

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 198-214.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024009
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-01-04
修回日期:2024-03-18
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-09-09
通讯作者:
梁国玲
作者简介:E-mail: qhliangguoling@163.com基金资助:
Feng-yu WANG( ), Guo-ling LIANG(
), Guo-ling LIANG( ), Ze-long HU, Wen-hui LIU
), Ze-long HU, Wen-hui LIU
Received:2024-01-04
Revised:2024-03-18
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-09-09
Contact:
Guo-ling LIANG
摘要:
以青藏高原地区不同来源的20份垂穗披碱草为研究对象,在青海省海北藏族自治州海晏县探究地理因子对其表型性状和种子产量的影响。选择出适宜采集垂穗披碱草材料的地理位置和海拔梯度,旨在为青藏高原垂穗披碱草种质资源的筛选和品种选育提供理论依据。结果表明:垂穗披碱草表型性状变异系数为6.560%~33.164%,各性状多样性指数均在1.4以上,说明种质资源具有丰富的遗传多样性。结构方程表明:旗叶长、花序长、穗轴第一节间长和单序籽粒重是影响种子产量的最主要影响因子;相关性分析发现,旗叶长、花序长、穗轴第一节间长、单序籽粒重以及种子产量受地理因子影响较大,均随着海拔的升高而降低,随着经度、纬度的升高而升高。通过聚类分析得出,分布在海拔为2600~3350 m,经度为101° E左右和纬度为35°-37° N的植物叶部和穗部性状表现优异并且具有丰富的变异类型,可以在此区域进行优良垂穗披碱草种质资源的筛选和品种选育。
王凤宇, 梁国玲, 胡泽龙, 刘文辉. 地理因子对青藏高原野生垂穗披碱草表型及种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 198-214.
Feng-yu WANG, Guo-ling LIANG, Ze-long HU, Wen-hui LIU. Effect of geographic factors on phenotypic traits and seed yield of Elymus nutans on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 198-214.
采集编号 Collection number | 来源地 Sources | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15-070 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°37′35″ | 37°09′10″ | 2960 | 路边Roadside |
| 15-087 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°36′07″ | 37°08′10″ | 2810 | 路边Roadside |
| 15-207 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°45′48″ | 37°00′38″ | 2600 | 路边Roadside |
| 16-121 | 青海省门源县Menyuan, Qinghai | 101°14′38″ | 37°37′03″ | 3130 | 路边Roadside |
| 16-177 | 青海省门源县Menyuan, Qinghai | 101°13′25″ | 37°45′13″ | 3350 | 河边滩地River beach |
| 16-330 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°49′39″ | 36°58′48″ | 2980 | 山坡草地Hillside grassland |
| 16-383 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°11′32″ | 37°08′08″ | 3040 | 封育草场Enclosure grassland |
| 17-123 | 青海省湟中县Huangzhong, Qinghai | 101°40′52″ | 36°18′09″ | 2915 | 山坡草地Hillside grassland |
| 17-221 | 青海省龙羊峡Longyang gorge, Qinghai | 101°03′43″ | 36°16′35″ | 3280 | 封育草场Enclosure grassland |
| 17-359 | 青海省玛多县Maduo, Qinghai | 98°57′36″ | 35°22′45″ | 4296 | 路边Roadside |
| 18-023 | 青海省贵德县Guide, Qinghai | 101°18′10″ | 35°48′38″ | 3200 | 路边Roadside |
| 18-114 | 青海省贵南县Guinan, Qinghai | 100°39′22″ | 35°38′45″ | 3080 | 路边Roadside |
| 18-175 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai, Qinghai | 100°14′49″ | 35°41′41″ | 2740 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-056 | 青海省河南县Henan, Qinghai | 101°20′27″ | 34°52′12″ | 3763 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-081 | 青海省泽库县Zeku, Qinghai | 101°31′09″ | 34°34′43″ | 3648 | 公路旁草场Grassland by the road |
| 20-088 | 青海省泽库县Zeku, Qinghai | 101°28′32″ | 35°13′32″ | 3894 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-100 | 青海省泽库县Zeku, Qinghai | 101°06′34″ | 35°16′12″ | 3527 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-436 | 西藏拉孜县Lazi, Tibet | 87°38′56″ | 29°05′30″ | 4010 | 农田边By the farmland |
| 20-439 | 西藏拉孜县Lazi, Tibet | 87°52′13″ | 29°20′13″ | 3940 | 河边滩地River beach |
| 20-479 | 西藏当雄县Dangxiong, Tibet | 91°27′20″ | 30°34′05″ | 4500 | 沼泽草甸Swamp meadow |
表1 试验材料及来源
Table 1 The test materials and sources
采集编号 Collection number | 来源地 Sources | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15-070 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°37′35″ | 37°09′10″ | 2960 | 路边Roadside |
| 15-087 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°36′07″ | 37°08′10″ | 2810 | 路边Roadside |
| 15-207 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°45′48″ | 37°00′38″ | 2600 | 路边Roadside |
| 16-121 | 青海省门源县Menyuan, Qinghai | 101°14′38″ | 37°37′03″ | 3130 | 路边Roadside |
| 16-177 | 青海省门源县Menyuan, Qinghai | 101°13′25″ | 37°45′13″ | 3350 | 河边滩地River beach |
| 16-330 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°49′39″ | 36°58′48″ | 2980 | 山坡草地Hillside grassland |
| 16-383 | 青海省大通县Datong, Qinghai | 101°11′32″ | 37°08′08″ | 3040 | 封育草场Enclosure grassland |
| 17-123 | 青海省湟中县Huangzhong, Qinghai | 101°40′52″ | 36°18′09″ | 2915 | 山坡草地Hillside grassland |
| 17-221 | 青海省龙羊峡Longyang gorge, Qinghai | 101°03′43″ | 36°16′35″ | 3280 | 封育草场Enclosure grassland |
| 17-359 | 青海省玛多县Maduo, Qinghai | 98°57′36″ | 35°22′45″ | 4296 | 路边Roadside |
| 18-023 | 青海省贵德县Guide, Qinghai | 101°18′10″ | 35°48′38″ | 3200 | 路边Roadside |
| 18-114 | 青海省贵南县Guinan, Qinghai | 100°39′22″ | 35°38′45″ | 3080 | 路边Roadside |
| 18-175 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai, Qinghai | 100°14′49″ | 35°41′41″ | 2740 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-056 | 青海省河南县Henan, Qinghai | 101°20′27″ | 34°52′12″ | 3763 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-081 | 青海省泽库县Zeku, Qinghai | 101°31′09″ | 34°34′43″ | 3648 | 公路旁草场Grassland by the road |
| 20-088 | 青海省泽库县Zeku, Qinghai | 101°28′32″ | 35°13′32″ | 3894 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-100 | 青海省泽库县Zeku, Qinghai | 101°06′34″ | 35°16′12″ | 3527 | 路边Roadside |
| 20-436 | 西藏拉孜县Lazi, Tibet | 87°38′56″ | 29°05′30″ | 4010 | 农田边By the farmland |
| 20-439 | 西藏拉孜县Lazi, Tibet | 87°52′13″ | 29°20′13″ | 3940 | 河边滩地River beach |
| 20-479 | 西藏当雄县Dangxiong, Tibet | 91°27′20″ | 30°34′05″ | 4500 | 沼泽草甸Swamp meadow |
项目 Item | 性状 Trait | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 Standard deviation | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 极差 Range | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) | 多样性指数 H′ | 广义遗传力 H2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
叶部性状 Leaf trait | 叶层高度TH (cm) | 13.938 | 3.052 | 8.667 | 18.667 | 10.000 | 21.898 | 1.917 | 0.986 |
| 旗叶长FL (cm) | 8.840 | 1.701 | 6.417 | 12.400 | 5.983 | 19.241 | 1.670 | 0.979 | |
| 旗叶宽FW (cm) | 0.657 | 0.098 | 0.483 | 0.889 | 0.406 | 14.894 | 1.496 | 0.945 | |
穗部性状 Spike trait | 花序长IL (cm) | 16.812 | 2.756 | 12.643 | 22.214 | 9.571 | 16.392 | 1.878 | 0.989 |
| 花序宽IW (cm) | 1.666 | 0.439 | 0.629 | 2.929 | 2.300 | 26.328 | 1.709 | 0.986 | |
| 穗轴第一节间长RL (cm) | 2.026 | 0.672 | 1.343 | 4.033 | 2.690 | 33.164 | 1.713 | 0.961 | |
| 小穗数SN (No.) | 35.939 | 5.650 | 27.571 | 46.400 | 18.829 | 15.722 | 1.904 | 0.977 | |
| 小花数FN (No.) | 3.550 | 0.387 | 2.833 | 4.000 | 1.167 | 10.889 | 1.617 | 0.916 | |
| 单序籽粒数SNi (No.) | 94.921 | 10.305 | 79.800 | 113.200 | 33.400 | 10.856 | 1.817 | 0.990 | |
| 单序籽粒重SWi (g) | 0.588 | 0.146 | 0.388 | 1.000 | 0.613 | 24.864 | 1.848 | 0.959 | |
籽粒性状 Grain trait | 内稃长LP (mm) | 9.210 | 0.647 | 7.953 | 10.353 | 2.400 | 7.023 | 1.973 | 0.958 |
| 外稃长LL (mm) | 9.798 | 0.643 | 8.608 | 10.888 | 2.280 | 6.560 | 1.895 | 0.951 | |
| 芒长AL (mm) | 14.123 | 2.567 | 9.848 | 20.753 | 10.905 | 18.179 | 1.822 | 0.985 | |
| 种子长SL (mm) | 6.971 | 0.390 | 6.163 | 7.962 | 1.799 | 5.601 | 1.861 | 0.866 | |
| 种子宽SW (mm) | 0.826 | 0.105 | 0.665 | 1.170 | 0.505 | 12.665 | 1.713 | 0.860 | |
| 千粒重TKW (g) | 4.119 | 0.380 | 3.567 | 4.733 | 1.167 | 9.231 | 1.805 | 0.918 |
表2 垂穗披碱草表型性状遗传多样性分析
Table 2 Genetic diversity analysis in phenotypic trait of E.nutans
项目 Item | 性状 Trait | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 Standard deviation | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 极差 Range | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) | 多样性指数 H′ | 广义遗传力 H2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
叶部性状 Leaf trait | 叶层高度TH (cm) | 13.938 | 3.052 | 8.667 | 18.667 | 10.000 | 21.898 | 1.917 | 0.986 |
| 旗叶长FL (cm) | 8.840 | 1.701 | 6.417 | 12.400 | 5.983 | 19.241 | 1.670 | 0.979 | |
| 旗叶宽FW (cm) | 0.657 | 0.098 | 0.483 | 0.889 | 0.406 | 14.894 | 1.496 | 0.945 | |
穗部性状 Spike trait | 花序长IL (cm) | 16.812 | 2.756 | 12.643 | 22.214 | 9.571 | 16.392 | 1.878 | 0.989 |
| 花序宽IW (cm) | 1.666 | 0.439 | 0.629 | 2.929 | 2.300 | 26.328 | 1.709 | 0.986 | |
| 穗轴第一节间长RL (cm) | 2.026 | 0.672 | 1.343 | 4.033 | 2.690 | 33.164 | 1.713 | 0.961 | |
| 小穗数SN (No.) | 35.939 | 5.650 | 27.571 | 46.400 | 18.829 | 15.722 | 1.904 | 0.977 | |
| 小花数FN (No.) | 3.550 | 0.387 | 2.833 | 4.000 | 1.167 | 10.889 | 1.617 | 0.916 | |
| 单序籽粒数SNi (No.) | 94.921 | 10.305 | 79.800 | 113.200 | 33.400 | 10.856 | 1.817 | 0.990 | |
| 单序籽粒重SWi (g) | 0.588 | 0.146 | 0.388 | 1.000 | 0.613 | 24.864 | 1.848 | 0.959 | |
籽粒性状 Grain trait | 内稃长LP (mm) | 9.210 | 0.647 | 7.953 | 10.353 | 2.400 | 7.023 | 1.973 | 0.958 |
| 外稃长LL (mm) | 9.798 | 0.643 | 8.608 | 10.888 | 2.280 | 6.560 | 1.895 | 0.951 | |
| 芒长AL (mm) | 14.123 | 2.567 | 9.848 | 20.753 | 10.905 | 18.179 | 1.822 | 0.985 | |
| 种子长SL (mm) | 6.971 | 0.390 | 6.163 | 7.962 | 1.799 | 5.601 | 1.861 | 0.866 | |
| 种子宽SW (mm) | 0.826 | 0.105 | 0.665 | 1.170 | 0.505 | 12.665 | 1.713 | 0.860 | |
| 千粒重TKW (g) | 4.119 | 0.380 | 3.567 | 4.733 | 1.167 | 9.231 | 1.805 | 0.918 |
采集编号 Collection number | 穗部性状Spike trait | 叶部性状Leaf trait | 籽粒性状Grain trait | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
花序长 IL | 花序宽 IW | 穗轴第一节间长RL | 小穗数 SN | 小花数 FN | 单序籽粒数 SNi | 单序籽粒重 SWi | 叶层高度 TH | 旗叶长 FL | 旗叶宽 FW | 内稃长 LP | 外稃长 LL | 芒长 AL | 种子长 SL | 种子宽SW | 千粒重TKW | |
| 15-207 | 20.75±0.70ab | 1.45±0.42gh | 2.79±0.24ab | 31.80±3.31fghij | 3.67±0.24abc | 92.80±4.07de | 0.61±0.14bcde | 12.33±0.94efgh | 9.00±0.70cde | 0.66±0.05bcd | 8.93±0.54defg | 9.30±0.48efg | 9.85±0.58g | 6.98±0.83abc | 0.86±0.16b | 3.63±0.12c |
| 18-175 | 19.18±0.26bcd | 2.04±0.43bc | 1.73±0.27bcde | 34.60±1.74efgh | 3.17±0.24abc | 82.75±6.42fg | 0.73±0.16b | 16.50±0.50abc | 8.48±0.33def | 0.70±0.11bc | 9.44±0.64bcdef | 9.54±0.52defg | 12.47±0.86ef | 6.73±1.19bc | 0.89±0.21b | 4.73±0.09a |
| 15-087 | 22.21±0.80a | 1.83±0.33bcdef | 2.85±0.65bcd | 39.50±2.93bcde | 4.00±0.00ab | 93.00±4.06de | 0.75±0.26b | 11.75±0.25fghi | 10.50±0.94bc | 0.79±0.11ab | 9.44±0.43bcdef | 9.64±0.24cdef | 12.66±0.62de | 6.90±0.83c | 0.87±0.12b | 4.57±0.12ab |
| 17-123 | 20.64±1.38ab | 1.94±0.44bcd | 2.63±0.67abc | 41.17±4.41abcd | 3.33±0.24abc | 106.40±2.58bc | 0.57±0.13bcdef | 12.00±1.41fghi | 10.48±0.25bc | 0.88±0.17a | 8.35±0.61gh | 9.00±0.50fg | 12.97±0.34def | 6.16±0.34c | 0.79±0.13b | 4.15±0.05ab |
| 15-070 | 17.40±1.71d | 2.93±0.42a | 2.12±0.42cdef | 42.00±3.41abc | 3.17±0.24abc | 89.00±7.04def | 0.74±0.26b | 18.00±1.00ab | 11.08±0.30ab | 0.89±0.20a | 7.95±0.72h | 8.61±0.75g | 14.10±0.22cde | 7.64±0.67ab | 1.17±0.01a | 3.93±0.19ab |
| 16-330 | 20.13±0.89bc | 2.14±0.37b | 4.03±0.60a | 37.33±9.37cdef | 4.00±0.00ab | 113.20±3.31a | 0.60±0.08bcdef | 8.67±0.47j | 8.48±0.44def | 0.63±0.10bcd | 8.88±0.66efg | 9.03±0.62fg | 10.96±1.05fg | 6.82±0.54bc | 0.74±0.16b | 4.57±0.12ab |
| 16-383 | 18.58±1.12cd | 1.66±0.24defgh | 2.59±0.36ab | 35.00±3.46efgh | 3.50±0.41abc | 99.83±5.30c | 0.60±0.20bcdef | 12.50±0.50efgh | 11.14±1.59ab | 0.62±0.07bcd | 8.36±0.39gh | 9.20±0.72fg | 12.50±1.29ef | 7.22±0.79abc | 0.87±0.14b | 3.87±0.12ab |
| 18-114 | 17.80±0.98d | 0.63±0.19i | 1.50±0.34cdef | 34.00±2.53efghi | 2.83±0.24c | 107.50±7.43ab | 0.50±0.08cdef | 11.67±1.25fghi | 9.52±0.16bcd | 0.61±0.12bcd | 10.35±0.30a | 10.38±0.14abcd | 12.74±0.65ef | 6.72±0.43bc | 0.89±0.01b | 4.03±0.12ab |
| 16-121 | 15.28±1.58e | 1.43±0.12gh | 1.64±0.55fg | 30.40±1.62ghij | 3.33±0.47abc | 92.00±7.16de | 0.48±0.13def | 18.00±1.41ab | 6.42±0.25h | 0.61±0.02bcd | 9.80±0.86abcd | 10.54±0.64abc | 13.90±1.37de | 6.65±0.36bc | 0.80±0.25b | 3.80±0.16abc |
| 18-023 | 17.42±0.96d | 1.58±0.19efgh | 1.99±0.37defg | 35.80±4.75defgh | 4.00±0.00ab | 102.17±4.26bc | 1.00±0.22a | 16.00±1.00abc | 12.40±0.96a | 0.67±0.09bcd | 10.09±0.37ab | 10.89±0.99a | 16.65±1.01b | 7.96±0.58a | 0.81±0.10b | 4.30±0.22ab |
| 17-221 | 15.48±1.01e | 1.33±0.12h | 1.92±0.36cdef | 31.00±1.87ghij | 3.83±0.00ab | 86.50±1.38efg | 0.67±0.17bcd | 9.83±0.24ij | 6.68±1.03gh | 0.57±0.11cd | 9.43±0.45bcdef | 9.76±0.28cdef | 20.75±1.55a | 6.91±0.12bc | 0.72±0.06b | 3.65±0.15bc |
| 16-177 | 14.86±2.41ef | 1.36±0.13h | 2.08±0.33defg | 32.17±1.34fghij | 4.00±0.24ab | 107.67±1.70ab | 0.56±0.09bcdef | 18.50±0.50a | 8.60±0.87def | 0.66±0.08bcd | 9.39±0.55bcdef | 9.92±0.56bcdef | 13.91±1.37de | 7.24±0.55abc | 0.67±0.07b | 3.57±0.12bc |
| 20-100 | 12.64±0.95g | 1.56±0.14efgh | 1.39±0.31efg | 35.67±1.70defgh | 3.50±0.41abc | 79.80±3.06g | 0.50±0.09cdef | 11.33±0.94ghi | 7.38±0.34efgh | 0.58±0.08cd | 8.36±0.88gh | 9.20±0.79fg | 12.54±0.61ef | 7.03±0.66abc | 0.77±0.08b | 3.73±0.09abc |
| 20-081 | 15.26±0.91e | 1.53±0.18fgh | 1.73±0.31efg | 28.33±2.69ij | 4.00±0.00ab | 82.00±3.03g | 0.48±0.12def | 17.00±0.82ab | 8.68±0.63def | 0.68±0.08bcd | 9.20±0.49bcdefg | 9.76±0.42cdef | 13.01±0.70def | 6.91±0.35bc | 0.79±0.18b | 4.55±0.15ab |
| 20-056 | 14.52±0.56ef | 1.46±0.14gh | 1.52±0.18efg | 30.00±1.91hij | 3.67±0.47abc | 88.67±2.69def | 0.40±0.08ef | 11.00±0.82hi | 8.03±1.26defgh | 0.48±0.07d | 9.81±0.68abcd | 10.52±0.62abcd | 19.31±1.79a | 6.86±0.50bc | 0.87±0.05b | 4.60±0.22ab |
| 20-088 | 14.58±1.81ef | 1.73±0.22cdefg | 2.09±0.41defg | 36.20±2.99defg | 4.00±0.41a | 104.33±3.09bc | 0.60±0.20bcdef | 14.67±0.47cde | 10.58±1.80defg | 0.63±0.09bcd | 9.92±0.40abc | 10.75±0.35ab | 14.02±0.90de | 7.17±0.60abc | 0.86±0.06b | 4.50±0.22ab |
| 20-439 | 13.68±1.02fg | 1.62±0.30defgh | 1.41±0.20defg | 46.40±5.24a | 3.33±0.47abc | 106.60±1.36b | 0.40±0.12ef | 12.67±0.47efgh | 7.83±1.73defgh | 0.65±0.10bcd | 9.04±0.48cdefg | 9.57±0.68cdefg | 14.43±0.83cde | 7.08±0.44abc | 0.86±0.21b | 4.37±0.33ab |
| 20-436 | 13.60±0.58efg | 1.43±0.15gh | 1.36±0.10g | 45.67±3.73a | 2.83±0.85c | 93.60±2.42d | 0.54±0.13bcdef | 13.67±0.94efg | 7.20±1.21efgh | 0.63±0.13bcd | 8.96±0.75defg | 9.73±0.62cdef | 14.53±0.77cde | 6.38±0.46c | 0.81±0.09b | 3.77±0.12abc |
| 17-359 | 17.60±1.55d | 1.79±0.11cdef | 1.81±0.32efg | 44.17±3.48ab | 3.50±0.41abc | 89.60±2.94de | 0.65±0.21bc | 14.00±0.82def | 7.35±1.09efgh | 0.63±0.08bcd | 9.71±0.46abcde | 10.24±0.20abcde | 15.06±1.21bcd | 7.02±0.39abc | 0.82±0.04b | 4.20±0.10ab |
| 20-479 | 14.63±1.49e | 1.88±0.21bcde | 1.34±0.23efg | 27.57±3.70j | 3.33±0.47bc | 81.00±6.53g | 0.39±0.08f | 18.67±1.89a | 7.00±0.61fgh | 0.58±0.20cd | 8.80±0.50fg | 10.40±0.45abcd | 16.11±1.15bc | 7.05±0.43abc | 0.69±0.00b | 3.87±0.12ab |
| F值F value | 22.661** | 17.194** | 6.123** | 10.393** | 2.732* | 23.592** | 5.818** | 17.275** | 11.490** | 4.279** | 5.676** | 4.880** | 16.623** | 1.611 | 1.549 | 2.798* |
表3 表型性状方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis of phenotypic trait
采集编号 Collection number | 穗部性状Spike trait | 叶部性状Leaf trait | 籽粒性状Grain trait | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
花序长 IL | 花序宽 IW | 穗轴第一节间长RL | 小穗数 SN | 小花数 FN | 单序籽粒数 SNi | 单序籽粒重 SWi | 叶层高度 TH | 旗叶长 FL | 旗叶宽 FW | 内稃长 LP | 外稃长 LL | 芒长 AL | 种子长 SL | 种子宽SW | 千粒重TKW | |
| 15-207 | 20.75±0.70ab | 1.45±0.42gh | 2.79±0.24ab | 31.80±3.31fghij | 3.67±0.24abc | 92.80±4.07de | 0.61±0.14bcde | 12.33±0.94efgh | 9.00±0.70cde | 0.66±0.05bcd | 8.93±0.54defg | 9.30±0.48efg | 9.85±0.58g | 6.98±0.83abc | 0.86±0.16b | 3.63±0.12c |
| 18-175 | 19.18±0.26bcd | 2.04±0.43bc | 1.73±0.27bcde | 34.60±1.74efgh | 3.17±0.24abc | 82.75±6.42fg | 0.73±0.16b | 16.50±0.50abc | 8.48±0.33def | 0.70±0.11bc | 9.44±0.64bcdef | 9.54±0.52defg | 12.47±0.86ef | 6.73±1.19bc | 0.89±0.21b | 4.73±0.09a |
| 15-087 | 22.21±0.80a | 1.83±0.33bcdef | 2.85±0.65bcd | 39.50±2.93bcde | 4.00±0.00ab | 93.00±4.06de | 0.75±0.26b | 11.75±0.25fghi | 10.50±0.94bc | 0.79±0.11ab | 9.44±0.43bcdef | 9.64±0.24cdef | 12.66±0.62de | 6.90±0.83c | 0.87±0.12b | 4.57±0.12ab |
| 17-123 | 20.64±1.38ab | 1.94±0.44bcd | 2.63±0.67abc | 41.17±4.41abcd | 3.33±0.24abc | 106.40±2.58bc | 0.57±0.13bcdef | 12.00±1.41fghi | 10.48±0.25bc | 0.88±0.17a | 8.35±0.61gh | 9.00±0.50fg | 12.97±0.34def | 6.16±0.34c | 0.79±0.13b | 4.15±0.05ab |
| 15-070 | 17.40±1.71d | 2.93±0.42a | 2.12±0.42cdef | 42.00±3.41abc | 3.17±0.24abc | 89.00±7.04def | 0.74±0.26b | 18.00±1.00ab | 11.08±0.30ab | 0.89±0.20a | 7.95±0.72h | 8.61±0.75g | 14.10±0.22cde | 7.64±0.67ab | 1.17±0.01a | 3.93±0.19ab |
| 16-330 | 20.13±0.89bc | 2.14±0.37b | 4.03±0.60a | 37.33±9.37cdef | 4.00±0.00ab | 113.20±3.31a | 0.60±0.08bcdef | 8.67±0.47j | 8.48±0.44def | 0.63±0.10bcd | 8.88±0.66efg | 9.03±0.62fg | 10.96±1.05fg | 6.82±0.54bc | 0.74±0.16b | 4.57±0.12ab |
| 16-383 | 18.58±1.12cd | 1.66±0.24defgh | 2.59±0.36ab | 35.00±3.46efgh | 3.50±0.41abc | 99.83±5.30c | 0.60±0.20bcdef | 12.50±0.50efgh | 11.14±1.59ab | 0.62±0.07bcd | 8.36±0.39gh | 9.20±0.72fg | 12.50±1.29ef | 7.22±0.79abc | 0.87±0.14b | 3.87±0.12ab |
| 18-114 | 17.80±0.98d | 0.63±0.19i | 1.50±0.34cdef | 34.00±2.53efghi | 2.83±0.24c | 107.50±7.43ab | 0.50±0.08cdef | 11.67±1.25fghi | 9.52±0.16bcd | 0.61±0.12bcd | 10.35±0.30a | 10.38±0.14abcd | 12.74±0.65ef | 6.72±0.43bc | 0.89±0.01b | 4.03±0.12ab |
| 16-121 | 15.28±1.58e | 1.43±0.12gh | 1.64±0.55fg | 30.40±1.62ghij | 3.33±0.47abc | 92.00±7.16de | 0.48±0.13def | 18.00±1.41ab | 6.42±0.25h | 0.61±0.02bcd | 9.80±0.86abcd | 10.54±0.64abc | 13.90±1.37de | 6.65±0.36bc | 0.80±0.25b | 3.80±0.16abc |
| 18-023 | 17.42±0.96d | 1.58±0.19efgh | 1.99±0.37defg | 35.80±4.75defgh | 4.00±0.00ab | 102.17±4.26bc | 1.00±0.22a | 16.00±1.00abc | 12.40±0.96a | 0.67±0.09bcd | 10.09±0.37ab | 10.89±0.99a | 16.65±1.01b | 7.96±0.58a | 0.81±0.10b | 4.30±0.22ab |
| 17-221 | 15.48±1.01e | 1.33±0.12h | 1.92±0.36cdef | 31.00±1.87ghij | 3.83±0.00ab | 86.50±1.38efg | 0.67±0.17bcd | 9.83±0.24ij | 6.68±1.03gh | 0.57±0.11cd | 9.43±0.45bcdef | 9.76±0.28cdef | 20.75±1.55a | 6.91±0.12bc | 0.72±0.06b | 3.65±0.15bc |
| 16-177 | 14.86±2.41ef | 1.36±0.13h | 2.08±0.33defg | 32.17±1.34fghij | 4.00±0.24ab | 107.67±1.70ab | 0.56±0.09bcdef | 18.50±0.50a | 8.60±0.87def | 0.66±0.08bcd | 9.39±0.55bcdef | 9.92±0.56bcdef | 13.91±1.37de | 7.24±0.55abc | 0.67±0.07b | 3.57±0.12bc |
| 20-100 | 12.64±0.95g | 1.56±0.14efgh | 1.39±0.31efg | 35.67±1.70defgh | 3.50±0.41abc | 79.80±3.06g | 0.50±0.09cdef | 11.33±0.94ghi | 7.38±0.34efgh | 0.58±0.08cd | 8.36±0.88gh | 9.20±0.79fg | 12.54±0.61ef | 7.03±0.66abc | 0.77±0.08b | 3.73±0.09abc |
| 20-081 | 15.26±0.91e | 1.53±0.18fgh | 1.73±0.31efg | 28.33±2.69ij | 4.00±0.00ab | 82.00±3.03g | 0.48±0.12def | 17.00±0.82ab | 8.68±0.63def | 0.68±0.08bcd | 9.20±0.49bcdefg | 9.76±0.42cdef | 13.01±0.70def | 6.91±0.35bc | 0.79±0.18b | 4.55±0.15ab |
| 20-056 | 14.52±0.56ef | 1.46±0.14gh | 1.52±0.18efg | 30.00±1.91hij | 3.67±0.47abc | 88.67±2.69def | 0.40±0.08ef | 11.00±0.82hi | 8.03±1.26defgh | 0.48±0.07d | 9.81±0.68abcd | 10.52±0.62abcd | 19.31±1.79a | 6.86±0.50bc | 0.87±0.05b | 4.60±0.22ab |
| 20-088 | 14.58±1.81ef | 1.73±0.22cdefg | 2.09±0.41defg | 36.20±2.99defg | 4.00±0.41a | 104.33±3.09bc | 0.60±0.20bcdef | 14.67±0.47cde | 10.58±1.80defg | 0.63±0.09bcd | 9.92±0.40abc | 10.75±0.35ab | 14.02±0.90de | 7.17±0.60abc | 0.86±0.06b | 4.50±0.22ab |
| 20-439 | 13.68±1.02fg | 1.62±0.30defgh | 1.41±0.20defg | 46.40±5.24a | 3.33±0.47abc | 106.60±1.36b | 0.40±0.12ef | 12.67±0.47efgh | 7.83±1.73defgh | 0.65±0.10bcd | 9.04±0.48cdefg | 9.57±0.68cdefg | 14.43±0.83cde | 7.08±0.44abc | 0.86±0.21b | 4.37±0.33ab |
| 20-436 | 13.60±0.58efg | 1.43±0.15gh | 1.36±0.10g | 45.67±3.73a | 2.83±0.85c | 93.60±2.42d | 0.54±0.13bcdef | 13.67±0.94efg | 7.20±1.21efgh | 0.63±0.13bcd | 8.96±0.75defg | 9.73±0.62cdef | 14.53±0.77cde | 6.38±0.46c | 0.81±0.09b | 3.77±0.12abc |
| 17-359 | 17.60±1.55d | 1.79±0.11cdef | 1.81±0.32efg | 44.17±3.48ab | 3.50±0.41abc | 89.60±2.94de | 0.65±0.21bc | 14.00±0.82def | 7.35±1.09efgh | 0.63±0.08bcd | 9.71±0.46abcde | 10.24±0.20abcde | 15.06±1.21bcd | 7.02±0.39abc | 0.82±0.04b | 4.20±0.10ab |
| 20-479 | 14.63±1.49e | 1.88±0.21bcde | 1.34±0.23efg | 27.57±3.70j | 3.33±0.47bc | 81.00±6.53g | 0.39±0.08f | 18.67±1.89a | 7.00±0.61fgh | 0.58±0.20cd | 8.80±0.50fg | 10.40±0.45abcd | 16.11±1.15bc | 7.05±0.43abc | 0.69±0.00b | 3.87±0.12ab |
| F值F value | 22.661** | 17.194** | 6.123** | 10.393** | 2.732* | 23.592** | 5.818** | 17.275** | 11.490** | 4.279** | 5.676** | 4.880** | 16.623** | 1.611 | 1.549 | 2.798* |
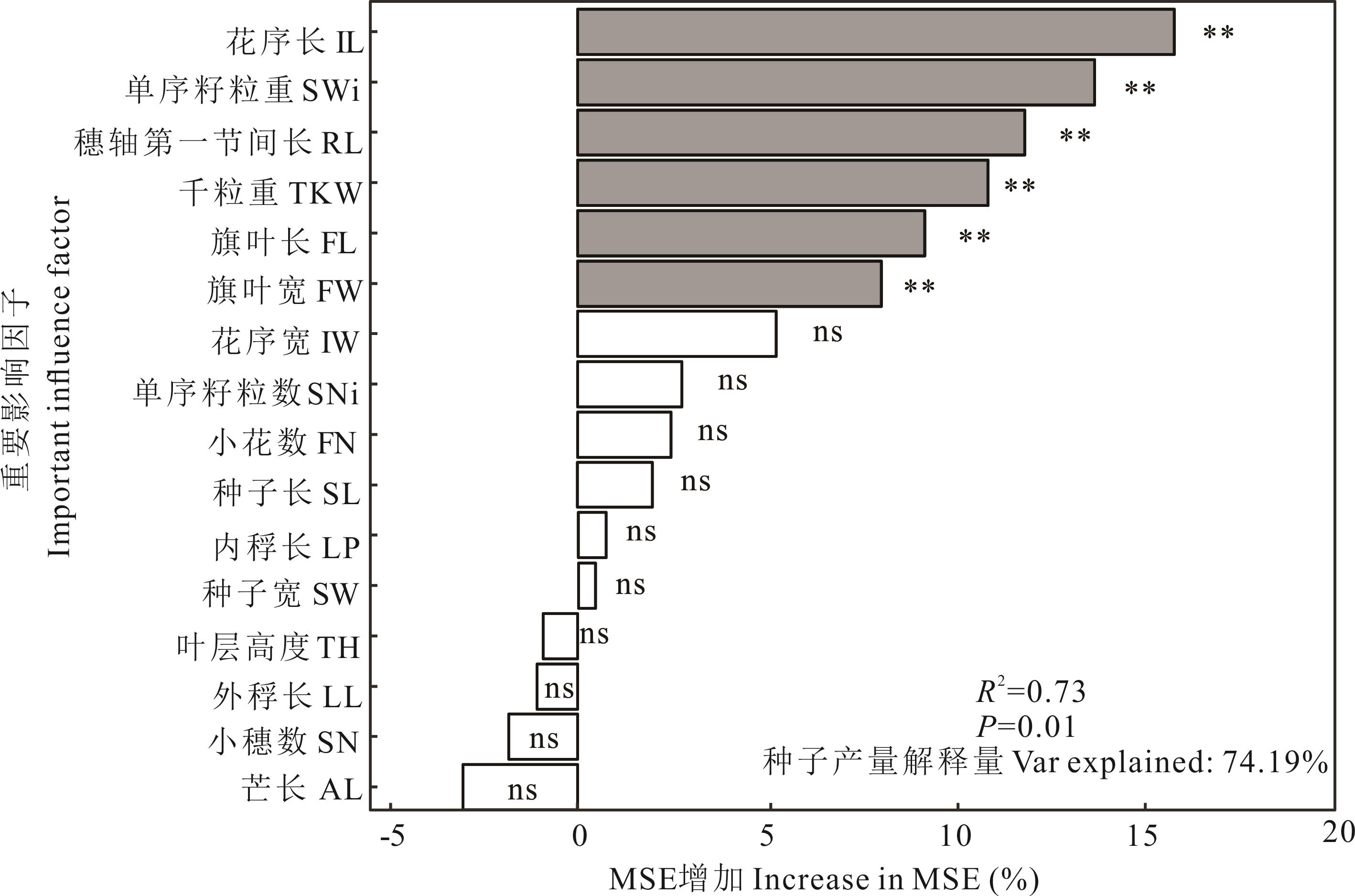
图1 重要影响因子随机森林模型**表示因素的影响达到极显著水平; ns表示因素无影响。** indicates that the effect of the factor reached an extremely significant level; ns indicates that the factor had no impact. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Random forest model of important influencing factors

图2 产量因子对种子产量影响的结构方程模型(a)及各因子的标准化效应值(b)SY: 种子产量Seed yield. 下同The same below. 图中实线箭头表示显著正的路径关系。数值为标准化路径系数。*表示在0.05水平差异显著,**表示在0.01水平差异显著。Solid arrows represent significantly positive effects at the 0.05 level. The significant standard path coefficients were shown on arrows. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01.
Fig.2 Structural equation model diagram of the effect of yield factor on seed yield (a) and the standardized effect values of each factor (b)
项目 Item | 性状 Traits | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
叶部性状 Leaf traits | 叶层高度TH | -0.105 | -0.065 | 0.204 |
| 旗叶长FL | 0.401* | 0.384* | -0.454* | |
| 旗叶宽FW | 0.170 | 0.278* | -0.474* | |
穗部性状 Spike traits | 花序长IL | 0.450* | 0.551** | -0.710** |
| 花序宽IW | 0.063 | 0.117 | -0.113 | |
| 穗轴第一节间长RL | 0.455* | 0.555** | -0.578** | |
| 小穗数SN | -0.420* | -0.294* | 0.093 | |
| 小花数FN | 0.482* | 0.404* | -0.083 | |
| 单序籽粒数SNi | 0.021 | 0.127 | -0.220 | |
| 单序籽粒重SWi | 0.393* | 0.441* | -0.470* | |
籽粒性状 Grain traits | 内稃长LP | 0.129 | 0.039 | 0.124 |
| 外稃长LL | -0.065 | -0.185 | 0.463* | |
| 芒长AL | -0.143 | -0.239* | 0.451* | |
| 种子长SL | 0.182 | 0.179 | 0.026 | |
| 种子宽SW | 0.124 | 0.152 | -0.304* | |
| 千粒重TKW | 0.108 | -0.066 | -0.004 | |
生产性能 Production performance | 种子产量SY | 0.370* | 0.380* | -0.581** |
表4 表型性状和地理因子的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of phenotypic traits and geographic factors
项目 Item | 性状 Traits | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
叶部性状 Leaf traits | 叶层高度TH | -0.105 | -0.065 | 0.204 |
| 旗叶长FL | 0.401* | 0.384* | -0.454* | |
| 旗叶宽FW | 0.170 | 0.278* | -0.474* | |
穗部性状 Spike traits | 花序长IL | 0.450* | 0.551** | -0.710** |
| 花序宽IW | 0.063 | 0.117 | -0.113 | |
| 穗轴第一节间长RL | 0.455* | 0.555** | -0.578** | |
| 小穗数SN | -0.420* | -0.294* | 0.093 | |
| 小花数FN | 0.482* | 0.404* | -0.083 | |
| 单序籽粒数SNi | 0.021 | 0.127 | -0.220 | |
| 单序籽粒重SWi | 0.393* | 0.441* | -0.470* | |
籽粒性状 Grain traits | 内稃长LP | 0.129 | 0.039 | 0.124 |
| 外稃长LL | -0.065 | -0.185 | 0.463* | |
| 芒长AL | -0.143 | -0.239* | 0.451* | |
| 种子长SL | 0.182 | 0.179 | 0.026 | |
| 种子宽SW | 0.124 | 0.152 | -0.304* | |
| 千粒重TKW | 0.108 | -0.066 | -0.004 | |
生产性能 Production performance | 种子产量SY | 0.370* | 0.380* | -0.581** |

图4 受海拔影响的表型性状箱线图不同差异字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.4 Box line diagram of phenotypic traits affected by altitude
项目 Item | 性状 Trait | I类Cluster I | II类Cluster II | III类Cluster III | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
平均值 Mean | 变异系数 CV (%) | 平均值 Mean | 变异系数 CV (%) | 平均值 Mean | 变异系数 CV (%) | ||
叶部性状 Leaf traits | 叶层高度TH (cm) | 13.813 | 24.640 | 13.389 | 16.769 | 16.333 | 20.203 |
| 旗叶长FL (cm) | 9.398 | 19.263 | 8.280 | 14.991 | 7.175 | 3.449 | |
| 旗叶宽FW (cm) | 0.690 | 15.326 | 0.608 | 11.341 | 0.601 | 5.552 | |
穗部性状 Spike traits | 花序长IL (cm) | 18.311 | 12.939 | 14.046 | 6.582 | 16.113 | 13.056 |
| 花序宽IW (cm) | 1.694 | 33.063 | 1.555 | 7.200 | 1.833 | 3.428 | |
| 穗轴第一节间长RL (cm) | 2.322 | 30.310 | 1.585 | 17.806 | 1.578 | 21.049 | |
| 小穗数SN (No.) | 35.397 | 11.042 | 37.044 | 20.558 | 35.869 | 32.715 | |
| 小花数FN (No.) | 3.569 | 11.343 | 3.556 | 12.461 | 3.417 | 3.449 | |
| 单序籽粒数SNi (No.) | 97.735 | 9.944 | 92.500 | 12.099 | 85.300 | 7.129 | |
| 单序籽粒重SWi (g) | 0.650 | 21.924 | 0.487 | 16.227 | 0.519 | 35.781 | |
籽粒性状 Grain traits | 内稃长LP (mm) | 9.201 | 7.930 | 9.213 | 6.286 | 9.255 | 6.927 |
| 外稃长LL (mm) | 9.649 | 7.112 | 9.920 | 5.971 | 10.321 | 1.110 | |
| 芒长AL (mm) | 13.622 | 20.581 | 14.639 | 16.550 | 15.586 | 4.734 | |
| 种子长SL (mm) | 6.995 | 6.767 | 6.904 | 4.047 | 7.033 | 0.251 | |
| 种子宽SW (mm) | 0.839 | 15.154 | 0.827 | 5.193 | 0.753 | 12.515 | |
| 千粒重TKW (g) | 4.067 | 9.800 | 4.253 | 9.341 | 4.033 | 5.844 | |
| 生产性能Production performance | 种子产量SY (g) | 20.064 | 31.176 | 11.251 | 25.691 | 13.417 | 23.014 |
表5 不同类群表型性状的平均值和变异系数
Table 5 The mean and coefficient of variation (CV) of phenotypic character in different groups
项目 Item | 性状 Trait | I类Cluster I | II类Cluster II | III类Cluster III | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
平均值 Mean | 变异系数 CV (%) | 平均值 Mean | 变异系数 CV (%) | 平均值 Mean | 变异系数 CV (%) | ||
叶部性状 Leaf traits | 叶层高度TH (cm) | 13.813 | 24.640 | 13.389 | 16.769 | 16.333 | 20.203 |
| 旗叶长FL (cm) | 9.398 | 19.263 | 8.280 | 14.991 | 7.175 | 3.449 | |
| 旗叶宽FW (cm) | 0.690 | 15.326 | 0.608 | 11.341 | 0.601 | 5.552 | |
穗部性状 Spike traits | 花序长IL (cm) | 18.311 | 12.939 | 14.046 | 6.582 | 16.113 | 13.056 |
| 花序宽IW (cm) | 1.694 | 33.063 | 1.555 | 7.200 | 1.833 | 3.428 | |
| 穗轴第一节间长RL (cm) | 2.322 | 30.310 | 1.585 | 17.806 | 1.578 | 21.049 | |
| 小穗数SN (No.) | 35.397 | 11.042 | 37.044 | 20.558 | 35.869 | 32.715 | |
| 小花数FN (No.) | 3.569 | 11.343 | 3.556 | 12.461 | 3.417 | 3.449 | |
| 单序籽粒数SNi (No.) | 97.735 | 9.944 | 92.500 | 12.099 | 85.300 | 7.129 | |
| 单序籽粒重SWi (g) | 0.650 | 21.924 | 0.487 | 16.227 | 0.519 | 35.781 | |
籽粒性状 Grain traits | 内稃长LP (mm) | 9.201 | 7.930 | 9.213 | 6.286 | 9.255 | 6.927 |
| 外稃长LL (mm) | 9.649 | 7.112 | 9.920 | 5.971 | 10.321 | 1.110 | |
| 芒长AL (mm) | 13.622 | 20.581 | 14.639 | 16.550 | 15.586 | 4.734 | |
| 种子长SL (mm) | 6.995 | 6.767 | 6.904 | 4.047 | 7.033 | 0.251 | |
| 种子宽SW (mm) | 0.839 | 15.154 | 0.827 | 5.193 | 0.753 | 12.515 | |
| 千粒重TKW (g) | 4.067 | 9.800 | 4.253 | 9.341 | 4.033 | 5.844 | |
| 生产性能Production performance | 种子产量SY (g) | 20.064 | 31.176 | 11.251 | 25.691 | 13.417 | 23.014 |
| 1 | Zhang M Q, Wang Y R, Zhang J Y, et al. A study on genetic diversity of reproductive characters in Elymus nutans germplasm resources. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(3): 182-191. |
| 张妙青, 王彦荣, 张吉宇, 等. 垂穗披碱草种质资源繁殖相关特性遗传多样性研究. 草业学报, 2011, 20(3): 182-191. | |
| 2 | Zheng J H, Chen S Y, Chen Z H, et al.Assessment of genetic diversity of Elymus nutans in northwest plateau of Sichuan Province using ISSR markers. Journal of Southwest University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 40(3): 330-335. |
| 郑经红, 陈仕勇, 陈智华, 等. 川西北高原野生垂穗披碱草遗传多样性的ISSR分析. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 40(3): 330-335. | |
| 3 | Chen X, Jiao T, Mu R, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Elymus nutans in alpine artificial grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(8): 1964-1971. |
| 陈鑫, 焦婷, 牧仁, 等. 氮添加对高寒人工草地垂穗披碱草(Elymus nutans)生长及光合特性的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(8): 1964-1971. | |
| 4 | Song J C, Yu X J, Wei K T, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on production performance and nutritional quality of Elymus nutans in alpine region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(7): 1555-1564. |
| 宋建超, 鱼小军, 魏孔涛, 等. 施氮对高寒区垂穗披碱草饲草生产性能及营养品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(7): 1555-1564. | |
| 5 | Deng Z J, Miao J M, Zhang X Q, et al. Study on genetic diversity of Elymus nutans Griseb. in northwest plateau of Sichuan Province. Prataculture & Animal Husbandry, 2010(12): 17-21. |
| 邓竹佳, 苗佳敏, 张新全, 等. 川西北高原野生垂穗披碱草RAPD变异研究. 草业与畜牧, 2010(12): 17-21. | |
| 6 | Luo W R, Li W H, Ganjurjav H, et al. Effects of nitrogen on leaf functional traits and population characteristics of the artificial grassland Elymus nutans in Northern Tibet. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 51-60. |
| 罗文蓉, 栗文瀚, 干珠扎布, 等. 施氮对藏北垂穗披碱草人工草地叶片功能性状和种群特征的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 51-60. | |
| 7 | Zhang J, Wang P, Wang P, et al. The comparison in drought resistance of 15 germplasms resource of Elymus nutans at seedling stage. Grassland and Turf, 2020, 40(2): 1-8. |
| 张静, 王沛, 王平, 等. 15份垂穗披碱草种质资源苗期抗旱性比较. 草原与草坪, 2020, 40(2): 1-8. | |
| 8 | Zhou J, Sun K, Zhou Z Y, et al. Evaluation of drought tolerance of three Elymus nutans in Tibet. Crops, 2021(5): 205-210. |
| 周晶, 孙侃, 周忠义, 等. 西藏3份垂穗披碱草耐旱性评价. 作物杂志, 2021(5): 205-210. | |
| 9 | Zhang R Z, Zhang X Y, Liu D K. Breeding of new variety of Elymus sibiricus cv. Kangba. Prataculture & Animal Husbandry, 2012(2): 8-12. |
| 张瑞珍, 张新跃, 刘登锴. 康巴垂穗披碱草品种选育研究. 草业与畜牧, 2012(2): 8-12. | |
| 10 | Roland P, Uli S. Plant phenotyping: Past, present, and future. Plant Phenomics, 2019, 5(26): 1-6. |
| 11 | Liu X. Stages in the history of crop cultivation and the formation and development of traditional agriculture in China. Leisure Agriculture and the Beautiful Countryside, 2014(6): 76-93. |
| 刘旭. 中国作物栽培历史的阶段划分和传统农业形成与发展. 休闲农业与美丽乡村, 2014(6): 76-93. | |
| 12 | Lozada D N, Carter A H. Insights into the genetic architecture of phenotypic stability traits in winter wheat. Agronomy, 2020, 10(3): 368-373. |
| 13 | Laitinen R A E, Nikoloski Z. Genetic basis of plasticity in plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(3): 739-745. |
| 14 | Zhao Y Q, Zhang J C, Zhang Z Y, et al. Elymus nutans genes for seed shattering and candidate gene-derived EST-SSR markers for germplasm evaluation. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 1-15. |
| 15 | Li J, Tian H Q, Ji W Q, et al. Inflorescence trait diversity and genotypic differentiation as influenced by the environment in Elymus nutans Griseb. from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agronomy, 2023, 13(4): 1004-1019. |
| 16 | Chen S Y, Zhang X Q, Ma X, et al. Assessment of genetic diversity and differentiation of Elymus nutans indigenous to Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using simple sequence repeats markers. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2013, 93(6): 1089-1096. |
| 17 | Zhang J B, Bai S Q, Zhang X Q, et al. Karyotypes of 12 Elymus nutans L. in the northwestern plateau of Sichuan Province. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2008, 28(5): 946-955. |
| 张建波, 白史且, 张新全, 等. 川西北高原12个垂穗披碱草居群的核型研究. 西北植物学报, 2008, 28(5): 946-955. | |
| 18 | Zhang J B. Genetic diversity of Elymus nutans in the northwestern plateau of Sichuan Province. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2007. |
| 张建波. 川西北高原野生垂穗披碱草遗传多样性研究. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2007. | |
| 19 | De Y, Liu X L, Zhao L X. Phenotypic diversity of native populations of Elymus nutans. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2013, 35(5): 62-68. |
| 德英, 刘新亮, 赵来喜. 垂穗披碱草表型多样性研究. 中国草地学报, 2013, 35(5): 62-68. | |
| 20 | Qiu Y S, Zheng Y Y, Xie W G. Advances in genetics and breeding of Elymus nutans in China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(2): 98-106. |
| 邱涌森, 郑玉莹, 谢文刚. 我国垂穗披碱草遗传育种研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(2): 98-106. | |
| 21 | Liu X L. Studies on genetic diversity of two species of Elymus germplasm resources. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2011. |
| 刘新亮. 两种披碱草属牧草种质资源遗传多样性研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2011. | |
| 22 | Zhang J B, Bai S Q, Zhang X Q, et al. Study on ear characters of Elymus nutans Griseb. in the northwestern plateau of Sichuan Province. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 46(5): 1505-1509. |
| 张建波, 白史且, 张新全, 等. 川西北高原不同野生垂穗披碱草种群穗部形态研究. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 46(5): 1505-1509. | |
| 23 | De Y, Mu H B, Liu X L, et al. Morphological diversity of plant ear among 8 wild Elymus spp. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(9): 1623-1631. |
| 德英, 穆怀彬, 刘新亮, 等. 披碱草属8种野生牧草居群穗部形态多样性. 草业科学, 2011, 28(9): 1623-1631. | |
| 24 | Chen S Y, Chen Z H, Zhou Q P, et al. Study on morphological diversity of Elymus nutans germplasm resources from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2016, 38(1): 27-33. |
| 陈仕勇, 陈智华, 周青平, 等. 青藏高原垂穗披碱草种质资源形态多样性分析. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(1): 27-33. | |
| 25 | Yang C R, Wei X X, Liang F X, et al. Phenotypic characteristics analysis of Elymus dahuricus from different altitudes in Northwestern Sichuan Plateau. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2020, 39(10): 14-20. |
| 杨财容, 魏小萱, 梁福轩, 等. 川西北高原不同海拔高度披碱草(Elymus dahuricus)的表型性状分析. 中国野生植物资源, 2020, 39(10): 14-20. | |
| 26 | Yuan Q H, Gu A L, Li X L. Description specifications and data standards for Elymus germplasm resources. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2010: 1-3. |
| 袁庆华, 谷安琳, 李向林. 披碱草属牧草种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010: 1-3. | |
| 27 | Hockett C F. The mathematical theory of communication. Jstor, 1953, 10(27): 69-93. |
| 28 | Zong X C, Shi S L. Genetic. Wuhan : Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2015: 142-161. |
| 宗宪春, 施树良. 遗传学. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2015: 142-161. | |
| 29 | He Z M. Modern genetics course. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2011: 291-298. |
| 贺竹梅. 现代遗传学教程. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2011: 291-298. | |
| 30 | Yin T T, Li L P, Meng Y, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of 22 Elymus spp. germplasm resources. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(7): 2409-2419. |
| 尹婷婷, 李莉萍, 孟岩, 等. 22份披碱草属种质资源的表型多样性分析. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(7): 2409-2419. | |
| 31 | Huang C Q, Liu G D, Bai C J, et al. A study on the morphological diversity of 475 accessions of Cynodon dactylon. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(4): 33-42. |
| 黄春琼, 刘国道, 白昌军, 等. 475份狗牙根种质资源形态多样性的研究. 草业学报, 2012, 21(4): 33-42. | |
| 32 | Bacilieri R, Ducousso A, Kremer A, et al. Genetic, morphological, ecological and phenological differentiation between Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. and Quercus robur L. in a mixed stand of northwest of France. Silvae Genetica, 1995, 44(1): 1-9. |
| 33 | Dudley J W, Moll R H. Interpretation and use of estimates of heritability and genetic variances in plant breeding. Crop Science, 1969, 9(3): 257-262. |
| 34 | Qi J, Cao W X, Yan W H. Phenotypic diversity and environment relations of wild Elymus populations. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(5): 1027-1033. |
| 祁娟, 曹文侠, 闫伟红. 披碱草属野生居群表型多样性及其与环境关系研究. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(5): 1027-1033. | |
| 35 | He B, Liu Y, Ma Y S. Effects of plant growth regulators on seed yield and yield components of Deschampsia cespitosa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(5): 1588-1598. |
| 何斌, 刘颖, 马玉寿. 植物生长调节剂对发草种子产量及产量构成因素的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(5): 1588-1598. | |
| 36 | Wang Q, Wang X C, Li X Y, et al. Effect of “3414” fertilization on seed yield and quality of Bromus inermis in arid area of Ningxia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(12): 3470-3480. |
| 王琴, 王旭成, 李小云, 等. “3414”施肥效应对宁夏干旱区无芒雀麦种子产量和质量的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(12): 3470-3480. | |
| 37 | Min X X, Ma Y S, Li S X. Effects of fertilization on seed yield and reproductive components of Poa pratensis L.‘Qinghai’. Xiandai Horticulture, 2017(3): 3-5. |
| 闵星星, 马玉寿, 李世雄. 施肥对青海草地早熟禾种子产量和生殖构件的影响. 现代园艺, 2017(3): 3-5. | |
| 38 | Ha X, Zhang J Q, Bai F X, et al. Analysis of traits related to seed yield and nutrient utilization in the Kentucky bluegrass germplasm in Gansu. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 54-67. |
| 哈雪, 张金青, 白方旭, 等. 甘肃野生草地早熟禾种质种子产量相关性状分析及其对矿质元素利用效应评价. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 54-67. | |
| 39 | Zhao W. Studies on seed yield components and seed production performance of five Gramineous plants. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2003. |
| 赵威. 5种禾本科牧草种子产量构成因子和种子生产性能的研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2003. | |
| 40 | Wu H J, Ma L X, Geng X L, et al. Effects of different sowing rates and row spacing on forage yield, seed yield and agronomic traits of “Xiayan No. 1”. China Herbivore Science, 2023, 43(2): 23-27, 36. |
| 武慧娟, 马隆喜, 耿小丽, 等. 不同播量和行距对“夏燕1号”牧草产量、种子产量及农艺性状的影响. 中国草食动物科学, 2023, 43(2): 23-27, 36. | |
| 41 | Wang X C, Wang Q, Song W X, et al. Correlation between agronomic traits and yield formation of 21 Elymus dahuricus. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(5): 1-11. |
| 王旭成, 王琴, 宋文学, 等. 21份披碱草农艺性状与产量形成的相关性分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(5): 1-11. | |
| 42 | Bourne E C, Bocedi G, Travis J M J, et al. Between migration load and evolutionary rescue: dispersal, adaptation and the response of spatially structured populations to environmental change. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2014, 281(1778): 1832-1842. |
| 43 | Zhang J, Wang L N, Cao L, et al. Fermentation properties of ensiled Elymus nutans from different altitude regions on the Tibetan Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(7): 1550-1556. |
| 张娟, 王丽娜, 曹蕾, 等. 青藏高原不同海拔区垂穗披碱草的发酵性能. 草业科学, 2017, 34(7): 1550-1556. | |
| 44 | Wei W, Zhou J J, Baimagaweng, et al. Effects of different altitudes gradient on seed size and germination characteristics of 3 grasses species from Tibet Plateau. Seed, 2018, 37(2): 29-33. |
| 魏巍, 周娟娟, 白玛嘎翁, 等. 海拔梯度对西藏高原3种禾本科牧草种子大小和萌发特性的影响. 种子, 2018, 37(2): 29-33. | |
| 45 | Chen S Y, Ma X, Zhang X Q, et al. Genetic variation and geographical divergence in Elymus nutans Griseb.(Poaceae: Triticeae) from West China. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 2009, 37(6): 716-722. |
| 46 | Qi J, Liu W H, Jiao T, et al. Variation in morphological and physiological characteristics of wild Elymus nutans ecotypes from different altitudes in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Sensors, 2020, DOI: 10.1155/2020/2869030. |
| 47 | Chen Z, Guan Y Z, Liang X P, et al. Effects of altitude on the morphological traits of Elymus species. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(5): 897-904. |
| 陈钊, 管永卓, 梁新平, 等. 海拔高度对披碱草属植物形态特征的可塑性. 草地学报, 2015, 23(5): 897-904. | |
| 48 | Bai X L, Liu Y C, Sheng G L, et al. Assessment of genetic diversity of 35 hulled oat accessions using SSR and SRAP makers. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 43(4): 6-11. |
| 白晓雷, 刘艳春, 生国利, 等. 35份皮燕麦种质遗传多样性的SSR和SRAP分析. 内蒙古农业科技, 2015, 43(4): 6-11. | |
| 49 | Yin T T, Gu L L, Yan F, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of 59 Elymus sibiricus germplasm resources. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(11): 2307-2317. |
| 尹婷婷, 谷丽丽, 闫锋, 等. 59份老芒麦种质资源的表型多样性分析. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(11): 2307-2317. | |
| 50 | Liu T N, Wang Y R, Hu X W. Seed yield and seed yield components of Elymus nutans from different elevations. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(3): 468-473. |
| 刘婷娜, 王彦荣, 胡小文. 不同海拔垂穗披碱草种子产量及其构成因素. 草业科学, 2014, 31(3): 468-473. | |
| 51 | Lu X W, Liu B, Tao X Y, et al. Genetic diversity and genetic structure in populations of sympatric Elymus nutans and E. dahuricus. Guihaia, 2021, 41(3): 418-428. |
| 路兴旺, 刘博, 陶小燕, 等. 同域分布垂穗披碱草和达乌力披碱草遗传多样性和遗传结构分析. 广西植物, 2021, 41(3): 418-428. |
| [1] | 慕平, 柴继宽, 苏玮娟, 章海龙, 赵桂琴. 燕麦不同组合正、反交杂种后代的表型及遗传参数分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 73-86. |
| [2] | 何伟鹏, 胡夏嵩, 刘昌义, 李璇, 李希来, 付江涛, 卢海静, 杨馥铖, 李国荣. 黄河源区不同禁牧年限对垂穗披碱草单根及其根-土复合体力学强度特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 106-117. |
| [3] | 李庭伦, 李一亨, 余慧, 江再莉, 唐立涛, 王长庭, 胡雷. 铅卤钙钛矿泄漏对垂穗披碱草幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 160-170. |
| [4] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. |
| [5] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生垂穗披碱草成苗期间的耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 76-85. |
| [6] | 杨晶, 刘文辉, 梁国玲, 贾志锋, 刘凯强, 张燕, 吴瑞, 杨钰洁. 高寒地区不同燕麦品系抗倒伏相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 50-60. |
| [7] | 梁国玲, 张永超, 贾志锋, 马祥, 刘文辉. 高寒区不同燕麦品种(系)表型性状和茎秆力学特征与抗倒伏性的关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 58-69. |
| [8] | 梁坤伦, 贾存智, 孙金豪, 王明艳, 傅华, 毛祝新. 高寒地区垂穗披碱草种质对低温胁迫的生理响应及其耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 111-121. |
| [9] | 若扎·扎尔汗, 李倩, 王玉祥, 张博. 海拔与黄花苜蓿表型性状的相关性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 79-85. |
| [10] | 蔺永和, 吴景, 方江平, 张卫红, 苗彦军, 李勇胜. 铝胁迫对西藏野生垂穗披碱草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 155-165. |
| [11] | 罗文蓉, 栗文瀚, 干珠扎布, 闫玉龙, 李钰, 曹旭娟, 何世丞, 旦久罗布, 高清竹, 胡国铮. 施氮对藏北垂穗披碱草人工草地叶片功能性状和种群特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 51-60. |
| [12] | 徐雅梅, 王传旗, 武俊喜, 张文静, 王小川, 赤列催珍, 徐德飞, 包赛很那, 苗彦军. Mn2+、Pb2+对野生垂穗披碱草种子萌发与幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 194-200. |
| [13] | 周媛媛,周向睿,周志宇,金茜,李金辉,宋鑫. 不同株龄蒙古岩黄芪表型性状的变异特征[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 134-141. |
| [14] | 刘英,白龙,雷家军. 辽宁省野古草野生居群表型性状多样性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(12): 164-179. |
| [15] | 梁小玉,张新全,白史且,季杨,黄琳凯,周凯. 菊苣主要表型性状的多元统计分析[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(6): 257-267. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||