

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 131-139.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020038
收稿日期:2020-02-05
修回日期:2020-04-26
出版日期:2020-12-28
发布日期:2020-12-28
通讯作者:
李彦忠
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: liyzh@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:Received:2020-02-05
Revised:2020-04-26
Online:2020-12-28
Published:2020-12-28
Contact:
Yan-zhong LI
摘要:
植物病原菌通过种子可进一步在时间上延续和空间上传播。为确定我国目前主要种植的苜蓿品种是否携带苜蓿黄萎病菌等毁灭性病害的病菌和其他重要病菌,为苜蓿的引种调运和病害防治提供数据支撑,本研究从我国苜蓿育种者和经营进口苜蓿种子的公司收集了32个苜蓿品种,采用PDA平皿法分离并鉴定了种带真菌,采用浸种法测定了其对中苜3号的种子萌发、幼苗生长的致病性影响。结果表明,供试种子中未检测出苜蓿黄萎病菌及其他生产上的检疫性病原菌,苜蓿种子上的真菌主要为环境普遍存在的链格孢属、青霉属、曲霉属等真菌,共有19属20种;不同品种的种子带菌率有显著差异,不消毒处理下带菌率为26.18%~67.54%;消毒处理后平均种带真菌率有效降低了25.10%;枝孢霉、黑附球菌、枝顶孢、细交链孢等显著降低发芽率,篮状菌、球毛壳菌、黄曲霉、茄匍柄霉等菌对幼苗的芽和根有显著的抑制作用,严重的可引起幼苗枯萎、腐烂。
马婷燕, 李彦忠. 32个紫花苜蓿品种的种带真菌种类及致病性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 131-139.
Ting-yan MA, Yan-zhong LI. Species and pathogenicity of seed-borne fungi in 32 varieties of alfalfa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 131-139.
| 品种编号Variety number | 品种Varieties | 来源Source | 育成国家Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 龙威3010 Longwei 3010 | 甘肃猛犸农业公司Gansu Mengma Agricultural Company | 中国 China |
| 2 | 龙威6010 Longwei 6010 | 甘肃猛犸农业公司Gansu Mengma Agricultural Company | 中国 China |
| 3 | 新牧1号 Xinmu No.1 | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 4 | 新牧2号 Xinmu No.2 | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 5 | 新牧3号 Xinmu No.3 | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 6 | 新疆大叶 Xinjiang daye | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 7 | 甘农3号 Gannong No.3 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 8 | 甘农4号 Gannong No.4 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 9 | 甘农5号 Gannong No.5 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 10 | 甘农6号 Gannong No.6 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 11 | 甘农9号 Gannong No.9 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 12 | 陇东苜蓿 Longdong alfalfa | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 13 | 中苜1号 Zhongmu No.1 | 中国农业科学院Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 中国 China |
| 14 | 中苜2号 Zhongmu No.2 | 中国农业科学院Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 中国 China |
| 15 | 中苜3号 Zhongmu No.3 | 中国农业科学院Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 中国 China |
| 16 | 敖汉苜蓿 Aohan alfalfa | 内蒙古农业大学 Inner Mongolia Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 17 | 巨能2 Magnum II | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 18 | 巨能6 Magnum VI | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 19 | 巨能7 Magnum VII | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 20 | 皇冠 Phabulous | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 21 | 金皇后 Golden | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 22 | 耐盐之星 Salt-tolerant star | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 23 | 太阳神 Sun god | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 24 | 驯鹿 Reindeer | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 25 | 阿尔冈金 Algonquin | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 26 | 阿迪娜 Adina | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 27 | MF4020 | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 28 | MF4030 | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 29 | SR4030 | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 30 | 北极熊 Gibraltar | 北京百斯特公司Beijing Best Company | 美国 America |
| 31 | 雷霆 Instict | 北京百斯特公司Beijing Best Company | 美国 America |
| 32 | 冲击波 Shock wave | 北京百斯特公司Beijing Best Company | 加拿大 Canada |
表1 苜蓿品种及种子来源
Table 1 Alfalfa cultivars and seeds sources
| 品种编号Variety number | 品种Varieties | 来源Source | 育成国家Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 龙威3010 Longwei 3010 | 甘肃猛犸农业公司Gansu Mengma Agricultural Company | 中国 China |
| 2 | 龙威6010 Longwei 6010 | 甘肃猛犸农业公司Gansu Mengma Agricultural Company | 中国 China |
| 3 | 新牧1号 Xinmu No.1 | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 4 | 新牧2号 Xinmu No.2 | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 5 | 新牧3号 Xinmu No.3 | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 6 | 新疆大叶 Xinjiang daye | 新疆农业大学Xinjiang Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 7 | 甘农3号 Gannong No.3 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 8 | 甘农4号 Gannong No.4 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 9 | 甘农5号 Gannong No.5 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 10 | 甘农6号 Gannong No.6 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 11 | 甘农9号 Gannong No.9 | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 12 | 陇东苜蓿 Longdong alfalfa | 甘肃农业大学Gansu Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 13 | 中苜1号 Zhongmu No.1 | 中国农业科学院Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 中国 China |
| 14 | 中苜2号 Zhongmu No.2 | 中国农业科学院Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 中国 China |
| 15 | 中苜3号 Zhongmu No.3 | 中国农业科学院Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 中国 China |
| 16 | 敖汉苜蓿 Aohan alfalfa | 内蒙古农业大学 Inner Mongolia Agricultural University | 中国 China |
| 17 | 巨能2 Magnum II | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 18 | 巨能6 Magnum VI | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 19 | 巨能7 Magnum VII | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 20 | 皇冠 Phabulous | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 21 | 金皇后 Golden | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 22 | 耐盐之星 Salt-tolerant star | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 23 | 太阳神 Sun god | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 美国 America |
| 24 | 驯鹿 Reindeer | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 25 | 阿尔冈金 Algonquin | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 26 | 阿迪娜 Adina | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 27 | MF4020 | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 28 | MF4030 | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 29 | SR4030 | 北京克劳沃公司Beijing Clover Company | 加拿大 Canada |
| 30 | 北极熊 Gibraltar | 北京百斯特公司Beijing Best Company | 美国 America |
| 31 | 雷霆 Instict | 北京百斯特公司Beijing Best Company | 美国 America |
| 32 | 冲击波 Shock wave | 北京百斯特公司Beijing Best Company | 加拿大 Canada |
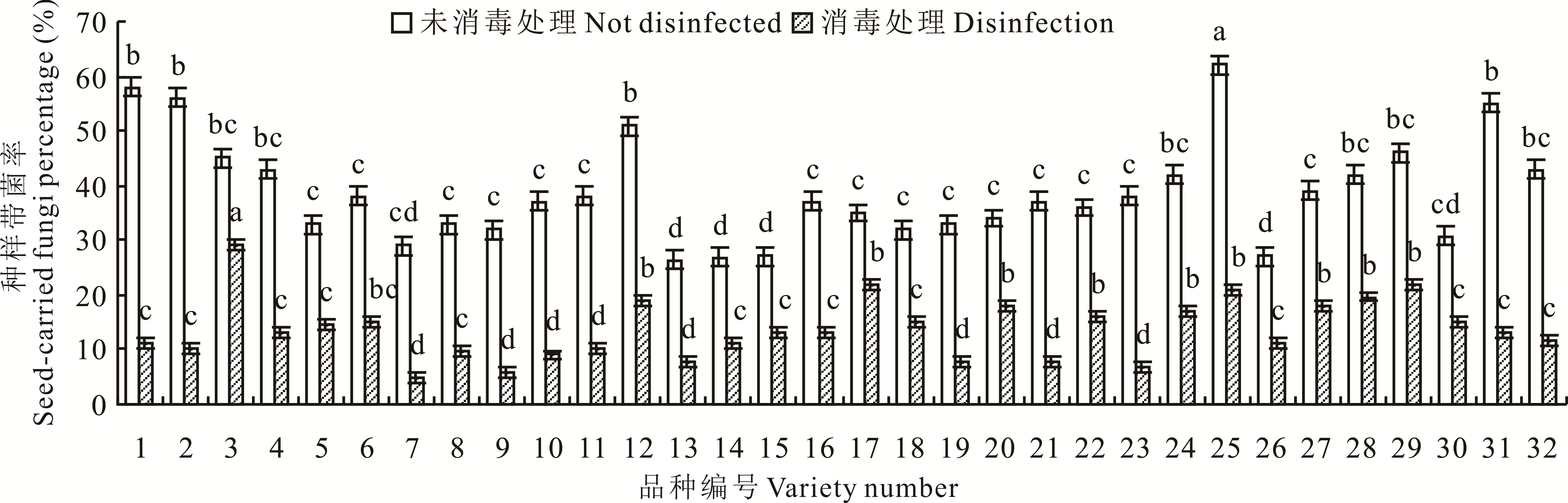
图1 苜蓿种样带菌率不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences at P<0.05. The same below.
Fig.1 Alfalfa seed-borne fungi infection
| 1 | Zhang L J, Bai Z X, Guan W B, et al. Geographic distributions of cultivated alfalfa in China. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2005, 20: 99-102. |
| 张丽君, 白占雄, 关文彬, 等. 我国苜蓿属植物栽培品种的地理分布. 华北农学报, 2005, 20: 99-102. | |
| 2 | Li C J, Nan Z B. Fungi in alfalfa seed belt and its pathogenicity. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2000, 9(1): 27-36. |
| 李春杰, 南志标. 苜蓿种带真菌及其致病性测定. 草业学报, 2000, 9(1): 27-36. | |
| 3 | Lu X S. China’s alfalfa industry development issues. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2013, 35(5): 3-7. |
| 卢欣石. 中国苜蓿产业发展问题. 中国草地学报, 2013, 35(5): 3-7. | |
| 4 | Wang X Y. Releationship between alfalfa supply and demand in China. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2017. |
| 王熙遥. 中国苜蓿市场供给和需求关系研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2017. | |
| 5 | Tian W, Yang Y X, Xu F, et al. Study on introduction and selection of alfalfa varieties. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2003, 37(1): 90-93. |
| 田玮, 杨雨鑫, 徐峰, 等. 紫花苜蓿品种引种筛选的研究. 河南农业大学学报, 2003, 37(1): 90-93. | |
| 6 | Zhang L. Alfalfa planting technology and pest control measures. Science and Technology & Innovation, 2017(11): 113. |
| 张岚. 紫花苜蓿的种植技术及病虫害防治措施. 科技与创新, 2017(11): 113. | |
| 7 | Chen G. Analysis on seven factors of alfalfa variety selection. China Dairy, 2019, 208(4): 16-22. |
| 陈谷. 苜蓿品种选择的七大考量因素分析. 中国乳业, 2019, 208(4): 16-22. | |
| 8 | Srivastava R N. Studies on location of conidia and mycelium of fungi in seeds. Journal of the Indian Botanical Society, 1986, 3: 279-284. |
| 9 | Nan Z B, Liu R. Detection of fungi in the seed zone of Astragalus adsurgens. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 1997, 6(4): 12-17. |
| 南志标, 刘若. 沙打旺种带真菌检测. 草业学报, 1997, 6(4): 12-17. | |
| 10 | Gao C X, Nan Z B. Progress in research on the seed-borne fungi of forage in China. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(7): 1792-1802. |
| 高晨轩, 南志标. 我国牧草种带真菌研究进展. 草业科学, 2019, 36(7): 1792-1802. | |
| 11 | Tai L M, Zheng W, Yan F Y, et al. Studies on fungi of rice seeds. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2003, 15(1): 31-33. |
| 台莲梅, 郑雯, 闫凤云, 等. 水稻种子真菌种群研究. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2003, 15(1): 31-33. | |
| 12 | Bai R, Hou T J. A report on pathogenic fungi carried by astragalus and lucerne seeds. Pratacultural Science, 1990, 7(1): 46-48. |
| 白儒, 侯天爵. 沙打旺和紫花苜蓿种带真菌检验初报. 草业科学, 1990, 7(1): 46-48. | |
| 13 | Yuan Q H, Sun J H, Li Q, et al. Examination of fungi in seed belt of Sorghum sudanense and Coronilla varia. Gansu Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, 1993, 23(2): 19-21. |
| 袁庆华, 孙建华, 李琪, 等. 苏丹草和小冠花等种子带真菌检验. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 1993, 23(2): 19-21. | |
| 14 | Li C J, Nan Z B, Zhu T H. Seed-borne fungi of alfalfa and its pathogenicity. Journal of China Agricultural University, 1998, 3(S1): 3-5. |
| 李春杰, 南志标, 朱廷恒. 苜蓿种子传带真菌及其致病性测定. 中国农业大学学报, 1998, 3(S1): 3-5. | |
| 15 | Gong Y J, Li J Q. Preliminary study on the detection of fungi in seeds of five forages and three turfgrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2004, 13(5): 118-122. |
| 龚月娟, 李健强. 五种牧草及三种草坪草种子寄藏真菌检测初探. 草业学报, 2004, 13(5): 118-122. | |
| 16 | Xu X L, Wu X H, Zhang G Z, et al. Analysis on the relationship between the seed borne fungi and the seed vigor of sweet corn. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2006, 39(8): 1565-1570. |
| 徐秀兰, 吴学宏, 张国珍, 等. 甜玉米种子携带真菌与种子活力关系分析. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(8): 1565-1570. | |
| 17 | Shen L, Jiang Y Y, Cao Y B. The research process of the synergistic antifungal effect of plant compositions. Chinese Journal of Mycology, 2013, 8(1): 55-60. |
| 申玲, 姜远英, 曹永兵. 植物成分协同抗真菌作用的研究进展. 中国真菌学杂志, 2013, 8(1): 55-60. | |
| 18 | Liu X Z. The research process of the synergistic antifungal effect of plant compositions advances and challenges in fungal researches—Preface to the special issue for the state key laboratory of mycology. Mycosystema, 2015, 34(5): 795-798. |
| 刘杏忠. 真菌学研究的进展及机遇—真菌学国家重点实验室专刊序言. 菌物学报, 2015, 34(5): 795-798. | |
| 19 | Yang Y X, Han J G, Li S T, et al. Effects of seed-borne fungi on germination and vigor of Zoysia japonica seed. Seed, 2006, 25(10): 16-19. |
| 杨颜霞, 韩建国, 李寿田, 等. 种带真菌对结缕草种子发芽和活力的影响. 种子, 2006, 25(10): 16-19. | |
| 20 | Ma T Y, Luo F, Nzabanita C, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on germination characteristics of 36 alfalfa varieties at home and abroad. Seed, 2019, 38(1): 48-57. |
| 马婷燕, 罗飞, Nzabanita C, 等. 国内外36个苜蓿品种的发芽特性综合评价. 种子, 2019, 38(1): 48-57. | |
| 21 | Gao Y. International association for seed testing (ISTA). China Standardization, 2017(1): 150-155. |
| 高燕. 国际种子检验协会(ISTA). 中国标准化, 2017(1): 150-155. | |
| 22 | Allen P J. Control of spore germination and infection structure formation in the fungi. Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, 1976. |
| 23 | Charlotte V D D H, Rep M. Adaptation to the host environment by plant-pathogenic fungi. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2017, 55(1): 427-450. |
| 24 | Nie X M, Zhao G Q, Lan X J, et al. Effects of producing areas on the seed borne fungi of oat. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(5): 1195-1203. |
| 聂秀美, 赵桂琴, 兰晓君, 等. 产地对燕麦种带真菌的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(5): 1195-1203. | |
| 25 | Chen T, Nan Z B. Seed-borne fungi infection of siberian wildrye: Effects on seed germination and seedling growth. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(2): 96-103. |
| 陈焘, 南志标. 不同储存年限老芒麦种子种带真菌检测及致病性测定. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 96-103. | |
| 26 | Xian M X N E R Z, Li K M, Aa T K M R Z. et al. Detection and identification of seed borne fungi in 11 alfalfa varieties. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(7): 1281-1287. |
| 先米西努尔·肉孜, 李克梅, 阿提开姆·如则, 等. 11个苜蓿品种种子寄藏真菌检测与鉴定. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(7): 1281-1287. | |
| 27 | Chen L. Study on seedborne fungi of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciaefolia Scop). Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. |
| 陈林. 红豆草(Onobrychis viciaefolia Scop)种带真菌研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2010. | |
| 28 | Nan Z B. Epiphyte of Astragalus adsurgens: Environment, pathogenicity and control. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 1998, 7(1): 13-19. |
| 南志标. 沙打旺种带真菌—环境、致病力及防治. 草业学报, 1998, 7(1): 13-19. | |
| 29 | Nan Z B, Hanson J. Detection of seedborne fungi in Stylosanthes guianensis, S. hamata, and S. scabra. Seed Science & Technology, 1998, 26(2): 333-345. |
| 30 | Singh D, Maheshwari V K. The influence of stack burn disease of paddy on seed health status. Seed Research, 2001, 29: 205-209. |
| 31 | De Filippis F, Laiola M, Blaiotta G, et al. Different amplicon targets for sequencing-based studies of fungal diversity. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(17): 905-917. |
| 32 | Liao X L, Zhu X X, Ren X G, et al. Studies on hybrid rice seedborn fungi and the controlling effects of fungicides. Hybrid Rice, 1993, 6(12): 28-32. |
| 廖晓兰, 朱晓湘, 任新国, 等. 杂交稻种传真菌及稻种药剂处理研究. 杂交水稻, 1993, 6(12): 28-32. |
| [1] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生垂穗披碱草成苗期间的耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 76-85. |
| [2] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [3] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静. 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| [4] | 古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33. |
| [5] | 周倩倩, 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 产硫化氢细菌的筛选及阻控苜蓿吸收铅和改良土壤的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 44-52. |
| [6] | 聂秀美, 慕平, 赵桂琴, 何海鹏, 吴文斌, 蔺豆豆, 苏伟娟, 张丽睿. 贮藏年限对裸燕麦种带真菌和真菌毒素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 106-120. |
| [7] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [8] | 谢展, 穆麟, 张志飞, 陈桂华, 刘洋, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 乳酸菌或有机酸盐与尿素复配添加对紫花苜蓿混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [9] | 王吉祥, 宫焕宇, 屠祥建, 郭侲洐, 赵嘉楠, 沈健, 栗振义, 孙娟. 耐亚磷酸盐紫花苜蓿品种筛选及评价指标的鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 186-199. |
| [10] | 张小芳, 魏小红, 刘放, 朱雪妹. PEG胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗内源激素对NO的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 160-169. |
| [11] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [12] | 马欣, 罗珠珠, 张耀全, 刘家鹤, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群. 黄土高原雨养区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿土壤细菌群落特征与生态功能预测[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 54-67. |
| [13] | 沙栢平, 谢应忠, 高雪芹, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲. 地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 102-114. |
| [14] | 马倩, 闫启, 张正社, 吴凡, 张吉宇. 紫花苜蓿CCoAOMT基因家族的鉴定、进化及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 144-156. |
| [15] | 王如月, 文武武, 赵恩华, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿MsWRKY11基因的克隆及其耐盐功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 157-169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
