

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 188-198.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021304
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-08-10
修回日期:2021-11-10
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-07-01
通讯作者:
孟林
作者简介:E-mail: menglin9599@sina.com基金资助:
Yong ZHANG( ), Xiao-xia TIAN, Ming-li ZHENG, Pei-chun MAO, Lin MENG(
), Xiao-xia TIAN, Ming-li ZHENG, Pei-chun MAO, Lin MENG( )
)
Received:2021-08-10
Revised:2021-11-10
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-07-01
Contact:
Lin MENG
摘要:
植物高亲和性K+转运蛋白基因(HKT)编码K+、Na+转运或K+-Na+共转运质膜通道蛋白,在植物抗逆过程中发挥重要作用。为了研究长穗偃麦草EeHKT1;4(GenBank: KF956112.1)的功能作用,构建了EeHKT1;4过表达植物表达载体转化拟南芥,进行拟南芥转基因植株的抗旱耐盐性评价分析。结果显示,正常生长条件下野生型(WT)与转基因株系的主根长度无差异,NaCl与甘露醇处理下WT和转基因株系根的生长受到抑制,转基因株系根长度均大于同等胁迫条件下(WT)的根长;正常生长条件下WT与转基因株系表型无显著差异,但在NaCl与甘露醇处理下WT表现出叶片萎缩和植株枯黄,转基因株系仅部分植株表现出叶片萎缩,同一胁迫条件下转基因株系的植株存活率皆高于WT。硝基氮蓝四唑(NBT)与二氨基联苯胺(DAB)染色结果显示,正常生长条件下WT与转基因株系叶片染色相对较浅,随着NaCl与甘露醇浓度提高,所有叶片染色程度逐渐加深且同等胁迫下WT染色程度高于转基因株系。以正常生长条件下基因的表达量为对照,随着NaCl浓度的增加,AtSOS1基因在WT和转基因植株中逐渐上调且在转基因中的表达量高于WT;AtNHX1基因在NaCl处理下上调表达且转基因植株中表达量低于WT,除转基因株系L5外并未检测到WT和转基因株系自身因NaCl浓度的提高AtNHX1基因表达量发生改变;在甘露醇处理下,AtRD29B和AtP5CS1基因均上调表达且转基因植株中表达量高于WT。综上所述,EeHKT1;4过表达降低了逆境胁迫下拟南芥中超氧阴离子和H2O2的积累,诱导抗逆基因上调表达,增强拟南芥抗旱耐盐性。
张勇, 田小霞, 郑明利, 毛培春, 孟林. 过表达长穗偃麦草EeHKT1;4基因增强拟南芥抗旱耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 188-198.
Yong ZHANG, Xiao-xia TIAN, Ming-li ZHENG, Pei-chun MAO, Lin MENG. Analysis of drought and salt resistance of EeHKT1;4 gene from Elytrigia elongata in Arabidopsis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 188-198.
| 功能Function | 引物名称Primer name | 序列Sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
载体构建 Construction of expression vector | EeHKT1;4-Xba I | CTAG |
| EeHKT1;4-Knp I | CGG | |
| EeHKT1;4-F | ATGCAACTCCCAAGTCATAACA | |
| EeHKT1;4-R | CTAACTAAGCTTCCAGGTCCTGC | |
| qPCR | qEeHKT1;4-F | CTACTGATCGGCTGCAACAGCAGC |
| qEeHKT1;4-R | ATGGAGAGGGAGATTGTAGCAGAG | |
| qAtSOS1-F | TCGTTTCAGCCAAATCAGAAAGT | |
| qAtSOS1-R | GCTACATAGTTCGGAGTTCCACA | |
| qAtNHX1-F | GACTCCTTCATGCGACCCG | |
| qAtNHX1-R | CCACGTTACCCTCAAGCCTTAC | |
| qAtP5CS1-F | TACACAGGCCCTCCAAGTGA | |
| qAtP5CS1-R | CTTGATTTGTCGCCGAATGT | |
| qAtRD29B-F | GGAGAGAGCAGAGAGGCTCA | |
| qAtRD29B-R | CCGTTGACCACCGAGATAGT | |
| qAtACTIN -F | AGCACTTGCACCAAGCAGCATG | |
| qAtACTIN -R | ACGATTCCTGGACCTGCCTCATC |
表1 本研究所用的引物序列及用途
Table 1 The primer sequence and application used in this study
| 功能Function | 引物名称Primer name | 序列Sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
载体构建 Construction of expression vector | EeHKT1;4-Xba I | CTAG |
| EeHKT1;4-Knp I | CGG | |
| EeHKT1;4-F | ATGCAACTCCCAAGTCATAACA | |
| EeHKT1;4-R | CTAACTAAGCTTCCAGGTCCTGC | |
| qPCR | qEeHKT1;4-F | CTACTGATCGGCTGCAACAGCAGC |
| qEeHKT1;4-R | ATGGAGAGGGAGATTGTAGCAGAG | |
| qAtSOS1-F | TCGTTTCAGCCAAATCAGAAAGT | |
| qAtSOS1-R | GCTACATAGTTCGGAGTTCCACA | |
| qAtNHX1-F | GACTCCTTCATGCGACCCG | |
| qAtNHX1-R | CCACGTTACCCTCAAGCCTTAC | |
| qAtP5CS1-F | TACACAGGCCCTCCAAGTGA | |
| qAtP5CS1-R | CTTGATTTGTCGCCGAATGT | |
| qAtRD29B-F | GGAGAGAGCAGAGAGGCTCA | |
| qAtRD29B-R | CCGTTGACCACCGAGATAGT | |
| qAtACTIN -F | AGCACTTGCACCAAGCAGCATG | |
| qAtACTIN -R | ACGATTCCTGGACCTGCCTCATC |

图1 转基因拟南芥植株的获得与鉴定A: EeHKT1;4植物表达载体示意图A diagram showing EeHKT1;4 overexpression vector; B: 转基因植株潮霉素筛选Hygromycin screening of transgenic plants; C: 转基因植株PCR鉴定PCR identification of transgenic plants; D: 转基因拟南芥转录水平鉴定Transcription level identification of transgenic Arabidopsis; DL2000: DL2000 Marker; L1~L5: 不同转基因株系Different transgenic lines; +: 阳性对照Positive control; -: 阴性对照Negative control; WT: 野生型Wild type.下同The same below.
Fig.1 Obtaining and identification of transgenic Arabidopsis
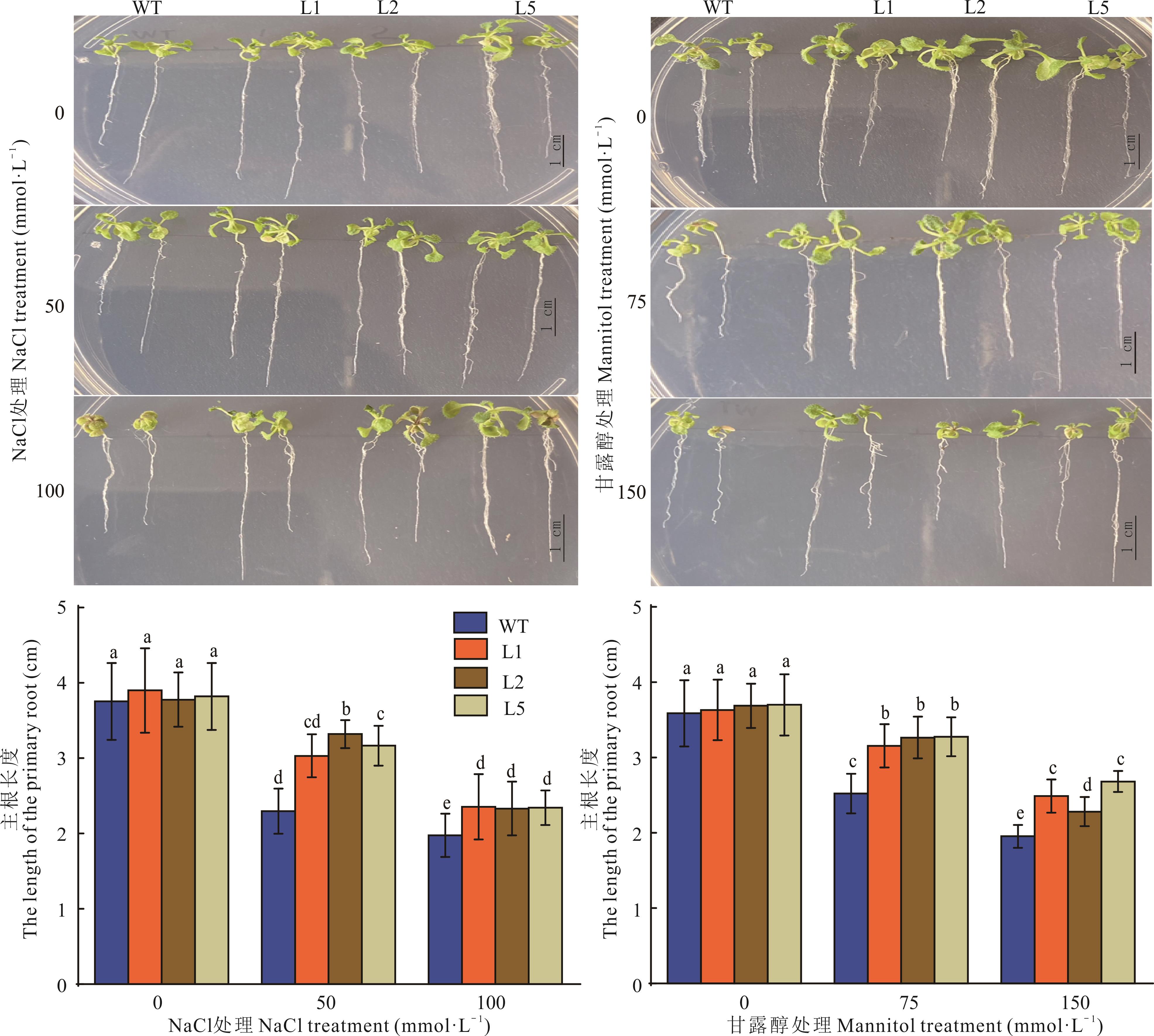
图2 NaCl与甘露醇处理下根的表型及根长统计不同小写字母表示在0.05水平上差异显著,下同。 Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level, the same below.
Fig.2 Root phenotype and root length statistics under NaCl and mannitol treatment
| 1 | Munns R, James R A, Xu B, et al. Wheat grain yield on saline soils is improved by an ancestral Na+ transporter gene. Nature Biotechnology, 2012, 30(4): 360-364. |
| 2 | Zorb C, Geilfus C M, Dietz K J. Salinity and crop yield. Plant Biology (Stuttg), 2019, 21(Suppl 1): 31-38. |
| 3 | Zhu J K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell, 2016, 167(2): 313-324. |
| 4 | Demidchik V. Mechanisms and physiological roles of K+ efflux from root cells. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2014, 171(9): 696-707. |
| 5 | Qi Z, Spalding E P. Protection of plasma membrane K+ transport by the salt overly sensitive1 Na+-H+ antiporter during salinity stress. Plant Physiology, 2004, 136(1): 2548-2555. |
| 6 | Munns R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell and Environment, 2002, 25(2): 239-250. |
| 7 | Shabala S, Pottosin I. Regulation of potassium transport in plants under hostile conditions: Implications for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Physiologia Plantarum, 2014, 151(3): 257-279. |
| 8 | Rubio F, Nieves-Cordones M, Horie T, et al. Doing 'business as usual' comes with a cost: Evaluating energy cost of maintaining plant intracellular K+ homeostasis under saline conditions. New Phytologist, 2020, 225(3): 1097-1104. |
| 9 | Raddatz N, Morales D L R L, Lindahl M, et al. Coordinated transport of nitrate, potassium, and sodium. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 247. |
| 10 | Shabala S. Learning from halophytes: Physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Annals of Botany, 2013, 112(7): 1209-1221. |
| 11 | Maathuis F J. Sodium in plants: Perception, signalling, and regulation of sodium fluxes. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(3): 849-858. |
| 12 | Very A A, Nieves-Cordones M, Daly M,et al. Molecular biology of K+ transport across the plant cell membrane: What do we learn from comparison between plant species. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2014, 171(9): 748-769. |
| 13 | Tounsi S, Ben A S, Masmoudi K, et al. Characterization of two HKT1;4 transporters from Triticum monococcum to elucidate the determinants of the wheat salt tolerance Nax1 QTL. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2016, 57(10): 2047-2057. |
| 14 | Huang S, Spielmeyer W, Lagudah E S, et al. Comparative mapping of HKT genes in wheat, barley, and rice, key determinants of Na+ transport, and salt tolerance. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(4): 927-937. |
| 15 | Platten J D, Cotsaftis O, Berthomieu P, et al. Nomenclature for HKT transporters, key determinants of plant salinity tolerance. Trends in Plant Science, 2006, 11(8): 372-374. |
| 16 | Byrt C S, Xu B, Krishnan M, et al. The Na+ transporter, TaHKT1;5-D, limits shoot Na+ accumulation in bread wheat. Plant Journal, 2014, 80(3): 516-526. |
| 17 | Suzuki K, Yamaji N, Costa A, et al. OsHKT1;4-mediated Na+ transport in stems contributes to Na+ exclusion from leaf blades of rice at the reproductive growth stage upon salt stress. BMC Plant Biology, 2016, 16: 22. |
| 18 | Horie T, Hauser F, Schroeder J I. HKT transporter-mediated salinity resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis and monocot crop plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2009, 14(12): 660-668. |
| 19 | Asins M J, Villalta I, Aly M M, et al. Two closely linked tomato HKT coding genes are positional candidates for the major tomato QTL involved in Na+/K+ homeostasis. Plant Cell and Environment, 2013, 36(6): 1171-1191. |
| 20 | Sunarpi, Horie T, Motoda J, et al. Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporter-induced Na+ unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells. Plant Journal, 2005, 44(6): 928-938. |
| 21 | Ren Z H, Gao J P, Li L G, et al. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nature Genetics, 2005, 37(10): 1141-1146. |
| 22 | Hauser F, Horie T. A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: A mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K+/Na+ ratio in leaves during salinity stress. Plant Cell and Environment, 2010, 33(4): 552-565. |
| 23 | Huang S, Spielmeyer W, Lagudah E S, et al. A sodium transporter (HKT7) is a candidate for Nax1, a gene for salt tolerance in durum wheat. Plant Physiology, 2006, 142(4): 1718-1727. |
| 24 | Huang L, Kuang L, Wu L, et al. The HKT transporter HvHKT1;5 negatively regulates salt tolerance. Plant Physiology, 2020, 182(1): 584-596. |
| 25 | Colmer T D, Flowers T J, Munns R. Use of wild relatives to improve salt tolerance in wheat. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(5): 1059-1078. |
| 26 | Zhang L. Cloning EeHKT1;4 gene in Elytrigia elongata and its transformation into tobacco. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 张琳. 长穗偃麦草高亲和K+转运蛋白基因EeHKT1;4的克隆及对烟草遗传转化研究. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2015. | |
| 27 | Li X D, Shang Y S, Wu Y D, et al. Overexpression of Medicago sativa Multi protein Bridging Factor 1c (MsMBF1c) enhances thermotolerance of Arabidopsis. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 187-189. |
| 李小冬, 尚以顺, 武语迪, 等. 紫花苜蓿MsMBF1c基因在拟南芥中表达提高转基因植株的耐热性. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 187-198. | |
| 28 | Hou J R, Duan X Y, Li Z, et al. Cloning and erpression analysis of TrSAMDC1 in white clover. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 170-178. |
| 侯洁茹, 段晓玥, 李州, 等. 白三叶TrSAMDC1克隆及表达分析. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 170-178. | |
| 29 | Gao Z Q, Wang J, Tang Y C, et al. Cloning and functional of the gene NtUFGT in Nitraria tangutorum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 159-170. |
| 高子奇, 王佳, 汤宇晨, 等. 唐古特白刺类黄酮-3-O-葡萄糖基转移酶基因(NtUFGT)的克隆与功能分析. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 159-170. | |
| 30 | Ningning L, Chao D, Binjie M, et al. Functional analysis of ion transport properties and salt tolerance mechanisms of RtHKT1 from the recretohalophyte Reaumuria trigyna. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2019, 60(1): 85-106. |
| 31 | Stadtman E R, Levine R L. Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids, 2003, 25(3/4): 207-218. |
| 32 | Vranová E, Inzé D, Van Breusegem F. Signal transduction during oxidative stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2002, 53: 1227-1236. |
| 33 | Carlos F G B, Juan C D R. Quantitative determination of superoxide in plant leaves using a modified NBT staining method. Phytochemical Analysis, 2011, 22(3): 268-271. |
| 34 | Vandenabeele S, Vanderauwera S, Vuylsteke M, et al. Catalase deficiency drastically affects gene expression induced by high light in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Journal, 2004, 39(1): 45-58. |
| 35 | Apse M P, Aharon G S, Snedden W A, et al. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science, 1999, 285(5431): 1256-1258. |
| 36 | Xu Y G, Zhan Y G. Progress of the research on plant drought-resistant mechanism and related genes. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2009(2): 11-17. |
| 徐云刚, 詹亚光. 植物抗旱机理及相关基因研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2009(2): 11-17. |
| [1] | 张晴, 邢静, 姚佳明, 殷庭超, 黄心如, 何悦, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草细胞分裂素信号通路B类ARR转录因子LpARR10的耐镉功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [2] | 李宏伟, 郑琪, 李滨, 赵茂林, 李振声. 一种耐盐碱牧草——长穗偃麦草研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 190-199. |
| [3] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [4] | 李倩, 李晓霞, 程丽琴, 陈双燕, 齐冬梅, 杨伟光, 高利军, 新巴音, 刘公社. 羊草LcCBF6基因的表达特性和功能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 105-115. |
| [5] | 刘文文, 崔会婷, 尉春雪, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿叶绿素酸酯a加氧酶(MtCAO)基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 171-181. |
| [6] | 董文科, 陈春艳, 马晖玲. 转OvBAN/bar双价基因的紫花苜蓿对虫蚀及除草剂的耐受性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 159-167. |
| [7] | 姜红岩, 滕珂, 檀鹏辉, 尹淑霞. 日本结缕草ZjZFN1基因对拟南芥的转化及其耐旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 129-138. |
| [8] | 李小冬, 莫本田, 牟琼, 娄芬, 陈文贵, 陈光吉, 张瑜, 韩永芬. 紫花苜蓿高温诱导启动子pMsMBF 1c 的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 128-137. |
| [9] | 才华, 许慧慧, 孙娜, 宋婷婷, 任永晶, 杨圣秋. 从光合作用和有机酸积累角度探索转GsPPCK1和GsPPCK3基因苜蓿耐碱性增强的生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 107-117. |
| [10] | 索雅飞,杜超,李宁宁,王燕,王迎春. 珍稀泌盐植物长叶红砂RtSOD基因的克隆及功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 98-110. |
| [11] | 李小冬, 吴佳海, 孙方, 陈光吉, 王小利. 过量表达Fa14-3-3C促进拟南芥对低氮胁迫耐受性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 104-112. |
| [12] | 檀鹏辉, 袁丽丽, 樊波, 于安东, 董笛, 滕珂, 晁跃辉. 日本结缕草滞绿基因 ZjSGR 对烟草的转化及功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 155-162. |
| [13] | 王晓蕾, 王建, 张庆玲, 闫静, 强胜, 宋小玲. 抗草丁膦转基因油菜与野芥菜的抗性回交3代子1代和子2代的适合度[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 138-151. |
| [14] | 周香艳, 张宁, 刘柏林, 裴瑞芳, 司怀军, 王蒂. ARF基因干扰表达对不同发育阶段和贮藏条件马铃薯酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 133-139. |
| [15] | 袁进成, 宋晋辉, 马海莲, 瓮巧云, 王凌云, 赵艳, 刘颖慧. 转玉米ZmABI3-L基因增加拟南芥的抗旱和耐盐性[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 124-131. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||