35bc | 0.80±0.08ab | 39.15±0.31b | 19.47±0.10f | |
| HV4 | 21.55±0.10d | 0.55±0.03b | 22.10±0.11d | 2.06±0.14f | 36.32±0.85c | 0.63±0.03b | 36.96±0.86b | 18.20±0.14f | |
| RP | HV1 | 11.67±0.13e | 0.48±0.01c | 18.24±0.22e | 4.18±0.11bc | 16.69±0.62d | 0.53±0.03b | 25.85±0.98c | 11.41±0.11bc |
| HV2 | 10.33±0.16f | 0.45±0.02c | 16.17±0.26f | 4.36±0.14b | 14.19±0.24de | 0.60±0.12b | 24.08±0.37c | 10.27±0.14b | |
| HV3 | 9.27±0.04g | 0.25±0.00f | 14.29±0.07g | 2.75±0.09e | 7.27±0.33h | 0.09±0.00c | 16.22±0.23d | 7.12±0.09e | |
| HV4 | 9.11±0.02g | 0.31±0.00e | 14.14±0.03g | 3.50±0.09d | 12.07±0.36efg | 0.11±0.00c | 16.78±0.37d | 7.25±0.09d | |
| 磷P | 14769.73*** | 120.56*** | 9292.87*** | 103.45*** | 595.91*** | 80.69*** | 1298.73*** | 423.13*** | |
| 品种HV | 230.20*** | 92.13*** | 252.82*** | 37.56*** | 10.44*** | 25.64*** | 41.77*** | 13.33*** | |
| 磷P×品种HV | 37.18*** | 3.60*** | 35.08*** | 63.92*** | 3.84** | 3.24* | 8.01*** | 0.67ns | |

图1 不同磷效率毛叶苕子品种(系)土壤总磷和微生物量磷含量P: 不同施磷处理P fertilizer treatments; HV: 不同磷效率毛叶苕子品种(系)Different phosphorus efficiency hairy vetch cultivars (lines); HV1, HV2: 磷高效的毛荚野苕子和苕藤选P-efficient ‘Maojiayeshaozi’ and ‘Shaotengxuan’; HV3, HV4: 磷低效的1399毛苕和苏联苕子P-inefficient 1399 hairy vetch and ‘Soviet Union shaozi’; CK: 不施磷肥对照The control without applying phosphate fertilizer; SP: 施用过磷酸钙The application of calcium superphosphate fertilizer; RP: 施用磷矿粉The application of phosphate rock; 不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著Different lowercase letter indicates significant differences among different treatments; *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ns: 无显著差异No significant difference; 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Soil total phosphorus and microbial biomass phosphorus content of different phosphorus efficiency hairy vetch cultivars (lines)
处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 活性磷Labile P | 中等活性磷Moderately labile P | 稳定性磷Stable P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resin-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Pi | NaOH-Po | Dil. HCl-P | Residual-P | ||
| CK | HV1 | 1.61±0.07b | 3.38±0.18e | 18.89±0.86c | 1.97±0.07bc | 3.58±0.14b | 514.28±4.17cd | 29.51±0.48f |
| HV2 | 0.53±0.06e | 1.58±0.09g | 43.06±1.78b | 1.85±0.04bc | 2.54±0.09d | 491.30±5.09e | 38.44±0.94ef | |
| HV3 | 0.30±0.02ef | 0.69±0.05h | 1.55±0.13f | 0.97±0.07e | 1.66±0.05f | 489.50±7.87e | 249.24±7.25b | |
| HV4 | 0.27±0.04ef | 0.88±0.13h | 1.14±0.05f | 0.94±0.05e | 1.00±0.03g | 451.95±1.48f | 313.51±0.89a | |
| SP | HV1 | 2.66±0.09a | 9.42±0.15a | 47.23±1.86a | 3.49±0.55e | 4.33±0.12a | 508.68±3.67d | 28.18±0.52f |
| HV2 | 2.69±0.12a | 9.79±0.20a | 46.76±1.15a | 3.45±0.06a | 2.38±0.09d | 517.86±1.12cd | 36.64±0.86ef | |
| HV3 | 1.57±0.20bc | 6.27±0.34c | 1.14±0.09f | 1.70±0.06cd | 1.65±0.13f | 528.59±5.88c | 113.00±3.56d | |
| HV4 | 1.36±0.07c | 7.02±0.07b | 1.39±0.11f | 1.91±0.15bc | 1.75±0.09f | 400.27±7.11g | 200.09±1.36c | |
| RP | HV1 | 1.68±0.06b | 4.62±0.05d | 15.76±0.31d | 2.39±0.04b | 2.93±0.09c | 607.57±2.58a | 32.40±0.59f |
| HV2 | 0.78±0.01d | 6.74±0.35bc | 11.10±0.30e | 1.91±0.09bc | 2.07±0.07e | 622.99±10.45a | 45.18±0.81e | |
| HV3 | 0.38±0.06ef | 1.17±0.12gh | 1.87±0.15f | 1.18±0.21de | 1.69±0.10f | 564.71±6.21b | 204.43±10.37c | |
| HV4 | 0.30±0.01f | 2.21±0.10f | 0.31±0.01f | 0.94±0.15e | 0.79±0.05g | 564.09±3.63b | 303.13±1.43a | |
| 磷P | 7.49*** | 953.82*** | 383.31*** | 298.71*** | 51.48*** | 444.51*** | 301.44*** | |
| 品种HV | 5.15*** | 192.21*** | 1177.09*** | 51.13*** | 399.11*** | 111.07*** | 2272.81*** | |
| 磷P×品种HV | 5.27*** | 70.96*** | 179.62*** | 18.34*** | 14.66*** | 26.44*** | 93.86*** | |
表3 土壤磷库中不同形态磷含量
Table 3 Different forms of phosphorus content in soil phosphorus pool (mg·kg-1)
处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 活性磷Labile P | 中等活性磷Moderately labile P | 稳定性磷Stable P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resin-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Pi | NaOH-Po | Dil. HCl-P | Residual-P | ||
| CK | HV1 | 1.61±0.07b | 3.38±0.18e | 18.89±0.86c | 1.97±0.07bc | 3.58±0.14b | 514.28±4.17cd | 29.51±0.48f |
| HV2 | 0.53±0.06e | 1.58±0.09g | 43.06±1.78b | 1.85±0.04bc | 2.54±0.09d | 491.30±5.09e | 38.44±0.94ef | |
| HV3 | 0.30±0.02ef | 0.69±0.05h | 1.55±0.13f | 0.97±0.07e | 1.66±0.05f | 489.50±7.87e | 249.24±7.25b | |
| HV4 | 0.27±0.04ef | 0.88±0.13h | 1.14±0.05f | 0.94±0.05e | 1.00±0.03g | 451.95±1.48f | 313.51±0.89a | |
| SP | HV1 | 2.66±0.09a | 9.42±0.15a | 47.23±1.86a | 3.49±0.55e | 4.33±0.12a | 508.68±3.67d | 28.18±0.52f |
| HV2 | 2.69±0.12a | 9.79±0.20a | 46.76±1.15a | 3.45±0.06a | 2.38±0.09d | 517.86±1.12cd | 36.64±0.86ef | |
| HV3 | 1.57±0.20bc | 6.27±0.34c | 1.14±0.09f | 1.70±0.06cd | 1.65±0.13f | 528.59±5.88c | 113.00±3.56d | |
| HV4 | 1.36±0.07c | 7.02±0.07b | 1.39±0.11f | 1.91±0.15bc | 1.75±0.09f | 400.27±7.11g | 200.09±1.36c | |
| RP | HV1 | 1.68±0.06b | 4.62±0.05d | 15.76±0.31d | 2.39±0.04b | 2.93±0.09c | 607.57±2.58a | 32.40±0.59f |
| HV2 | 0.78±0.01d | 6.74±0.35bc | 11.10±0.30e | 1.91±0.09bc | 2.07±0.07e | 622.99±10.45a | 45.18±0.81e | |
| HV3 | 0.38±0.06ef | 1.17±0.12gh | 1.87±0.15f | 1.18±0.21de | 1.69±0.10f | 564.71±6.21b | 204.43±10.37c | |
| HV4 | 0.30±0.01f | 2.21±0.10f | 0.31±0.01f | 0.94±0.15e | 0.79±0.05g | 564.09±3.63b | 303.13±1.43a | |
| 磷P | 7.49*** | 953.82*** | 383.31*** | 298.71*** | 51.48*** | 444.51*** | 301.44*** | |
| 品种HV | 5.15*** | 192.21*** | 1177.09*** | 51.13*** | 399.11*** | 111.07*** | 2272.81*** | |
| 磷P×品种HV | 5.27*** | 70.96*** | 179.62*** | 18.34*** | 14.66*** | 26.44*** | 93.86*** | |
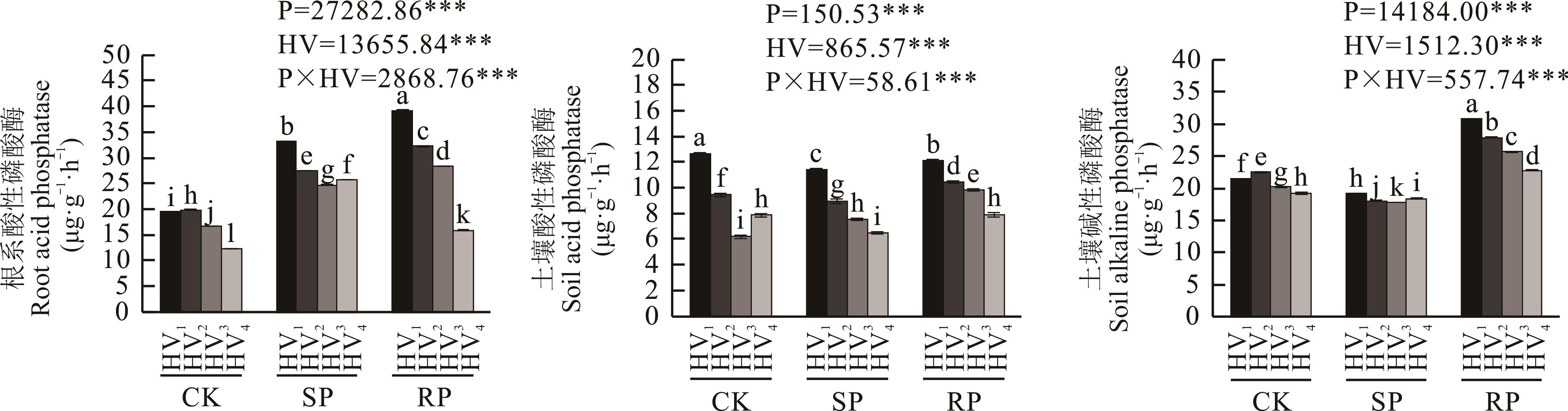
图4 不同磷效率毛叶苕子品种(系)的根系酸性磷酸酶及土壤酸性、碱性磷酸酶活性
Fig.4 Root acid phosphatase, soil acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase activity of different phosphorus efficiency hairy vetch cultivars (lines)

图5 不同磷效率毛叶苕子品种(系)的土壤磷酸酶基因phoC和 phoD丰度
Fig.5 Abundance of soil phosphatase genes phoC and phoD of different phosphorus efficiency hairy vetch cultivars (lines)

图6 有机酸、根系磷酸酶、土壤磷酸酶活性与土壤中活性磷、稳定性磷、有机磷的相关性
Fig.6 Correlation among organic acid, root phosphatase activity, soil phosphatase activity, labile, stable and organic phosphorus
| 1 | Feng G, Gai J P, Feng X H, et al. Strategies for improving fertilizer phosphorus use efficiency in Chinese cropping systems. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2019, 6(4): 341-347. |
| 2 | Ji B J, Li W H, Xu M Y, et al. Varying synthetic phosphorus varieties lead to different fractions in calcareous soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(12): 2581-2594. |
| 吉冰洁, 李文海, 徐梦洋, 等. 不同磷肥品种在石灰性土壤中的磷形态差异. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(12): 2581-2594. | |
| 3 | Zhang F S, Wang J Q, Zhang W F, et al. Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in China and measures for improvement. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(5): 915-924. |
| 张福锁, 王激清, 张卫峰, 等. 中国主要粮食作物肥料利用率现状与提高途径. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 915-924. | |
| 4 | Cooper J, Lombardi R, Boardman D, et al. The future distribution and production of global phosphate rock reserves. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2011, 57: 78-86. |
| 5 | Cordell D, Drangert J O, White S. The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change, 2009, 19(2): 292-305. |
| 6 | Zhang H W, Huang Y, Ye X S, et al. Genotypic differences in phosphorus acquisition and the rhizosphere properties of Brassica napus in response to low phosphorus stress. Plant and Soil, 2009, 320(1/2): 91-102. |
| 7 | Sugihara S, Tomita Y, Nishigaki T, et al. Effects of different phosphorus-efficient legumes and soil texture on fractionated rhizosphere soil phosphorus of strongly weathered soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2016, 52: 367-376. |
| 8 | Cao W D, Bao X G, Xu C X, et al. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| 9 | Gao S J, Zhou G P, Chang D N, et al. Southern China can produce more high-quality rice with less N by green manuring. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 196: 107025. |
| 10 | Cao W D, Huang H X. Ideas on restoration and development of green manures in China. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2009(4): 1-3. |
| 曹卫东, 黄鸿翔. 关于我国恢复和发展绿肥若干问题的思考. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009(4): 1-3. | |
| 11 | Cao W D, Xu C X. Atlas of main green manure varieties in China. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2021. |
| 曹卫东, 徐昌旭. 中国主要绿肥品种资源图集. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2021. | |
| 12 | Lu B L, Che Z X, Zhang J D, et al. Effects of long-term intercropping of maize with hairy vetch root returning to field on crop yield and nitrogen use efficiency under nitrogen fertilizer reduction. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(12): 2384-2397. |
| 卢秉林, 车宗贤, 张久东, 等. 氮肥减量下长期间作毛叶苕子根茬还田对玉米产量及氮肥利用率的影响. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(12): 2384-2397. | |
| 13 | Ma B J, Gou Z W, Yin W, et al. Effects of multiple cropping green manure after wheat harvest and nitrogen application levels on wheat photosynthetic performance and yield in arid irrigated areas. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(18): 3501-3515. |
| 麻碧娇, 苟志文, 殷文, 等. 干旱灌区麦后复种绿肥与施氮水平对小麦光合性能与产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(18): 3501-3515. | |
| 14 | Luo Y, Lu B L, Zhou G P, et al. Effects of returning the root of green manure on reducing N application in maize within their intercropping system in Hexi oasis irrigation area. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(12): 2125-2135. |
| 罗跃, 卢秉林, 周国朋, 等. 河西绿洲灌区玉米间作绿肥根茬还田的氮肥减施效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(12): 2125-2135. | |
| 15 | Xu X F, Mi Q, Liu D, et al. Effect of phosphorus fertilizer rate on phosphorus fractions contents in calcareous soil and phosphorus accumulation amount in crop. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(11): 1857-1866. |
| 徐晓峰, 米倩, 刘迪, 等. 磷肥施用量对石灰性土壤磷组分和作物磷积累量的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2021, 29(11): 1857-1866. | |
| 16 | Hasnuri M H, Marschne P, McNeill A, et al. Growth, P uptake in grain legumes and changes in rhizosphere soil P pools. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2011, 48(2): 151-159. |
| 17 | Lv Y, Cheng W D, Huang K, et al. Comparison of rhizosphere processes of Vicia sativa and Vicia villosa in response to phosphorus deficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2011, 17(3): 674-679. |
| 吕阳, 程文达, 黄珂, 等. 低磷胁迫下箭筈豌豆和毛叶苕子根际过程的差异比较. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(3): 674-679. | |
| 18 | Hu Y F, Liu J P, Wang Z K, et al. Rotation increases soil phosphorous bioavailability and improves phosphorous nutrition of the latter crop in rotation. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(8): 1305-1310. |
| 胡怡凡, 刘佳坪, 王子楷, 等. 轮作提高土壤磷生物有效性改善后茬作物磷素营养. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(8): 1305-1310. | |
| 19 | Chen Z Y, Chang D N, Han M, et al. Capability evaluation of 50 hairy vetch cultivars (lines) as autumn green manure in Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(4): 701-714. |
| 陈子英, 常单娜, 韩梅, 等. 50份毛叶苕子品种(系)在青海作秋绿肥的能力评价. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(4): 701-714. | |
| 20 | Liu X, Yan Q B, Li Z P, et al. Evaluation of germplasm resources and selection of excellent varieties of Vicia villosa Roth as a green fertilizer crop. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(9): 3110-3121. |
| 刘翔, 严清彪, 李正鹏, 等. 绿肥作物毛叶苕子种质资源性状评价及优异品种筛选. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(9): 3110-3121. | |
| 21 | Liu Y, Mi G H, Chen F J, et al. Rhizosphere effect and root growth of two maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes with contrasting P efficiency at low P availability. Plant Science, 2004, 167(2): 217-223. |
| 22 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (the third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 263-270. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 263-270. | |
| 23 | Tabatabai M A, Bremner J M. Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1969, 1(4): 301-307. |
| 24 | Liu X C, Mo S X. Studies on the colorimetric determination of organic acids in soil. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1985(3): 290-296. |
| 刘修才, 莫淑勋. 土壤中有机酸比色法测定的研究. 土壤学报, 1985(3): 290-296. | |
| 25 | Li X Y, Liu H Y, Xue S Q, et al. Zinc mobilization effect by root exudates of different green manure. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022, 297(1): 81-89. |
| 李欣雨, 刘函亦, 薛少琪, 等. 几种绿肥的根系分泌物对土壤锌的活化效应. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022, 297(1): 81-89. | |
| 26 | Tiessen H, Moir J O. Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1993: 75-86. |
| 27 | Cao N, Zhang M L, Zhi W Q, et al. Straw retention combined with phosphorus fertilizer promotes soil phosphorus availability by enhancing soil P-related enzymes and the abundance of phoC and phoD genes. Soil and Tillage Research, 2022, 220: 105390. |
| 28 | Wang X R, Shen J B, Liao H. Acquisition or utilization, which is more critical for enhancing phosphorus efficiency in modern crops? Plant Science, 2010, 179(4): 302-306. |
| 29 | Krasilnikoff G, Gahoonia T, Nielsen N E. Variation in phosphorus uptake efficiency by genotypes of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) due to differences in root and root hair length and induced rhizosphere processes. Plant and Soil, 2003, 251(1): 83-91. |
| 30 | Hernandez G, Ramírez M, Valdes-Lopez O, et al. Phosphorus stress in common bean: Root transcript and metabolic responses. Plant Physiology, 2007, 144: 752-767. |
| 31 | Ye D H, Zhang X Z, Li T X, et al. Phosphorus-acquisition characteristics and rhizosphere properties of wild barley in relation to genotypic differences as dependent on soil phosphorus availability. Plant and Soil, 2017, 423(1/2): 503-516. |
| 32 | Wang Z R, Zang H L. Fertilizer efficiency of phosphate rock on several acidic soils in Jiangsu Province. Soils, 1974(4) :29-32. |
| 王振荣, 臧惠林. 磷矿粉肥在江苏几种酸性土壤上的肥效. 土壤, 1974(4): 29-32. | |
| 33 | Wu L L. Research on the phosphorus forms of typical soils in northern China based on the Hedley method. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2021. |
| 吴璐璐. 基于Hedley法对我国北方典型土壤磷素形态的研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. | |
| 34 | Wang K K, Ren T, Yan J Y, et al. Straw returning mediates soil microbial biomass carbon and phosphorus turnover to enhance soil phosphorus availability in a rice-oilseed rape rotation with different soil phosphorus levels. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2022, 335: 107991. |
| 35 | Wang W H, Zhou X B, Zhou Y X, et al. The mechanism of rhizosphere phosphorus activation of two rape genotypes (Brassica napus L.) with different P efficiencies. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2011, 17(6): 1379-1387. |
| 王文华, 周鑫斌, 周永祥, 等. 不同磷效率油菜根际土壤磷活化机理研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(6): 1379-1387. | |
| 36 | Wang X J, Tang C X, Guppy C N, et al. Phosphorus acquisition characteristics of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) under P deficient conditions. Plant and Soil, 2008, 312(1/2): 117-128. |
| 37 | Wen Z H, Li H B, Shen Q, et al. Tradeoffs among root morphology, exudation and mycorrhizal symbioses for phosphorus-acquisition strategies of 16 crop species. New Phytologist, 2009, 223(2): 882-895. |
| 38 | Wang Y L, Lambers H. Root-released organic anions in response to low phosphorus availability: recent progress, challenges and future perspectives. Plant and Soil, 2020, 447(1): 135-156. |
| 39 | Ryan P R, Delhaize E, Jones D L. Function and mechanism of organic anion exudation from plant roots. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2001, 52: 527-560. |
| 40 | Wang B L, Tang X Y, Cheng L Y, et al. Nitric oxide is involved in phosphorus deficiency-induced cluster-root development and citrate exudation in white lupin. New Phytologist, 2010, 187: 1112-1123. |
| 41 | Liu H X, Wu J J, Wang J S, et al. Progress of research on tolerance to low-phosphorus stress in soybean. Soybean Science, 2017, 36(4): 639-644. |
| 刘海旭, 吴俊江, 王金生, 等. 大豆耐低磷研究进展. 大豆科学, 2017, 36(4): 639-644. | |
| 42 | Lan Z M, Lin X J, Zhang W G, et al. Effect of P deficiency on the emergence of Astragalus L. root exudates and mobilization of sparingly soluble phosphorus. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(8): 1521-1531. |
| 兰忠明, 林新坚, 张伟光, 等. 缺磷对紫云英根系分泌物产生及难溶性磷活化的影响. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(8): 1521-1531. | |
| 43 | Wang L S, Liu D. Functions and regulation of phosphate starvation-induced secreted acid phosphatases in higher plants. Plant Science, 2018, 271: 108-116. |
| 44 | Wu J S, Huang M, Xiao H A, et al. Dynamics in microbial immobilization and transformations of phosphorus in highly weathered subtropical soil following organic amendments. Plant and Soil, 2007, 290: 333-342. |
| [1] | 李秀芳, 魏文静, 蒲勇, 李廷轩, 叶代桦. 水蓼种植下猪粪处理土壤剖面磷组分与磷酸酶活性变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 61-72. |
| [2] | 安晓霞, 张盈盈, 马春晖, 李曼, 张前兵. 施磷与接种丛枝菌根真菌对苜蓿产量和磷素利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 71-84. |
| [3] | 田政, 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 罗奔, 张茂, 董瑞. 44个紫花苜蓿品种的酸铝适应性与耐受性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| [4] | 谢展, 穆麟, 张志飞, 陈桂华, 刘洋, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 乳酸菌或有机酸盐与尿素复配添加对紫花苜蓿混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [5] | 王如月, 袁世力, 文武武, 周鹏, 安渊. 磷对铝胁迫紫花苜蓿幼苗根系生长和生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 53-62. |
| [6] | 雷玮倩, 胡玉福, 杨泽鹏, 何剑锋, 肖海华, 舒向阳, 阳帆, 李正青. 垦殖对川西北高寒草地土壤中不同磷组分含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 36-45. |
| [7] | 李振松, 栗振义, 张绮芯, 何峰, 王宇菲, 万里强, 李向林, 仝宗永. 敖汉和维多利亚紫花苜蓿对低磷环境应激机制的比较[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 50-59. |
| [8] | 才华, 许慧慧, 孙娜, 宋婷婷, 任永晶, 杨圣秋. 从光合作用和有机酸积累角度探索转GsPPCK1和GsPPCK3基因苜蓿耐碱性增强的生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 107-117. |
| [9] | 薛博晗, 李娜, 宋桂龙, 李诗刚, 濮阳雪华, 李金波. 外源柠檬酸、苹果酸和草酸对披碱草镉耐受及富集的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 128-136. |
| [10] | 李海云,姚拓,张榕,张洁,李智燕,荣良燕,路晓雯,杨晓蕾,夏东慧,罗慧琴. 红三叶根际溶磷菌株分泌有机酸与溶磷能力的相关性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 113-121. |
| [11] | 李小冬, 王小利, 陈锡, 蔡璐, 曾庆飞, 舒健虹, 蔡一鸣. 转录组解析白三叶根际溶磷菌株RW8的解磷机制[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 168-179. |
| [12] | 麻莹, 王晓苹, 姜海波, 石德成. 盐碱胁迫下碱地肤体内的有机酸积累及其草酸代谢特点[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 158-165. |
| [13] | 蔡璐, 王小利, 陈莹, 王子苑, 李小冬. 无机磷溶解菌RW8的筛选、鉴定及对白三叶促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 181-188. |
| [14] | 张强, 刘宁芳, 向佐湘, 杨知建, 蒋元利, 胡龙兴. 盐碱胁迫对草地早熟禾生长和生理代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 67-76. |
| [15] | 吕家强,李长有,杨春武,胡锐. 天然盐碱土壤对虎尾草茎叶有机酸积累影响及胁迫因子分析[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 95-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||