

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1-10.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020434
收稿日期:2020-09-27
修回日期:2020-11-24
出版日期:2021-07-20
发布日期:2021-06-03
通讯作者:
宋彦涛
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: yantaosong@dlnu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xin-lei XU( ), Yan-tao SONG(
), Yan-tao SONG( ), Jing-dong ZHAO, Yun-na WU
), Jing-dong ZHAO, Yun-na WU
Received:2020-09-27
Revised:2020-11-24
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-06-03
Contact:
Yan-tao SONG
摘要:
为探索施肥和刈割对呼伦贝尔草甸草原牧草营养品质的影响及其与植物多样性的关系,于2019年8月在中国科学院沈阳应用生态研究所额尔古纳森林草原过渡带生态系统研究站刈割实验平台(建立于2016年)进行取样,对2个施肥梯度和6个刈割留茬高度处理下的植物样品进行品质测定,并分析牧草品质与物种丰富度的关系。结果表明,施肥处理下牧草粗蛋白含量和相对饲喂价值显著高于不施肥处理,而不施肥处理的酸性洗涤纤维含量显著高于施肥处理。刈割留茬高度3 cm时牧草粗蛋白、粗脂肪、可溶性碳水化合物、相对牧草品质和产奶量最高,而不刈割处理的牧草的中性洗涤纤维和酸性洗涤纤维含量最高。施肥和刈割无显著交互作用。牧草中的相对牧草质量、相对饲用价值、产奶量、非纤维性碳水化合物、钙含量与牧草物种丰富度呈显著正相关关系,牧草中性洗涤纤维与牧草物种丰富度呈显著负相关关系,表明增加物种多样性有助于提高牧草的营养品质。因此,维持草地植物群落中植物物种丰富度可能是对呼伦贝尔草原家畜生产的有效管理方式。
徐鑫磊, 宋彦涛, 赵京东, 乌云娜. 施肥和刈割对呼伦贝尔草甸草原牧草品质的影响及其与植物多样性的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 1-10.
Xin-lei XU, Yan-tao SONG, Jing-dong ZHAO, Yun-na WU. Changes in forage quality and its relationship with plant diversity under fertilization and mowing in Hulun Buir meadow steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 1-10.
因子 Parameters | 施肥 Fertilization (F) | 刈割 Mowing (D) | 施肥×刈割 F×D |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粗灰分 Ash | ns | ns | ns |
| 粗脂肪 EE | ns | *** | ns |
| 粗蛋白 CP | *** | *** | ns |
| 木质素 Lignin | ns | * | ns |
| 可溶性碳水化合物 WSC | ns | ** | ns |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF | ** | *** | ns |
| 中性洗涤纤维 NDF | ns | *** | ns |
| 非纤维性碳水化合物 NFC | ns | *** | ns |
| 体外30 h干物质消化率IVTDMD30 | ** | *** | ns |
| 体外30 h中性洗涤纤维消化率 NDFD30 | ns | * | ns |
| 产奶净能 NEL | ns | *** | ns |
| 维持净能 NEM | ns | *** | ns |
| 增重净能 NEG | ns | *** | ns |
| 相对饲养价值 RFV | * | *** | ns |
| 相对牧草质量 RFQ | ns | *** | ns |
| 产奶量 Milk production | ns | *** | ns |
表1 施肥和刈割及其交互作用对牧草品质指标的方差分析
Table 1 Analysis of variance of fertilization and mowing and their interactions on various forage quality indices
因子 Parameters | 施肥 Fertilization (F) | 刈割 Mowing (D) | 施肥×刈割 F×D |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粗灰分 Ash | ns | ns | ns |
| 粗脂肪 EE | ns | *** | ns |
| 粗蛋白 CP | *** | *** | ns |
| 木质素 Lignin | ns | * | ns |
| 可溶性碳水化合物 WSC | ns | ** | ns |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF | ** | *** | ns |
| 中性洗涤纤维 NDF | ns | *** | ns |
| 非纤维性碳水化合物 NFC | ns | *** | ns |
| 体外30 h干物质消化率IVTDMD30 | ** | *** | ns |
| 体外30 h中性洗涤纤维消化率 NDFD30 | ns | * | ns |
| 产奶净能 NEL | ns | *** | ns |
| 维持净能 NEM | ns | *** | ns |
| 增重净能 NEG | ns | *** | ns |
| 相对饲养价值 RFV | * | *** | ns |
| 相对牧草质量 RFQ | ns | *** | ns |
| 产奶量 Milk production | ns | *** | ns |
施肥处理 Fertilization treatment | 留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 粗灰分 Ash | 粗脂肪 EE | 粗蛋白 CP | 木质素 Lignin | 非纤维性碳水化合物 NFC | 可溶性碳水化合物 WSC | 酸性洗涤 纤维 ADF | 中性洗涤 纤维 NDF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
施肥 Fertilization | 3 | 5.53±0.18 | 3.71±0.16 | 15.46±0.48 | 23.72±1.54 | 7.17±0.35 | 9.23±0.75 | 29.73±0.89 | 54.06±1.82 |
| 6 | 4.60±0.55 | 2.99±0.10 | 14.02±0.47 | 26.54±1.47 | 6.87±0.35 | 9.19±0.55 | 31.91±1.04 | 54.33±1.25 | |
| 9 | 5.76±0.37 | 3.12±0.12 | 12.53±0.44 | 20.01±1.53 | 5.87±0.16 | 7.64±0.63 | 34.62±0.90 | 61.06±1.21 | |
| 12 | 6.02±0.55 | 2.96±0.22 | 12.70±0.96 | 22.75±2.02 | 5.85±0.43 | 7.67±0.78 | 34.13±1.42 | 58.05±1.21 | |
| 15 | 5.25±0.44 | 2.73±0.14 | 12.95±0.43 | 20.60±2.23 | 5.05±0.48 | 7.16±0.86 | 35.18±1.16 | 60.94±2.93 | |
| ND | 5.13±0.33 | 2.86±0.13 | 12.54±0.53 | 16.92±1.64 | 4.12±0.68 | 5.49±0.79 | 37.00±1.08 | 65.03±2.20 | |
不施肥 Not fertilization | 3 | 4.64±0.35 | 3.64±0.14 | 13.14±0.05 | 26.14±1.51 | 7.63±0.19 | 8.88±0.48 | 31.06±0.42 | 54.93±1.41 |
| 6 | 5.28±0.40 | 3.05±0.06 | 11.44±0.64 | 25.53±1.18 | 6.92±0.47 | 8.91±0.64 | 33.97±1.03 | 57.19±0.69 | |
| 9 | 5.15±0.62 | 2.96±0.10 | 9.97±0.34 | 22.47±2.22 | 5.50±0.40 | 6.79±0.66 | 36.97±0.89 | 61.93±1.83 | |
| 12 | 7.03±1.84 | 3.03±0.04 | 9.81±0.73 | 22.13±0.61 | 4.68±0.93 | 6.07±1.05 | 37.93±1.89 | 60.47±1.71 | |
| 15 | 4.89±0.37 | 2.70±0.10 | 10.23±0.52 | 23.96±1.40 | 5.71±0.46 | 7.44±0.64 | 37.16±0.77 | 60.69±1.63 | |
| ND | 5.29±1.08 | 3.35±0.07 | 9.57±0.33 | 17.41±2.80 | 5.44±0.41 | 6.57±0.73 | 37.39±1.05 | 66.87±2.65 | |
| l.s.d0.05 | 2.04 | 0.35 | 1.50 | 0.99 | 4.90 | 0.95 | 2.03 | 3.06 | |
表2 施肥和不同留茬高度处理下牧草的营养组分含量的差异性
Table 2 The difference of forage nutrient content under treatments of fertilization and different stubble height (%)
施肥处理 Fertilization treatment | 留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 粗灰分 Ash | 粗脂肪 EE | 粗蛋白 CP | 木质素 Lignin | 非纤维性碳水化合物 NFC | 可溶性碳水化合物 WSC | 酸性洗涤 纤维 ADF | 中性洗涤 纤维 NDF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
施肥 Fertilization | 3 | 5.53±0.18 | 3.71±0.16 | 15.46±0.48 | 23.72±1.54 | 7.17±0.35 | 9.23±0.75 | 29.73±0.89 | 54.06±1.82 |
| 6 | 4.60±0.55 | 2.99±0.10 | 14.02±0.47 | 26.54±1.47 | 6.87±0.35 | 9.19±0.55 | 31.91±1.04 | 54.33±1.25 | |
| 9 | 5.76±0.37 | 3.12±0.12 | 12.53±0.44 | 20.01±1.53 | 5.87±0.16 | 7.64±0.63 | 34.62±0.90 | 61.06±1.21 | |
| 12 | 6.02±0.55 | 2.96±0.22 | 12.70±0.96 | 22.75±2.02 | 5.85±0.43 | 7.67±0.78 | 34.13±1.42 | 58.05±1.21 | |
| 15 | 5.25±0.44 | 2.73±0.14 | 12.95±0.43 | 20.60±2.23 | 5.05±0.48 | 7.16±0.86 | 35.18±1.16 | 60.94±2.93 | |
| ND | 5.13±0.33 | 2.86±0.13 | 12.54±0.53 | 16.92±1.64 | 4.12±0.68 | 5.49±0.79 | 37.00±1.08 | 65.03±2.20 | |
不施肥 Not fertilization | 3 | 4.64±0.35 | 3.64±0.14 | 13.14±0.05 | 26.14±1.51 | 7.63±0.19 | 8.88±0.48 | 31.06±0.42 | 54.93±1.41 |
| 6 | 5.28±0.40 | 3.05±0.06 | 11.44±0.64 | 25.53±1.18 | 6.92±0.47 | 8.91±0.64 | 33.97±1.03 | 57.19±0.69 | |
| 9 | 5.15±0.62 | 2.96±0.10 | 9.97±0.34 | 22.47±2.22 | 5.50±0.40 | 6.79±0.66 | 36.97±0.89 | 61.93±1.83 | |
| 12 | 7.03±1.84 | 3.03±0.04 | 9.81±0.73 | 22.13±0.61 | 4.68±0.93 | 6.07±1.05 | 37.93±1.89 | 60.47±1.71 | |
| 15 | 4.89±0.37 | 2.70±0.10 | 10.23±0.52 | 23.96±1.40 | 5.71±0.46 | 7.44±0.64 | 37.16±0.77 | 60.69±1.63 | |
| ND | 5.29±1.08 | 3.35±0.07 | 9.57±0.33 | 17.41±2.80 | 5.44±0.41 | 6.57±0.73 | 37.39±1.05 | 66.87±2.65 | |
| l.s.d0.05 | 2.04 | 0.35 | 1.50 | 0.99 | 4.90 | 0.95 | 2.03 | 3.06 | |
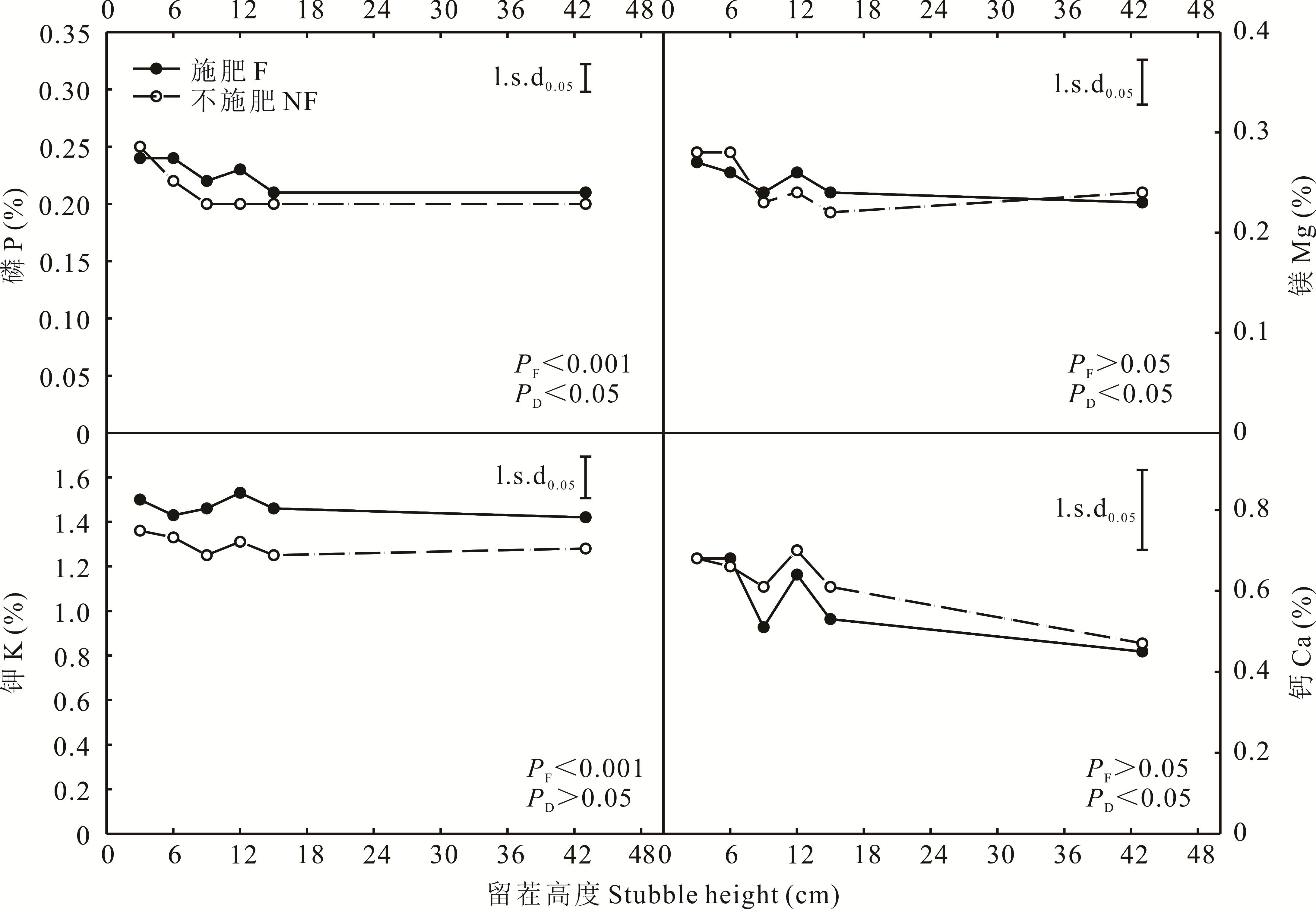
图1 施肥和不同刈割留茬高度处理下牧草矿物质磷、镁、钾和钙含量的变化l.s.d0.05表示不同处理间LSD多重比较在0.05水平上的显著性,不同处理之间平均值的差值大于该值说明处理间有显著差异(P<0.05)。PF表示牧草矿物质含量在不同施肥水平上的显著性,PD表示牧草矿物质含量在不同刈割留茬高度水平上的显著性。l.s.d0.05 indicates the significance of the multiple comparison between LSD different treatments at the 0.05 level, and the mean difference between two treatments is greater than this value, indicating that there is significant difference (P<0.05). PF indicates the significance of forage mineral content at different fertilization levels, while PD indicates the significance of forage mineral content at different stubble height levels.
Fig.1 Forage mineral contents of P, Mg, K and Ca under treatments of fertilization and different stubble height
施肥处理 Fertilization treatment | 留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 体外30 h干物质消化率 IVTDMD30 (%) | 体外30 h中性洗涤纤维消化率 NDFD30 (%) | 产奶净能 NEL (Mcal·kg-1) | 维持净能 NEM (Mcal·kg-1) | 增重净能 NEG (Mcal·kg-1) | 相对饲养 价值 RFV | 相对牧草 质量 RFQ | 产奶量 Milk production (kg·MT-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
施肥 Fertilization | 3 | 61.06±0.33 | 32.35±1.72 | 1.46±0.02 | 1.42±0.02 | 0.69±0.02 | 113.50±4.40 | 113.75±3.79 | 1496.75±31.49 |
| 6 | 61.10±1.20 | 34.10±2.96 | 1.45±0.02 | 1.38±0.02 | 0.66±0.02 | 110.00±3.71 | 107.00±3.18 | 1466.00±38.24 | |
| 9 | 58.56±0.88 | 33.45±1.94 | 1.32±0.02 | 1.22±0.03 | 0.50±0.03 | 94.50±2.32 | 85.25±4.55 | 1278.75±35.29 | |
| 12 | 60.69±1.36 | 37.21±3.75 | 1.36±0.02 | 1.28±0.03 | 0.56±0.03 | 100.00±2.79 | 95.50±5.17 | 1339.25±43.71 | |
| 15 | 57.65±1.86 | 32.26±3.11 | 1.32±0.04 | 1.19±0.08 | 0.47±0.08 | 94.75±5.39 | 82.50±10.78 | 1249.75±85.03 | |
| ND | 53.99±1.74 | 26.86±1.62 | 1.25±0.04 | 1.09±0.06 | 0.36±0.06 | 86.25±4.32 | 68.75±7.53 | 1149.00±66.76 | |
不施肥 Not fertilization | 3 | 59.19±1.39 | 31.89±2.94 | 1.47±0.01 | 1.42±0.01 | 0.70±0.01 | 110.00±2.79 | 111.25±2.95 | 1511.25±9.80 |
| 6 | 57.51±1.50 | 34.07±2.11 | 1.40±0.01 | 1.32±0.01 | 0.60±0.01 | 101.50±1.19 | 98.25±2.59 | 1389.00±22.40 | |
| 9 | 55.37±0.80 | 35.18±2.28 | 1.34±0.02 | 1.25±0.03 | 0.53±0.03 | 90.50±3.57 | 88.25±5.02 | 1307.25±39.76 | |
| 12 | 57.85±2.25 | 32.90±4.16 | 1.30±0.03 | 1.21±0.03 | 0.49±0.03 | 91.50±1.65 | 87.25±5.28 | 1251.75±48.54 | |
| 15 | 54.94±1.27 | 33.95±1.94 | 1.35±0.02 | 1.26±0.04 | 0.54±0.04 | 92.25±2.59 | 89.50±7.35 | 1318.00±46.33 | |
| ND | 51.17±1.96 | 25.32±2.44 | 1.26±0.05 | 1.10±0.06 | 0.38±0.06 | 83.50±4.29 | 69.75±7.64 | 1161.50±82.65 | |
| l.s.d0.05 | 4.09 | 7.49 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 9.61 | 16.52 | 140.47 | |
表3 施肥和不同留茬高度刈割处理下牧草饲喂价值的差异性
Table 3 Difference in indices of forage feeding value under treatments of fertilization and different stubble height
施肥处理 Fertilization treatment | 留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 体外30 h干物质消化率 IVTDMD30 (%) | 体外30 h中性洗涤纤维消化率 NDFD30 (%) | 产奶净能 NEL (Mcal·kg-1) | 维持净能 NEM (Mcal·kg-1) | 增重净能 NEG (Mcal·kg-1) | 相对饲养 价值 RFV | 相对牧草 质量 RFQ | 产奶量 Milk production (kg·MT-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
施肥 Fertilization | 3 | 61.06±0.33 | 32.35±1.72 | 1.46±0.02 | 1.42±0.02 | 0.69±0.02 | 113.50±4.40 | 113.75±3.79 | 1496.75±31.49 |
| 6 | 61.10±1.20 | 34.10±2.96 | 1.45±0.02 | 1.38±0.02 | 0.66±0.02 | 110.00±3.71 | 107.00±3.18 | 1466.00±38.24 | |
| 9 | 58.56±0.88 | 33.45±1.94 | 1.32±0.02 | 1.22±0.03 | 0.50±0.03 | 94.50±2.32 | 85.25±4.55 | 1278.75±35.29 | |
| 12 | 60.69±1.36 | 37.21±3.75 | 1.36±0.02 | 1.28±0.03 | 0.56±0.03 | 100.00±2.79 | 95.50±5.17 | 1339.25±43.71 | |
| 15 | 57.65±1.86 | 32.26±3.11 | 1.32±0.04 | 1.19±0.08 | 0.47±0.08 | 94.75±5.39 | 82.50±10.78 | 1249.75±85.03 | |
| ND | 53.99±1.74 | 26.86±1.62 | 1.25±0.04 | 1.09±0.06 | 0.36±0.06 | 86.25±4.32 | 68.75±7.53 | 1149.00±66.76 | |
不施肥 Not fertilization | 3 | 59.19±1.39 | 31.89±2.94 | 1.47±0.01 | 1.42±0.01 | 0.70±0.01 | 110.00±2.79 | 111.25±2.95 | 1511.25±9.80 |
| 6 | 57.51±1.50 | 34.07±2.11 | 1.40±0.01 | 1.32±0.01 | 0.60±0.01 | 101.50±1.19 | 98.25±2.59 | 1389.00±22.40 | |
| 9 | 55.37±0.80 | 35.18±2.28 | 1.34±0.02 | 1.25±0.03 | 0.53±0.03 | 90.50±3.57 | 88.25±5.02 | 1307.25±39.76 | |
| 12 | 57.85±2.25 | 32.90±4.16 | 1.30±0.03 | 1.21±0.03 | 0.49±0.03 | 91.50±1.65 | 87.25±5.28 | 1251.75±48.54 | |
| 15 | 54.94±1.27 | 33.95±1.94 | 1.35±0.02 | 1.26±0.04 | 0.54±0.04 | 92.25±2.59 | 89.50±7.35 | 1318.00±46.33 | |
| ND | 51.17±1.96 | 25.32±2.44 | 1.26±0.05 | 1.10±0.06 | 0.38±0.06 | 83.50±4.29 | 69.75±7.64 | 1161.50±82.65 | |
| l.s.d0.05 | 4.09 | 7.49 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 9.61 | 16.52 | 140.47 | |
留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 施肥 Fertilization | 不施肥 Not fertilization | 留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 施肥 Fertilization | 不施肥 Not fertilization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 11.5±1.6 | 11.3±0.5 | 15 | 12.3±0.6 | 11.3±0.8 |
| 6 | 11.5±1.7 | 9.5±1.8 | ND | 7.0±1.2 | 8.0±1.3 |
| 9 | 8.0±1.5 | 10.5±1.6 | l.s.d0.05 | 2.3 | 1.8 |
| 12 | 11.0±2.6 | 12.0±1.4 |
表4 施肥和不同留茬高度刈割处理下物种丰富度的差异性
Table 4 Differences in species richness under treatments of fertilization and different stubble height (species·m-2)
留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 施肥 Fertilization | 不施肥 Not fertilization | 留茬高度 Stubble height (cm) | 施肥 Fertilization | 不施肥 Not fertilization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 11.5±1.6 | 11.3±0.5 | 15 | 12.3±0.6 | 11.3±0.8 |
| 6 | 11.5±1.7 | 9.5±1.8 | ND | 7.0±1.2 | 8.0±1.3 |
| 9 | 8.0±1.5 | 10.5±1.6 | l.s.d0.05 | 2.3 | 1.8 |
| 12 | 11.0±2.6 | 12.0±1.4 |
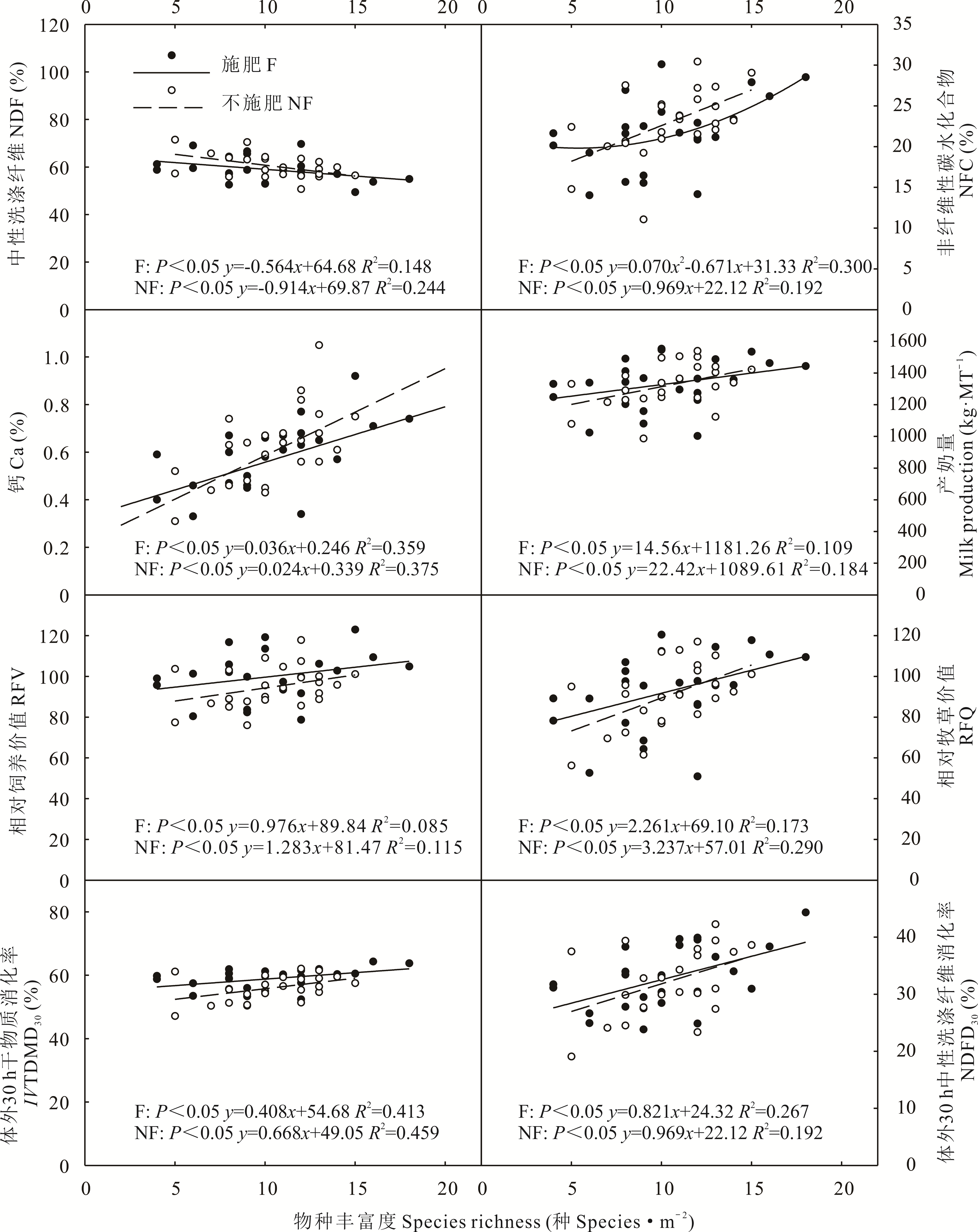
图2 牧草品质中性洗涤纤维、非纤维性碳水化合物、Ca含量、产奶量、相对饲养价值、相对牧草价值、体外30 h干物质消化率和体外30 h中性洗涤纤维消化率与物种丰富度之间的线性关系
Fig.2 The linear relationships between forage quality of NDF, NFC, Ca, milk production, RFV, RFQ, IVTDMD30, NDFD30 and species richness
| 1 | Hou X Y. Priority approaches, techniques and models to sustainably tap the grassland productivity potential. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(16): 3229-3238. |
| 侯向阳. 可持续挖掘草原生产潜力的途径、技术及政策建议. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(16): 3229-3238. | |
| 2 | Richman S E, Leafloor J O, Karasov W H, et al. Ecological implications of reduced forage quality on growth and survival of sympatric geese. Journal of Animal Ecology, 2015, 84(1): 284-298. |
| 3 | Hasan B, Shah W A. Biomass, grain production and quality of oats (Avena sativa) under different cutting regimes and nitrogen levels. Cereal Research Communications, 2000, 28(1): 203-210. |
| 4 | Han X G, Li L H. The maintenance mechanism of grassland ecosystem in Inner Mongolia. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2012. |
| 韩兴国, 李凌浩. 内蒙古草地生态系统维持机理. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2012. | |
| 5 | Wang D P, Chen W J, Zhao T Q, et al. Effect of cutting regime on yield and nutritional value of Stipa grandis steppe. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(1): 91-95. |
| 王德平, 陈万杰, 赵天启, 等. 刈割对大针茅草原产量和牧草营养品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(1): 91-95. | |
| 6 | Wang Z F, Wang D J, Yu H Z, et al. Effects of cutting time and stubble height on hay yield and quality of Leymus chinensis meadow. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(2): 108-114. |
| 王志锋, 王多伽, 于洪柱, 等. 刈割时间与留茬高度对羊草草甸草产量和品质的影响. 草业科学, 2016, 33(2): 108-114. | |
| 7 | Jiang H. General evaluation on study of yield, qualities and degradability about mix-sowing of alfalfa& smooth bromegrass. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2007. |
| 蒋慧.紫花苜蓿与无芒雀麦混播草地产量、品质和降解率研究及其综合评价. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2007. | |
| 8 | Hrevušová Z, Hejcman M, Hakl J. Soil chemical properties, plant species composition, herbage quality, production and nutrient uptake of an alluvial meadow after 45 years of N, P and K application. Grass and Forage Science, 2014, 70(2): 205-218. |
| 9 | Zhang Q Q, Liang Q W, Narisu, et al. Effects of clipping on native grassland: A review. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2018, 39(1): 33-42. |
| 张晴晴, 梁庆伟, 娜日苏, 等. 刈割对天然草地影响的研究进展. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2018, 39(1): 33-42. | |
| 10 | Gough L, Osenberg C W, Gross K L. Fertilization effects on species density and primary productivity in several herbaceous plant communities. Oikos, 2000, 89(3): 428-439. |
| 11 | Provenza F D. Acquired aversions as the basis for varied diets of ruminants foraging on rangelands. Journal of Animal Science, 1996, 74(8): 2010-2020. |
| 12 | Westoby M. What are the biological bases of varied diets? The American Naturalist, 1978, 112(985): 627-631. |
| 13 | Wiggins N L, Mcarthur C, Davies N W. Diet switching in a generalist mammalian folivore: Fundamental to maximising intake. Oecologia, 2006, 147(4): 650-657. |
| 14 | Wang L, Wang D, He Z, et al. Mechanisms linking plant species richness to foraging of a large herbivore. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 47(4): 868-875. |
| 15 | Early D M, Provenza F D. Food flavor and nutritional characteristics alter dynamics of food preference in lambs. Journal of Animal Science, 1998, 76(3): 728-734. |
| 16 | Hasi M, Zhang X Y, Niu G X, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on ecosystem CO2 exchange in a meadow steppe, Inner Mongolia. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(1): 27-41. |
| 哈斯木其尔, 张学耀, 牛国祥, 等. 氮素添加对内蒙古草甸草原生态系统 CO2交换的影响. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 27-41. | |
| 17 | Rohweder D A, Barnes R F, Neal J. Proposed hay grading standards based on laboratory analyses for evaluating quality. Journal of Animal Science, 2018, 47(3): 747-759. |
| 18 | Sergei S, Robert F, Florian L, et al. Plant diversity effects on forage quality, yield and revenues of semi-natural grasslands. Nature Communications, 2020, 768(11): 1-11. |
| 19 | Huo C J, Han J G, Hong F Z, et al. Effect of the first clipping dates and different stubble heights on the yield and quality of mixture pasture. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2001, 9(4): 257-264. |
| 霍成君, 韩建国, 洪绂曾, 等. 刈割期和留茬高度对混播草地产草量及品质的影响. 草地学报, 2001, 9(4): 257-264. | |
| 20 | Yang K H, Yu L, Zhang Q B, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on Phleum pretense pasture’s forage yield and quality. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 32(12): 2071-2077. |
| 杨开虎, 于磊, 张前兵, 等. 施氮对猫尾草栽培草地饲草产量和品质的影响. 草业科学, 2015, 32(12): 2071-2077. | |
| 21 | De K J, Zhou Q P, Liu W H, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on the yield and quality of oat in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2007, 29(5): 43-48. |
| 德科加, 周青平, 刘文辉, 等. 施氮量对青藏高原燕麦产量和品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2007, 29(5): 43-48. | |
| 22 | Hu H F, Jie X L, Guo X, et al. Effects of Se application as basal fertilizer on the nutrient contents and distribution rates of alfalfa at different growth stages. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2014, 22(4): 871-877. |
| 胡华锋, 介晓磊, 郭孝, 等. 基施硒肥对不同生育期紫花苜蓿营养含量及分配的影响. 草地学报, 2014, 22(4): 871-877. | |
| 23 | Ji Y F, Wu B L, Ding Y H, et al. Nutritional components of Phragmites australis and Spartina alterniflora in Dafeng freerange David’s Deer habitat of Jiangsu Province, East China: A comparative analysis. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(10): 2240-2244. |
| 纪一帆, 吴宝镭, 丁玉华, 等. 大丰野放麋鹿生境中芦苇和互花米草的营养对比分析. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(10): 2240-2244. | |
| 24 | Wu F L, Wang Z S, Yang Q, et al. Analysis of growth characteristics, nutritional components and feeding values of native forage grass from the high-cold steppes in the Luqu and Hezuo region of Gannan in summer and winter. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 31-38. |
| 吴发莉, 王之盛, 杨勤, 等. 甘南碌曲和合作地区冬夏季高寒天然牧草生产特性、营养成分和饲用价值分析. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 31-38. | |
| 25 | Fu Q, Liu Y. Recent progress in research on the effects of calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D on bone metabolism in animals. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine, 2006, 16(8): 502-505. |
| 付强, 刘源. 钙、磷与维生素D对动物骨代谢的影响研究进展. 中国比较医学杂志, 2006, 16(8): 502-505. | |
| 26 | Zhang Y, Bai X, Guo C H, et al. Analysis of nutritional value of common used forages in the goat production area in Sichuan Province. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(2): 285-290. |
| 张艳, 柏雪, 郭春华, 等. 四川省山羊主产区常用饲料营养价值分析. 草业科学, 2012, 29(2): 285-290. | |
| 27 | Xiong Y, Xu Q F, Yu Z, et al. Evaluation of nutritional and feeding value of oat hay from different regions. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(10): 2457-2462. |
| 熊乙, 许庆方, 玉柱, 等. 不同产地燕麦干草养分及饲用价值. 草业科学, 2018, 35(10): 2457-2462. | |
| 28 | Lincoln T, Eduardo Z. Plant physiology (Fourth Edition). Song C P, Wang X L,translation. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. |
| Lincoln T, Eduardo Z. 植物生理学(第四版). 宋纯鹏, 王学路, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. | |
| 29 | Ozier-lafontaine H, Lesueur-jannoyer M. Sustainable agriculture reviews 14. Berlin: Springer, 2014. |
| 30 | Mu Y, Geng Y B. The element content characteristics of main species in Leymus chinensis grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. Ecology and Environment, 2015, 24(7): 1118-1124. |
| 母悦, 耿元波. 内蒙古羊草草原植物营养元素的含量特征. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(7): 1118-1124. | |
| 31 | Liu Z Y, Wang X G, Wei H W, et al. Effects of nitrogen supplementation on forage yield and quality of a degraded grassland in Hulunbuir, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(9): 2992-2998. |
| 刘卓艺, 王晓光, 魏海伟, 等. 氮素补给对呼伦贝尔草甸草原退化草地牧草产量和品质的影响. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(9): 2992-2998. | |
| 32 | Wang Q H, Li C, Pang Z, et al. Poisonous weeds in chinese grassland and control technology. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(5): 831-841. |
| 王庆海, 李翠, 庞卓, 等. 中国草地主要有毒植物及其防控技术. 草地学报, 2013, 21(5): 831-841. | |
| 33 | Güsewell S, Lenedic C. Effect of winter mowing on vegetation success in a lake shore fen. Applied Vegetation Science, 2004, 7(1): 41-48. |
| 34 | Antonsen H, Olsson P A. Relative importance of burning, mowing and species translocation in the restoration of a former boreal hayfield: Responses of plant diversity and the microbial community. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 42(2): 337-347. |
| 35 | Huhta A P, Rautio P, Tuomi J, et al. Restorative mowing on an abandoned semi-natural meadow: Short-term and predicted long-term effects. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2009, 12(5): 677-686. |
| 36 | Zobel M, Osus M, Liira J, et al. Is small-scale species richness limited by seed availability or microsite availability? Ecology, 2000, 81(12): 3274-3282. |
| 37 | Dee J R, Thomas S M, Thompson S D, et al. Long-term late season mowing maintains diversity in southern US tallgrass prairie invaded by Bothriochloa ischaemum. Applied Vegetation Science, 2016, 19(3): 442-453. |
| 38 | Early D M, Provenza F D. Food flavor and nutritional characteristics alter dynamics of food preference in lambs. Journal of Animal Science, 1998, 76(3): 728-734. |
| 39 | Sergei S, Nina B, Andreas L, et al. Economic benefits from plant species diversity in intensively managed grasslands. Ecological Economics, 2020, 168(2): 1-12. |
| 40 | Yao X X, Gong X Y, Zhang L P, et al. Effects of grazing and long-term fencing on nutritive values of dominant species in alpine meadow of Qilian Mountains. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(6): 1354-1362. |
| 姚喜喜, 宫旭胤, 张利平, 等. 放牧和长期围封对祁连山高寒草甸优势牧草营养品质的影响. 草地学报, 2018, 26(6): 1354-1362. |
| [1] | 吴勇, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 童长春. 河西荒漠灌区紫花苜蓿施肥效应及其基于数据包络分析法的经济效益研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 94-105. |
| [2] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 于铁峰. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| [3] | 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 吐尔逊·吐尔洪, 涂振东, 王卉, 山其米克, 艾克拜尔·伊拉洪. 长期不同施肥处理对连作高粱生长规律及产量的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 81-92. |
| [4] | 徐绮雯, 马淑敏, 朱波, 张小短, 邢毅, 段美春, 王龙昌. 生物炭与化肥配施对紫色土肥力与微生物特征及油菜产量品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 121-131. |
| [5] | 游永亮, 李源, 赵海明, 武瑞鑫, 刘贵波. 海河平原区施氮磷肥对饲用小黑麦生产性能及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 137-146. |
| [6] | 方彦杰, 张绪成, 于显枫, 侯慧芝, 王红丽, 马一凡, 张国平, 雷康宁. 地膜覆盖和施肥对半干旱区苦荞土壤水分利用及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 46-56. |
| [7] | 张永亮, 于铁峰, 郝凤, 高凯. 施肥与混播比例对豆禾混播牧草产量及氮磷钾利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 91-101. |
| [8] | 于铁峰, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 蒯佳琳. 西北干旱灌区紫花苜蓿高产田施肥效应及推荐施肥量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 15-27. |
| [9] | 张礼军, 鲁清林, 白斌, 汪恒兴, 张文涛, 周刚, 白玉龙, 张耀辉. 施肥和地膜覆盖对黄土高原旱地冬小麦籽粒品质和产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 70-80. |
| [10] | 田梦, 孙宗玖, 李莹, 李培英, 谢开云. 蒿类荒漠草地土壤种子库特征及其萌发植物多样性对降水增加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 17-28. |
| [11] | 秦燕, 刘文辉, 何峰, 仝宗永, 李向林. 施肥与切根对退化羊草草原土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 5-14. |
| [12] | 谢军, 徐春丽, 陈轩敬, 王珂, 李丹萍, 张跃强, 石孝均. 不同施肥模式对玉米各器官碳氮累积和分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 50-58. |
| [13] | 张建军, 樊廷录, 赵刚, 党翼, 王磊, 王勇, 李尚中, 程万莉. 耕作方式与长期定位施肥对雨养农田冬小麦产量的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 175-186. |
| [14] | 王玉琴, 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 尹亚丽, 刘生财, 杨有武, 杨铭, 王宏生. 两种措施下施氮肥对狼毒型退化草地群落及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 177-186. |
| [15] | 黄岩, 多田琦, 遇瑶, 姚凤娇, 季婧, 邝肖, 崔国文, 胡国富. 施肥对提高秣食豆产量和饲用品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 211-217. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||