

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 107-117.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024068
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
邱亚娟1( ), 邵晓龄1, 陈莺宇1, 黄钰芳1,2,4(
), 邵晓龄1, 陈莺宇1, 黄钰芳1,2,4( ), 陈红刚1,2, 杨扶德1, 高素芳1,2, 袁菊丽3, 高健5
), 陈红刚1,2, 杨扶德1, 高素芳1,2, 袁菊丽3, 高健5
收稿日期:2024-03-04
修回日期:2024-04-25
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
黄钰芳
作者简介:E-mail: 1049395950@qq.com基金资助:
Ya-juan QIU1( ), Xiao-ling SHAO1, Ying-yu CHEN1, Yu-fang HUANG1,2,4(
), Xiao-ling SHAO1, Ying-yu CHEN1, Yu-fang HUANG1,2,4( ), Hong-gang CHEN1,2, Fu-de YANG1, Su-fang GAO1,2, Ju-li YUAN3, Jian GAO5
), Hong-gang CHEN1,2, Fu-de YANG1, Su-fang GAO1,2, Ju-li YUAN3, Jian GAO5
Received:2024-03-04
Revised:2024-04-25
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Yu-fang HUANG
摘要:
为探究纹党连作障碍效应及发生机制,以正茬(CK)和连作1年(CC1)、连作2年(CC2)及连作3年(CC3)土壤为试验对象,开展盆栽试验,动态研究连作对纹党生长、抗氧化酶系统及叶绿素的影响,并利用气相色谱-质谱联用技术(GC-MS)分析了不同连作年限土壤中自毒物质的种类及含量。结果显示,苗期、开花期、生长旺盛期及收获期各个生育时期内,连作对纹党的生长均存在抑制作用,且随连作年限的延长作用逐渐加强;同一连作年限,随着生育进程的推进,叶片中过氧化氢酶(CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性先增加后下降,过氧化物酶(POD)活性先下降后增加再下降,但在同一生长阶段,3种抗氧化酶活性均随连作年限增加逐年下降,而丙二醛(MDA)、脯氨酸(Pro)、可溶性糖含量和相对电导率均逐年增加;从CK、CC1、CC2和CC3中分别鉴定出5、17、13和4种化学物质,主要包括:邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯、邻苯二甲酸二丁酯、丙酸乙酯和油酸酰胺等物质,其中邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯在各种处理土壤中均存在,其相对含量均较高。连作可以通过破坏纹党植株中抗氧化酶系统,降低叶片叶绿素含量抑制纹党生长,产生连作障碍;连作条件下自毒作用是导致纹党发生连作障碍的主要原因之一。
邱亚娟, 邵晓龄, 陈莺宇, 黄钰芳, 陈红刚, 杨扶德, 高素芳, 袁菊丽, 高健. 连作对纹党生长、生理特性及自毒物质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 107-117.
Ya-juan QIU, Xiao-ling SHAO, Ying-yu CHEN, Yu-fang HUANG, Hong-gang CHEN, Fu-de YANG, Su-fang GAO, Ju-li YUAN, Jian GAO. Research on effects of continuous cropping on the growth, physiological characteristics and autotoxic substances of Codonopsis pilosula var. modesta[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(1): 107-117.
生育时期 Growth stages | 处理 Treatment | 根长 Root length (cm·plant-1) | 根直径 Root diameter (mm·plant-1) | 根鲜重 Root fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 根干重 Root dry weight (g·plant-1) | 藤长 Vine length (cm·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苗期 Seedling stage | CK | 24.96±0.238a | 1.18±0.067a | 2.7989±0.286a | 1.0653±0.285a | 52.98±0.748a |
| CC1 | 20.90±0.527b | 1.07±0.040a | 1.9657±0.112b | 0.4196±0.091b | 37.07±3.418b | |
| CC2 | 17.72±2.069c | 0.86±0.101b | 1.4378±0.081c | 0.3659±0.115b | 33.96±3.025b | |
| CC3 | 16.46±0.186c | 0.61±0.072c | 1.2526±0.160c | 0.3197±0.056b | 26.38±2.038c | |
开花期 Flowering stage | CK | 25.39±1.346a | 6.91±1.635a | 3.4110±0.145a | 1.4091±0.109a | 96.17±39.391a |
| CC1 | 21.47±0.751b | 4.55±0.142b | 3.1096±0.011b | 1.2741±0.005b | 83.18±8.506ab | |
| CC2 | 18.32±0.504c | 4.44±0.189b | 2.7827±0.238c | 1.1582±0.007c | 48.42±12.541ab | |
| CC3 | 16.84±0.298c | 3.79±0.617b | 2.4734±0.114d | 1.0183±0.013d | 44.76±19.578b | |
生长旺盛期 Growth peak stage | CK | 26.68±0.761a | 7.14±0.391a | 5.4969±0.071a | 3.6628±0.072a | 115.27±13.019a |
| CC1 | 22.90±0.070b | 5.24±0.399b | 4.7162±0.309b | 2.6613±0.070b | 96.37±1.683b | |
| CC2 | 19.87±0.503c | 5.11±0.578b | 4.4752±0.103b | 2.4587±0.085c | 94.43±0.646b | |
| CC3 | 17.50±0.351d | 4.21±0.207c | 4.4629±0.045b | 2.3155±0.116c | 85.88±0.921b | |
收获期 Harvest stage | CK | 27.39±0.221a | 7.21±0.709a | 6.5721±0.109a | 4.2388±0.017a | 64.07±15.907a |
| CC1 | 23.64±0.068b | 5.45±0.782b | 5.3405±0.065b | 3.6394±0.081b | 52.04±6.917ab | |
| CC2 | 22.09±0.785c | 5.15±0.163b | 5.0363±0.027c | 3.5178±0.099b | 42.01±7.289b | |
| CC3 | 19.94±0.125d | 4.43±0.339b | 4.6860±0.057d | 2.5348±0.024c | 39.84±3.914b |
表1 连作对纹党植株生长指标的影响
Table 1 Effects of continuous cropping on growth indexes of C. pilosula var. modesta
生育时期 Growth stages | 处理 Treatment | 根长 Root length (cm·plant-1) | 根直径 Root diameter (mm·plant-1) | 根鲜重 Root fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 根干重 Root dry weight (g·plant-1) | 藤长 Vine length (cm·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苗期 Seedling stage | CK | 24.96±0.238a | 1.18±0.067a | 2.7989±0.286a | 1.0653±0.285a | 52.98±0.748a |
| CC1 | 20.90±0.527b | 1.07±0.040a | 1.9657±0.112b | 0.4196±0.091b | 37.07±3.418b | |
| CC2 | 17.72±2.069c | 0.86±0.101b | 1.4378±0.081c | 0.3659±0.115b | 33.96±3.025b | |
| CC3 | 16.46±0.186c | 0.61±0.072c | 1.2526±0.160c | 0.3197±0.056b | 26.38±2.038c | |
开花期 Flowering stage | CK | 25.39±1.346a | 6.91±1.635a | 3.4110±0.145a | 1.4091±0.109a | 96.17±39.391a |
| CC1 | 21.47±0.751b | 4.55±0.142b | 3.1096±0.011b | 1.2741±0.005b | 83.18±8.506ab | |
| CC2 | 18.32±0.504c | 4.44±0.189b | 2.7827±0.238c | 1.1582±0.007c | 48.42±12.541ab | |
| CC3 | 16.84±0.298c | 3.79±0.617b | 2.4734±0.114d | 1.0183±0.013d | 44.76±19.578b | |
生长旺盛期 Growth peak stage | CK | 26.68±0.761a | 7.14±0.391a | 5.4969±0.071a | 3.6628±0.072a | 115.27±13.019a |
| CC1 | 22.90±0.070b | 5.24±0.399b | 4.7162±0.309b | 2.6613±0.070b | 96.37±1.683b | |
| CC2 | 19.87±0.503c | 5.11±0.578b | 4.4752±0.103b | 2.4587±0.085c | 94.43±0.646b | |
| CC3 | 17.50±0.351d | 4.21±0.207c | 4.4629±0.045b | 2.3155±0.116c | 85.88±0.921b | |
收获期 Harvest stage | CK | 27.39±0.221a | 7.21±0.709a | 6.5721±0.109a | 4.2388±0.017a | 64.07±15.907a |
| CC1 | 23.64±0.068b | 5.45±0.782b | 5.3405±0.065b | 3.6394±0.081b | 52.04±6.917ab | |
| CC2 | 22.09±0.785c | 5.15±0.163b | 5.0363±0.027c | 3.5178±0.099b | 42.01±7.289b | |
| CC3 | 19.94±0.125d | 4.43±0.339b | 4.6860±0.057d | 2.5348±0.024c | 39.84±3.914b |
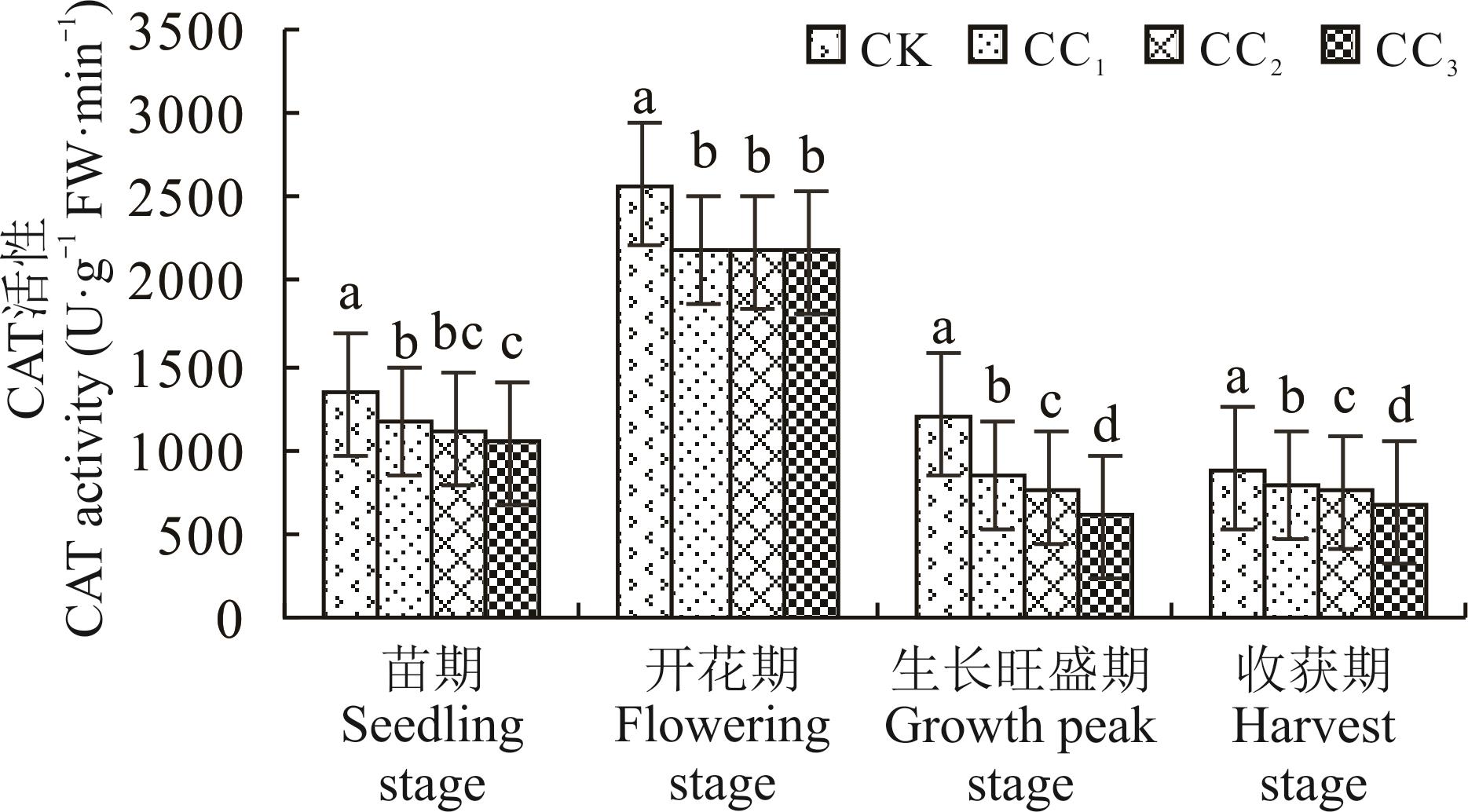
图1 连作对纹党不同生育时期叶片CAT活性的影响不同小写字母表示同一生育时期不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments in the same growth stage (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Effects of continuous cropping on CAT activity in leaves at different growth stages of C. pilosula var. modesta
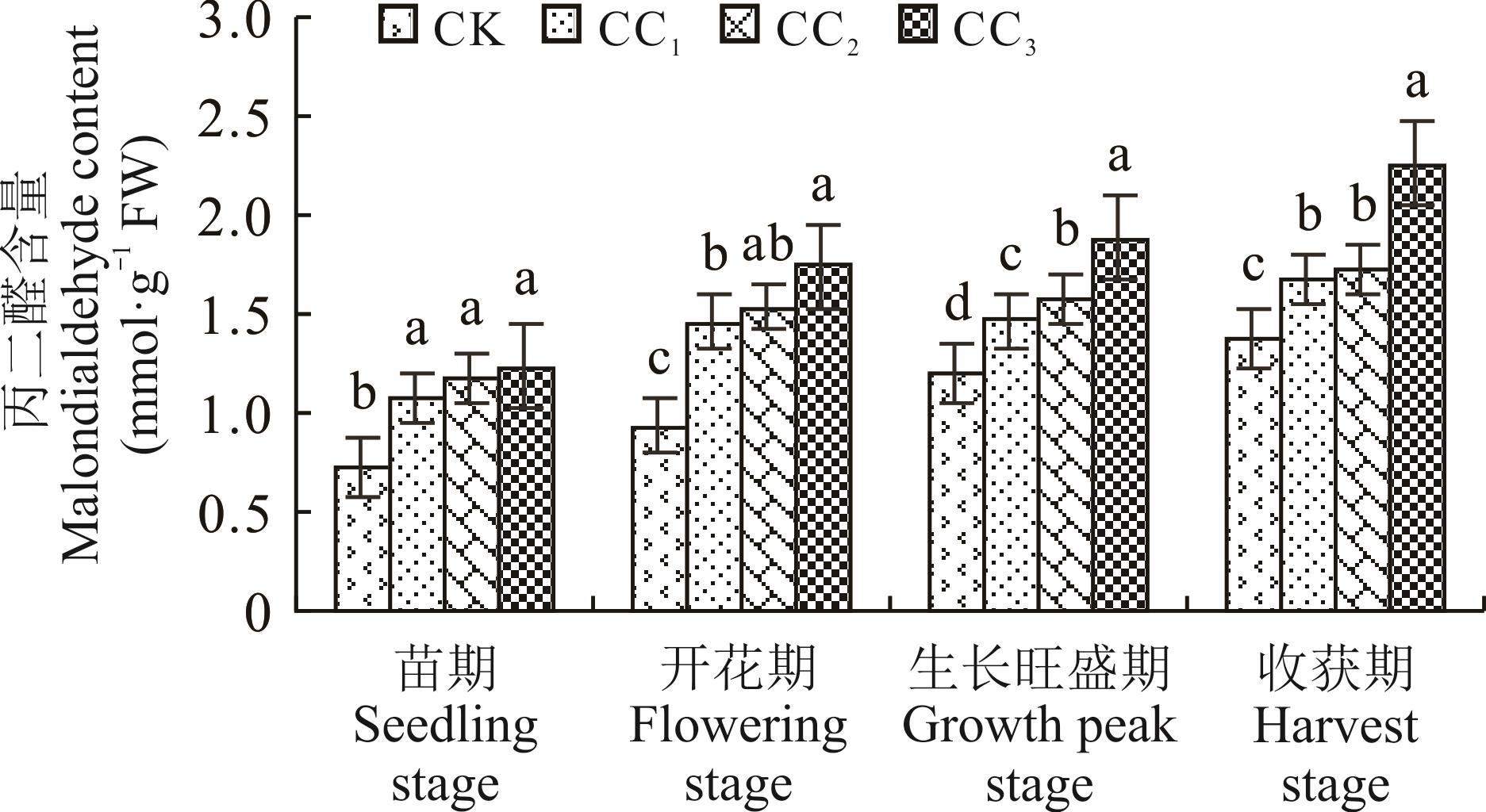
图4 连作对纹党不同生育时期叶片丙二醛含量的影响
Fig.4 Effects of continuous cropping on malondialdehyde content in leaves at different growth stages of C. pilosula var. modesta

图6 连作对纹党不同生育时期叶片可溶性糖含量的影响
Fig.6 Effects of continuous cropping on soluble sugar content in leaves at different growth stages of C. pilosula var. modesta

图7 连作对纹党不同生育时期叶片相对电导率的影响
Fig.7 Effects of continuous cropping on relative conductivity in leaves at different growth stages of C. pilosula var. modesta
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.236 | 丙烯醛Acrolein | 56.06 | C3H4O | 18.06 |
| 30.387 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 4.82 |
| 37.557 | 顺-9-十六烯酸庚酯Cis-9-Hexadecenoic acid, heptyl ester | 352.30 | C23H44O2 | 2.56 |
| 43.782 | 9-十八烯酸丁酯Butyl 9-octadecenoate | 338.57 | C22H42O2 | 2.42 |
| 48.068 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 72.14 |
表2 正茬土壤中存在的主要化学物质
Table 2 Main chemical substances present in regular soil
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.236 | 丙烯醛Acrolein | 56.06 | C3H4O | 18.06 |
| 30.387 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 4.82 |
| 37.557 | 顺-9-十六烯酸庚酯Cis-9-Hexadecenoic acid, heptyl ester | 352.30 | C23H44O2 | 2.56 |
| 43.782 | 9-十八烯酸丁酯Butyl 9-octadecenoate | 338.57 | C22H42O2 | 2.42 |
| 48.068 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 72.14 |
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.179 | 丙酸乙酯Ethyl propionate | 102.13 | C5H10O2 | 13.71 |
| 3.671 | 甲苯Toluene | 92.14 | C7H8 | 3.19 |
| 4.043 | 四氯乙烯Tetrachloroethylene | 165.83 | C2Cl4 | 1.62 |
| 4.655 | 乙基苯Ethyl benzene | 106.17 | C8H10 | 0.66 |
| 4.764 | 对二甲苯P-xylene | 106.17 | C8H10 | 5.34 |
| 6.028 | 苯甲醛Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | C7H6O | 3.53 |
| 7.573 | 苯乙酮Acetophenone | 120.15 | C8H8O | 2.28 |
| 7.865 | 1-甲氧基丙苯1-methoxypropylbenzene | 150.22 | C10H14O | 2.30 |
| 8.312 | 磷酸三乙酯Triethyl phosphate | 182.15 | C6H15O4P | 1.58 |
| 8.918 | 四环[5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>]癸-4,8-二烯Tetracyclic [5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>] decan-4, 8-diene | 130.10 | C10H10 | 2.04 |
| 15.332 | 癸酸十四醇酯Undec-10-ynoic acid, tetradecyl ester | 378.40 | C25H46O2 | 0.99 |
| 17.164 | γ-苯基-γ-丁内酯Gamma-phenyl-gamma-butyrolactone | 162.19 | C19H10O2 | 3.45 |
| 19.790 | 癸酸十六醇酯Undec-10-ynoic acid, hexadecyl ester | 406.40 | C27H50O2 | 0.62 |
| 27.292 | 邻苯二甲酸丁十四烷基酯Phthalic acid, butyl tetradecyl ester | 418.30 | C26H42O4 | 3.35 |
| 30.479 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 44.73 |
| 36.945 | E, E, Z-1, 3, 12-十九碳三烯-5, 14-二醇E, E, Z-1, 3, 12-Nonadecatriene-5, 14-diol | 294.30 | C19H34O2 | 0.51 |
| 47.925 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 10.10 |
表3 连作1年土壤中存在的主要化学物质
Table 3 The main chemical substances present in the soil of continuous cropping for 1 year
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.179 | 丙酸乙酯Ethyl propionate | 102.13 | C5H10O2 | 13.71 |
| 3.671 | 甲苯Toluene | 92.14 | C7H8 | 3.19 |
| 4.043 | 四氯乙烯Tetrachloroethylene | 165.83 | C2Cl4 | 1.62 |
| 4.655 | 乙基苯Ethyl benzene | 106.17 | C8H10 | 0.66 |
| 4.764 | 对二甲苯P-xylene | 106.17 | C8H10 | 5.34 |
| 6.028 | 苯甲醛Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | C7H6O | 3.53 |
| 7.573 | 苯乙酮Acetophenone | 120.15 | C8H8O | 2.28 |
| 7.865 | 1-甲氧基丙苯1-methoxypropylbenzene | 150.22 | C10H14O | 2.30 |
| 8.312 | 磷酸三乙酯Triethyl phosphate | 182.15 | C6H15O4P | 1.58 |
| 8.918 | 四环[5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>]癸-4,8-二烯Tetracyclic [5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>] decan-4, 8-diene | 130.10 | C10H10 | 2.04 |
| 15.332 | 癸酸十四醇酯Undec-10-ynoic acid, tetradecyl ester | 378.40 | C25H46O2 | 0.99 |
| 17.164 | γ-苯基-γ-丁内酯Gamma-phenyl-gamma-butyrolactone | 162.19 | C19H10O2 | 3.45 |
| 19.790 | 癸酸十六醇酯Undec-10-ynoic acid, hexadecyl ester | 406.40 | C27H50O2 | 0.62 |
| 27.292 | 邻苯二甲酸丁十四烷基酯Phthalic acid, butyl tetradecyl ester | 418.30 | C26H42O4 | 3.35 |
| 30.479 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 44.73 |
| 36.945 | E, E, Z-1, 3, 12-十九碳三烯-5, 14-二醇E, E, Z-1, 3, 12-Nonadecatriene-5, 14-diol | 294.30 | C19H34O2 | 0.51 |
| 47.925 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 10.10 |
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.282 | 丙酸乙酯Ethyl propionate | 102.13 | C5H10O2 | 2.78 |
| 3.705 | 甲苯Toluene | 92.14 | C7H8 | 0.66 |
| 4.781 | 对二甲苯P-xylene | 106.17 | C8H10 | 0.64 |
| 5.073 | 苯乙烯Styrene | 104.15 | C8H8 | 8.84 |
| 6.040 | 苯甲醛Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | C7H6O | 1.06 |
| 7.579 | 苯乙酮Acetophenone | 120.15 | C8H8O | 0.88 |
| 8.918 | 四环[5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>]癸-4,8-二烯 Tetracyclic [5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>] decan-4, 8-diene | 130.10 | C10H10 | 0.49 |
| 16.774 | 2, 4-二叔丁基苯酚2, 4-di-tert-butylphenol | 206.32 | C14H22O | 0.67 |
| 17.426 | 3-氯三环[5.2.1.0(4, 8)]癸-2, 5-二烯3-Chlorotricyclo[5.2.1.0(4, 8)]deca-2,5-diene | 166.10 | C10H11Cl | 1.42 |
| 20.917 | 3-苯甲酰基丙酸乙酯Ethyl 3-benzoylpropionate | 206.24 | C12H14O3 | 1.46 |
| 30.724 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 64.15 |
| 43.782 | 油酸酰胺Oleamide | 281.48 | C18H35NO | 4.77 |
| 47.982 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 12.18 |
表4 连作2年土壤中存在的主要化学物质
Table 4 The main chemical substances present in soil after 2 years of continuous cropping
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.282 | 丙酸乙酯Ethyl propionate | 102.13 | C5H10O2 | 2.78 |
| 3.705 | 甲苯Toluene | 92.14 | C7H8 | 0.66 |
| 4.781 | 对二甲苯P-xylene | 106.17 | C8H10 | 0.64 |
| 5.073 | 苯乙烯Styrene | 104.15 | C8H8 | 8.84 |
| 6.040 | 苯甲醛Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | C7H6O | 1.06 |
| 7.579 | 苯乙酮Acetophenone | 120.15 | C8H8O | 0.88 |
| 8.918 | 四环[5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>]癸-4,8-二烯 Tetracyclic [5.3.0.0<2, 6>.0<3, 10>] decan-4, 8-diene | 130.10 | C10H10 | 0.49 |
| 16.774 | 2, 4-二叔丁基苯酚2, 4-di-tert-butylphenol | 206.32 | C14H22O | 0.67 |
| 17.426 | 3-氯三环[5.2.1.0(4, 8)]癸-2, 5-二烯3-Chlorotricyclo[5.2.1.0(4, 8)]deca-2,5-diene | 166.10 | C10H11Cl | 1.42 |
| 20.917 | 3-苯甲酰基丙酸乙酯Ethyl 3-benzoylpropionate | 206.24 | C12H14O3 | 1.46 |
| 30.724 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 64.15 |
| 43.782 | 油酸酰胺Oleamide | 281.48 | C18H35NO | 4.77 |
| 47.982 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 12.18 |
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.282 | 丙酸乙酯Ethyl propionate | 102.13 | C5H10O2 | 0.84 |
| 30.810 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 86.01 |
| 43.920 | 油酸酰胺Oleamide | 281.48 | C18H35NO | 7.41 |
| 48.028 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 5.74 |
表5 连作3年土壤中存在的主要化学物质
Table 5 The main chemical substances present in soil after 3 years of continuous cropping
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子量 Molecular weight | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.282 | 丙酸乙酯Ethyl propionate | 102.13 | C5H10O2 | 0.84 |
| 30.810 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | 278.34 | C16H22O4 | 86.01 |
| 43.920 | 油酸酰胺Oleamide | 281.48 | C18H35NO | 7.41 |
| 48.028 | 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己)酯Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 390.56 | C24H38O4 | 5.74 |
| 1 | National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopoeia (one). Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 281-282. |
| 国家药典委员会. 中国药典(一部). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 281-282. | |
| 2 | Yang Y, Li H L, Ma K L, et al. Effect of continuous cropping on the physicochemical properties, microbial activity, and community characteristics of the rhizosphere soil of Codonopsis pilosula. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(11): 6387-6398. |
| 杨阳, 李海亮, 马凯丽, 等. 连作对党参根际土壤理化性质、微生物活性及群落特征的影响. 环境科学, 2023, 44(11): 6387-6398. | |
| 3 | Wu H M, Lin W X. A commentary and development perspective on the consecutive monoculture problems of medicinal plants. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(6): 775-793. |
| 吴红淼, 林文雄. 药用植物连作障碍研究评述和发展透视. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(6): 775-793. | |
| 4 | Shen Y L, Cheng L Y, Meng X R, et al. Effects of ginseng continuous soil crop on growth development and antioxidant system of ginseng at different fertility stages. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(1): 109-115. |
| 沈彦龙, 程立业, 孟祥茹, 等. 人参连作土壤对不同生育期人参生长发育及抗氧化系统的影响. 应用化学, 2023, 40(1): 109-115. | |
| 5 | An Y, Yang D, Li X, et al. Study on the effect and physiological mechanism of continuous cropping obstruction of Pinellia ternata. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2018, 27(7): 1017-1022. |
| 安艳, 杨丹, 李鑫, 等. 半夏连作障碍效应及生理机制研究. 西北农业学报, 2018, 27(7): 1017-1022. | |
| 6 | Wang M, Qu C L, Zhang Y, et al. Identification of autotoxic compounds in root exudates of Atractylodes lancea and their effects on seedling growth. Journal of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, 2023, 25(2): 47-51. |
| 王萌, 瞿彩丽, 张燕, 等. 茅苍术根际自毒物质鉴定及其对幼苗生长的影响. 湖北中医药大学学报, 2023, 25(2): 47-51. | |
| 7 | Zhang Z L, Qu W J, Li X F. Experimental guidance in plant physiology (The 4th Edition). Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009. |
| 张志良, 瞿伟菁, 李小芳. 植物生理学实验指导(第四版). 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009. | |
| 8 | Jothimani K, Arulbalachandran D. Physiological and biochemical studies of black gram (Vigna mungo(L.)Hepper) under polyethylene glycol induced drought stress. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2020, 29: 101777. |
| 9 | Qi J W, Lu S S, Huang H X, et al. Identification of superoxide dismutase gene family in Gymnocarpos przewalskii and its response to salt stress. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2023, 38(5): 856-867. |
| 齐建伟, 鲁松松, 黄海霞, 等. 裸果木超氧化物歧化酶基因家族鉴定及对盐胁迫的响应分析. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2023, 38(5): 856-867. | |
| 10 | Yang X X, Liu R, Jing M, et al. Variation of root soluble sugar and starch response to drought stress in Foxtail millet. Agronomy, 2023, 13(2): 359. |
| 11 | Nie M. Research on growth and physiological charateristics of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. at different continuous cropping years and allelochemicals of its rhizosphere soil. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 聂铭. 不同连作年限地黄生长生理特性及其根区土壤化感物质研究. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2017. | |
| 12 | Wang Z W. The effects of growth development and composition accumulation of Codonopsis pilosula under different soil moisture. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2018. |
| 王赞文. 土壤水分对党参生长发育和成分积累的影响. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2018. | |
| 13 | Bian H, Cao Y, Ge Y. Study on determination of total flavomycin in feedstuff based on area normalization method. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2024, 39(1): 204-211, 217. |
| 卞华, 曹莹, 葛宇. 基于面积归一化法对饲料中黄霉素总残留量的研究. 中国粮油学报, 2024, 39(1): 204-211, 217. | |
| 14 | Zhao Z L, Li H K, Li X Z, et al. Effects of continuous cropping on the growth and endophyte and rhizosphere microbial community structure of Paulownia fortunei. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2023, 43(4): 407-415. |
| 赵振利, 李慧珂, 李烜桢, 等. 连作对白花泡桐生长及根内外微生物群落的影响. 森林与环境学报, 2023, 43(4): 407-415. | |
| 15 | Liu S R, Wang H L, Yang P, et al. Effects of continuous cropping on the growth and secondary metabolites of Pinellia ternata. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2022, 45(1): 1-6. |
| 刘诗蓉, 王红兰, 杨萍, 等. 连作对半夏生长及次生代谢产物的影响. 中药材, 2022, 45(1): 1-6. | |
| 16 | Zeng L S, Li P Y, Sun Z J, et al. Analysis of antioxidant enzyme protection systems and gene expression differences in two Xinjiang bermudagrass genotypes with contrasting drought resistance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. |
| 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 等. 两类新疆狗牙根抗旱基因型抗氧化酶保护系统及其基因表达差异分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. | |
| 17 | Shi G Y, Sun H Q, Yu Y L, et al. Effect of long-term consecutive cropping on leaf PSⅡ photochemical efficiency and antioxidant enzyme activity of Lanzhou lily. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 206-213. |
| 师桂英, 孙鸿强, 于彦琳, 等. 连作栽培对兰州百合(Lilium davidii var. unicolor)叶片PSⅡ光化学效率和抗氧化作用的影响. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 206-213. | |
| 18 | Yang X, Wang X J, Tang Z L, et al. Effects of continuous cropping on plant morphology and physiological characteristics of tartary buckwheat seedlings under hydroponics. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2023, 54(3): 887-893. |
| 杨雪, 王晓静, 唐卓磊, 等. 水培条件下连作对苦荞幼苗植株形态和生理特性的影响. 南方农业学报, 2023, 54(3): 887-893. | |
| 19 | Yang K, Liu W Y, Wang W T, et al. Effects of continuous cropping on growth and physiological characteristics of quinoa. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2021, 43(2): 244-252. |
| 杨科, 刘文瑜, 王旺田, 等. 连作对藜麦生长和生理特性的影响. 江西农业大学学报, 2021, 43(2): 244-252. | |
| 20 | Chen W, Teng Y, Li Z A, et al. Mechanisms by which organic fertilizer and effective microbes mitigate peanut continuous cropping yield constraints in a red soil of south China. Applied Soil Ecology, 2018, 128: 23-34. |
| 21 | Liu H, Pan F J, Han X Z, et al. A comprehensive analysis of the response of the fungal community structure to long-term continuous cropping in three typical upland crops. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2020, 19(3): 866-880. |
| 22 | Ju J D, Fu X Y, Jiao H R, et al. Rhizosphere exudate-mediated synergistic harm of soil microorganisms to medicinal plants in continuous cropping. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2022, 28(20): 92-99. |
| 鞠吉东, 付心雨, 焦焕然, 等. 根际分泌物介导土壤微生物协同致害连作药用植物的分析与探讨. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(20): 92-99. | |
| 23 | Lu J, Li W X, Yang Y H, et al. The impact of different rotation regime on the soil bacterial and fungal communities in an intensively managed agricultural region. Archives of Microbiology, 2022, 204(2): 142-154. |
| 24 | Kato N H, Nakamura K, Ohno O, et al. Asparagus decline: Autotoxicity and autotoxic compounds in asparagus rhizomes. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2017, 213: 23-29. |
| 25 | Arafat Y, Din I U, Tayyab M, et al. Soil sickness in aged tea plantation is associated with a shift in microbial communities as a result of plant polyphenol accumulation in the tea gardens. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 601. |
| 26 | Ma S Y, Chen G P, Wang N, et al. Identification of potential autotoxic substances in pea soil and analysis of their autotoxic effects. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. |
| 马绍英, 陈桂平, 王娜, 等. 豌豆土壤中潜在自毒物质的鉴定及自毒效应研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. | |
| 27 | Zheng F, Chen L, Gao J M, et al. Identification of autotoxic compounds from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz and preliminary investigations of their influences on immune system. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2018, 230: 33-39. |
| [1] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [2] | 陈莺宇, 邱亚娟, 邵晓龄, 黄钰芳, 杨扶德, 陈林杰, 陈红刚, 谢田朋. 纹党连作土壤浸提液对其种子萌发及幼苗生长的自毒效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 122-133. |
| [3] | 黄丽娟, 孙镕基, 高文婧, 张志飞, 陈桂华. 全株水稻表面优势乳酸菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 117-125. |
| [4] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [5] | 张彩霞, 方香玲. 草类植物抗病机制研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 203-215. |
| [6] | 彭彤, 马少兰, 马彩霞, 宋燕芳, 高娜, 李凯乐, 张传继, 李静雯, 纳小凡, 王立光. 长期单作对枸杞园不同土层土壤微生物代谢活性和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 89-98. |
| [7] | 李欣航, 肖泽华, 匡雪韶, 王悟敏, 罗亮宇, 刘文胜. 锰胁迫下鸡眼草的富集特征及生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 139-147. |
| [8] | 谢德金, 李静文, 叶友杰, 殷彪, 任可, 陈凌艳, 荣俊冬, 郑郁善. 光质对草珊瑚幼苗生长及其生理生化基础的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 104-115. |
| [9] | 王宁, 付亚军, 袁美丽, 刘征阳, 张铭鑫, 米银法. GA3浸种对入侵植物节节麦种子破眠及发芽特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 73-81. |
| [10] | 方美烟, 王贤东, 于全平, 陈勇. 不同消化能、粗蛋白质水平饲粮对泌乳前期伊犁马营养物质消化代谢、血液生理生化指标和激素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 129-138. |
| [11] | 杨成德, 崔月贞, 冯中红, 薛莉, 金梦军. 内生枯草芽孢杆菌265ZY4对温度和紫外光胁迫下紫花针茅生化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 101-108. |
| [12] | 李继伟, 悦飞雪, 王艳芳, 张亚梅, 倪瑞景, 王发园, 付国占, 刘领. 施用生物炭和AM真菌对镉胁迫下玉米生长和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 120-129. |
| [13] | 黄钰芳, 张恩和, 张新慧, 王惠珍, 王琦, 刘青林, 石雨仟. 兰州百合连作障碍效应及机制研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 146-155. |
| [14] | 靳军英, 张卫华, 王大可, 寇青青, 运剑苇, 黄建国. 扁穗牛鞭草的水肥耦合效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 106-114. |
| [15] | 黄钰芳, 张恩和, 张新慧, 王惠珍, 王琦, 刘青林, 石雨仟. 兰州百合根及鳞茎水浸液自毒作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 93-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||