

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 170-179.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020181
候怡谣1,2( ), 李霄2, 龙瑞才2, 杨青川1,2, 康俊梅2, 郭长虹1(
), 李霄2, 龙瑞才2, 杨青川1,2, 康俊梅2, 郭长虹1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-21
修回日期:2020-05-25
出版日期:2021-04-20
发布日期:2021-03-16
通讯作者:
郭长虹
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: kaku3008@126.com基金资助:
Yi-yao HOU1,2( ), Xiao LI2, Rui-cai LONG2, Qing-chuan YANG1,2, Jun-mei KANG2, Chang-hong GUO1(
), Xiao LI2, Rui-cai LONG2, Qing-chuan YANG1,2, Jun-mei KANG2, Chang-hong GUO1( )
)
Received:2020-04-21
Revised:2020-05-25
Online:2021-04-20
Published:2021-03-16
Contact:
Chang-hong GUO
摘要:
同源异型域-亮氨酸拉链蛋白(HD-Zip)第I类亚家族在植物非生物胁迫调控过程中起着重要作用,已在多个物种中进行了克隆鉴定,但关于紫花苜蓿该家族基因的研究还鲜有报道。本研究旨在研究紫花苜蓿HD-Zip第I类亚家族基因MsHB7对拟南芥抗旱性的调控功能。通过克隆得到大小为738 bp、编码245个氨基酸的MsHB7基因的开放阅读框。多重序列比对和系统进化树分析结果显示,MsHB7蛋白属于HD-Zip I亚家族,且与拟南芥中ATHB7和ATHB12亲缘关系较近。实时荧光定量分析表明,MsHB7基因受干旱诱导。将MsHB7基因转化拟南芥并获得了阳性植株。干旱处理后,转基因拟南芥比野生型拟南芥萎蔫程度更明显,转基因植株相对含水量显著低于野生型拟南芥,并积累了更多的脯氨酸和丙二醛。qRT-PCR检测发现处理之后逆境胁迫指示基因ATCAT1、 ATDREB2A和ATRD29A在转基因拟南芥中的表达量显著升高,而ATLEA3的表达量显著下降。上述结果表明MsHB7基因的过表达可降低转基因拟南芥的耐旱性,为进一步开发利用该基因提供理论依据。
候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179.
Yi-yao HOU, Xiao LI, Rui-cai LONG, Qing-chuan YANG, Jun-mei KANG, Chang-hong GUO. Effect of overexpression of the alfalfa MsHB7 gene on drought tolerance of Arabidopsis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(4): 170-179.
| 引物Primer | 引物Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| MsHB7F | CAAAACTTAGGCCTTAGCCATATAT |
| MsHB7R | GCAACATAGAAGAACATGGTGCA |
| qMsHB7F | ATGAGGGTTTGGAGGATAAAATCGT |
| qMsHB7R | CAAGTCCAAAAATCCAACCATTGAG |
| qMsactin2F | CAAAAGATGGCAGATGCTGAGGAT |
| qMsactin2R | CATGCACCAGTATGACGAGGTCG |
| pMsHB7F | TGCTCTAGAATGATGGAGGAAGAAGAG |
| pMsHB7R | ACGGGATCCTCAAGTCCAAAAATCC |
| MsHB7F1 | CGACACACTTGTCTACTCCAAAAAT |
| MsHB7R1 | TTCAAGTCCAAAAATCCAACCATTG |
| qMsHB7F1 | TGGAGCCAAGGAAGAAGATGC |
| qMsHB7R1 | CCATCATGCGATGTTTCCACC |
| qATactin7F | AGCTAGAGACAGCCAAGAGC |
| qATactin7R | GCTTCCATTCCGATGAGCGA |
| qATCAT1F | CGCCATGCCGAAAAATACCC |
| qATCAT1R | CTTGCCTGTCTGAATCCCAGGAC |
| qATDREB2AF | CTGGAGAATGGTGCGGAAGA |
| qATDREB2AR | CAGATAGCGAATCCTGCTGTTGT |
| qATLEA3F | GATTGACCCGGCTGAGCTACGA |
| qATLEA3R | AGATGGGATTCACCACAAAAGA |
| qATRD29AF | GATATCGACAAGGATGTGCCG |
| qATRD29AR | GTATCCAGGTCTTCCCTTCGC |
表1 引物列表
Table 1 Primer list
| 引物Primer | 引物Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| MsHB7F | CAAAACTTAGGCCTTAGCCATATAT |
| MsHB7R | GCAACATAGAAGAACATGGTGCA |
| qMsHB7F | ATGAGGGTTTGGAGGATAAAATCGT |
| qMsHB7R | CAAGTCCAAAAATCCAACCATTGAG |
| qMsactin2F | CAAAAGATGGCAGATGCTGAGGAT |
| qMsactin2R | CATGCACCAGTATGACGAGGTCG |
| pMsHB7F | TGCTCTAGAATGATGGAGGAAGAAGAG |
| pMsHB7R | ACGGGATCCTCAAGTCCAAAAATCC |
| MsHB7F1 | CGACACACTTGTCTACTCCAAAAAT |
| MsHB7R1 | TTCAAGTCCAAAAATCCAACCATTG |
| qMsHB7F1 | TGGAGCCAAGGAAGAAGATGC |
| qMsHB7R1 | CCATCATGCGATGTTTCCACC |
| qATactin7F | AGCTAGAGACAGCCAAGAGC |
| qATactin7R | GCTTCCATTCCGATGAGCGA |
| qATCAT1F | CGCCATGCCGAAAAATACCC |
| qATCAT1R | CTTGCCTGTCTGAATCCCAGGAC |
| qATDREB2AF | CTGGAGAATGGTGCGGAAGA |
| qATDREB2AR | CAGATAGCGAATCCTGCTGTTGT |
| qATLEA3F | GATTGACCCGGCTGAGCTACGA |
| qATLEA3R | AGATGGGATTCACCACAAAAGA |
| qATRD29AF | GATATCGACAAGGATGTGCCG |
| qATRD29AR | GTATCCAGGTCTTCCCTTCGC |
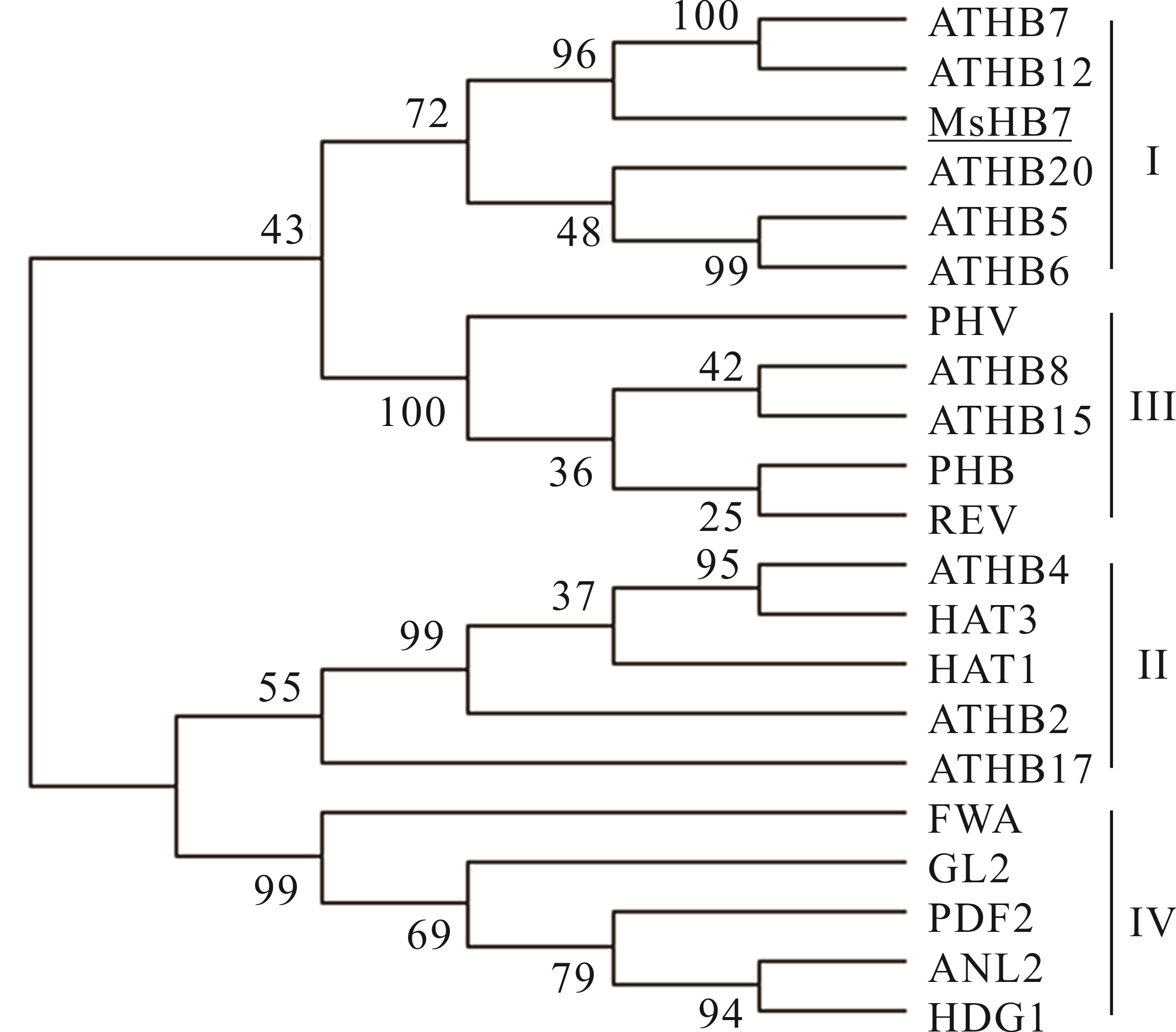
图 1 MsHB7与拟南芥中一些同源异型域-亮氨酸拉链蛋白进化树分析ATHB7: NP_182191.1; ATHB12: NP_191748.1; ATHB20: NP_186771.1; ATHB5: NP_201334.1; ATHB6: NP_565536.1; PHV: NP_174337.1; ATHB8: NP_195014.1; ATHB15: NP_849795.1; PHB: NP_181018.1; REV: NP_200877.1; ATHB4: NP_182018.1; HAT3: NP_191598.1; HAT1: NP_193476.1; ATHB2: NP_193411.1; ATHB17: NP_178252.2; FWA: NP_567722.1; GL2: NP_001185443.1; PDF2: NP_567274.1; ANL2: NP_567183.2; HDG1: NP_191674.1.
Fig.1 Phylogenetic tree analysis of MsHB7 and some homeodomain-leucine zipper proteins from A. thaliana

图 2 MsHB7与其他植物中同源异型域-亮氨酸拉链蛋白的氨基酸序列比对分析A: 同源异型框结构域序列比对 Sequence alignment of homeobox domain; B: 亮氨酸拉链结构域序列比对,6个保守的亮氨酸残基用“L”表示 Sequence alignment of leucine zipper domain, the six conserved leucine residues are represented by “L”. XP_003602321.2: 蒺藜苜蓿 M. truncatula ATHB-12; XP_004502719.1: 鹰嘴豆 Cicer arietinum ATHB-12-like; XP_017420762.1: 小豆 Vigna angularis ATHB-12-like; XP_016695089.1: 陆地棉 Gossypium hirsutum ATHB-12-like; XP_018842791.1: 核桃 Juglans regia ATHB-12-like; XP_002320889.1: 毛果杨Populus trichocarpa ATHB-7; XP_018729630.1: 巨桉 Eucalyptus grandis ATHB-12-like; XP_007218213.1: 桃树 Prunus persica ATHB-12; XP_012088620.1: 麻疯树 Jatropha curcas ATHB-12; NP_001281285.1: 苹果 Malus domestica ATHB-12-like; XP_016538252.1: 辣椒 Capsicum annuum ATHB-12-like; NP_001311821.1 ATHB-12-like: 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum ATHB-12-like; XP_006491341.1: 橙 Citrus sinensis ATHB-7; XP_003548207.2: 大豆 Glycine max ATHB-12; XP_004230017.1: 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum ATHB-12; NP_191748.1: 拟南芥 A. thaliana ATHB-12.
Fig.2 The amino acid sequence alignment analysis between MsHB7 and homeodomain-leucine zipper proteins from other plants
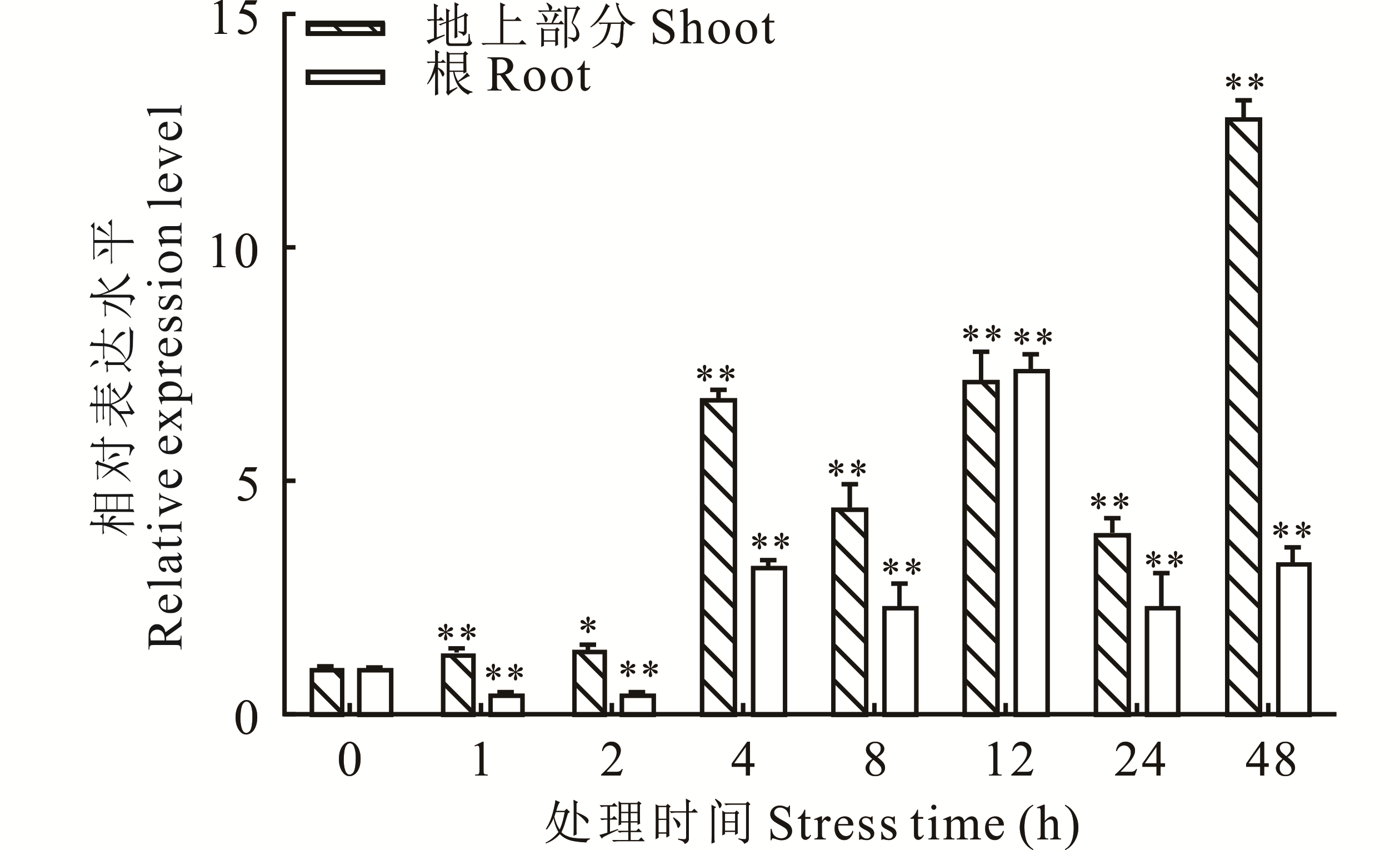
图3 紫花苜蓿在PEG处理下MsHB7基因的相对表达量分析*和**分别表示同一组织中不同时间点与0 h相比差异显著(P<0.05)和极显著(P<0.01)。* and ** respectively indicate that the difference between different time points in the same organization and 0 h is significant (P<0.05) and extremely significant (P<0.01).
Fig.3 Analysis of relative expression of MsHB7 gene in alfalfa treated with PEG

图4 MsHB7转基因拟南芥的PCR检测M: DNA分子量标准DNA marker; 0: 水ddH2O; -: 阴性对照Negative control; +: 阳性对照Positive control.
Fig.4 PCR identification of transgenic A. thaliana with MsHB7
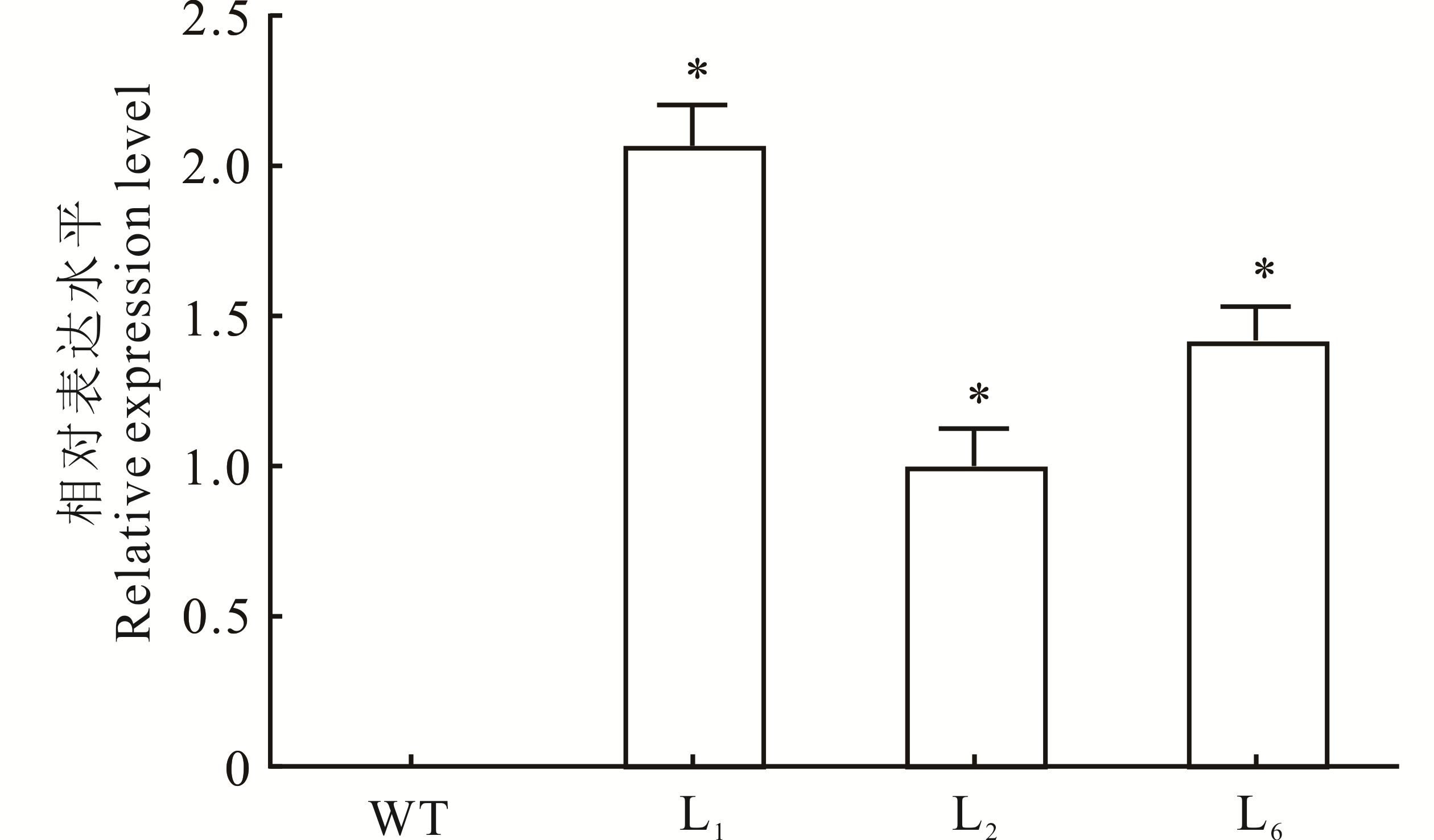
图5 转基因拟南芥中MsHB7的相对表达水平*表示转基因拟南芥与WT相比差异显著(P<0.05)。* indicates that the difference between transgenic A. thaliana and WT is significant (P<0.05).
Fig.5 The relative expression level of MsHB7 in transgenic A. thaliana
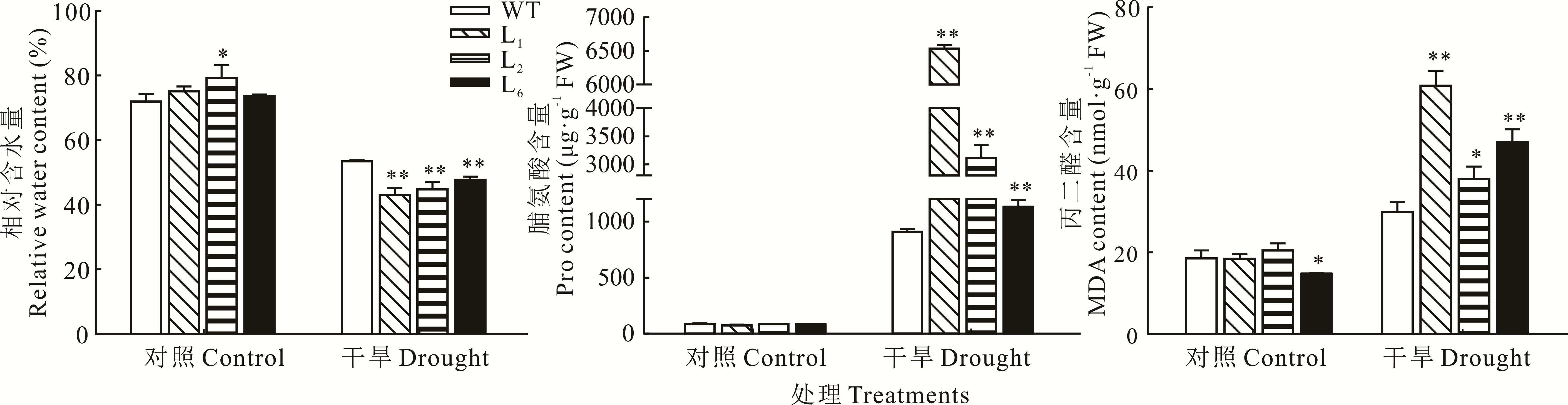
图7 干旱胁迫下拟南芥生理指标分析*表示转基因拟南芥与WT相比差异显著(P<0.05),**表示转基因拟南芥与WT相比差异极显著(P<0.01)。下同。* indicates that the difference between transgenic A. thaliana and WT is significant (P<0.05); ** indicates that the difference between transgenic A. thaliana and WT is extremely significant (P<0.01). The same below.
Fig.7 Analysis of physiological indexes of A. thaliana under drought stress
| 1 | Liu D, Yang L, Luo M, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of PtrZPT2-1, a ZPT2 family gene encoding a Cys2/His2-type zinc finger protein from trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata L. Raf.) that enhances plant tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses. Plant Science, 2017, 263: 66-78. |
| 2 | Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-shinozaki K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiology, 2009, 149(1): 88-95. |
| 3 | Tang L L, Cai H, Ji W, et al. Overexpression of GsZFP1 enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2013, 71: 22-30. |
| 4 | Duan J Z, Li Y, Zhao M Z, et al. Progress on application of NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic tolerance genetic engineering. Crops, 2017(2): 14-22. |
| 段俊枝, 李莹, 赵明忠, 等. NAC转录因子在植物抗非生物胁迫基因工程中的应用进展. 作物杂志, 2017(2): 14-22. | |
| 5 | Ariel F D, Manavella P A, Dezar C A, et al. The true story of the HD-Zip family. Trends in Plant Science, 2007, 12(9): 419-426. |
| 6 | Vollbrecht E, Veit B, Sinha N, et al. The developmental gene Knotted-1 is a member of a maize homeobox gene family. Nature, 1991, 350: 241-243. |
| 7 | Harris J C, Hrmova M, Lopato S, et al. Modulation of plant growth by HD-Zip class I and Ⅱ transcription factors in response to environmental stimuli. New Phytologist, 2011, 190(4): 823-837. |
| 8 | Zhao Y, Zhou Y Q, Jiang H Y, et al. Systematic analysis of sequences and expression patterns of drought-responsive members of the HD-Zip gene family in maize. PLoS One, 2011, 6(12): e28488. |
| 9 | Söderman E, Hjellström M, Fahleson J, et al. The HD-Zip gene ATHB6 in Arabidopsis is expressed in developing leaves, roots and carpels and up-regulated by water deficit conditions. Plant Molecular Biology, 1999, 40(6): 1073-1083. |
| 10 | Söderman E, Mattsson J, Engström P. The Arabidopsis homeobox gene ATHB-7 is induced by water deficit and by abscisic acid. the Plant Journal, 1996, 10(2): 375-381. |
| 11 | Olsson A S B, Engström P, Söderman E. The homeobox genes ATHB12 and ATHB7 encode potential regulators of growth in response to water deficit in Arabidopsis. Plant Molecular Biology, 2004, 55(5): 663-677. |
| 12 | Hjellström M, Olsson A S B, Engström P, et al. Constitutive expression of the water deficit-inducible homeobox gene ATHB7 in transgenic Arabidopsis causes a suppression of stem elongation growth. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2003, 26(7): 1127-1136. |
| 13 | Turchi L, Carabelli M, Ruzza V, et al. Arabidopsis HD-Zip Ⅱ transcription factors control apical embryo development and meristem function. Development, 2013, 140(10): 2118-2129. |
| 14 | Prigge M J, Otsuga D, Alonso J M, et al. Class Ⅲ homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family members have overlapping, antagonistic, and distinct roles in Arabidopsis development. the Plant Cell, 2005, 17(1): 61-76. |
| 15 | Rerie W G, Feldmann K A, Marks M D. The GLABRA2 gene encodes a homeo domain protein required for normal trichome development in Arabidopsis. Genes & Development, 1994, 8(12): 1388-1399. |
| 16 | Zhao M R, Shen Y H, Li Y C, et al. Research progress in the genetic engineer of alfalfa stress resistance. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2014, 22(2): 243-248. |
| 赵美荣, 申玉华, 李永春, 等. 紫花苜蓿抗逆基因工程研究进展. 草地学报, 2014, 22(2): 243-248. | |
| 17 | Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular biology and Evolution, 2016, 33(7): 1870-1874. |
| 18 | Li Z Y. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of MsHSP70 gene in Medicago sativa L. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science, 2015. |
| 栗振义. 紫花苜蓿热激蛋白基因MsHSP70的克隆及功能分析. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015. | |
| 19 | Roodbarkelari F, Groot E P. Regulatory function of homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-ZIP) family proteins during embryogenesis. New Phytologist, 2017, 213(1): 95-104. |
| 20 | Sen S, Chakraborty J, Ghosh P, et al. Chickpea WRKY70 regulates the expression of a Homeodomain-Leucine Zipper (HD-Zip) I transcription factor CaHDZ12, which confers abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco and chickpea. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2017, 58(11): 1934-1952. |
| 21 | Zuo Z F, Kang H G, Park M Y, et al. Zoysia japonica MYC type transcription factor ZjICE1 regulates cold tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Science, 2019, 289: 110254. |
| 22 | Li Q, Wu Q, Wang A, et al. Tartary buckwheat transcription factor FtbZIP83 improves the drought/salt tolerance of Arabidopsis via an ABA-mediated pathway. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019, 144: 312-323. |
| 23 | Ju Y L, Yue X F, Min Z, et al. VvNAC17, a novel stress-responsive grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) NAC transcription factor, increases sensitivity to abscisic acid and enhances salinity, freezing, and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, 146: 98-111. |
| 24 | Zhao Y, Ma Q, Jin X L, et al. A novel maize homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-Zip) I gene, Zmhdz10, positively regulates drought and salt tolerance in both rice and Arabidopsis. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2014, 55(6): 1142-1156. |
| 25 | Tang Y H, Bao X X, Wang S, et al. A Physic nut stress-responsive HD-Zip transcription factor, JcHDZ07, confers enhanced sensitivity to salinity stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 942. |
| 26 | Zhang S X, Haider I, Kohlen W, et al. Function of the HD-Zip I gene Oshox22 in ABA-mediated drought and salt tolerances in rice. Plant Molecular Biology, 2012, 80(6): 571-585. |
| 27 | Li M N, Long R C, Yang Q C, et al. Cloning and function analysis of a salt-stress-induced HD-Zip transcription factor MsHB2 from alfalfa. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(4): 622-632. |
| 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 等. 紫花苜蓿盐诱导HD-Zip类转录因子MsHB2的克隆及功能分析. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(4): 622-632. | |
| 28 | Zhang H, Wang P H. Determination of relative water content in plant leaves in vivo. Plant Physiology Communications, 1991(3): 217-219. |
| 张慧, 汪沛洪. 叶片相对含水量的活体测定. 植物生理学报, 1991(3): 217-219. | |
| 29 | Kong W W, Liu F, Zhang C, et al. Non-destructive determination of malondialdehyde (MDA) distribution in oilseed rape leaves by laboratory scale NIR hyperspectral imaging. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 35393. |
| 30 | Székely G, Abrahám E, Cséplo A, et al. Duplicated P5CS genes of Arabidopsis play distinct roles in stress regulation and developmental control of proline biosynthesis. the Plant Journal, 2008, 53(1): 11-28. |
| 31 | Jiang H Y, Teng K, Tan P H, et al. Heterogeneous expression of a novel Zoysia japonica C2H2 zinc finger protein gene, ZjZFN1, caused drought sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(4): 129-138. |
| 姜红岩, 滕珂, 檀鹏辉, 等. 日本结缕草 ZjZFN1 基因对拟南芥的转化及其耐旱性分析. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 129-138. | |
| 32 | Pruthvi V, Narasimhan R, Nataraja K N, et al. Simultaneous expression of abiotic stress responsive transcription factors, AtDREB2A, AtHB7 and AtABF3 improves salinity and drought tolerance in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). PLoS One, 9(12): e111152. |
| 33 | Qin F, Kakimoto M, Sakuma Y, et al. Regulation and functional analysis of ZmDREB2A in response to drought and heat stresses in Zea mays L. the Plant Journal, 2007, 50(1): 54-69. |
| [1] | 张小芳, 魏小红, 刘放, 朱雪妹. PEG胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗内源激素对NO的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 160-169. |
| [2] | 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 梁国玲, 马祥. 干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦产量及干物质积累与分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 177-188. |
| [3] | 马欣, 罗珠珠, 张耀全, 刘家鹤, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群. 黄土高原雨养区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿土壤细菌群落特征与生态功能预测[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 54-67. |
| [4] | 沙栢平, 谢应忠, 高雪芹, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲. 地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 102-114. |
| [5] | 李冬, 申洪涛, 王艳芳, 王悦华, 王丽君, 赵世民, 刘领. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗光合碳同化和内源激素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. |
| [6] | 李振松, 万里强, 李硕, 李向林. 苜蓿根系构型及生理特性对干旱复水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [7] | 吴勇, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 童长春. 河西荒漠灌区紫花苜蓿施肥效应及其基于数据包络分析法的经济效益研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 94-105. |
| [8] | 邢易梅, 蕫理, 战力峰, 才华, 杨圣秋, 孙娜. 混合接种摩西球囊霉和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿耐碱能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [9] | 覃凤飞, 李志华, 刘信宝, 渠晖, 平措卓玛, 洛松群措, 苏梦涵. 外源2,4表油菜素内酯对越夏期高温与弱光胁迫下紫花苜蓿生长和光合性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 146-160. |
| [10] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 于铁峰. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| [11] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙晓梵, 孙宗玖. 新疆不同生境狗牙根种质抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 155-169. |
| [12] | 张宇君, 尚以顺, 王普昶, 丁磊磊, 张文, 邹超. 干旱胁迫下保水剂对盘江白刺花幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 90-98. |
| [13] | 王泳超, 张颖蕾, 闫东良, 何灵芝, 李卓, 燕博文, 邵瑞鑫, 郭家萌, 杨青华. 干旱胁迫下γ-氨基丁酸保护玉米幼苗光合系统的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 191-203. |
| [14] | 何国兴, 宋建超, 温雅洁, 刘彩婷, 祁娟. 不同根瘤菌肥对紫花苜蓿生产力及土壤肥力的综合影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. |
| [15] | 李柯, 周庄煜, 李四菊, 姚浩铮, 周莹, 缪雨静, 唐晓清, 王康才. 荆芥的生长、渗透调节和抗氧化能力对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 150-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||