

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 71-84.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024195
马利利1( ), 蒋福祯2, 马玉寿1, 祁凯斌2, 贾顺斌3, 李正鹏2(
), 蒋福祯2, 马玉寿1, 祁凯斌2, 贾顺斌3, 李正鹏2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-22
修回日期:2024-07-15
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-01-02
通讯作者:
李正鹏
作者简介:E-mail: lipengzheng131@163.com基金资助:
Li-li MA1( ), Fu-zhen JIANG2, Yu-shou MA1, Kai-bin QI2, Shun-bin JIA3, Zheng-peng LI2(
), Fu-zhen JIANG2, Yu-shou MA1, Kai-bin QI2, Shun-bin JIA3, Zheng-peng LI2( )
)
Received:2024-05-22
Revised:2024-07-15
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-01-02
Contact:
Zheng-peng LI
摘要:
煤矸石作为采矿活动产生的固体废弃物,物理结构差,所含养分不能被植物直接有效利用。因此,煤矸石的基质改良是矿区生态恢复过程中的首要任务。本试验采用L9(34)正交设计,研究煤矸石<7 mm粒径占比(A)、有机肥施用量(B)、缓释尿素施用量(C)和播量(D)4个因素组合对植被生长和土壤养分的影响,并通过TOPSIS综合分析优选出最佳改良模式。结果表明:不同处理的地上生物量和土壤养分随着试验年限的增加而减少,尤其是土壤有机质、全氮、全磷、碱解氮、速效磷以及速效钾含量极显著减少,而全钾含量则显著增加。极差分析结果显示,缓释尿素施用量和播量是影响地上生物量的关键因素,而<7 mm粒径占比和有机肥施用量是影响土壤养分含量的关键因素。结合地上生物量和土壤肥力指标进行TOPSIS综合分析得出,T2(A1B2C2D2)处理(<7 mm粒径占比为0,有机肥施用量为羊板粪30 m3·hm-2 +商品有机肥15 t·hm-2,缓释尿素施用量为60 kg·hm-2,播量为120 kg·hm-2)时综合效果最好。该研究结果可为木里矿区生态修复提供参考依据。
马利利, 蒋福祯, 马玉寿, 祁凯斌, 贾顺斌, 李正鹏. 粒径配比、施肥量以及播量耦合对矿区煤矸石基质的改良效果[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 71-84.
Li-li MA, Fu-zhen JIANG, Yu-shou MA, Kai-bin QI, Shun-bin JIA, Zheng-peng LI. Effect of particle size ratio, fertilizer application amount, and seeding rate combinations coal gangue matrix properties in restoration of a mining area[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(3): 71-84.

图1 采样点及试验样地位置XN、HD、HN1、HX、HB、HN2、GL、YS分别代表西宁市、海东市、海南藏族自治州、海西蒙古族藏族自治州、海北藏族自治州、黄南藏族自治州、果洛藏族自治州、玉树藏族自治州。基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)333号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。The map depicts Xining City (XN), Haidong City (HD), Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (HN1), Haixi Mongolian Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (HX), Haibei Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (HB), Huangnan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (HN2), Goluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (GL), and Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (YS). Based on the standard map service GS(2019)333 website of the Ministry of Natural Resources Standard Map Service, with no modifications to the base map boundary.
Fig.1 Location map of sampling points and test plots
处理 Treatment | <7 mm粒径占比 Proportion of particle size less than 7 mm (A, % ) | 有机肥施用量(羊板粪+商品有机肥) Amount of organic fertilizer applied (sheep manure+commercial organic fertilizer) (B, m3·hm-2+t·hm-2) | 缓释尿素施用量 Amount of slow-release urea applied (C, kg·hm-2) | 播量 Seeding rate (D, kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1(A1B1C1D1) | 0(A1) | 15+7.5(B1) | 30(C1) | 60(D1) |
| T2(A1B2C2D2) | 0(A1) | 30+15(B2) | 60(C2) | 120(D2) |
| T3(A1B3C3D3) | 0(A1) | 45+22.5(B3) | 90(C3) | 180(D3) |
| T4(A2B1C2D3) | 25(A2) | 15+7.5(B1) | 60(C2) | 180(D3) |
| T5(A2B2C3D1) | 25(A2) | 30+15(B2) | 90(C3) | 60(D1) |
| T6(A2B3C1D2) | 25(A2) | 45+22.5(B3) | 30(C1) | 120(D2) |
| T7(A3B1C3D2) | 50(A3) | 15+7.5(B1) | 90(C3) | 120(D2) |
| T8(A3B2C1D3) | 50(A3) | 30+15(B2) | 30(C1) | 180(D3) |
| T9(A3B3C2D1) | 50(A3) | 45+22.5(B3) | 60(C2) | 60(D1) |
表1 正交试验
Table 1 The orthogonal tests
处理 Treatment | <7 mm粒径占比 Proportion of particle size less than 7 mm (A, % ) | 有机肥施用量(羊板粪+商品有机肥) Amount of organic fertilizer applied (sheep manure+commercial organic fertilizer) (B, m3·hm-2+t·hm-2) | 缓释尿素施用量 Amount of slow-release urea applied (C, kg·hm-2) | 播量 Seeding rate (D, kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1(A1B1C1D1) | 0(A1) | 15+7.5(B1) | 30(C1) | 60(D1) |
| T2(A1B2C2D2) | 0(A1) | 30+15(B2) | 60(C2) | 120(D2) |
| T3(A1B3C3D3) | 0(A1) | 45+22.5(B3) | 90(C3) | 180(D3) |
| T4(A2B1C2D3) | 25(A2) | 15+7.5(B1) | 60(C2) | 180(D3) |
| T5(A2B2C3D1) | 25(A2) | 30+15(B2) | 90(C3) | 60(D1) |
| T6(A2B3C1D2) | 25(A2) | 45+22.5(B3) | 30(C1) | 120(D2) |
| T7(A3B1C3D2) | 50(A3) | 15+7.5(B1) | 90(C3) | 120(D2) |
| T8(A3B2C1D3) | 50(A3) | 30+15(B2) | 30(C1) | 180(D3) |
| T9(A3B3C2D1) | 50(A3) | 45+22.5(B3) | 60(C2) | 60(D1) |
项目 Items | 全氮Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 有机质Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石Coal gangue | 1.5 | 0.7 | 27.3 | 12.4 | 7.8 | 189.2 | 127.8 |
| 羊板粪Sheep manure | 11.1 | 3.7 | 13.0 | - | - | - | 400.8 |
| 商品有机肥Commercial organic fertilizer | 23.1 | 12.3 | 16.7 | - | - | - | 354.7 |
表2 煤矸石、羊板粪和有机肥的基本化学性质
Table 2 Basic chemical property of coal gangue, sheep manure and organic fertilizer
项目 Items | 全氮Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 有机质Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石Coal gangue | 1.5 | 0.7 | 27.3 | 12.4 | 7.8 | 189.2 | 127.8 |
| 羊板粪Sheep manure | 11.1 | 3.7 | 13.0 | - | - | - | 400.8 |
| 商品有机肥Commercial organic fertilizer | 23.1 | 12.3 | 16.7 | - | - | - | 354.7 |
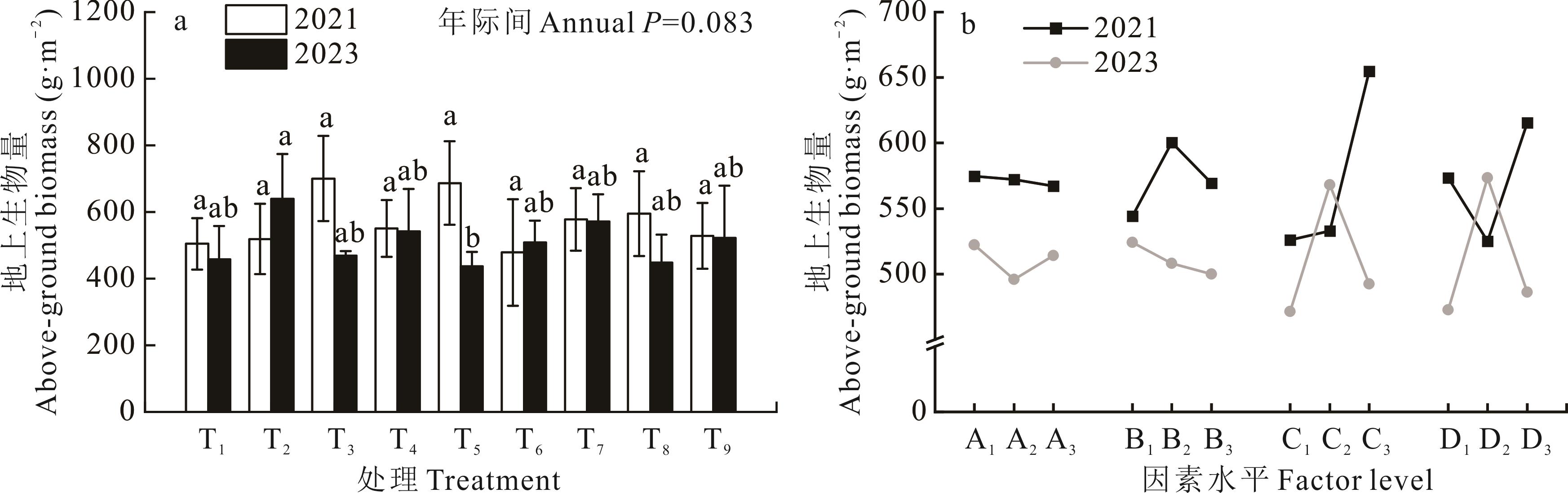
图2 不同处理和不同因素水平对地上生物量的影响a为不同处理下地上生物量变化,b为正交效应曲线。A代表<7 mm粒径占比,B代表有机肥施用量,C代表缓释尿素施用量,D代表播量,A1、A2和A3代表<7 mm粒径占比因素下不同水平;B1、B2和B3代表有机肥施用量因素下的不同水平;C1、C2和C3代表缓释尿素施用量因素下的不同水平;D1、D2和D3代表播量因素下的不同水平。不同小写字母代表同一年份不同处理间在0.05水平下差异显著,下同。 a is the change of aboveground biomass under different treatments, b is the orthogonal effect curve. A represents the proportion of <7 mm particle size, B represents the amount of organic fertilizer applied, C represents the amount of slow-release urea applied, and D represents the seeding rate. Different levels of the factor of <7 mm particle size are denoted as A1, A2, and A3, while different levels of organic fertilizer applied are denoted as B1, B2, and B3, and different levels of slow-release urea applied are denoted as C1, C2, and C3. Similarly, different levels of sowing amount are denoted as D1, D2, and D3. Lowercase letters are used to indicate significant differences among treatments in the same year at the 0.05 level, the same below.
Fig.2 The effects of different treatments and factor level on above-ground biomass
参数 Parameter | 2021 | 2023 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| K1 | 574.56 | 544.35 | 526.10 | 573.41 | 522.16 | 524.08 | 471.47 | 472.62 |
| K2 | 572.17 | 600.27 | 532.90 | 525.10 | 495.88 | 508.05 | 568.09 | 573.27 |
| K3 | 567.15 | 569.25 | 654.89 | 615.37 | 513.98 | 499.89 | 492.46 | 486.13 |
| R | 7.41 | 55.92 | 128.79 | 90.27 | 26.28 | 24.18 | 96.63 | 100.65 |
| P | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
表3 地上生物量的极差分析
Table 3 Range analysis of above-ground biomass
参数 Parameter | 2021 | 2023 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| K1 | 574.56 | 544.35 | 526.10 | 573.41 | 522.16 | 524.08 | 471.47 | 472.62 |
| K2 | 572.17 | 600.27 | 532.90 | 525.10 | 495.88 | 508.05 | 568.09 | 573.27 |
| K3 | 567.15 | 569.25 | 654.89 | 615.37 | 513.98 | 499.89 | 492.46 | 486.13 |
| R | 7.41 | 55.92 | 128.79 | 90.27 | 26.28 | 24.18 | 96.63 | 100.65 |
| P | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
指标 Index | 参数 Parameter | 2021 | 2023 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | ||
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | K1 | 136.18 | 134.40 | 134.50 | 131.36 | 85.48 | 81.19 | 88.49 | 87.64 |
| K2 | 134.74 | 133.79 | 130.24 | 134.89 | 89.46 | 89.90 | 86.50 | 89.47 | |
| K3 | 138.12 | 140.85 | 144.29 | 142.79 | 89.15 | 93.00 | 89.11 | 86.99 | |
| R | 3.38 | 7.05 | 14.06 | 11.43 | 3.97 | 11.81 | 2.61 | 2.48 | |
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | K1 | 4.38 | 4.78 | 4.82 | 4.54 | 1.95 | 1.71 | 2.06 | 2.14 |
| K2 | 4.78 | 4.63 | 4.59 | 4.90 | 2.30 | 2.25 | 2.12 | 2.16 | |
| K3 | 5.22 | 4.96 | 4.96 | 4.93 | 2.10 | 2.39 | 2.17 | 2.05 | |
| R | 0.84 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | K1 | 1.78 | 1.93 | 1.89 | 1.91 | 1.35 | 1.22 | 1.32 | 1.28 |
| K2 | 1.90 | 1.93 | 1.88 | 1.89 | 1.38 | 1.35 | 1.37 | 1.41 | |
| K3 | 2.08 | 1.89 | 1.98 | 1.95 | 1.32 | 1.48 | 1.35 | 1.36 | |
| R | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.13 | |
全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | K1 | 23.27 | 23.05 | 22.84 | 23.48 | 24.69 | 25.01 | 24.17 | 24.50 |
| K2 | 23.37 | 23.48 | 23.05 | 22.84 | 23.47 | 23.77 | 24.09 | 24.29 | |
| K3 | 22.52 | 22.62 | 23.27 | 22.84 | 24.28 | 23.66 | 24.18 | 23.65 | |
| R | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 0.64 | 1.22 | 1.34 | 0.10 | 0.85 | |
碱解氮 Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | K1 | 186.44 | 206.33 | 202.89 | 220.89 | 52.89 | 45.22 | 50.67 | 57.22 |
| K2 | 202.33 | 213.11 | 207.11 | 190.22 | 56.44 | 62.44 | 60.44 | 54.56 | |
| K3 | 240.11 | 209.44 | 218.89 | 217.78 | 57.00 | 58.67 | 55.22 | 54.56 | |
| R | 53.67 | 6.78 | 16.00 | 30.67 | 4.11 | 17.22 | 9.78 | 2.67 | |
速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | K1 | 31.14 | 42.18 | 42.56 | 42.57 | 15.13 | 10.96 | 13.51 | 15.00 |
| K2 | 47.98 | 42.58 | 35.90 | 46.66 | 14.31 | 16.39 | 15.96 | 13.82 | |
| K3 | 49.66 | 44.02 | 50.32 | 39.56 | 13.76 | 15.86 | 13.73 | 14.38 | |
| R | 18.51 | 1.84 | 14.42 | 7.10 | 1.38 | 5.43 | 2.44 | 1.18 | |
速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | K1 | 510.22 | 573.67 | 570.00 | 569.44 | 225.44 | 206.00 | 223.56 | 235.33 |
| K2 | 552.78 | 559.00 | 538.89 | 549.22 | 227.33 | 238.89 | 231.67 | 223.67 | |
| K3 | 615.33 | 545.67 | 569.44 | 559.67 | 237.22 | 245.11 | 234.78 | 231.00 | |
| R | 105.11 | 28.00 | 31.11 | 20.22 | 11.78 | 39.11 | 11.22 | 11.67 | |
表4 土壤有机质和速效养分的极差分析
Table 4 Range analysis of soil organic matter and available nutrients
指标 Index | 参数 Parameter | 2021 | 2023 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | ||
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | K1 | 136.18 | 134.40 | 134.50 | 131.36 | 85.48 | 81.19 | 88.49 | 87.64 |
| K2 | 134.74 | 133.79 | 130.24 | 134.89 | 89.46 | 89.90 | 86.50 | 89.47 | |
| K3 | 138.12 | 140.85 | 144.29 | 142.79 | 89.15 | 93.00 | 89.11 | 86.99 | |
| R | 3.38 | 7.05 | 14.06 | 11.43 | 3.97 | 11.81 | 2.61 | 2.48 | |
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | K1 | 4.38 | 4.78 | 4.82 | 4.54 | 1.95 | 1.71 | 2.06 | 2.14 |
| K2 | 4.78 | 4.63 | 4.59 | 4.90 | 2.30 | 2.25 | 2.12 | 2.16 | |
| K3 | 5.22 | 4.96 | 4.96 | 4.93 | 2.10 | 2.39 | 2.17 | 2.05 | |
| R | 0.84 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | K1 | 1.78 | 1.93 | 1.89 | 1.91 | 1.35 | 1.22 | 1.32 | 1.28 |
| K2 | 1.90 | 1.93 | 1.88 | 1.89 | 1.38 | 1.35 | 1.37 | 1.41 | |
| K3 | 2.08 | 1.89 | 1.98 | 1.95 | 1.32 | 1.48 | 1.35 | 1.36 | |
| R | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.13 | |
全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | K1 | 23.27 | 23.05 | 22.84 | 23.48 | 24.69 | 25.01 | 24.17 | 24.50 |
| K2 | 23.37 | 23.48 | 23.05 | 22.84 | 23.47 | 23.77 | 24.09 | 24.29 | |
| K3 | 22.52 | 22.62 | 23.27 | 22.84 | 24.28 | 23.66 | 24.18 | 23.65 | |
| R | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 0.64 | 1.22 | 1.34 | 0.10 | 0.85 | |
碱解氮 Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | K1 | 186.44 | 206.33 | 202.89 | 220.89 | 52.89 | 45.22 | 50.67 | 57.22 |
| K2 | 202.33 | 213.11 | 207.11 | 190.22 | 56.44 | 62.44 | 60.44 | 54.56 | |
| K3 | 240.11 | 209.44 | 218.89 | 217.78 | 57.00 | 58.67 | 55.22 | 54.56 | |
| R | 53.67 | 6.78 | 16.00 | 30.67 | 4.11 | 17.22 | 9.78 | 2.67 | |
速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | K1 | 31.14 | 42.18 | 42.56 | 42.57 | 15.13 | 10.96 | 13.51 | 15.00 |
| K2 | 47.98 | 42.58 | 35.90 | 46.66 | 14.31 | 16.39 | 15.96 | 13.82 | |
| K3 | 49.66 | 44.02 | 50.32 | 39.56 | 13.76 | 15.86 | 13.73 | 14.38 | |
| R | 18.51 | 1.84 | 14.42 | 7.10 | 1.38 | 5.43 | 2.44 | 1.18 | |
速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | K1 | 510.22 | 573.67 | 570.00 | 569.44 | 225.44 | 206.00 | 223.56 | 235.33 |
| K2 | 552.78 | 559.00 | 538.89 | 549.22 | 227.33 | 238.89 | 231.67 | 223.67 | |
| K3 | 615.33 | 545.67 | 569.44 | 559.67 | 237.22 | 245.11 | 234.78 | 231.00 | |
| R | 105.11 | 28.00 | 31.11 | 20.22 | 11.78 | 39.11 | 11.22 | 11.67 | |
年份 Year | 因素 Factor | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | <7 mm粒径占比Proportion of particle size less than 7 mm (A) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | * | NS |
| 有机肥施用量Amount of organic fertilizer applied (B) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 缓释尿素施用量Amount of slow-release urea applied (C) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 播量Seeding rate (D) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 2023 | <7 mm粒径占比Proportion of particle size less than 7 mm (A) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 有机肥施用量Amount of organic fertilizer applied (B) | * | ** | ** | NS | * | * | ** | |
| 缓释尿素施用量Amount of slow-release urea applied (C) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 播量Seeding rate (D) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
表5 不同因素下土壤养分指标的方差分析
Table 5 Variance analysis of different factors on soil nutrient indicators
年份 Year | 因素 Factor | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | <7 mm粒径占比Proportion of particle size less than 7 mm (A) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | * | NS |
| 有机肥施用量Amount of organic fertilizer applied (B) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 缓释尿素施用量Amount of slow-release urea applied (C) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 播量Seeding rate (D) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 2023 | <7 mm粒径占比Proportion of particle size less than 7 mm (A) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 有机肥施用量Amount of organic fertilizer applied (B) | * | ** | ** | NS | * | * | ** | |
| 缓释尿素施用量Amount of slow-release urea applied (C) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 播量Seeding rate (D) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 有机质 Organic matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 权重Weight | 0.1798 | 0.1263 | 0.1227 | 0.1458 | 0.1317 | 0.1510 | 0.1527 |
表6 土壤养分指标权重值
Table 6 The weight value of soil nutrient index
处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 有机质 Organic matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 权重Weight | 0.1798 | 0.1263 | 0.1227 | 0.1458 | 0.1317 | 0.1510 | 0.1527 |
处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 有机质 Organic matter | 土壤肥力综合指数 Integrated fertility index (IFI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1.52 | 1.12 | 25.93 | 39.67 | 11.40 | 200.33 | 78.71 | 0.2411 |
| T2 | 2.14 | 1.44 | 24.40 | 64.00 | 18.10 | 229.67 | 87.26 | 0.6989 |
| T3 | 2.21 | 1.49 | 23.74 | 55.00 | 15.90 | 246.33 | 90.48 | 0.6856 |
| T4 | 1.82 | 1.27 | 23.77 | 50.33 | 12.40 | 206.00 | 80.04 | 0.3295 |
| T5 | 2.52 | 1.32 | 23.48 | 65.00 | 16.23 | 246.33 | 92.01 | 0.7388 |
| T6 | 2.56 | 1.54 | 23.16 | 54.00 | 14.30 | 229.67 | 96.32 | 0.7091 |
| T7 | 1.79 | 1.25 | 25.32 | 45.67 | 9.07 | 211.67 | 84.83 | 0.3632 |
| T8 | 2.11 | 1.30 | 23.44 | 58.33 | 14.83 | 240.67 | 90.44 | 0.5953 |
| T9 | 2.40 | 1.40 | 24.09 | 67.00 | 17.37 | 259.33 | 92.20 | 0.8215 |
表7 不同处理组土壤养分综合评价
Table 7 Comprehensive evaluation of soil nutrients in different treatment groups
处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 有机质 Organic matter | 土壤肥力综合指数 Integrated fertility index (IFI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1.52 | 1.12 | 25.93 | 39.67 | 11.40 | 200.33 | 78.71 | 0.2411 |
| T2 | 2.14 | 1.44 | 24.40 | 64.00 | 18.10 | 229.67 | 87.26 | 0.6989 |
| T3 | 2.21 | 1.49 | 23.74 | 55.00 | 15.90 | 246.33 | 90.48 | 0.6856 |
| T4 | 1.82 | 1.27 | 23.77 | 50.33 | 12.40 | 206.00 | 80.04 | 0.3295 |
| T5 | 2.52 | 1.32 | 23.48 | 65.00 | 16.23 | 246.33 | 92.01 | 0.7388 |
| T6 | 2.56 | 1.54 | 23.16 | 54.00 | 14.30 | 229.67 | 96.32 | 0.7091 |
| T7 | 1.79 | 1.25 | 25.32 | 45.67 | 9.07 | 211.67 | 84.83 | 0.3632 |
| T8 | 2.11 | 1.30 | 23.44 | 58.33 | 14.83 | 240.67 | 90.44 | 0.5953 |
| T9 | 2.40 | 1.40 | 24.09 | 67.00 | 17.37 | 259.33 | 92.20 | 0.8215 |
处理 Treatment | 正理想解距离 Distance of positive ideal solution (Di+ ) | 负理想解距离 Distance of negative ideal solution (Di- ) | 相对接近度 Relative proximity (Ci ) | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.9333 | 0.0866 | 0.0849 | 9 |
| T2 | 0.1303 | 0.9252 | 0.8765 | 1 |
| T3 | 0.6831 | 0.4873 | 0.4163 | 5 |
| T4 | 0.6404 | 0.4277 | 0.4004 | 7 |
| T5 | 0.7918 | 0.5290 | 0.4005 | 6 |
| T6 | 0.5219 | 0.5702 | 0.5221 | 3 |
| T7 | 0.5460 | 0.5556 | 0.5044 | 4 |
| T8 | 0.7799 | 0.3791 | 0.3271 | 8 |
| T9 | 0.4386 | 0.7084 | 0.6176 | 2 |
表8 不同处理TOPSIS综合评价结果
Table 8 Comprehensive evaluation results of TOPSIS for different treatments
处理 Treatment | 正理想解距离 Distance of positive ideal solution (Di+ ) | 负理想解距离 Distance of negative ideal solution (Di- ) | 相对接近度 Relative proximity (Ci ) | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.9333 | 0.0866 | 0.0849 | 9 |
| T2 | 0.1303 | 0.9252 | 0.8765 | 1 |
| T3 | 0.6831 | 0.4873 | 0.4163 | 5 |
| T4 | 0.6404 | 0.4277 | 0.4004 | 7 |
| T5 | 0.7918 | 0.5290 | 0.4005 | 6 |
| T6 | 0.5219 | 0.5702 | 0.5221 | 3 |
| T7 | 0.5460 | 0.5556 | 0.5044 | 4 |
| T8 | 0.7799 | 0.3791 | 0.3271 | 8 |
| T9 | 0.4386 | 0.7084 | 0.6176 | 2 |
| 1 | Fan L Y. Effect and assessment of vegetation restoration on soil quality in abandoned wasteland. Shanxi Forestry Science and Technology, 2014, 43(1): 25-27, 30. |
| 樊兰英. 煤矿废弃地植被恢复对土壤质量的影响及评价.山西林业科技, 2014, 43(1): 25-27, 30. | |
| 2 | Yan S. Study on the artificial re-vegetation techniques in coal gangue. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2015. |
| 闫帅. 煤矸石山人工植被恢复技术研究.北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2015. | |
| 3 | Gu D M. Research of coal gangue storage impact on surface and shallow groundwater environment-A case of Panji mining area in Huainan. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2015. |
| 谷得明. 煤矸石堆存对地表与浅层地下水环境的影响研究——以淮南潘集矿区为例. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2015. | |
| 4 | Wang T, Zhang M, Xu H, et al. Soil fertility and heavy metal risk assessment in Jvhugeng mining area, Muli Coalfield, Qinghai Province. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(4): 113-120. |
| 王佟, 章梅, 徐辉, 等. 青海木里煤田聚乎更矿区土壤肥力及重金属风险评价. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(4): 113-120. | |
| 5 | Zhao Y C, Zhang J Y, Chou C L, et al. Trace element emissions from spontaneous combustion of gob piles in coal mines, Shanxi, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2008, 73(1): 52-62. |
| 6 | Wang S B, Luo K, Wang X, et al. Estimate of sulfur, arsenic, mercury, fluorine emissions due to spontaneous combustion of coal gangue: An important part of Chinese emission inventories. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 209(2): 107-113. |
| 7 | Li S Q, Liber K. Influence of different re-vegetation choices on plant community and soil development nine years after initial planting on a reclaimed coal gob pile in the Shanxi mining area, China. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 618: 1314-1323. |
| 8 | Zhang L, Wang J M, Bai Z K, et al. Effects of vegetation on runoff and soil erosion on reclaimed land in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Catena, 2015, 128: 44-53. |
| 9 | Sheoran V, Sheoran A S, Poonia P. Soil reclamation of abandoned mine land by revegetation: A review. International Journal of Soil, Sediment and Water, 2010, 3(2): 1-20. |
| 10 | Ni H B, Zhang L P, Wu X Y, et al. A research progress on soil reconstruction and property restoration in mine regions. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2007, 38(2): 399-403. |
| 倪含斌, 张丽萍, 吴希媛, 等. 矿区废弃地土壤重构与性能恢复研究进展. 土壤通报, 2007, 38(2): 399-403. | |
| 11 | Han X N, Dong Y, Geng Y Q, et al. Influence of coal gangue mulching on chemical characteristics of soil in the mining area. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(11): 2251-2256. |
| 韩秀娜, 董颖, 耿玉清, 等. 覆盖煤矸石对矿区土壤养分及盐分特征的影响. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2251-2256. | |
| 12 | Niu Y F, Zhou Z C. Progress in the study of site conditions and reclamation technologies of coal gangue dump. Environmental Protection Science, 2015, 41(5): 147-152. |
| 牛桠枫, 周正朝. 煤矸石山立地条件及复垦技术研究进展. 环境保护科学, 2015, 41(5): 147-152. | |
| 13 | Luo K. Study on the soil fertility improvement of mining wasteland by plants under different fertilizations. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016. |
| 罗珂. 不同施肥条件下植物对矿山废弃地土壤肥力改良的研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. | |
| 14 | Yang X G, Li X L, Ma P P, et al. Effects of fertilizer application rate on vegetation and soil restoration of coal mine spoils in an alpine mining area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(8): 98-108. |
| 杨鑫光, 李希来, 马盼盼, 等. 不同施肥水平下高寒矿区煤矸石山植被和土壤恢复效果研究. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 98-108. | |
| 15 | Bai Z K, Zhou W, Wang J M, et al. Rethink on ecosystem restoration and rehabilitation of mining areas. China Land Science, 2018, 32(11): 1-9. |
| 白中科, 周伟, 王金满, 等. 再论矿区生态系统恢复重建. 中国土地科学, 2018, 32(11): 1-9. | |
| 16 | Feng G B, Ruan M Y, Li H B, et al. Analysis on ecological reconstruction technology and benefit of vegetation in gangue dump of Changcun Coal Mine. China Coal, 2021, 47(2): 76-82. |
| 冯国宝, 阮梦颖, 李海波, 等. 浅析常村煤矿矸石山植被生态重建技术及效益. 中国煤炭, 2021, 47(2): 76-82. | |
| 17 | Yang X G, Li X L, Jin L Q, et al. Effectiveness of different artificial restoration measures for soil and vegetation recovery on coal mine tailings in an alpine area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(3): 1-11. |
| 杨鑫光, 李希来, 金立群, 等. 不同人工恢复措施下高寒矿区煤矸石山植被和土壤恢复效果研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 1-11. | |
| 18 | Bao S D. Soil agro-chemical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 19 | Jiang B, Wang S T, Sun Z B, et al. Evaluation of cultivated land soil fertility based on membership function and principal component analysis. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(2): 22-27. |
| 姜冰, 王松涛, 孙增兵, 等. 基于隶属度函数和主成分分析的耕地土壤肥力评价. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(2): 22-27. | |
| 20 | Xu Y Z, Hou Y M, Yuan H, et al. Soil fertility evaluation of Chinese fir planted forest based on Nemerow method and membership function in Hubei. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021, 41(5): 1-11, 28. |
| 许业洲, 侯义梅, 袁慧, 等. 基于Nemerow法和隶属度函数的湖北杉木人工林土壤肥力评价. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 1-11, 28. | |
| 21 | Luo B S, Zhong J H, Chen J J. Integrated digitization evaluation on soil fertility. Soils, 2004, 36(1): 104-106. |
| 骆伯胜, 钟继洪, 陈俊坚. 土壤肥力数值化综合评价研究. 土壤, 2004, 36(1): 104-106. | |
| 22 | Yang X C, Ye H C, Li D M, et al. Assessment of red soil upland fertility in long-term fertilization based on fuzzy mathematics and principal component analysis. Soils and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2018(3): 79-84. |
| 杨旭初, 叶会财, 李大明, 等. 基于模糊数学和主成分分析的长期施肥红壤旱地土壤肥力评价. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018(3): 79-84. | |
| 23 | Wu Y H, Tian X H, Tong Y A, et al. Assessment of integrated soil fertility index based on principal components analysis. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(1): 173-180. |
| 吴玉红, 田霄鸿, 同延安, 等. 基于主成分分析的土壤肥力综合指数评价.生态学杂志, 2010, 29(1): 173-180. | |
| 24 | Wen Y C, Li Y Q, Yuan L, et al. Comprehensive assessment methodology of characteristics of soil fertility under different fertilization regimes in North China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(7): 91-99. |
| 温延臣, 李燕青, 袁亮, 等. 长期不同施肥制度土壤肥力特征综合评价方法. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(7): 91-99. | |
| 25 | Wang H, Chen L, Chen K, et al. Multi index comprehensive evaluation method and selection of weight coefficient. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2007, 23(5): 583-589. |
| 王晖, 陈丽, 陈垦, 等. 多指标综合评价方法及权重系数的选择. 广东药学院学报, 2007, 23(5): 583-589. | |
| 26 | Yu X F, Fu D. Review of multi index comprehensive evaluation methods. Statistics and Decision, 2004(11): 119-121. |
| 虞晓芬, 傅玳. 多指标综合评价方法综述. 统计与决策, 2004(11): 119-121. | |
| 27 | Zhang R C, Wang D M, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of green substrates composed of coal gangue on the growth of Trifolium repens L. and its resistance to heavy metal pollution. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2018, 24(4): 908-914. |
| 张汝翀, 王冬梅, 张英, 等. 煤矸石绿化基质对白三叶草生长及其抵御重金属污染的影响.应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(4): 908-914. | |
| 28 | Xu L, Zhou X C, Wang D M. Progress on the reclamation of gangue waste area. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 3(3): 117-122. |
| 许丽, 周心澄, 王冬梅. 煤矸石废弃地复垦研究进展. 中国水土保持科学, 2005, 3(3): 117-122. | |
| 29 | Xie J Y, Zhang H F, Luo Y Q, et al. Driving factors of improving fertility and maize yields in the reclaimed soils by seven years of applied organic manure and chemical fertilizer. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(1): 150-160. |
| 谢钧宇, 张慧芳, 罗云琪, 等. 连续7年施有机肥和化肥提高复垦土壤上玉米产量的驱动因子. 农业工程学报, 2024, 40(1): 150-160. | |
| 30 | Nan Y C, Yang Y G, Wang Z Q, et al. Effects of coal gangue on soil property and plant growth in mining area. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(5): 1253-1262. |
| 南益聪, 杨永刚, 王泽青, 等. 煤矸石对矿区土壤特性与植物生长的影响. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(5): 1253-1262. | |
| 31 | Zhang Y F, Xu Y X, Tang J W, et al. Effects of sowing, fertilization and non-woven covering on vegetation restoration and soil temperature and humidity in alpine coalmine area. Qinghai Prataculture, 2022, 31(2): 2-6. |
| 张玉芳, 徐有学, 唐俊伟, 等. 播量和施肥及无纺布覆盖对高寒矿区植被恢复和土壤温湿度的影响. 青海草业, 2022, 31(2): 2-6. | |
| 32 | Jiang S X, Zhao P. Morphological structure and biomass allocation of Agriophyllum squarrosum in different habitats of east section of Hexi Corridor. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2023, 41(3): 248-256. |
| 姜生秀, 赵鹏. 河西走廊东段不同生境对沙米形态结构及生物量分配的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2023, 41(3): 248-256. | |
| 33 | Ma J L, Hao J T, Zhang Y Q, et al. Response of Macleaya cordata biomass and its distribution characteristics to nitrogen in reclamation area of coal mine. Pratacultural Science, 2024, 41(5): 1039-1047. |
| 马嘉丽, 郝嘉湉, 张永清, 等. 煤矿复垦区博落回生物量及其分配特征对氮的响应. 草业科学, 2024, 41(5): 1039-1047. | |
| 34 | Shaviv A, Mikkelsen R L. Controlled-release fertilizers to increase efficiency of nutrient use and minimize environmental degradation-A review. Fertilizer Research, 1993, 35(1/2): 1-12. |
| 35 | Wang Y L, Li C H, Wang J, et al. Application and prospect of slow/controlled release fertilizers in maize production. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(24): 254-257. |
| 王宜伦, 李潮海, 王瑾, 等. 缓/控释肥在玉米生产中的应用与展望. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(24): 254-257. | |
| 36 | Zhou L P, Yang L P, Bai Y L, et al. Comparison of several slow-released nitrogen fertilizers in ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization in summer maize field. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(6): 1449-1457. |
| 周丽平, 杨俐苹, 白由路, 等. 不同氮肥缓释化处理对夏玉米田间氨挥发和氮素利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(6): 1449-1457. | |
| 37 | Liu Z H, Zhang X, Xia Q, et al. Effects of phosphate fertilizer application and sowing rate on the dry matter content of multiple-cropping forage rape after wheat and soil fertility. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(10): 1446-1454. |
| 刘振华, 张霞, 夏清, 等. 磷肥与播量对麦后复种饲料油菜干物质量及土壤肥力的影响. 山西农业科学, 2022, 50(10): 1446-1454. | |
| 38 | Fang X M, Li Y S, Nie J, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and planting density on the leaf photosynthetic characteristics, agronomic traits and grain yield in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum M.). Field Crops Research, 2018, 219: 160-168. |
| 39 | Yang W Y, Li T F, Dong B, et al. Effects of seeding rate on rapeseed biological yield and soil nutrient in wheat stubble multiple cropping rape. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2017, 26(4): 583-587. |
| 杨文元, 李腾飞, 董博, 等. 播量对麦后复种油菜生物产量及耕层土壤养分的影响. 西北农业学报, 2017, 26(4): 583-587. | |
| 40 | Bai D S. Ecological reconstruction model and driving factors of soil hydrological properties optimization in gangue accumulation area. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2022. |
| 白东升. 煤矸石堆积区生态重构模式与土壤水文性质优化的驱动要素. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2022. | |
| 41 | Zhang R C. Effects of the improvement measures of coal gangue matrix on plant growth and heavy metal enrichment. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2018. |
| 张汝翀. 煤矸石基质改良措施对植物生长及重金属富集影响研究. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2018. | |
| 42 | Zhang Y G. Study on fertilization effect of mature Ziziphus jujuba ‘Junzao’ in Aksu. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 张亚鸽. 阿克苏成龄骏枣施肥效应研究. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2015. | |
| 43 | Ding J N, Li D P, Wu Z J, et al. Responses of soil physicochemical properties and biological activity to continuous application of slow/controlled releasing urea. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(7): 1769-1778. |
| 丁济娜, 李东坡, 武志杰, 等. 土壤理化性质与生物活性对持续施用缓/控释尿素肥料的响应. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(7): 1769-1778. | |
| 44 | Zhang Y H, Song Z L, Kong T, et al. Amelioration effect of coal gangue on physical and chemical properties of saline-alkaline soil. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(1): 195-204. |
| 张宇航, 宋子岭, 孔涛, 等. 煤矸石对盐碱土壤理化性质的改良效果. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(1): 195-204. | |
| 45 | Ke K E, Dong X Y, Zhou J X, et al. Evaluation of the formula for coal gangue ecological substrate and its fertility indexes. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2021(4): 308-317. |
| 柯凯恩, 董晓芸, 周金星, 等. 煤矸石生态基质的制备配方及其肥力特征研究. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(4): 308-317. | |
| 46 | Kong T, Ma Y, Liu M, et al. Effect of applying biological organic fertilizer on soil nutrients and soil microbes. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(4): 884-891. |
| 孔涛, 马瑜, 刘民, 等. 生物有机肥对土壤养分和土壤微生物的影响. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(4): 884-891. | |
| 47 | Zhang J Z, Wang Q C, Bian M W, et al. Effects of different planting years on soil nutrient evolution and variation characteristics of greenhouse vegetables. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 2022, 42(1): 77-82. |
| 张敬智, 王青川, 边明文, 等. 不同种植年限对设施蔬菜土壤养分演变规律及其变异特征的影响. 农业工程技术, 2022, 42(1): 77-82. | |
| 48 | Wander M M, Bollero G A. Soil quality assessment of tillage impacts in Illinois. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1999, 63(4): 961-971. |
| 49 | Zhang W X, Wang S X, Liu Z B, et al. Evaluating soil fertility improvement effects of chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizers in a red paddy soil using the soil fertility index. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(5): 777-790. |
| 张文学, 王少先, 刘增兵, 等. 基于土壤肥力质量综合指数评价化肥与有机肥配施对红壤稻田肥力的提升作用. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(5): 777-790. |
| [1] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 刘文新, 杨海军, 杨延成, 江智诚, 闫江超, 刘江慧. 短期氮、水添加和刈割对苦豆子型退化草地植物群落特征与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 41-55. |
| [2] | 王文虎, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 王凤宇, 李文. 青藏高原区8份老芒麦资源农艺性状与生产性能综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 123-132. |
| [3] | 杜文盼, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 杨莉, 张建贵, 史怡超, 张官禄. 根系分隔方式对燕麦/豌豆间作地上生物量、土壤养分及根系性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 25-36. |
| [4] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [5] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [6] | 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [7] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [8] | 王金兰, 王小军, 刘启林, 梁国玲, 琚泽亮, 石红梅, 汪小兵, 文培, 青梅然丁null, 李文. 不同燕麦品种在三江源区的生产性能和营养品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 83-95. |
| [9] | 郁国梁, 马紫荆, 吕自立, 刘彬. 海拔和植物群落共同调节天山中段南坡巴伦台地区天然草场土壤化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 68-78. |
| [10] | 康燕霞, 姜渊博, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 红豆草与无芒雀麦混播草地生产力提升的水分调控模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 115-128. |
| [11] | 路欣, 祁娟, 师尚礼, 车美美, 李霞, 独双双, 赛宁刚, 贾燕伟. 阔叶类草抑制剂与氮素配施对高寒草甸土壤特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 38-48. |
| [12] | 刘欢, 董凯, 仁增旺堆, 王敬龙, 刘云飞, 赵桂琴. 藏沙蒿与多年生禾草混播对西藏沙化草地植被及土壤真菌群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 45-57. |
| [13] | 许开宏, 施招, 马磊超, 王平, 陈昂, 王兴, 成明, 肖粤新, 王荣谭. 基于机载激光雷达与高景一号数据的草原地上生物量反演研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 40-49. |
| [14] | 郭芮, 伏帅, 侯蒙京, 刘洁, 苗春丽, 孟新月, 冯琦胜, 贺金生, 钱大文, 梁天刚. 基于Sentinel-2数据的青海门源县天然草地生物量遥感反演研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 15-29. |
| [15] | 史正军, 潘松, 冯世秀, 袁峰均. 园林废弃物地表覆盖处理对植物生长及土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 153-160. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||