

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 107-117.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021369
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
苗阳阳( ), 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民(
), 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-09
修回日期:2022-01-11
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
曲善民
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: qushanmin@126.com基金资助:
Yang-yang MIAO( ), Yan-rui ZHANG, Biao SONG, Xu-tong LIU, An-qi ZHANG, Jin-ze LV, Hao ZHANG, Xiao-hua ZHANG, Jia-hui OUYANG, Wang LI, Shan-min QU(
), Yan-rui ZHANG, Biao SONG, Xu-tong LIU, An-qi ZHANG, Jin-ze LV, Hao ZHANG, Xiao-hua ZHANG, Jia-hui OUYANG, Wang LI, Shan-min QU( )
)
Received:2021-10-09
Revised:2022-01-11
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Shan-min QU
摘要:
为研究碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿幼苗生长的影响,试验以龙牧801紫花苜蓿为供试品种,将前期从碱蓬根内(JG1)、根际土壤(JT4)和茎内(JJ5)筛选出的具有较强耐盐碱胁迫能力的根际及内生细菌菌株接种于苜蓿幼苗根部。接菌1周后将中性盐(NaCl、Na2SO4)和碱性盐(NaHCO3、Na2CO3)按NaCl∶Na2SO4∶NaHCO3∶Na2CO3=9∶1∶1∶9混合,并设置0、100、150、200 mmol·L-1盐碱浓度溶液浇灌苜蓿幼苗根部,进行盐碱胁迫处理。分析盐碱胁迫下碱蓬根际及内生细菌菌株对苜蓿生长及生理的影响,并通过隶属函数和主成分分析综合评价碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿生长的影响。结果表明:3株促生细菌均能缓解盐碱胁迫对紫花苜蓿生长的抑制作用,促进紫花苜蓿生长,不同促生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿促生效果为JT4>JG1>JJ5。
苗阳阳, 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民. 碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 107-117.
Yang-yang MIAO, Yan-rui ZHANG, Biao SONG, Xu-tong LIU, An-qi ZHANG, Jin-ze LV, Hao ZHANG, Xiao-hua ZHANG, Jia-hui OUYANG, Wang LI, Shan-min QU. Effects of Suaeda glauca rhizobacteria and endophytic bacterial strains on alfalfa growth under salt-alkaline stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 107-117.
| 菌株编号Strain number | 菌株Strain | 分离部位Separation site |
|---|---|---|
| JG1 | 普城沙雷氏菌Serratia plymuthica | 碱蓬根内S. glauca root |
| JT4 | 嗜麦芽寡养单胞菌Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 碱蓬根际土壤S. glauca rhizosphere soil |
| JJ5 | 普城沙雷氏菌S. plymuthica | 碱蓬茎内S. glauca stem |
表1 碱蓬根际细菌和内生细菌菌株
Table 1 Rhizobacteria and endophytic bacteria of S. glauca
| 菌株编号Strain number | 菌株Strain | 分离部位Separation site |
|---|---|---|
| JG1 | 普城沙雷氏菌Serratia plymuthica | 碱蓬根内S. glauca root |
| JT4 | 嗜麦芽寡养单胞菌Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 碱蓬根际土壤S. glauca rhizosphere soil |
| JJ5 | 普城沙雷氏菌S. plymuthica | 碱蓬茎内S. glauca stem |
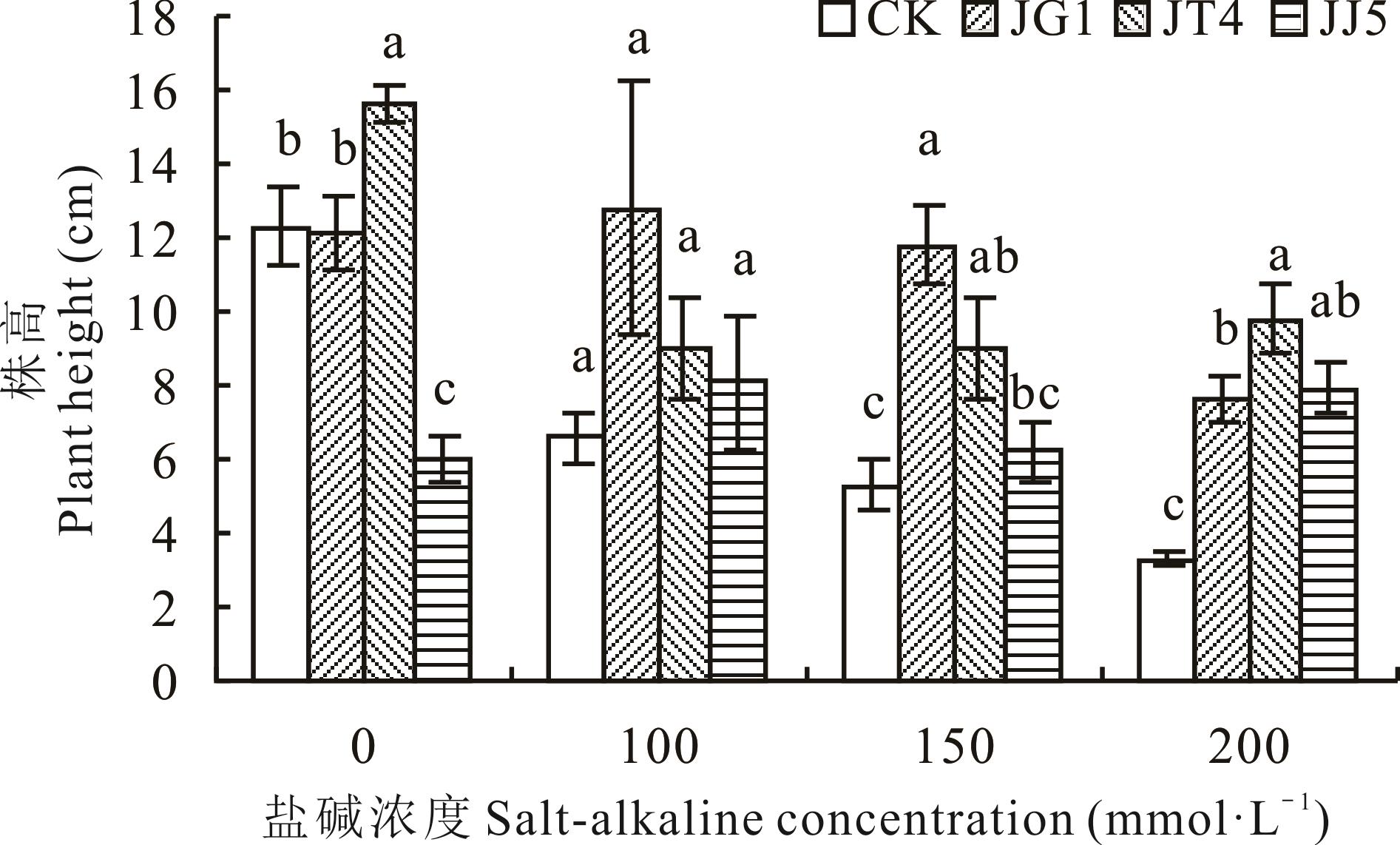
图1 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿株高的影响不同小写字母表示同一盐碱浓度处理下,不同菌株处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters mean there were significant differences among different strains under the same salt-alkaline concentration treatment at P<0.05. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on plant height of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
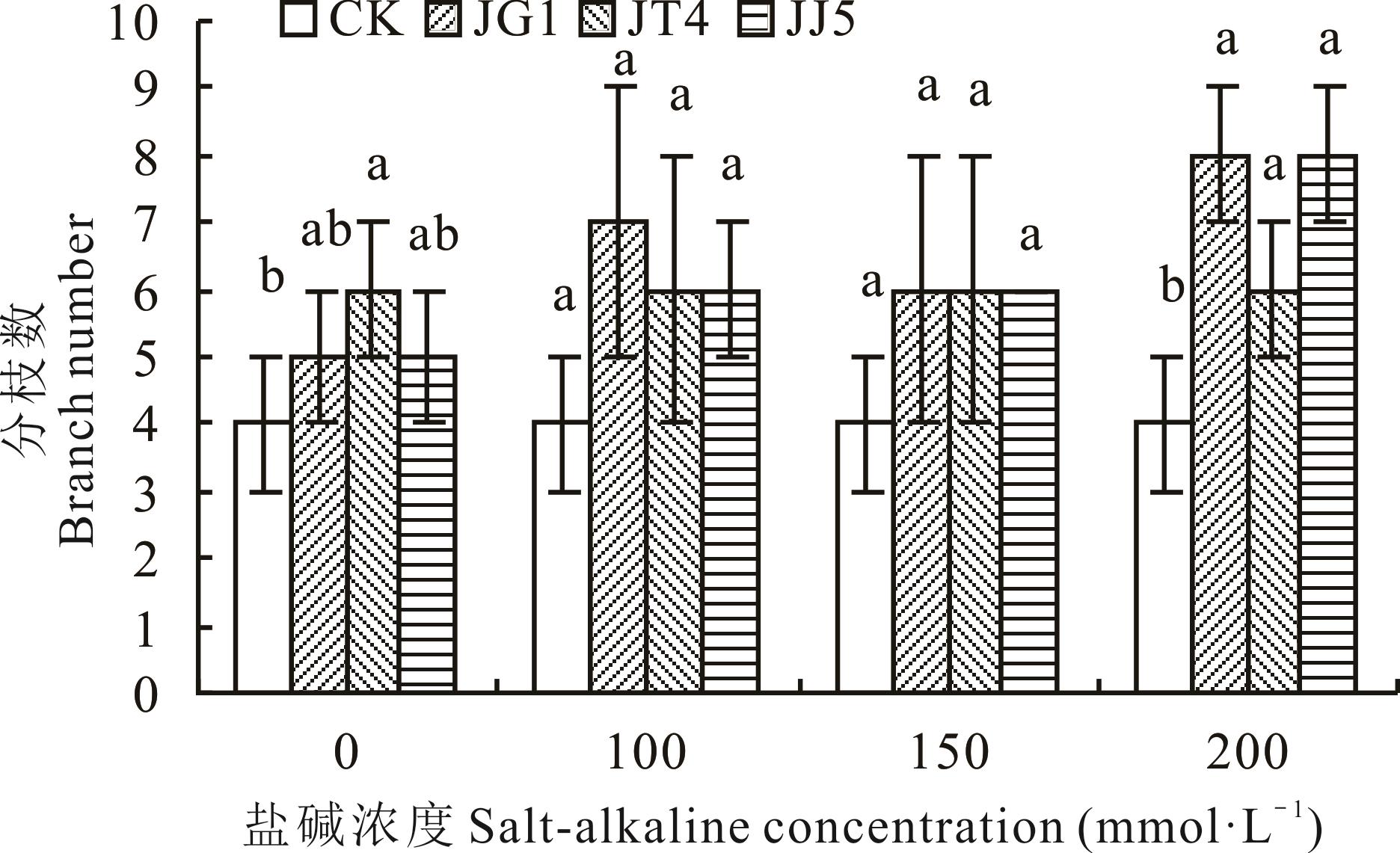
图2 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿分枝数的影响
Fig.2 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on branches number of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
菌株编号 Strain number | 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
| CK | 0.5370±0.0153b | 0.4598±0.2188b | 0.4175±0.0143c | 0.2780±0.0134d |
| JG1 | 0.9474±0.0111b | 0.5206±0.1197b | 1.0704±0.1087a | 1.1538±0.0716a |
| JT4 | 2.2427±0.3351a | 0.6021±0.1345b | 0.7770±0.0874b | 0.6577±0.0144c |
| JJ5 | 0.5847±0.0767b | 1.1492±0.1753a | 0.6565±0.0270b | 0.9697±0.0289b |
表2 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿地上鲜重的影响
Table 2 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on the aboveground fresh weight of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress (g·5 plant-1)
菌株编号 Strain number | 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
| CK | 0.5370±0.0153b | 0.4598±0.2188b | 0.4175±0.0143c | 0.2780±0.0134d |
| JG1 | 0.9474±0.0111b | 0.5206±0.1197b | 1.0704±0.1087a | 1.1538±0.0716a |
| JT4 | 2.2427±0.3351a | 0.6021±0.1345b | 0.7770±0.0874b | 0.6577±0.0144c |
| JJ5 | 0.5847±0.0767b | 1.1492±0.1753a | 0.6565±0.0270b | 0.9697±0.0289b |
菌株编号 Strain number | 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
| CK | 0.0870±0.0048b | 0.3374±0.0607c | 0.2560±0.0158c | 0.2405±0.0231c |
| JG1 | 0.1982±0.0061b | 0.7080±0.0748b | 0.7244±0.0797b | 2.4406±0.4290a |
| JT4 | 0.5099±0.0790a | 0.5305±0.0035bc | 0.8993±0.0690b | 0.9783±0.4650bc |
| JJ5 | 0.1196±0.0291b | 1.2271±0.1562a | 2.9968±0.2218a | 2.1134±0.4620ab |
表3 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿根鲜重的影响
Table 3 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on root fresh weight of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress (g·5 plant-1)
菌株编号 Strain number | 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
| CK | 0.0870±0.0048b | 0.3374±0.0607c | 0.2560±0.0158c | 0.2405±0.0231c |
| JG1 | 0.1982±0.0061b | 0.7080±0.0748b | 0.7244±0.0797b | 2.4406±0.4290a |
| JT4 | 0.5099±0.0790a | 0.5305±0.0035bc | 0.8993±0.0690b | 0.9783±0.4650bc |
| JJ5 | 0.1196±0.0291b | 1.2271±0.1562a | 2.9968±0.2218a | 2.1134±0.4620ab |
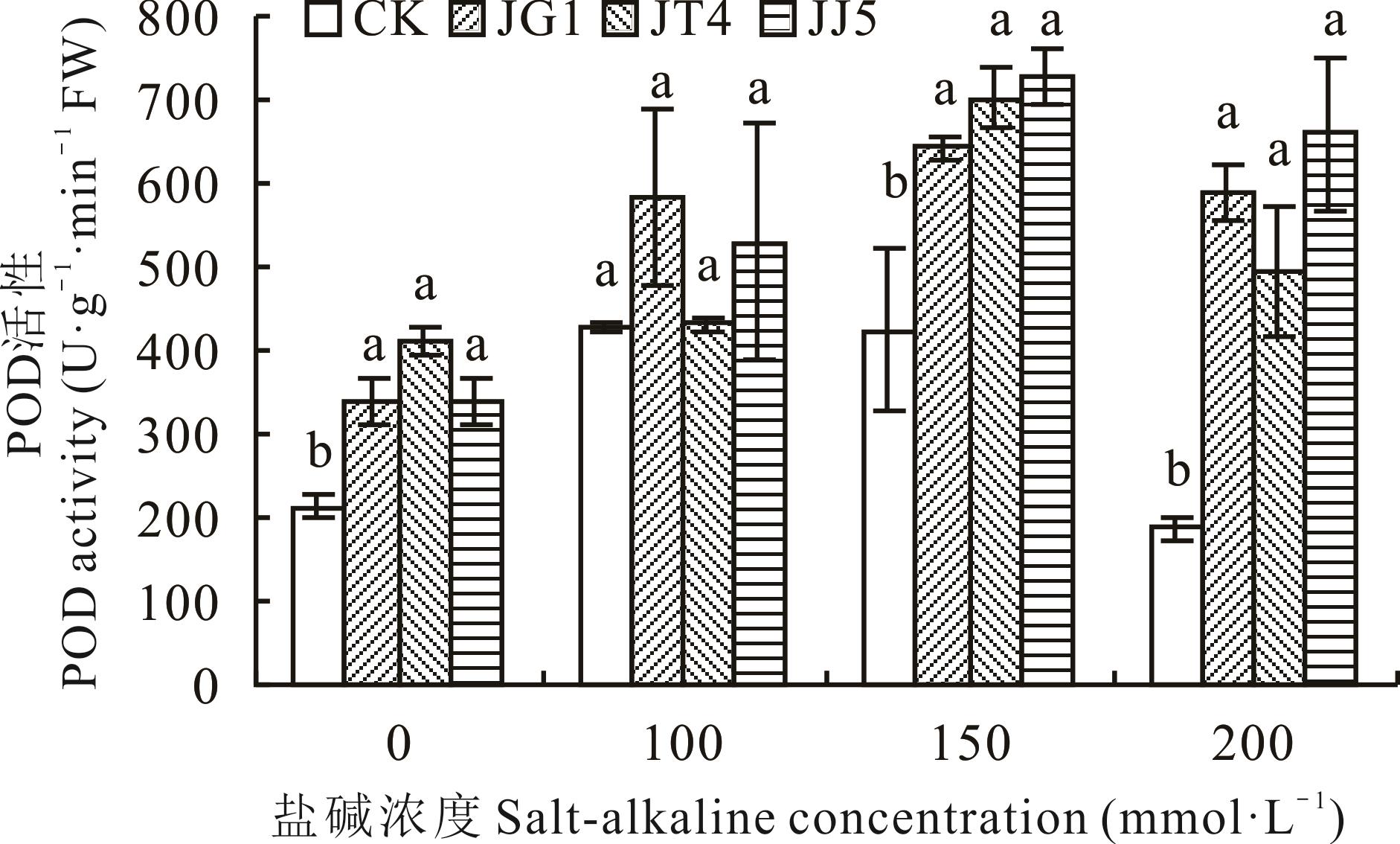
图3 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿POD活性的影响
Fig.3 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on POD activity of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
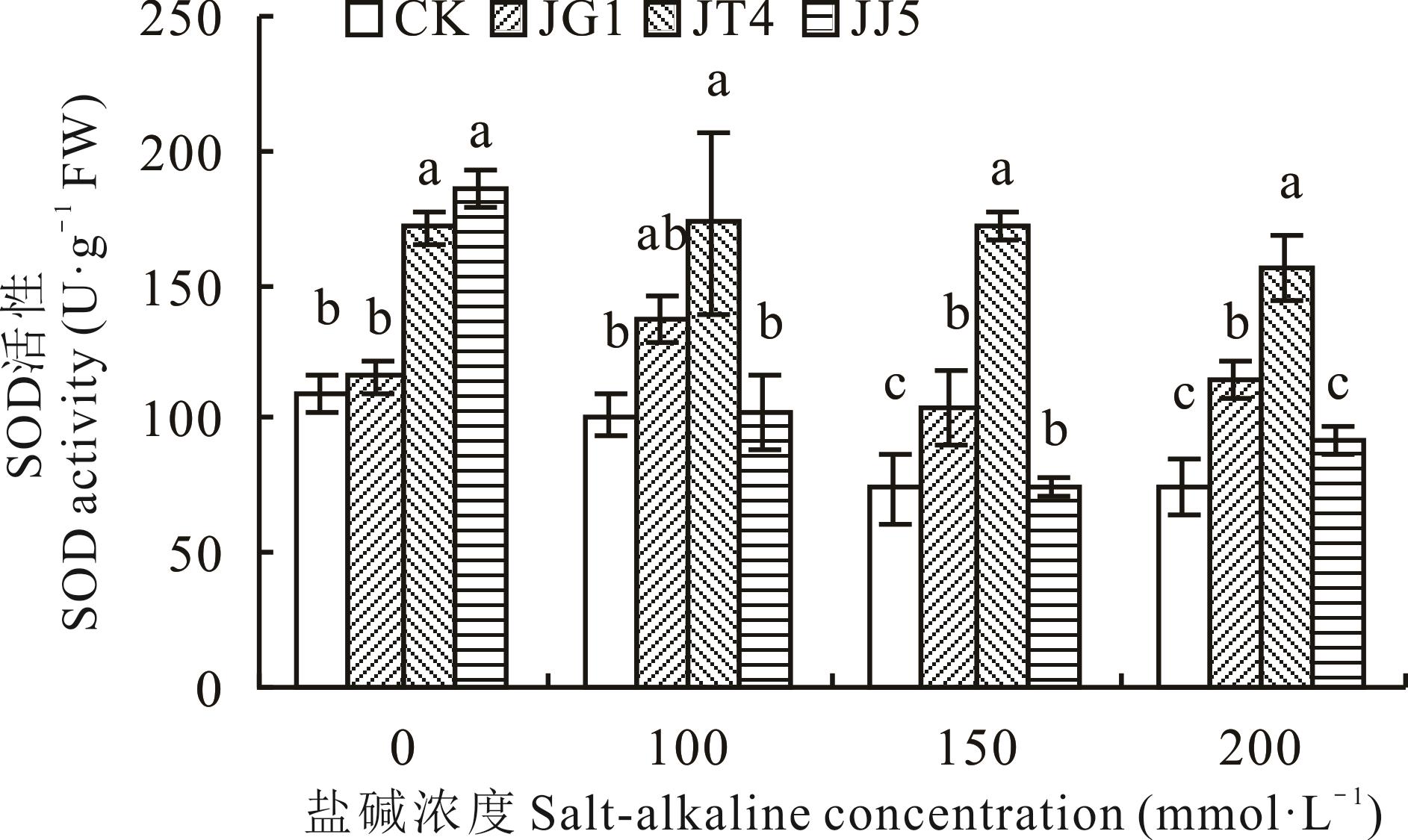
图4 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿SOD活性的影响
Fig.4 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on SOD activity of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
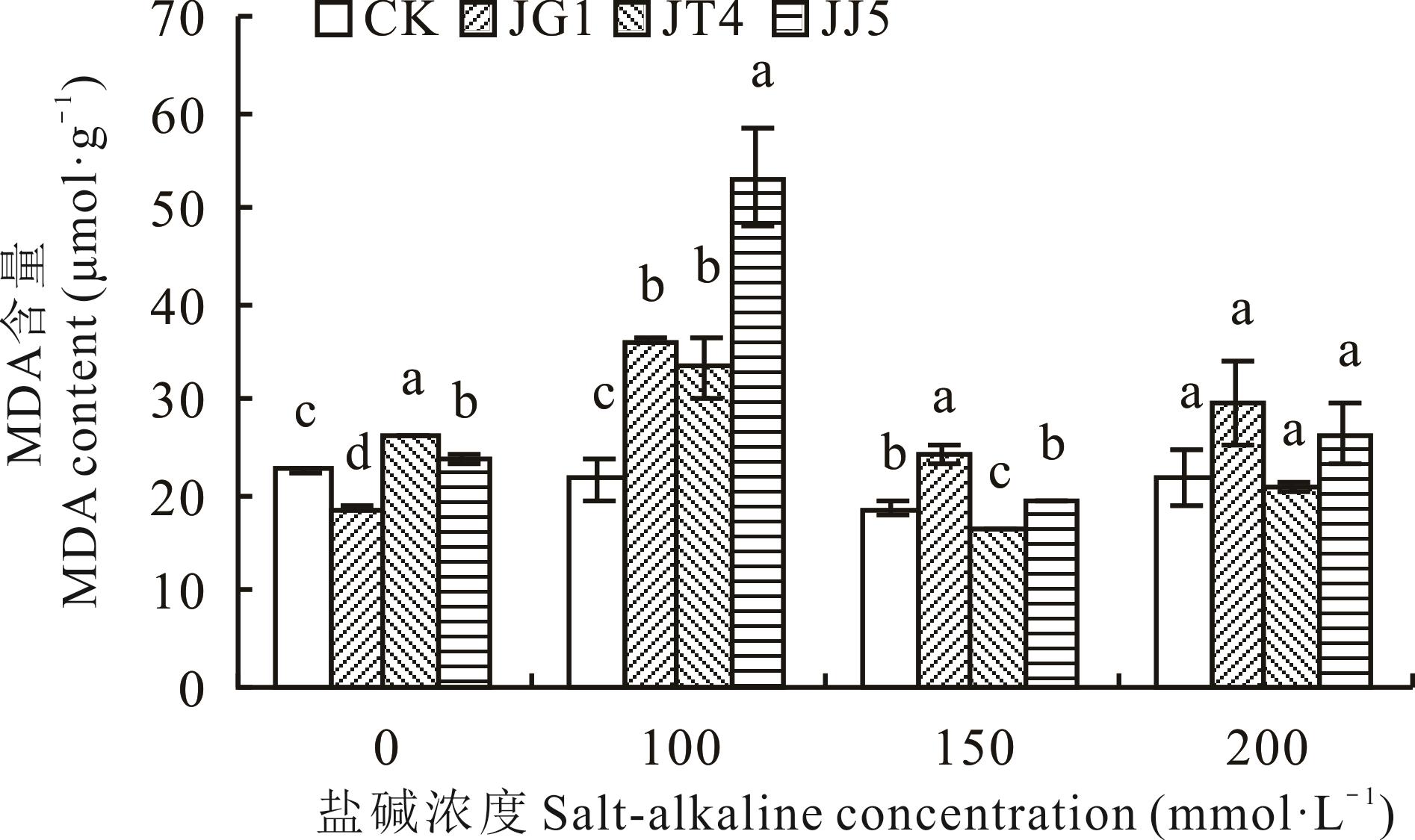
图5 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿MDA含量的影响
Fig.5 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on MDA content of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
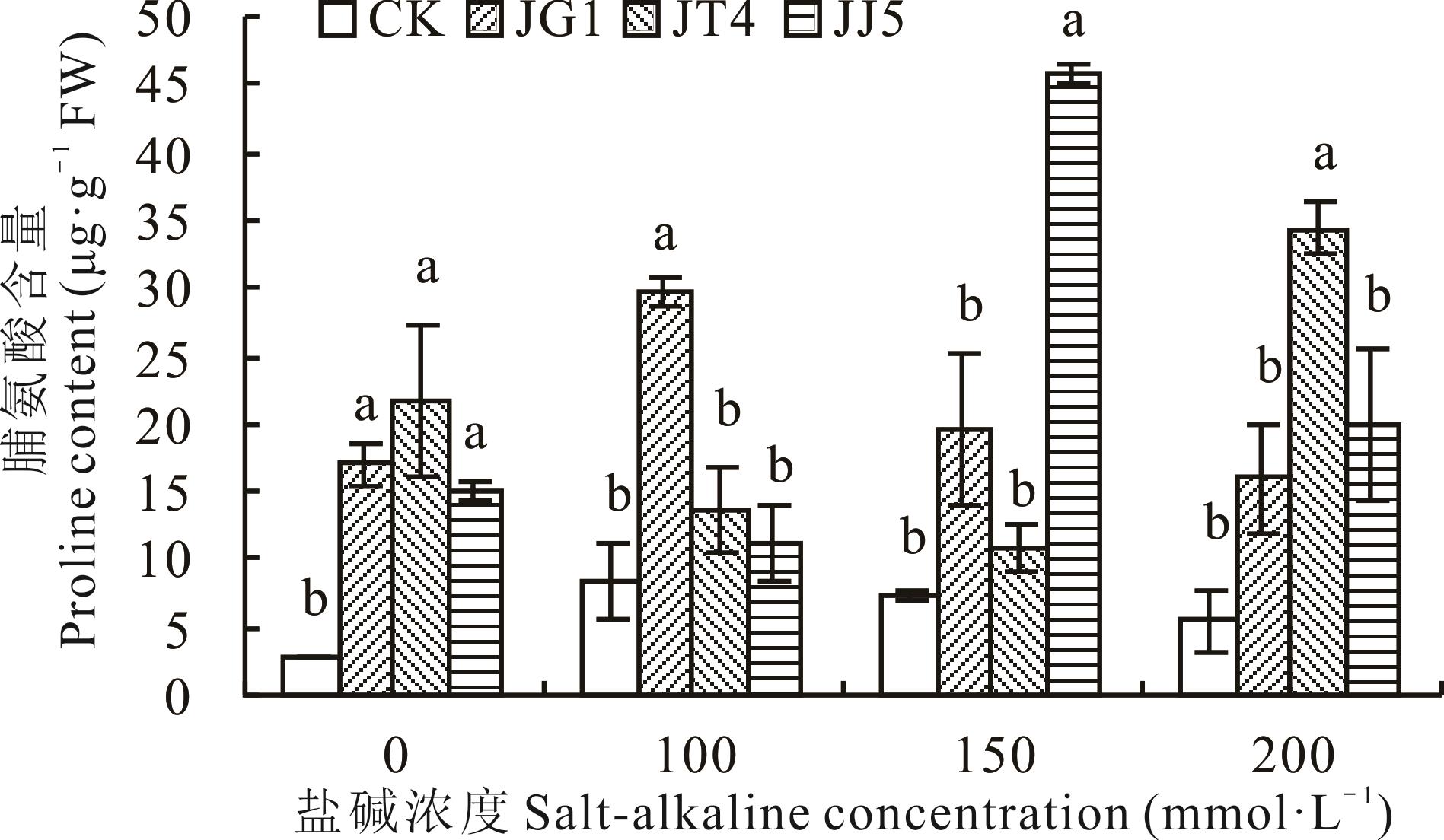
图6 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿脯氨酸含量的影响
Fig.6 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on proline content of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
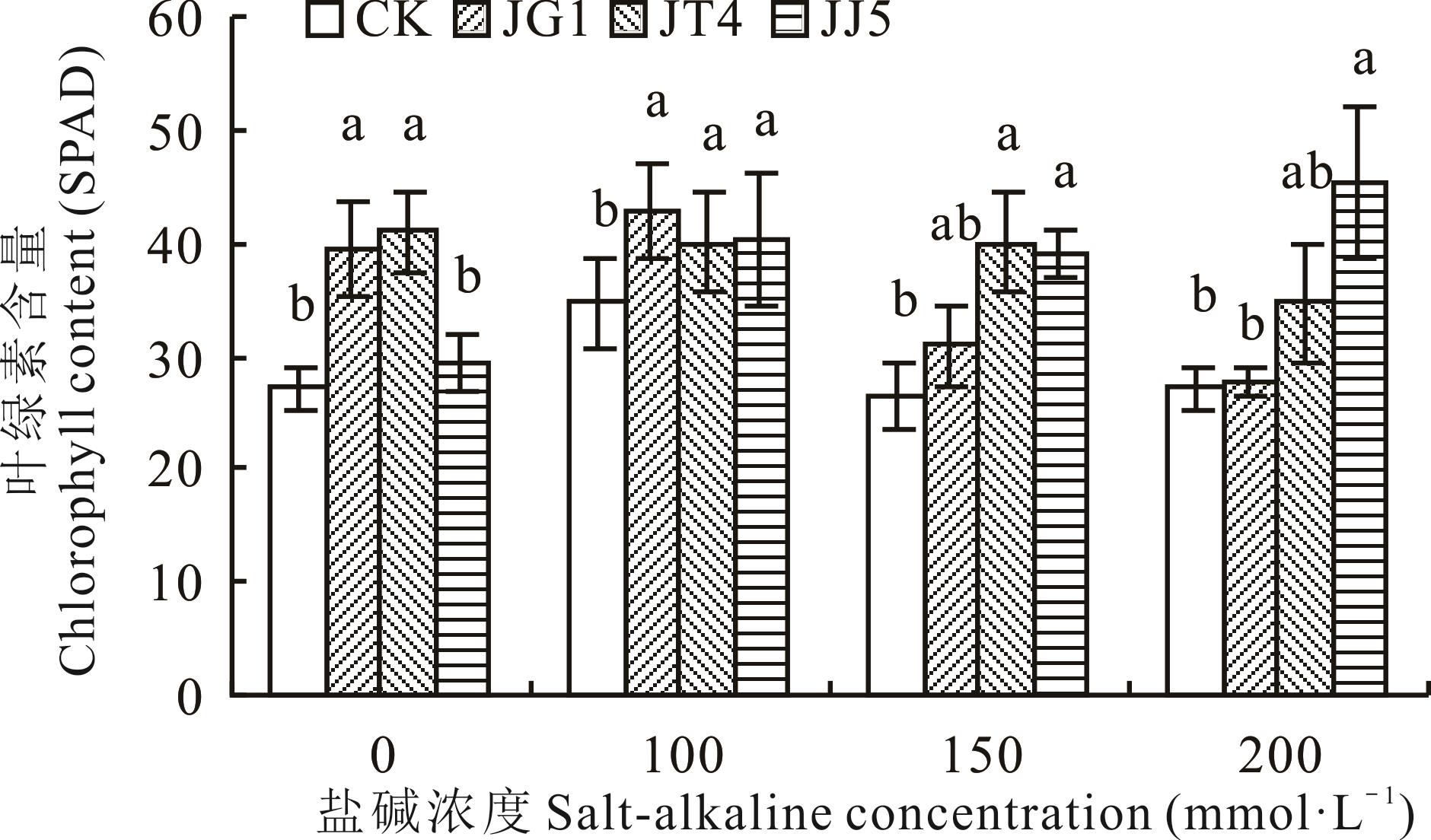
图7 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿叶片叶绿素含量的影响
Fig.7 Effects of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on leaf chlorophyll content of alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
菌株编号 Strain number | 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (mmol·L-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |||||
| 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | |
| CK | 0.114 | 3 | 0.000 | 4 | 0.034 | 4 | 0.019 | 4 |
| JG1 | 0.448 | 2 | 0.388 | 2 | 0.427 | 2 | 0.546 | 2 |
| JT4 | 1.677 | 1 | 1.185 | 1 | 1.164 | 1 | 1.125 | 1 |
| JJ5 | -0.217 | 4 | 0.001 | 3 | 0.053 | 3 | 0.107 | 3 |
表4 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿耐盐碱指标隶属函数分析
Table 4 Comprehensive analysis of membership function values of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on alfalfa salt-alkaline tolerance indexes under salt-alkaline stress
菌株编号 Strain number | 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (mmol·L-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |||||
| 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | 平均值Mean | 综合排名Rank | |
| CK | 0.114 | 3 | 0.000 | 4 | 0.034 | 4 | 0.019 | 4 |
| JG1 | 0.448 | 2 | 0.388 | 2 | 0.427 | 2 | 0.546 | 2 |
| JT4 | 1.677 | 1 | 1.185 | 1 | 1.164 | 1 | 1.125 | 1 |
| JJ5 | -0.217 | 4 | 0.001 | 3 | 0.053 | 3 | 0.107 | 3 |
项目 Item | 苜蓿耐盐碱性指标 Salt-alkaline tolerance indexes of alfalfa | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | ||||
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (0 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 6.03 | 66.98 | 66.98 |
| Ⅱ | 0.13 | -0.19 | -0.22 | 0.19 | 0.13 | -0.42 | 0.82 | -0.79 | 0.45 | 1.83 | 20.29 | 87.26 |
| Ⅲ | -0.12 | 0.22 | 0.24 | -0.28 | -0.40 | -0.34 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 1.15 | 12.74 | 100.00 |
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (100 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.28 | 5.00 | 55.53 | 55.53 |
| Ⅱ | -0.10 | -0.28 | 0.10 | -0.50 | -0.55 | 0.92 | 0.77 | 0.71 | -0.65 | 3.01 | 33.41 | 88.94 |
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (150 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.45 | 4.36 | 48.45 | 48.45 |
| Ⅱ | 0.09 | -0.16 | -0.37 | 0.65 | 0.81 | -0.77 | -0.66 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 2.71 | 30.06 | 78.51 |
| Ⅲ | -0.07 | -0.08 | -0.42 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.49 | 0.86 | -0.78 | 1.93 | 21.49 | 100.00 |
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (200 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 5.35 | 59.46 | 59.46 |
| Ⅱ | -0.06 | -0.23 | -0.32 | -0.43 | 0.70 | 0.14 | 0.81 | 0.79 | -0.77 | 2.70 | 29.99 | 89.45 |
表5 碱蓬根际促生细菌和内生细菌对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿耐盐碱性指标主成分分析
Table 5 Principal component analysis of salt-alkaline tolerance index of S. glauca rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and endophytic bacteria on alfalfa under salt-alkaline stress
项目 Item | 苜蓿耐盐碱性指标 Salt-alkaline tolerance indexes of alfalfa | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | ||||
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (0 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 6.03 | 66.98 | 66.98 |
| Ⅱ | 0.13 | -0.19 | -0.22 | 0.19 | 0.13 | -0.42 | 0.82 | -0.79 | 0.45 | 1.83 | 20.29 | 87.26 |
| Ⅲ | -0.12 | 0.22 | 0.24 | -0.28 | -0.40 | -0.34 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 1.15 | 12.74 | 100.00 |
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (100 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.28 | 5.00 | 55.53 | 55.53 |
| Ⅱ | -0.10 | -0.28 | 0.10 | -0.50 | -0.55 | 0.92 | 0.77 | 0.71 | -0.65 | 3.01 | 33.41 | 88.94 |
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (150 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.45 | 4.36 | 48.45 | 48.45 |
| Ⅱ | 0.09 | -0.16 | -0.37 | 0.65 | 0.81 | -0.77 | -0.66 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 2.71 | 30.06 | 78.51 |
| Ⅲ | -0.07 | -0.08 | -0.42 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.49 | 0.86 | -0.78 | 1.93 | 21.49 | 100.00 |
| 盐碱浓度Salt-alkaline concentration (200 mmol·L-1) | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 5.35 | 59.46 | 59.46 |
| Ⅱ | -0.06 | -0.23 | -0.32 | -0.43 | 0.70 | 0.14 | 0.81 | 0.79 | -0.77 | 2.70 | 29.99 | 89.45 |
| 1 | Yamazaki K, Ishimori M, Kajiya-Kanegae H, et al. Effect of salt tolerance on biomass production in a large population of sorghum accessions. Breed Science, 2020, 70(2): 167-175. |
| 2 | Li M, Chen R, Jiang Q, et al. GmNAC06, a NAC domain transcription factor enhances salt stress tolerance in soybean. Plant Molecular Biology, 2021, 105(3): 333-345. |
| 3 | Liu Q, Gao Y N, Liu X, et al. Effects of inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia on growth of Medicago sativa under saline-alkaline stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(17): 6143-6155. |
| 刘倩, 高娅妮, 柳旭, 等. 混合盐碱胁迫下接种丛枝菌根真菌和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿生长的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(17): 6143-6155. | |
| 4 | Wang S. Biodiversity and polyphasic taxonomy of culturable halophilic bacteria and archaea from saline-alkaline soil in Daqing. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011. |
| 王爽. 大庆盐碱土可培养嗜盐细菌与古菌多样性及多相分类研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2011. | |
| 5 | Bai S H, Ma F Y, Hou D, et al. Change in population niche during vegetation community succession in the Yellow River Delta. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(3): 581-587. |
| 白世红, 马风云, 侯栋, 等. 黄河三角洲植被演替过程种群生态位变化研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(3): 581-587. | |
| 6 | Yang C, Chen H Y, Li J S, et al. Soil improving effect of Suaeda salsa on heavy coastal saline-alkaline land. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(10): 1578-1586. |
| 杨策, 陈环宇, 李劲松, 等. 盐地碱蓬生长对滨海重盐碱地的改土效应. 中国生态农业学报, 2019, 27(10): 1578-1586. | |
| 7 | Hu Y L, Li H D, Wang H F, et al. Enzyme screening and isolation of Suaeda salsa endophytes. Journal of Tangshan Normal University, 2018, 40(6): 70-72, 76. |
| 胡宇玲, 厉海笛, 王会芳, 等. 盐地碱蓬内生菌的分离及功能酶的检测. 唐山师范学院学报, 2018, 40(6): 70-72, 76. | |
| 8 | Ma X, Cheng Y, Ma R L. Research progress of plant growth-promoting mechanisms of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 51(5): 148-154. |
| 马欣, 成妍, 马蓉丽. 植物根围促生细菌促生机制研究进展. 山东农业科学, 2019, 51(5): 148-154. | |
| 9 | Cao M M, Wang F, Zhou B H, et al. Community distribution of the rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria of Phragmites australis and their limiting factors in iron tailings. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(10): 4998-5009. |
| 曹曼曼, 王飞, 周北海, 等. 铁尾矿芦苇根际微生物和根内生菌群落分布及其限制性因子解析. 环境科学, 2021, 42(10): 4998-5009. | |
| 10 | Kang Y J, Cheng J, Mei L J, et al. Action mechanisms of plant growth-promoting rhizabacteria (PGPR): A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(1): 232-238. |
| 康贻军, 程洁, 梅丽娟, 等. 植物根际促生菌作用机制研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(1): 232-238. | |
| 11 | Zahir Z A, Zafar-ul-Hye M, Sajjad S, et al. Comparative effectiveness of Pseudomonas and Serratia sp. containing ACC-deaminase for coinoculation with Rhizobium leguminosarum to improve growth, nodulation, and yield of lentil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2011, 47(4): 457-465. |
| 12 | Estevez J, Dardanelli M S, Megias M, et al. Symbiotic performance of common bean and soybean co-inoculated with rhizobia and Chryseobacterium balustinum Aur9 under moderate saline conditions. Symbiosis, 2009, 49(1): 29-36. |
| 13 | Xiang J L, Tang C R, Wang J Q, et al. Screening and identification of Medicago sativa Linn growth promoting rhizobacteria under saline-alkali stress. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2019, 37(2): 266-272. |
| 向君亮, 唐呈瑞, 王佳琦, 等. 盐碱胁迫下一株促进苜蓿生长的细菌筛选与鉴定. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(2): 266-272. | |
| 14 | Liu J L. Isolation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and the mechanism of relieving saline-alkaline stress on alfalfa. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2017. |
| 刘佳莉. 植物根际促生细菌的筛选及其缓解紫花苜蓿盐碱胁迫的作用研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2017. | |
| 15 | Zhao X, Ye L. Effects of salt alkali stress on growth, quality and photosynthetic characteristics of alfalfa. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(21): 176-180. |
| 赵霞, 叶林. 盐碱胁迫对紫花苜蓿生长、品质及光合特性的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(21): 176-180. | |
| 16 | Wu Y, Tian Y, Zhang H X, et al. Effects of salinity, alkalinity, temperature and their interactions on seed germination of Medicago falcata. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 32(11): 1847-1853. |
| 武祎, 田雨, 张红香, 等. 盐、碱胁迫与温度对黄花苜蓿种子发芽的影响. 草业科学, 2015, 32(11): 1847-1853. | |
| 17 | Jiang Y M, Gao Y M, Yao T, et al. Effect of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on the growth of Uraria crinita and ×Triticale Wittmack. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(8): 1910-1918. |
| 蒋永梅, 高亚敏, 姚拓, 等. 植物根际促生菌(PGPR)对非宿主植物猫尾草和小黑麦生长的促生作用. 草业科学, 2018, 35(8): 1910-1918. | |
| 18 | Shi D C, Zhao K F. Effects of sodium chloride and carbonate on growth of Puccinellia and on present state of mineral elements in nutrient solution. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 1997, 6(2): 51-61. |
| 石德成, 赵可夫. NaCl和Na2CO3对星星草生长及营养液中主要矿质元素存在状态的影响. 草业学报, 1997, 6(2): 51-61. | |
| 19 | Yang H T, An F H, Zhao D D, et al. Biological characteristics responses of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) to soil salinity alkalinity. Soils and Crops, 2019, 8(3): 242-250. |
| 杨洪涛, 安丰华, 赵丹丹, 等. 土壤盐碱化对紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa L.)生物学特征的影响. 土壤与作物, 2019, 8(3): 242-250. | |
| 20 | Tong S P, Liang Z W, Guan F C, et al. Biodiversity characteristics and biomass of artificial transplanting Leymus chinensis grassland in soda saline-alkali land of Songnen Plain. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(1): 22-27. |
| 仝淑萍, 梁正伟, 关法春, 等. 松嫩平原苏打盐碱地羊草人工移栽草地生物多样性特征和生物量. 草地学报, 2019, 27(1): 22-27. | |
| 21 | Cai Y P. Experimental guide for plant physiology. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2014. |
| 蔡永萍. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2014. | |
| 22 | Ding Y F, Jin P, Liu P. Advances in gene expression, activity regulation and stress resistance of plant SOD. Biology Teaching, 2012, 37(7): 6-8. |
| 丁义峰, 靳萍, 刘萍. 植物SOD的基因表达、活性调节及抗逆作用研究进展. 生物学教学, 2012, 37(7): 6-8. | |
| 23 | Dou J H, Yu S X, Fan S L, et al. SOD and plant stress resistance. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2010, 8(2): 359-364. |
| 窦俊辉, 喻树迅, 范术丽, 等. SOD与植物胁迫抗性. 分子植物育种, 2010, 8(2): 359-364. | |
| 24 | Wang L. Research on salt tolerant peroxidases in wheat and arsenic resistant transgenic plant. Jinan: Shandong University, 2009. |
| 王乐. 山融3号小麦耐盐相关过氧化物酶基因及植物抗砷基因工程初步研究. 济南: 山东大学, 2009. | |
| 25 | Fu M Y. Biological and physiological-biochemical characteristics of high-yield insect-resistant transgenic Bt cotton “SCRC21”. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 傅明焱. 转Bt基因抗虫棉鲁棉研21号高产的生物学和生理生化特性. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2012. | |
| 26 | Wang C P, Chen J W, Qiao G X. Proline inhibits plant root growth through signal of auxin pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiology Journal, 2017, 53(8): 1428-1434. |
| 王翠平, 陈建伟, 乔改霞. 脯氨酸通过影响生长素途径相关信号抑制拟南芥根的生长. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(8): 1428-1434. | |
| 27 | Miao Y Y, Zhou T, Shi S L, et al. Effect of boron on migration and colonization by rhizobia and seedling growth in Medicago sativa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(4): 120-133. |
| 苗阳阳, 周彤, 师尚礼, 等. 硼对根瘤菌在紫花苜蓿体内运移和定殖及对幼苗生长的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 120-133. | |
| 28 | Gao J Y. Diversity of bacteria associated with Dongxiang wild rice and isolation of plant promoting bacteria containing ACC deaminase activity. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2017. |
| 高洁云. 东乡野生稻内生、根际细菌多样性及具ACC脱氨酶活性菌株筛选. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2017. | |
| 29 | Xie J H. Studies on the improvement of saline-alkali soil and rice growth promotion by wild rice rhizosphere bacteria. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 谢金宏. 野生稻根际细菌改良盐碱地及水稻促生的研究. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2020. | |
| 30 | Zhang Z, Yuen G Y. The role of chitinase production by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain C3 in biological control of Bipolaris sorokiniana. Phytopathology, 2000, 90(4): 384-389. |
| 31 | Baldiris R, Acosta-Tapia N, Montes A, et al. Reduction of hexavalent chromium and detection of chromate reductase (ChrR) in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Molecules, 2018, 23(2): 406. |
| [1] | 赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34. |
| [2] | 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| [3] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [4] | 王雪萌, 何欣, 张涵, 宋瑞, 毛培胜, 贾善刚. 基于多光谱成像技术快速无损检测紫花苜蓿人工老化种子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 197-208. |
| [5] | 刘亚男, 于人杰, 高燕丽, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 武志海, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白MtANN2基因的表达模式及盐胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 124-134. |
| [6] | 李满有, 李东宁, 王斌, 李小云, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 倪旺, 王腾飞, 兰剑. 不同苜蓿品种混播和播种量对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 61-75. |
| [7] | 张欢, 牟怡晓, 张桂杰. 添加枸杞副产物对紫花苜蓿青贮发酵品质及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 136-144. |
| [8] | 孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 乔楠, 任波. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 32-42. |
| [9] | 高丽敏, 陈春, 沈益新. 氮磷肥对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿生长及再生的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 43-52. |
| [10] | 欧成明, 赵美琦, 孙铭, 毛培胜. 抗坏血酸和水杨酸丸衣对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子发芽特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 93-101. |
| [11] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 赵雅姣, 王静. 内源异黄酮对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮及氮效率的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 124-135. |
| [12] | 吴玉环, 王自奎, 刘亚男, 马千虎. 带幅设计对玉米/苜蓿间作群体光环境特征及光能利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 144-155. |
| [13] | 刘丽英, 贾玉山, 范文强, 尹强, 成启明, 王志军. 影响苜蓿自然干燥的主要环境因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 121-132. |
| [14] | 张岳阳, 李芳, 梁维维, 李彦忠. 新疆昌吉32个紫花苜蓿品种的田间抗病性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 133-146. |
| [15] | 王斌, 杨雨琦, 李满有, 倪旺, 海艺蕊, 张顺香, 董秀, 兰剑. 不同播种量下行距配置对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||