

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 200-207.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021424
• 综合评述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-11-23
修回日期:2022-03-17
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2022-10-17
通讯作者:
刘志民
作者简介:E-mail: zmliu@iae.ac.cn基金资助:
Chao-qun BA1( ), Qun MA1, Hai-yang WANG2, Zhi-min LIU1(
), Qun MA1, Hai-yang WANG2, Zhi-min LIU1( )
)
Received:2021-11-23
Revised:2022-03-17
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2022-10-17
Contact:
Zhi-min LIU
摘要:
根茎克隆植物是克隆植物的一个类型,地下系统的特殊性赋予其独特的繁殖和生长方式,也赋予其对环境的特有适应能力。但是,受研究手段限制,人们对根茎克隆植物在表型可塑性、克隆整合、觅食行为和克隆分工等方面与其他类型克隆植物有何异同,这些行为对预防植物入侵、应对气候变化、进行退化生态系统恢复有何特殊意义尚不很清晰。鉴于此,通过梳理和总结前人工作,提出了根茎克隆植物研究面临的挑战。根茎克隆植物下一步研究重点应体现在下述方面:1)可塑性性状的选择与测定方法;2)环境因子对克隆整合的影响机制;3)综合植物特征和环境特征的觅食模型。
巴超群, 马群, 汪海洋, 刘志民. 根茎克隆植物研究面临的挑战[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 200-207.
Chao-qun BA, Qun MA, Hai-yang WANG, Zhi-min LIU. Challenges in research on rhizomatous clonal plants[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 200-207.
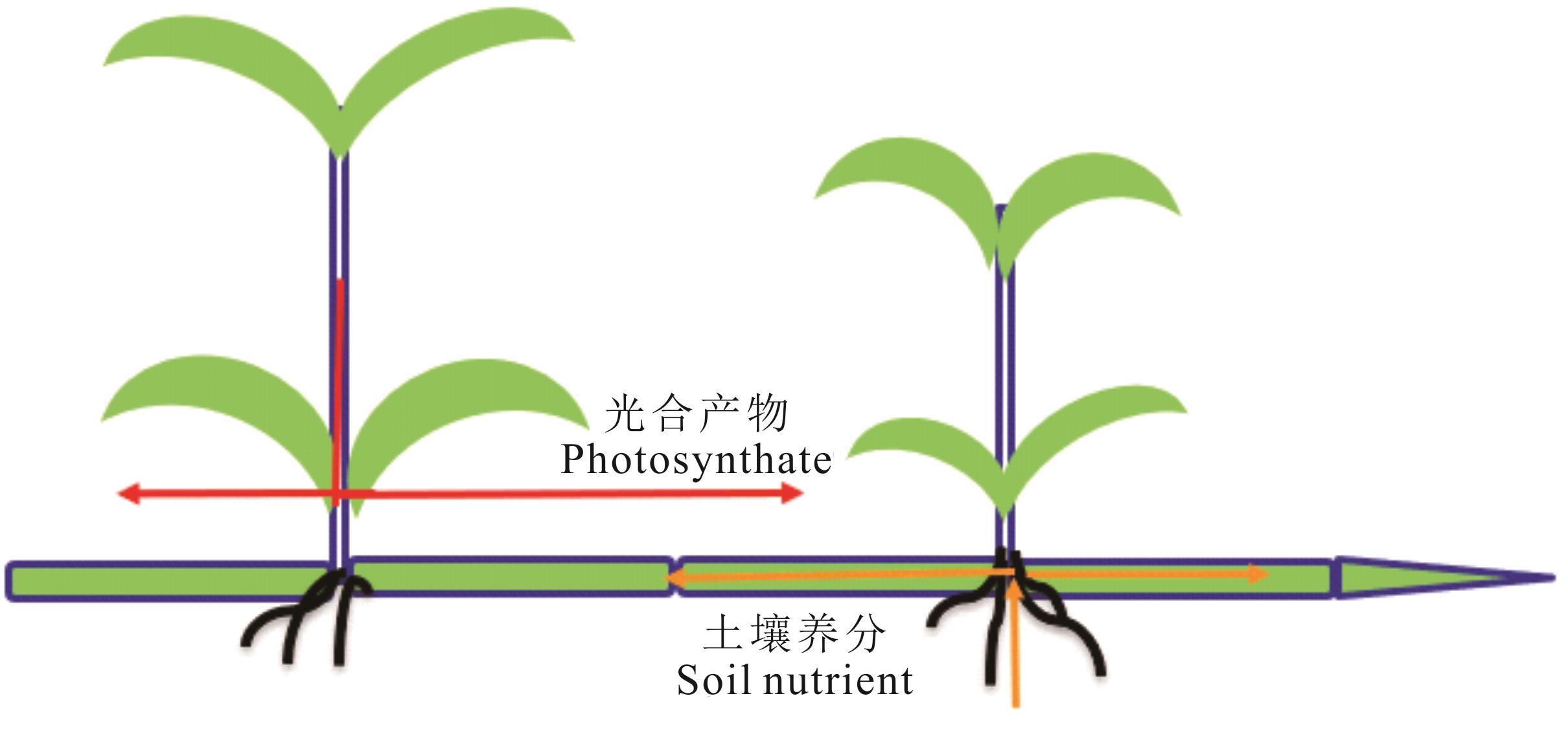
图1 光合产物和土壤养分在克隆分株间的克隆整合光照资源丰富生境中的分株(左)向光照资源缺乏生境中的分株(右)输送光合产物,土壤资源丰富生境中的分株(右)向土壤资源贫瘠生境中的分株(左)输送土壤养分。Ramets in light resource-rich habitats (left) deliver photosynthate to ramets in light resource-deficient habitats (right), and ramets in soil resource-rich habitats (right) deliver soil nutrients to ramets in soil resource-poor habitats (left).
Fig.1 Cloning integration of photosynthate and soil nutrients between clone ramets
| 1 | Dong M, Yu F H. Terms and concepts of clonal plant ecology. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(4): 689-694. |
| 董鸣, 于飞海. 克隆植物生态学术语和概念. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(4): 689-694. | |
| 2 | Zou Y C, Lv X G, Jiang M, et al. Adaptive phenotypic plasticity of clonal plant rhizomes in wetlands. Wetland Science, 2007, 5(4): 305-310. |
| 邹元春, 吕宪国, 姜明, 等. 湿地克隆植物根茎对变境适应的表型可塑性. 湿地科学, 2007, 5(4): 305-310. | |
| 3 | Dong M. Clonal growth in plants in relation to resource heterogeneity: Foraging behavior. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1996, 38(10): 828-835. |
| 4 | Li B, Yong S P. Grassland of China. Beijing: Science Press, 1990. |
| 李博, 雍世鹏. 中国的草原. 北京: 科学出版社出版, 1990. | |
| 5 | Su W H, Zhang N, Hou S G, et al. Morphology and clonal growth and reproduction of the plant rhizomes in wetland. Journal of Anyang Institute of Technology, 2008, 7(6): 23-26. |
| 苏文辉, 张楠, 侯绍刚, 等. 湿地植物根茎的形态特征及其克隆生长繁殖. 安阳工学院学报, 2008, 7(6): 23-26. | |
| 6 | Liu B, Liu Z M, Wang L, et al. The colonization of active sand dunes by rhizomatous plants through vegetative propagation and its role in vegetation restoration. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 44: 344-347. |
| 7 | Chen Y F, Yu F H, Zhang C Y, et al. Role of clonal growth of the rehizomatous grass Psammochloa villosa in patch dynamics of Mu Us sandy land. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(11): 1745-1750. |
| 陈玉福, 于飞海, 张称意, 等. 根茎禾草沙鞭的克隆生长与毛乌素沙地斑块动态中的作用. 生态学报, 2001, 21(11): 1745-1750. | |
| 8 | Deng Z, An S, Zhao C, et al. Sediment burial stimulates the growth and propagule production of Spartina alterniflora Loisel. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2008, 76(4): 818-826. |
| 9 | Lu P, Sang W G, Ma K P, et al. Differential responses of the activities of antioxidant enzymes to thermal stresses between two invasive Eupatorium species in China. Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 50(4): 393-401. |
| 10 | Gao F L, He Q S, Zhang Y D, et al. Effects of soil nutrient heterogeneity on the growth and invasion success of alien plants: A multi-species study. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2021, DOI: 10.3389/fevo.2020.619861. |
| 11 | Nelson L, Blumenthal D M, Williams D G, et al. Digging into the roots of belowground carbon cycling following seven years of prairie heating and CO2 enrichment (PHACE), Wyoming USA. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2017, 115: 169-177. |
| 12 | Ji L. Effect of grazing and mowing on soil respiration and soil microbialin communities in Leymus chinensis steppe of Inner Mongolia. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2021. |
| 纪磊. 放牧和割草对内蒙古羊草草原土壤呼吸及土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2021. | |
| 13 | Yi J, Li Q F, Gu A L, et al. Advances on biology characteristics the rhizomatous grasses. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2001(S1): 1-16. |
| 易津, 李青丰, 谷安琳, 等. 根茎类禾草生物学特性研究进展. 干旱区资源与环境, 2001(增刊): 1-16. | |
| 14 | Tang J B, Xiao Y, An S Q, et al. Advance of studies on rhizomatous clonal plants ecology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(11): 232-240. |
| 汤俊兵, 肖燕, 安树青, 等. 根茎克隆植物生态学研究进展. 生态学报, 2010, 30(11): 232-240. | |
| 15 | Shi J M, Ye X H, Chen F S, et al. Adaptation of bamboo to heterogeneous habitat: Phenotypic plasticity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(20): 5687-5695. |
| 施建敏, 叶学华, 陈伏生, 等. 竹类植物对异质生境的适应—表型可塑性. 生态学报, 2014, 34(20): 5687-5695. | |
| 16 | Perez-Ramos I M, Matías L, Aparicio L G, et al. Functional traits and phenotypic plasticity modulate species coexistence across contrasting climatic conditions. Nature Communications, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10453-0. |
| 17 | Meng T T, Ni J, Wang G H. Plant functional traits, environments and ecosystem functioning. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(1): 150-165. |
| 孟婷婷, 倪健, 王国宏. 植物功能性状与环境和生态系统功能. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(1): 150-165. | |
| 18 | Liu Y F, Chen S L, Li Y C, et al. Enviromental stress on physiological plasticity of bamboo: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 31(3): 473-480. |
| 刘玉芳, 陈双林, 李迎春, 等. 竹子生理可塑性的环境胁迫效应研究进展. 浙江农林大学学报, 2014, 31(3): 473-480. | |
| 19 | Xuan Y C, Bao G Z, Wang X, et al. Effect of water stress on branch pattern of Leymus chinensis rhizome in Songnen plain of China. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(17): 174-177. |
| 轩弋淳, 包国章, 王鑫, 等. 松嫩平原羊草根茎分枝格局对水分梯度的响应. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(17): 174-177. | |
| 20 | Zhang Y H, Zhang F C, Li Y X, et al. Influence of exogenous N import on growth and leaf character of Spartina alterniflora. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(10): 2297-2301. |
| 张耀鸿, 张富存, 李映雪, 等. 外源氮输入对互花米草生长及叶特征的影响. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(10): 2297-2301. | |
| 21 | Deng C N, Zhang G X, Pan X L, et al. Eco-physiological responses of Phragmites australis to different salinity conditions in Momoge wetland. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 41(5): 67-70, 79. |
| 邓春暖, 章光新, 潘响亮, 等. 莫莫格湿地不同盐分梯度对芦苇生理生态的影响. 河南农业科学, 2012, 41(5): 67-70, 79. | |
| 22 | Wang R. Effects of saline-alkali stress on the individual and leaf and clonal growth traits of Phargmites australias. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2017. |
| 王瑞. 盐碱胁迫对芦苇生长、叶性状和克隆繁殖性状的影响. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2017. | |
| 23 | Tao J P, Song L X. Response of clonal plasticity of Fargesia nitida to different canopy conditions of subalpine coniferous forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(12): 4019-4026. |
| 陶建平, 宋利霞. 亚高山暗针叶林不同林冠环境下华西箭竹的克隆可塑性. 生态学报, 2006, 26(12): 4019-4026. | |
| 24 | Xia G J, He T H, Zhao Y Q, et al. Influence of and different soil types on reed growth photosynthesis characteristics. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(6): 1252-1258. |
| 夏贵菊, 何彤慧, 赵永全, 等. 不同土壤类型对芦苇生长及光合特征的影响. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(6): 1252-1258. | |
| 25 | Ma Q, Qian J Q, Tian L, et al. Responses of belowground bud bank to disturbance and stress in the sand dune ecosystem-ScienceDirect. Ecological Indicators, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105521. |
| 26 | Goldberg D E, Batzer E, Elgersma K, et al. Allocation to clonal growth: Critical questions and protocols to answer them. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppees.2020.125511. |
| 27 | Bai L. Study on remote sensing inversion of LAI and chlorophyll content in maize based on hyperspectral data. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2020. |
| 白丽. 基于高光谱数据的玉米LAI和叶绿素含量遥感反演方法的研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2020. | |
| 28 | Ren G B, Zhou L, Liang J, et al. Monitoring the invasion of Spartina alterniflora using hyperspectral remote sensing image of gf-5. Advances in Marine Science, 2021, 39(2): 312-326. |
| 任广波, 周莉, 梁建, 等. “高分五号”高光谱互花米草遥感识别与制图研究. 海洋科学进展, 2021, 39(2): 312-326. | |
| 29 | Xiao L D, Li C, Cai Y, et al. Interactions between soil properties and the rhizome-root distribution in a 12-year Moso bamboo reforested region: Combining ground-penetrating radar and soil coring in the field. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149467. |
| 30 | Hutchings M J. Morphological plasticity in clonal plants: The foraging concept reconsidered. Journal of Ecology, 1995, 83(1): 143-152. |
| 31 | Yu F H. Adaptive strategies of clonal plants growing in heterogeneous environments. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2002. |
| 于飞海. 克隆植物对异质性环境的生态适应对策. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2002. | |
| 32 | Stuefer J F, Dekroon H, During H. Exploitation of environmental heterogeneity by spatial division of labor in a clonal plant. Functional Ecology, 1996, 10(3): 328-334. |
| 33 | Roiloa S R, Alpert P, Tharayil N, et al. Greater capacity for division of labour in clones of Fragaria chiloensis from patchier habitats. Journal of Ecology, 2007, 95: 397-405. |
| 34 | Dong M. Clonal plant ecology. Beijing: Science Press, 2011. |
| 董鸣. 克隆植物生态学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011. | |
| 35 | Amsberry L, Baker M A, Bertness M D, et al. Clonal integration and the expansion of Phragmites australis. Ecological Applications, 2000, 10(4): 1110-1118. |
| 36 | Zhang Y, Chen J S. Effects of clonal integration on the nitrogen availability of rhizosphere soil in Phyllostachys nigra suffering from heterogeneous light. Guihaia, 2017, 37(6): 757-762. |
| 张云, 陈劲松. 克隆整合对异质性光照环境下紫竹根际土壤氮素有效性的影响. 广西植物, 2017, 37(6): 757-762. | |
| 37 | Evans J P, Whitney S. Clonal integration across a salt gradient by a nonhalophyte, Hydrocotyle bonariensis (apiaceae). American Journal of Botany, 1992, 79(12): 1344-1347. |
| 38 | Hartnett D, Bazzaz F. Physiological integration among intraclonal ramets in Solidago canadensis. Ecology, 1983, 64(4): 779-788. |
| 39 | Dekroon H, Fransen B, Vanrheenen J W A, et al. High levels of inter-ramet water translocation in two rhizomatous Carex species, as quantified by deuterium labelling. Oecologia, 1996, 106(1): 73-84. |
| 40 | Estrada J A, Wilson C H, Flory S L. Clonal integration enhances performance of an invasive grass. Oikos, 2020, 129(11): 1623-1631. |
| 41 | Zhang L L, Dong M, Li R Q, et al. Soil-nutrient patch contrast modifies intensity and direction of clonal integration in Glechoma longituba. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(4): 619-624. |
| 张丽丽, 董鸣, 李仁强, 等. 土壤养分斑块对比度改变活血丹克隆整合强度和方向. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(4): 619-624. | |
| 42 | Liu F H, Ye X H, Yu F H, et al. Clonal integration modifies responses of Hedysarum laeve to local sand burial in Mu Us sandland. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2006, 21(12): 278-285. |
| 刘凤红, 叶学华, 于飞海, 等. 毛乌素沙地游击型克隆半灌木羊柴对局部沙埋的反应. 植物生态学报, 2006, 21(12): 278-285. | |
| 43 | Liu B. Adaptation of plant vegetative reproduction to aeolian activities. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009. |
| 刘博. 植物适应风沙活动的营养繁殖对策. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2009. | |
| 44 | Yu F H, Wang N, He W M, et al. Adaptation of rhizome connections in drylands: Increasing tolerance of clones to wind erosion. Annals of Botany, 2008, 102(4): 571-577. |
| 45 | Luo W C, Zhao W Z. Effects of wind erosion and sand burial on growth and reproduction of a clonal shrub. Flora, 2015, 217: 164-169. |
| 46 | Du J, Yu F H, Peter A, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduce effects of physiological integration in Trifolium repens. Annals of Botany, 2009, 104: 335-343. |
| 47 | Dong S, Liu Z M, Alamusa, et al. The role and potential application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in preventing desertification. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 70-78. |
| 董硕, 刘志民, 阿拉木萨, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌在荒漠化防治中的作用及应用潜力. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 70-78. | |
| 48 | Soti P G, Jayachandran K, Purcell M, et al. Mycorrhizal symbiosis and Lygodium microphyllum invasion in south florida-A biogeographic comparison. Symbiosis, 2014, 62(2): 81-90. |
| 49 | Qin H, Niu L, Wu Q, et al. Bamboo forest expansion increases soil organic carbon through its effect on soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community and abundance. Plant and Soil, 2017, 420: 407-421. |
| 50 | Sutherland W J, Stillman R A. The foraging tactics of plants. Oikos, 1988, 52: 239-244. |
| 51 | Slade A J, Hutchings M J. The effects of nutrient availability on foraging in the clonal herb Glechoma hederacea. Journal of Ecology, 1987, 75(1): 95-112. |
| 52 | Li T J, Li G Q, Xu D B, et al. The clonal growth of Hippophae rhamniodes in response to irrigation intensity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(24): 6950-6960. |
| 李甜江, 李根前, 徐德兵, 等. 中国沙棘克隆生长对灌水强度的响应. 生态学报, 2010, 30(24): 6950-6960. | |
| 53 | Cain M L. Consequences of foraging in clonal plant species. Ecology, 1994, 75(4): 933-944. |
| 54 | Cain M L, Dudle D A, Evans J P. Spatial models of foraging in clonal plant species. American Journal of Botany, 1996, 83(1): 76-85. |
| 55 | Li L, Wang G. The ideal free distribution of clonal plant’s ramets among patches in a heterogeneous environment. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2006, 68(8): 1837-1850. |
| 56 | Oborny B, Hubai A G. Patch size and distance: Modelling habitat structure from the perspective of clonal growth. Annals of Botany, 2014, 114(2): 389-398. |
| [1] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [2] | 刘万龙, 许冬梅, 史佳梅, 许爱云. 不同群落生境蒙古冰草种群株丛结构和叶片功能性状的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 72-80. |
| [3] | 李媛媛, 徐婷婷, 艾喆, 周兆娜, 马飞. 锦鸡儿属植物功能性状与根际土壤细菌群落结构的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 38-49. |
| [4] | 连鹤娜, 李春杰. 不同栽培措施对醉马草坪用性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 178-188. |
| [5] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. |
| [6] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 黄书超, 杨琰珊, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 张银翠. 微生物肥料与化肥减量配施对多年生黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [7] | 杨克彤, 陈国鹏, 鲜骏仁, 俞筱押, 张金武, 王立. 甘肃省扎尕梁北坡头花杜鹃枝叶性状特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 111-120. |
| [8] | 韩重阳, 王栓, 左粟田, 闫三博, 汪阳, 蔡家邦, 马骢毓, 张新全, 聂刚. 10个白三叶品种在成都平原的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 105-117. |
| [9] | 常利芳, 李欣, 郭慧娟, 乔麟轶, 张树伟, 陈芳, 畅志坚, 张晓军. 小偃麦衍生系表型遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 61-74. |
| [10] | 周涛, 牟乐, 苏楷淇, 张筠钰, 杨惠敏. 间作比例和调亏灌溉对春小麦/紫花苜蓿间作中春小麦灌浆期旗叶性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 145-153. |
| [11] | 吴欣明, 方志红, 池惠武, 贾会丽, 刘建宁, 石永红, 王学敏. 30个青贮玉米在雁门关地区品种评比试验[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. |
| [12] | 吴国芳, 于肖夏, 于卓, 杨东升, 卢倩倩. 基于BSA-SSR技术的高丹草低氢氰酸性状目的片段的筛选与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 82-92. |
| [13] | 王云霞, 张萍, 葛蓓蕾, 雅蓉, 杨英, 靳磊. 渥丹百合农艺性状及活性成分对钾元素的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 205-213. |
| [14] | 赵小强, 钟源, 周文期. 不同水分环境下玉米叶面积QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 103-120. |
| [15] | 骆望龙, 夏建强, 李佳欣, 孙淑范, 汪睿, 张勃. 高寒退化草地狼毒繁殖性状的选择及其适应性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 121-129. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||