

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 84-98.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024056
收稿日期:2024-02-26
修回日期:2024-04-16
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
李明,张小明
作者简介:xiaomingzhang1982@126.com
Chang-zhuang LIU( ), Yu-zhao TAO, Ming LI(
), Yu-zhao TAO, Ming LI( ), Xiao-ming ZHANG(
), Xiao-ming ZHANG( )
)
Received:2024-02-26
Revised:2024-04-16
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Ming LI,Xiao-ming ZHANG
摘要:
土壤盐碱化降低了锰的有效性,严重影响作物的生长和产量形成,而外源补充硫酸锰改善苏打盐碱条件下作物生长的生理机制尚不清楚。本试验以栽培稗为材料,设置硫酸锰浸种(JZ)和施肥(SF)两种处理,探讨硫酸锰对盐碱胁迫下作物幼苗(V5)的生理调节作用。结果表明:栽培稗在盐碱胁迫下叶绿素含量显著减少且最大光化学效率(Fv/Fm)下降,抑制了叶绿素荧光参数在光响应曲线上的表现,导致光合效率显著降低。同时硝酸还原酶、谷氨酰胺合成酶等氮同化关键酶活性下降,硝态氮含量增加,最终引起碳氮代谢平衡失调,地上部生长受到抑制,干物质更多地分配于根部,根冠比显著增加。在施用硫酸锰肥料或浸种处理后,进一步促进了栽培稗根系的发育,提高了吸收氮素的能力,增强了氮代谢关键酶的活性,有效促进了游离氨基酸的积累,提高了植物整体氮同化效率,而且促进了叶绿素和类胡萝卜素的积累,提高了Fv/Fm及光系统的能量传递,盐碱胁迫下作物苗期光合能力得到显著提升,作物生长得到明显改善。两种处理方式相比,施肥处理更能够有效减轻盐碱胁迫对作物造成的损伤,平衡作物整体碳氮代谢能力。
刘昌壮, 陶雨朝, 李明, 张小明. 硫酸锰对盐碱胁迫下栽培稗幼苗光合与氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 84-98.
Chang-zhuang LIU, Yu-zhao TAO, Ming LI, Xiao-ming ZHANG. Effect of manganese sulfate on photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism of cultivated Indian barnyard grass seedlings under saline-alkali stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 84-98.
土壤类型 Soil type | pH | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorous (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑土Dark soil (H) | 6.66 | 1.46 | 110.37 | 20.54 | 116.77 | 2.81 |
| 苏打盐碱土Soda saline-alkali soil (S) | 9.44 | 1.65 | 79.57 | 13.72 | 95.83 | 2.41 |
表1 土壤基础肥力
Table 1 Soil basic fertility
土壤类型 Soil type | pH | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorous (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑土Dark soil (H) | 6.66 | 1.46 | 110.37 | 20.54 | 116.77 | 2.81 |
| 苏打盐碱土Soda saline-alkali soil (S) | 9.44 | 1.65 | 79.57 | 13.72 | 95.83 | 2.41 |
| 土壤类型Soil type | Na (mg·g-1) | Ca (mg·g-1) | Mg (mg·g-1) | Mn (mg·kg-1) | Cu (mg·kg-1) | Zn (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑土Dark soil | 4.25 | 2.481 | 9.953 | 926.673 | 29.906 | 121.553 |
| 苏打盐碱土Soda saline-alkali soil | 11.24 | 9.641 | 10.255 | 718.460 | 24.094 | 90.323 |
表2 土壤中微量元素含量
Table 2 Trace element content in soils
| 土壤类型Soil type | Na (mg·g-1) | Ca (mg·g-1) | Mg (mg·g-1) | Mn (mg·kg-1) | Cu (mg·kg-1) | Zn (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑土Dark soil | 4.25 | 2.481 | 9.953 | 926.673 | 29.906 | 121.553 |
| 苏打盐碱土Soda saline-alkali soil | 11.24 | 9.641 | 10.255 | 718.460 | 24.094 | 90.323 |
| 处理Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 叶面积Leaf area (cm2) | 干物质重Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 根冠比Root/shoot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-SF | 58.73±0.66Aa | 111.64±8.10Aa | 0.356±0.01Ba | 0.147±0.00Db |
| H-CK | 53.20±1.77Bb | 84.16±0.98Bb | 0.309±0.00Dc | 0.163±0.00Db |
| H-JZ | 51.40±1.64Bb | 90.42±5.43Bb | 0.333±0.01Cb | 0.276±0.01CDa |
| S- SF | 56.40±0.65Aa | 87.66±1.64Ba | 0.495±0.01Aa | 0.338±0.02Cc |
| S-CK | 27.97±0.42Cb | 38.08±3.10Cb | 0.177±0.01Eb | 0.657±0.06Bb |
| S-JZ | 25.90±0.22Cc | 32.57±2.37Cb | 0.162±0.01Eb | 1.414±0.09Aa |
表3 锰肥及浸种处理对栽培稗地上部生长的影响
Table 3 Manganese fertilizer and seed soaking treatment on the aboveground growth of cultivated barnyardgrass
| 处理Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 叶面积Leaf area (cm2) | 干物质重Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 根冠比Root/shoot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-SF | 58.73±0.66Aa | 111.64±8.10Aa | 0.356±0.01Ba | 0.147±0.00Db |
| H-CK | 53.20±1.77Bb | 84.16±0.98Bb | 0.309±0.00Dc | 0.163±0.00Db |
| H-JZ | 51.40±1.64Bb | 90.42±5.43Bb | 0.333±0.01Cb | 0.276±0.01CDa |
| S- SF | 56.40±0.65Aa | 87.66±1.64Ba | 0.495±0.01Aa | 0.338±0.02Cc |
| S-CK | 27.97±0.42Cb | 38.08±3.10Cb | 0.177±0.01Eb | 0.657±0.06Bb |
| S-JZ | 25.90±0.22Cc | 32.57±2.37Cb | 0.162±0.01Eb | 1.414±0.09Aa |
处理 Treatment | 干物质重 Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根平均直径 Root average diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-SF | 0.05±0.00Eb | 293.12±6.36Cb | 58.93±4.47Bb | 1.17±0.05Ba | 0.65±0.01Aa |
| H-CK | 0.05±0.00Eb | 246.74±26.19Dc | 38.88±2.43Cc | 0.64±0.08Cb | 0.52±0.02BCb |
| H-JZ | 0.09±0.01Da | 414.33±11.52Ba | 75.56±5.60ABa | 1.39±0.12ABa | 0.60±0.02ABa |
| S-SF | 0.17±0.01Bb | 435.90±18.31Bb | 69.13±7.14ABb | 1.35±0.14ABa | 0.46±0.02Cb |
| S-CK | 0.12±0.01Cc | 321.24±9.18Cc | 48.32±3.49Cc | 0.73±0.01Cb | 0.60±0.06ABa |
| S-JZ | 0.23±0.01Aa | 517.76±17.47Aa | 84.22±10.70Aa | 1.59±0.14Aa | 0.63±0.04Aa |
表4 锰肥及浸种处理对栽培稗根系生长的影响
Table 4 Manganese fertilizer and seed soaking treatment on the root growth of cultivated barnyardgrass
处理 Treatment | 干物质重 Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根平均直径 Root average diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-SF | 0.05±0.00Eb | 293.12±6.36Cb | 58.93±4.47Bb | 1.17±0.05Ba | 0.65±0.01Aa |
| H-CK | 0.05±0.00Eb | 246.74±26.19Dc | 38.88±2.43Cc | 0.64±0.08Cb | 0.52±0.02BCb |
| H-JZ | 0.09±0.01Da | 414.33±11.52Ba | 75.56±5.60ABa | 1.39±0.12ABa | 0.60±0.02ABa |
| S-SF | 0.17±0.01Bb | 435.90±18.31Bb | 69.13±7.14ABb | 1.35±0.14ABa | 0.46±0.02Cb |
| S-CK | 0.12±0.01Cc | 321.24±9.18Cc | 48.32±3.49Cc | 0.73±0.01Cb | 0.60±0.06ABa |
| S-JZ | 0.23±0.01Aa | 517.76±17.47Aa | 84.22±10.70Aa | 1.59±0.14Aa | 0.63±0.04Aa |
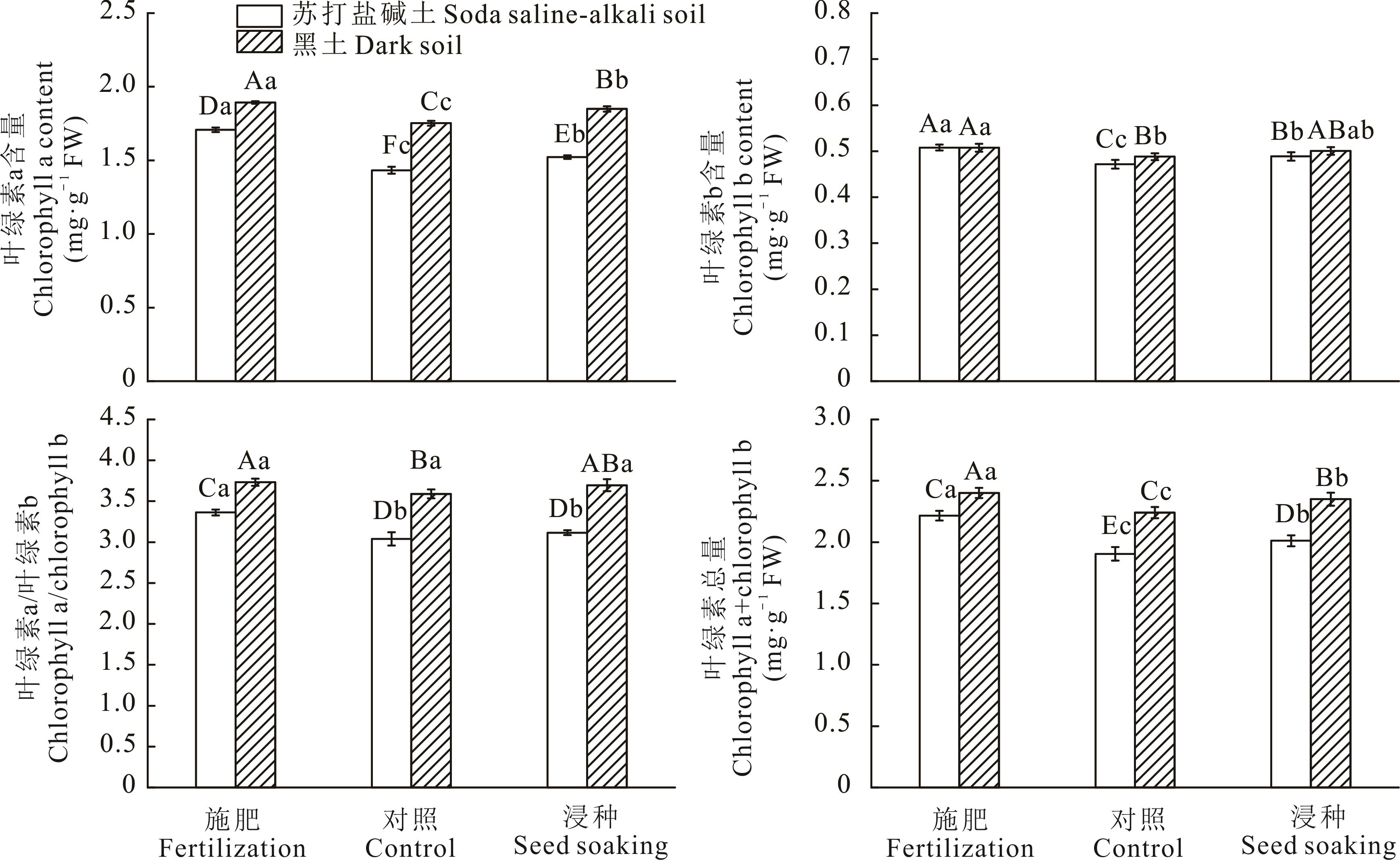
图1 锰肥及浸种处理对栽培稗叶绿素含量的影响大写字母表示土壤条件与硫酸锰处理相互影响下差异达到5%显著水平,小写字母表示同一土壤条件下不同硫酸锰处理之间差异达到5%显著水平,下同。Capital letters indicate that the differences among soil conditions and manganese sulfate treatments interacted at the 5% significant level, and lowercase letters indicate differences among different Mn sulfate treatments under the same soil condition at the 5% significant level, the same below.
Fig.1 Manganese fertilizer and seed soaking treatment on chlorophyll in cultivated barnyardgrass

图6 黑土及苏打盐碱土下栽培稗光合及荧光参数与生长指标的相关分析*: P≤0.05; **: P≤0.01; A: 黑土栽培稗Cultivated barnyardgrass on dark soil; B: 苏打盐碱土栽培稗Cultivated barnyardgrass on soda saline-alkali soil; 下同The same below.
Fig.6 Correlation analysis of photosynthetic and fluorescence parameters and growth indices of cultivated barnyardgrass under black soil and soda saline-alkali soil

图7 锰肥及浸种处理对栽培稗氮代谢相关酶活性的影响
Fig.7 Manganese fertilizer and seed soaking treatment on NR, GS, NADH-GDH, and Fd-GOGAT activities of cultivated barnyardgrass
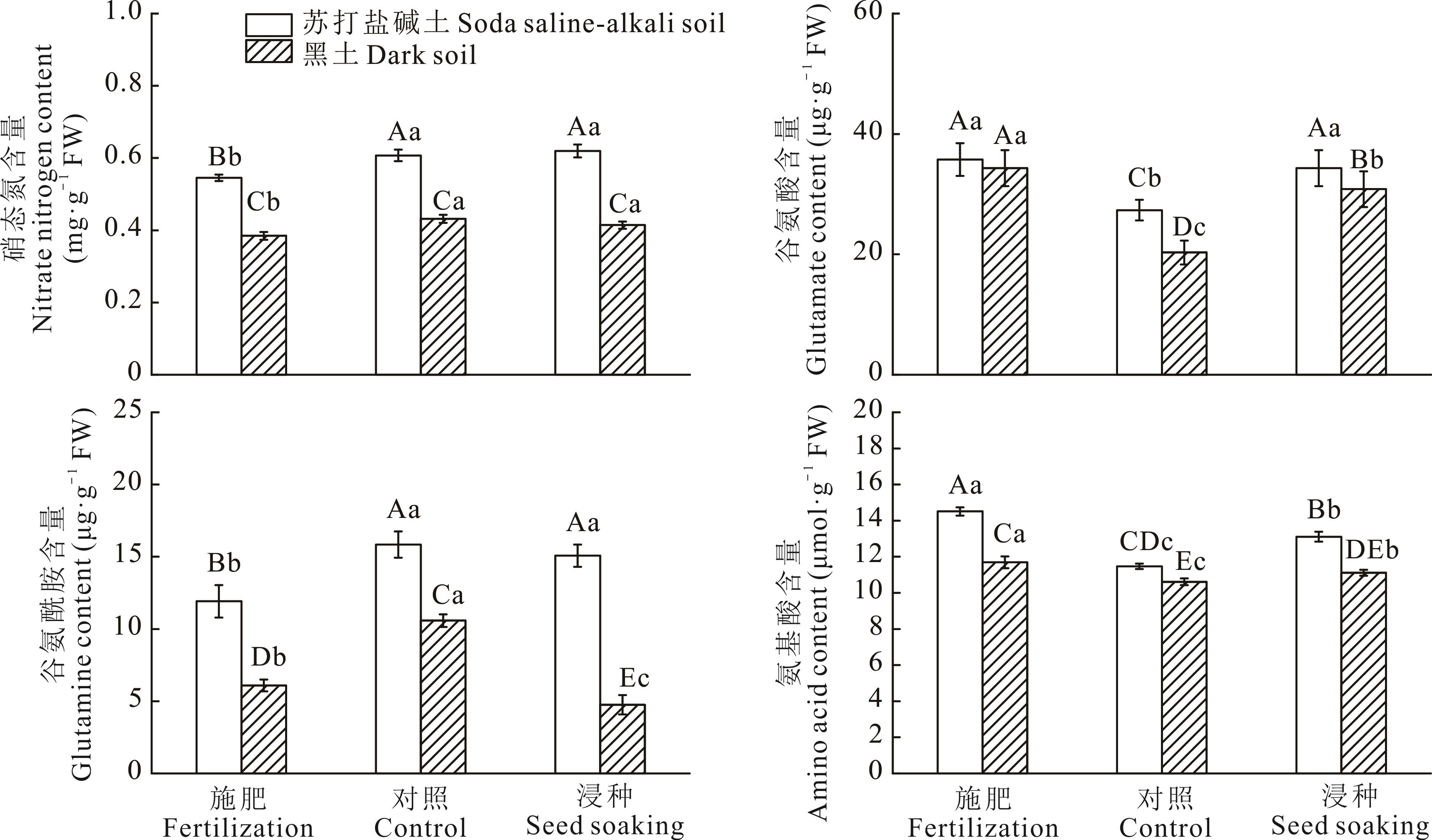
图10 锰肥及浸种处理对栽培稗硝态氮、谷氨酸、谷氨酰胺、氨基酸含量的影响
Fig.10 Manganese fertilizer and seed soaking treatment on nitrate nitrogen, glutamate, glutamine and amino acid contents of cultivated barnyardgrass

图11 黑土及苏打盐碱土下栽培稗氮代谢相关指标与生长指标相关性分析
Fig.11 Correlation analysis of nitrogen metabolism related indexes and growth indexes of cultivated barnyardgrass under black soil and soda saline-alkali soil
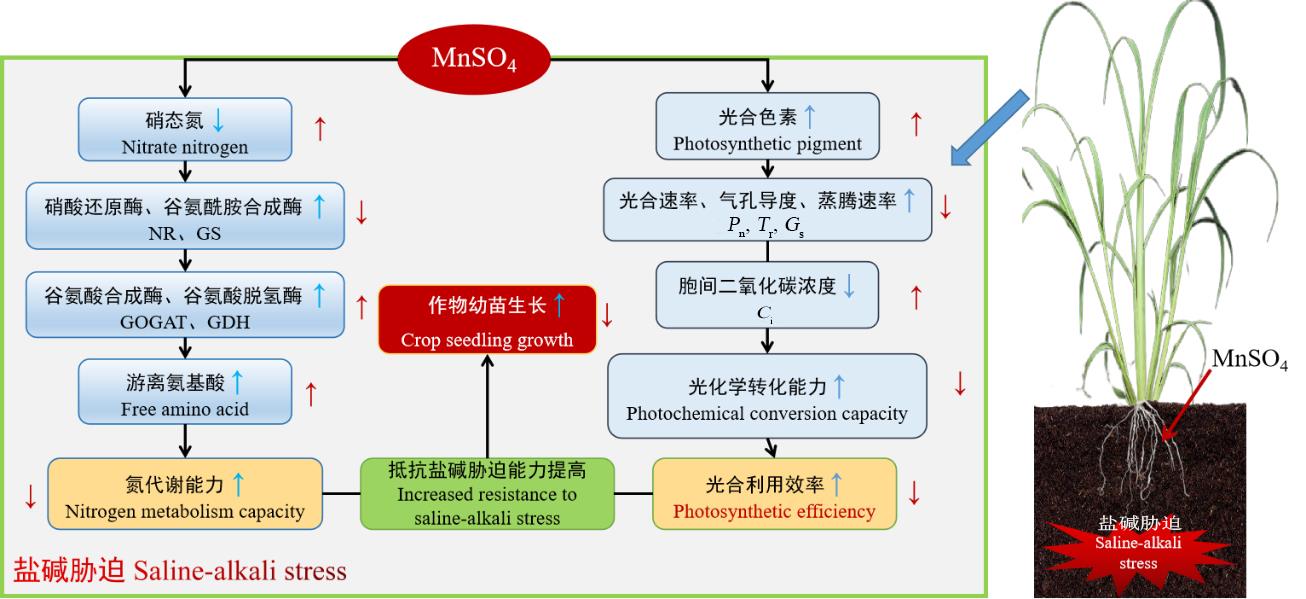
图12 硫酸锰提高盐碱胁迫下栽培稗光合及氮代谢能力模式图中蓝色箭头表示施用硫酸锰对于生理指标的影响,红色箭头指盐碱胁迫对于生理指标的影响,其中上升箭头代表增强,下降箭头表示减弱。The blue arrows in the figure indicate the effects of manganese sulfate application on physiological indices, and the red arrows refer to the effects of saline-alkali stress on physiological indices, where the rising arrows represent enhancement and the falling arrows represent weakening.
Fig.12 Manganese sulfate improves photosynthetic and nitrogen metabolism of cultivated barnyard grass under saline-alkali stress
| 1 | Hu J, Zhou D W, Wang X Y, et al. Effects of different sand-cover thicknesses on crops in bare saline-alkali land in the Songnen Plain. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(3): 410-418. |
| 胡娟, 周道玮, 王晓禹, 等. 不同覆沙厚度下松嫩平原盐碱裸地上的种植效果. 草业科学, 2021, 38(3): 410-418. | |
| 2 | Zhang H, Yu F, Xie P, et al. A Gγ protein regulates alkaline sensitivity in crops. Science, 2023, 379(6638): e8416. |
| 3 | Brennan R F, Bolland M D A. Application of fertilizer manganese doubled yields of lentil grown on alkaline soils. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2003, 26(6): 1263-1276. |
| 4 | Schmidt S B, Jensen P E, Husted S. Manganese deficiency in plants: the impact on photosystem Ⅱ. Trends in Plant Science, 2016, 21(7): 622-632. |
| 5 | Liu Z, Zhu Q Q, Tang L H, et al. Geographical distribution of trace elements deficient soils in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1982, 19(3): 209-223. |
| 刘铮, 朱其清, 唐丽华, 等. 我国缺乏微量元素的土壤及其区域分布. 土壤学报, 1982, 19 (3): 209-223. | |
| 6 | Sun W J, Zhang H, Yang S, et al. Genetic modification of Gγ subunit AT1 enhances salt-alkali tolerance in main graminaceous crops. National Science Review, 2023, 10 (6): nwad075. |
| 7 | Xu P Y, Wu Y X, He T M. Research progress on adaptation mechanism of plants to saline-alkali stress. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2020, 39(10): 41-49. |
| 许盼云, 吴玉霞, 何天明. 植物对盐碱胁迫的适应机理研究进展. 中国野生植物资源, 2020, 39(10): 41-49. | |
| 8 | Yao X M, Ou C, Zhang Y L, et al.Effects of abscisic acid on ion absorption and photosynthesis of Toona sinensis seedlings under salt stress. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2020, 48(8): 27-32. |
| 姚侠妹, 偶春, 张源丽, 等. 脱落酸对盐胁迫下香椿幼苗离子吸收和光合作用的影响. 东北林业大学学报, 2020, 48(8): 27-32. | |
| 9 | Hussain S, Hussain S, Ali B, et al. Recent progress in understanding salinity tolerance in plants: Story of Na+/K+ balance and beyond. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 160: 239-256. |
| 10 | Ma X, Jia Z F, Liu Y.Study on photosynthesis and chlorophyll metabolism of Avena sativa L. under salt stress. Chinese Qinghai Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2021, 51(3): 7-14. |
| 马祥, 贾志峰, 刘勇. 盐胁迫下燕麦光合及叶绿素代谢变化研究. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2021, 51(3): 7-14. | |
| 11 | Najar R, Aydi S, Sassi-Aydi S, et al. Effect of salt stress on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in Medicago truncatula. Plant Biosystems, 2019, 153(1): 88-97. |
| 12 | Dluzniewska P, Gessler A, Dietrich H, et al. Nitrogen uptake and metabolism in Populus×canescens as affected by salinity. New Phytologist, 2007, 173(2): 279-293. |
| 13 | Abdelgadir E A O M. Characteristics of nitrate uptake by plants under salinity. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2005, 28(1): 33-46. |
| 14 | Xu Z Z. Research advance in nitrogen metabolism of plant and its environmental regulation. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(3): 511-516. |
| 许振柱. 植物氮代谢及其环境调节研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(3): 511-516. | |
| 15 | Millaleo R, Reyes-Díaz M, Ivanov A G, et al. Manganese as essential and toxic element for plants: transport, accumulation and resistance mechanisms. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2010, 10(4): 470-481. |
| 16 | Wang Z H, Tang J X, Dai H F, et al. Effect of Zn2+ and Mn2+ on the salt tolerance of rice seedlings growth. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 46(4): 547-549. |
| 王振河, 汤菊香, 代海芳, 等. 锰和锌对盐渍土中水稻幼苗生长的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2007, 46(4): 547-549. | |
| 17 | Ma G S, Liu W, Lian H, et al. Effect of spraying manganese sulfate on potato physiological characteristics and yield. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2012(8): 52-56. |
| 马光恕, 刘伟, 廉华, 等. 叶面喷施硫酸锰对马铃薯生理指标和产量的影响. 长江蔬菜, 2012(8): 52-56. | |
| 18 | Meng X P, Li C X, Guo H Y, et al. Effects of manganese soaking on wheat seedling photosynthetic characteristics and root system, root vigor. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(4): 745-750. |
| 孟祥萍, 李春霞, 国海燕, 等. 锰素浸种对小麦幼苗光合特性及其根系形态与活力的影响. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(4): 745-750. | |
| 19 | Zhang L, Wang L, Li F, et al. Effect of divalent manganese (Mn2+) concentration on the growth and nitrate nitrogen content of lettuce during aeroponic intercropping with cherry radish. Horticulture Environment and Biotechnology, 2021, 62(2): 243-251. |
| 20 | Cheng Z, Mcconkey B J, Glick B R. Proteomic studies of plant-bacterial interactions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2010, 42(10): 1673-1684. |
| 21 | Ma R, Nuerziya·hayiken, Zhou X M, et al. Manganese: An essential trace element for plants in balanced cultivation systems. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 44(S2): 200. |
| 马瑞, 努尔孜亚·哈依肯, 周雪梅, 等. 平衡栽培体系中植物必须的微量元素锰. 新疆农业科学, 2007, 44(S2): 200. | |
| 22 | Graham P A O. The biochemistry of manganese in plants. Plant Physiology, 1988(67): 310. |
| 23 | Sood S A K R. Barnyard millet-a potential food and feed crop of future. Plant Breeding, 2015, 134(2): 135-147. |
| 24 | Arthi N, Rajagopal B, Geethanjali S, et al. Screening of barnyard millet (Echinochloa frumentacea) germplasm for salinity tolerance. Electronic Journal of Plant Breeding, 2019, 10(2): 659-666. |
| 25 | Lu A Q, Zhang F J, Xu X, et al. Effects of salt stress on growth and physiological characteristics of Echinochloa frumentacea seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 等. 盐胁迫对栽培稗苗期生长及生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. | |
| 26 | Lu A Q, Zhang F J, Wang X Q, et al. Effects of NaCl and Na2SO4 stress on content and distribution of K+ and Na+ of Echinochloa frumentacea seedlings. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(3): 396-403. |
| 陆安桥, 张峰举, 王学琴, 等. 盐胁迫对苗期湖南稷子K+, Na+含量与分布的影响. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(3): 396-403. | |
| 27 | Gao J F. Experimental guidance on plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 28 | Guo S, Mu L, Sun S, et al. Concurrence of microplastics and heat waves reduces rice yields and disturbs the agroecosystem nitrogen cycle. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 452: 131340. |
| 29 | Tan M, Hassan M J, Peng Y, et al. Polyamines metabolism interacts with γ-aminobutyric acid, proline and nitrogen metabolisms to affect drought tolerance of creeping bentgrass. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(5): 2779. |
| 30 | Tang Z C. Laboratory guide to modern plant physiology. Beijing: Science Press, 1999. |
| 汤章城. 现代植物生理学实验指南. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999. | |
| 31 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 32 | Wang Y K, Yang Y R, Wang D L. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on ion absorption and distribution in Leymus chinensis under saline-alkaline stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 95-104. |
| 王英逵, 杨玉荣, 王德利. 盐碱胁迫下AMF对羊草的离子吸收和分配作用. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 95-104. | |
| 33 | Sun H R, Feng X H, Zhang X M, et al. Root growth response of Hibiscus moscheutos seedling to salt stress. Northern Horticulture, 2015(16): 76-81. |
| 孙焕荣, 封晓辉, 张秀梅, 等. 芙蓉葵苗期根系生长对盐胁迫的响应. 北方园艺, 2015(16): 76-81. | |
| 34 | Xiu Y, Liang X Y, Shi R C, et al. Effects of complex salt-alkail stress on the plant and root growth of Chenopodium quinoa.Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(4): 89-94. |
| 修妤, 梁晓艳, 石瑞常, 等. 混合盐碱胁迫对藜麦苗期植株及根系生长特征的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(4): 89-94. | |
| 35 | Lan Y. Physiological response of three Echinochloa forages to saline-alkaline stress and comprehensive evaluation for their saline-alkaline tolerance. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2022. |
| 兰艳. 三种稗属牧草种子萌发和幼苗对盐碱胁迫的生理响应及耐性评估. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2022. | |
| 36 | Bernstein N, Meiri A, Zilberstaine M. Root growth of avocado is more sensitive to salinity than shoot growth. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 2004, 129(2): 188-192. |
| 37 | Dong X B, Guo X F, Yang W G, et al. Effects of trace element fertilizers on the growth of Leymus chinensis under drought condition. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 44(2): 111-116. |
| 董晓兵, 郭秀芳, 杨伟光, 等. 干旱条件下微肥对羊草生长的影响. 西南民族大学学报 (自然科学版), 2018, 44(2): 111-116. | |
| 38 | Yang Q. Effects of zinc fertilizer on growth and nutrient absorption of maize in saline-alkali soil. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2021. |
| 杨茜. 锌肥对盐碱地玉米生长及养分吸收的影响. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2021. | |
| 39 | Hu Y J, Wu X, Wang Z D, et al. Research progress on effects of saline-alkali stress on physiological and ecological characteristics of potato. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2022, 42(12): 80-85. |
| 胡钰婕, 吴玺, 王证德, 等. 盐碱胁迫对马铃薯生理生态特性的影响研究进展. 热带农业科学, 2022, 42(12): 80-85. | |
| 40 | Cao C H, Sun S C, Wang X K, et al. Effects of manganese concentration on the chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and growth of Karenia mikimotoi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(19): 5280-5288. |
| 曹春晖, 孙世春, 王学魁, 等. 锰浓度对米氏凯伦藻叶绿素荧光特性及生长的影响. 生态学报, 2010, 30(19): 5280-5288. | |
| 41 | Wang F, Liu Y, Wang T B, et al. Mitigation effect and mechanism of exogenous melatonin on maize seedling under salt stress. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(5): 14-21. |
| 王芳, 刘燕, 王铁兵, 等. 外源褪黑素对玉米幼苗盐胁迫的缓解效应研究. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(5): 14-21. | |
| 42 | Muhammad I, Yang L, Ahmad S, et al. Melatonin application alleviates stress-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative damage by regulating antioxidant defense system of maize: A meta-analysis. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(3): 512. |
| 43 | Xu W Y, Wang F, Wang J. Effect of manganese sulfate(MnSO4) solution soaking seeds on potato(Solanum tuberosum) seedlings growth and development. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(2): 558-559. |
| 许文一, 王芳, 王舰. 硫酸锰浸种对马铃薯苗期的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(2): 558-559. | |
| 44 | Liu J X, Liu R R, Liu X L, et al. Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on nitrogen metabolism in leaves and yield components of naked oat under saline-alkail stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023, 42(2): 324-332. |
| 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 等. 盐碱胁迫下外源硫化氢对裸燕麦叶片氮代谢和产量构成因素的影响. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(2): 324-332. | |
| 45 | Wang H, Ahan J, Wu Z, et al. Alteration of nitrogen metabolism in rice variety ‘Nipponbare’ induced by alkali stress. Plant and Soil, 2012, 355: 131-147. |
| 46 | Zhang Y, Shi Y, Hu X H, et al. Effects of exogenous spermidine on the nitrogen metabolism and main mineral elements contents of tomato seedlings under saline-alkail stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(5): 1401-1408. |
| 张毅, 石玉, 胡晓辉, 等. 外源Spd对盐碱胁迫下番茄幼苗氮代谢及主要矿质元素含量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(5): 1401-1408. | |
| 47 | Ahanger M A, Agarwal R M. Salinity stress induced alterations in antioxidant metabolism and nitrogen assimilation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) as influenced by potassium supplementation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 115: 449-460. |
| [1] | 李超男, 王磊, 周继强, 赵长兴, 谢晓蓉, 刘金荣. 微塑料对紫花苜蓿生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 138-146. |
| [2] | 郑甲成, 余婕, 李凡, 黄小奕, 李杰勤, 陈海州, 王歆, 詹秋文, 徐兆师. SbER10_X1调控饲用高粱光合作用和生物产量的功能特性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 91-100. |
| [3] | 周晓瑾, 黄海霞, 张君霞, 马步东, 陆刚, 齐建伟, 张婷, 朱珠. 盐胁迫对裸果木幼苗光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 75-83. |
| [4] | 邹博坤, 王欣铭, 褚章杉, 黄馨慧, 陈雨峰, 钱永强. 氮素形态对野牛草生长及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 118-127. |
| [5] | 韩云华, 米素娟, 石晓琪, 钟天航. 纳米粒子的植物促生效应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 204-213. |
| [6] | 陈林, 陈高路, 宋乃平, 李学斌, 万红云, 何文强. 宁夏东部荒漠草原猪毛蒿光合特征和水分利用效率对降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 87-98. |
| [7] | 张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. |
| [8] | 赵利清, 彭向永, 刘俊祥, 毛金梅, 孙振元. GSH对铅胁迫下多年生黑麦草生长及光合生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 97-104. |
| [9] | 汪辉, 田浩琦, 毛培胜, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 魏露萍, 周青平. 植物非叶绿色器官光合特征研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 191-200. |
| [10] | 王泳超, 张颖蕾, 闫东良, 何灵芝, 李卓, 燕博文, 邵瑞鑫, 郭家萌, 杨青华. 干旱胁迫下γ-氨基丁酸保护玉米幼苗光合系统的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 191-203. |
| [11] | 黄曦叶, 何林江, 刘金平, 游明鸿, 刘航江. 葎草水分和光合特征及抗性物质含量响应冬季降温的性别差异[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 103-113. |
| [12] | 王日明, 王志强, 向佐湘. γ-氨基丁酸对高温胁迫下黑麦草光合特性及碳水化合物代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 168-178. |
| [13] | 郭海燕, 段婧, 刘金平, 游明鸿, 谢瑞娟. 温度对雌雄葎草花芽分化和色素含量及光合作用影响的性别差异[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 104-112. |
| [14] | 李杨, 史娟, 崔娜娜, 韩宇. 苜蓿褐斑病对紫花苜蓿光合作用及草品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(10): 149-157. |
| [15] | 寇江涛, 康文娟, 苗阳阳, 师尚礼. 外源2,4-表油菜素内酯对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗光合特性及离子吸收、运输和分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 91-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||