

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 164-173.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024427
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
柯丹霞( ), 侯仕博, 周兆源, 马云浩, 陈志杰, 宋晓莉, 林佳诺
), 侯仕博, 周兆源, 马云浩, 陈志杰, 宋晓莉, 林佳诺
收稿日期:2024-10-28
修回日期:2024-12-30
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
柯丹霞
作者简介:E-mail: kdx_029@163.com基金资助:
Dan-xia KE( ), Shi-bo HOU, Zhao-yuan ZHOU, Yun-hao MA, Zhi-jie CHEN, Xiao-li SONG, Jia-nuo LIN
), Shi-bo HOU, Zhao-yuan ZHOU, Yun-hao MA, Zhi-jie CHEN, Xiao-li SONG, Jia-nuo LIN
Received:2024-10-28
Revised:2024-12-30
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Dan-xia KE
摘要:
植物蛋白磷酸酶PP2C是植物至关重要的一类丝/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶。该家族基因在植物发育及多种逆境响应中起着关键作用,关于其在豆科植物与根瘤菌共生结瘤过程中的功能研究相对较少。本研究前期克隆了1个大豆PP2C家族基因GmPP2C28,并证实其受根瘤菌诱导表达。构建GmPP2C28基因的过表达载体p1302G-GmPP2C28,利用发根农杆菌LBA1334介导的百脉根毛根转化法获得带转基因毛状根的百脉根嵌合体植株。通过结瘤试验发现转GmPP2C28基因百脉根结瘤数目明显高于转空载体的对照植株,结瘤指示基因的转录水平显著上调。对根瘤切片进行甲苯胺蓝染色发现,过量表达GmPP2C28基因显著增加根瘤侵染区类菌体的数量。进一步对根瘤的固氮酶活性进行测定发现,过量表达GmPP2C28基因显著增加成熟期及衰老期根瘤的固氮酶活性。以上结果表明在百脉根中异源表达GmPP2C28基因,显著增加了嵌合体百脉根植株结瘤数目以及根瘤中类菌体的数量。此外,过表达GmPP2C28显著提高了成熟期以及衰亡期根瘤的固氮酶活性,从而大大延缓了根瘤的衰老。研究结果可为创制优良百脉根品种,充分发挥百脉根的生物固氮作用提供新的候选基因。
柯丹霞, 侯仕博, 周兆源, 马云浩, 陈志杰, 宋晓莉, 林佳诺. 大豆GmPP2C28基因对百脉根结瘤固氮的功能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 164-173.
Dan-xia KE, Shi-bo HOU, Zhao-yuan ZHOU, Yun-hao MA, Zhi-jie CHEN, Xiao-li SONG, Jia-nuo LIN. Functional identification of the role of soybean gene GmPP2C28 in the nitrogen-fixation process of Lotus japonicus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(10): 164-173.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Sequence of primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| F-OX | G |
| R-OX | TCC |
| F-GUS | GTCGCGCAAGACTGTAACCA |
| R-GUS | CGGCGAAATTCCATACCTG |
| F-NIN-rt | AACTCACTGGAAACAGGTGCTTTC |
| R-NIN-rt | CTATTGCGGAATGTATTAGCTAGA |
| F-ENOD40-1-rt | GGAGGTATGCTCAAACATTC |
| R-ENOD40-1-rt | GTAACTTCTCAAGAGAAGACC |
| F-ENOD40-2-rt | CAAAACTCGTTATGTTGCGG |
| R-ENOD40-2-rt | CACCTCAAAGGAAGAAGAACA |
| F-GmPP2C28-rt | TTGCAACGGTCGTGTATTTGCG |
| R-GmPP2C28-rt | TGGGTAACCACACTCTCTGGATG |
| F-UBI | TTCACCTTGTGCTCCGTCTTC |
| R-UBI | AACAACAGCACACACAGACAATC |
表1 本研究中所使用的引物
Table 1 The primers used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Sequence of primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| F-OX | G |
| R-OX | TCC |
| F-GUS | GTCGCGCAAGACTGTAACCA |
| R-GUS | CGGCGAAATTCCATACCTG |
| F-NIN-rt | AACTCACTGGAAACAGGTGCTTTC |
| R-NIN-rt | CTATTGCGGAATGTATTAGCTAGA |
| F-ENOD40-1-rt | GGAGGTATGCTCAAACATTC |
| R-ENOD40-1-rt | GTAACTTCTCAAGAGAAGACC |
| F-ENOD40-2-rt | CAAAACTCGTTATGTTGCGG |
| R-ENOD40-2-rt | CACCTCAAAGGAAGAAGAACA |
| F-GmPP2C28-rt | TTGCAACGGTCGTGTATTTGCG |
| R-GmPP2C28-rt | TGGGTAACCACACTCTCTGGATG |
| F-UBI | TTCACCTTGTGCTCCGTCTTC |
| R-UBI | AACAACAGCACACACAGACAATC |

图1 GmPP2C28蛋白的生物信息学分析A: GmPP2C28蛋白的保守结构域分析。B: GmPP2C28蛋白的3D结构预测。C: GmPP2C28蛋白的磷酸化位点分析。A: Conservative domain analysis of GmPP2C28 protein; B: 3D structure prediction of GmPP2C28 protein; C: Phosphorylation site analysis of GmPP2C28 protein.
Fig.1 Bioinformatics analysis of GmPP2C28 protein
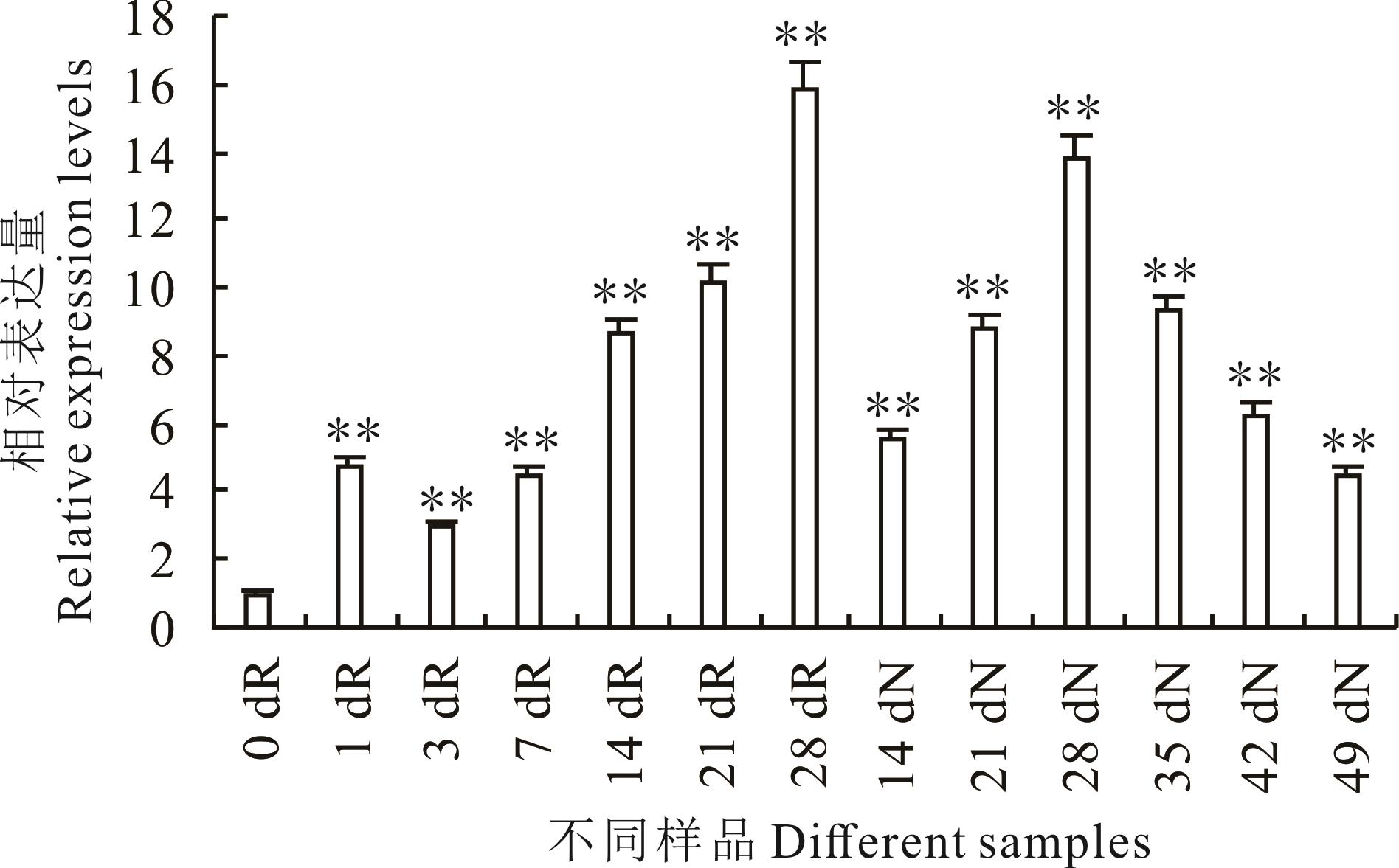
图2 GmPP2C28基因在不同时期大豆根和根瘤中的表达水平dR代表接种不同天数的根组织。dN代表接种不同天数的根瘤组织。**代表P<0.01。下同。dR represents root tissues inoculated for different days. dN represents nodule tissues inoculated for different days. ** represents P<0.01. The same below.
Fig.2 Expression levels of GmPP2C28 gene in soybean roots and nodules at different stages
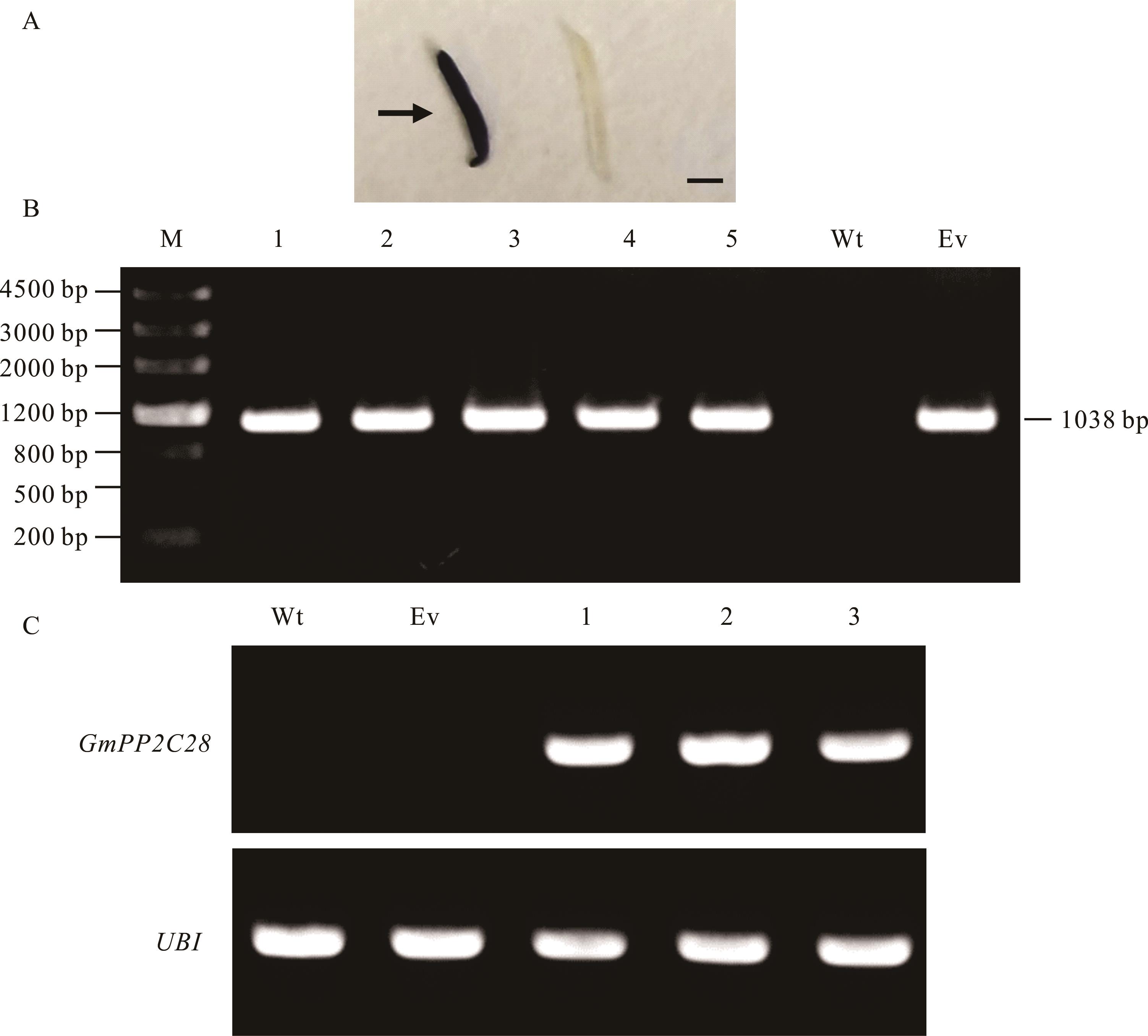
图3 嵌合体百脉根阳性毛状根的分子生物学检测A: 毛状根根尖的GUS染色图,箭头所示为深蓝色的阳性毛状根。B: PCR检测毛状根中GUS基因的表达。C: RT-PCR检测毛状根中GmPP2C28的表达。多聚泛素 (UBI) 作为内参基因。Wt:野生型。Ev:空载体对照。M:DNA Marker Ⅲ。Bars=5 mm。A: The GUS staining image of the root tip of the hair root, the dark blue positive hair root indicated by the arrow. B: PCR detection of GUS gene expression in transgenic and control hairy roots. C: RT-PCR was used to detect the expression level of GmPP2C28 in transgenic and control hairy roots. Polyubiquitin as an internal reference gene. Wt: Wild-type. Ev: Empty vector control. M: DNA Marker Ⅲ molecular weight standard.
Fig.3 Molecular biology detection of positive hairy roots in composite L. japonicus
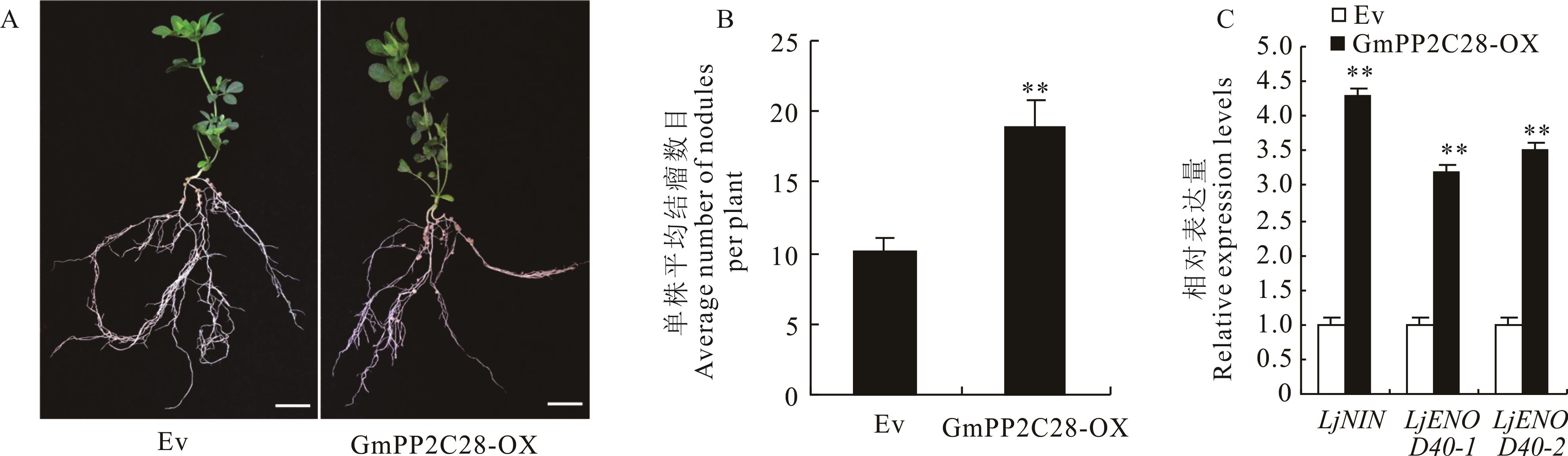
图4 过表达GmPP2C28基因对百脉根结瘤的影响A: 接种根瘤菌28 d后嵌合体植株的结瘤表型。B: 单株嵌合体植株的平均结瘤数目。C: 荧光定量PCR检测嵌合体百脉根毛状根中结瘤指示基因的表达水平。GmPP2C28-OX: 超表达GmPP2C28嵌合体植株。Ev: 空载体对照。下同。Bars=10 mm。n=15。A: The nodulation phenotype of complex plants after 28 days of inoculation with rhizobia. B: The average number of nodules in a single composite plant. C: Fluorescence quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression levels of nodule indicator genes in the hairy roots of complex L. japonicus. GmPP2C28-OX: Over-expressing GmPP2C28 complex plants. Ev: Empty vector control. The same below.
Fig.4 Effect of overexpression GmPP2C28 gene on nodulation in composite L. japonicus

图5 转基因根瘤的切片染色分析A,B: 分别为接种根瘤菌28 d时对照(Ev)和GmPP2C28-OX根瘤的横切面甲苯胺蓝染色图片。C,D: 分别为A和B的高倍放大图片。黑框部分为放大位置。ic:侵染细胞。ui:非侵染细胞。E:接种根瘤菌28 d时Ev和GmPP2C28-OX根瘤切片单位面积侵染细胞的数目。*代表 P<0.05。Bars=200 μm (A,B),50 μm(C,D)。n=20。A,B: Cross sectional images of Ev and GmPP2C28-OX nodules stained with toluidine blue after 28 days of inoculation with rhizobia, respectively. C,D: High magnification images of A and B respectively. The black box indicates the enlarged position. ic: Infecting cells. ui: Non invasive cells. E: The number of infected cells per unit area in Ev and GmPP2C28-OX nodule sections after 28 days of inoculation with rhizobia. * represents P<0.05.
Fig.5 Section staining analysis of the transgenic nodules
| [1] | Xu Q Z, Wang X, Wang N, et al. Nitrogen inhibition of nitrogenase activity involves the modulation of cytosolic invertase in soybean nodule. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2024, 51(12): 1404-1412. |
| [2] | Ke D X, Peng K P, Xia Y J, et al. Cloning of salt-stressed responsive gene GmWRKY6 and salt resistance analysis of transgenic Lotus japonicus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(8): 95-106. |
| 柯丹霞, 彭昆鹏, 夏远君, 等. 盐胁迫应答基因GmWRKY6的克隆及转基因百脉根的抗盐分析. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 95-106. | |
| [3] | Schmid A C, Woscholski R. Phosphatases as small-molecule targets: inhibiting the endogenous inhibitors of kinases. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2004, 32(2): 348-349. |
| [4] | Singh A, Jha S K, Bagri J, et al. ABA inducible rice protein phosphatase 2C confers ABA insensitivity and abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0125168. |
| [5] | Zhang F, Wei Q H, Shi J C, et al. Brachypodium distachyon BdPP2CA6 interacts with BdPYLs and BdSnRK2 and positively regulates salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 264. |
| [6] | Schweighofer A, Kazanaviciute V, Scheikl E, et al. The PP2C-type phosphatase AP2C1, which negatively regulates MPK4 and MPK6, modulates innate immunity, jasmonic acid, and ethylene levels in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2007, 19(7): 2213-2224. |
| [7] | Umbrasaite J, Schweighofer A, Kazanaviciute V, et al. MAPK phosphatase AP2C3 induces ectopic proliferation of epidermal cells leading to stomata development in Arabidopsis. PLoS One, 2010, 5(12): e15357. |
| [8] | Kapranov P, Jensen T J, Poulsen C, et al. A protein phosphatase 2C gene, LjNPP2C1, from Lotus japonicus induced during root nodule development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(4): 1738-1743. |
| [9] | Guan X M. LjPP2C, a protein phosphatases 2C from Lotus japonicus, functions as a negative regulator of MPK6 pathway. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 官晓敏. 百脉根LjPP2C蛋白磷酸酶负调控MPK6信号转导途径. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2015. | |
| [10] | Lu X, Lai Y C, Du W G, et al. A PP2C-1 allele underlying a quantitative trait locus enhances soybean 100-seed weight. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(5): 670-684. |
| [11] | Chen C, Yu Y, Ding X D, et al. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of PP2C clade D under saline and alkali stresses in wild soybean and Arabidopsis. Protoplasma, 2018, 255(2): 643-654. |
| [12] | Bai G, Yang D H, Zhao Y, et al. Interactions between soybean ABA receptors and type 2C protein phosphatases. Plant Molecular Biology, 2013, 83(6): 651-664. |
| [13] | Yang X X, Tang M S, Zhang B. Identification of soybean PP2C family genes and transcriptome analysis in response to salt stress. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(2): 207-220. |
| 杨昕霞, 唐满生, 张斌. 大豆PP2C家族基因鉴定与响应盐胁迫的转录组分析. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(2): 207-220. | |
| [14] | Zhang B. Functional analysis of soybean GmPP2C89 gene under salt stress. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2022, 37(4): 20-27. |
| 张斌. 大豆GmPP2C89基因在盐胁迫中的功能分析. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(4): 20-27. | |
| [15] | Zhang Y J, Liu X Y, Chen L, et al. Mining for genes encoding proteins associated with NopL of Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 using quantitative trait loci in soybean (Glycine max Merr.) recombinant inbred lines. Plant and Soil, 2018, 431: 245-255. |
| [16] | Wang J H, Wang J Q, Ma C, et al. QTL mapping and data mining to identify genes associated with the Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 T3SS effector NopD in soybean. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 453. |
| [17] | Ke D X, Hou S B, Ma S Y, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of the protein phosphatase gene GmPP2C28 of soybean. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 37(3): 343-348. |
| 柯丹霞, 侯仕博, 马斯羽, 等. 大豆蛋白磷酸酶基因GmPP2C28的克隆与表达分析. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2024, 37(3): 343-348. | |
| [18] | Ke D X, Peng K P, Zhang M K, et al. Function of the soybean GmCYS20 gene in symbiotic nodulation of Lotus japonicus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(9): 132-141. |
| 柯丹霞, 彭昆鹏, 张孟珂, 等. 大豆GmCYS20基因在百脉根共生结瘤过程中的功能研究. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 132-141. | |
| [19] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [20] | Ke D X, Feng S, Hu Y H, et al. Functional identification of soybean NADPH oxidase gene GmRbohL in the nodulation process of soybean. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2023, 38(5): 29-38. |
| 柯丹霞, 冯爽, 胡艺涵, 等. 大豆NADPH氧化酶基因GmRbohL在共生结瘤过程中的功能鉴定. 华北农学报, 2023, 38(5): 29-38. | |
| [21] | Yuan S, Ke D, Liu B, et al. The Bax inhibitor GmBI-1α interacts with a Nod factor receptor and plays a dual role in the legume-rhizobia symbiosis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2023, 74(18): 5820-5839. |
| [22] | Fan K, Yuan S N, Chen J, et al. Molecular evolution and lineage-specific expansion of the PP2C family in Zea mays. Planta, 2019, 250(5): 1521-1538. |
| [23] | Shazadee H, Khan N, Wang J J, et al. Identification and expression profiling of protein phosphatases (PP2C) gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(6): 1395. |
| [24] | Yu X F, Han J P, Wang E F, et al. Genome-wide identification and homoeologous expression analysis of PP2C genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Frontiers in Genetics, 2019, 10: 561. |
| [25] | Wang Y F, Liao Y Q, Wang Y P, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of StPP2C gene family in response to multiple stresses in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2020, 19(6): 1609-1624. |
| [26] | Han Y G, Luo Y, Wei Z X, et al. Structure prediction and function analysis of protein phosphatase PPH1 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2013, 19(1): 69-73. |
| 韩永光, 骆玥, 魏徵霄, 等. 拟南芥蛋白磷酸酶PPH1的结构预测与功能分析. 应用与环境生物学报, 2013, 19(1): 69-73. | |
| [27] | Singh A, Pandey A, Srivastava A K, et al. Plant protein phosphatases 2C: from genomic diversity to functional multiplicity and importance in stress management. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2016, 36(6): 1023-1035. |
| [28] | Lin X, Duan X Y, Liang Y Y, et al. PPM1A functions as a Smad phosphatase to terminate TGFbeta signaling. Cell, 2006, 125(5): 915-928. |
| [29] | Akhurst R J, Derynck R. TGF-beta signaling in cancer-a double-edged sword. Trends in Cell Biology, 2001, 11(11): S44-S51. |
| [30] | Hanada M, Kobayashi T, Ohnishi M, et al. Selective suppression of stress-activated protein kinase pathway by protein phosphatase 2C in mammalian cells. FEBS Letters, 1998, 437(3): 172-176. |
| [31] | Takekawa M, Maeda T, Saito H. Protein phosphatase 2C alpha inhibits the human stress-responsive p38 and JNK MAPK pathways. The EMBO Journal, 1998, 17(16): 4744-4752. |
| [32] | Zhou B, Wang Z X, Zhao Y, et al. The specificity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 dephosphorylation by protein phosphatases. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(35): 31818-31825. |
| [33] | Hu X, Song F, Zheng Z. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a rice protein phosphatase 2C gene, OsBIPP2C1, and overexpression in transgenic tobacco conferred enhanced disease resistance and abiotic tolerance. Plant Physiology, 2006, 127: 225-236. |
| [34] | Seo J K, Kwon S J, Cho W K, et al. Type 2C protein phosphatase is a key regulator of antiviral extreme resistance limiting virus spread. Science Report, 2014, 4: 5905. |
| [35] | Meskiene I, Baudouin E, Schweighofer A, et al. Stress-induced protein phosphatase 2C is a negative regulator of a mitogen-activated protein kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(21): 18945-18952. |
| [36] | Cristina M S, Petersen M, Mundy J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 621-649. |
| [37] | Schoenbeck M A, Samac D A, Fedorova M, et al. The alfalfa (Medicago sativa) TDY1 gene encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase homolog. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 1999, 12(10): 882-893. |
| [38] | Fernandez-Pascual M, Lucas M M, de Felipe M R, et al. Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the symbiosis Bradyrhizobium-Lupinus. Journal of Experimental Botany,2006, 57(11): 2735-2742. |
| [39] | Lee H, Kim J, Im J H, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase is involved in the symbiotic interaction between Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110 and soybean. Journal of Plant Biology, 2008, 51(4): 291-296. |
| [1] | 毛海龙, 邰继承, 杨恒山, 张玉芹, 张瑞富, 王真真. 带型配置对青贮玉米-大豆复合种植体冠层特性、产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 30-42. |
| [2] | 匡宗洋, 穆麟, 魏岚, 郭阳, 胥贵, 陈瑶, 石雪云, 魏仲珊, 张志飞. 不同混合比例和乳酸菌添加对全株玉米和大豆混合青贮品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 227-238. |
| [3] | 徐宗昌, 鲁雪莉, 魏云冲, 孟晨, 张梦超, 张缘杨, 王萌, 王菊英, 张成省, 李义强. 航天诱变野大豆SP1群体苗期耐盐性鉴定与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 168-178. |
| [4] | 许代香, 杨建峰, 苏杭, 翟建荣, 綦才, 赵龙刚, 郭彦军. 间作模式下作物根际土壤代谢物对微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 65-80. |
| [5] | 王升升, 段珍, 周培, 张吉宇. 白花草木樨结瘤缺失型突变体的结瘤表型及生物量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 247-256. |
| [6] | 刘福, 陈诚, 张凯旋, 周美亮, 张新全. 日本百脉根LjbHLH34基因克隆及耐旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| [7] | 王诗雅, 郑殿峰, 冯乃杰, 梁喜龙, 项洪涛, 冯胜杰, 王新欣, 左官强. 鼓粒期淹水胁迫对大豆叶片AsA-GSH循环的损伤及烯效唑的缓解效应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 157-166. |
| [8] | 马亚玲, 刘辉, 刘阳, 李春杰. 两种色型豌豆蚜生物学特征对不同大豆品种的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 96-102. |
| [9] | 姜妍, 薛恩玉, 鹿文成, 崔国文, 李远明, 韩天富, 王绍东. Kunitz型胰蛋白酶抑制剂缺失大豆新品系培育及其饲草价值分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 91-98. |
| [10] | 李琬. 干旱对大豆根系生育的影响及灌溉缓解效应研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 192-202. |
| [11] | 任胜茂, 邓榆川, 文凤君, 刘明洁, 袁小琴, SajadHussain, 蒲全明, 刘卫国, 杨文钰. 套作对大豆苗期碳氮物质代谢的影响及其与抗倒伏性的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 85-94. |
| [12] | 柯丹霞, 彭昆鹏, 张孟珂, 贾妍. 大豆GmCYS20基因在百脉根共生结瘤过程中的功能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 132-141. |
| [13] | 柯丹霞, 彭昆鹏, 夏远君, 朱玉莹, 张丹丹. 盐胁迫应答基因GmWRKY6的克隆及转基因百脉根的抗盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 95-106. |
| [14] | 韦兴燚, 李昱, 刘文献, 金小煜, 闵学阳, 张正社, NdayambazaBoniface, 王彦荣. 大豆和百脉根古老原核基因的全基因组鉴定与比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 49-57. |
| [15] | 陈冉冉, 朱娉慧, 贾博为, 宋雪薇, 王子君, 李佶娜, 李强, 丁晓东, 朱延明. 碱胁迫应答基因GsARHP的克隆及转基因紫花苜蓿的耐碱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 92-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||