

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 17-28.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024088
王文虎1,2,3( ), 王世林3, 梁国玲1,2, 李文1,2,3(
), 王世林3, 梁国玲1,2, 李文1,2,3( ), 曹文侠3(
), 曹文侠3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-19
修回日期:2024-04-17
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
李文,曹文侠
作者简介:caowx@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Wen-hu WANG1,2,3( ), Shi-lin WANG3, Guo-ling LIANG1,2, Wen LI1,2,3(
), Shi-lin WANG3, Guo-ling LIANG1,2, Wen LI1,2,3( ), Wen-xia CAO3(
), Wen-xia CAO3( )
)
Received:2024-03-19
Revised:2024-04-17
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Wen LI,Wen-xia CAO
摘要:
明晰坡向和坡位对祁连山高寒灌丛植物群落多样性的影响过程及其路径系数,能够为祁连山地区高寒灌丛系统进行精准分区利用管理提供科学依据。本研究以祁连山地区山体不同坡向和坡位高寒灌丛为对象,对阴坡、半阴坡和半阳坡高寒灌丛植物群落组成与结构、光照强度和土壤理化特征进行了系统研究,并采用分段式结构方程模型解析坡向和坡位对高寒灌丛植物群落多样性的影响过程及其路径系数。结果表明:草本和灌木的高度、盖度及地上、地下生物量均在下坡位最高(P<0.05)。β多样性在阴坡最高、半阳坡最低(P<0.05)。草本、灌木和群落Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、丰富度指数、Pielou均匀度指数均随坡位的上升而呈降低趋势。光照强度和土壤物理化学性质均在下坡位显著高于上坡位。分段式结构方程模型分析表明,坡向和坡位主要通过影响光照强度和土壤有机质含量影响草本植物群落的多样性,而坡向和坡位主要通过影响光照强度、土壤含水量和土壤速效氮含量影响灌木植物群落的多样性。在山地小尺度地形条件下,坡向和坡位主要通过影响光照、水分、土壤有机质含量、土壤速效氮含量等因子进而影响植物群落多样性分布格局。因此,对山地高寒灌丛系统进行精准分区利用管理及退化草地生态恢复时,应考虑小尺度地形条件下坡向和坡位变化引起的植物群落微生境条件及植被分布格局异质性差异。
王文虎, 王世林, 梁国玲, 李文, 曹文侠. 坡向和坡位对祁连山高寒灌丛植物群落多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 17-28.
Wen-hu WANG, Shi-lin WANG, Guo-ling LIANG, Wen LI, Wen-xia CAO. Effects of slope categories of differing aspect and position on plant community diversity in alpine shrubland in the Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(1): 17-28.
坡向 Aspect | 坡位 Position | 优势种 Dominant species | 草本高度 Herb height (cm) | 草本盖度 Herb coverage (%) | 灌木高度 Shrub height (cm) | 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage (%) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | 地下生物量 Underground biomass (g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
阴坡 Shady slope | 上Upper | 头花杜鹃R. capitatum, 黑褐穗苔草C. atrofusca, 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 4.54±0.48b | 69.50±3.52c | 58.97±1.41c | 71.00±3.48b | 183.35±8.00c | 1442.47±30.13b |
| 中Middle | 绣线菊Spiraea salicifolia, 千里香杜鹃R. thymifolium, 黑褐穗苔草C. atrofusca | 6.95±0.48b | 89.00±1.58b | 74.68±3.25b | 83.75±0.85a | 223.75±9.01b | 1750.79±85.99b | |
| 下Lower | 金露梅P. fruticosa, 川滇柳S. rehderiana, 珠芽蓼P. viviparum | 9.52±0.16a | 98.25±1.18a | 108.61±2.21a | 91.75±2.28a | 435.98±12.40a | 2311.91±229.15a | |
半阴坡 Semi-shady slope | 上Upper | 火绒草L. leontopodioides, 狭叶锦鸡儿C. stenophylla, 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 1.55±0.13b | 54.50±4.25b | 58.19±4.93b | 68.75±2.83c | 138.77±10.95c | 1304.54±21.98c |
| 中Middle | 银露梅P. fruticosa, 狭叶锦鸡儿C. stenophylla, 火绒草L. leontopodioides | 2.83±0.18b | 68.25±1.93a | 81.02±5.55a | 76.50±1.50b | 211.40±8.77b | 1482.08±11.53b | |
| 下Lower | 沙棘H. rhamnoides, 鲜黄小檗Berberis diaphana, 蕨麻Potentilla anserina | 8.15±0.66a | 74.50±0.50a | 87.77±4.31a | 92.75±1.11a | 339.19±13.03a | 1710.59±64.47a | |
半阳坡 Semi-sunny slope | 上Upper | 鬼箭锦鸡儿C. jubata, 矮生嵩草K. humilis, 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila | 4.01±0.29b | 65.25±3.77c | 68.23±4.31b | 74.25±0.85b | 143.99±3.89c | 1862.74±14.35b |
| 中Middle | 头花杜鹃R. capitatum, 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila, 鬼箭锦鸡儿C. jubata | 6.96±0.41a | 76.25±1.31b | 80.38±1.06a | 80.00±1.47a | 171.40±2.45b | 2051.56±10.98ab | |
| 下Lower | 山生柳S. oritrepha, 珠芽蓼P. viviparum, 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 8.17±0.39a | 87.00±2.38a | 85.27±2.28a | 83.00±1.15a | 192.34±6.33a | 2228.70±97.08a |
表1 不同坡向和坡位植物群落特征
Table 1 Characteristics of plant communities in different slope aspects and positions
坡向 Aspect | 坡位 Position | 优势种 Dominant species | 草本高度 Herb height (cm) | 草本盖度 Herb coverage (%) | 灌木高度 Shrub height (cm) | 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage (%) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | 地下生物量 Underground biomass (g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
阴坡 Shady slope | 上Upper | 头花杜鹃R. capitatum, 黑褐穗苔草C. atrofusca, 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 4.54±0.48b | 69.50±3.52c | 58.97±1.41c | 71.00±3.48b | 183.35±8.00c | 1442.47±30.13b |
| 中Middle | 绣线菊Spiraea salicifolia, 千里香杜鹃R. thymifolium, 黑褐穗苔草C. atrofusca | 6.95±0.48b | 89.00±1.58b | 74.68±3.25b | 83.75±0.85a | 223.75±9.01b | 1750.79±85.99b | |
| 下Lower | 金露梅P. fruticosa, 川滇柳S. rehderiana, 珠芽蓼P. viviparum | 9.52±0.16a | 98.25±1.18a | 108.61±2.21a | 91.75±2.28a | 435.98±12.40a | 2311.91±229.15a | |
半阴坡 Semi-shady slope | 上Upper | 火绒草L. leontopodioides, 狭叶锦鸡儿C. stenophylla, 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 1.55±0.13b | 54.50±4.25b | 58.19±4.93b | 68.75±2.83c | 138.77±10.95c | 1304.54±21.98c |
| 中Middle | 银露梅P. fruticosa, 狭叶锦鸡儿C. stenophylla, 火绒草L. leontopodioides | 2.83±0.18b | 68.25±1.93a | 81.02±5.55a | 76.50±1.50b | 211.40±8.77b | 1482.08±11.53b | |
| 下Lower | 沙棘H. rhamnoides, 鲜黄小檗Berberis diaphana, 蕨麻Potentilla anserina | 8.15±0.66a | 74.50±0.50a | 87.77±4.31a | 92.75±1.11a | 339.19±13.03a | 1710.59±64.47a | |
半阳坡 Semi-sunny slope | 上Upper | 鬼箭锦鸡儿C. jubata, 矮生嵩草K. humilis, 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila | 4.01±0.29b | 65.25±3.77c | 68.23±4.31b | 74.25±0.85b | 143.99±3.89c | 1862.74±14.35b |
| 中Middle | 头花杜鹃R. capitatum, 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila, 鬼箭锦鸡儿C. jubata | 6.96±0.41a | 76.25±1.31b | 80.38±1.06a | 80.00±1.47a | 171.40±2.45b | 2051.56±10.98ab | |
| 下Lower | 山生柳S. oritrepha, 珠芽蓼P. viviparum, 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 8.17±0.39a | 87.00±2.38a | 85.27±2.28a | 83.00±1.15a | 192.34±6.33a | 2228.70±97.08a |

图1 不同坡向、坡位植物群落α多样性上、中、下分别表示上坡位、中坡位和下坡位。*表示坡向间差异显著(P<0.05),ns表示坡向间无显著差异(P>0.05)。不同小写字母表示同一坡向不同坡位间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Upper, middle and lower indicate upper position, middle position, lower position, respectively. * indicates significant differences among different slope aspects (P<0.05), ns indicates no significant difference among different slope aspects. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the slope positions in the same slope aspect (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 α-diversity among different slope aspects and positions
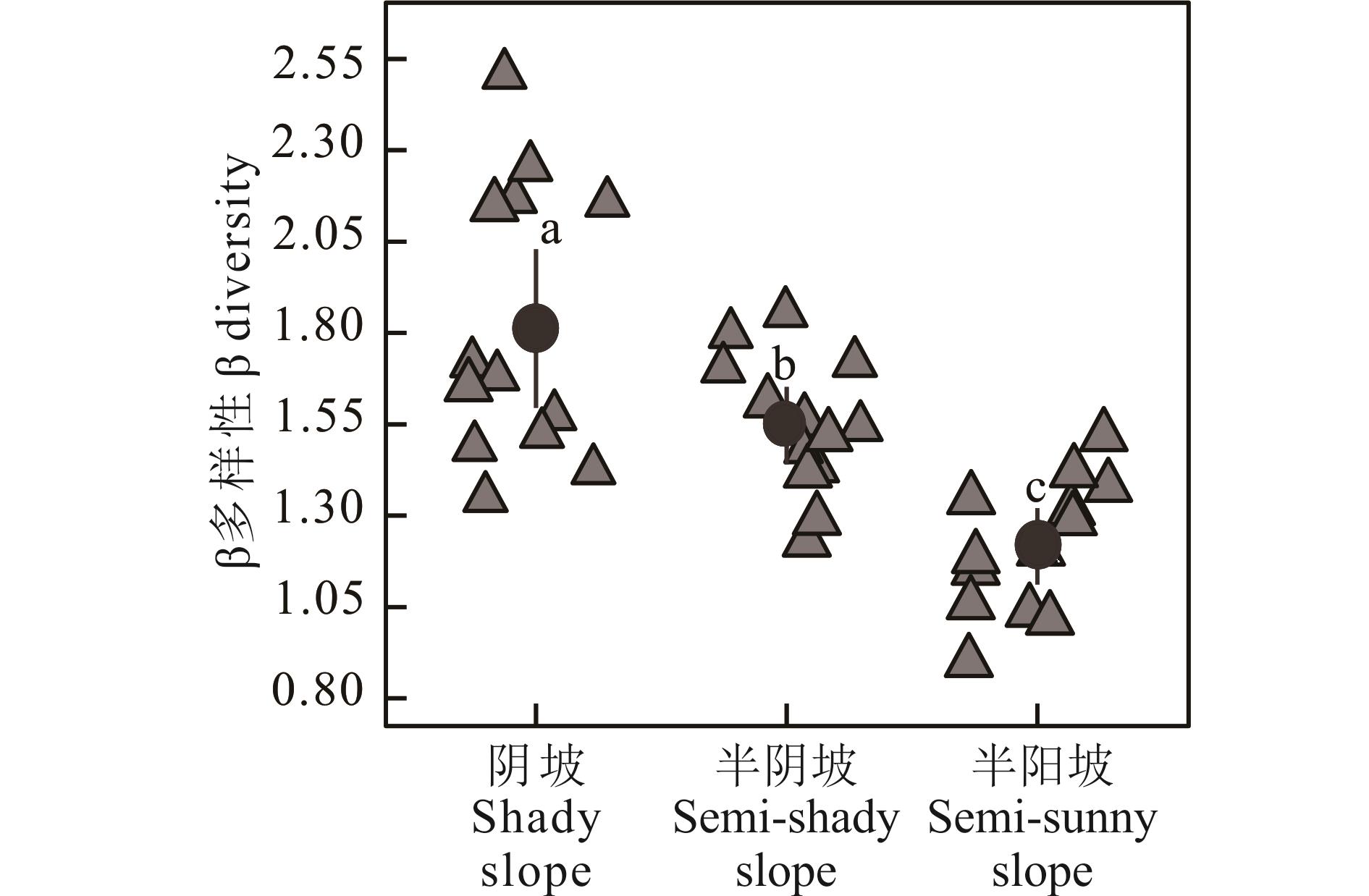
图2 不同坡向植物群落β多样性不同小写字母表示不同坡向间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the different slope aspects (P<0.05).
Fig.2 β-diversity of plant communities among different slope aspects

图5 植物群落多样性变量因子重要性排序SM: 土壤含水量Soil moisture content; LX: 光照强度Light intensity; TP: 全磷Total phosphorus; BD: 土壤容重Bulk density; SOM: 土壤有机质Soil organic matter; ST: 土壤温度Soil temperature; AN: 速效氮Available nitrogen; AP: 速效磷Available phosphorus; TN: 全氮Total nitrogen; AK: 速效钾Available potassium; TK: 全钾 Total potassium; MSE: 均方误差Mean square error. *: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P<0.001, ns: 无显著差异No significant difference. 下同The same below.
Fig.5 The importance ranking of variable factors in plant community diversity

图6 结构方程模型分析坡向和坡位对草本(A、B)和灌木(C、D)多样性的影响路径及各因子的标准化效应值图中实线和虚线箭头分别表示显著正和负的路径关系。数值为标准化路径系数。Solid and dashed arrows represent significantly positive or negative effects at the 0.05 level, respectively. The standard path coefficients were shown on arrows.
Fig.6 The structural equation model to analyze the effect of slope aspect and position on herb diversity (A, B) and shrub diversity (C, D) and standardized effects for each impact factor of herb and shrub diversity
| 1 | Ma J J, Li X B, Qi P, et al. Ecological security assessment of Qilian Mountain National Park of China. Mountain Research, 2022, 40(4): 504-515. |
| 马娟娟, 李晓兵, 齐鹏, 等. 祁连山国家公园生态安全评价. 山地学报, 2022, 40(4): 504-515. | |
| 2 | Duan H, Qi Y, Kang W, et al. Seasonal variation of vegetation and its spatiotemporal response to climatic factors in the Qilian Mountains, China. Sustainability, 2022, 14(9): 4926. |
| 3 | Wang J L, Li W, Cao W X, et al. Soil bacterial community responses to short term grazing exclusion in a degraded alpine shrubland-grassland ecotone. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 130: 108043. |
| 4 | Wang R, Peng Q, Zhang W, et al. Ecohydrological service characteristics of Qilian Mountain ecosystem in the next 30 years based on scenario simulation. Sustainability, 2022, 14(3): 1819. |
| 5 | Wang J L, Li W, Cao W X, et al. Effects of different intensities of long-term grazing on plant diversity, biomass and carbon stock in alpine shrubland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. PeerJ, 2022, 10: e12771. |
| 6 | Zhang F, Du H, Zeng F P, et al. Changes of woody community structure and diversity in karst peak-cluster depressions in Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(12): 4094-4104. |
| 张芳, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 等. 西南喀斯特峰丛洼地木本植物群落结构与多样性变化. 生态学报, 2020, 40(12): 4094-4104. | |
| 7 | Gao W Q, Lei X D, Liang M W, et al. Biodiversity increased both productivity and its spatial stability in temperate forests in northeastern China. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 780: 146674. |
| 8 | Xu Y D, Dong S K, Li S, et al. Research progress on ecological filtering mechanisms for plant community assembly. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(7): 2267-2281. |
| 许驭丹, 董世魁, 李帅, 等. 植物群落构建的生态过滤机制研究进展. 生态学报, 2019, 39(7): 2267-2281. | |
| 9 | Zhang R, Yu F Y, Zhou R H, et al. Effects of slope position and aspect on structure and species diversity of shrub community in the Jiajin Mountains, Sichuan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(8): 2507-2514. |
| 张荣, 余飞燕, 周润惠, 等. 坡向和坡位对四川夹金山灌丛群落结构与物种多样性特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(8): 2507-2514. | |
| 10 | Zhang Q, Sun X M, Yang J, et al. Effect of slope aspect on species functional groups and species diversity of alpine meadow of the east of Qilian Mountains. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(8): 1480-1490. |
| 张倩, 孙小妹, 杨晶, 等. 坡向对东祁连山高寒草甸群落物种功能群及其多样性的影响. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(8): 1480-1490. | |
| 11 | Xu C L. Variations in vegetation composition and nutrient characteristics related to aspect in an alpine meadow in the northeast margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(4): 26-35. |
| 徐长林. 坡向对青藏高原东北缘高寒草甸植被构成和养分特征的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 26-35. | |
| 12 | Zhu Y Y, Wang X A, Wang X, et al. Effect of slope aspect on the functional diversity of grass communities in the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(21): 6823-6833. |
| 朱云云, 王孝安, 王贤, 等. 坡向因子对黄土高原草地群落功能多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2016, 36(21): 6823-6833. | |
| 13 | Niu Y J, Zhou J W, Yang S W, et al. Quantitative apportionment of slope aspect and altitude to soil moisture and temperature and plant distribution on alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(5): 1489-1497. |
| 牛钰杰, 周建伟, 杨思维, 等. 坡向和海拔对高寒草甸山体土壤水热和植物分布格局的定量分解. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(5): 1489-1497. | |
| 14 | Zhang J T. Quantitative ecology. Beijing: Science Press, 2018. |
| 张金屯. 数量生态学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. | |
| 15 | Deng L, Han Q S, Zhang C, et al. Above-ground and below-ground ecosystem biomass accumulation and carbon sequestration with Caragana korshinskii Kom plantation development. Land Degradation & Development, 2017, 28(3): 4-16. |
| 16 | Bao S D. Agrochemical analysis of soil. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 17 | Ma K P, Huang J H, Yu S L, et al. Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China: Ⅱ. species richness, evenness and species diversities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1995, 15(3): 268-277. |
| 马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 等. 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究Ⅱ丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数. 生态学报, 1995, 15(3): 268-277. | |
| 18 | Xu Y J, Chen Y N, Li W H, et al. Distribution pattern and environmental interpretation of species diversity in the mountainous region of Ili River Valley, Xinjiang, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(10): 1142-1154. |
| 徐远杰, 陈亚宁, 李卫红, 等. 伊犁河谷山地植物群落物种多样性分布格局及环境解释. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(10): 1142-1154. | |
| 19 | Liang M, Liang C, Hautier Y, et al. Grazing-induced biodiversity loss impairs grassland ecosystem stability at multiple scales. Ecology Letters, 2021, 24(10): 2054-2064. |
| 20 | Wen P Y, Jin G Z. Effects of topography on species diversity in a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(3): 945-956. |
| 温佩颖, 金光泽. 地形对阔叶红松林物种多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(3): 945-956. | |
| 21 | Wang P C, Yu H, Xiao H L, et al. Effects of habitat factors on the plant diversity on naturally-restored wind farm slopes. PeerJ, 2023, 11: 14912. |
| 22 | Wang X Y, Zhou B R, Su S L, et al. Characteristics of carbon exchange in alpine meadow and desert of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its meteorological influence mechanism. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(3): 1194-1208. |
| 王秀英, 周秉荣, 苏淑兰, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸和荒漠碳交换特征及其气象影响机制. 生态学报, 2023, 43(3): 1194-1208. | |
| 23 | Bátori Z, Valkó O, Vojtkó A, et al. Environmental heterogeneity increases the conservation value of small natural features in karst landscapes. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 872: 162120. |
| 24 | Zhang Q P, Fang R Y, Deng C Y, et al. Slope aspect effects on plant community characteristics and soil properties of alpine meadows on Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 143: 109400. |
| 25 | Dong Y J, Wu N Q, Li F J, et al. Influence of monsoonal water-energy dynamics on terrestrial mollusk species-diversity gradients in northern China. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 676: 206-214. |
| 26 | Chen K Q, Pan Y F, Li Y Q, et al. Slope position-mediated soil environmental filtering drives plant community assembly processes in hilly shrublands of Guilin, China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 13: 1074191. |
| 27 | Lv Z L, Liu B, Chang F, et al. Relationship between plant functional diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality in Bayanbulak alpine meadow along an altitude gradient. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2023, 47(6): 822-832. |
| 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 等. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸植物功能多样性与生态系统多功能性关系沿海拔梯度的变化. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(6): 822-832. | |
| 28 | Li Q, Rong L, Wang M. Effects of topography on diversity and distribution patterns of plant species in karst mountain area. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(6): 27-34. |
| 李芹, 容丽, 王敏. 地形对喀斯特山地植物物种多样性及分布格局的影响. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(6): 27-34. | |
| 29 | Ma Y R, Guan Q Y, Sun Y F, et al. Three-dimensional dynamic characteristics of vegetation and its response to climatic factors in the Qilian Mountains. Catena, 2022, 208: 105694. |
| 30 | Du Y D, Yuan X Y, Feng Z Z. Effects of different nitrogen forms on photosynthetic characteristics and growth of poplar. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2023, 47(3): 348-360. |
| 杜英东, 袁相洋, 冯兆忠. 不同形态氮对杨树光合特性及生长的影响. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(3): 348-360. | |
| 31 | Zhu S K, Wang S, Zhang J T, et al. Microclimate characteristics of photovoltaic arrays and their effects on plant growth in a solar power station area. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(10): 3078-3087. |
| 朱少康, 王珊, 张军涛, 等. 光伏阵列的微气候特征及其对站区植物生长特性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(10): 3078-3087. | |
| 32 | Xie M Y, Feng X X, Ma H F, et al. Characteristics of soil enzyme activity and stoichiometric and its influencing factors in Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata forest in the Qinling Mountains. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(8): 885-894. |
| 解梦怡, 冯秀秀, 马寰菲, 等. 秦岭锐齿栎林土壤酶活性与化学计量比变化特征及其影响因素. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(8): 885-894. | |
| 33 | Liu J H, Xin Z B, Huang Y Z. Climate suitability assessment on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 816: 151653. |
| [1] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [2] | 刘增辉, 卢素锦, 王雨欣, 张春辉, 尹鑫. 三江源地区人工克隆植物群落生物多样性对初级生产力的影响及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 27-38. |
| [3] | 赵敏, 赵坤, 王赟博, 殷国梅, 刘思博, 闫宝龙, 孟卫军, 吕世杰, 韩国栋. 长期放牧干扰降低了短花针茅荒漠草原植物多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 39-49. |
| [4] | 雷石龙, 廖李容, 王杰, 张路, 叶振城, 刘国彬, 张超. 高寒草地植物多样性与Godron群落稳定性关系及其环境驱动因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 1-12. |
| [5] | 马文明, 刘超文, 周青平, 邓增卓玛, 唐思洪, 迪力亚尔·莫合塔尔null, 侯晨. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体生态化学计量学及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 57-68. |
| [6] | 徐鑫磊, 宋彦涛, 赵京东, 乌云娜. 施肥和刈割对呼伦贝尔草甸草原牧草品质的影响及其与植物多样性的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 1-10. |
| [7] | 侯帅君, 王迎新. 马鹿夏季放牧对祁连山草原群落多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 206-210. |
| [8] | 田梦, 孙宗玖, 李莹, 李培英, 谢开云. 蒿类荒漠草地土壤种子库特征及其萌发植物多样性对降水增加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 17-28. |
| [9] | 曹文侠, 李文. 千里香杜鹃根系生物量时空动态特征及其生态适应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(7): 52-61. |
| [10] | 徐长林. 坡向对青藏高原东北缘高寒草甸植被构成和养分特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 26-35. |
| [11] | 卢慧, 丛静, 刘晓, 王秀磊, 唐军, 李迪强, 张于光. 三江源区高寒草甸植物多样性的海拔分布格局[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 197-204. |
| [12] | 王兴,宋乃平,杨新国,杨明秀,肖绪培. 放牧扰动下草地植物多样性对土壤因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 27-36. |
| [13] | 张永超,牛得草,韩潼,陈鸿洋,傅华. 补播对高寒草甸生产力和植物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(2): 305-309. |
| [14] | 王国荣,陈秀蓉,张俊忠,韩玉竹,胡宜刚,杨成德,徐长林. 东祁连山高寒灌丛草地土壤微生物生理功能群的动态分布研究[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 31-38. |
| [15] | 郑华平,陈子萱, 牛俊义,高玉红. 补播禾草对玛曲高寒沙化草地植物多样性和生产力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(3): 28-33. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||