

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 59-72.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024039
喻启坤1( ), 李雯1, 汤丽斯1, 韩宇1, 李培英1,2,3(
), 李雯1, 汤丽斯1, 韩宇1, 李培英1,2,3( ), 孙宗玖1,2,3
), 孙宗玖1,2,3
收稿日期:2024-01-27
修回日期:2024-03-28
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
李培英
作者简介:. E-mail: lpy@xjau.edu.cn基金资助:
Qi-kun YU1( ), Wen LI1, Li-si TANG1, Yu HAN1, Pei-ying LI1,2,3(
), Wen LI1, Li-si TANG1, Yu HAN1, Pei-ying LI1,2,3( ), Zong-jiu SUN1,2,3
), Zong-jiu SUN1,2,3
Received:2024-01-27
Revised:2024-03-28
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Pei-ying LI
摘要:
为了探讨高光谱技术在监测植物受干旱胁迫程度及筛选抗旱材料中的应用,以18个狗牙根基因型为材料,进行为期12 d的自然干旱,测定各材料土壤含水量和叶片相对含水量,同时利用美国SVC HR-768便携式光谱仪,获取不同干旱时间各材料的高光谱相片,以经过高光谱SG平滑和SG平滑+一阶导数结合处理的光谱反射率作为自变量,经Pearson相关性分析和连续投影筛选与叶片相对含水量相关性较好且各材料共有的特征波段,并利用方差膨胀因子检验其共线性,之后通过BP神经网络、支持向量机和随机森林3种机器学习算法建立狗牙根叶片相对含水量的反演模型。结果表明:1)通过连续投影算法共筛选出5个SG平滑+一阶导数特征波段,分别为406、569、706、736、786 nm,与叶片相对含水量的相关性较高(P>0.5),且波段间共线性较弱,可作为抗旱监测的敏感波段。2)以敏感波段为基础建立的随机森林反演模型,决定系数(R2)和均方根误差(RMSE)分别为0.939和8.552,相较于支持向量机和BP神经网络,R2分别提高了5%和8%,表现出最好的预测效果和普适性,其测试集的R2为0.925,RMSE为9.008。研究结果可为未来利用高光谱进行广谱性狗牙根叶片相对含水量无损高精监测提供技术支撑。
喻启坤, 李雯, 汤丽斯, 韩宇, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶片相对含水量高光谱反演估算[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 59-72.
Qi-kun YU, Wen LI, Li-si TANG, Yu HAN, Pei-ying LI, Zong-jiu SUN. Estimation of relative water content in bermudagrass leaves based on hyperspectroscopy[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 59-72.
项目 Item | 干旱时间 Drought time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 3 d | 6 d | 9 d | 12 d | |
| C136 | 90.22±5.19Aab | 74.41±16.60Aa | 35.52±19.86Ba | 14.26±14.92BCa | 4.91±3.31Ca |
| C121 | 97.00±5.19Aa | 70.01±10.50Ba | 18.20±0.63Cabc | 7.31±1.39Da | 3.69±0.57Da |
| C100 | 93.39±5.74Aab | 61.18±21.04Bab | 15.56±9.13Cabc | 14.05±10.94Ca | 3.87±1.14Ca |
| C99 | 84.50±0.47Aab | 53.91±10.38Bab | 20.30±16.70Cabc | 10.19±6.63Ca | 3.06±0.71Ca |
| C92 | 90.15±4.07Aab | 60.10±6.02Bab | 13.39±5.15Cabc | 9.96±3.77CDa | 4.34±2.30Da |
| C87 | 84.18±13.52Aab | 56.39±14.12Bab | 9.88±5.34Cbc | 7.64±0.37Ca | 4.15±1.17Ca |
| C84 | 80.97±11.63Ab | 65.00±18.82Aa | 13.01±8.24Bbc | 7.24±0.79Ba | 3.95±0.97Ba |
| C76 | 83.23±3.86Aab | 48.20±14.36Bab | 10.72±7.67Cbc | 9.87±2.38Ca | 4.09±0.81Ca |
| C75 | 81.09±9.36Ab | 57.29±13.27Aab | 26.96±26.18Babc | 7.07±3.07Ba | 4.29±2.07Ba |
| C72 | 84.67±4.54Aab | 60.56±19.65Bab | 6.35±1.18Cc | 8.90±3.47Ca | 3.82±1.62Ca |
| C63 | 84.74±6.82Aab | 63.32±10.07Bab | 15.54±8.09Cabc | 7.49±0.97Ca | 4.27±3.40Ca |
| C40 | 90.85±9.85Aab | 48.02±13.85Bab | 13.48±6.11Cabc | 6.30±0.16Ca | 3.16±0.83Ca |
| C28 | 92.89±6.16Aab | 59.30±18.39Bab | 20.62±19.99Cabc | 12.10±8.29Ca | 3.65±1.01Ca |
| C22 | 91.87±3.03Aab | 68.87±10.92Ba | 31.19±15.50Cab | 9.44±4.46Da | 3.98±1.38Da |
| X1 | 96.11±6.74Aa | 65.50±27.13Ba | 13.59±3.27Cabc | 6.86±1.99Ca | 4.31±1.09Ca |
| X2 | 94.66±8.67Aab | 63.61±6.53Ba | 8.10±1.78Cc | 7.39±1.21Ca | 5.21±0.30Ca |
| KS | 96.87±5.42Aa | 46.30±11.16Bab | 12.44±7.65Cbc | 6.88±0.32Ca | 4.89±1.29Ca |
| PG | 88.93±1.23Aab | 33.79±12.71Bb | 6.44±2.01Cc | 6.78±1.11Ca | 3.44±0.33Ca |
| 最大值Maximun | 97.00 | 74.41 | 35.52 | 14.26 | 5.21 |
| 最小值Minimum | 80.97 | 33.79 | 6.35 | 6.30 | 3.06 |
| 平均值Mean | 89.24 | 58.65 | 16.18 | 8.87 | 4.06 |
| 标准差Standard deviation | 5.41 | 9.85 | 8.15 | 2.47 | 0.57 |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient | 6.06 | 16.80 | 50.36 | 27.80 | 14.10 |
表1 18份狗牙根不同干旱时间的土壤含水量
Table 1 Soil water content of 18 bermudagrass materials at different drought times (%)
项目 Item | 干旱时间 Drought time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 3 d | 6 d | 9 d | 12 d | |
| C136 | 90.22±5.19Aab | 74.41±16.60Aa | 35.52±19.86Ba | 14.26±14.92BCa | 4.91±3.31Ca |
| C121 | 97.00±5.19Aa | 70.01±10.50Ba | 18.20±0.63Cabc | 7.31±1.39Da | 3.69±0.57Da |
| C100 | 93.39±5.74Aab | 61.18±21.04Bab | 15.56±9.13Cabc | 14.05±10.94Ca | 3.87±1.14Ca |
| C99 | 84.50±0.47Aab | 53.91±10.38Bab | 20.30±16.70Cabc | 10.19±6.63Ca | 3.06±0.71Ca |
| C92 | 90.15±4.07Aab | 60.10±6.02Bab | 13.39±5.15Cabc | 9.96±3.77CDa | 4.34±2.30Da |
| C87 | 84.18±13.52Aab | 56.39±14.12Bab | 9.88±5.34Cbc | 7.64±0.37Ca | 4.15±1.17Ca |
| C84 | 80.97±11.63Ab | 65.00±18.82Aa | 13.01±8.24Bbc | 7.24±0.79Ba | 3.95±0.97Ba |
| C76 | 83.23±3.86Aab | 48.20±14.36Bab | 10.72±7.67Cbc | 9.87±2.38Ca | 4.09±0.81Ca |
| C75 | 81.09±9.36Ab | 57.29±13.27Aab | 26.96±26.18Babc | 7.07±3.07Ba | 4.29±2.07Ba |
| C72 | 84.67±4.54Aab | 60.56±19.65Bab | 6.35±1.18Cc | 8.90±3.47Ca | 3.82±1.62Ca |
| C63 | 84.74±6.82Aab | 63.32±10.07Bab | 15.54±8.09Cabc | 7.49±0.97Ca | 4.27±3.40Ca |
| C40 | 90.85±9.85Aab | 48.02±13.85Bab | 13.48±6.11Cabc | 6.30±0.16Ca | 3.16±0.83Ca |
| C28 | 92.89±6.16Aab | 59.30±18.39Bab | 20.62±19.99Cabc | 12.10±8.29Ca | 3.65±1.01Ca |
| C22 | 91.87±3.03Aab | 68.87±10.92Ba | 31.19±15.50Cab | 9.44±4.46Da | 3.98±1.38Da |
| X1 | 96.11±6.74Aa | 65.50±27.13Ba | 13.59±3.27Cabc | 6.86±1.99Ca | 4.31±1.09Ca |
| X2 | 94.66±8.67Aab | 63.61±6.53Ba | 8.10±1.78Cc | 7.39±1.21Ca | 5.21±0.30Ca |
| KS | 96.87±5.42Aa | 46.30±11.16Bab | 12.44±7.65Cbc | 6.88±0.32Ca | 4.89±1.29Ca |
| PG | 88.93±1.23Aab | 33.79±12.71Bb | 6.44±2.01Cc | 6.78±1.11Ca | 3.44±0.33Ca |
| 最大值Maximun | 97.00 | 74.41 | 35.52 | 14.26 | 5.21 |
| 最小值Minimum | 80.97 | 33.79 | 6.35 | 6.30 | 3.06 |
| 平均值Mean | 89.24 | 58.65 | 16.18 | 8.87 | 4.06 |
| 标准差Standard deviation | 5.41 | 9.85 | 8.15 | 2.47 | 0.57 |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient | 6.06 | 16.80 | 50.36 | 27.80 | 14.10 |
编号 Code | 干旱时间 Drought time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 3 d | 6 d | 9 d | 12 d | |
| C136 | 94.57±4.72abc | 84.11±14.42abc | 68.36±2.93bc | 49.43±7.59a | 26.00±3.84a |
| C121 | 99.51±0.62ab | 86.01±1.19abc | 67.51±2.43bc | 18.48±5.68bcdef | 15.08±2.70bcd |
| C100 | 95.13±4.60abc | 87.80±10.46abc | 73.90±1.56ab | 21.77±2.52bcde | 14.99±2.47bcd |
| C99 | 95.31±5.90abc | 77.35±8.19abc | 58.79±7.00def | 24.37±11.38bcd | 15.11±4.26bcd |
| C92 | 99.87±0.00a | 92.13±13.39ab | 68.59±3.49bc | 25.00±5.37bc | 14.21±1.06bcde |
| C87 | 99.06±1.50abc | 89.73±8.79abc | 57.81±1.97efg | 16.82±7.34cdefg | 13.17±1.05cdefg |
| C84 | 96.82±4.22abc | 95.74±7.14ab | 66.48±1.48bcd | 24.89±0.74bc | 12.43±1.48cdefgh |
| C76 | 96.30±3.15abc | 84.29±0.82abc | 57.00±3.11efg | 13.19±0.90efg | 10.36±1.22efghi |
| C75 | 94.30±9.66abc | 87.30±10.93abc | 64.89±6.77cde | 25.22±2.01bc | 16.38±3.25bc |
| C72 | 95.47±4.21abc | 90.10±8.62abc | 57.89±6.07efg | 14.94±5.36efg | 9.55±2.11fghi |
| C63 | 98.54±2.29abc | 99.87±0.00a | 71.88±8.49abc | 25.68±3.28bc | 14.81±3.62bcd |
| C40 | 99.87±0.01a | 95.32±7.86ab | 49.89±4.59g | 8.92±0.51g | 8.23±0.23hi |
| C28 | 98.60±1.31abc | 99.88±0.00a | 68.14±5.19bc | 15.01±0.26efg | 13.63±0.53bcdef |
| C22 | 93.06±7.10abc | 88.78±9.66abc | 76.99±5.22a | 26.07±1.88b | 17.96±2.79b |
| X1 | 89.91±7.64bc | 78.36±37.21abc | 58.92±2.10def | 13.65±2.23efg | 7.77±0.42i |
| X2 | 89.49±6.09c | 75.41±3.81bc | 67.26±3.09bcd | 18.03±3.70bcdef | 9.07±1.25ghi |
| KS | 91.77±7.06abc | 92.17±13.29ab | 51.14±6.51fg | 15.82±1.95defg | 8.47±2.44hi |
| PG | 91.30±4.97abc | 67.87±1.10c | 13.14±1.80h | 11.40±1.93fg | 11.04±0.38defghi |
| 最大值Maximun | 99.87 | 99.88 | 76.99 | 49.43 | 26.00 |
| 最小值Minimum | 89.49 | 67.87 | 13.14 | 8.92 | 7.77 |
| 平均值Mean | 95.49 | 87.34 | 61.03 | 20.48 | 13.24 |
| 标准差Standard deviation | 3.39 | 8.52 | 14.11 | 9.07 | 4.41 |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient | 3.55 | 9.75 | 23.13 | 44.26 | 33.34 |
表2 18份狗牙根不同干旱时间的叶片相对含水量
Table 2 Relative leaf water content of 18 bermudagrass at different drought times (%)
编号 Code | 干旱时间 Drought time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 3 d | 6 d | 9 d | 12 d | |
| C136 | 94.57±4.72abc | 84.11±14.42abc | 68.36±2.93bc | 49.43±7.59a | 26.00±3.84a |
| C121 | 99.51±0.62ab | 86.01±1.19abc | 67.51±2.43bc | 18.48±5.68bcdef | 15.08±2.70bcd |
| C100 | 95.13±4.60abc | 87.80±10.46abc | 73.90±1.56ab | 21.77±2.52bcde | 14.99±2.47bcd |
| C99 | 95.31±5.90abc | 77.35±8.19abc | 58.79±7.00def | 24.37±11.38bcd | 15.11±4.26bcd |
| C92 | 99.87±0.00a | 92.13±13.39ab | 68.59±3.49bc | 25.00±5.37bc | 14.21±1.06bcde |
| C87 | 99.06±1.50abc | 89.73±8.79abc | 57.81±1.97efg | 16.82±7.34cdefg | 13.17±1.05cdefg |
| C84 | 96.82±4.22abc | 95.74±7.14ab | 66.48±1.48bcd | 24.89±0.74bc | 12.43±1.48cdefgh |
| C76 | 96.30±3.15abc | 84.29±0.82abc | 57.00±3.11efg | 13.19±0.90efg | 10.36±1.22efghi |
| C75 | 94.30±9.66abc | 87.30±10.93abc | 64.89±6.77cde | 25.22±2.01bc | 16.38±3.25bc |
| C72 | 95.47±4.21abc | 90.10±8.62abc | 57.89±6.07efg | 14.94±5.36efg | 9.55±2.11fghi |
| C63 | 98.54±2.29abc | 99.87±0.00a | 71.88±8.49abc | 25.68±3.28bc | 14.81±3.62bcd |
| C40 | 99.87±0.01a | 95.32±7.86ab | 49.89±4.59g | 8.92±0.51g | 8.23±0.23hi |
| C28 | 98.60±1.31abc | 99.88±0.00a | 68.14±5.19bc | 15.01±0.26efg | 13.63±0.53bcdef |
| C22 | 93.06±7.10abc | 88.78±9.66abc | 76.99±5.22a | 26.07±1.88b | 17.96±2.79b |
| X1 | 89.91±7.64bc | 78.36±37.21abc | 58.92±2.10def | 13.65±2.23efg | 7.77±0.42i |
| X2 | 89.49±6.09c | 75.41±3.81bc | 67.26±3.09bcd | 18.03±3.70bcdef | 9.07±1.25ghi |
| KS | 91.77±7.06abc | 92.17±13.29ab | 51.14±6.51fg | 15.82±1.95defg | 8.47±2.44hi |
| PG | 91.30±4.97abc | 67.87±1.10c | 13.14±1.80h | 11.40±1.93fg | 11.04±0.38defghi |
| 最大值Maximun | 99.87 | 99.88 | 76.99 | 49.43 | 26.00 |
| 最小值Minimum | 89.49 | 67.87 | 13.14 | 8.92 | 7.77 |
| 平均值Mean | 95.49 | 87.34 | 61.03 | 20.48 | 13.24 |
| 标准差Standard deviation | 3.39 | 8.52 | 14.11 | 9.07 | 4.41 |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient | 3.55 | 9.75 | 23.13 | 44.26 | 33.34 |
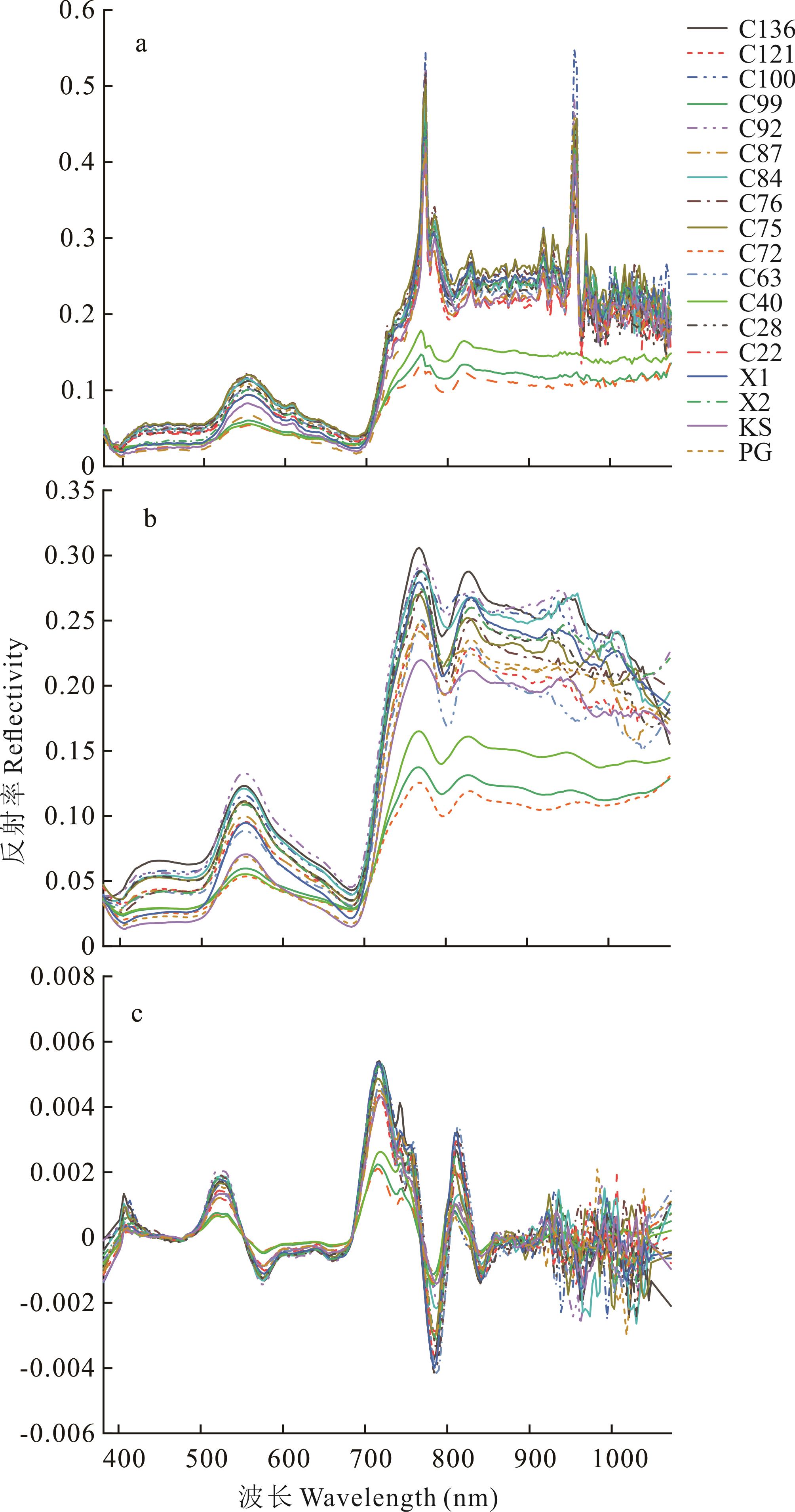
图3 干旱胁迫第0天不同光谱数据预处理后的狗牙根光谱反射率a: 原始光谱Original reflectance; b: SG平滑Savitzkye Golay smoothing; c: SG平滑+一阶导数Savitzkye Golay smoothing+First derivative.
Fig.3 Spectral reflectance of bermudagrass after preprocessing of different spectral data at day 0 of drought stress
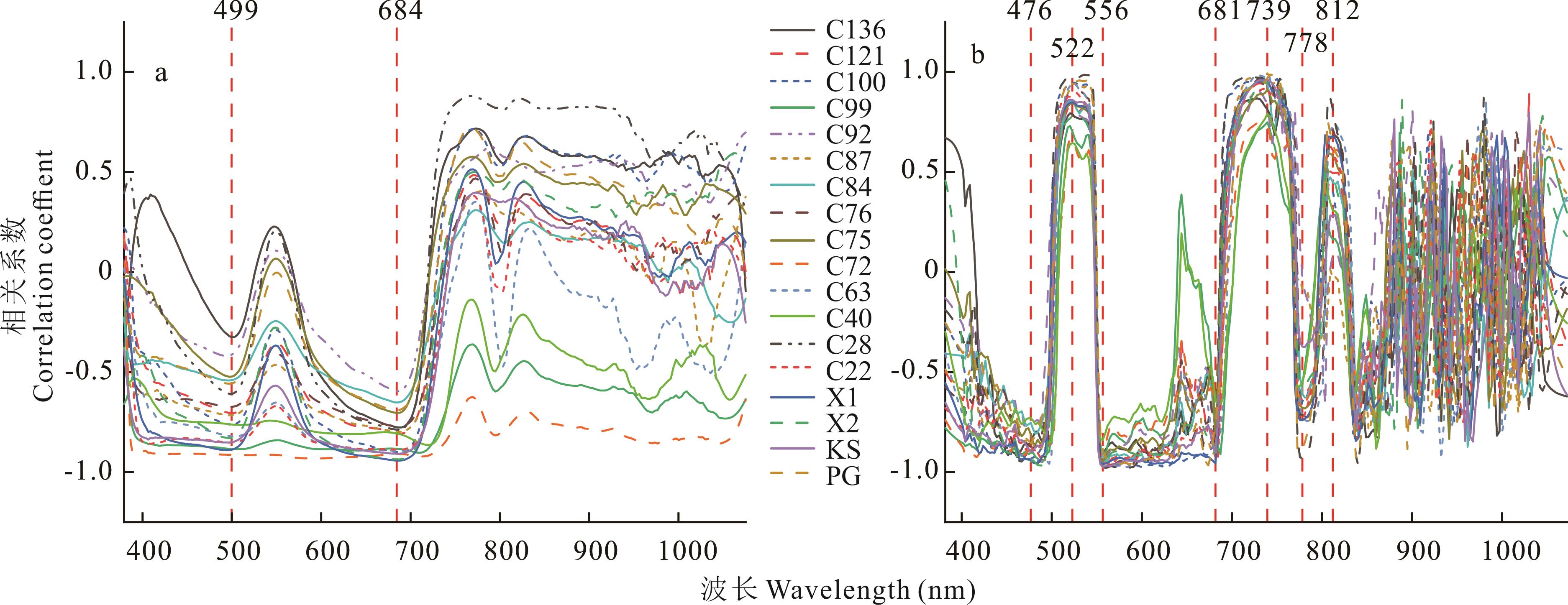
图4 Pearson相关性系数提取特征波长a: SG平滑光谱与叶片相对含水量的相关性Correlation of Savitzkye Golay smoothing spectra with relative water content of 18 bermudagrass leaves; b: SG平滑+一阶导数结合光谱与叶片相对含水量的相关性Correlation of Savitzkye Golay smoothing+first-order derivative combined spectra with relative water content of 18 bermudagrass leaves.
Fig.4 Pearson correlation coefficients to extract characteristic wavelengths
特征波段 Characteristic band (nm) | 方差膨胀因子 Variance inflation factor (VIF) |
|---|---|
| 499 | 9.976 |
| 684 | 9.976 |
表3 SG平滑特征波段的方差膨胀因子检验
Table 3 Variance inflation factor test for Savitzkye Golay smoothing characteristic wavelength
特征波段 Characteristic band (nm) | 方差膨胀因子 Variance inflation factor (VIF) |
|---|---|
| 499 | 9.976 |
| 684 | 9.976 |
特征波段 Characteristic band (nm) | 方差膨胀因子 Variance inflation factor (VIF) |
|---|---|
| 476 | 6.977 |
| 522 | 5.238 |
| 556 | 11.942 |
| 681 | 3.309 |
| 739 | 6.953 |
| 778 | 8.625 |
| 812 | 6.488 |
表4 SG平滑+一阶导数结合特征波段的方差膨胀因子检验
Table 4 Variance inflation factor test for Savitzkye Golay smoothing+first derivative combined characteristic wavelength
特征波段 Characteristic band (nm) | 方差膨胀因子 Variance inflation factor (VIF) |
|---|---|
| 476 | 6.977 |
| 522 | 5.238 |
| 556 | 11.942 |
| 681 | 3.309 |
| 739 | 6.953 |
| 778 | 8.625 |
| 812 | 6.488 |
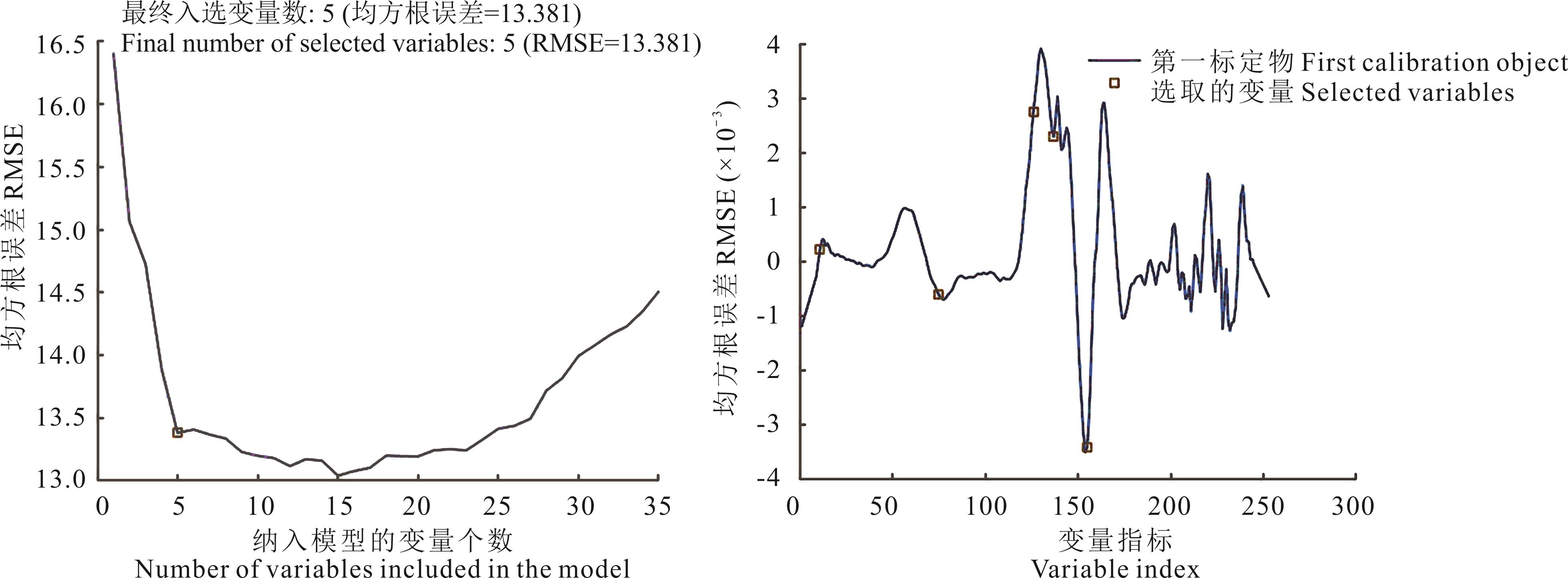
图6 SPA算法提取SG平滑+一阶导数结合特征波长过程
Fig.6 SPA algorithm to extract Savitzkye Golay smoothing+first derivative combined with the characteristic wavelength process

图7 验证BP神经网络模型分析RWC: 叶片相对含水量 Leaf relative water content; SG+Per: SG平滑+Pearson相关性分析 Savitzkye Golay smoothing+Pearson correlation analysis; SG+SPA: SG平滑+连续投影算法 Savitzkye Golay smoothing+successive projections algorithm; FD+Per: 一阶导数+Pearson相关性分析 First derivative+Pearson correlation analysis; FD+SPA: 一阶导数+连续投影算法 First derivative+successive projections algorithm; 下同The same below.
Fig.7 BP neural network model verification
预处理 Pretreatment | 筛选 Screen | 建模 Modeling | 训练集 Train (n=151) | 测试集 Test (n=65) | 预处理 Pretreatment | 筛选 Screen | 建模 Modeling | 训练集 Train (n=151) | 测试集 Test (n=65) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | ||||||
| FD | Per | BP | 0.852 | 13.120 | 0.838 | 14.027 | SG | Per | BP | 0.826 | 14.419 | 0.822 | 14.225 |
| SVM | 0.860 | 12.376 | 0.854 | 13.730 | SVM | 0.767 | 16.418 | 0.761 | 16.864 | ||||
| RF | 0.927 | 9.344 | 0.908 | 10.119 | RF | 0.867 | 12.359 | 0.848 | 13.705 | ||||
| SPA | BP | 0.867 | 12.484 | 0.849 | 13.454 | SPA | BP | 0.846 | 13.589 | 0.832 | 13.794 | ||
| SVM | 0.891 | 11.070 | 0.882 | 12.320 | SVM | 0.869 | 12.287 | 0.865 | 12.892 | ||||
| RF | 0.939 | 8.552 | 0.925 | 9.008 | RF | 0.900 | 10.639 | 0.888 | 11.936 | ||||
表5 18份狗牙根叶片相对含水量估算反演模型对比
Table 5 Comparison of inverse models for estimating relative water content of 18 bermudagrass leaves
预处理 Pretreatment | 筛选 Screen | 建模 Modeling | 训练集 Train (n=151) | 测试集 Test (n=65) | 预处理 Pretreatment | 筛选 Screen | 建模 Modeling | 训练集 Train (n=151) | 测试集 Test (n=65) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | ||||||
| FD | Per | BP | 0.852 | 13.120 | 0.838 | 14.027 | SG | Per | BP | 0.826 | 14.419 | 0.822 | 14.225 |
| SVM | 0.860 | 12.376 | 0.854 | 13.730 | SVM | 0.767 | 16.418 | 0.761 | 16.864 | ||||
| RF | 0.927 | 9.344 | 0.908 | 10.119 | RF | 0.867 | 12.359 | 0.848 | 13.705 | ||||
| SPA | BP | 0.867 | 12.484 | 0.849 | 13.454 | SPA | BP | 0.846 | 13.589 | 0.832 | 13.794 | ||
| SVM | 0.891 | 11.070 | 0.882 | 12.320 | SVM | 0.869 | 12.287 | 0.865 | 12.892 | ||||
| RF | 0.939 | 8.552 | 0.925 | 9.008 | RF | 0.900 | 10.639 | 0.888 | 11.936 | ||||
| 1 | Chan Z L, Shi H T, Wang Y P. Response of bermuda grass to abiotic stress. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(8): 1182-1187. |
| 产祝龙, 施海涛, 王艳平. 狗牙根抗非生物胁迫的研究进展. 草业科学, 2013, 30(8): 1182-1187. | |
| 2 | Abulaiti, Shi D S, Yang G, et al. Preliminary research report on the native Cynodon dactylon in Xinjiang. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 1998, 21(2): 124-127. |
| 阿不来提, 石定燧, 杨光, 等. 新疆野生狗牙根研究初报. 新疆农业大学学报, 1998, 21(2): 124-127. | |
| 3 | Qian Y L, Fry J D. Water relations and drought tolerance of four turfgrasses. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 1997, 122(1): 129-133. |
| 4 | Yang L L, Hua K, Zhang X X. Physiological response and spectral characteristics of tall fescue under different drought stress and CO2 concentrations. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2014, 36(4): 72-78. |
| 杨璐璐, 华开, 张学霞. 不同CO2浓度及干旱胁迫下高羊茅的生理响应和光谱特征. 中国草地学报, 2014, 36(4): 72-78. | |
| 5 | Zhao Z J, Shan G L, Duan X H, et al. Study on spectral reflectance and physiological characteristics of three cool-season turfgrass under drought stress. Grassland and Turf, 2016, 36(6): 23-29. |
| 赵志军, 单贵莲, 段新慧, 等. 干旱胁迫对3种冷季型草坪草光谱反射率及生理特征的影响. 草原与草坪, 2016, 36(6): 23-29. | |
| 6 | Jiang Y, Liu H, Cline V. Correlations of leaf relative water content, canopy temperature, and spectral reflectance in perennial ryegrass under water deficit conditions. HortScience: A Publication of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 2009, 44(2): 459-462. |
| 7 | Chen G, Che W G, Jiang H. Turf hyperspectral analysis techniques and their applications. Yunnan: Yunnan Publishing Group Corporation, 2009: 25-26. |
| 陈功, 车伟光, 姜华. 草坪高光谱分析技术及其应用. 云南: 云南出版集团公司, 2009: 25-26. | |
| 8 | Jiang Y, Carrow R N. Broadband spectral reflectance models of turfgrass species and cultivars to drought stress. Crop Science, 2007, 47(4): 1611-1618. |
| 9 | Cen H, He Y. Theory and application of near infrared reflectance spectroscopy in determination of food quality. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2007, 18(2): 72-83. |
| 10 | Perkins J H, Tenge B, Honigs D E. Resolution enhancement using an approximate-inverse Savitzky-Golay smooth. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 1988, 43(4/5): 575-603. |
| 11 | Pontes M J C, Santos S R B, Araujo M C U, et al. Classification of distilled alcoholic beverages and verification of adulteration by near infrared spectrometry. Food Research International, 2006, 39(2): 182-189. |
| 12 | Jia Z C, Wang Z J, Li X Y, et al. Marine sediment particle size classification based on the fusion of principal component analysis and continuous projection algorithm. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2023, 43(10): 3075-3080. |
| 贾宗潮, 王子鉴, 李雪莹, 等. 主成分分析和连续投影融合的海洋沉积物粒度分类研究. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2023, 43(10): 3075-3080. | |
| 13 | Gou J, Liu G, He J. Estimation of SPAD values for potato leaves based on least squares support vector machine. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 8(11): 82-86. |
| 苟静, 刘刚, 何敬. 基于最小二乘支持向量机的马铃薯叶片SPAD值估算. 湖南农业科学, 2021, 8(11): 82-86. | |
| 14 | Wang W D, Chang Q R, Wang Y N. Hyperspectral monitoring of anthocyanins relative content in winter wheat leaves. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(6): 754-761. |
| 王伟东, 常庆瑞, 王玉娜. 冬小麦叶片花青素相对含量高光谱监测. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(6): 754-761. | |
| 15 | He Y, Peng J Y, Liu F, et al. Critical review of fast detection of crop nutrient and physiological information with spectral and imaging technology. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(3): 174-189. |
| 何勇, 彭继宇, 刘飞, 等. 基于光谱和成像技术的作物养分生理信息快速检测研究进展. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(3): 174-189. | |
| 16 | Niu F P, Li X G, Mamattursun·Eziz, et al. Hyperspectral estimation of soil organic carbon content in the west lakeside oasis of Bosten Lake based on successive projection algorithm. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Sciences), 2021, 47(5): 673-682. |
| 牛芳鹏, 李新国, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 等. 基于连续投影算法的博斯腾湖西岸湖滨绿洲土壤有机碳含量的高光谱估算. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2021, 47(5): 673-682. | |
| 17 | Guo S, Chang Q R, Zhang Y M, et al. Hyperspectral estimation of maize nitrogen balance index by successive projection combined with SSA-ELM. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 130-138. |
| 郭松, 常庆瑞, 张佑铭, 等. 连续投影与SSA-ELM结合的玉米氮平衡指数高光谱估测. 西北农业学报, 2023, 32(1): 130-138. | |
| 18 | Bannari A, Khurshid K S, Staenz K, et al. A comparison of hyperspectral chlorophyll indices for wheat crop chlorophyll content estimation using laboratory reflectance measurements. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(10): 3063-3074. |
| 19 | Katuwal K B, Yang H, Huang B. Evaluation of phenotypic and photosynthetic indices to detect water stress in perennial grass species using hyperspectral, multispectral and chlorophyll fluorescence imaging. Grass Research, 2023, 3(1): 4-16. |
| 20 | Wang P P. Hyperspectral prediction model for moisture content of ramie leaves based on SVR. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 汪佩佩. 基于SVR的苎麻叶片含水率高光谱预测模型. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2020. | |
| 21 | Guo R, Fu S, Hou M J, et al. Remote sensing retrieval of nature grassland biomass in Menyuan County, Qinghai Province experimental area based on Sentinel-2 data. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 15-29. |
| 郭芮, 伏帅, 侯蒙京, 等. 基于Sentinel-2数据的青海门源县天然草地生物量遥感反演研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 15-29. | |
| 22 | Jiang Y Y, Liu B W, Zhang C J, et al. Multi-variety maize maturity monitoring based on UAV multi-spectral images. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(20): 84-91. |
| 姜友谊, 刘博伟, 张成健, 等. 利用无人机多光谱影像的多品种玉米成熟度监测. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(20): 84-91. | |
| 23 | Yue Y K, Chen J F, Zhao L, et al. Inversion of chlorophyll content in ramie based on UAV multispectral remote sensing. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 55(7): 152-158. |
| 岳云开, 陈建福, 赵亮, 等. 基于无人机多光谱遥感的苎麻叶绿素含量反演. 山东农业科学, 2023, 55(7): 152-158. | |
| 24 | Tao X Y, Zhu Y J, Su X X, et al. Estimation of nitrogen nutrition before flowering stage of winter wheat based on UAV multispectral imagery. Journal of Anhui Science and Technology University, 2023, 37(3): 50-59. |
| 陶新宇, 朱永基, 苏祥祥, 等. 基于无人机多光谱影像的冬小麦花前期氮素营养估测. 安徽科技学院学报, 2023, 37(3): 50-59. |
| [1] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [2] | 朱城强, 温绍福, 江润海, 张梅, 蔡治宏, 何玥琛, 陈鑫, 侯秀丽. 铅胁迫下吲哚乙酸对狗牙根铅累积及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 96-107. |
| [3] | 张一龙, 李雯, 喻启坤, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶与根氮代谢对不同干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [4] | 张一龙, 喻启坤, 李雯, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根地上地下表型特征及内源激素对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 163-178. |
| [5] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 孙晓梵. 两类新疆狗牙根抗旱基因型抗氧化酶保护系统及其基因表达差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. |
| [6] | 孙晓梵, 张一龙, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同施氮量对干旱下狗牙根抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 69-78. |
| [7] | 卫宏健, 丁杰, 张巨明, 杨文, 王咏琪, 刘天增. 践踏胁迫下狗牙根草坪土壤真菌群落结构的变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 102-112. |
| [8] | 任雪锋, 邓亚博, 臧国长, 郑轶琦. 基于SSR标记的河南省狗牙根遗传多样性及群体遗传结构分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 60-70. |
| [9] | 赵欣桐, 陈晓东, 李子吉, 张巨明, 刘天增. 植物内生肠杆菌对狗牙根耐盐性的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 127-136. |
| [10] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙晓梵, 孙宗玖. 新疆不同生境狗牙根种质抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 155-169. |
| [11] | 李晓雪, 李昌晓, 宋虹, 袁中勋. 水淹和密度配置对牛鞭草与狗牙根扦插苗光合作用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 197-206. |
| [12] | 杨文航, 任庆水, 秦红, 宋虹, 袁中勋, 李昌晓. 三峡库区消落带不同海拔狗牙根草地土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷含量特征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 57-68. |
| [13] | 舒必超, 杨勇, 刘雪勇, 蒋元利, 向佐湘, 胡龙兴. 低温胁迫对狗牙根生理及基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 106-119. |
| [14] | 柴艳, 孙宗玖, 李培英, 巴德木其其格, 张向向, 杨静. 新疆狗牙根种质芽期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 154-167. |
| [15] | 韩文娇, 白林利, 李昌晓. 水淹胁迫对狗牙根光合、生长及营养元素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 49-59. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||