

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 105-115.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020375
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
李倩1,2( ), 李晓霞1(
), 李晓霞1( ), 程丽琴1, 陈双燕1, 齐冬梅1, 杨伟光3, 高利军1, 新巴音1, 刘公社1(
), 程丽琴1, 陈双燕1, 齐冬梅1, 杨伟光3, 高利军1, 新巴音1, 刘公社1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-08-04
修回日期:2020-09-21
出版日期:2021-09-16
发布日期:2021-09-16
通讯作者:
李晓霞,刘公社
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: lixx2013@ibcas.ac.cn基金资助:
Qian LI1,2( ), Xiao-xia LI1(
), Xiao-xia LI1( ), Li-qin CHENG1, Shuang-yan CHEN1, Dong-mei QI1, Wei-guang YANG3, Li-jun GAO1, Ba-yin XIN1, Gong-she LIU1(
), Li-qin CHENG1, Shuang-yan CHEN1, Dong-mei QI1, Wei-guang YANG3, Li-jun GAO1, Ba-yin XIN1, Gong-she LIU1( )
)
Received:2020-08-04
Revised:2020-09-21
Online:2021-09-16
Published:2021-09-16
Contact:
Xiao-xia LI,Gong-she LIU
摘要:
羊草是我国重要的牧草和生态草资源,具有耐盐碱、耐旱、耐低温等特性,是天然的抗逆基因资源库。CBF/DREB属于AP2转录因子家族,在植物抗逆中发挥着重要作用。本研究克隆得到羊草LcCBF6(Leymus chinensis C-repeat binding factor
李倩, 李晓霞, 程丽琴, 陈双燕, 齐冬梅, 杨伟光, 高利军, 新巴音, 刘公社. 羊草LcCBF6基因的表达特性和功能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 105-115.
Qian LI, Xiao-xia LI, Li-qin CHENG, Shuang-yan CHEN, Dong-mei QI, Wei-guang YANG, Li-jun GAO, Ba-yin XIN, Gong-she LIU. Expression characteristics and functional analysis of the LcCBF6 gene from Leymus chinensis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 105-115.

图2 LcCBF6系统进化树Aegilops biuncialis两芒山羊草;Aegilops tauschii节节麦;Agropyron mongolicum沙芦草;Brachypodium distachyon短柄草;Eragrostis curvula弯叶画眉草;Festuca arundinacea苇状羊茅;Festuca pratensis草甸羊茅;Hordeum vulgare大麦;Leymus chinensis羊草;Lolium perenne黑麦草;Oryza brachyantha短花药野生稻;Oryza sativa水稻;Panicum miliaceum糜子;Paspalum vaginatum海雀稗;Poa pratensis草地早熟禾;Secale cereale黑麦;Setaria italica小米;Setaria viridis狗尾草;Sorghum bicolor高粱;Triticum aestivum普通小麦;Triticum turgidum硬粒小麦;Zoysia japonica结缕草。
Fig.2 LcCBF6 phylogenetic tree
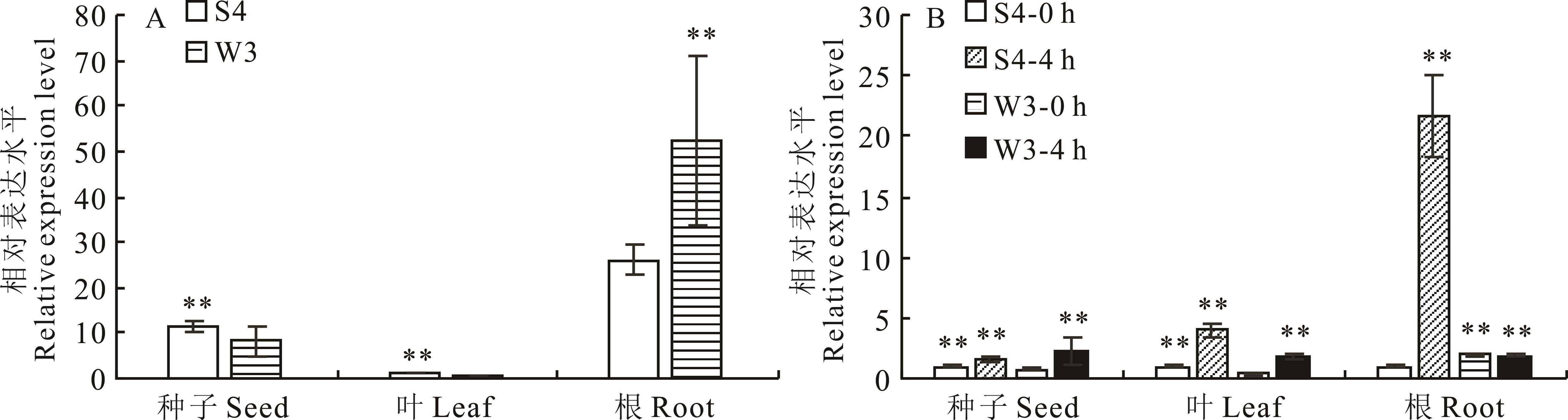
图3 LcCBF6基因的表达模式A:组织特异性表达模式;B:盐胁迫下表达模式。*表示P<0.05差异显著,**表示P<0.01差异极显著,下同。A: Tissue specific expression pattern; B: Expression patterns under salt stress; * Indicates a significant difference at P<0.05, ** Indicates a significant difference at P<0.01, the same below.
Fig.3 Expression patterns of LcCBF6 gene
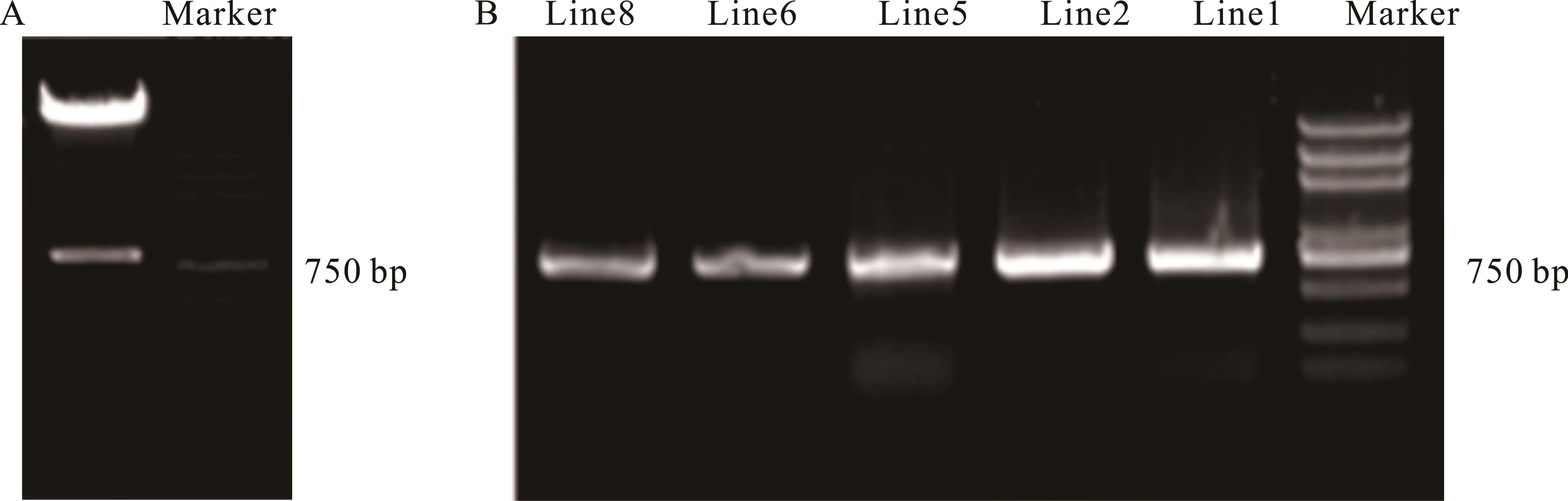
图4 植物表达载体pCAMBIA3301-LcCBF6酶切鉴定及转基因株系PCR鉴定
Fig.4 Identification of plant expression vector pCAMBIA3301-LcCBF6 by enzyme digestion and PCR identification of transgenic line

图5 NaCl胁迫对LcCBF6转基因拟南芥种子萌发的影响A表型;B绿色子叶率;C鲜重。A: Phenotype; B: Cotyledons greening rate; C: Fresh weight. WT: 野生型Wild type. 下同 The same below.
Fig. 5 Effects of LcCBF6-over-expressing Arabidopsis seed germination under NaCl stress (mean±SD, n=3)

图6 转LcCBF6基因拟南芥幼苗抗盐表型A:表型;B:存活率;C:鲜重。A: Phenotype; B: Survival rate; C: Fresh weight.
Fig.6 Salt-resistant phenotype of LcCBF6-over-expressing Arabidopsis in seedlings stage (mean±SD, n=3)
| 1 | Zhuang J, Chen J M, Yao Q H, et al. Discovery and expression profile analysis of AP2/ERF family genes from Triticum aestivum. Molecular Biology Reports, 2011, 38(2): 745-753. |
| 2 | Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, et al. Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought-and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 1998, 10(8): 1391-1406. |
| 3 | Gilmour S J, Zarka D G, Stockinger E J, et al. Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold‐induced COR gene expression. The Plant Journal, 1998, 16(4): 433-442. |
| 4 | Haake V, Cook D, Riechmann J L, et al. Transcription factor CBF4 is a regulator of drought adaptation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 2002, 130(2): 639-648. |
| 5 | Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet J G, et al. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration-and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2002, 290(3): 998-1009. |
| 6 | Eric J, Stockinger, Sarah J, et al. Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1997, 94(3): 1035-1040. |
| 7 | Jaglo-Ottosen K R, Gilmour S J, Zarka D G, et al. Arabidopsis CBF1 overexpression induces COR genes and enhances freezing tolerance. Science, 1998, 280(5360): 104-106. |
| 8 | Maceluch J, Kmieciak M, Szweykowska-Kulińska Z, et al. Cloning and characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana AtNAP57-A homologue of yeast pseudouridine synthase Cbf5p. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 2001, 48(3): 699-709. |
| 9 | Lermontova I, Schubert V, Börnke F, et al. ArabidopsisCBF5 interacts with the H/ACA snoRNP assembly factor NAF1. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(5): 615-626. |
| 10 | Magome H, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, et al. Dwarf and delayed‐flowering 1, a novel Arabidopsis mutant deficient in gibberellin biosynthesis because of overexpression of a putative AP2 transcription factor. The Plant Journal, 2004, 37(5): 720-729. |
| 11 | Magome H, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, et al. The DDF1 transcriptional activator upregulates expression of a gibberellin-deactivating gene, GA2ox7, under high-salinity stress in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 2008, 56(4): 613-626. |
| 12 | Sutton F, Chen D G, Ge X, et al. CBF genes of the Fr-A2 allele are differentially regulated between long-term cold acclimated crown tissue of freeze-resistant and-susceptible, winter wheat mutant lines. BMC Plant Biology, 2009, 9(1): 34. |
| 13 | Choi D W, Rodriguez E M, Close T J. Barley CBF3 gene identification, expression pattern, and map location. Plant Physiology, 2002, 129(4): 1781-1787. |
| 14 | Dubouzet J G, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, et al. OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. The Plant Journal, 2003, 33(4): 751-763. |
| 15 | Ito Y, Katsura K, Maruyama K, et al. Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2006, 47(1): 141-153. |
| 16 | Xiao H, Tattersall E A R, Siddiqua M K, et al. CBF4 is a unique member of the CBF transcription factor family of Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2008, 31(1): 1-10. |
| 17 | Akhtar M, Jaiswal A, Taj G, et al. DREB1/CBF transcription factors: Their structure, function and role in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Journal of Genetics, 2012, 91(3): 385-395. |
| 18 | Zhu T C. Leymus chinensis biological ecology. Jilin: Jilin Science Technology Press, 2004. |
| 祝廷成. 羊草生物生态学. 吉林: 吉林科学技术出版社, 2004. | |
| 19 | Liu G S, Li X F. Leymus chinensis germplasm resources research. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 89-93. |
| 刘公社, 李晓峰.羊草种质资源研究.北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 89-93. | |
| 20 | Chen S, Huang X, Yan X, et al. Transcriptome analysis in sheepgrass (Leymus chinensis): A dominant perennial grass of the Eurasian Steppe. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e67974. |
| 21 | Cheng L, Peng X, Su M, et al. Cloning and function research of sheepgrass (Leymus chinensis) genes//Sheepgrass (Leymus chinensis): An environmentally friendly native grass for animals. Singapore: Springer, 2019: 247-268. |
| 22 | Peng X, Zhang L, Zhang L, et al. The transcriptional factor LcDREB2 cooperates with LcSAMDC2 to contribute to salt tolerance in Leymus chinensis. Plant Cell Tissue & Organ Culture, 2013, 113(2): 245-256. |
| 23 | Cheng L, Li X, Huang X, et al. Overexpression of sheepgrass R1-MYB transcription factor LcMYB1 confers salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2013, 70: 252-260. |
| 24 | Li X, Gao Q, Liang Y, et al. A novel salt-induced gene from sheepgrass, LcSAIN2, enhances salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem, 2013, 64: 52-59. |
| 25 | Li X, Hou S, Gao Q, et al. LcSAIN1, a novel salt-induced gene from sheepgrass, confers salt stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell Physiology, 2013, 54(7): 1172-1185. |
| 26 | Gao Q, Li X, Jia J, et al. Overexpression of a novel cold-responsive transcript factor LcFIN1 from sheepgrass enhances tolerance to low temperature stress in transgenic plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(3): 861-874. |
| 27 | Liu Y G, Whittier R F. Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: Automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from P1 and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics, 1995, 25(3): 674-681. |
| 28 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods, 2002, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 29 | Clough S J, Bent A F. Floral dip: A simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 1998, 16(6): 735-743. |
| 30 | Gao H J, Lv X P, Wang R J, et al. Application of RNA-seq technology in research on herb, shrub and tree stress resistance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(12): 184-196. |
| 高慧娟, 吕昕培, 王润娟, 等. 转录组测序在林草植物抗逆性研究中的应用. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 184-196. | |
| 31 | Kidokoro S, Watanabe K, Ohori T, et al. Soybean DREB 1/CBF‐type transcription factors function in heat and drought as well as cold stress-responsive gene expression. The Plant Journal, 2015, 81(3): 505-518. |
| 32 | Zhang X, Fowler S G, Cheng H, et al. Freezing-sensitive tomato has a functional CBF cold response pathway, but a CBF regulon that differs from that of freezing-tolerant Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 2004, 39(6): 905-919. |
| 33 | Qin F, Sakuma Y, Li J, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of a novel DREB1/CBF transcription factor involved in cold-responsive gene expression in Zea mays L. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2004, 45(8): 1042-1052. |
| 34 | Zhao C, Zhang Z, Xie S, et al. Mutational evidence for the critical role of CBF genes in cold acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171: 2744-2759. |
| 35 | Shan L W, Zhang Q, Zhu R F, et al. Effects of AMF on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Leymus chinensis and Medicago sativa with and without nitrogen and phosphorus application. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 46-57. |
| 单立文, 张强, 朱瑞芬, 等. 氮、磷添加下AMF对羊草和苜蓿生长与光合生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 46-57. | |
| 36 | Badawi M, Danyluk J, Boucho B, et al. The CBF gene family in hexaploid wheat and its relationship to the phylogenetic complexity of cereal CBFs. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2007, 277(5): 533-554. |
| 37 | Skinner J S, von Zitzewitz J, Szűcs P, et al. Structural, functional, and phylogenetic characterization of a large CBF gene family in barley. Plant Molecular Biology, 2005, 59(4): 533-551. |
| 38 | Peng X J. Leymus chinensis art related DREB transcription factors and SAMDC gene function research. Beijing: Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011. |
| 彭献军. 羊草抗逆相关DREB转录因子及SAMDC基因功能研究. 北京: 中国科学院植物研究所, 2011. | |
| 39 | Xiao H, Siddiqua M, Braybrook S, et al. Three grape CBF/DREB1 genes respond to low temperature, drought and abscisic acid. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2006, 29(7): 1410-1421. |
| [1] | 郭丰辉, 丁勇, 马文静, 李贤松, 李西良, 侯向阳. 母体放牧经历对羊草克隆后代干旱敏感性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 119-126. |
| [2] | 王晔, 陈慧萍, 李润枝, 彭真, 范希峰, 武菊英, 段留生. 奇岗微繁技术建立及幼苗耐盐性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 214-220. |
| [3] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [4] | 张丽星, 海春兴, 常耀文, 高晓媚, 高文邦, 解云虎. 羊草及芨芨草草原和西北针茅草原土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 68-79. |
| [5] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [6] | 漫静, 唐波, 邓波, 李佳欢, 何玉娟, 张佳良. 羊草根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 59-71. |
| [7] | 李茹霞, 耿元波. 应用13C同位素标记法区分羊草草原生态系统呼吸[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 56-70. |
| [8] | 伏兵哲, 周燕飞, 李雪, 倪彪, 高雪芹. 宁夏引黄灌区羊草水肥耦合效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 98-108. |
| [9] | 刘文文, 崔会婷, 尉春雪, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿叶绿素酸酯a加氧酶(MtCAO)基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 171-181. |
| [10] | 白乌云, 侯向阳, 武自念, 田春育, 丁勇. 羊草不同地理种群表型变异及其对根茎克隆繁殖的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 86-94. |
| [11] | 王英逵, 杨玉荣, 王德利. 盐碱胁迫下AMF对羊草的离子吸收和分配作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 95-104. |
| [12] | 董文科, 陈春艳, 马晖玲. 转OvBAN/bar双价基因的紫花苜蓿对虫蚀及除草剂的耐受性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 159-167. |
| [13] | 姜红岩, 滕珂, 檀鹏辉, 尹淑霞. 日本结缕草ZjZFN1基因对拟南芥的转化及其耐旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 129-138. |
| [14] | 任伟忠, 高艳霞, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 李建国. 全株玉米青贮、谷草和羊草组合全混合日粮饲喂干奶前期奶牛对其围产期生产性能和血液生化及免疫指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 124-136. |
| [15] | 秦燕, 刘文辉, 何峰, 仝宗永, 李向林. 施肥与切根对退化羊草草原土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 5-14. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||