

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 54-67.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020381
马欣1,3( ), 罗珠珠1,2(
), 罗珠珠1,2( ), 张耀全1, 刘家鹤1, 牛伊宁2, 蔡立群1,2
), 张耀全1, 刘家鹤1, 牛伊宁2, 蔡立群1,2
收稿日期:2020-08-04
修回日期:2020-09-27
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2021-03-09
通讯作者:
罗珠珠
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: luozz@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Xin MA1,3( ), Zhu-zhu LUO1,2(
), Zhu-zhu LUO1,2( ), Yao-quan ZHANG1, Jia-he LIU1, Yi-ning NIU2, Li-qun CAI1,2
), Yao-quan ZHANG1, Jia-he LIU1, Yi-ning NIU2, Li-qun CAI1,2
Received:2020-08-04
Revised:2020-09-27
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2021-03-09
Contact:
Zhu-zhu LUO
摘要:
依托布设在黄土高原雨养农业区的长期田间定位试验,以农田土壤为对照,不同种植年限紫花苜蓿地(L2003,L2005,L2012)土壤为研究对象,采用细菌16S rRNA高通量测序技术探究以上3种土壤细菌群落分布格局与演替特征,并借助冗余分析等方法探讨土壤理化性质与细菌群落结构和多样性的关系,最后利用PICRUSt方法预测了土壤细菌群落生态功能。结果表明,黄绵土区门水平优势菌群为放线菌门(20.34%~32.40%)、变形菌门(18.99%~23.14%)、酸杆菌门(12.50%~13.39%)和绿弯菌门(11.41%~12.55%)。放线菌门、变形菌门和绿弯菌门相对丰度表现为农田土壤高于苜蓿土壤,且放线菌门相对丰度随苜蓿种植时间延长呈降低趋势,变形菌门和绿弯菌门相对丰度随苜蓿种植时间的延长先增加后降低;酸杆菌门相对丰度在农田和苜蓿地无明显差异。黄绵土属水平优势类群包括Gaiella属(1.65%~3.33%)、硝化螺菌属(1.52%~2.34%)、假节杆菌属(1.36%~2.61%)和Solirubrobacter属(1.03%~2.24%)。与农田相比,苜蓿土壤Solirubrobacter属相对丰度显著增加(P<0.05)。冗余分析(RDA)表明,土壤全磷(P=0.002)是影响细菌群落结构变化的主要因子。PICRUSt功能预测表明,黄绵土细菌菌群共有46个子功能,其中代谢为最主要的功能,占比为69.20%~70.22%;苜蓿土壤代谢、生物体系统功能基因丰度均显著高于农田土壤,具体表现在碳水化合物代谢、外源物质降解及代谢、萜类和酮类化合物代谢、内分泌系统、神经系统和物质依赖功能基因中。苜蓿种植年限可影响黄绵土细菌群落结构和代谢功能,该结果可为西部黄土高原紫花苜蓿人工草地的可持续利用和黄绵土细菌代谢潜力及功能预测提供参考。
马欣, 罗珠珠, 张耀全, 刘家鹤, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群. 黄土高原雨养区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿土壤细菌群落特征与生态功能预测[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 54-67.
Xin MA, Zhu-zhu LUO, Yao-quan ZHANG, Jia-he LIU, Yi-ning NIU, Li-qun CAI. Distribution characteristics and ecological function predictions of soil bacterial communities in rainfed alfalfa fields on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 54-67.
处理 Treatments | 全氮 TN (g·kg-1) | 土壤有机碳 SOC (g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP (g·kg-1) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 AP (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农田Farmland | 0.84±0.08c | 8.28±0.70b | 0.86±0.06a | 32.98±8.49a | 6.67±0.42a | 201.27±9.26a | 8.30±0.08c |
| L2003 | 1.18±0.00a | 10.06±0.05a | 0.72±0.01b | 12.97±0.72b | 0.98±0.16c | 200.77±20.01a | 8.64±0.02ab |
| L2005 | 1.14±0.04ab | 9.94±0.20a | 0.77±0.01b | 10.85±0.10b | 2.87±0.59b | 233.90±8.96a | 8.75±0.01a |
| L2012 | 1.02±0.03b | 8.24±0.14b | 0.76±0.01b | 8.12±0.45b | 3.21±0.15b | 214.86±11.77a | 8.57±0.02b |
表1 不同处理土壤化学性质
Table 1 Chemical properties of different treatments
处理 Treatments | 全氮 TN (g·kg-1) | 土壤有机碳 SOC (g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP (g·kg-1) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 AP (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农田Farmland | 0.84±0.08c | 8.28±0.70b | 0.86±0.06a | 32.98±8.49a | 6.67±0.42a | 201.27±9.26a | 8.30±0.08c |
| L2003 | 1.18±0.00a | 10.06±0.05a | 0.72±0.01b | 12.97±0.72b | 0.98±0.16c | 200.77±20.01a | 8.64±0.02ab |
| L2005 | 1.14±0.04ab | 9.94±0.20a | 0.77±0.01b | 10.85±0.10b | 2.87±0.59b | 233.90±8.96a | 8.75±0.01a |
| L2012 | 1.02±0.03b | 8.24±0.14b | 0.76±0.01b | 8.12±0.45b | 3.21±0.15b | 214.86±11.77a | 8.57±0.02b |
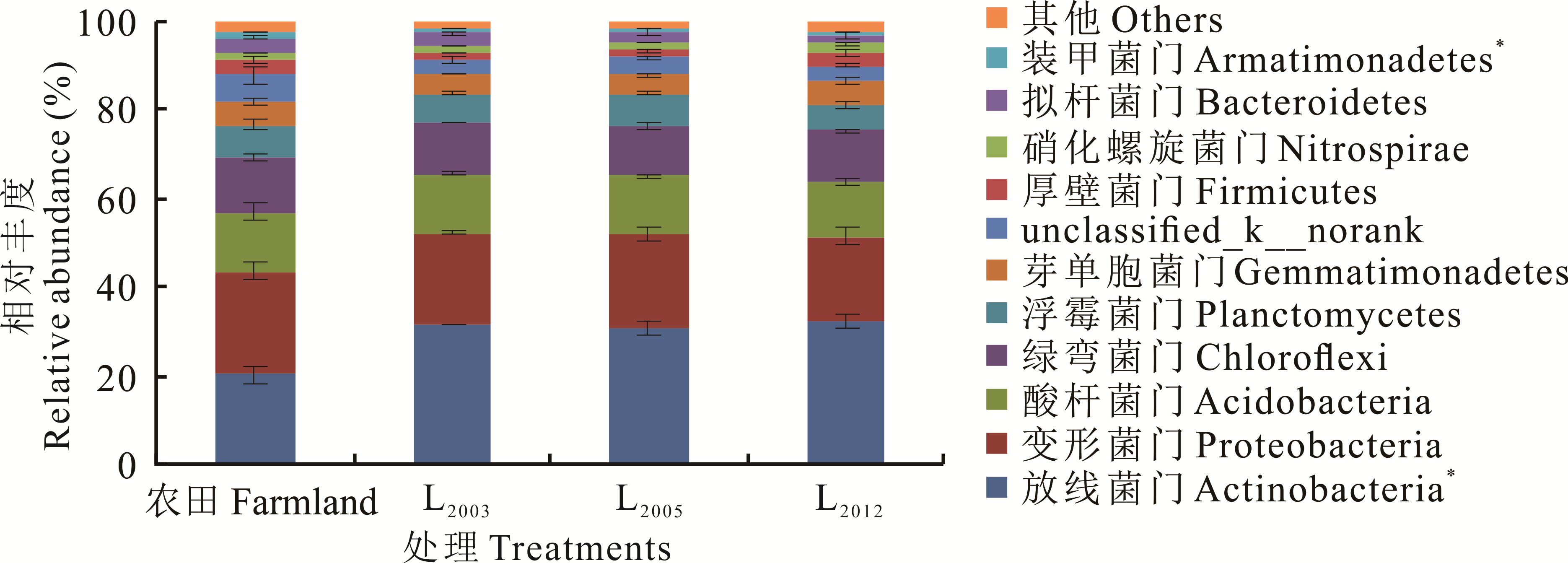
图1 不同处理土壤细菌门水平的相对丰度*表示不同处理中的相对丰度差异显著(P<0.05)。* represent significant differences in relative abundance between different treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.1 Phylum groups of soil bacterial community in different treatments
菌属 Bacteria genus | 农田Farmland | L2003 | L2005 | L2012 | 菌属 Bacteria genus | 农田Farmland | L2003 | L2005 | L2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| norank_c__Acidobacteria | 9.37a | 8.95a | 8.89a | 8.43a | norank_f__MSB-1E8 | 1.10a | 1.15a | 1.16a | 1.22a |
| norank_o__Gaiellales | 2.03a | 2.98a | 3.22a | 5.23a | norank_c__Gitt-GS-136 | 0.49b | 0.85ab | 0.89ab | 1.23a |
| norank_c__Actinobacteria | 2.00a | 2.25a | 2.62a | 4.50a | norank_o__Acidimicrobiales | 0.72b | 1.21a | 1.22a | 1.25a |
| norank_f__Gemmatimonadaceae | 3.45a | 3.27a | 3.16a | 4.15a | H16 | 1.28a | 0.80b | 0.78b | 0.95b |
| unclassified_k__norank | 6.01a | 3.09b | 3.81b | 3.58b | 微枝形杆菌属 Microvirga | 1.45a | 1.79a | 1.97a | 1.47a |
| Gaiella | 1.65a | 2.57a | 2.73a | 3.33a | 芽球菌属 Blastococcus | 0.99b | 2.08a | 1.73ab | 1.37ab |
| norank_o__JG30-KF-CM45 | 3.59a | 3.59a | 3.46a | 2.60a | norank_c__P2-11E | 0.45a | 0.51a | 0.54a | 0.92a |
| 硝化螺菌属 Nitrospira | 1.81a | 1.52a | 1.61a | 2.34a | 类诺卡氏菌属 Nocardioides | 0.72b | 1.79a | 1.77a | 1.26ab |
| norank_f__Nitrosomonadaceae | 1.94a | 1.74a | 1.78a | 2.30a | norank_f__288-2 | 0.85a | 0.87a | 0.72a | 1.11a |
| 芽孢杆菌属 Bacillus | 1.94a | 1.10a | 1.01a | 1.42a | norank_f__Elev-16S-1332 | 0.53b | 0.96a | 1.12a | 1.01a |
| norank_f__Tepidisphaeraceae | 2.15a | 2.44a | 2.29a | 1.90a | norank_c__TK10 | 1.07a | 1.31a | 1.42a | 1.01a |
| norank_f__Planctomycetaceae | 1.35b | 1.73ab | 1.94a | 1.72ab | RB41 | 1.15a | 1.25a | 0.93a | 1.17a |
| norank_f__0319-6M6 | 1.04b | 1.73a | 1.59a | 1.77a | norank_p__Armatimonadetes | 1.15a | 0.97ab | 0.92ab | 0.78b |
| Solirubrobacter | 1.03c | 2.02ab | 2.24a | 1.66b | Pir4_lineage | 1.32a | 0.40b | 0.45b | 0.50b |
| norank_f__Anaerolineaceae | 2.01a | 1.00b | 1.11b | 1.42b | norank_f__Cytophagaceae | 1.26a | 0.62b | 0.59b | 0.33b |
| norank_c__KD4-96 | 0.90b | 1.37a | 1.46a | 1.42a | 溶杆菌属 Lysobacter | 1.06a | 0.18b | 0.31b | 0.16b |
| 链霉菌属 Streptomyces | 1.50a | 1.61a | 1.21a | 1.11a | 其他Others | 39.26a | 37.67a | 37.62a | 33.88a |
| 假节杆菌属 Pseudarthrobacter | 1.36a | 2.61a | 1.73a | 1.49a |
表2 不同处理细菌优势属相对丰度
Table 2 Microbial community composition at genus rank in different treatments (%)
菌属 Bacteria genus | 农田Farmland | L2003 | L2005 | L2012 | 菌属 Bacteria genus | 农田Farmland | L2003 | L2005 | L2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| norank_c__Acidobacteria | 9.37a | 8.95a | 8.89a | 8.43a | norank_f__MSB-1E8 | 1.10a | 1.15a | 1.16a | 1.22a |
| norank_o__Gaiellales | 2.03a | 2.98a | 3.22a | 5.23a | norank_c__Gitt-GS-136 | 0.49b | 0.85ab | 0.89ab | 1.23a |
| norank_c__Actinobacteria | 2.00a | 2.25a | 2.62a | 4.50a | norank_o__Acidimicrobiales | 0.72b | 1.21a | 1.22a | 1.25a |
| norank_f__Gemmatimonadaceae | 3.45a | 3.27a | 3.16a | 4.15a | H16 | 1.28a | 0.80b | 0.78b | 0.95b |
| unclassified_k__norank | 6.01a | 3.09b | 3.81b | 3.58b | 微枝形杆菌属 Microvirga | 1.45a | 1.79a | 1.97a | 1.47a |
| Gaiella | 1.65a | 2.57a | 2.73a | 3.33a | 芽球菌属 Blastococcus | 0.99b | 2.08a | 1.73ab | 1.37ab |
| norank_o__JG30-KF-CM45 | 3.59a | 3.59a | 3.46a | 2.60a | norank_c__P2-11E | 0.45a | 0.51a | 0.54a | 0.92a |
| 硝化螺菌属 Nitrospira | 1.81a | 1.52a | 1.61a | 2.34a | 类诺卡氏菌属 Nocardioides | 0.72b | 1.79a | 1.77a | 1.26ab |
| norank_f__Nitrosomonadaceae | 1.94a | 1.74a | 1.78a | 2.30a | norank_f__288-2 | 0.85a | 0.87a | 0.72a | 1.11a |
| 芽孢杆菌属 Bacillus | 1.94a | 1.10a | 1.01a | 1.42a | norank_f__Elev-16S-1332 | 0.53b | 0.96a | 1.12a | 1.01a |
| norank_f__Tepidisphaeraceae | 2.15a | 2.44a | 2.29a | 1.90a | norank_c__TK10 | 1.07a | 1.31a | 1.42a | 1.01a |
| norank_f__Planctomycetaceae | 1.35b | 1.73ab | 1.94a | 1.72ab | RB41 | 1.15a | 1.25a | 0.93a | 1.17a |
| norank_f__0319-6M6 | 1.04b | 1.73a | 1.59a | 1.77a | norank_p__Armatimonadetes | 1.15a | 0.97ab | 0.92ab | 0.78b |
| Solirubrobacter | 1.03c | 2.02ab | 2.24a | 1.66b | Pir4_lineage | 1.32a | 0.40b | 0.45b | 0.50b |
| norank_f__Anaerolineaceae | 2.01a | 1.00b | 1.11b | 1.42b | norank_f__Cytophagaceae | 1.26a | 0.62b | 0.59b | 0.33b |
| norank_c__KD4-96 | 0.90b | 1.37a | 1.46a | 1.42a | 溶杆菌属 Lysobacter | 1.06a | 0.18b | 0.31b | 0.16b |
| 链霉菌属 Streptomyces | 1.50a | 1.61a | 1.21a | 1.11a | 其他Others | 39.26a | 37.67a | 37.62a | 33.88a |
| 假节杆菌属 Pseudarthrobacter | 1.36a | 2.61a | 1.73a | 1.49a |

图2 土壤环境因子与细菌门水平相关性热图*表示相关达显著水平(P<0.05);**表示相关达极显著水平(P<0.01)。* means significant level of correlation (P <0.05); ** means extremely significant level of correlation(P<0.01).
Fig.2 Correlation heatmap between soil environmental factors and phylum of bacterial

图 3 细菌群落与环境因子的RDA图TN: 全氮Total nitrogen; NO3--N: 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen; SOC: 有机碳Organic carbon; TP: 全磷Total phosphorus; AP: 速效磷Available phosphorus; AK: 速效钾Available potassium; Nitrospr: 硝化螺菌属Nitrospira; Bacillus: 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus; Streptm: 链霉菌属Streptomyces; Pseudar: 假节杆菌属Pseudarthrobacter; Microvir: 微枝形杆菌属Microvirga; Blastoco: 芽球菌属Blastococcus; Nocardio: 类诺卡氏菌属Nocardioides; Lysobact: 溶杆菌属Lysobacter.
Fig.3 RDA ordination graph for the bacterial community and environmental factors

图 4 不同种植年限土壤细菌功能基因KEGG丰度图(一级功能层)不同小写字母代表处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters represent significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.4 Soil bacterial function prediction in different growth years (hierarchy level 1)

图6 细菌功能多样性主成分分析CarbMetb: 碳水化合物代谢Carbohydrate metabolism; GlbAndOv: 全局和概览通路Global and overview maps; AmnAcdMt: 氨基酸代谢Amino acid metabolism; EnerMetb: 能量代谢Energy metabolism; MetbOf Cf: 辅助因子和维生素代谢Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins; NuclMetb: 核苷酸代谢Nucleotide metabolism; MembTran: 膜运输Membrane transport; Translat: 翻译Translation; LipdMetb: 脂质代谢Lipid metabolism; CellCom- : 细胞群落-原核生物Cellular community-prokaryotes; RepAndRp: 复制和修复Replication and repair; SignTran: 信号转导Signal transduction; XenBioAn: 外源物质降解及代谢Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism; MetbOfOt: 其他氨基酸代谢Metabolism of other amino acids; FolSorAn: 折叠、整理和降解Folding, sorting and degradation; BiosOfOt: 次级代谢产物的生物合成Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites; MetbOfTr: 萜类和聚酮类化合物代谢Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides; GlcBioAn: 糖的生物合成和代谢Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism; Cell Motl: 细胞运动Cell motility; CelGrwAn: 细胞生长与死亡Cell growth and death; DruResAn: 耐药性:抗菌Drug resistance: Antimicrobial; EndcSyst: 内分泌系统Endocrine system; CancOver: 癌症:概述Cancers: Overview; InfDisBa: 传染病:细菌Infectious diseases: Bacterial; Aging: 老化Aging; TrnAndCt: 运输和分解代谢Transport and catabolism; NeurDise: 神经退行性疾病Neurodegenerative diseases; DrugResAn: 耐药性:抗肿瘤药Drug resistance: Antineoplastic; EndAndMt: 内分泌代谢性疾病Endocrine and metabolic diseases; NervSyst: 神经系统Nervous system; CardDise: 心血管疾病Cardiovascular diseases; Transcrp: 转录Transcription; ImmSyst: 免疫系统Immune system; CanSpeTy: 癌症:特定类型Cancers: Specific types; EnvrAdap: 环境适应Environmental adaptation; InfDisVi: 传染性疾病:病毒性Infectious diseases: Viral; SubsDepn: 物质依赖Substance dependence; InfDisPa: 传染病:寄生Infectious diseases: Parasitic; CircSyst: 循环系统Circulatory system; ExcrSyst: 排泄系统Excretory system; ImmnDise: 免疫性疾病Immune diseases; DigsSyst: 消化系统Digestive system; Cellular Community-Amn: 细胞群落-真核生物Cellular community-eukaryotes; Developm: 发育Development; SigMoAnd: 信号分子及相互作用Signaling molecules and interaction; SensSyst: 感觉系统Sensory system.
Fig.6 Principal component analysis of bacterial functional diversity
| 1 | Yang X M, Kay B D. Rotation and tillage effects on soil organic carbon sequestration in a typical Hapludalf in Southern Ontario. Soil and Tillage Research, 2001, 59(3/4): 107-114. |
| 2 | Anthony M W, Craeme J B. Managing legume leys, residues and fertilizers to enhance the sustainability of wheat yields and nutrient balance: 2. Soil physical fertility and carbon. Soil and Tillage Research, 2000, 54(1/2): 77-89. |
| 3 | Li L L, Huang G B, Zhang R Z, et al. Effects of lucerne removal time on soil water and productivity in a lucerne-wheat rotation on the western Loess Plateau. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(4): 686-693. |
| 4 | Li Y S, Huang M B. Pasture yield and soil water depletion of continuous growing alfalfa in the Loess Plateau of China. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2008, 124(1): 24-32. |
| 5 | Jia Y, Li F M, Wang X L. Soil quality responses to alfalfa watered with a field micro-catchment technique in the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crops Research, 2005, 95(1): 64-74. |
| 6 | Han Q F, Zhou F, Jia J, et al. Effect of fertilization on productivity different producing performance alfalfa varieties and soil fertility. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2009, 15(6): 1413-1418. |
| 韩清芳, 周芳, 贾珺, 等. 施肥对不同品种苜蓿生产力及土壤肥力的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(6): 1413-1418. | |
| 7 | Rillig M C, Mummey D L. Mycorrhizas and soil structure. The New Phytologist, 2006, 171(1): 41-53. |
| 8 | Sun B J, Jia S X, Zhang X P, et al. Impact of tillage practices on microbial biomass carbon in top layer of black soils. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(1): 101-107. |
| 孙冰洁, 贾淑霞, 张晓平, 等. 耕作方式对黑土表层土壤微生物生物量碳的影响. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(1): 101-107. | |
| 9 | Zhang W, Wei H L, Gao H W, et al. Advances of studies on soil microbial diversity and environmental impact factors. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(1): 48-52. |
| 张薇, 魏海雷, 高洪文, 等. 土壤微生物多样性及其环境影响因子研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(1): 48-52. | |
| 10 | Jin F X, Ma D M, Liu H Y, et al. Effects of planting years of alfalfa on soil quality. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2014, 32(2): 73-77. |
| 金风霞, 麻冬梅, 刘昊焱, 等. 不同种植年限苜蓿地土壤环境效应的研究. 干旱地区农业研究, 2014, 32(2): 73-77. | |
| 11 | Peter H, Sommaruga R. Shift in diversity and function of lake bacteria communities upon glacier retreat. The International Society for Music Education Journal, 2016, 10(7): 1545-1554. |
| 12 | Mohammad B, Falk H, Forslund S K, et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature, 2018, 560(7717): 233-237. |
| 13 | Maestre F T, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Jeffries T C, et al. Increasing aridity reduces soil microbial diversity and abundance in global drylands. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112(51): 15684-15689. |
| 14 | Aßhauer K P, Bernd W, Rolf D, et al. Tax4 Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(17): 2882-2884. |
| 15 | Stilianos L, Saulo M S, Aliny P, et al. High taxonomic variability despite stable functional structure across microbial communities. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2016, 1(1): 15. |
| 16 | Dong Z Y, Hong M, Hu H J, et al. Effect of excess nitrogen loading on the metabolic potential of the bacterial community in oligotrophic coastal water. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(2): 457-466. |
| 董志颖, 洪慢, 胡晗静, 等. 过量氮输入对寡营养海水细菌群落代谢潜力的影响. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(2): 457-466. | |
| 17 | Sun F, Tian W, Zhang F, et al. Composition and predictive functional analysis of rhizosphere bacterial communities in riparian buffer strips in the Danjiangkou reservoir, China. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(1): 421-429. |
| 孙峰, 田伟, 张菲, 等. 丹江口库区库滨带植被土壤细菌群落多样性及 PICRUSt 功能预测分析.环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 421-429. | |
| 18 | Agnello A C, Huguenot D, Van Hullebusch E D, et al. Citric acid- and Tween 80-assisted phytoremediation of a co-contaminated soil: Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) performance and remediation potential. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(9): 9215-9226. |
| 19 | Tai J C. Study on effects of planting years on alfalfa soil physical-chemical characteristics and microorganisms. Tongliao: Inner Mongolia University for the Nationalities, 2008. |
| 邰继承. 种植年限对紫花苜蓿地土壤理化特性及其微生物影响的研究. 通辽: 内蒙古民族大学, 2008. | |
| 20 | Cai Y, Hao M D, Zhang L Q, et al. Effect of cropping systems on microbial diversity in black loessial soil tested by 454 sequencing technology. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2015, 41(2): 339-346. |
| 蔡艳, 郝明德, 张丽琼, 等. 应用454测序技术分析种植制度对黑垆土微生物多样性的影响. 作物学报, 2015, 41(2): 339-346. | |
| 21 | Gen D Z, Huang J H, Huo N, et al. Characteristics of soil microbial and nematode communities under artificial Medicago sativa grasslands with different cultivation years in semi-arid region of Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(4): 1365-1377. |
| 耿德洲, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 等. 黄土高原半干旱区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿人工草地土壤微生物和线虫群落特征.应用生态学报, 2020, 31(4): 1365-1377. | |
| 22 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 23 | Sinclair L, Osman O A, Bertilsson S, et al. Microbial community composition and diversity via 16S rRNA gene amplicons: Evaluating the illumine platform. PLoS One, 2015, 10(2): e0116955. |
| 24 | Mueller R C, Paula F S, Mirza B S, et al. Links between plant and fungal communities across a deforestation chronosequence in the Amazon rainforest. The International Society for Music Education Journal, 2014, 8(7): 1548-1550. |
| 25 | Morgan G L, Jesse Z, Caporaso J G, et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(9): 814-821. |
| 26 | Zhang C X, Hao M D, Wang X G, et al. Study on soil nitrogen and fertility distribution characteristics in alfalfa field in gully region of the Loess Plateau. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2004, 24(6): 1107-1111. |
| 张春霞, 郝明德, 王旭刚, 等. 黄土高原地区紫花苜蓿生长过程中土壤养分的变化规律. 西北植物学报, 2004, 24(6): 1107-1111. | |
| 27 | Li W J, Wang Z, Han Q F, et al. Evaluation on carbon sequestration effects of artificial alfalfa pastures in the Loess Plateau area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(23): 7467-7477. |
| 李文静, 王振, 韩清芳, 等. 黄土高原人工苜蓿草地固碳效应评估. 生态学报, 2013, 33(23): 7467-7477. | |
| 28 | Liu R L, Zhang A P, Li Y H, et al. Rice yield, nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and nitrogen leaching losses as affected by long-term combined applications of manure and chemical fertilizers in Yellow River irrigated region of Ningxia, China. The Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(5): 947-954. |
| 刘汝亮, 张爱平, 李友宏, 等. 长期配施有机肥对宁夏引黄灌区水稻产量和稻田氮素淋失及平衡特征的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(5): 947-954. | |
| 29 | Yang H S, Cao M J, Fan F, et al. Effects of the number of growthyears of alfalfa on the physical and chemical properties of soil.Chinese Journal Grassland, 2006, 28(6): 29-32. |
| 杨恒山, 曹敏建, 范富, 等. 紫花苜蓿生长年限对土壤理化性状的影响. 中国草地学报, 2006, 28(6): 29-32. | |
| 30 | Wen X Y, Eric D, Wu Y, et al. Wheat, maize and sunflower cropping systems selectively influence bacteria community structure and diversity in their and succeeding crop’s rhizosphere. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(8): 1892-1902. |
| 31 | Liang Z T, Deng J Q, Wang Z K, et al. Differences in soil bacterial community composition among three forage-crop rotations on the Longdong Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(8): 180-191. |
| 梁志婷, 邓建强, 王自奎, 等. 陇东旱塬区不同粮草轮作模式下土壤细菌群落组成特征.草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 180-191. | |
| 32 | Rui J, Peng J, Lu Y. Succession of bacterial populations during plant residue decomposition in rice field soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(14): 4879-4886. |
| 33 | Luo Z Z, Niu Y N, Li L L, et al. Soil moisture and alfalfa productivity response from different years of growth on the Loess Plateau of central Gansu. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(1): 31-38. |
| 罗珠珠, 牛伊宁, 李玲玲, 等. 陇中黄土高原不同种植年限苜蓿草地土壤水分及产量响应. 草业学报, 2015, 24(1): 31-38. | |
| 34 | Cai L, Wang L L, Luo Z Z, et al. Meta-analysis of alfalfa yield and WUE response to growing ages in China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 27-38. |
| 才璐, 王林林, 罗珠珠, 等. 中国苜蓿产量及水分利用效率对种植年限响应的Meta分析. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 27-38. | |
| 35 | Liu F C, Xing S J, Ma H L, et al. Effects of continuous drought on soil bacteria populations and community diversity in sweet cherry rhizosphere. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(3): 642-649. |
| 刘方春, 邢尚军, 马海林, 等. 持续干旱对樱桃根际土壤细菌数量及结构多样性影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(3): 642-649. | |
| 36 | Fei Y C, Huang Y, Zhang X, et al. Effects of different organic fertilizer treatments on soil microbial community structure of camellia oleifera plantation in purple soil area. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2020, 26(4): 1-12. |
| 费裕翀, 黄樱, 张筱, 等. 不同有机肥处理对紫色土油茶林土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2020, 26(4): 1-12. | |
| 37 | Jennings J A, Nelson C J. Influence of soil texture on alfalfa auto toxicity. Agronomy Journal, 1998, 90(1): 54-58. |
| 38 | Faulwetter J L, Burr M D, Parker A E, et al. Influence of season and plant species on the abundance and diversity of sulfate reducing bacteria and ammonia oxidizing bacteria in constructed wetland microcosms. Microbial Ecology, 2013, 65(1): 111-127. |
| 39 | Liu Q C, Zhang Q Q, Tian X L, et al. Composition of bacterial community in maize rhizosphere and screening of biocontrol bacteria strains. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2018, 34(5): 771-778. |
| 刘泉成, 张茜茜, 田雪亮, 等. 玉米根际细菌群落特征及生防菌筛选. 中国生物防治学报, 2018, 34(5): 771-778. | |
| 40 | Deng C F, Luo Z Z, Li L L, et al. Characterization of greenhouse gases emissions from rainfed soils in different cropping systems on the Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(9): 1-13. |
| 邓长芳, 罗珠珠, 李玲玲, 等. 黄土高原雨养农业区不同种植模式土壤温室气体排放特征. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 1-13. | |
| 41 | Yang X M, Xu Y C, Huang Q W, et al. Organic-link fertilizers and its relation to sustainable development of agriculture and protection of eco-environment. Acta Pedologica sinica, 2008, 45(5): 925-932. |
| 杨兴明, 徐阳春, 黄启为, 等. 有机(类)肥料与农业可持续发展和生态环境保护. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 925-932. | |
| 42 | Yao H Y, Jiao X D, Wu F Z. Effects of continuous cucumber cropping and alternative rotations under protected cultivation on soil microbial community diversity. Plant and Soil, 2006, 284(1/2): 195-203. |
| 43 | Yuan H C, Qin H L, Liu S L, et al. Response of abundance and composition of the bacterial community to long-term fertilization in paddy soils. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(22): 66-73. |
| 袁红朝, 秦红灵, 刘守龙, 等.长期施肥对红壤性水稻土细菌群落结构和数量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(22): 66-73. | |
| 44 | Ramirez K S, Lauber C L, Knight R, et al. Consistent effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial communities in contrasting systems. Ecology, 2010, 91(12): 3463-3470. |
| 45 | Lakshmanan V, Selvaraj G, Bais H P. Functional soil microbiome: Belowground solutions to an aboveground problem. Plant Physiology, 2014, 166(2): 689-700. |
| 46 | Berendsen R L, Pieter S E C M, Bakker P A. The rhizo-sphere microbiome and plant health. Trends in Plant Science, 2012, 17(8): 478-486. |
| 47 | Song L, Pan K W, Wang J C, et al. Effects of phenolic acids on seed germination and seedling antioxidant enzyme activity of alfalfa. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(10): 3393-3403. |
| 宋亮, 潘开文, 王进闯, 等. 酚酸类物质对苜蓿种子萌发及抗氧化物酶活性的影响. 生态学报, 2006, 26(10): 3393-3403. | |
| 48 | Zhao X, Liu H L, Yang P, et al. Effects of drip irrigation on bacterial diversity and community structure in rhizosphere soil of alfalfa. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(10): 2579-2590. |
| 赵祥, 刘红玲, 杨盼, 等. 滴灌对苜蓿根际土壤细菌多样性和群落结构的影响.微生物学通报, 2019, 46(10): 2579-2590. | |
| 49 | Kessel M A H J, Speth D R, Albertsen M, et al. Complete nitrification by a single microorganism. Nature, 2015, 528(7583): 555-559. |
| 50 | Baker B J, Sheik C S, Taylor C A, et al. Community transcriptomic assembly reveals microbes that contribute to deep-sea carbon and nitrogen cycling. International Society for Music Education Journal, 2013, 7(10): 1962-1973. |
| 51 | de Vries F T, Griffiths R I, Mark B, et al. Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 30-33. |
| 52 | Yang P, Zhai Y P, Zhao X, et al. Effect of interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobium on Medicago sativa rhizosphere soil bacterial community structure and PICRUSt functional prediction. Microbiology China, 2020, 47(11): 3868-3879. |
| 杨盼, 翟亚萍, 赵祥, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌和根瘤菌互作对苜蓿根际土壤细菌群落结构的影响及PICRUSt功能预测分析. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(11): 3868-3879. | |
| 53 | Du Y J, Gao G L, Chen L H, et al. Soil bacteria community structure and function prediction in the Hulun Buir sandy area. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(11): 4840-4848. |
| 杜宇佳, 高广磊, 陈丽华, 等. 呼伦贝尔沙区土壤细菌群落结构与功能预测. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(11): 4840-4848. | |
| 54 | Song M, Yun H Y, Kim Y H. Antagonistic Bacillus species as a biological control of ginseng root rot caused by Fusarium cf. incarnatum. Journal of Ginseng Research, 2014, 38(2): 136-145. |
| 55 | Zhang P, Yang P Z, Wang W D, et al. Study on physiological change of alfalfa with symbiotic rhizobium under drought stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(5): 938-944. |
| 张攀, 杨培志, 王卫栋, 等. 干旱胁迫下根瘤菌共生紫花苜蓿抗旱生理变化研究. 草地学报, 2013, 21(5): 938-944. | |
| 56 | Sun X, Lin Y L, Li B L, et al. Analysis and function prediction of soil microbial communities of Cynomorium songaricum in two daodi-origins. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2020, 55(6): 1334-1344. |
| 孙晓, 林余霖, 李葆莉, 等. 干旱沙生药用植物锁阳土壤微生物群落分析与功能预测. 药学学报, 2020, 55(6): 1334-1344. |
| [1] | 张小芳, 魏小红, 刘放, 朱雪妹. PEG胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗内源激素对NO的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 160-169. |
| [2] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [3] | 沙栢平, 谢应忠, 高雪芹, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲. 地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 102-114. |
| [4] | 李振松, 万里强, 李硕, 李向林. 苜蓿根系构型及生理特性对干旱复水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [5] | 吴勇, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 童长春. 河西荒漠灌区紫花苜蓿施肥效应及其基于数据包络分析法的经济效益研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 94-105. |
| [6] | 邢易梅, 蕫理, 战力峰, 才华, 杨圣秋, 孙娜. 混合接种摩西球囊霉和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿耐碱能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [7] | 覃凤飞, 李志华, 刘信宝, 渠晖, 平措卓玛, 洛松群措, 苏梦涵. 外源2,4表油菜素内酯对越夏期高温与弱光胁迫下紫花苜蓿生长和光合性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 146-160. |
| [8] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 于铁峰. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| [9] | 李志龙, 罗超越, 邱慧珍, 付笑, 邓德雷, 张春红, 沈其荣. 连续施氮对马铃薯根际细菌群落结构及反硝化作用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 105-116. |
| [10] | 何国兴, 宋建超, 温雅洁, 刘彩婷, 祁娟. 不同根瘤菌肥对紫花苜蓿生产力及土壤肥力的综合影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. |
| [11] | 魏鹏, 安沙舟, 董乙强, 孙宗玖, 别尔达吾列提·希哈依, 李超. 基于高通量测序的准噶尔盆地荒漠土壤细菌多样性及群落结构特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 182-190. |
| [12] | 于浩然, 格根图, 王志军, 贾玉山, 连植, 贾鹏飞. 甲酸添加剂及青贮时间对紫花苜蓿青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 89-95. |
| [13] | 高丽敏, 苏晶, 田倩, 沈益新. 施氮对不同水分条件下紫花苜蓿氮素吸收及根系固氮酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. |
| [14] | 钱志豪, 韩丙芳, 刘自婷, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲, 马红彬. 渗灌对宁夏引黄灌区苜蓿生长性状及水分利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 147-156. |
| [15] | 马婷燕, 李彦忠. 32个紫花苜蓿品种的种带真菌种类及致病性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 131-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||