

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 139-146.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021463
收稿日期:2021-12-13
修回日期:2022-02-28
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-10-01
通讯作者:
徐博
作者简介:E-mail: xubo6299@jlau.edu.cn基金资助:
Hai-ting MU( ), Ying-zhe WANG, Yi-fan MIAO, Wei-jie YU, Bo XU(
), Ying-zhe WANG, Yi-fan MIAO, Wei-jie YU, Bo XU( )
)
Received:2021-12-13
Revised:2022-02-28
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-10-01
Contact:
Bo XU
摘要:
为研究土壤中Cu、Pb胁迫对东方山羊豆幼苗生长及生理特性的影响,本试验以东方山羊豆为材料,采用盆栽进行胁迫试验,研究5种浓度的Cu、Pb胁迫下东方山羊豆生长及生理特性指标的变化规律。结果表明:随着2种金属胁迫浓度和胁迫时间的增加,在胁迫第7天,胁迫浓度达480 mg·kg-1时,东方山羊豆芽长、根长、叶鲜重、根鲜重总体呈上升趋势,但随着胁迫浓度增加和处理时间的延长,在Pb胁迫第15天,根长在处理浓度为600 mg·kg-1时,与CK相比降低23.60%。而东方山羊豆的脯氨酸、过氧化物酶随着胁迫浓度的增加总体呈现不断上升的趋势。当Pb浓度小于480 mg·kg-1,随着Pb浓度的增加,植物体内丙二醛含量呈上升趋势,当处理浓度为600 mg·kg-1时,东方山羊豆幼苗的丙二醛含量出现明显下降,而在Cu处理下,丙二醛含量呈上升的趋势。可溶性糖含量在Pb胁迫下,随着浓度的不断增加,呈先上升后下降的趋势,在Cu浓度低于480 mg·kg-1时,东方山羊豆的可溶性糖含量均低于CK。可溶性蛋白含量则在Pb胁迫下呈先下降后上升的趋势,与CK相比,在处理浓度为600 mg·kg-1时,可溶性蛋白含量增加78.35%。Cu胁迫浓度在240 mg·kg-1时,植物的可溶性蛋白含量显著高于600 mg·kg-1时,并在此时达到最大值,而随着胁迫浓度增加,可溶性蛋白含量呈下降趋势。综上表明,在重金属Cu和Pb的胁迫下,东方山羊豆表现出一定的耐受力和富集重金属铜和铅的能力。
穆海婷, 王英哲, 苗一凡, 郁伟杰, 徐博. 重金属铜和铅胁迫对东方山羊豆幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 139-146.
Hai-ting MU, Ying-zhe WANG, Yi-fan MIAO, Wei-jie YU, Bo XU. Effects of heavy metal Cu and Pb stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of Galega orientalis seedlings[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 139-146.
项目 Item | 浓度 Concentration (mg·kg-1) | 芽长 Shoot length (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根鲜重 Root fresh weight (mg) | 叶鲜重 Leaf fresh weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.47±0.42d | 5.83±1.51cde | 0.02±0.05b | 0.20±0.03c | |
| Cu | 240 | 6.58±0.24c | 8.83±1.15a | 0.03±0.22b | 0.24±0.67abc |
| 360 | 6.30±0.36e | 5.87±1.29cde | 0.03±0.21b | 0.29±0.37a | |
| 480 | 7.22±0.30a | 7.15±1.43abc | 0.05±0.20a | 0.29±0.11a | |
| 600 | 6.68±0.76b | 8.35±0.79ab | 0.05±0.12a | 0.28±0.10ab | |
| Pb | 240 | 4.77±0.56h | 4.63±0.81e | 0.03±0.02b | 0.26±0.05abc |
| 360 | 4.68±0.72i | 4.91±0.62de | 0.03±0.04b | 0.22±0.05bc | |
| 480 | 5.24±0.46f | 6.79±0.67bcd | 0.02±0.02b | 0.24±0.04abc | |
| 600 | 5.17±0.20g | 5.57±0.88cde | 0.03±0.03b | 0.14±0.04d |
表1 不同Cu、Pb浓度胁迫7 d对东方山羊豆生长的影响
Table 1 Effects of different concentrations of Cu and Pb stress for 7 days on the growth of G. orientalis
项目 Item | 浓度 Concentration (mg·kg-1) | 芽长 Shoot length (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根鲜重 Root fresh weight (mg) | 叶鲜重 Leaf fresh weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.47±0.42d | 5.83±1.51cde | 0.02±0.05b | 0.20±0.03c | |
| Cu | 240 | 6.58±0.24c | 8.83±1.15a | 0.03±0.22b | 0.24±0.67abc |
| 360 | 6.30±0.36e | 5.87±1.29cde | 0.03±0.21b | 0.29±0.37a | |
| 480 | 7.22±0.30a | 7.15±1.43abc | 0.05±0.20a | 0.29±0.11a | |
| 600 | 6.68±0.76b | 8.35±0.79ab | 0.05±0.12a | 0.28±0.10ab | |
| Pb | 240 | 4.77±0.56h | 4.63±0.81e | 0.03±0.02b | 0.26±0.05abc |
| 360 | 4.68±0.72i | 4.91±0.62de | 0.03±0.04b | 0.22±0.05bc | |
| 480 | 5.24±0.46f | 6.79±0.67bcd | 0.02±0.02b | 0.24±0.04abc | |
| 600 | 5.17±0.20g | 5.57±0.88cde | 0.03±0.03b | 0.14±0.04d |
项目 Item | 浓度 Concentration (mg·kg-1) | 芽长 Shoot length (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根鲜重 Root fresh weight (mg) | 叶鲜重 Leaf fresh weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.43±0.42b | 11.23±0.62a | 0.09±0.01ab | 0.22±0.03c | |
| Cu | 240 | 9.83±0.42ab | 11.08±0.79a | 0.13±0.59a | 0.46±0.04b |
| 360 | 9.87±0.58ab | 9.02±0.79abc | 0.07±0.01ab | 0.46±0.03b | |
| 480 | 9.68±0.86ab | 9.27±0.89abc | 0.07±0.01ab | 0.42±0.33b | |
| 600 | 9.56±1.00ab | 9.63±0.54abc | 0.13±0.04a | 0.43±0.02b | |
| Pb | 240 | 9.51±0.23ab | 7.81±0.55c | 0.05±0.03b | 0.48±0.02b |
| 360 | 8.98±1.14b | 7.91±1.59c | 0.05±0.03b | 0.43±0.05b | |
| 480 | 10.83±1.12a | 10.85±1.09ab | 0.13±0.62a | 0.62±0.12a | |
| 600 | 8.90±1.51b | 8.58±2.29bc | 0.11±0.03ab | 0.49±0.04b |
表2 不同Cu、Pb浓度胁迫15 d对东方山羊豆生长的影响
Table 2 Effects of different concentrations of Cu and Pb stress for 15 days on the growth of G. orientalis
项目 Item | 浓度 Concentration (mg·kg-1) | 芽长 Shoot length (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根鲜重 Root fresh weight (mg) | 叶鲜重 Leaf fresh weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.43±0.42b | 11.23±0.62a | 0.09±0.01ab | 0.22±0.03c | |
| Cu | 240 | 9.83±0.42ab | 11.08±0.79a | 0.13±0.59a | 0.46±0.04b |
| 360 | 9.87±0.58ab | 9.02±0.79abc | 0.07±0.01ab | 0.46±0.03b | |
| 480 | 9.68±0.86ab | 9.27±0.89abc | 0.07±0.01ab | 0.42±0.33b | |
| 600 | 9.56±1.00ab | 9.63±0.54abc | 0.13±0.04a | 0.43±0.02b | |
| Pb | 240 | 9.51±0.23ab | 7.81±0.55c | 0.05±0.03b | 0.48±0.02b |
| 360 | 8.98±1.14b | 7.91±1.59c | 0.05±0.03b | 0.43±0.05b | |
| 480 | 10.83±1.12a | 10.85±1.09ab | 0.13±0.62a | 0.62±0.12a | |
| 600 | 8.90±1.51b | 8.58±2.29bc | 0.11±0.03ab | 0.49±0.04b |
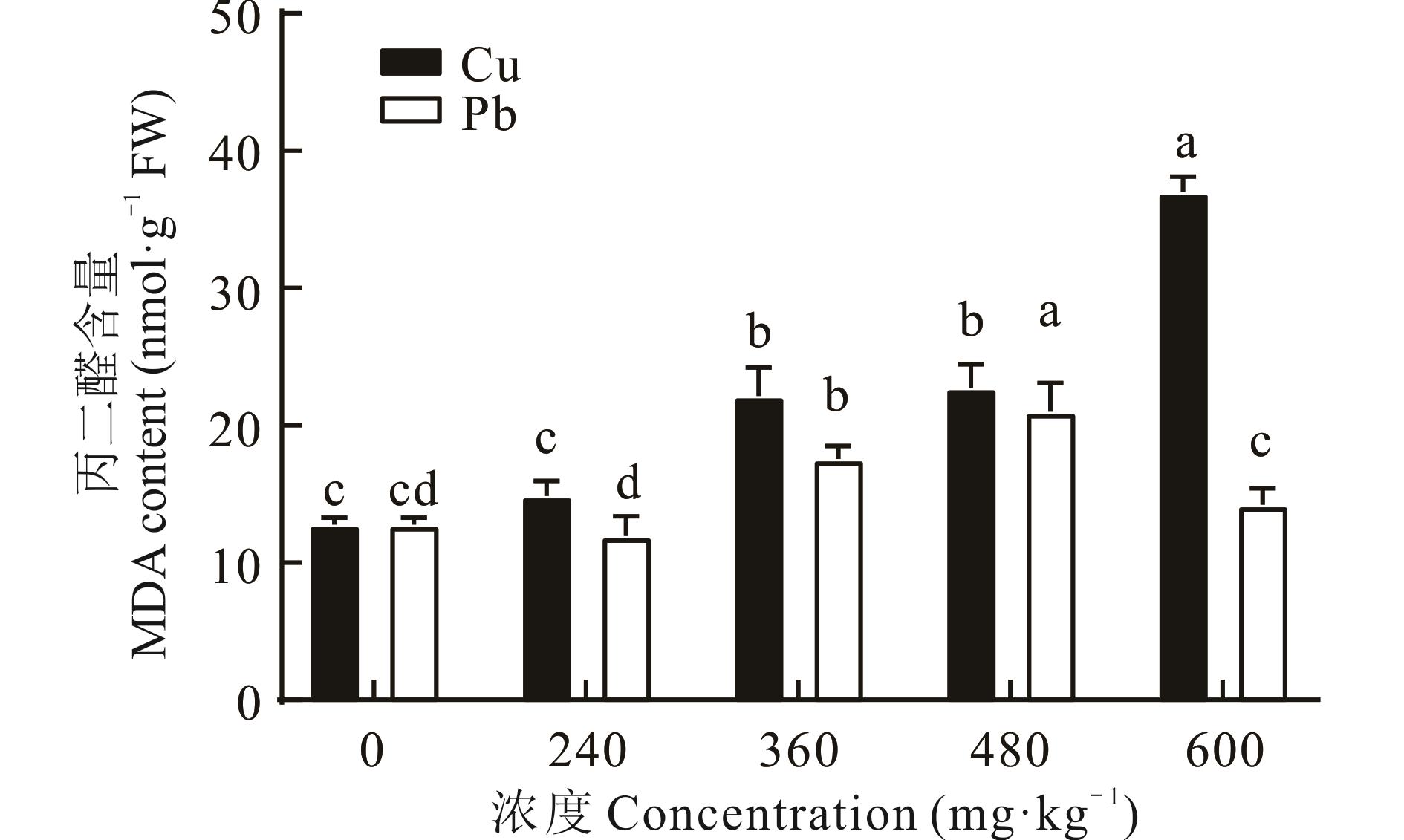
图1 不同浓度Cu、Pb胁迫下丙二醛含量的变化不同小写字母表示差异达显著水平(P<0.05) , 下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Changes in malondialdehyde (MDA) content under different concentrations of Cu and Pb stress
| 1 | Hui L. Soil contaminated by heavy metals and its phytoremediation technology. Journal of Heilongjiang Water Science, 2006, 33(1): 102-104. |
| 惠琳. 土壤重金属污染及植物修复技术. 黑龙江水专学报, 2006, 33(1): 102-104. | |
| 2 | Wang X W, Wang Q H, Yu L H. Heavy metal contamination and its effect on organism in soil: A review. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(19): 86-92. |
| 王皙玮, 王秋红, 於丽华. 土壤重金属污染及对生物体影响的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(19): 86-92. | |
| 3 | Yu X H, Xu H Y, Yan L. Effects of soil moisture on cucumber growth and cadmium accumulation under cadmium stress. Northern Horticulture, 2021(1): 1-6. |
| 于锡宏, 许铧月, 闫雷. 镉胁迫下土壤水分对黄瓜生长及镉积累的影响. 北方园艺, 2021(1): 1-6. | |
| 4 | Wang M, Li S T. Heavy metals in fertilizers and effect of the fertilization on heavy metal accumulation in soils and crops. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(2): 466-480. |
| 王美, 李书田. 肥料重金属含量状况及施肥对土壤和作物重金属富集的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(2): 466-480. | |
| 5 | Zhai F Q. The mechanism of copper toxicity to crop seedlings and the study of iron and calcium to mitigate copper toxicity. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2007. |
| 翟福勤. 铜对作物幼苗的毒害机理及铁钙缓解铜毒害的研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2007. | |
| 6 | Zhang B Y, Teng W C. Effects of lead stress on growth and physiology of Tabebuia chrysantha seedlings. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2020, 48(7): 7-10. |
| 张博宇, 滕维超. 铅胁迫对黄花风铃木幼苗生长和生理指标的影响. 东北林业大学学报, 2020, 48(7): 7-10. | |
| 7 | Li X Z, Li B. Effects of heavy metal on plant growth and quality. Anhui Agricultural Science, 2008, 36(14): 42-46. |
| 李秀珍, 李彬. 重金属对植物生长发育及品质的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(14): 42-46. | |
| 8 | Sun L, Ji N N, Mu L Q. Effect of heavy metal stress on leaf anatomical structure of Syringa microphylla. Journal of Northeastern Forestry University, 2012, 40(4): 1-4. |
| 孙龙, 纪楠楠, 穆立蔷. 重金属胁迫对小叶丁香叶片解剖结构的影响. 东北林业大学学报, 2012, 40(4): 1-4. | |
| 9 | Wang Q H. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide and salicylic acid on physiological characteristics of ryegrass under copper, lead and cadmium stress. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 王全辉. 外源一氧化氮与水杨酸对铜,铅,镉胁迫下黑麦草生理特性的影响. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2012. | |
| 10 | Ning B, Chen F L. Promising grass species-Galega orientalis L. Journal of Neimongol Prataculture, 2000(3): 64. |
| 宁布, 陈凤林. 有希望的草种—东方山羊豆. 内蒙古草业, 2000(3): 64. | |
| 11 | Tian C, Zhang Q B, Gu X. Current status and trend analysis of the excellent legume forage Galega orientalis L. Herbivorous Livestock, 2009(4): 64-67. |
| 田聪, 张清斌, 顾祥. 优良豆科牧草东方山羊豆研究现状与趋势分析. 草食家畜, 2009(4): 64-67. | |
| 12 | Zhang X F, Xia H P, Li Z A. Forage grass in phytoremediation of heavy metals-contaminated soils: A review. Journal of Ecology, 2009, 28(8): 40-46. |
| 张杏锋, 夏汉平, 李志安. 牧草对重金属污染土壤的植物修复综述. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(8): 40-46. | |
| 13 | Zhu G L, Deng X W, Zuo W N. Determination of free proline in plants. Plant Physiology Communications, 1983(1): 37-39. |
| 朱广廉, 邓兴旺, 左卫能. 植物体内游离脯氨酸的测定. 植物生理学通讯, 1983(1): 37-39. | |
| 14 | Li H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical experiments. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. | |
| 15 | Gao J F. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 16 | Cui L Y, Shi G, Li G. Effects of Zn and Cd on physiological and biochemical characteristics, and heavy metal accumulation of landscape plants. Journal of Anqing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 27(2): 79-87. |
| 崔龙雨, 时光, 李刚. 锌镉单一胁迫对景观植物生理生化特性及重金属富集的影响. 安庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 27(2): 79-87. | |
| 17 | Wu X Q, Cao D, Chen S Y, et al. Physiological and biochemical responses of three sedum plants. Journal of Heilongjiang Ecological Engineering Vocational College, 2021, 34(4): 30-32. |
| 吴小青, 曹丹, 陈思逸, 等. 3种景天植物对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应. 黑龙江生态工程职业学院学报, 2021, 34(4): 30-32. | |
| 18 | Li L. Physio-biochemical and molecular mechanism of exogenous brassinosteroids in regulating growth of Brassica napus under copper and chromium stress. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019. |
| 李兰. 油菜素内酯调控铜和铬胁迫下油菜生理生化与分子机制研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. | |
| 19 | Wightwick A M, Mollah M R, Partington D L. Copper fungicide residues in Australian vineyard soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2008, 56(7): 2457-2464. |
| 20 | Singh R, Tripathi R D, Dwivedi S. Lead bioaccumulation potential of an aquatic macrophyte Najas indica are related to antioxidant system. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(9): 3025-3032. |
| 21 | Bakker J. Seeds, ecology, biogeography and evolution of dormancy, and germination. Plant Ecology, 2001, 152(2): 204-205. |
| 22 | Yu X J, Zhang J W, Pan T T, et al. Effects of heavy metals: Copper, cadmium and lead on the seed germination and seeding growth of leguminous forage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(4): 793-803. |
| 鱼小军, 张建文, 潘涛涛, 等. 铜、镉、铅对7种豆科牧草种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 草地学报, 2015, 23(4): 793-803. | |
| 23 | Wang L K, Zhu Z H, Wen X. Effects of heavy metal copper stress on growth and copper accumulation of rape seedlings.Journal of Hubei Engineering University, 2021, 41(6): 31-36. |
| 王立凯, 朱震昊, 温馨. 重金属铜胁迫对油菜幼苗生长和铜累积的影响. 湖北工程学院学报, 2021, 41(6): 31-36. | |
| 24 | Zhu S M, Song H L, Zhang L. Effect of lead stress on growth and physio-biochemical indices of tobacco. Plant Physiology Journal, 2018, 54(3): 465-472. |
| 朱诗苗, 宋杭霖, 张丽. 铅胁迫对烟草生长及生理生化指标的影响. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(3): 465-472. | |
| 25 | Ji Y, Zhang X Q, Peng Y, et al. Effects of drought stress on lipid peroxidation, osmotic adjustment and activities of protective enzymes in the roots and leaves of orchardgrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 144-151. |
| 季杨, 张新全, 彭燕, 等. 干旱胁迫对鸭茅根,叶保护酶活性,渗透物质含量及膜质过氧化作用的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 144-151. | |
| 26 | Lu Q J, Chao J G, Gu W, et al. Effects of copper stress on photosynthetic properties and physiological indicators of Atractylodes lancea. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2018, 41(7): 1534-1538. |
| 陆奇杰, 巢建国, 谷巍, 等. 铜胁迫对茅苍术光合特性及生理指标的影响. 中药材, 2018, 41(7): 1534-1538. | |
| 27 | Miya S P, Modi A T, Tesfay S Z. Maize grain soluble sugar and protein contents in response to simulated hail damage. South African Journal of Plant & Soil, 2018, 18(8): 377-383. |
| 28 | Mostapha M, Mourad B. Overexpression of LeNHX4 improved yield, fruit quality and salt tolerance in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47(6): 4145-4153. |
| 29 | Mao X F, He J J, Han Z K. Effects of lead stress on growth and physiological metabolism and accumulation characteristics of Lonicera japonica. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 44(5): 69-75. |
| 毛雪飞, 何金娇, 韩忠康. 铅胁迫对金银花生长,生理及积累特性的影响. 东北农业科学, 2019, 44(5): 69-75. | |
| 30 | Hei Z W, Xiang H M, Zhang J E. Advances in legumes-based remediation of heavy metals contaminated soil. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(3): 218-224. |
| [1] | 许浩宇, 赵颖, 阮倩, 朱晓林, 王宝强, 魏小红. 不同混合盐碱下藜麦幼苗的抗性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 122-130. |
| [2] | 苏世平, 李毅, 刘小娥, 种培芳, 单立山, 后有丽. 外源脯氨酸对缓解红砂干旱胁迫的机理研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 127-138. |
| [3] | 张铎, 李岚涛, 林迪, 郑龙辉, 耿赛男, 石纹碹, 盛开, 苗玉红, 王宜伦. 施磷水平对菊芋块茎产量、品质、植株生理特性与磷利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 139-149. |
| [4] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [5] | 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 王学琴, 姚姗. 盐胁迫对湖南稷子苗期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| [6] | 王龙, 樊婕, 魏畅, 李鸽子, 张静静, 焦秋娟, 陈果, 孙娈姿, 柳海涛. 外源抗坏血酸对铜胁迫菊苣幼苗生长的缓解效应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 150-159. |
| [7] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [8] | 黄海霞, 杨琦琦, 崔鹏, 陆刚, 韩国君. 裸果木幼苗根系形态和生理特征对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 197-207. |
| [9] | 孙小富, 黄莉娟, 王普昶, 赵丽丽, 刘芳. 不同供磷水平对宽叶雀稗形态及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 58-69. |
| [10] | 李柯, 施宠, 何飞焱, 李昊宇. Pb胁迫下内生真菌侵染对德兰臭草生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 112-120. |
| [11] | 沙洁, 陈垣, 郭凤霞, 白刚, 周传猛. 外源Ca2+调控野生抚育独一味幼株抗寒生理特性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 11-21. |
| [12] | 张盼盼, 杨裕然, 薛佳欣, 王涛, 刘涵, 刘翠英, 冯佰利, 张雄. 烯效唑对盐胁迫下糜子幼苗形态和生理特性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 81-90. |
| [13] | 李珍, 云岚, 石子英, 王俊, 张晨, 郭宏宇, 盛誉. 盐胁迫对新麦草种子萌发及幼苗期生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 119-129. |
| [14] | 王雨, 周睿颖, 马立敏, 白钰, 关佳莉, 唐晓清. 5个产地菘蓝种子萌发及幼苗生长对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 145-154. |
| [15] | 尹国丽, 吴芳, 陶茸, 师尚礼, 蔡卓山. 苜蓿轮作玉米\小麦土壤浸提液对苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理及生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 153-161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||