

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 26-35.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021374
高玮( ), 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙(
), 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-18
修回日期:2022-01-17
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
杨宪龙
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: yangxianl@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Wei GAO( ), Na SHOU, Cong-ze JIANG, Ren-shi MA, Yu-ying SHEN, Xian-long YANG(
), Na SHOU, Cong-ze JIANG, Ren-shi MA, Yu-ying SHEN, Xian-long YANG( )
)
Received:2021-10-18
Revised:2022-01-17
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Xian-long YANG
摘要:
为探明陇东旱塬区饲用高粱的适宜氮肥用量,于2019-2020年研究了不同施氮水平(0、80、160、240、320 kg·hm-2,分别用N0、N80、N160、N240、N320表示)对饲用高粱‘F10’干物质积累、分配、耗水量及水分利用效率的影响。结果表明,随着施氮量的增加,饲用高粱拔节、抽穗、开花和灌浆期的干物质积累量均表现为增加趋势,至乳熟收获期,饲用高粱干物质积累量表现为先增后降的特点,其中N160处理下干物质积累量最大,2019和2020年分别为22.3和18.0 t·hm-2。随着生育时期的推进,饲用高粱叶片干物质分配比例逐渐降低,茎的干物质分配比例先增加后降低。乳熟收获期,茎的干物质分配比例最高,2019和2020年平均分配比例分别为70.8%和73.8%。2019年收获期,与N0处理相比,施氮处理下穗的干物质分配比例显著增加,茎的干物质分配比例显著降低,但2020年整体差异不显著。2019年,不同施氮水平下饲用高粱耗水量和耗水强度均无显著差异。2020年,不同处理饲用高粱耗水量为483.4~505.8 mm,耗水强度为3.1~3.3 mm·d-1,其中,N80和N320处理下饲用高粱耗水量较N0处理分别显著增加4.6%和3.9%,耗水强度较N0处理均显著增加6.5%。2019和2020年,N160处理下饲用高粱水分利用效率均最高,分别为42.9和36.4 kg·hm-2·mm-1。回归分析显示,当施氮量为166.7 kg·hm-2时(接近于160.0 kg·hm-2),饲用高粱收获期可获得最大干物质积累量(19.2 t·hm-2);当施氮量为150.0 kg·hm-2时,饲用高粱可达最大水分利用效率(37.8 kg·hm-2·mm-1)。因此,综合干物质积累与水分利用效率,初步推荐陇东旱塬区饲用高粱适宜施氮量为150~160 kg·hm-2。
高玮, 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 施氮量对饲用高粱干物质积累、分配及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 26-35.
Wei GAO, Na SHOU, Cong-ze JIANG, Ren-shi MA, Yu-ying SHEN, Xian-long YANG. Effect of nitrogen application rate on dry matter accumulation, allocation and water use efficiency of forage sorghum[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 26-35.
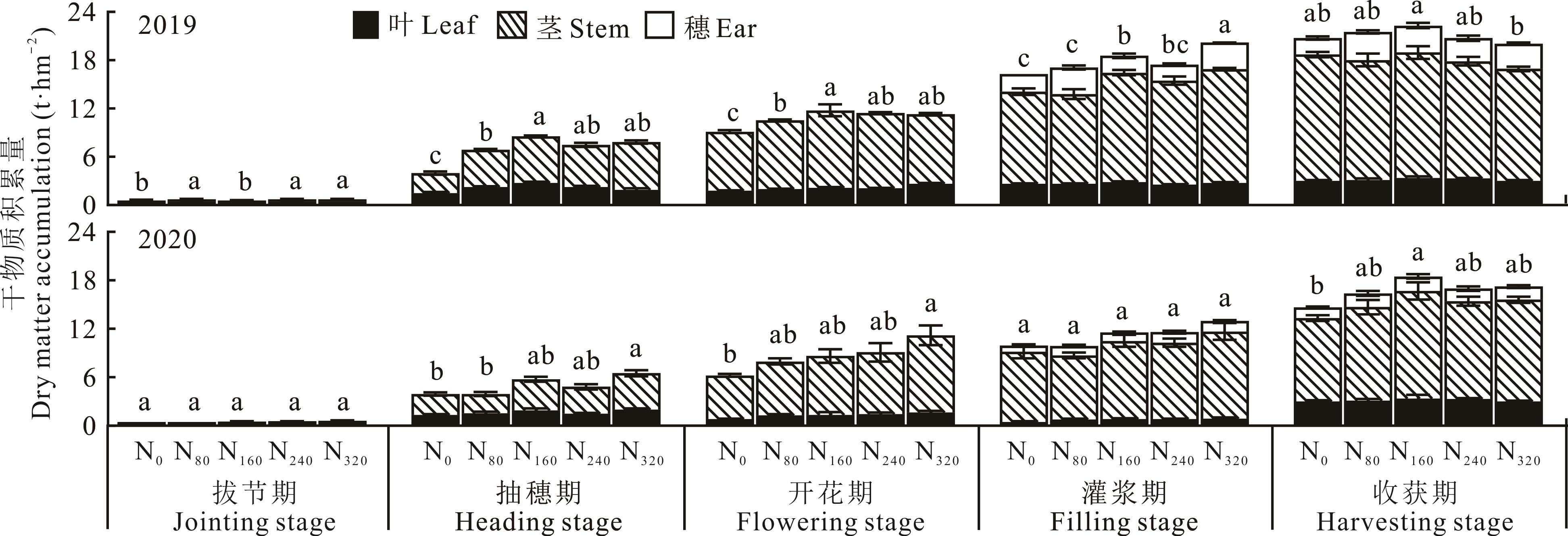
图2 2019和2020年不同施氮处理对饲用高粱各生育时期干物质积累量的影响同一生育时期不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters in the same growth stage indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.2 Effects of different nitrogen treatments on dry matter accumulation of forage sorghum in different growth stages in 2019 and 2020
年份 Year | 处理 Treatments | 拔节期Jointing stage | 开花期Flowering stage | 收获期Harvesting stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 穗Ear | ||
| 2019 | N0 | 61.0±1.65a | 39.0±1.65a | 19.6±0.73b | 80.4±0.73a | 14.6±0.12b | 75.5±0.98a | 9.9±0.90b |
| N80 | 62.4±1.49a | 37.6±1.49a | 19.2±0.53b | 80.8±0.53a | 14.6±0.38b | 69.3±0.29b | 16.1±0.66a | |
| N160 | 62.6±0.79a | 37.5±0.79a | 18.6±1.05b | 81.4±1.05a | 15.1±0.04ab | 70.0±0.82b | 14.8±0.82a | |
| N240 | 61.0±0.52a | 39.4±0.52a | 18.3±0.39b | 81.7±0.39a | 16.0±0.47a | 70.1±2.14b | 13.9±1.67a | |
| N320 | 59.4±1.63a | 41.0±1.63a | 23.4±0.93a | 76.6±0.93b | 15.0±0.25ab | 69.3±0.59b | 15.7±0.84a | |
| 2020 | N0 | 68.4±1.85a | 31.6±1.85a | 14.0±0.73a | 86.3±0.73a | 20.0±0.32a | 71.0±0.69a | 9.1±1.01a |
| N80 | 68.7±3.19a | 31.3±3.19a | 16.4±2.78a | 83.6±2.78a | 16.6±1.38ab | 72.6±3.25a | 10.7±1.93a | |
| N160 | 68.9±1.26a | 31.1±1.26a | 15.1±2.50a | 84.9±2.50a | 15.9±2.24ab | 74.2±1.58a | 9.9±0.90a | |
| N240 | 71.8±3.42a | 29.2±3.42a | 15.4±1.41a | 84.6±1.41a | 15.9±0.56ab | 74.6±0.93a | 9.5±1.48a | |
| N320 | 68.4±3.26a | 31.6±3.26a | 15.0±1.08a | 85.0±1.08a | 13.6±0.52b | 76.5±0.73a | 10.0±1.22a | |
表1 2019和2020年不同施氮处理对饲用高粱各生育时期干物质分配的影响
Table 1 Effects of different nitrogen treatments on dry matter allocation of forage sorghum in different growth stages of 2019 and 2020 (%)
年份 Year | 处理 Treatments | 拔节期Jointing stage | 开花期Flowering stage | 收获期Harvesting stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 穗Ear | ||
| 2019 | N0 | 61.0±1.65a | 39.0±1.65a | 19.6±0.73b | 80.4±0.73a | 14.6±0.12b | 75.5±0.98a | 9.9±0.90b |
| N80 | 62.4±1.49a | 37.6±1.49a | 19.2±0.53b | 80.8±0.53a | 14.6±0.38b | 69.3±0.29b | 16.1±0.66a | |
| N160 | 62.6±0.79a | 37.5±0.79a | 18.6±1.05b | 81.4±1.05a | 15.1±0.04ab | 70.0±0.82b | 14.8±0.82a | |
| N240 | 61.0±0.52a | 39.4±0.52a | 18.3±0.39b | 81.7±0.39a | 16.0±0.47a | 70.1±2.14b | 13.9±1.67a | |
| N320 | 59.4±1.63a | 41.0±1.63a | 23.4±0.93a | 76.6±0.93b | 15.0±0.25ab | 69.3±0.59b | 15.7±0.84a | |
| 2020 | N0 | 68.4±1.85a | 31.6±1.85a | 14.0±0.73a | 86.3±0.73a | 20.0±0.32a | 71.0±0.69a | 9.1±1.01a |
| N80 | 68.7±3.19a | 31.3±3.19a | 16.4±2.78a | 83.6±2.78a | 16.6±1.38ab | 72.6±3.25a | 10.7±1.93a | |
| N160 | 68.9±1.26a | 31.1±1.26a | 15.1±2.50a | 84.9±2.50a | 15.9±2.24ab | 74.2±1.58a | 9.9±0.90a | |
| N240 | 71.8±3.42a | 29.2±3.42a | 15.4±1.41a | 84.6±1.41a | 15.9±0.56ab | 74.6±0.93a | 9.5±1.48a | |
| N320 | 68.4±3.26a | 31.6±3.26a | 15.0±1.08a | 85.0±1.08a | 13.6±0.52b | 76.5±0.73a | 10.0±1.22a | |
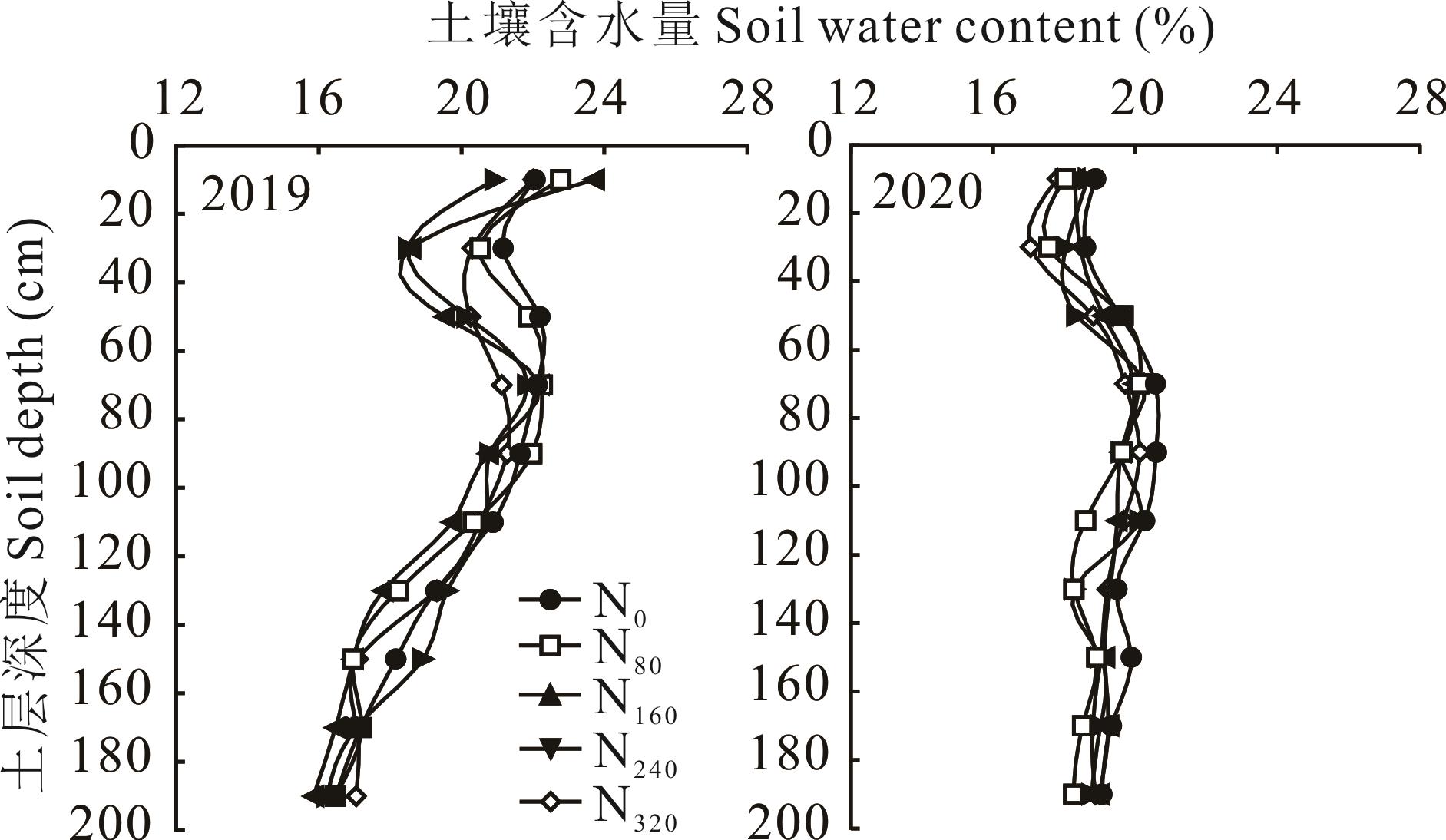
图3 2019和2020年不同施氮处理对收获期饲用高粱0~200 cm土层土壤含水量的影响
Fig.3 Effects of different nitrogen treatments on soil water content in 0-200 cm soil layer at the harvest stage of forage sorghum of 2019 and 2020
年份 Year | 处理 Treatments | 生育期内降水量 Precipitation in the growth period (mm) | 0~200 cm土层土壤储水量 Soil water storage in the 0-200 cm soil layer (mm) | 耗水量 Water consumption (mm) | 耗水强度 Water consumption rate (mm·d-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 播前Pre-sowing | 收获Harvest | 差值Difference | |||||
| 2019 | N0 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 520.4±10.9a | 85.8 | 504.3±10.9a | 3.0±0.06a |
| N80 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 513.3±15.8a | 78.7 | 511.4±15.8a | 3.0±0.09a | |
| N160 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 500.0±24.3a | 65.4 | 521.6±24.3a | 3.1±0.14a | |
| N240 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 494.0±24.8a | 59.4 | 530.7±24.8a | 3.1±0.15a | |
| N320 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 507.0±15.4a | 72.4 | 517.7±15.4a | 3.1±0.09a | |
| 2020 | N0 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 506.6±7.4a | -11.3 | 483.4±7.4b | 3.1±0.05b |
| N80 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 484.2±1.1b | -33.7 | 505.8±1.1a | 3.3±0.01a | |
| N160 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 495.7±3.4ab | -22.2 | 494.3±3.4ab | 3.2±0.02ab | |
| N240 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 494.8±5.7ab | -23.1 | 495.2±5.7ab | 3.2±0.04ab | |
| N320 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 487.9±4.2b | -30.0 | 502.1±4.2a | 3.3±0.03a | |
表2 2019和2020年不同施氮处理对饲用高粱耗水量与耗水强度的影响
Table 2 Effects of different nitrogen treatments on water consumption and water consumption rate of forage sorghum in 2019 and 2020
年份 Year | 处理 Treatments | 生育期内降水量 Precipitation in the growth period (mm) | 0~200 cm土层土壤储水量 Soil water storage in the 0-200 cm soil layer (mm) | 耗水量 Water consumption (mm) | 耗水强度 Water consumption rate (mm·d-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 播前Pre-sowing | 收获Harvest | 差值Difference | |||||
| 2019 | N0 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 520.4±10.9a | 85.8 | 504.3±10.9a | 3.0±0.06a |
| N80 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 513.3±15.8a | 78.7 | 511.4±15.8a | 3.0±0.09a | |
| N160 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 500.0±24.3a | 65.4 | 521.6±24.3a | 3.1±0.14a | |
| N240 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 494.0±24.8a | 59.4 | 530.7±24.8a | 3.1±0.15a | |
| N320 | 590.1 | 434.6 | 507.0±15.4a | 72.4 | 517.7±15.4a | 3.1±0.09a | |
| 2020 | N0 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 506.6±7.4a | -11.3 | 483.4±7.4b | 3.1±0.05b |
| N80 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 484.2±1.1b | -33.7 | 505.8±1.1a | 3.3±0.01a | |
| N160 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 495.7±3.4ab | -22.2 | 494.3±3.4ab | 3.2±0.02ab | |
| N240 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 494.8±5.7ab | -23.1 | 495.2±5.7ab | 3.2±0.04ab | |
| N320 | 472.1 | 517.9 | 487.9±4.2b | -30.0 | 502.1±4.2a | 3.3±0.03a | |
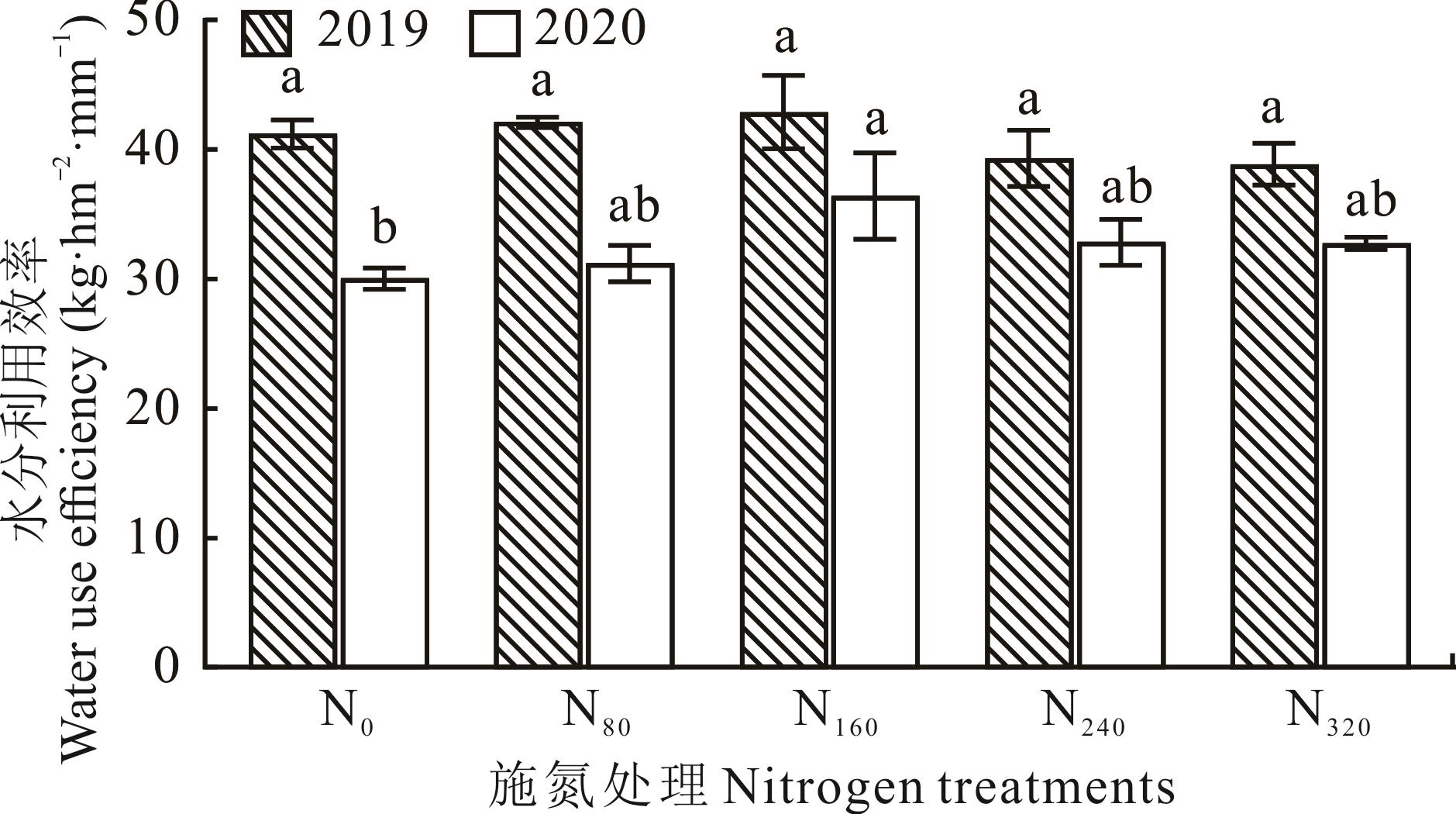
图4 2019和2020年不同施氮处理对饲用高粱水分利用效率的影响同一年份不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters in the same year indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.4 Effects of different nitrogen treatments on water use efficiency of forage sorghum in 2019 and 2020
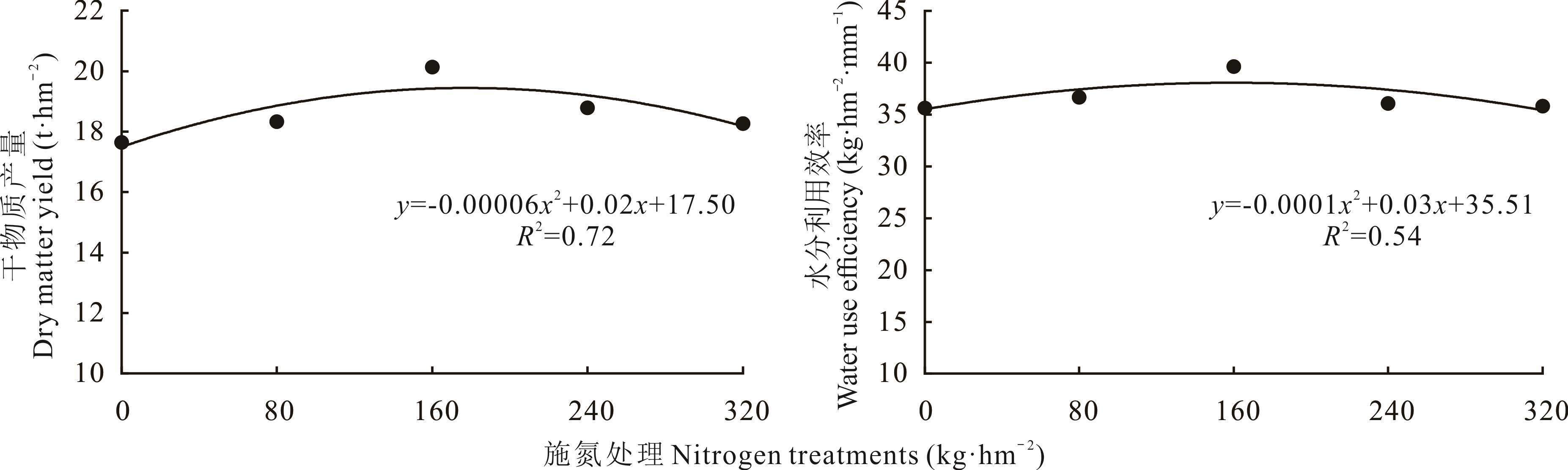
图5 2019和2020年饲用高粱平均干物质产量、水分利用效率与施氮量的关系
Fig.5 Relationships of two-year averages of dry matter yield and water use efficiency of forage sorghum with nitrogen application rate in 2019 and 2020
| 1 | Su P, Shan L. Physiological basis for grain yield and water use efficiency variation in sorghum and maize under low and high variable water conditions//Wu D. Plant physiology and trans-century agricultural research. Beijing: Science Press, 1999: 199-202. |
| 苏佩, 山仑. 多变低水环境下高粱、玉米籽粒产量及水分利用效率的变化生理基础研究//吴丁. 植物生理学与跨世纪农业研究. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 199-202. | |
| 2 | Farre I, Faci J M. Comparative response of maize (Zea mays L.) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) to deficit irrigation in a mediterranean environment. Agricultural Water Management, 2005, 83(1): 135-143. |
| 3 | Zhang S J, Amerjan O, Xue X Z, et al. Quality analysis on different sweet sorghum silages in Southern Xinjiang compared with a corn silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 232-240. |
| 张苏江, 艾买尔江·吾斯曼, 薛兴中, 等. 南疆玉米和不同糖分高粱的青贮品质分析. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 232-240. | |
| 4 | Shao Y J, Shan L. Advances in the research of drought resistance in sorghum. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2004, 20(3): 120-123. |
| 邵艳军, 山仑. 高粱抗旱机理研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2004, 20(3): 120-123. | |
| 5 | Li S S, Li F, Bai Y F, et al. Sweet sorghum feeding value and feeding dairy cows technology. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(7): 1534-1541. |
| 李珊珊, 李飞, 白彦福, 等. 甜高粱饲用价值及饲喂奶牛技术. 草业科学, 2017, 34(7): 1534-1541. | |
| 6 | Zhou L B, Wang C, Lu X J, et al. Effects of fertilizer application rate and planting density on photosynthetic characteristics, agronomic traits and yield of waxy sorghum Qiangao 7. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2016, 47(5): 644-648. |
| 周棱波, 汪灿, 陆秀娟, 等. 施肥量和种植密度对糯高粱黔高7号光合特性、农艺性状及产量的影响. 南方农业学报, 2016, 47(5): 644-648. | |
| 7 | Su F Y, Hao M D, Zhang X J, et al. Effects of fertilization on yield, nutrition uptake and quality of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2016, 25(3): 396-405. |
| 苏富源, 郝明德, 张晓娟, 等. 施肥对甜高粱产量、养分吸收及品质的影响. 西北农业学报, 2016, 25(3): 396-405. | |
| 8 | Cao X Y, Wu A L, Wang J S, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on yield, quality and nitrogen utilization efficiency of sorghum. Crops, 2021(2): 108-115. |
| 曹晓燕, 武爱莲, 王劲松, 等. 施氮量对高粱产量、品质及氮利用效率的影响. 作物杂志, 2021(2): 108-115. | |
| 9 | Liu P, Wu A L, Wang J S, et al. Nitrogen use efficiency and physiological responses of different sorghum genotypes influenced by nitrogen deficiency. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(16): 3074-3083. |
| 刘鹏, 武爱莲, 王劲松, 等. 不同基因型高粱的氮效率及对低氮胁迫的生理响应. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(16): 3074-3083. | |
| 10 | Huang C, Yao L, Zhang Y, et al. Spatial and temporal variation in autochthonous and allochthonous contributors to increased organic carbon and nitrogen burial in a plateau lake. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 603/604(Supplement C): 390-400. |
| 11 | Ma S Y, Wang Y Y, Liu Y N, et al. Effect of sowing date, planting density, and nitrogen application on dry matter accumulation, transfer, distribution, and yield of wheat. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(3): 375-385. |
| 马尚宇, 王艳艳, 刘雅男, 等. 播期、播量和施氮量对小麦干物质积累、转运和分配及产量的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(3): 375-385. | |
| 12 | Patil S L, Sheelavantar M N. Soil water conservation and yield of winter sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) as influenced by tillage, organic materials and nitrogen fertilizer in semi-arid tropical India. Soil and Tillage Research, 2006, 89(2): 246-257. |
| 13 | Cosentino S L, Mantineo M, Testa G. Water and nitrogen balance of sweet sorghum [Sorghum bicolor moench (L.)] cv. Keller under semi-arid conditions. Industrial Crops and Products, 2012, 36(1): 329-342. |
| 14 | Ajeigbe H A, Akinseye F M, Ayuba K, et al. Productivity and water use efficiency of sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] grown under different nitrogen applications in Sudan Savanna Zone, Nigeria. International Journal of Agronomy, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7676058. |
| 15 | Niu Y N, Nan Z B. Dry matter yield and productivity of forage crops under rotation systems in Longdong Loess Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(9): 1422-1427 |
| 牛伊宁, 南志标. 陇东黄土高原饲草作物生产力研究. 草业科学, 2012, 29(9): 1422-1427. | |
| 16 | Chang D D, Wang X, Tian X H, et al. Studies on multiple intercropping effects and quality of autumn sown triticale and sweet sorghum in central Gansu Province. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 212-220. |
| 常丹丹, 王旭, 田新会, 等. 甘肃中部地区秋播小黑麦套作式复种甜高粱的效应及品质研究. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 212-220. | |
| 17 | Cao Q, Wang Z K, Shen Y Y. Seasonal variation of soil moisture content in apple orchard and grass intercropping system in Longdong. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(1): 77-84. |
| 曹铨, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 陇东苹果园生草复合体系土壤水分季节动态. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(1): 77-84. | |
| 18 | Fang Y J, Zhang X C, Yu X F, et al. Effects of substitution of organic fertilizer on water consumption and yields under vertical rotary subsoiling on arid area in forage maize. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 1958-1969. |
| 方彦杰, 张绪成, 于显枫, 等. 旱地立式深旋耕方式下有机肥替代对饲用玉米耗水特性和产量的影响. 作物学报, 2020, 46(12): 1958-1969. | |
| 19 | Tang C, Yang X, Chen X, et al. Sorghum biomass and quality and soil nitrogen balance response to nitrogen rate on semiarid marginal land. Field Crops Research, 2018, 215(2): 12-22. |
| 20 | Nematpour A, Eshghizadeh H R, Zahedi M. Comparing the corn, millet and sorghum as silage crops under different irrigation regime and nitrogen fertilizer levels. International Journal of Plant Production, 2021, 15(3): 351-361. |
| 21 | Qu H, Cheng L, Chen J F, et al. Effects of nitrogen on agronomic traits and dry matter yield and their relationship sweet sorghum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(6): 13-25. |
| 渠晖, 程亮, 陈俊峰, 等. 施氮水平对甜高粱主要农艺性状及其与干物质产量相关关系的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 13-25. | |
| 22 | Restelatto R, Pavinato P S, Sartor L R, et al. Production and nutritional value of sorghum and black oat forages under nitrogen fertilization. Grass and Forage Science, 2014, 69(4): 693-704. |
| 23 | Cheng Q, Li G H, Lu W P, et al. Increasing planting density and decreasing nitrogen rate increase yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(6): 1035-1046. |
| 程前, 李广浩, 陆卫平, 等. 增密减氮提高夏玉米产量和氮素利用效率. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(6): 1035-1046. | |
| 24 | Qu Y, Zhang F, Wang K Z, et al. Response of sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] yield and quality to climatic and ecological conditions on the west Yellow-Huaihe-Haihe rivers plain. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(18): 3242-3257. |
| 屈洋, 张飞, 王可珍, 等. 黄淮西部高粱籽粒产量与品质对气候生态条件的响应. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(18): 3242-3257. | |
| 25 | Tang C C, Luo F, Li X Y, et al. Responsiveness of sweet sorghum in yield and quality related traits to environmental factors. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2015, 41(10): 1612-1618. |
| 唐朝臣, 罗峰, 李欣禹, 等. 甜高粱及品质相关性状对环境因子的反应度分析. 作物学报, 2015, 41(10): 1612-1618. | |
| 26 | Zaituniguli K, Tuerxun T, Zhu M, et al. Effects of continuous cropping on agronomic shape and yield of sweet sorghum No.3. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(7): 1211-1222. |
| 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 吐尔逊·吐尔洪, 朱敏, 等. 干旱区连作对甜高粱农艺性状及产量的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(7): 1211-1222. | |
| 27 | Fan F F, Wang J S, Dong E W, et al. Effects of sorghum continuous cropping on the growth of sorghum and soil environment. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016, 4(3): 127-133. |
| 樊芳芳, 王劲松, 董二伟, 等. 连作对高粱生长及根区土壤环境的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016, 4(3): 127-133. | |
| 28 | Li H B, Zhai W X, Yu G R, et al. A comparative study on the accumulation and distribution of dry matter and formation of yield of sweet sorghum and grain sorghum. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1991, 17(3): 204-212. |
| 李淮滨, 翟婉萱, 于贵瑞, 等. 甜高粱与粒用高粱干物质积累分配与产量形成的比较研究. 作物学报, 1991, 17(3): 204-212. | |
| 29 | Zou X, Cao G J, Geng Y H, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on maize yield and dry matter accumulation and nitrogen uptake and distribution. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2020, 44: 1-13. |
| 邹欣, 曹国军, 耿玉辉, 等. 水氮耦合效应对玉米产量、干物质积累及氮素吸收分配的影响. 吉林农业大学学报, 2020, 44: 1-13. | |
| 30 | Zhang L, Kong L L, Hou Y P, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on dry matter accumulation, translocation, and inorganic nitrogen content in soil after anthesis of maize. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2020, 28(4): 155-164. |
| 张磊, 孔丽丽, 侯云鹏, 等. 施氮水平对玉米开花后干物质积累、转运及土壤无机氮含量的影响. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(4): 155-164. | |
| 31 | Wang J S, Jiao X Y, Dong E W, et al. Effect of different irrigation periods and nitrogen fertilizer levels on sorghum water use efficiency and yield. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(6): 777-783. |
| 王劲松, 焦晓燕, 董二伟, 等. 不同灌溉时期和施氮量对高粱水分利用及产量的影响. 山西农业科学, 2016, 44(6): 777-783. | |
| 32 | Liang X H, Zhang R D, Huang M J, et al. Interaction of film mulching and nitrogen application on yield, water and nitrogen use efficiency of sorghum. Crops, 2019(5): 135-142. |
| 梁晓红, 张瑞栋, 黄敏佳, 等. 覆膜与施氮互作对高粱产量及水氮利用效率的影响. 作物杂志, 2019(5): 135-142. | |
| 33 | Bennett J M, Mutti L S M, Rao P S C, et al. Interactive effects of nitrogen and water stresses on biomass accumulation, nitrogen uptake, and seed yield of maize. Field Crops Research, 1989, 19(4): 297-311. |
| [1] | 周大梁, 石薇, 蒋紫薇, 魏正业, 梁欢欢, 贾倩民. 沟垄集雨下密度和施氮对黄土高原青贮玉米叶片酶活性及水氮利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 126-143. |
| [2] | 牛伟玲, 陈辉, 侯慧新, 郭晨睿, 马娇林, 武建双. 10年禁牧未改变藏西北高寒荒漠植物水氮利用效率[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 35-48. |
| [3] | 古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33. |
| [4] | 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 梁国玲, 马祥. 干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦产量及干物质积累与分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 177-188. |
| [5] | 王红林, 左艳春, 严旭, 周晓康, 寇晶, 杨希智, 郭俊英, 蒲军, 张浩仁, 杜周和. 刈割高度与施氮量对饲料桑全株产量及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 203-211. |
| [6] | 才璐, 王林林, 罗珠珠, 李玲玲, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群, 谢军红. 中国苜蓿产量及水分利用效率对种植年限响应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 27-38. |
| [7] | 康彩睿, 谢军红, 李玲玲, 王嘉男, 郭喜军, 彭正凯, 王进斌, Setor kwami Fudjoe, 王林林. 种植密度与施氮量对陇中旱农区玉米产量及光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 141-149. |
| [8] | 方彦杰, 张绪成, 于显枫, 侯慧芝, 王红丽, 马一凡, 张国平, 雷康宁. 地膜覆盖和施肥对半干旱区苦荞土壤水分利用及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 46-56. |
| [9] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 常雯雯. 施氮量对柳枝稷叶片叶绿素荧光特性及干物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 141-150. |
| [10] | 方彦杰, 张绪成, 于显枫, 侯慧芝, 王红丽, 马一凡, 张国平, 雷康宁. 立式深旋松耕对半干旱区饲草玉米水分利用和产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 161-171. |
| [11] | 李尚中, 樊廷录, 赵晖, 李城德, 赵贵宾, 赵刚, 党翼, 王磊, 张建军, 唐小明, 王淑英, 程万莉. 不同地膜覆盖栽培模式对玉米产量、水分利用效率和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 182-191. |
| [12] | 周旭姣, 王琦, 张登奎, 尹鑫卫, 李晓玲, 刘青林, 贾生海. 垄沟集雨种植对土壤水热效应及紫花苜蓿产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 60-74. |
| [13] | 李愈哲, 邵全琴, 樊江文, 陈一, 陈智, 官惠玲, 张馨元. 开垦对放牧温性草原生态系统水分利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 110-121. |
| [14] | 王进斌, 谢军红, 李玲玲, Eunice Essel, 彭正凯, 邓超超, 沈吉成, 颉健辉. 氮肥运筹对陇中旱农区玉米光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 60-69. |
| [15] | 刘家鹤, 牛伊宁, 罗珠珠, 蔡立群, 张仁陟, 谢军红. 黄土高原坡耕地植物篱-作物间作系统水分利用特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 111-119. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||