

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 203-212.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020521
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
高鹏飞( ), 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧(
), 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧( )
)
收稿日期:2020-11-25
修回日期:2021-03-15
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2021-12-22
通讯作者:
吴建慧
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: wujianhui660915@126.com基金资助:
Peng-fei GAO( ), Jing ZHANG, Wei-fang FAN, Bing GAO, Hong-juan HAO, Jian-hui WU(
), Jing ZHANG, Wei-fang FAN, Bing GAO, Hong-juan HAO, Jian-hui WU( )
)
Received:2020-11-25
Revised:2021-03-15
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2021-12-22
Contact:
Jian-hui WU
摘要:
以光叉委陵菜的多年生植株作为试验材料,通过自然控水法,研究不同干旱处理对植株根系的表型特征、超微结构和生理指标的影响,探究光叉委陵菜的耐旱性。结果表明:干旱胁迫下,光叉委陵菜根系总长度、总表面积、总体积和平均直径持续增加,根系干重在0~15 d增加,20~25 d干重显著降低(P<0.05)。随干旱胁迫程度的增加,根系细胞壁变形破损,线粒体解体消失,淀粉粒出现并不断膨大。丙二醛(MDA)含量、脯氨酸含量在25 d内持续升高,可溶性蛋白含量、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性在0~15 d显著升高,在20~25 d均显著下降(P<0.05);复水后,脯氨酸含量下降但不显著(P>0.05),MDA含量、可溶性蛋白含量、SOD活性均出现显著降低(P<0.05)。综合来看,光叉委陵菜能耐20 d的自然干旱,具有较强的抗旱性,这为东北地区选育耐旱植物提供了参考。
高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212.
Peng-fei GAO, Jing ZHANG, Wei-fang FAN, Bing GAO, Hong-juan HAO, Jian-hui WU. Effects of drought stress on root characteristics structure and physiological characteristics of Potentilla bifurca var. glabrata[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 203-212.
时间Time (d) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根总表面积 Total surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根系平均直径 Average root diameter (mm) | 根系干重 Root dry weight (g·plant-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | |
| 0 | 35.39±0.49b | 34.95±0.78b | 4.48±0.13c | 4.50±0.08b | 0.10±0.01b | 0.10±0.01b | 0.40±0.02c | 0.39±0.02b | 0.47±0.01b | 0.47±0.01b |
| 5 | 42.41±0.55b | 40.60±0.91b | 4.81±0.09b | 4.75±0.06b | 0.12±0.01b | 0.10±0.01b | 0.50±0.03b | 0.49±0.02a | 0.47±0.01b | 0.47±0.18b |
| 10 | 55.58±1.25a | 53.67±0.78b | 5.37±0.05a | 5.23±0.06a | 0.14±0.01a | 0.13±0.01b | 0.52±0.01a | 0.50±0.01a | 0.52±0.02a | 0.62±0.04a |
| 15 | 63.55±0.93a | 60.41±0.64b | 5.78±0.06a | 5.56±0.06a | 0.18±0.01a | 0.17±0.01b | 0.56±0.01a | 0.53±0.01a | 0.56±0.01a | 0.65±0.64a |
| 20 | 71.38±0.61a | 67.57±0.88a | 5.97±0.03a | 5.89±0.03a | 0.19±0.01a | 0.18±0.01a | 0.60±0.01a | 0.59±0.01a | 0.57±0.01a | 0.26±0.04c |
| 25 | 78.60±0.67a | 76.35±0.55a | 6.15±0.07a | 6.05±0.05a | 0.19±0.01a | 0.18±0.05a | 0.68±0.01a | 0.64±0.01a | 0.56±0.01a | 0.22±0.04c |
表1 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系表型特征的影响
Table 1 Effect of drought stress on root characteristics of P. bifurca var. glabrata
时间Time (d) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根总表面积 Total surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根系平均直径 Average root diameter (mm) | 根系干重 Root dry weight (g·plant-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | 对照组 Control group | 胁迫组 Coercion group | |
| 0 | 35.39±0.49b | 34.95±0.78b | 4.48±0.13c | 4.50±0.08b | 0.10±0.01b | 0.10±0.01b | 0.40±0.02c | 0.39±0.02b | 0.47±0.01b | 0.47±0.01b |
| 5 | 42.41±0.55b | 40.60±0.91b | 4.81±0.09b | 4.75±0.06b | 0.12±0.01b | 0.10±0.01b | 0.50±0.03b | 0.49±0.02a | 0.47±0.01b | 0.47±0.18b |
| 10 | 55.58±1.25a | 53.67±0.78b | 5.37±0.05a | 5.23±0.06a | 0.14±0.01a | 0.13±0.01b | 0.52±0.01a | 0.50±0.01a | 0.52±0.02a | 0.62±0.04a |
| 15 | 63.55±0.93a | 60.41±0.64b | 5.78±0.06a | 5.56±0.06a | 0.18±0.01a | 0.17±0.01b | 0.56±0.01a | 0.53±0.01a | 0.56±0.01a | 0.65±0.64a |
| 20 | 71.38±0.61a | 67.57±0.88a | 5.97±0.03a | 5.89±0.03a | 0.19±0.01a | 0.18±0.01a | 0.60±0.01a | 0.59±0.01a | 0.57±0.01a | 0.26±0.04c |
| 25 | 78.60±0.67a | 76.35±0.55a | 6.15±0.07a | 6.05±0.05a | 0.19±0.01a | 0.18±0.05a | 0.68±0.01a | 0.64±0.01a | 0.56±0.01a | 0.22±0.04c |
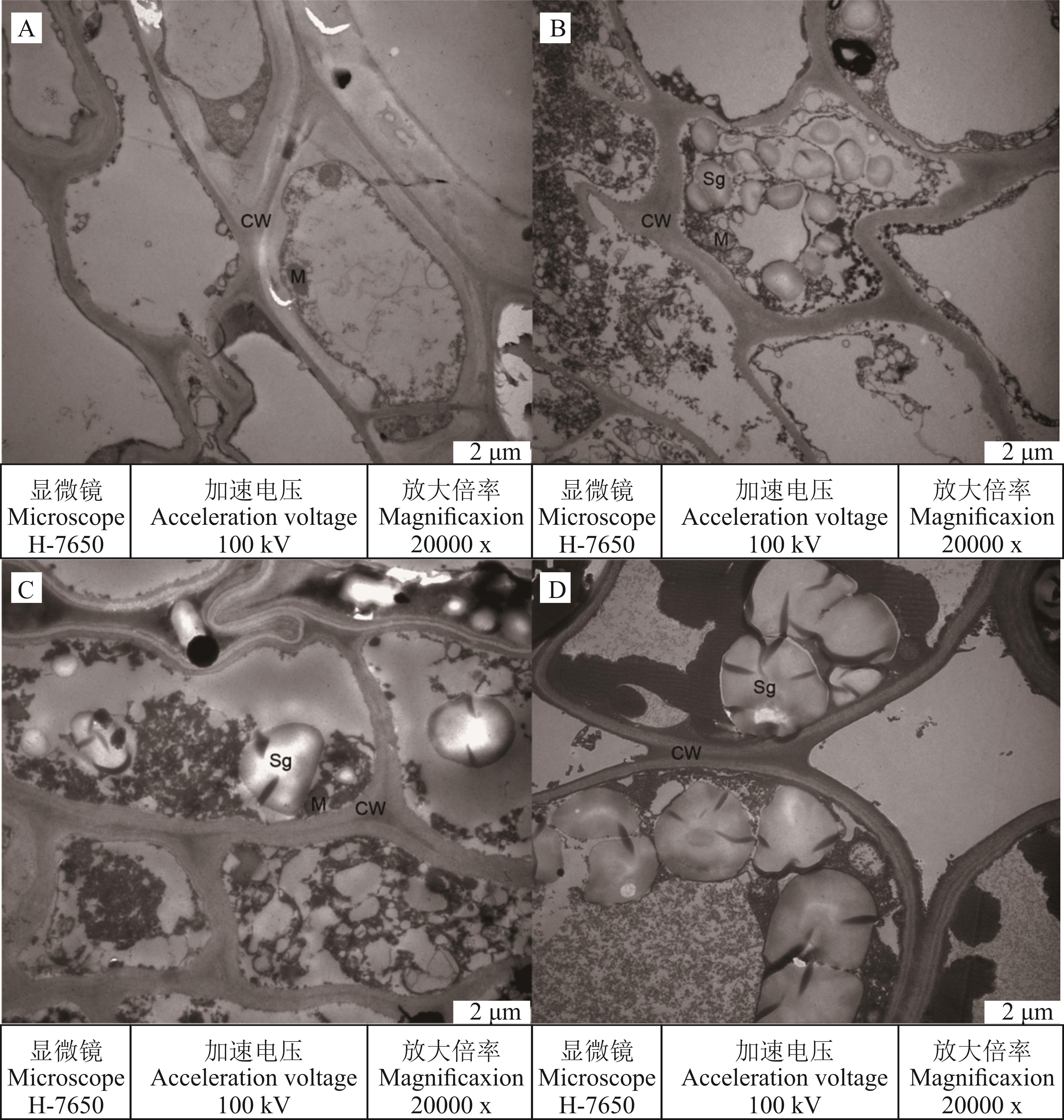
图1 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系超微结构的影响A. 0 d(自然状态);B. 5 d(轻度胁迫);C. 15 d(中度胁迫);D. 25 d(重度胁迫)。A. 0 d (Well water condition); B. 5 d (Mild water stress); C. 15 d (Moderate water stress); D. 25 d (Severe water stress). CW:细胞壁 Cell wall;Sg:淀粉粒 Starch granules;M:线粒体 Mitochondria.
Fig. 1 Effect of drought stress on root ultrastructure of P. bifurca var. glabrata
时间 Time (d) | 细胞壁厚度 Cell wall thickness (μm) | 淀粉粒平均直径 Average starch granule diameter (μm) | 淀粉粒个数 Starch granules (number) | 线粒体个数 Mitochondria (number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (自然状态State of nature) | 0.84±0.26a | 0.00±0.00d | 0.00±0.00c | 3.33±0.58a |
| 5 (轻度胁迫Mild stress) | 0.36±0.05b | 0.61±0.08c | 11.33±1.86a | 1.37±0.32b |
| 15 (中度胁迫Moderate stress) | 0.33±0.03b | 1.24±0.37b | 5.33±0.88b | 0.79±0.23c |
| 25 (重度胁迫Severe stress) | 0.30±0.08b | 2.06±0.21a | 6.00±1.15b | 0.00±0.00d |
表2 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜超微结构细胞器的影响
Table 2 Effect of drought stress on ultrastructure organelles of P. bifurca var. glabrata
时间 Time (d) | 细胞壁厚度 Cell wall thickness (μm) | 淀粉粒平均直径 Average starch granule diameter (μm) | 淀粉粒个数 Starch granules (number) | 线粒体个数 Mitochondria (number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (自然状态State of nature) | 0.84±0.26a | 0.00±0.00d | 0.00±0.00c | 3.33±0.58a |
| 5 (轻度胁迫Mild stress) | 0.36±0.05b | 0.61±0.08c | 11.33±1.86a | 1.37±0.32b |
| 15 (中度胁迫Moderate stress) | 0.33±0.03b | 1.24±0.37b | 5.33±0.88b | 0.79±0.23c |
| 25 (重度胁迫Severe stress) | 0.30±0.08b | 2.06±0.21a | 6.00±1.15b | 0.00±0.00d |
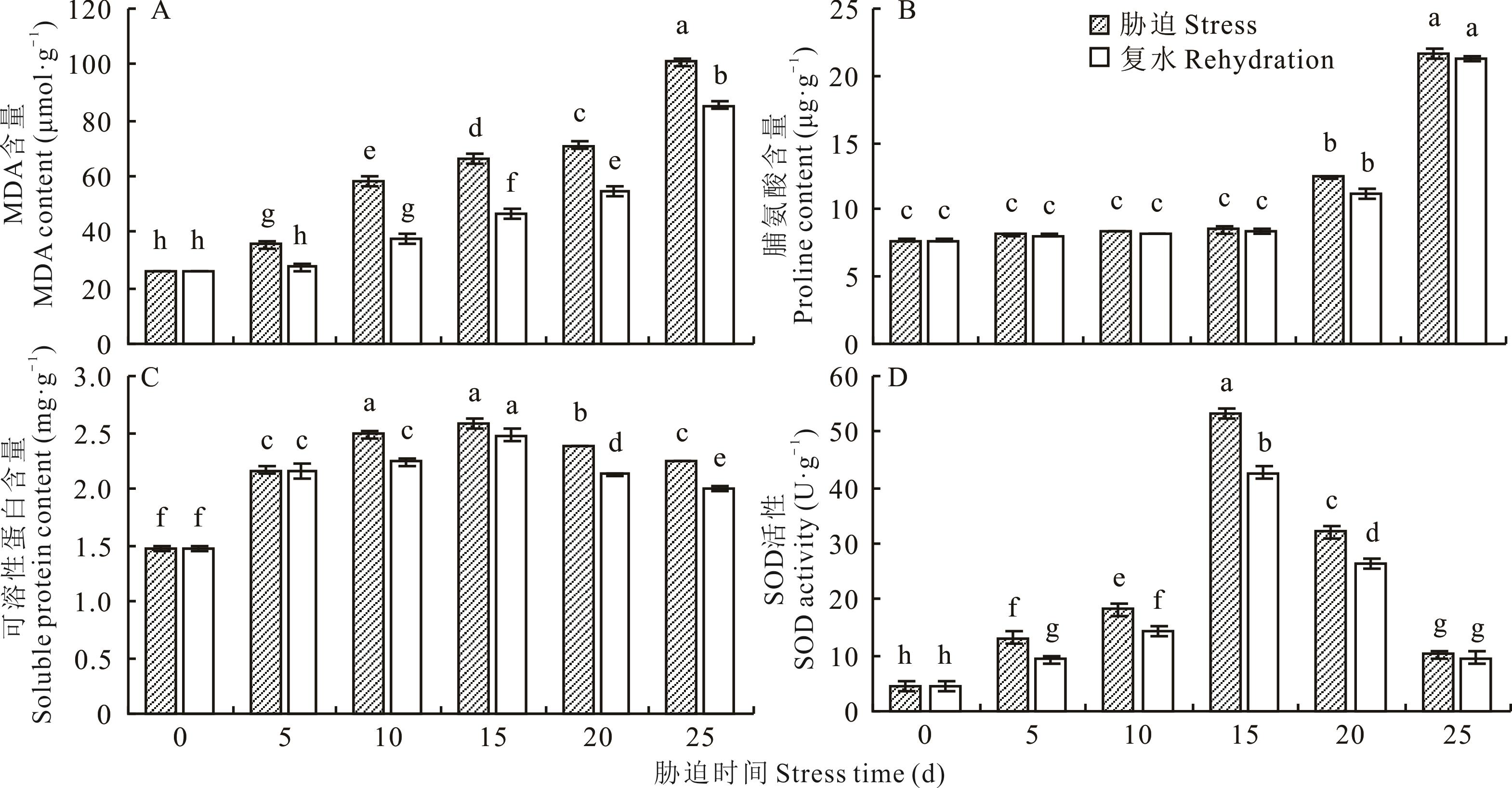
图2 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系生理指标的影响不同字母表示不同时间和不同处理下差异显著(P<0.05)。Different letters indicate significant difference at different times and treatments (P<0.05).
Fig. 2 Effect of drought stress on physiological index of root system of P. bifurca var. glabrata
| 1 | Zhang C M, Shi S L, Liu Z, et al. Effects of drought stress on the root morphology and anatomical structure of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) varieties with differing drought-tolerance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(5): 79-89. |
| 张翠梅, 师尚礼, 刘珍, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性苜蓿品种根系形态及解剖结构的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 79-89. | |
| 2 | Zhang G F, Sun H Y. Effects of drought stress with PEG6000 on morphology and structure in Camellia oleifera seedlings. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55 (11): 2830-2833. |
| 张规富, 孙航远. PEG6000模拟干旱对油茶幼苗形态结构的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(11): 2830-2833. | |
| 3 | Liu Y, Yue X, Chen G L. Effects of water stress on ultrastructure and membrane lipid peroxidation of leaf and root cells of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(6): 79-86. |
| 刘艳, 岳鑫, 陈贵林. 水分胁迫对甘草叶片和根系细胞超微结构与膜脂过氧化的影响. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 79-86. | |
| 4 | Hong X X, Yu X Y. Research progress in drought resistance mechanism of ground cover plants. Shandong Agricultural Science, 2009(5): 62-66. |
| 洪晓晓, 于晓英. 园林地被植物抗旱机制研究进展. 山东农业科学, 2009(5): 62-66. | |
| 5 | Zhang H P, Niu J Y, Xuan C X, et al. Effects of drought stress and rewatering on content of proline and malondiadehyde in pea leaves. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2008, 10(5): 50-54. |
| 张红萍, 牛俊义, 轩春香, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对豌豆叶片脯氨酸和丙二醛含量的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2008, 10(5): 50-54. | |
| 6 | Ji X L, Gai Y P, Mou Z M, et al. Effect of water stress on physiological and biochemical character of mulberry. Science of Sericulture, 2004, 30(2): 117-122. |
| 冀宪领, 盖英萍, 牟志美, 等. 干旱胁迫对桑树生理生化特性的影响. 蚕业科学, 2004, 30(2): 117-122. | |
| 7 | Huang Y M, Zhang J, Luo C D. Literature review on tree’s drought resistance capacities. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 1997, 15(1): 52-57. |
| 黄颜梅, 张健, 罗承德. 树木抗旱性研究(综述). 四川农业大学学报, 1997, 15(1): 52-57. | |
| 8 | Huang Y, Chen A A, Wu Y B. Effects of drought stress on physiology and biochemistry of Paeonia suffruticosa Seedlings. Modern Horticultural Science, 2019(21): 10-14. |
| 黄燕, 陈安安, 吴永彬. 干旱胁迫对野牡丹苗木生理生化的影响. 现代园艺, 2019(21): 10-14. | |
| 9 | Wu Z H, Zeng F H, Ma S J. A review of advances in active oxygen metabolism in plants under water stress. Subtropical Plant Science, 2004(3): 77-80. |
| 吴志华, 曾富华, 马生健. 水分胁迫下植物活性氧代谢研究进展. 亚热带植物科学, 2004(3): 77-80. | |
| 10 | Bowler C, Montagu M V, Inzé D. Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1992, 43(1): 83-116. |
| 11 | Xu Y M, Chen Y Z, Chen Y, et al. Effects of drought stress on physiological and biochemical indexes of the leaves and roots of Camellia oleifera. Hunan Forestry Science and Technology, 2016, 43(4): 7-11. |
| 许彦明, 陈永忠, 陈勇, 等. 持续干旱对油茶叶片及根系生理生化指标的影响. 湖南林业科技, 2016, 43(4): 7-11. | |
| 12 | Zheng M, Guo Y, Wang L M. Effect of drought stress on root morphology and physiological characteristics of Malus micromalus cv. ‘ruby’. China Agricultural Science and Technology Herald, 2020, 22(3): 24-30. |
| 郑淼, 郭毅, 王丽敏. 干旱胁迫对红宝石海棠根系形态及生理特性的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(3): 24-30. | |
| 13 | Zhang Y, Wang Y F. Plant resources of the genus Potentilla in China. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science), 1998, 34(1): 59. |
| 张勇, 王一峰. 国产委陵菜属植物资源. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 34(1): 59. | |
| 14 | Bian Y, Lv D X, Zhang Y Q, et al. The study on lawn use of Potentilla aviculare and Potentilla bifurca. Grassland Science, 2004, 21(7): 66-68. |
| 卞勇, 吕冬霞, 张玉泉, 等. 扁蓄和叉叶委陵菜的草坪利用研究. 草业科学, 2004, 21(7): 66-68. | |
| 15 | Wang X H, Wang S L, Jiang D Q, et al. Introduction and cultivation on a wild cover plant species, Potentilla bifurca L. var. glabrata. Journal of Changchun University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 16(3): 69-71. |
| 王晓红, 王索玲, 姜殿勤, 等. 野生地被植物光叉叶委陵菜的引种栽培. 长春大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 16(3): 69-71. | |
| 16 | You F L, Liang Y T, Qu L N, et al. Study on pollen morphology of Potentilla species in Daqing area. China Agronomy Bulletin, 2010, 26(16): 337-340. |
| 由凤丽, 梁彦涛, 曲丽娜, 等. 大庆地区委陵菜属植物花粉形态研究. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(16): 337-340. | |
| 17 | Tian L, Zhou X Z, Sun H, et al. The leaf epidermal micro-morphology of the seven species of Potentilla. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(2): 53-56. |
| 田丽, 周新宗, 孙航, 等. 7种委陵菜属植物叶表皮微形态的研究. 草业科学, 2009, 26(2): 53-56. | |
| 18 | Huang L, Gao Y, Li X Q, et al. Effects of water stress on dry matter accumulation and translocation in winter wheat cultivars planted at different ages. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 2013, 21(8): 943-950. |
| 黄玲, 高阳, 李新强, 等. 水分胁迫下不同年代冬小麦品种干物质积累与转运特性. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(8): 943-950. | |
| 19 | Huo Z G, Bai Y M, Wen M, et al. The experimental research on water stress effects on growth and development of winter wheat. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(9): 1527-1535. |
| 霍治国, 白月明, 温民, 等. 水分胁迫效应对冬小麦生长发育影响的试验研究. 生态学报, 2001, 21(9): 1527-1535. | |
| 20 | Chen L F. The effect of shading and water stress on physiological characteristics of Hemerocallis middendorffii. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2007. |
| 陈丽飞. 遮荫及干旱胁迫对大花萱草生理特性的影响. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2007. | |
| 21 | Xi M. Effect of drought stress on anatomical structure and physiological characteristics of Solanum nigrum. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010. |
| 袭梅. 干旱胁迫对龙葵解剖结构和生理特性的影响. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010. | |
| 22 | Wang X K. Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical experiments. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 王学奎. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 23 | Pan X D, Zhang Y, Shao M, et al. Research progress on adaptive responses of crop root structure to drought stress. China Agricultural Science and Technology Herald, 2017, 19(2): 51-58. |
| 潘晓迪, 张颖, 邵萌, 等. 作物根系结构对干旱胁迫的适应性研究进展. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(2): 51-58. | |
| 24 | Zhang T, Qi L. Review of prospects for mechanism of plant drought tolerance. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2005(4): 107-110. |
| 张彤, 齐麟. 植物抗旱机理研究进展. 湖北农业科学, 2005(4): 107-110. | |
| 25 | Wang J P, Bughrara S S, Nelson C J. Morpho-physiological responses of several fescue grasses to drought stress. HortScience, 2008, 43(3): 161-173. |
| 26 | Pirnajmedin F, Majidi M M, Gheysari M. Root and physiological characteristics associated with drought tolerance in Iranian tall fescue. Euphytica, 2015, 202(1): 141-155. |
| 27 | Liu J C, Zhong Z C. Influence of water stress and re-watering on the root growth of Cupressus funebris Endl. seedlings in the limestone area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(12): 6439-6445. |
| 刘锦春, 钟章成. 水分胁迫和复水对石灰岩地区柏木幼苗根系生长的影响. 生态学报, 2009, 29(12): 6439-6445. | |
| 28 | Zhang J, Li X P, Chen X H, et al. Biochemical response of winter wheat to long-term soil drought at flowering stage and drought resistance. Journal of Wheat Crops, 2014, 34(6): 765-773. |
| 张军, 李晓萍, 陈新宏, 等. 长期土壤干旱下扬花期冬小麦部分生理生化反应及抗旱性分析. 麦类作物学报, 2014, 34(6): 765-773. | |
| 29 | Wei X, Wang Z Q, Zhang G Z. Morphological and activity variation of mitochondria in fine roots of Fraxinus mandshurica seedling under drought stress. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(12): 1454-1462. |
| 卫星, 王政权, 张国珍. 干旱胁迫下水曲柳苗木细根线粒体的形态及活性变化. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(12): 1454-1462. | |
| 30 | Xu P, Li J, Lv H Y, et al. Effects of drought stress on ultrastructure of chloroplast and mitochondria and membrane lipid peroxidation of ammodendron argenteum. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(1): 120-130. |
| 徐萍, 李进, 吕海英, 等. 干旱胁迫对银沙槐幼苗叶绿体和线粒体超微结构及膜脂过氧化的影响.干旱区研究, 2016, 33(1): 120-130. | |
| 31 | Wang Z Y, Wang K, Jiang T, et al. Staged responses of non-structural carbohydrates of Pinus tabulaeformis seedlings to drought stress. Plant Research, 2018, 38(3): 460-466. |
| 王宗琰, 王凯, 姜涛, 等. 油松幼苗非结构性碳水化合物对干旱胁迫的阶段性响应. 植物研究, 2018, 38(3): 460-466. | |
| 32 | Huang X, Zhang L M. Research on the relationship between the thylakoid membranes and drought resistance. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 37(18): 8320-8321, 8330. |
| 黄霄, 张令梅. 植物类囊体膜与抗旱性关系研究. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(18): 8320-8321, 8330. | |
| 33 | Tari I, Camen D, Coradini G, et al. Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and oxidative stress responses of bush bean genotypes for selecting contrasting acclimation strategies under water stress. Acta Biologica Hungarica, 2008, 59(3): 335-345. |
| 34 | Xiao F, Jiang J L, Duan M. Growth and physiological-biochemical responses of Cucumis sativus L. seedlings under drought and re-watering conditionss. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(10): 2241-2248. |
| 肖凡, 蒋景龙, 段敏. 干旱和复水条件下黄瓜幼苗生长和生理生化的响应. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(10): 2241-2248. | |
| 35 | Chen J, Wang Z H, Zhou Q G. Effects of PEG treatment on ultrastructure in mesophyll cells of sweet potato. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 1997, 22(4): 398-404. |
| 陈京, 王支槐, 周启贵. PEG处理对甘薯叶肉细胞超微结构的影响. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 22(4): 398-404. | |
| 36 | Jorge V D S, Aubrey W N, Paul J K. Some ultrastructural and enzymatic effects of water stress in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) leaves. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1974, 71(8): 3243-3247. |
| 37 | Guo C F, Sun Y. Progress in the study of plants’ osmotic adjustment and proline metabolism under drought stress. Journal of Fujian Institute of Education, 2015, 16(1): 114-118, 128. |
| 郭春芳, 孙云. 干旱胁迫下植物的渗透调节及脯氨酸代谢研究进展. 福建教育学院学报, 2015, 16(1): 114-118, 128. | |
| 38 | Huang Y L, Yin K D, Xiang J L, et al. Research progress on physiological reaction and DNA methylation under drought stress in plant. Corn Science, 2016, 24(2): 96-102. |
| 黄玉兰, 殷奎德, 向君亮, 等. 干旱胁迫下植物生理生化及DNA甲基化的研究进展. 玉米科学, 2016, 24(2): 96-102. | |
| 39 | Li P, Lin Y D. Ecological response of Potentilla reptans var. sericophylla on adversity stress. China Agronomy Bulletin, 2015, 31(1): 132-139. |
| 李鹏, 蔺银鼎. 绢毛匍匐委陵菜对栽培逆境胁迫的生态响应. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(1): 132-139. | |
| 40 | Mattioni C, Lacerenza N G, Troccoli A, et al. Water and salt stress induced alterations on proline metabolism of Triticum durum seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum, 1997, 101(4): 787-792. |
| 41 | Chen M T, Zhao Z, Quan J E. Variation of soluble protein components and contents in seedling root tips of four trees under drought stress. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2010, 30(6): 1157-1165. |
| 陈明涛, 赵忠, 权金娥. 干旱对4种苗木根尖可溶性蛋白组分和含量的影响. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(6): 1157-1165. | |
| 42 | Ahmed I M, Cao F, Zhang M, et al. Difference in yield and physiological features in response to drought and salinity combined stress during anthesis in Tibetan wild and cultivated barleys. PLoS One, 2013(8): e77869. |
| 43 | Han R L, Li L X, Liang Z S. Seabuckthorn relative membrane conductivity and osmotic adjustment under drought stress. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2003, 23(1): 23-27. |
| 韩蕊莲, 李丽霞, 梁宗锁. 干旱胁迫下沙棘叶片细胞膜透性与渗透调节物质研究. 西北植物学报, 2003, 23(1): 23-27. | |
| 44 | Chen J H, Yu X X, Sun M G, et al. Relation between activity of antioxidant enzymes and drought resistance of different tree species in North China. Agricultural Research in Arid Areas, 2006(5): 120-125. |
| 陈吉虎, 余新晓, 孙明高, 等. 北方旱区不同树种抗氧化酶活性变化及与抗旱性的关系. 干旱地区农业研究, 2006(5): 120-125. | |
| 45 | Wang H H, Yang L D, Huang J J. Effects of NO on the activity of antioxidative enzymes in soybean seedlings under drought stress. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(11): 2493-2496. |
| 王华华, 杨丽丹, 黄俊骏. 干旱胁迫下NO对大豆幼苗抗氧化酶活性的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(11): 2493-2496. | |
| 46 | Sun X G, Zhang X, Gu N, et al. Effects of drought stress on physiological characteristics of Malus ‘Jimei’. Northern Horticulture, 2020(12): 82-88. |
| 孙晓刚, 张雪, 谷娜, 等. 干旱胁迫对‘吉美’海棠生理特性的影响. 北方园艺, 2020(12): 82-88. | |
| 47 | Ji Y, Zhang X Q, Peng Y, et al. Effects of drought stress on lipid peroxidation, osmotic adjustment and activities of protective enzymes in the roots and leaves of orchard grass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 144-151. |
| 季杨, 张新全, 彭燕, 等. 干旱胁迫对鸭茅根、叶保护酶活性、渗透物质含量及膜质过氧化作用的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 144-151. |
| [1] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [2] | 唐立涛, 毛睿, 王长庭, 李洁, 胡雷, 字洪标. 氮磷添加对高寒草甸植物群落根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 105-116. |
| [3] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [4] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [5] | 罗巧玉, 王彦龙, 陈志, 马永贵, 任启梅, 马玉寿. 水分逆境对发草脯氨酸及其代谢途径的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 75-83. |
| [6] | 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 王学琴, 姚姗. 盐胁迫对湖南稷子苗期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| [7] | 王龙, 樊婕, 魏畅, 李鸽子, 张静静, 焦秋娟, 陈果, 孙娈姿, 柳海涛. 外源抗坏血酸对铜胁迫菊苣幼苗生长的缓解效应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 150-159. |
| [8] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [9] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [10] | 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 梁国玲, 马祥. 干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦产量及干物质积累与分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 177-188. |
| [11] | 刘斯莉, 王长庭, 张昌兵, 胡雷, 唐立涛, 潘攀. 川西北高原3种禾本科牧草根系特征比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 41-53. |
| [12] | 宋洁, 刘学录. 基于多源遥感数据提高山地森林识别精度——以祁连山国家公园肃南县段为例[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 1-14. |
| [13] | 李冬, 申洪涛, 王艳芳, 王悦华, 王丽君, 赵世民, 刘领. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗光合碳同化和内源激素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. |
| [14] | 黄海霞, 杨琦琦, 崔鹏, 陆刚, 韩国君. 裸果木幼苗根系形态和生理特征对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 197-207. |
| [15] | 孙小富, 黄莉娟, 王普昶, 赵丽丽, 刘芳. 不同供磷水平对宽叶雀稗形态及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 58-69. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||