

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 94-110.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023379
收稿日期:2023-10-11
修回日期:2023-12-04
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-06-20
通讯作者:
伍国强
作者简介:E-mail: gqwu@lut.edu.cn基金资助:
Ya-jing MENG( ), Guo-qiang WU(
), Guo-qiang WU( ), Ming WEI
), Ming WEI
Received:2023-10-11
Revised:2023-12-04
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-06-20
Contact:
Guo-qiang WU
摘要:
ABA响应元件结合因子(ABRE binding factor,ABF)作为植物中 bZIP 转录因子的一个独特亚家族,在脱落酸(abscisic acid, ABA)依赖型和非依赖型信号通路中发挥重要作用。为挖掘和鉴定糖料作物甜菜BvABF基因家族生物学功能及其表达模式,本研究采用生物信息学方法,预测了蛋白理化特性、系统进化、染色体位置、基因结构、保守基序、顺式作用元件、二级结构和蛋白互作网络等,并通过qRT-PCR方法分析了在100 μmol·L-1 ABA处理下 BvABF在根和叶中的表达模式。结果表明,从甜菜中鉴定出6个BvABF基因家族成员,将其分为A、B和C簇,它们均含有一个bZIP区域。BvABF分布在1、3、6、7和9号染色体,含有3~4个外显子。BvABF蛋白拥有4个含有潜在磷酸化位点(R-X-X-S/T)的保守区域C1、C2、C3和C4,在C端含有一个碱性区域和4个重复的由亮氨酸(Leu)残基组成的七肽重复序列。BvABF基因家族启动子含有多种激素和光响应元件,其中4个基因含有ABA响应元件(ABA-responsive element, ABRE);另外,干旱诱导的响应元件(MBS)、低温响应元件(LTR)和厌氧响应元件(anaerobic responsive element, ARE)等也存在于该基因家族。此外,BvABF可能与磷酸化相关蛋白(PP2CCNBD-X2、SRK2I、SRK2E-X1和 PP2C50)和ABA受体(PYL2、PYL4和PYR1)发生互作。进一步对BvABF在ABA处理下甜菜不同组织中的表达模式分析发现,所有BvABF基因在甜菜根和叶中均受ABA诱导和调控,且不同基因在ABA处理下呈现出不同的表达模式。这些结果表明,BvABFs在糖料作物甜菜响应ABA过程中扮演着重要角色。
孟亚静, 伍国强, 魏明. 甜菜BvABF基因家族全基因组鉴定及其ABA处理下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 94-110.
Ya-jing MENG, Guo-qiang WU, Ming WEI. Genome-wide identification of the Beta vulgaris ABF (BvABF) gene family and analysis of the expression pattern in sugar beet under ABA treatment[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 94-110.
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) | 反向引物 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | GCCGAATACCTTGCTTGATGCT | 58.2 | GAATTTCCGCATCCTCGCCAT | 58.4 |
| BvABF2 | CTCAATTGGCAGTTTCAACCAC | 54.7 | CTCAACAGTCTTCTCGACCAC | 55.4 |
| BvABF3 | CTGGAGTTGGAAGTTGTCCAATA | 54.3 | AGCATGGCGTTTTCTTTCGTT | 49.3 |
| BvABF4 | AATGCACAATTAAAGCAAGCC | 51.6 | GCCCTGCTTAGTATTACCTGT | 54.0 |
| BvABF5 | ACTACCTAGGACGCTTAGTCA | 54.2 | GTGATCTCCCCAAGTGTCTG | 55.4 |
| BvABF6 | CTGTGTGATAAGCCCAATTCG | 53.8 | AATTCATTGTGGTAAGCCTGT | 51.5 |
| BvACTIN | ACTGGTATTGTGCTTGACTC | 51.9 | ATGAGATAATCAGTGAGATC | 44.8 |
表1 本研究所用引物序列
Table 1 The primers used in this study
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) | 反向引物 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | GCCGAATACCTTGCTTGATGCT | 58.2 | GAATTTCCGCATCCTCGCCAT | 58.4 |
| BvABF2 | CTCAATTGGCAGTTTCAACCAC | 54.7 | CTCAACAGTCTTCTCGACCAC | 55.4 |
| BvABF3 | CTGGAGTTGGAAGTTGTCCAATA | 54.3 | AGCATGGCGTTTTCTTTCGTT | 49.3 |
| BvABF4 | AATGCACAATTAAAGCAAGCC | 51.6 | GCCCTGCTTAGTATTACCTGT | 54.0 |
| BvABF5 | ACTACCTAGGACGCTTAGTCA | 54.2 | GTGATCTCCCCAAGTGTCTG | 55.4 |
| BvABF6 | CTGTGTGATAAGCCCAATTCG | 53.8 | AATTCATTGTGGTAAGCCTGT | 51.5 |
| BvACTIN | ACTGGTATTGTGCTTGACTC | 51.9 | ATGAGATAATCAGTGAGATC | 44.8 |
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 位置 Locus | CDS (bp) | 蛋白长度 Protein length (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | Bv1_011670_nwdc | Bvchr1.sca004:3786136..3794120(-) | 813 | 270 | 29.49 | 5.55 | -0.607 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF2 | Bv3_064480_rnwf | Bvchr3.sca011:690504..695203(-) | 1002 | 333 | 36.54 | 9.27 | -0.807 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF3 | Bv6_134230_aref | Bvchr6.sca003:2686565..2693985(+) | 723 | 240 | 26.69 | 9.35 | -0.697 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF4 | Bv7_159570_afnu | Bvchr7.sca001:3838771..3848492(-) | 1356 | 451 | 49.19 | 8.30 | -0.793 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF5 | Bv7_169340_mcdu | Bvchr7.sca021:1716062..1720374(-) | 1470 | 489 | 51.59 | 9.49 | -0.655 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF6 | Bv9_207080_uszh | Bvchr9.sca010:874741..883695(+) | 795 | 264 | 29.46 | 6.92 | -0.653 | 细胞核Nucleus |
表2 甜菜BvABF基因家族成员鉴定
Table 2 Identification of BvABF gene family members in sugar beet
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 位置 Locus | CDS (bp) | 蛋白长度 Protein length (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | Bv1_011670_nwdc | Bvchr1.sca004:3786136..3794120(-) | 813 | 270 | 29.49 | 5.55 | -0.607 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF2 | Bv3_064480_rnwf | Bvchr3.sca011:690504..695203(-) | 1002 | 333 | 36.54 | 9.27 | -0.807 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF3 | Bv6_134230_aref | Bvchr6.sca003:2686565..2693985(+) | 723 | 240 | 26.69 | 9.35 | -0.697 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF4 | Bv7_159570_afnu | Bvchr7.sca001:3838771..3848492(-) | 1356 | 451 | 49.19 | 8.30 | -0.793 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF5 | Bv7_169340_mcdu | Bvchr7.sca021:1716062..1720374(-) | 1470 | 489 | 51.59 | 9.49 | -0.655 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF6 | Bv9_207080_uszh | Bvchr9.sca010:874741..883695(+) | 795 | 264 | 29.46 | 6.92 | -0.653 | 细胞核Nucleus |

图 1 植物ABF基因家族系统进化分析红色五角星表示拟南芥,浅天蓝色圆圈表示油菜,蓝色三角形表示甜菜,浅绿色正方形表示藜麦,粉色正方形表示菠萝,橘红色五角星表示水稻,紫红色圆圈表示狗尾草,黄色三角形表示小米。Red stars indicate A. thaliana, light-sky blue circles indicate B. napus, blue triangles indicate B. vulgaris, light green rectangles indicate C. quinoa, pink rectangles indicate A. comosus, and the light-salmon stars indicate O. sativa, plum circles indicate S. viridis, and yellow triangles indicate S. italica. ABF来源、名称和登录号如下The source, name and accession number of ABFs are as follows: 拟南芥A. thaliana: AtABF1 (At1g49720); AtABF2 (At1g45249); AtABF3 (At4g34000);AtABF4 (At3g19290); AtABI5 (At2g36270); AtDPBF2 (At3g44460); AtDPBF3 (At3g56850); AtDPBF4 (At2g41070); AtbZIP15 (At5g42910); 油菜B. napus: BnaABF1 (JX122892); BnaABF3 (JX122893); BnaABF4 (JX122894); BnaAREB3 (JX122898); BnaABI5 (KC414029); 藜麦C. quinoa: CqABF1 (AUR62006172-RA); CqABF2 (AUR62018275-RA); CqABF3 (AUR62000445-RA); CqABF4 (AUR62009948-RA); CqABF5 (AUR62001422-RA); CqABF6 (AUR62006793-RA); CqABF7 (AUR62018468-RA); CqABF8 (AUR62020955-RA); 菠萝A. comosus: AcABF1 (Aco027121.1.mrna1); AcABF2 (Aco001326.1.mrna1); AcABF3 (Aco015030.1.mrna1); AcABF4 (Aco012631.1.mrna1); AcABF5 (Aco024142.1.mrna1); AcABF6 (Aco009346.1.mrna1); AcABF7 (Aco007192.1.mrna1); 水稻O. sativa: OsABF1 (Os01t0813100-01); OsABF2 (Os01t0859300-01); OsABF3 (Os01t0859300-02); OsABF4 (Os01t0867300-01); OsABF5 (Os02t0766700-01); OsABF6 (Os02t0833600-01); OsABF7 (Os03t0322700-00); OsABF8 (Os05t0437700-01); OsABF9 (Os05t0489700-01); OsABF10 (Os06t0211200-01); OsABF11 (Os06t0211200-02); OsABF12 (Os06t0719500-00); OsABF13 (Os06t0720900-01); OsABF14 (Os06t0724000-03); OsABF15 (Os06t0724000-01); OsABF16 (Os07t0686100-01); OsABF17 (Os08t0472000-01); OsABF18 (Os08t0549600-00); OsABF19 (Os09t0456200-01); OsABF20 (Os09t0540800-01); 狗尾草S. viridis: SvABF1 (TKW41752); SvABF2 (TKW33491); SvABF3 (TKW34365); SvABF4 (TKW36627); SvABF5 (TKW36626); SvABF6 (TKW26631); SvABF7 (TKW26630); SvABF8 (TKW26629); SvABF9 (TKW27066); SvABF10 (TKW27105); SvABF11 (TKW20342); SvABF12 (TKW23488); SvABF13 (TKW23489); SvABF14 (TKW17362); SvABF15 (TKW17361); SvABF16 (TKW17363); SvABF17 (TKW17364); SvABF18 (TKW17834); SvABF19 (TKW17899); SvABF20 (TKW10745); SvABF21 (TKV96388); SvABF22 (TKV96387); 小米S. italica: SiABF1 (KQL31656); SiABF2 (KQL31657); SiABF3 (KQL24787); SiABF4 (KQL24788); SiABF5 (KQL25503); SiABF6 (KQL14946); SiABF7 (KQL15345); SiABF8 (KQL09837); SiABF9 (KQL12258); SiABF10 (KQL07423); SiABF11 (KQL07825); SiABF12 (KQL07880); SiABF13 (KQL02162); SiABF14 (KQL02163); SiABF15 (KQK91092).甜菜BvABF的名称和登录号见表2。The name and accession number of sugar beet (B. vulgaris) BvABF are shown in Table 2.
Fig.1 Phylogenetic analysis of the ABF genesfamily in plants
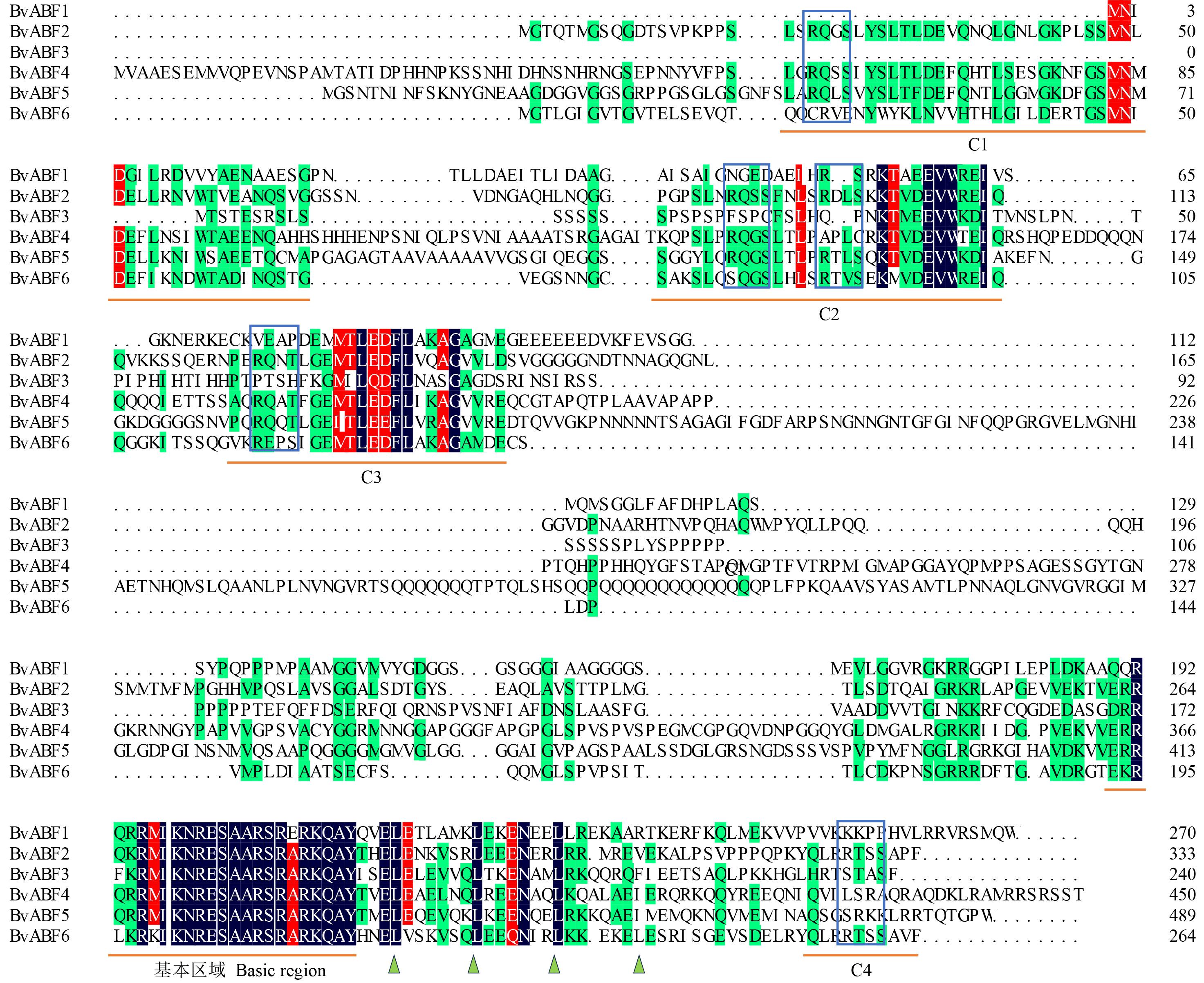
图3 甜菜BvABF蛋白序列多重比对相同的和保守的残基分别用黑色和红色表示。C1到C4的保守结构域和基本区域的位置由蛋白质序列下方的横线表示,与拟南芥ABF2/AREB1中表征的磷酸化位点相对应的潜在磷酸化残基(R-X-X-S/T)用蓝框表示,保守的Leu残基在Leu拉链域中的位置用一个绿色小三角形表示。Identical and conserved residues are indicated in black and red, respectively. The positions of conserved domains and basic regions from C1 to C4 are indicated by lines below the protein sequences. Potential phosphorylation sites corresponding to the characteristic phosphorylation sites in A. thaliana ABF2/AREB1 (R-X-X-S/T) are highlighted in blue boxes. The positions of conserved Leu residues in the Leu zipper domain are represented by a small green triangle.
Fig.3 Sequence multi-alignment of the BvABF proteins in sugar beet
| 基序Motif | 序列长度Sequence length (aa) | 基序序列Motif sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Motif 1 | 49 | VDKVVERRQKRMIKNRESAARSRARKQAYTVELESEVSQLEEENEELRK |
| Motif 2 | 45 | RQVSIYSLTLDEFQNTLGGLGKDFGSMNMDEFLKNIWTAEENQSV |
| Motif 3 | 26 | SLPRQGSLTLPRHLSRKTVDEVWREI |
| Motif 4 | 24 | PKRZATLGEMTLEDFLVKAGVVRE |
| Motif 5 | 12 | KYQLRRTSSAPF |
| Motif 6 | 10 | PPPHQHPPHH |
| Motif 7 | 11 | MTAFIDGHHNP |
| Motif 8 | 6 | FFAFDN |
| Motif 9 | 6 | NHIDEN |
| Motif 10 | 9 | TKECFKQQM |
表3 甜菜BvABF蛋白10个保守基序的序列信息
Table 3 Sequence information of 10 conserved motifs of BvABF in sugar beet
| 基序Motif | 序列长度Sequence length (aa) | 基序序列Motif sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Motif 1 | 49 | VDKVVERRQKRMIKNRESAARSRARKQAYTVELESEVSQLEEENEELRK |
| Motif 2 | 45 | RQVSIYSLTLDEFQNTLGGLGKDFGSMNMDEFLKNIWTAEENQSV |
| Motif 3 | 26 | SLPRQGSLTLPRHLSRKTVDEVWREI |
| Motif 4 | 24 | PKRZATLGEMTLEDFLVKAGVVRE |
| Motif 5 | 12 | KYQLRRTSSAPF |
| Motif 6 | 10 | PPPHQHPPHH |
| Motif 7 | 11 | MTAFIDGHHNP |
| Motif 8 | 6 | FFAFDN |
| Motif 9 | 6 | NHIDEN |
| Motif 10 | 9 | TKECFKQQM |
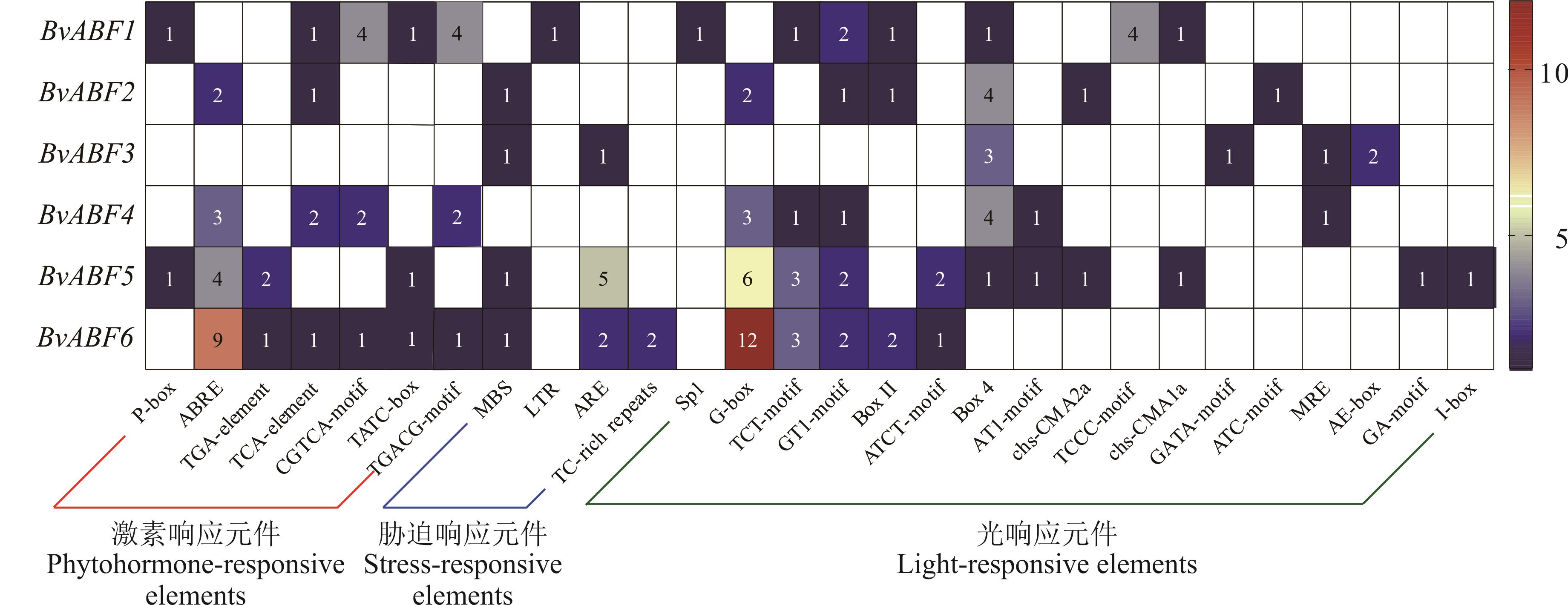
图5 甜菜 BvABF 基因顺式作用元件分析图中的数字表示顺式作用元件的个数。The numbers in the figure represent the number of cis-acting elements. P-box/TATC-box: 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element; ABRE: ABA响应元件ABA-responsive element; TGA-element: 生长素响应元件Auxin-responsive element; TCA-element: 水杨酸响应元件Salicylic acid-responsive element; CGTCA-motif/TGACG-motif: 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件MeJA-responsive element; MBS: 干旱诱导响应元件MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility; LTR: 低温响应元件Low-temperature-responsive element; ARE: 厌氧响应元件Anaerobic responsive element; TC-rich repeats: 防御和应激响应元件Defense and stress response element.
Fig.5 Analysis of cis-acting elements in sugar beet BvABF genes
蛋白名称 Protein name | α-螺旋 Alpha helix (%) | β-折叠 Beta fold (%) | β-转角 Beta turn (%) | 无规卷曲 Random coil (%) | 二级结构组成分布 Distribution of secondery structure elements (aa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | 55.93 | 15.19 | 2.22 | 26.67 |  |
| BvABF2 | 33.03 | 6.91 | 1.20 | 58.86 |  |
| BvABF3 | 30.83 | 7.08 | 0.00 | 62.08 |  |
| BvABF4 | 33.48 | 5.99 | 1.33 | 59.20 |  |
| BvABF5 | 26.99 | 10.84 | 2.25 | 59.92 |  |
| BvABF6 | 44.32 | 4.92 | 2.65 | 48.11 |  |
表4 甜菜BvABF蛋白二级结构预测
Table 4 Prediction of secondary structure of the BvABF proteins in sugar beet
蛋白名称 Protein name | α-螺旋 Alpha helix (%) | β-折叠 Beta fold (%) | β-转角 Beta turn (%) | 无规卷曲 Random coil (%) | 二级结构组成分布 Distribution of secondery structure elements (aa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | 55.93 | 15.19 | 2.22 | 26.67 |  |
| BvABF2 | 33.03 | 6.91 | 1.20 | 58.86 |  |
| BvABF3 | 30.83 | 7.08 | 0.00 | 62.08 |  |
| BvABF4 | 33.48 | 5.99 | 1.33 | 59.20 |  |
| BvABF5 | 26.99 | 10.84 | 2.25 | 59.92 |  |
| BvABF6 | 44.32 | 4.92 | 2.65 | 48.11 |  |
基因1 Gene 1 | 基因2 Gene 2 | 非同义替换 Non-synonymous substitution (dN) | 同义替换 Synonymous substitution (dS) | dN/dS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | BvABF2 | 0.6972 | 27.9790 | 0.0249 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF3 | 0.8324 | 6.9155 | 0.1204 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF4 | 0.6323 | 60.5700 | 0.0104 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF5 | 0.5167 | 54.6018 | 0.0095 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF6 | 0.7298 | 58.7015 | 0.0124 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF3 | 0.7702 | 10.6805 | 0.0721 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF4 | 0.5773 | 31.4895 | 0.0183 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF5 | 0.5274 | 23.5223 | 0.0224 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF6 | 0.4581 | 3.1932 | 0.1434 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF4 | 0.6850 | 53.4818 | 0.0128 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF5 | 0.7556 | 55.0648 | 0.0137 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF6 | 0.9365 | 64.0495 | 0.0146 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF5 | 0.6265 | 23.8488 | 0.0263 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF6 | 0.5877 | 55.3501 | 0.0106 |
| BvABF5 | BvABF6 | 0.5938 | 60.9069 | 0.0097 |
表5 甜菜BvABF基因dN和dS的比率
Table 5 The ratio of dN and dS of the BvABF genes in sugar beet
基因1 Gene 1 | 基因2 Gene 2 | 非同义替换 Non-synonymous substitution (dN) | 同义替换 Synonymous substitution (dS) | dN/dS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | BvABF2 | 0.6972 | 27.9790 | 0.0249 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF3 | 0.8324 | 6.9155 | 0.1204 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF4 | 0.6323 | 60.5700 | 0.0104 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF5 | 0.5167 | 54.6018 | 0.0095 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF6 | 0.7298 | 58.7015 | 0.0124 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF3 | 0.7702 | 10.6805 | 0.0721 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF4 | 0.5773 | 31.4895 | 0.0183 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF5 | 0.5274 | 23.5223 | 0.0224 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF6 | 0.4581 | 3.1932 | 0.1434 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF4 | 0.6850 | 53.4818 | 0.0128 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF5 | 0.7556 | 55.0648 | 0.0137 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF6 | 0.9365 | 64.0495 | 0.0146 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF5 | 0.6265 | 23.8488 | 0.0263 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF6 | 0.5877 | 55.3501 | 0.0106 |
| BvABF5 | BvABF6 | 0.5938 | 60.9069 | 0.0097 |
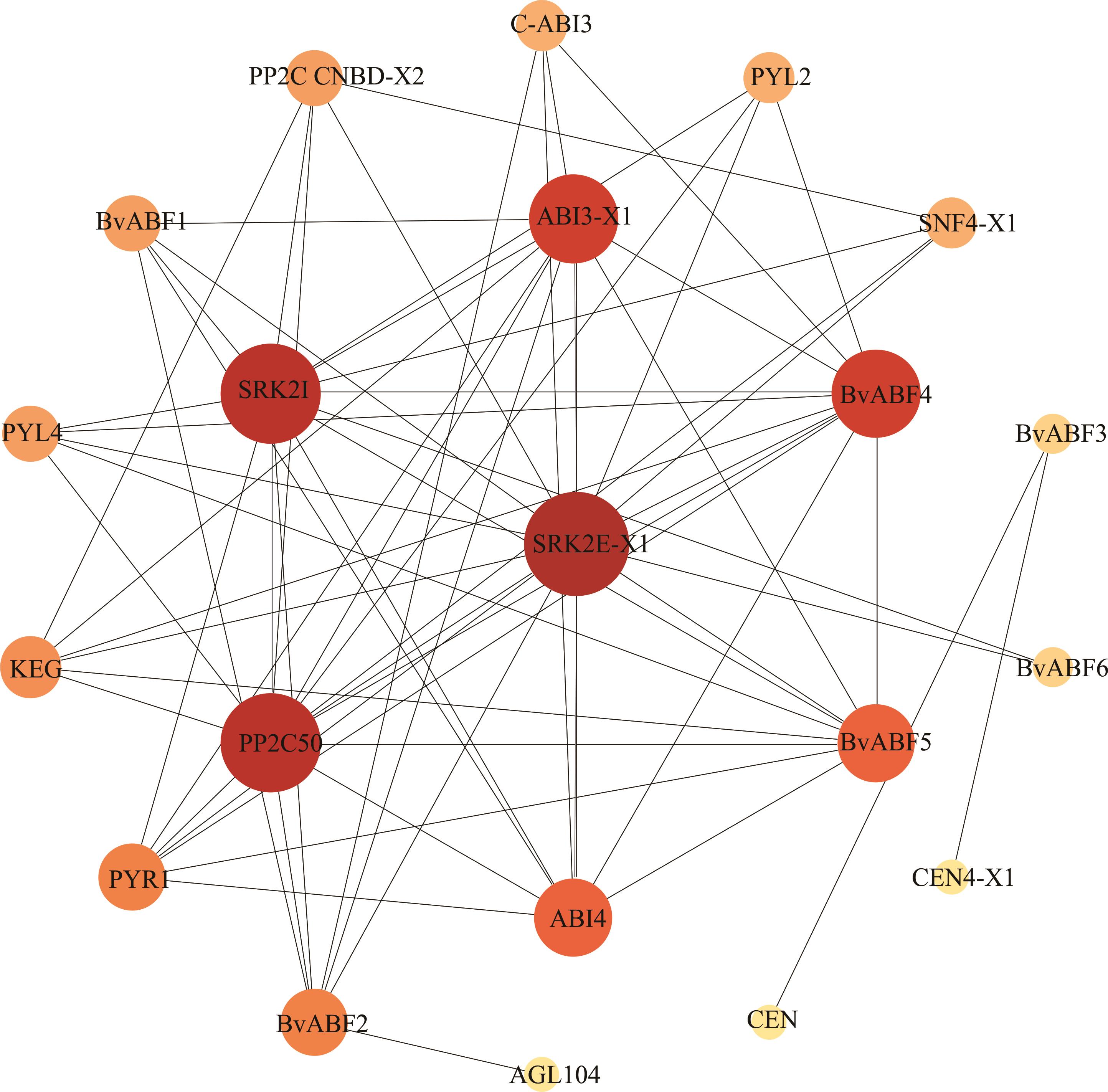
图6 甜菜BvABF蛋白互作网络预测蛋白登录号如下The accession number of proteins are as follows: PP2CCNBD-X2 (XP_010688278.1); C-ABI3 (XP_010676772.1); PYL2 (XP_010667133.1); SNF4-X1 (XP_010674700.1); ABI3-X1 (XP_010684986.1); PYL4 (XP_010692925.1); SRK2I (XP_010680446.1); SRK2E-X1 (XP_010691012.1); KEG (XP_010693345.1); PP2C50 (XP_010696551.1); PYR1 (XP_010677239.1); ABI4 (XP_010689445.1); CEN4-X1 (XP_010683747.1); AGL104 (XP_010680585.1); CEN(XP_010686025.1). 甜菜BvABFs基因号见表2。The gene ID of BvABFs are shown in Table 2.
Fig.6 Interaction network predicts of BvABF proteins in sugar beet
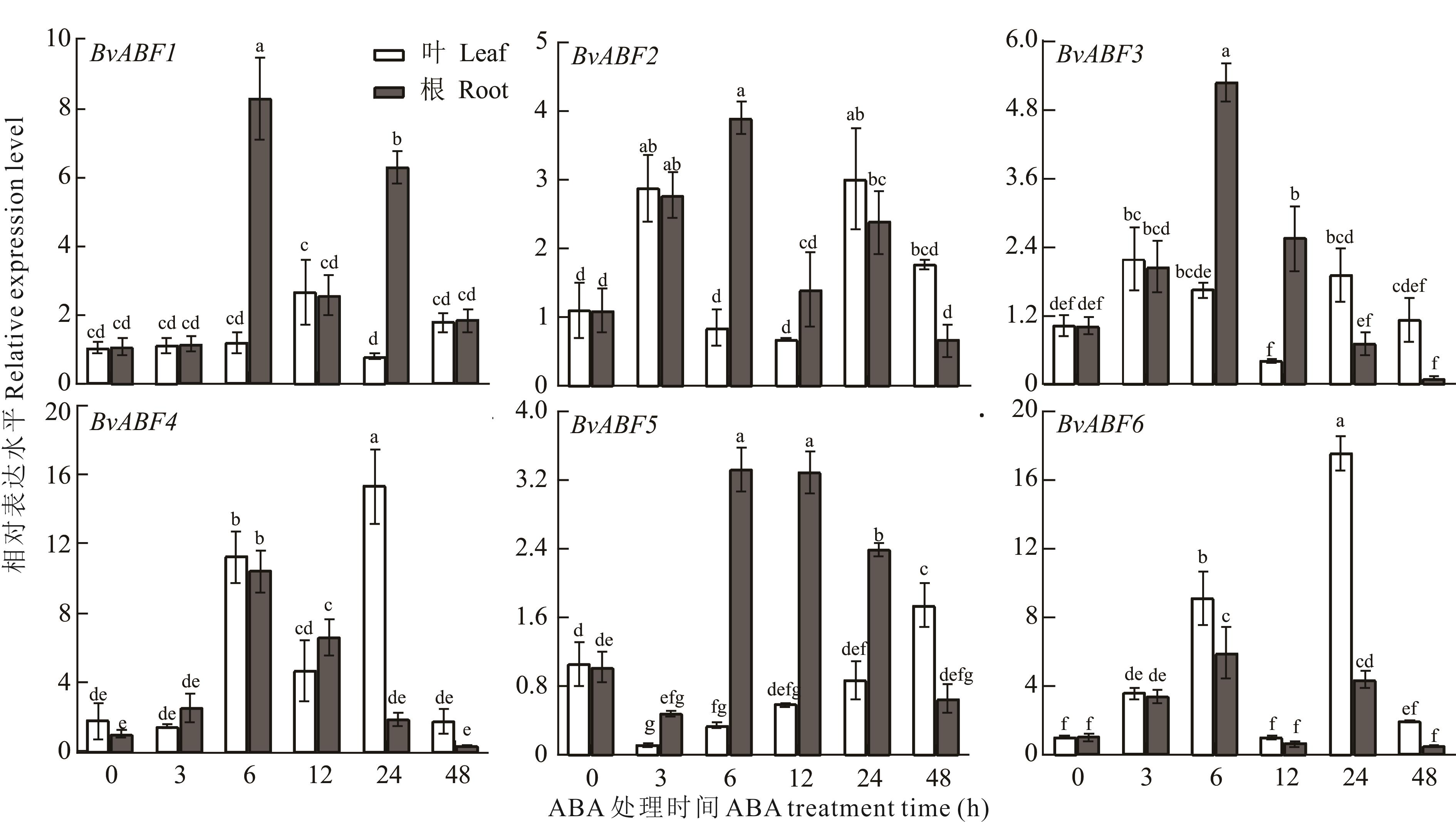
图7 ABA处理下BvABF基因相对表达分析不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平上差异显著。Different lowercase letters mean significant difference at P<0.05 level.
Fig.7 Relative expression analysis of the BvABF genes under ABA treatment
| 1 | Zhang H M, Zhu J H, Gong Z Z, et al. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2022, 23(2): 104-119. |
| 2 | Yoshida T, Mogami J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. ABA-dependent and ABA-independent signaling in response to osmotic stress in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2014, 21: 133-139. |
| 3 | Soma F, Takahashi F, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, et al. Cellular phosphorylation signaling and gene expression in drought stress responses: ABA-dependent and ABA-independent regulatory systems. Plants, 2021, 10(4): 756. |
| 4 | Choi H, Hong J, Ha J, et al. ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(3): 1723-1730. |
| 5 | Zhao G Y, Cheng Q, Zhao Y T, et al. The abscisic acid-responsive element binding factors MAPKKK18 module regulates abscisic acid-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2023, 299(4): 103060. |
| 6 | Yu Z D, Ding F, Feng Y R, et al. ABA promotes sulfite stress tolerance by ABF4-mediated upregulation of SOX expression. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 203: 105070. |
| 7 | Zhang C W, Zhou Q, Liu W S, et al. BrABF3 promotes flowering through the direct activation of CONSTANS transcription in pak choi. The Plant Journal, 2022, 111(1): 134-148. |
| 8 | Zeng Z, Lyu T, Lyu Y M. LoSWEET14, a sugar transporter in lily, is regulated by transcription factor LoABF2 to participate in the ABA signaling pathway and enhance tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in tobacco. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(23): 15093. |
| 9 | Song J, Sun P P, Kong W N, et al. SnRK2.4-mediated phosphorylation of ABF2 regulates ARGININE DECARBOXYLASE expression and putrescine accumulation under drought stress. New Phytologist, 2023, 238(1): 216-236. |
| 10 | Wu L, Liu X, Zhang M Y, et al. Self S-RNase inhibits ABF-LRX signaling to arrest pollen tube growth to achieve self-incompatibility in pear. The Plant Journal, 2023, 113(3): 595-609. |
| 11 | Hou Z H, Zhang X Z, Tang Y M, et al. GmSAP5, a soybean A20/AN1 domain-containing stress-associated protein gene activated by GmAREB3, increases drought stress resistance in soybean by mediating ABA signaling. The Crop Journal, 2022, 10(6): 1601-1610. |
| 12 | Zhang H J, Mao L L, Xin M, et al. Overexpression of GhABF3 increases cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) tolerance to salt and drought. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22(1): 313. |
| 13 | Yang Q S, Wu X Y, Gao Y H, et al. PpyABF3 recruits the COMPASS-like complex to regulate bud dormancy maintenance via integrating ABA signaling and GA catabolism. New Phytologist, 2023, 237(1): 192-203. |
| 14 | Kou S, Chen Y, Liu T T, et al. Crosstalk of putrescine synthetic pathway with abscisic acid signaling pathway in cold tolerance of potato. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 204: 105085. |
| 15 | Cheng H K, Pan G Y, Zhou N, et al. Calcium-dependent protein kinase 5 (CPK5) positively modulates drought tolerance through phosphorylating ABA-responsive element binding factors in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Plant Science, 2021, 315: 111125. |
| 16 | Wei X B, Wei X P, Guan W L, et al. ABA-responsive transcription factor ABF1-1 promotes JA biosynthesis to accelerate suberin polyphenolic formation in wounded kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis). Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2022, 187: 111850. |
| 17 | Jiang Y Q, Wu X, Shi M, et al. The miR159‐MYB33‐ABI5 module regulates seed germination in Arabidopsis. Physiologia Plantarum, 2022, 174(2): e13659. |
| 18 | Chang H C, Tsai M C, Wu S S, et al. Regulation of ABI5 expression by ABF3 during salt stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Botanical Studies, 2019, 60(1): 16. |
| 19 | Finkelstein R, Gampala S S L, Lynch T J, et al. Redundant and distinct functions of the ABA response loci ABA-INSENSITIVE (ABI) 5 and ABRE-BINDING FACTOR (ABF) 3. Plant Molecular Biology, 2005, 59(2): 253-267. |
| 20 | Fernando V C D, Khateeb W A, Belmonte M F, et al. Role of Arabidopsis ABF1/3/4 during det1 germination in salt and osmotic stress conditions. Plant Molecular Biology, 2018, 97(1/2): 149-163. |
| 21 | Kobayashi F, Maeta E, Terashima A, et al. Positive role of a wheat HvABI5 ortholog in abiotic stress response of seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum, 2008, 134(1): 74-86. |
| 22 | Huang X S, Liu J H, Chen X J. Overexpression of PtrABF gene, a bZIP transcription factor isolated from Poncirus trifoliata, enhances dehydration and drought tolerance in tobacco via scavenging ROS and modulating expression of stress-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biology, 2010, 10: 230. |
| 23 | Xu Z J, Wang F, Ma Y B, et al. Transcription factor SlAREB1 is involved in the antioxidant regulation under saline-alkaline stress in tomato. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(9): 1673. |
| 24 | Kim S Y. The role of ABF family bZIP class transcription factors in stress response. Physiologia Plantarum, 2006, 126(4): 519-527. |
| 25 | Mirzaei K, Bahramnejad B, Fatemi S. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bZIP gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Plant Gene, 2020, 24: 100257. |
| 26 | Fiallos-Salguero M S, Li J, Li Y, et al. Identification of AREB/ABF gene family involved in the response of ABA under salt and drought stresses in jute (Corchorus olitorius L.). Plants, 2023, 12(5): 1161. |
| 27 | Ji L X, Wang J, Ye M X, et al. Identification and characterization of the Populus AREB/ABF subfamily. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2013, 55(2): 177-186. |
| 28 | Pan X J, Wang C L, Liu Z S, et al. Identification of ABF/AREB gene family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and functional analysis of ABF/AREB in response to ABA and abiotic stresses. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e15310. |
| 29 | Rui L, Yang Y Y, Zheng P F, et al. Genome-wide analysis of MdABF subfamily and functional identification of MdABF1 in drought tolerance in apple. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 199: 104904. |
| 30 | Liu X J, Cheng R W, Chen Y, et al. Identification and characterization of the AREB/ABF/ABI5 gene family in sandalwood (Santalum album L.) and its potential role in drought stress and ABA treatment. Forests, 2023, 14(8): 1691. |
| 31 | Guo S J, Sun Y, Zheng H Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of ABF/AREB/ ABI5 gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2023, 31(4): 667-681. |
| 郭树娟, 孙月, 郑昊元, 等. 小麦ABF/AREB/ABI5基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2023, 31(4): 667-681. | |
| 32 | Zhang H F, Liu W Z, Zhang Y P, et al. Identification, expression and interaction analyses of calcium-dependent protein kinase (CPK) genes in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 211. |
| 33 | Yong X, Zheng T C, Zhuo X K, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterisation, and evolution of ABF/AREB subfamily in nine Rosaceae species and expression analysis in mei (Prunus mume). PeerJ, 2021, 9: e10785. |
| 34 | Que F, Wang G L, Huang Y, et al. Genomic identification of group A bZIP transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stress in carrot. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2015, 14(4): 13274-13288. |
| 35 | Kerr T C C, Abdel-Mageed H, Kang M Y, et al. Functional characterization of the ABF gene family in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). bioRxiv, 2017: 186015. |
| 36 | Zandkarimi H, Ebadi A, Salami S A, et al. Analyzing the expression profile of AREB/ABF and DREB/CBF genes under drought and salinity stresses in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0134288. |
| 37 | Vysotskii D A, de Vries-van Leeuwen I J, Souer E, et al. ABF transcription factors of Thellungiella salsuginea: structure, expression profiles and interaction with 14-3-3 regulatory proteins. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2013, 8(1): e22672. |
| 38 | Hu H B. Study of high yield and high efficiency cultivation technology of sugar beet in Xinjiang. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2014. |
| 胡华兵. 新疆甜菜高产高效种植技术研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2014. | |
| 39 | Yolcu S, Alavilli H, Ganesh P, et al. An insight into the abiotic stress responses of cultivated beets (Beta vulgaris L.). Plants, 2021, 11(1): 12. |
| 40 | Skorupa M, Gołębiewski M, Kurnik K, et al. Salt stress vs. salt shock-the case of sugar beet and its halophytic ancestor. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 57. |
| 41 | Dohm J C, Minoche A E, Holtgräwe D, et al. The genome of the recently domesticated crop plant sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Nature, 2014, 505(7484): 546-549. |
| 42 | Wu G Q, Li Z Q, Cao H, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY genes in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) under alkaline stress. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e7817. |
| 43 | Yang X H, Wu G Q, Wei M, et al. Genome-wide identification of BvHAK gene family in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) and their expression analysis under salt treatments. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(10): 3773-3789. |
| 杨小涵, 伍国强, 魏明, 等. 甜菜 BvHAK 基因家族全基因组鉴定及其在盐处理下的表达分析. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(10): 3773-3789. | |
| 44 | Wu G Q, Liu Z X, Xie L L, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the BvSnRK2 genes family in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) under salt conditions. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 40: 519-532. |
| 45 | Genies L, Orjollet D, Carasco L, et al. Uptake and translocation of cesium by Arabidopsis thaliana in hydroponics conditions: Links between kinetics and molecular mechanisms. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 138: 164-172. |
| 46 | Guan R, Xu S, Lu Z M, et al. Genomic characterization of bZIP transcription factors related to andrographolide biosynthesis in Andrographis paniculata. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 223(Pt A): 1619-1631. |
| 47 | Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D412-D419. |
| 48 | Letunic I, Khedkar S, Bork P. SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D458-D460. |
| 49 | Lu S N, Wang J Y, Chitsaz F, et al. CDD/SPARCLE: the conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(D1): D265-D268. |
| 50 | Waterhouse A M, Procter J B, Martin D M A, et al. Jalview Version 2——a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(9): 1189-1191. |
| 51 | Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, et al. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2018, 35(6): 1547. |
| 52 | Subramanian B, Gao S, Lercher M J, et al. Evolview v3: a webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(W1): W270-W275. |
| 53 | Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, et al. ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 2003, 31(13): 3784-3788. |
| 54 | Chou K C, Shen H B. Plant-mPLoc: a top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS One, 2010, 5(6): e11335. |
| 55 | Hu B, Jin J P, Guo A Y, et al. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(8): 1296-1297. |
| 56 | Jing Z B, Fu H Q. Identification of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor and analysis of expression responses to biotic and abiotic stresses in kiwifruit (Actinidia lind L.). European Journal of Horticultural Science, 2018, 83(4): 212-223. |
| 57 | Bailey T L, Williams N, Misleh C, et al. MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, 34(suppl_2): W369-W373. |
| 58 | Chen C J, Chen H, Zhang Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194-1202. |
| 59 | Tu M X, Wang X H, Huang L, et al. Expression of a grape bZIP transcription factor, VqbZIP39, in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana confers tolerance of multiple abiotic stresses. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2016, 125: 537-551. |
| 60 | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, 30(1): 325-327. |
| 61 | Goldman N, Yang Z. A codon-based model of nucleotide substitution for protein-coding DNA sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1994, 11(5): 725-736. |
| 62 | Cao H L, Wang L, Yue C, et al. Isolation and expression analysis of 18 CsbZIP genes implicated in abiotic stress responses in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2015, 97: 432-442. |
| 63 | Szklarczyk D, Gable A L, Nastou K C, et al. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D605-D612. |
| 64 | Wu G Q, Xie L L, Wang J L, et al. Genome-wide identification of CIPK genes in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) and their expression under NaCl stress. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 42(1): 260-274. |
| 65 | Swift M L. GraphPad prism, data analysis, and scientific graphing. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1997, 37(2): 411-412. |
| 66 | Schwechheimer C, Bevan M. The regulation of transcription factor activity in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 1998, 3(10): 378-383. |
| 67 | Samad A F A, Sajad M, Nazaruddin N, et al. MicroRNA and transcription factor: key players in plant regulatory network. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 565. |
| 68 | Jakoby M, Weisshaar B, Dröge-Laser W, et al. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 2002, 7(3): 106-111. |
| 69 | Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Reports, 2013, 32(3): 959-970. |
| 70 | Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Kumar N, et al. Abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a review on current knowledge and future prospects. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8(120): 161. |
| 71 | Raghavendra A S, Gonugunta V K, Christmann A, et al. ABA perception and signaling. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(7): 395-401. |
| 72 | Kang J, Choi H, Im M, et al. Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper proteins that mediate stress-responsive abscisic acid signaling. The Plant Cell, 2002, 14(2): 343-357. |
| 73 | Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, et al. Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2000, 97(21): 11632-11637. |
| 74 | Hsieh T H, Li C W, Su R C, et al. A tomato bZIP transcription factor, SlAREB, is involved in water deficit and salt stress response. Planta, 2010, 231(6): 1459-1473. |
| 75 | Hong L, Hu B, Liu X, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a new stress-related AREB gene from Arachis hypogaea. Biologia Plantarum, 2013, 57(1): 56-62. |
| 76 | Wang J Y, Li Q, Mao X G, et al. Wheat transcription factor TaAREB3 participates in drought and freezing tolerances in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2016, 12(2): 257-269. |
| 77 | Schindler U, Menkens A E, Beckmann H, et al. Heterodimerization between light-regulated and ubiquitously expressed Arabidopsis GBF bZIP proteins. The EMBO Journal, 1992, 11(4): 1261-1273. |
| 78 | Nijhawan A, Jain M, Tyagi A K, et al. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiology, 2008, 146(2): 333-350. |
| 79 | Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Sayama H, et al. AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. The Plant Journal, 2010, 61(4): 672-685. |
| 80 | Bensmihen S, Rippa S, Lambert G, et al. The homologous ABI5 and EEL transcription factors function antagonistically to fine-tune gene expression during late embryogenesis. The Plant Cell, 2002, 14(6): 1391-1403. |
| 81 | Chinnusamy V, Novella S R, Park S Y, et al. In vitro reconstitution of an ABA signaling pathway. Nature, 2009, 462(7273): 660-664. |
| 82 | Furihata T, Maruyama K, Fujita Y, et al. Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2006, 103(6): 1988-1993. |
| 83 | Li H L, Duan L H, Fang S M, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of AREB1 from red bean and kidney bean. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 31(8): 1559-1564. |
| 李海龙, 段立华, 方淑梅, 等. 红小豆与芸豆AREB1基因生物信息学分析. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(8): 1559-1564. | |
| 84 | Amparo R D, Branco C, Arenas J, et al. Analysis of selection in protein-coding sequences accounting for common biases. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2021, 22(5): bbaa431. |
| 85 | Zhang J Z. Positive selection, not negative selection, in the pseudogenization of rcsA in Yersinia pestis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2008, 105(42): E69-E70. |
| 86 | Kim S Y, Thomas T L. A family of novel basic leucine zipper proteins binds to seed-specification elements in the carrot Dc3 gene promoter. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1998, 152(6): 607-613. |
| 87 | Kim S Y, Chung H J, Thomas T L. Isolation of a novel class of bZIP transcription factors that interact with ABA-responsive and embryo-specification elements in the Dc3 promoter using a modified yeast one-hybrid system. The Plant Journal, 1997, 11(6): 1237-1251. |
| 88 | Fode B, Siemsen T, Thurow C, et al. The Arabidopsis GRAS protein SCL14 interacts with class Ⅱ TGA transcription factors and is essential for the activation of stress-inducible promoters. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(11): 3122-3135. |
| 89 | Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu J K. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2007, 12(10): 444-451. |
| 90 | Chen W J, Zhu T. Networks of transcription factors with roles in environmental stress response. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(12): 591-596. |
| 91 | Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiologia Plantarum, 2013, 147(1): 15-27. |
| 92 | Hossain M A, Cho J I, Han M, et al. The ABRE-binding bZIP transcription factor OsABF2 is a positive regulator of abiotic stress and ABA signaling in rice. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2010, 167(17): 1512-1520. |
| [1] | 崔红丽, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族鉴定及低温逆境表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 111-125. |
| [2] | 郝丽芬, 徐晓阳, 季玉, 王瑞, 吴德宝, 李宇宇, 林克剑. 长刺蒺藜草两异型种子形态和萌发过程的生理动态特征比较[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 40-50. |
| [3] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [4] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [5] | 张适阳, 刘凤民, 崔均涛, 何磊, 冯月燕, 张伟丽. 三种外源物质对低温胁迫下柱花草生理与荧光特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 85-99. |
| [6] | 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 李杭, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [7] | 李振松, 万里强, 李硕, 李向林. 苜蓿根系构型及生理特性对干旱复水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [8] | 项洪涛, 郑殿峰, 何宁, 李琬, 王曼力, 王诗雅. 植物对低温胁迫的生理响应及外源脱落酸缓解胁迫效应的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 208-219. |
| [9] | 崔雪莲, 夏超. 外源脱落酸对醉马草内生真菌共生体幼苗建植过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 70-80. |
| [10] | 芦岩, 张伶俐, 罗远琴, 魏利, 薛雪, 孙新文, 向春和, 毛胜勇, 王新峰, 张文举. 不同比例棉秆和甜菜渣混合发酵产物的体外产气特性及发酵参数的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 58-66. |
| [11] | 李思忠, 张立明, 高卫时, 白晓山, 刘军, 董心久, 杨洪泽, 沙红, 高燕. 滴灌模式下旱后复水对甜菜叶丛期光合光响应特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 198-204. |
| [12] | 伍国强, 冯瑞军, 李善家, 王春梅, 焦琦, 刘海龙. 盐处理对甜菜生长和渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 169-177. |
| [13] | 刘金平, 王大伟, 游明鸿, 张小晶, 蔡捡, 曾晓琳. 种子发育过程老芒麦生殖枝生物量和能量分配及激素含量变化分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 135-142. |
| [14] | 梁小红,安勐颍,宋峥,徐广臣,濮阳雪华. 外源甜菜碱对低温胁迫下结缕草生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 181-188. |
| [15] | 刘思露,杨鹏,尹淑霞. 外源甜菜碱对匍匐翦股颖的抗旱性调控作用分析[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 80-88. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||