

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 52-67.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025187
李向1,2( ), 李航4, 李润杰1,2,3(
), 李航4, 李润杰1,2,3( ), 张永坤3(
), 张永坤3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-09
修回日期:2025-06-25
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
李润杰,张永坤
作者简介:rjl@126.com基金资助:
Xiang LI1,2( ), Hang LI4, Run-jie LI1,2,3(
), Hang LI4, Run-jie LI1,2,3( ), Yong-kun ZHANG3(
), Yong-kun ZHANG3( )
)
Received:2025-05-09
Revised:2025-06-25
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Run-jie LI,Yong-kun ZHANG
摘要:
为揭示高寒沼泽草甸退化与人工建植草地对土壤水力性质的影响,本研究以青海省玛沁县天然、轻度退化、重度退化高寒沼泽草甸和人工建植草地(为生态修复于2018年在退化草甸种植的冷地早熟禾)为研究对象,测定了几种基本土壤性质,分析了0~30 cm土层土壤水力性质变化特征及其驱动因素。结果表明:1)生物量、土壤孔隙度、有机碳与总氮含量随高寒沼泽草甸退化与建植人工草地进程推进表现为先降低后升高的趋势(P<0.05)。2)0~20 cm土层的土壤持水量、田间持水量、凋萎系数与饱和含水量排序为:天然沼泽草甸>人工草地>重度退化沼泽草甸。饱和导水率在0~10 cm土层显著高于10~30 cm土层,且随草甸退化与建植人工草地进程推进表现为先下降后上升的趋势(P<0.05)。3)饱和导水率、饱和含水量、植物有效水含量与土壤孔隙度、有机碳和总氮含量呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05),与土壤pH呈显著负相关关系(P<0.05)。偏最小二乘回归分析表明:影响土壤水力性质的重要因子是土壤孔隙度与有机碳含量。综上所述,高寒沼泽草甸退化与建植人工草地显著改变了土壤水力性质,对于表层(0~10 cm)土壤影响最为显著,加强表层土壤的研究和保护是高寒沼泽草甸生态修复的关键所在。
李向, 李航, 李润杰, 张永坤. 土壤水力性质对高寒沼泽草甸退化与建植人工草地的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(3): 52-67.
Xiang LI, Hang LI, Run-jie LI, Yong-kun ZHANG. Response of soil hydraulic properties to alpine swamp meadow degradation and sown grassland planting[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 52-67.
图1 研究区位置信息基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2024)0650号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS(2024)0650 of the Ministry of Natural Resources. The boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.1 Study area location information
类型 Type | 盖度 Coverage (%) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 叶面积指数 Leaf area index | 优势物种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMM | 95.0±2.5a | 32.0±1.5a | 3.9±0.9a | 藏嵩草K.tibetica;小嵩草K. pygmaea |
| LDMM | 91.0±1.0b | 3.4±1.0b | 1.3±0.3b | 矮嵩草K. humilis |
| HDMM | 82.0±3.5c | 3.3±0.3b | 1.2±0.3b | 夏秋季:密花香薷、葵花大蓟等Summer-autumn season: E.densa, C. souliei, etc.;春冬季:裸土Spring-winter season: Bare soil |
| AEG | 94.0±1.5a | 21.3±2.1a | 3.0±0.8a | 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila |
表1 研究区样地基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of sample plots in the study area
类型 Type | 盖度 Coverage (%) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 叶面积指数 Leaf area index | 优势物种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMM | 95.0±2.5a | 32.0±1.5a | 3.9±0.9a | 藏嵩草K.tibetica;小嵩草K. pygmaea |
| LDMM | 91.0±1.0b | 3.4±1.0b | 1.3±0.3b | 矮嵩草K. humilis |
| HDMM | 82.0±3.5c | 3.3±0.3b | 1.2±0.3b | 夏秋季:密花香薷、葵花大蓟等Summer-autumn season: E.densa, C. souliei, etc.;春冬季:裸土Spring-winter season: Bare soil |
| AEG | 94.0±1.5a | 21.3±2.1a | 3.0±0.8a | 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila |

图4 不同退化阶段地上生物量与地下生物量特征不同大写字母表示同一类型不同土层深度差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示同一土层深度不同类型差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different uppercase letters denote significant differences among different soil layers within the same type (P<0.05). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different types at the same soil depth (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.4 Characteristics of aboveground biomass and belowground biomass at different degradation stages and artificially established grassland
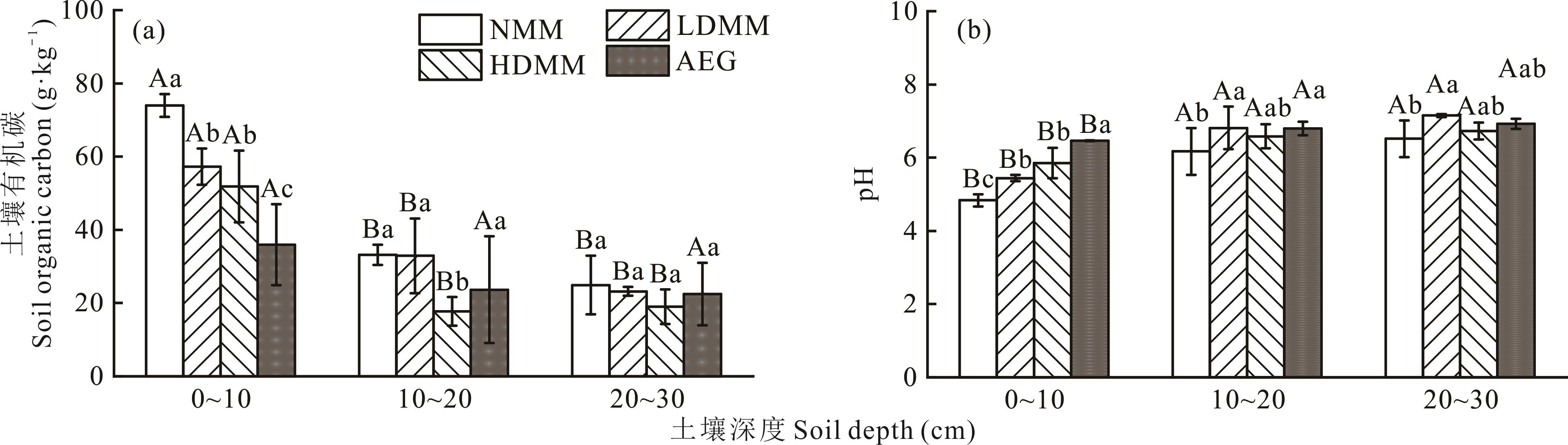
图5 不同退化阶段高寒沼泽草甸和人工建植草地土壤有机碳与pH
Fig.5 Soil organic carbon and pH in alpine swamp meadows at different degradation stages and artificially established grassland
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 类型 Type | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity (%) | 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity (%) | 非毛管孔隙度 Non-capillary porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | NMM | 0.73±0.07Bc | 67.91±2.35Aa | 62.82±1.68Aa | 5.10±1.02Aa |
| LDMM | 0.90±0.02Bab | 61.61±2.77Ab | 57.00±1.92Ab | 4.61±1.33Aa | |
| HDMM | 0.98±0.04Aa | 62.76±2.45Aab | 58.90±2.50Aab | 3.86±0.16Ba | |
| AEG | 0.88±0.06Bb | 61.83±1.48Ab | 57.71±2.36Ab | 4.12±1.37Aa | |
| 10~20 | NMM | 1.12±0.03Aa | 55.18±4.71Ba | 51.65±4.33Bab | 3.54±0.58Ab |
| LDMM | 1.11±0.14Aa | 56.76±4.75ABa | 53.65±4.90ABa | 3.11±0.54Ab | |
| HDMM | 1.11±0.11Aa | 51.00±1.86Ba | 42.65±3.24Bb | 8.31±2.50Aa | |
| AEG | 1.17±0.03Aa | 57.19±4.11Aa | 54.01±3.99Aa | 3.18±0.19Ab | |
| 20~30 | NMM | 1.22±0.14Aa | 54.82±3.60Bab | 50.07±3.88Bab | 4.75±0.28Aa |
| LDMM | 1.27±0.06Aa | 50.03±1.93Bb | 46.48±1.05Bb | 3.55±0.95Aa | |
| HDMM | 1.09±0.07Aa | 51.05±2.78Bb | 46.43±1.91Bb | 4.63±0.97Ba | |
| AEG | 1.22±0.12Aa | 57.19±1.15Aa | 52.44±2.16Aa | 4.75±1.15Aa |
表2 不同退化阶段高寒沼泽草甸和人工建植草地土壤容重与孔隙度
Table 2 Soil bulk density and porosity of alpine marsh meadows at different degradation stages and artificially established grassland
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 类型 Type | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity (%) | 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity (%) | 非毛管孔隙度 Non-capillary porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | NMM | 0.73±0.07Bc | 67.91±2.35Aa | 62.82±1.68Aa | 5.10±1.02Aa |
| LDMM | 0.90±0.02Bab | 61.61±2.77Ab | 57.00±1.92Ab | 4.61±1.33Aa | |
| HDMM | 0.98±0.04Aa | 62.76±2.45Aab | 58.90±2.50Aab | 3.86±0.16Ba | |
| AEG | 0.88±0.06Bb | 61.83±1.48Ab | 57.71±2.36Ab | 4.12±1.37Aa | |
| 10~20 | NMM | 1.12±0.03Aa | 55.18±4.71Ba | 51.65±4.33Bab | 3.54±0.58Ab |
| LDMM | 1.11±0.14Aa | 56.76±4.75ABa | 53.65±4.90ABa | 3.11±0.54Ab | |
| HDMM | 1.11±0.11Aa | 51.00±1.86Ba | 42.65±3.24Bb | 8.31±2.50Aa | |
| AEG | 1.17±0.03Aa | 57.19±4.11Aa | 54.01±3.99Aa | 3.18±0.19Ab | |
| 20~30 | NMM | 1.22±0.14Aa | 54.82±3.60Bab | 50.07±3.88Bab | 4.75±0.28Aa |
| LDMM | 1.27±0.06Aa | 50.03±1.93Bb | 46.48±1.05Bb | 3.55±0.95Aa | |
| HDMM | 1.09±0.07Aa | 51.05±2.78Bb | 46.43±1.91Bb | 4.63±0.97Ba | |
| AEG | 1.22±0.12Aa | 57.19±1.15Aa | 52.44±2.16Aa | 4.75±1.15Aa |
| 土壤深度Soil depth (cm) | 类型Type | 全碳Total carbon (g·kg-1) | 总氮Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碳氮比Carbon to nitrogen ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | NMM | 73.79±3.08Aa | 6.48±0.19Aa | 11.63±0.47Aab |
| LDMM | 57.28±4.98Ab | 5.24±0.12Ab | 12.02±0.45Aa | |
| HDMM | 51.86±9.76Ab | 4.98±0.78Ab | 11.13±0.58Ab | |
| AEG | 35.96±11.02Ac | 3.32±0.94Ac | 12.12±0.10Aa | |
| 10~20 | NMM | 35.97±2.77Ba | 3.39±0.28Ba | 10.60±0.27Aa |
| LDMM | 32.93±10.21Ba | 3.36±0.96Ba | 11.46±0.63Aa | |
| HDMM | 17.73±3.88Bb | 1.98±0.40Ba | 11.14±2.00Aa | |
| AEG | 23.67±14.59Aab | 2.10±1.09Aa | 12.56±0.25Aa | |
| 20~30 | NMM | 24.94±8.00Ba | 2.69±0.93Ba | 11.65±2.40Aa |
| LDMM | 23.20±1.25Bab | 2.66±0.16Ba | 11.27±0.46Aa | |
| HDMM | 19.01±4.69Bb | 1.94±0.27Ba | 12.50±1.52Aa | |
| AEG | 22.50±8.54Aab | 2.08±0.82Aa | 11.90±0.68Aa |
表3 不同退化阶段高寒沼泽草甸和人工建植草地土壤养分含量变化
Table 3 Changes in total nutrient content of soils in alpine marsh meadows at different degradation stages and artificial established grasslands
| 土壤深度Soil depth (cm) | 类型Type | 全碳Total carbon (g·kg-1) | 总氮Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碳氮比Carbon to nitrogen ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | NMM | 73.79±3.08Aa | 6.48±0.19Aa | 11.63±0.47Aab |
| LDMM | 57.28±4.98Ab | 5.24±0.12Ab | 12.02±0.45Aa | |
| HDMM | 51.86±9.76Ab | 4.98±0.78Ab | 11.13±0.58Ab | |
| AEG | 35.96±11.02Ac | 3.32±0.94Ac | 12.12±0.10Aa | |
| 10~20 | NMM | 35.97±2.77Ba | 3.39±0.28Ba | 10.60±0.27Aa |
| LDMM | 32.93±10.21Ba | 3.36±0.96Ba | 11.46±0.63Aa | |
| HDMM | 17.73±3.88Bb | 1.98±0.40Ba | 11.14±2.00Aa | |
| AEG | 23.67±14.59Aab | 2.10±1.09Aa | 12.56±0.25Aa | |
| 20~30 | NMM | 24.94±8.00Ba | 2.69±0.93Ba | 11.65±2.40Aa |
| LDMM | 23.20±1.25Bab | 2.66±0.16Ba | 11.27±0.46Aa | |
| HDMM | 19.01±4.69Bb | 1.94±0.27Ba | 12.50±1.52Aa | |
| AEG | 22.50±8.54Aab | 2.08±0.82Aa | 11.90±0.68Aa |
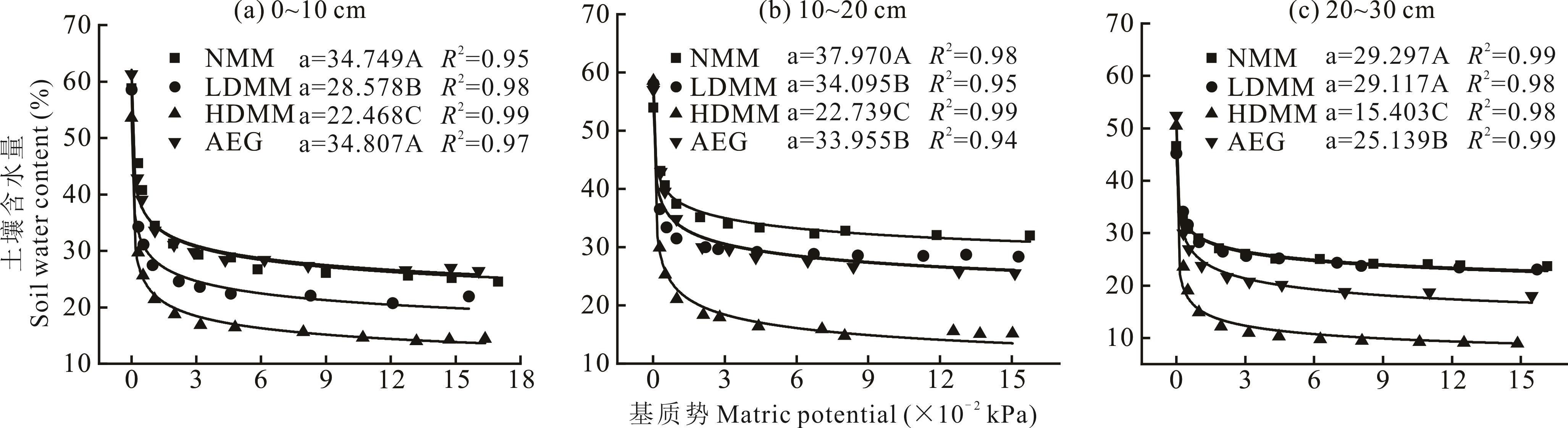
图6 不同退化阶段土壤水分特征曲线a为模型参数a is the model parameter;不同大写字母表示同一土层深度不同类型差异显著(P<0.05)。Different uppercase letters denote significant differences among different types at the same soil depth (P<0.05).
Fig.6 Soil water characteristic curves at different degradation stages and artificially established grassland
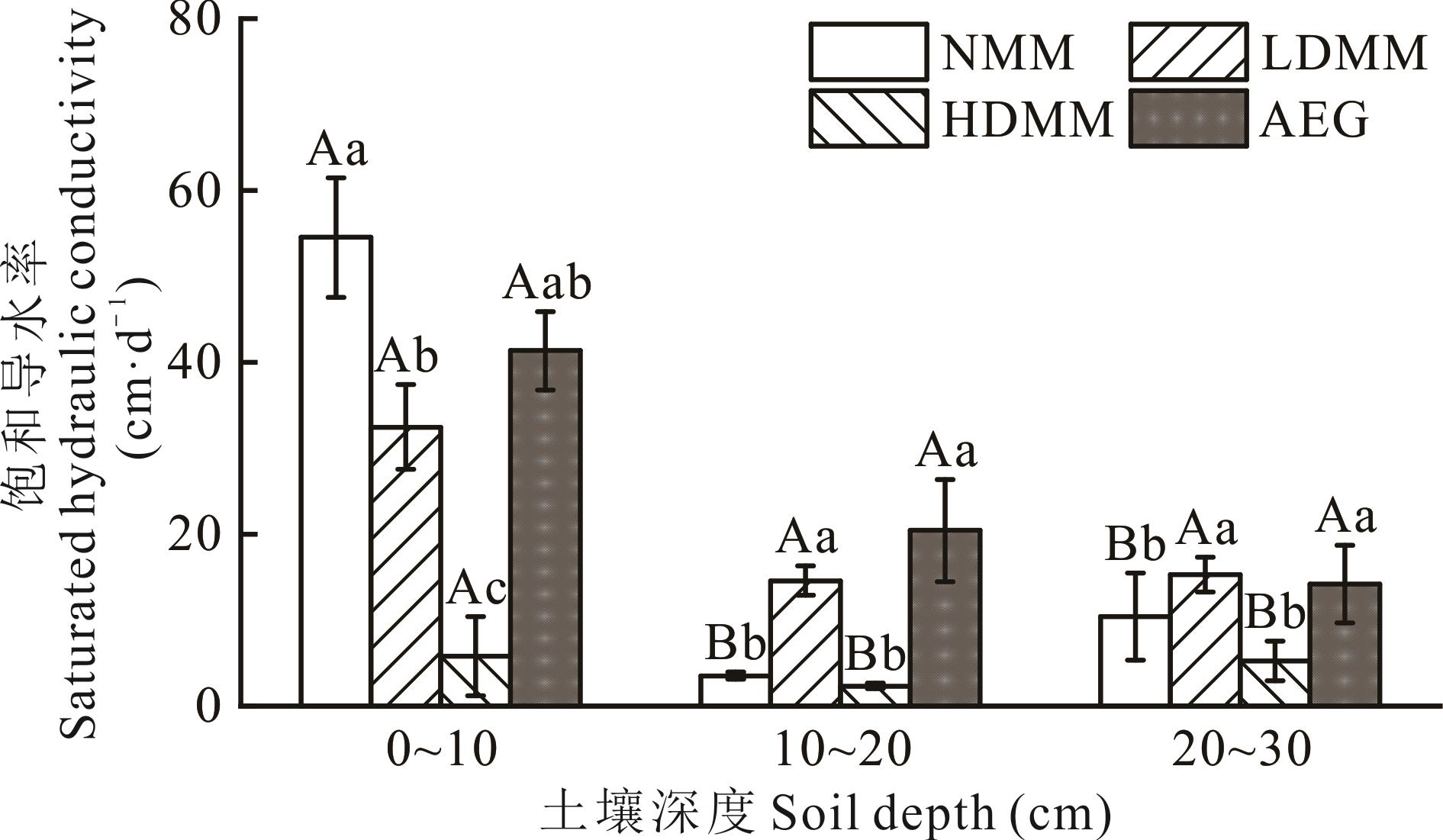
图7 不同退化阶段高寒沼泽草甸和人工建植草地土壤饱和导水率
Fig.7 Saturated hydraulic conductivity of soils in alpine swamp meadows at different degradation stages and artificial established grasslands
土层深度 Soil depth (cm) | 类型 Type | 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -30 kPa (FC) | -1500 kPa (WC) | PAWC | SSWC | ||
| 0~10 | NMM | 45.359a | 25.566a | 19.793a | 68.953a |
| LDMM | 34.158b | 20.980b | 13.178b | 63.923ab | |
| HDMM | 30.071b | 14.148c | 15.923b | 62.773b | |
| AEG | 30.770b | 15.559c | 15.212b | 63.057b | |
| 10~20 | NMM | 43.247a | 28.828a | 14.419a | 56.523a |
| LDMM | 40.247ab | 27.493a | 12.754a | 52.363a | |
| HDMM | 28.827b | 15.145b | 13.682a | 58.077a | |
| AEG | 38.253ab | 24.371a | 13.882a | 58.503a | |
| 20~30 | NMM | 33.977a | 22.737a | 11.240a | 56.193ab |
| LDMM | 32.581a | 23.134a | 9.447b | 52.560ab | |
| HDMM | 22.739b | 10.953c | 11.786a | 51.563b | |
| AEG | 29.865a | 18.070b | 11.795a | 58.503a | |
表4 不同退化阶段高寒沼泽草甸和人工建植草地植物有效水含量和土壤饱和含水量
Table 4 Plant-available water content and soil saturated water content in alpine swamp meadow at different degradation stages and artificial established grassland ?
土层深度 Soil depth (cm) | 类型 Type | 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -30 kPa (FC) | -1500 kPa (WC) | PAWC | SSWC | ||
| 0~10 | NMM | 45.359a | 25.566a | 19.793a | 68.953a |
| LDMM | 34.158b | 20.980b | 13.178b | 63.923ab | |
| HDMM | 30.071b | 14.148c | 15.923b | 62.773b | |
| AEG | 30.770b | 15.559c | 15.212b | 63.057b | |
| 10~20 | NMM | 43.247a | 28.828a | 14.419a | 56.523a |
| LDMM | 40.247ab | 27.493a | 12.754a | 52.363a | |
| HDMM | 28.827b | 15.145b | 13.682a | 58.077a | |
| AEG | 38.253ab | 24.371a | 13.882a | 58.503a | |
| 20~30 | NMM | 33.977a | 22.737a | 11.240a | 56.193ab |
| LDMM | 32.581a | 23.134a | 9.447b | 52.560ab | |
| HDMM | 22.739b | 10.953c | 11.786a | 51.563b | |
| AEG | 29.865a | 18.070b | 11.795a | 58.503a | |

图8 最小二乘法分析变量相关矩阵热图SOC: 土壤有机碳Soil organic carbon; TC: 全碳Total carbon; TN: 总氮Total nitrogen; C/N: 碳氮比Carbon to nitrogen ratio; TP: 总孔隙度Total porosity; CP: 毛管孔隙度Capillary porosity; NCP: 非毛管孔隙度Non-capillary porosity; BGB: 地下生物量Belowground biomass; Clay: 黏粒; Silt: 粉粒; Sand: 砂粒; Ks: 饱和导水率Saturated hydraulic conductivity. a为模型参数a is the model parameter; PAWC: 植物有效水含量Plant available water content; SSWC: 土壤饱和含水量Soil saturated water content. *: P<0.05,**: P<0.01,****: P<0.001. 下同The same below.
Fig.8 Heat map of variable correlation matrix analyzed by small squares method

图9 饱和导水率、Gardner模型参数a、植物有效水含量和土壤饱和含水量投影重要性分析
Fig.9 Projection importance analysis of saturated hydraulic conductivity, Gardner model parameter a, plant available water content, and soil saturated water content
| [1] | Lou S L, Liu M X, Yi J, et al. Influence of vegetation coverage and topographic position on soil hydrological function in the hillslope of the three gorges area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(13): 4844-4854. |
| 娄淑兰, 刘目兴, 易军, 等. 三峡山地不同类型植被和坡位对土壤水文功能的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(13): 4844-4854. | |
| [2] | Lv G, Wu X Y. Review on influential factors of soil infiltration characteristics. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008, 34(7): 494-499. |
| 吕刚, 吴祥云. 土壤入渗特性影响因素研究综述. 中国农学通报, 2008, 34(7): 494-499. | |
| [3] | Su Y, Zhu J, Wang P, et al. Research progress on soil water holding capacity. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(14): 140-145. |
| 苏杨, 朱健, 王平, 等. 土壤持水能力研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(14): 140-145. | |
| [4] | Vereecken H, Amelung W, Bauke S L, et al. Soil hydrology in the earth system. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(9): 573-587. |
| [5] | Lu C H, Xie G D, Xiao Y, et al. Ecosytem diversity and economic valuation of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(12): 2749-2755. |
| 鲁春霞, 谢高地, 肖玉, 等. 青藏高原生态系统服务功能的价值评估. 生态学报, 2004, 24(12): 2749-2755. | |
| [6] | Dong S K, Shang Z H, Gao J X, et al. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, 287: 106683. |
| [7] | Khaznadar M, Vogiatzakis I N, Griffiths G H, et al. Land degradation and vegetation distribution in Chott El Beida wetland, Algeria. Journal of Arid Environments, 2008, 73(3): 321-330. |
| [8] | Wu G L, Liu Z H, Zhang L, et al. Effects of artificial grassland establishment on soil nutrients and carbon properties in a black-soil-type degraded grassland. Plant and Soil, 2010, 333(1): 469-479. |
| [9] | Li F, Liu Z H, Jia T H, et al. Functional diversity of soil microbial community carbon metabolism with the degradation and restoration of alpine wetlands and meadows. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(17): 6006-6015. |
| 李飞, 刘振恒, 贾甜华, 等. 高寒湿地和草甸退化及恢复对土壤微生物碳代谢功能多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(17): 6006-6015. | |
| [10] | Xing Y F, Wang X L, Liu Y Q, et al. Characteristics of plant community and soil organic carbon and nitrogen in artificial grassland with different establishment years. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 521-528. |
| 邢云飞, 王晓丽, 刘永琦, 等. 不同建植年限人工草地植物群落和土壤有机碳氮特征. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 521-528. | |
| [11] | Shang Z H, Dong Q M, Shi J J, et al. Research progress in recent ten years of ecological restoration for ‘black soil land’ degraded grassland on Tibetan Plateau-concurrently discuss of ecological restration in Sanjiangyuan region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. |
| 尚占环, 董全民, 施建军, 等. 青藏高原“黑土滩”退化草地及其生态恢复近10年研究进展—兼论三江源生态恢复问题. 草地学报, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. | |
| [12] | Wosten J H M, Pachepsky Y A, Rawls W J, et al. Pedotransfer functions: bridging the gap between available basic soil data and missing soil hydraulic characteristics. Journal of Hydrology, 2001, 251(3/4): 123-150. |
| [13] | Zhou B R, Han B H, Xiao H B, et al. Study on estimating diurnal evapotranspiration model of alpine marsh meadow in Three-river Headwater Region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(4): 928-937. |
| 周秉荣, 韩炳宏, 肖宏斌, 等. 三江源区高寒沼泽草甸日蒸散估算模型研究. 草地学报, 2019, 27(4): 928-937. | |
| [14] | Sun Y, Yang Y S, He Q, et al. Responses of soil water conservation function and soil physicochemical properties to a range of degradation conditions in alpine meadows of the Three River Headwater Region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 16-29. |
| 孙玉, 杨永胜, 何琦, 等. 三江源高寒草甸水源涵养功能及土壤理化性质对退化程度的响应. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 16-29. | |
| [15] | Dai L C, Yuan Y M, Guo X W, et al. Soil water retention in alpine meadows under different degradation stages on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 590: 125397. |
| [16] | Yi X S, Li G S, Yin Y Y, et al. The impacts of grassland vegetation degradation on soil hydrological and ecological effects in the source region of the Yellow River-a case study in Junmuchang region of Maqin Country. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2012, 13: 967-981. |
| [17] | Yang Y S, Zhang L, Wei Y X, et al. Effects of degradation degree on soil physicochemical properties and soil water-holding capacity in the Zeku alpine meadow in the headwater region of Three Rivers in China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(5): 54-61. |
| 杨永胜, 张莉, 未亚西, 等. 退化程度对三江源泽库高寒草甸土壤理化性质及持水能力的影响. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(5): 54-61. | |
| [18] | Pan T, Hou S, Wu S H, et al. Variation of soil hydraulic properties with alpine grassland degradation in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2017, 21(4): 2249-2261. |
| [19] | Zeng C, Zhang F, Wang Q J, et al. Impact of alpine meadow degradation on soil hydraulic properties over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 478: 148-156. |
| [20] | Shang Z H, Feng Q S, Wu G L, et al. Grasslandification has significant impacts on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of alpine wetlands on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 58: 170-179. |
| [21] | Yang S H, Li Y N, Pu J Y, et al. Investigation of the plant community and soil environmental factors of three alpine vegetation types. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2006, 26(1): 77-83. |
| 杨时海, 李英年, 蒲继延, 等. 三种高寒草甸植被类型植物群落结构及其土壤环境因子研究. 草地学报, 2006, 26(1): 77-83. | |
| [22] | Hu X Q, Wang X L, Liu H, et al. Effects of different restoration measures on plant communities and soil nutrients in alpine mining areas. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2025, 33(4): 1218-1227. |
| 胡晓晴, 王晓丽, 刘和, 等. 不同恢复措施对高寒矿区植物群落与土壤养分的影响. 草地学报, 2025, 33(4): 1218-1227. | |
| [23] | Adihaze, Chang T, Su H Y, et al. Effects of monoculture and mixed-sown grasses on soil physicochemical properties and microbial biomass. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(7): 2072-2080. |
| 阿的哈则, 常涛, 苏洪烨, 等. 单播和混播禾草对土壤理化性质和微生物生物量的影响. 草地学报, 2024, 32(7): 2072-2080. | |
| [24] | Zheng S K, Xia F, Wei W, et al. Effects of artificial restoration and simulated warming on soil aggregate stability and nutrient distribution in alpine grassland. Grassland and Turf, 2025, 45(2): 32-42. |
| 郑晒坤, 夏菲, 魏巍, 等. 人工修复和模拟增温对高寒草地土壤团聚体稳定性及其养分分布的影响. 草原与草坪, 2025, 45(2): 32-42. | |
| [25] | Lin C Y, Li X L, Zhang J, et al. Effects of degradation succession of alpine wetland on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in the Yellow River source zone, west China. Journal of Mountain Science, 2021, 18(3): 694-702. |
| [26] | Sun J J, Wang P B, Wang H B, et al. Changes in plant communities, soil characteristics, and microbial communities in alpine meadows degraded to different degrees by pika on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2021, 27: e01621. |
| [27] | Wang G X, Wang Y B, Li Y S, et al. Influences of alpine ecosystem responses to climatic change on soil properties on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Catena, 2007, 70(3): 506-514. |
| [28] | Huang Q, Ding M J, Chen L W, et al. Variations of moisture in surface soil of alpine meadow with different degradation degrees in the Three River Source Region. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(1): 189-195. |
| 黄倩, 丁明军, 陈利文, 等. 三江源区不同退化程度高寒草甸表土层的土壤水分变化特征. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(1): 189-195. | |
| [29] | Wang Q J. Technology rules for restoration of light and middle degraded grassland in alpine meadow. Xining: Qinghai Provincial Administration for Market Regulation, 2006. |
| 王启基. 高寒草甸中、轻度退化草地植被恢复技术规程. 西宁: 青海省质量技术监督局, 2006. | |
| [30] | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (The Third Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| [31] | Yin X, Li D M, Li Y, et al. Effects of shrub encroachment on soil hydraulic properties in alpine meadow. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(5): 121-129. |
| 尹霞, 李冬梅, 李易, 等. 灌丛化对高寒草甸土壤水力性质的影响. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(5): 121-129. | |
| [32] | Li S Y, Yuan Y Y, Zhang C C, et al. Response characteristics of soil saturated hydraulic conductivity after returning orchard to farmland on the loess plateau. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2025, 39(1): 66-72. |
| 李舒怡, 袁遥遥, 张晨晨, 等. 黄土塬区土壤饱和导水率对果园还耕的响应特征. 水土保持学报, 2025, 39(1): 66-72. | |
| [33] | Gardner W R, Hillel D, Benyamini Y. Post-irrigation movement of soil water: 1. redistribution. Water Resources Research, 1971, 7(3): 753-760. |
| [34] | Zha X C, Tang K L. Soil erosion and changes of soil properties in loess hilly woodland. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2003, 53(3): 464-469. |
| 查小春, 唐克丽. 黄土丘陵林地土壤侵蚀与土壤性质变化. 地理学报, 2003, 53(3): 464-469. | |
| [35] | Alegre J C, Cassel D K. Dynamics of soil physical properties under alternative systems to slash-and-burn. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 1996, 58(1): 39-48. |
| [36] | Fu T G, Chen H S, Zhang W, et al. Vertical distribution of soil saturated hydraulic conductivity and its influencing factors in a small Karst catchment in southwest China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(3): 92. |
| [37] | Hallema D W, Lafond J A, Periard Y, et al. Long-term effects of peatland cultivation on soil physical and hydraulic properties: Case study in Canada. Vadose Zone Journal, 2015, 14(6): 1-12. |
| [38] | Gao Q Z, Wan Y F, Xu H M, et al. Alpine grassland degradation index and its response to recent climate variability in Northern Tibet, China. Quaternary International, 2010, 226(1/2): 143-150. |
| [39] | Zhang F W, Li H Q, Yi L B, et al. Spatial response of topsoil organic carbon, total nitrogen, and total phosphor content of alpine meadows to grassland degradation in the Sanjiangyuan National Park. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(14): 5586-5592. |
| 张法伟, 李红琴, 仪律北, 等. 草地退化对三江源国家公园高寒草甸表层土壤有机碳、全氮、全磷的空间驱动. 生态学报, 2022, 42(14): 5586-5592. | |
| [40] | Li W, Wang J L, Zhang X B, et al. Effect of degradation and rebuilding of artificial grasslands on soil respiration and carbon and nitrogen pools on an alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 2018, 111: 134-142. |
| [41] | Niu B, Zhang L F, Ma R R, et al. Study of microbial biomass and enzymatic activity on the alpine meadow. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaien, 2016, 49(4): 53-60. |
| 牛犇, 张立峰, 马荣荣, 等. 高寒草甸土壤微生物量及酶活性的研究. 南开大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 49(4): 53-60. | |
| [42] | Zhan T Y, Hou G, Liu M, et al. Different characteristics of vegetation and soil properties along degraded gradients of alpine grasslands in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(4): 1010-1021. |
| 詹天宇, 侯阁, 刘苗, 等. 青藏高原不同退化梯度高寒草地植被与土壤属性分异特征. 草业科学, 2019, 36(4): 1010-1021. | |
| [43] | Su X K, Wu Y, Dong S K, et al. Effects of grassland degradation and re-vegetation on carbon and nitrogen storage in the soils of the Headwater Area Nature Reserve on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Journal of Mountain Science, 2015, 12(3): 582-591. |
| [44] | Qimanguli·Palati, Liu D, Mao J, et al. Contents and eco-stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in alpine grasslands with different degradation degrees. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43(6): 1612-1620. |
| 帕拉提其曼古丽, 刘丹, 毛军, 等. 不同退化程度高寒草地土壤碳氮磷含量及生态化学计量特征. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(6): 1612-1620. | |
| [45] | Xu C, Zhang L B, Du J Q, et al. Impact of alpine meadow degradation on soil water conservation in the source region of three rivers. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(8): 2388-2399. |
| 徐翠, 张林波, 杜加强, 等. 三江源区高寒草甸退化对土壤水源涵养功能的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(8): 2388-2399. | |
| [46] | Ge X G, Huang Z L, Cheng R M, et al. Effects of litterfall and root input on soil physical and chemical properties in Pinus massoniana plantations in Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(12): 3301-3308. |
| 葛晓改, 黄志霖, 程瑞梅, 等. 三峡库区马尾松人工林凋落物和根系输入对土壤理化性质的影响. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(12): 3301-3308. | |
| [47] | Plante P M, Rivest D, Vézina A, et al. Root distribution of different mature tree species growing on contrasting textured soils in temperate windbreaks. Plant and Soil, 2014, 380(1/2): 429-439. |
| [48] | Li C Y, Liang Z H, Li Z M, et al. Plant community characteristics and soil characteristics of degraded alpine meadows in the Beilu River Basin of the Yangtze River source area. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071. |
| 李成阳, 梁志辉, 李臻明, 等. 长江源区北麓河流域退化高寒草甸植物群落特征和土壤特性. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071. | |
| [49] | Wen J, Wang Y B, Gao Z Y, et al. Soil hydrological characteristics of the degrading meadow in permafrost in the Beiluhe River basin. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2013, 35(4): 929-937. |
| 文晶, 王一博, 高泽永, 等. 北麓河流域多年冻土区退化草甸的土壤水文特征分析. 冰川冻土, 2013, 35(4): 929-937. | |
| [50] | Liu X, Cui N J, Tan F C, et al. The soil water holding capacity and its indicative effect on soil organic carbon of Cryptomeria japonica plantations in the rainy area of west China. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2023, 29(3): 670-679. |
| 刘宣, 崔宁洁, 谭飞川, 等. 华西雨屏区柳杉人工林土壤持水能力及其对土壤有机碳的指示作用. 应用与环境生物学报, 2023, 29(3): 670-679. | |
| [51] | Li J, Du Y G, Zhang F W, et al. Impact of mattic epipedon on soil water conservation in alpine meadows. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2012, 20(5): 836-841. |
| 李婧, 杜岩功, 张法伟, 等. 草毡表层演化对高寒草甸水源涵藏功能的影响. 草地学报, 2012, 20(5): 836-841. | |
| [52] | Wang Y B, Wang G X, Wu Q B, et al. The impact of vegetation degeneration on hydrology features of alpine soil. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2010, 32(5): 989-998. |
| 王一博, 王根绪, 吴青柏, 等. 植被退化对高寒土壤水文特征的影响. 冰川冻土, 2010, 32(5): 989-998. | |
| [53] | Zhang Y H, Zhang L, Zhang X J, et al. Effects of degradation degree on plant communities and soil water holding capacity of Maqin alpine meadow. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(2): 235-246. |
| 张宇恒, 张莉, 张秀娟, 等. 退化程度对玛沁高寒草甸植物群落及土壤持水能力的影响. 草业科学, 2022, 39(2): 235-246. | |
| [54] | Wei Q, Wang F, Chen W Y, et al. Soil physical characteristics on different degraded alpine grasslands in Maqu County in upper Yellow River. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 30(5): 16-21. |
| 魏强, 王芳, 陈文业, 等. 黄河上游玛曲不同退化程度高寒草地土壤物理特性研究. 水土保持通报, 2010, 30(5): 16-21. | |
| [55] | Fan B, Lin L, Cao G M, et al. Relationship between plant roots and physical soil properties in alpine meadows at different degradation stages. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(7): 2300-2309. |
| 樊博, 林丽, 曹广民, 等. 不同演替状态下高寒草甸土壤物理性质与植物根系的相互关系. 生态学报, 2020, 40(7): 2300-2309. | |
| [56] | Li J H, Yang G J, Wang S P. Vegetation and soil characteristics of degraded alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(6): 2109-2118. |
| 李军豪, 杨国靖, 王少平. 青藏高原区退化高寒草甸植被和土壤特征. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(6): 2109-2118. | |
| [57] | Yue D L, Li G R, Li J F, et al. Soil wind erosion and nutrient loss in typical rodent mounds in a degraded alpine grassland in the Yellow River source zone. Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(4): 603-617. |
| 越大林, 李国荣, 李进芳, 等. 黄河源高寒退化草地典型鼠丘土壤风蚀及养分流失规律研究. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(4): 603-617. |
| [1] | 赵琳兴, 王雁鹤, 王子超, 徐马强, 李泽宇, 祁昌贤, 崔宝祖, 王宗保. 基于无人机和Landsat数据的近30年三江源地区土地退化动态监测[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 1-14. |
| [2] | 康佳惠, 郑敏娜, 龚瑞杰, 韩志顺, 陈燕妮, 梁秀芝. 氮磷添加对一年生人工草地土壤微生物-胞外酶生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 13-24. |
| [3] | 冉健民, 宋小艳, 王丹, 王长庭. 退化高寒草甸土壤有机碳组分变化与增汇潜力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 38-52. |
| [4] | 张琨, 乔建霞, 李金升, 王育鹏, 刘克思. 不同修复材料对退化高寒草地土壤理化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 132-148. |
| [5] | 徐倩, 郭帅, 张亮亮, 王占军, 辛国省. 补饲对放牧滩羊生长性能、血清生化及代谢组的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 122-138. |
| [6] | 霍佳娟, 宋明华. 青藏高原高寒草甸不同退化阶段植物氮利用速率变化[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 16-26. |
| [7] | 尹龙, 韩其飞, 赵阳, 刘文新. 基于多特征融合的新疆托乎拉苏草原白喉乌头分布区识别及草地退化监测[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 73-84. |
| [8] | 李婷, 杨鑫光, 段成伟, 孙华方, 高涛, 陈同德, 杨凯, 杨千慧. 不同施肥和混播条件下高寒受损煤矿区人工草地生态系统健康评价研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 16-29. |
| [9] | 曹颖, 聂明鹤, 沈艳, 胡艳, 马登宝, 李东, 候腾思, 方鹏, 王学琴. 宁夏干旱风沙区荒漠草原不同退化阶段植被土壤变化特征及其相关性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 1-14. |
| [10] | 罗原骏, 蒲玉琳, 袁大刚, 李亚丽, 钱虹宇. 基于31P 核磁共振探究退化高寒湿地土壤磷素演变特征及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 1-12. |
| [11] | 马源, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 张德罡. 高寒草甸退化程度对优势物种根际土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 125-137. |
| [12] | 段鹏, 韦鎔宜, 王芳萍, 姚步青, 赵之重, 胡碧霞, 宋词, 杨萍, 王婷. 不同养分添加对黄河源区退化高寒湿地土壤微生物碳源利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 138-153. |
| [13] | 李林芝, 张德罡, 马源, 罗珠珠, 林栋, 海龙, 白兰鸽. 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤团聚体养分及生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 48-60. |
| [14] | 孙玉, 杨永胜, 何琦, 王军邦, 张秀娟, 李慧婷, 徐兴良, 周华坤, 张宇恒. 三江源高寒草甸水源涵养功能及土壤理化性质对退化程度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 16-29. |
| [15] | 马源, 王晓丽, 王彦龙, 马玉寿, 崔海鹏. 生态恢复领域草种丸粒化研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 197-207. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||