

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 1-14.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025108
赵琳兴1( ), 王雁鹤1, 王子超2, 徐马强1(
), 王雁鹤1, 王子超2, 徐马强1( ), 李泽宇1, 祁昌贤1, 崔宝祖1, 王宗保1
), 李泽宇1, 祁昌贤1, 崔宝祖1, 王宗保1
收稿日期:2025-03-27
修回日期:2025-04-21
出版日期:2026-02-20
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
徐马强
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: 651110732@qq.com基金资助:
Lin-xing ZHAO1( ), Yan-he WANG1, Zi-chao WANG2, Ma-qiang XU1(
), Yan-he WANG1, Zi-chao WANG2, Ma-qiang XU1( ), Ze-yu LI1, Chang-xian QI1, Bao-zu CUI1, Zong-bao WANG1
), Ze-yu LI1, Chang-xian QI1, Bao-zu CUI1, Zong-bao WANG1
Received:2025-03-27
Revised:2025-04-21
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
Ma-qiang XU
摘要:
土地退化严重威胁我国生态系统稳定与粮食安全。三江源地区作为西部重要的生态屏障,面临突出的土地退化问题,影响区域生态安全与社会经济发展。本研究基于实地采样、无人机与Landsat数据,随机森林(RF)、支持向量机(SVM)、分类和回归树模型(CART),构建多源数据的土地退化监测框架,监测近30年(1993、2003、2013、2023年)三江源地区土地退化动态,并分析其时空演变特征。结果表明:1)无人机与卫星数据结合使用可以明显提高退化识别精度,基于“光谱-植被指数-地形”特征的随机森林模型精度最优,土地沙化识别精度达94.73%,F1分数为95.85%,“黑土滩”型退化识别精度达90.98%,F1分数为95.18%。2)1993-2023年,未退化与“黑土滩”型退化面积先增后减,盐渍化面积呈波动变化,先增加后减少再增加,沙化面积持续减少,各类型面积稳定不变的面积占比超1/2。3)总体上,黑土滩和沙化等级呈减轻趋势,重度黑土滩与中度沙化面积明显减少;轻中度盐渍化变化较小,重度盐渍化面积下降。本研究可为生态脆弱区土地退化监测提供新思路,并为区域生态保护与可持续发展提供科学依据。
赵琳兴, 王雁鹤, 王子超, 徐马强, 李泽宇, 祁昌贤, 崔宝祖, 王宗保. 基于无人机和Landsat数据的近30年三江源地区土地退化动态监测[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 1-14.
Lin-xing ZHAO, Yan-he WANG, Zi-chao WANG, Ma-qiang XU, Ze-yu LI, Chang-xian QI, Bao-zu CUI, Zong-bao WANG. Dynamic monitoring of land degradation in the Three-River Headwaters Region over the past 30 years using unoccupied aerial vehicle imagery and Landsat data[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 1-14.
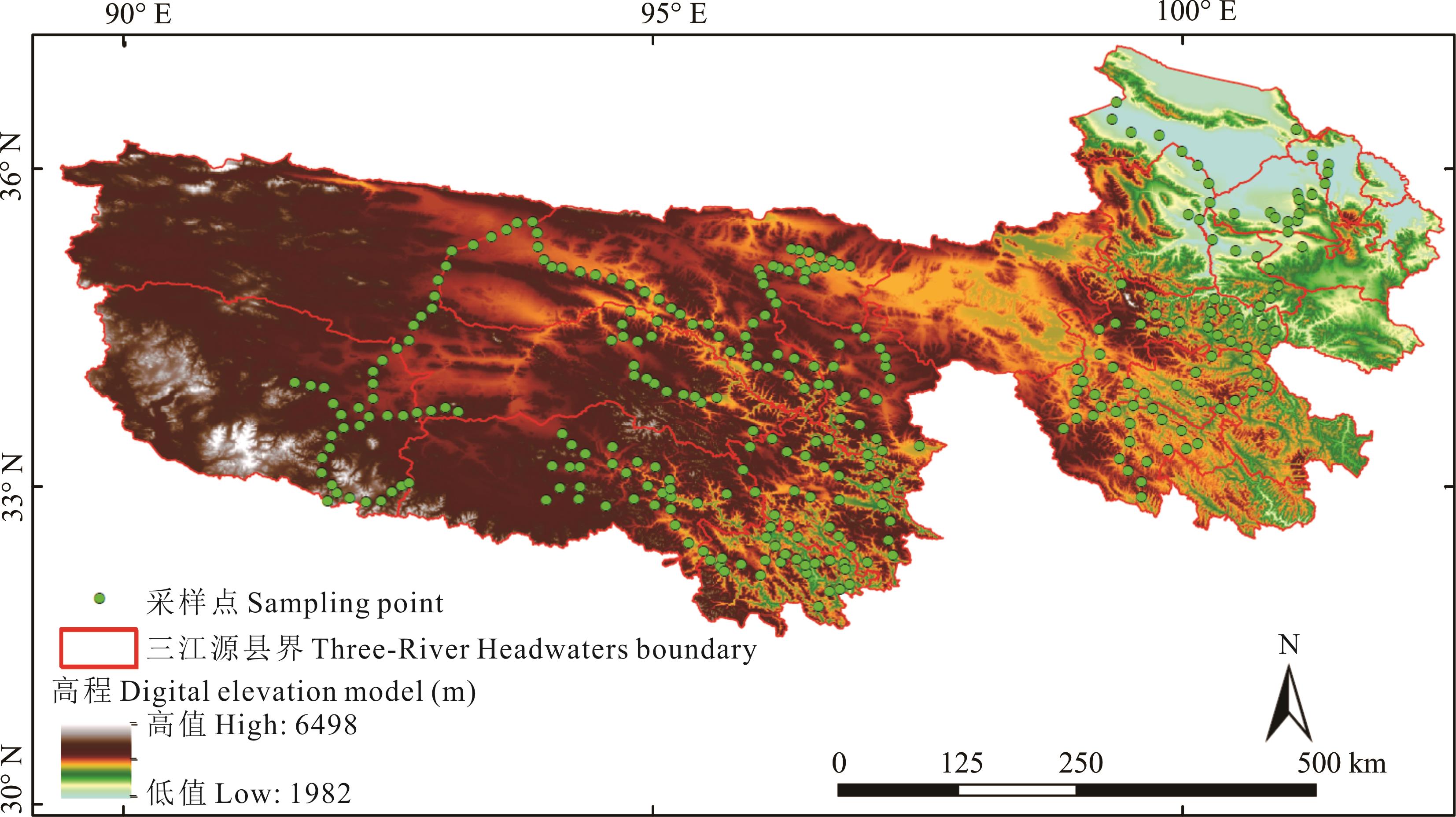
图1 研究区及采样点空间分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1822号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2019) 1822 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig. 1 Spatial distribution of research area and sampling points
情景 Scene | 遥感特征类型 Remote sensing feature types | 特征 Feature |
|---|---|---|
| 情景1 Scene 1 | 光谱波段Spectral band | 蓝波段Blue、绿波段Green、红波段Red、近红外波段NIR、短波红外1波段SWIR1、短波红外2波段SWIR2 |
| 情景2 Scene 2 | 指数特征Index feature | 归一化植被指数NDVI、比值植被指数RVI、增强型植被指数EVI、修正型土壤调节植被指数MSAVI、裸土指数BSI、过量绿色植被指数EXG、归一化绿蓝差异指数NGBDI、归一化绿红差异指数NGRDI、可见抗大气指数VARI、绿红比率指数GRRI、植被盖度FVC |
| 情景3 Scene 3 | 地形数据Terrain data | 高程DEM、坡度Slope、坡向Aspect |
表1 模型所需的遥感特征
Table 1 Remote sensing features required for the model
情景 Scene | 遥感特征类型 Remote sensing feature types | 特征 Feature |
|---|---|---|
| 情景1 Scene 1 | 光谱波段Spectral band | 蓝波段Blue、绿波段Green、红波段Red、近红外波段NIR、短波红外1波段SWIR1、短波红外2波段SWIR2 |
| 情景2 Scene 2 | 指数特征Index feature | 归一化植被指数NDVI、比值植被指数RVI、增强型植被指数EVI、修正型土壤调节植被指数MSAVI、裸土指数BSI、过量绿色植被指数EXG、归一化绿蓝差异指数NGBDI、归一化绿红差异指数NGRDI、可见抗大气指数VARI、绿红比率指数GRRI、植被盖度FVC |
| 情景3 Scene 3 | 地形数据Terrain data | 高程DEM、坡度Slope、坡向Aspect |
沙化等级 Desertification level | 特征描述 Characteristic description |
|---|---|
未沙化土地 Non-desertified land | 植被覆盖度在70%以上;Landsat像元主要是绿色或浅红色。The vegetation coverage is above 70%; Landsat pixels are mainly green or light red. |
轻度沙化土地 Slightly desertified land | 植被覆盖度大于40%,小于70%;固定或半固定沙丘为主;Landsat像元主要为浅绿色。The vegetation coverage is between 40% and 70%; the area is mainly composed of fixed or semi-fixed dunes; Landsat pixels are primarily light green. |
中度沙化土地 Moderately desertified land | 植被覆盖度大于20%,小于40%;大部分为半固定沙丘,出现明显的风蚀坑;Landsat像元主要为黄色。The vegetation coverage is between 20% and 40%; most of the area consists of semi-fixed dunes with noticeable wind erosion pits; Landsat pixels are primarily yellow. |
重度沙化土地 Severely desertified land | 植被覆盖度低于20%;大部分是流动或半流动沙丘,带有大型风蚀坑;Landsat像元大部分像素是浅黄色和白色。The vegetation coverage is below 20%; most of the area consists of mobile or semi-mobile dunes with large wind erosion pits; Landsat pixels are primarily light yellow and white. |
表2 沙化土地目视解译标志
Table 2 Visual interpretation signs of desertified land
沙化等级 Desertification level | 特征描述 Characteristic description |
|---|---|
未沙化土地 Non-desertified land | 植被覆盖度在70%以上;Landsat像元主要是绿色或浅红色。The vegetation coverage is above 70%; Landsat pixels are mainly green or light red. |
轻度沙化土地 Slightly desertified land | 植被覆盖度大于40%,小于70%;固定或半固定沙丘为主;Landsat像元主要为浅绿色。The vegetation coverage is between 40% and 70%; the area is mainly composed of fixed or semi-fixed dunes; Landsat pixels are primarily light green. |
中度沙化土地 Moderately desertified land | 植被覆盖度大于20%,小于40%;大部分为半固定沙丘,出现明显的风蚀坑;Landsat像元主要为黄色。The vegetation coverage is between 20% and 40%; most of the area consists of semi-fixed dunes with noticeable wind erosion pits; Landsat pixels are primarily yellow. |
重度沙化土地 Severely desertified land | 植被覆盖度低于20%;大部分是流动或半流动沙丘,带有大型风蚀坑;Landsat像元大部分像素是浅黄色和白色。The vegetation coverage is below 20%; most of the area consists of mobile or semi-mobile dunes with large wind erosion pits; Landsat pixels are primarily light yellow and white. |
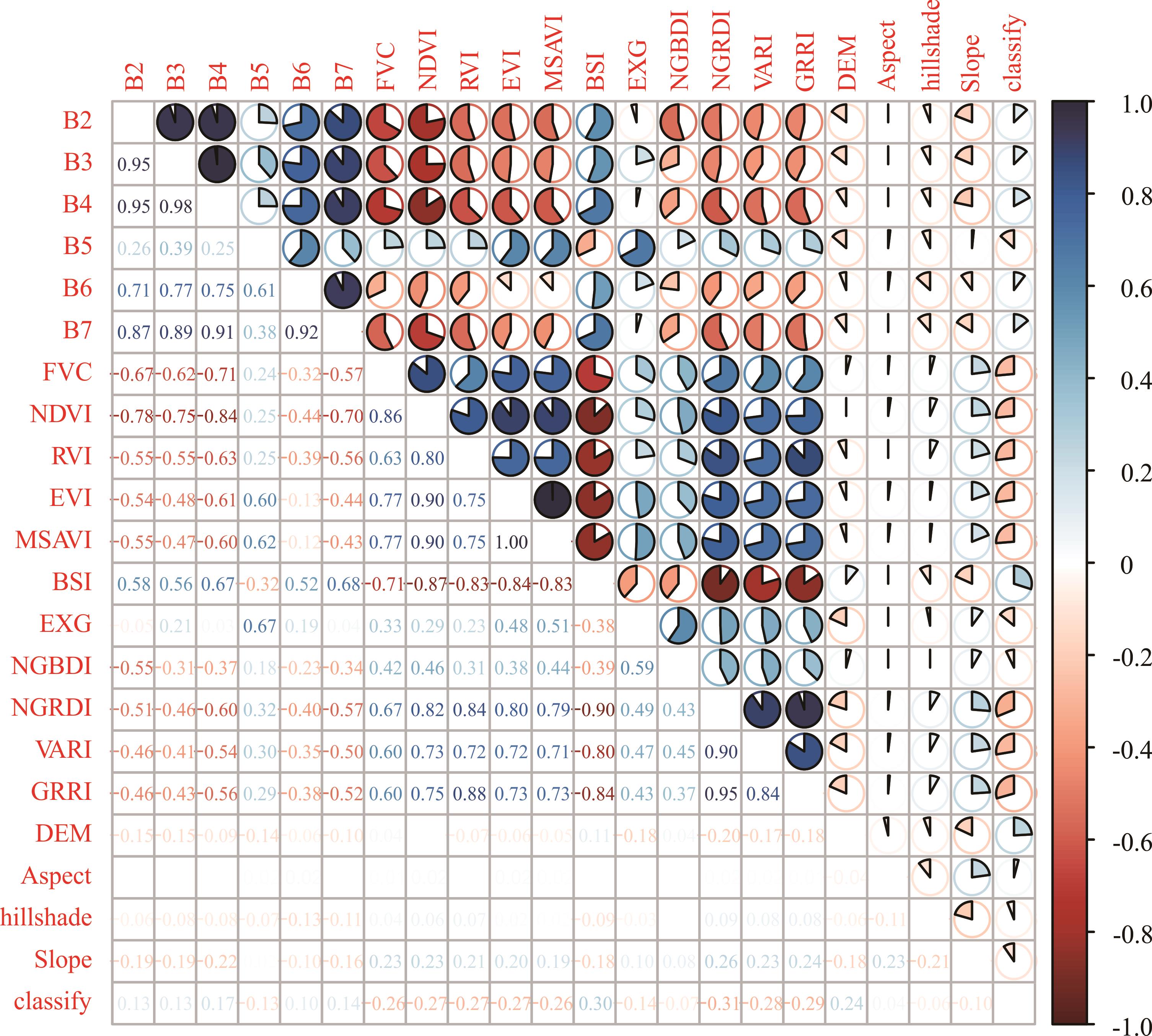
图3 皮尔逊相关系数B2: 蓝波段Blue;B3: 绿波段Green;B4: 红波段Red;B5: 近红外波段Near infrared;B6: 短波红外波段1 Shortwave infrared 1;B7: 短波红外波段2 Shortwave infrared 2;FVC: 植被覆盖度Fractional vegetaion coverage;NDVI: 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index;RVI: 比值植被指数Ratio vegetation index;EVI: 增强型植被指数Enhanced vegetation index;MSAVI: 修正型土壤调节植被指数Modified soil adjusted vegetation index;BSI: 裸土指数Bare soil index;EXG: 过量绿色植被指数Excess green vegetation index;NGBDI: 归一化绿蓝差异指数Normalized green-blue difference index;NGRDI: 归一化绿红差异指数Normalized green-red difference index;VARI: 可见抗大气指数Visible atmospherically resistant index;GRRI: 绿红比率指数Green-red ratio index;DEM: 高程Digital elevation model;Aspect: 坡向Aspect;hillshade: 山影Hillshade;Slope: 坡度S1ope;classify: 退化类型Degradation types.
Fig.3 Pearson correlation coefficient
情景 Scene | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy (%) | 类型 Type | 精确率 Precision (%) | F1分数 F1 score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
情景1 Scene 1 | 82.65 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 84.75 | 81.13 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 79.01 | 88.04 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 87.88 | 89.61 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 79.08 | 69.51 | ||
情景2 Scene 2 | 85.00 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 84.65 | 84.77 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 80.06 | 88.45 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 91.96 | 92.33 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 84.24 | 72.48 | ||
情景1+情景2 Scene 1+scene 2 | 86.88 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 85.87 | 85.48 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 82.61 | 90.19 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 93.48 | 93.34 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 86.30 | 77.24 | ||
情景1+情景2+情景3 Scene 1+scene 2+scene 3 | 92.85 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 92.48 | 92.34 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 90.98 | 95.18 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 94.73 | 95.85 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 93.31 | 87.46 |
表3 随机森林精度评价
Table 3 Random forest model accuracy evaluation
情景 Scene | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy (%) | 类型 Type | 精确率 Precision (%) | F1分数 F1 score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
情景1 Scene 1 | 82.65 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 84.75 | 81.13 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 79.01 | 88.04 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 87.88 | 89.61 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 79.08 | 69.51 | ||
情景2 Scene 2 | 85.00 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 84.65 | 84.77 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 80.06 | 88.45 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 91.96 | 92.33 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 84.24 | 72.48 | ||
情景1+情景2 Scene 1+scene 2 | 86.88 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 85.87 | 85.48 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 82.61 | 90.19 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 93.48 | 93.34 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 86.30 | 77.24 | ||
情景1+情景2+情景3 Scene 1+scene 2+scene 3 | 92.85 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 92.48 | 92.34 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 90.98 | 95.18 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 94.73 | 95.85 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 93.31 | 87.46 |
方法 Method | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy (%) | 类型 Type | 精确率 Precision (%) | F1分数 F1 score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
支持向量机 Support vector machine (SVM) | 70.38 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 98.74 | 47.53 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 98.46 | 97.32 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 99.47 | 71.49 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 45.78 | 62.45 | ||
分类回归树 Classification and regression tree (CART) | 72.00 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 87.69 | 77.29 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 58.14 | 71.28 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 83.19 | 81.15 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 70.41 | 56.80 | ||
随机森林 Random forest (RF) | 92.85 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 92.48 | 92.34 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 90.98 | 95.18 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 94.73 | 95.85 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 93.31 | 87.46 |
表4 情景1+情景2+情景3下不同算法精度对比
Table 4 Comparison of accuracy of different algorithms in scenario 1+scenario 2+scenario 3
方法 Method | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy (%) | 类型 Type | 精确率 Precision (%) | F1分数 F1 score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
支持向量机 Support vector machine (SVM) | 70.38 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 98.74 | 47.53 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 98.46 | 97.32 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 99.47 | 71.49 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 45.78 | 62.45 | ||
分类回归树 Classification and regression tree (CART) | 72.00 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 87.69 | 77.29 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 58.14 | 71.28 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 83.19 | 81.15 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 70.41 | 56.80 | ||
随机森林 Random forest (RF) | 92.85 | 未退化 Non-degraded | 92.48 | 92.34 |
| 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 90.98 | 95.18 | ||
| 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 94.73 | 95.85 | ||
| 其他类型退化 Other types of degradation | 93.31 | 87.46 |
年份 Year | 未退化 Non-degraded | 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 盐渍型退化 Salinization degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 75781.8747 | 44293.1067 | 223330.4289 | 107463.0735 |
| 2003 | 91086.8787 | 53386.1712 | 179527.6494 | 110216.2338 |
| 2013 | 101463.3261 | 59735.6037 | 171860.2281 | 90162.9081 |
| 2023 | 94859.8380 | 57372.4323 | 170713.3590 | 105526.4580 |
表5 各种类型退化面积统计
Table 5 Statistics of various types of degraded areas (km2)
年份 Year | 未退化 Non-degraded | 黑土滩型退化 Black soil beach-type degradation | 沙化型退化 Desertification-type degradation | 盐渍型退化 Salinization degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 75781.8747 | 44293.1067 | 223330.4289 | 107463.0735 |
| 2003 | 91086.8787 | 53386.1712 | 179527.6494 | 110216.2338 |
| 2013 | 101463.3261 | 59735.6037 | 171860.2281 | 90162.9081 |
| 2023 | 94859.8380 | 57372.4323 | 170713.3590 | 105526.4580 |

图4 三江源地区土地退化类型分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1822号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS(2019)1822 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig. 4 Distribution of land degradation types in Three-River Headwaters region
年份 Year | 未退化 Non-degraded | 轻度退化 Slight degradation | 中度退化 Moderate degradation | 重度退化 Severe degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 75781.8747 | 92374.6311 | 119822.5017 | 162889.4763 |
| 2003 | 91086.8787 | 87078.9942 | 90068.4612 | 165982.5990 |
| 2013 | 101463.3261 | 91723.8735 | 82493.1720 | 147541.6944 |
| 2023 | 94859.8380 | 104022.7740 | 90080.8839 | 139508.5914 |
表6 各种退化级别面积统计
Table 6 Statistics on the area of various degradation levels (km2)
年份 Year | 未退化 Non-degraded | 轻度退化 Slight degradation | 中度退化 Moderate degradation | 重度退化 Severe degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 75781.8747 | 92374.6311 | 119822.5017 | 162889.4763 |
| 2003 | 91086.8787 | 87078.9942 | 90068.4612 | 165982.5990 |
| 2013 | 101463.3261 | 91723.8735 | 82493.1720 | 147541.6944 |
| 2023 | 94859.8380 | 104022.7740 | 90080.8839 | 139508.5914 |

图5 三江源地区土地退化等级分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1822号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS(2019)1822 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig. 5 Distribution of land degradation levels in the Three-River Headwaters region

图6 三江源地区土地退化类型面积转移情况图中数据代表各退化类型及其转换面积(km2)。The data in the figure represents the types of degradation and their corresponding conversion areas (km2).
Fig. 6 Transfer situation of land degradation types and areas in the Three-River Headwaters region
| [1] | Ren Q, He C Y, Huang Q X, et al. Impacts of urban expansion on natural habitats in global drylands. Nature Sustainability, 2022, 5(10): 869-878. |
| [2] | Peng W Y, Li B J, Liu C. Xi Jinping’s important exposition on ecological security and the construction of ecological security system. Chinese Journal of Urban and Enviromental Studies, 2021(1): 20-34. |
| 彭文英, 李碧君, 刘灿. 习近平关于生态安全重要论述及生态安全体系建设研究. 城市与环境研究, 2021(1): 20-34. | |
| [3] | Chen Y N, Li Z Q, Xu J H, et al. Changes and protection suggestions in water resources and ecological environment in arid region of Northwest China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023, 38(3): 385-393. |
| 陈亚宁, 李忠勤, 徐建华, 等.中国西北干旱区水资源与生态环境变化及保护建议. 中国科学院院刊, 2023, 38(3): 385-393. | |
| [4] | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Land degradation. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 1971. |
| [5] | Chen A, Yang X C, Guo J, et al. Synthesized remote sensing-based desertification index reveals ecological restoration and its driving forces in the northern sand-prevention belt of China. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 131: 108230. |
| [6] | Wang Z, Song D X, He T, et al. Developing spatial and temporal continuous fractional vegetation cover based on Landsat and Sentinel-2 data with a deep learning approach. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(11): 2948. |
| [7] | Zhong G R, Chen J J, Huang R J, et al. High spatial resolution fractional vegetation coverage inversion based on UAV and Sentinel-2 data: A case study of alpine grassland. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(17): 4266. |
| [8] | Gao X C. Research on rodent damage and degradation of desert grassland based on UAV hyperspectral remote sensing. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2024. |
| 高新超. 基于无人机高光谱遥感的荒漠草原鼠害及退化研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2024. | |
| [9] | Jin E E D M T. Research on identification and inversion of degradation indicator of desert grassland based on hyperspectral remote sensing by unmanned aerial vehicle. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2024. |
| 金额尔都木吐. 基于无人机高光谱遥感的荒漠草原退化指示地物识别与反演研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2024. | |
| [10] | Wang H J, Fan W J, Cui Y K, et al. Hyperspectral remote sensing monitoring of grassland degradation. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2010, 30(10): 2734-2738. |
| 王焕炯, 范闻捷, 崔要奎, 等. 草地退化的高光谱遥感监测方法. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2010, 30(10): 2734-2738. | |
| [11] | Liu X D, Liu R T, Liu A J, et al. Study on information extraction and the dynamic monitoring of grassland coverage in Three River Source area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(2): 154-159. |
| 刘晓东, 刘荣堂, 刘爱军, 等.三江源地区草地覆盖遥感信息提取方法及动态研究. 草地学报, 2010, 18(2): 154-159. | |
| [12] | Li Y J, Zhang L. Sandy land monitoring method based on classification index model. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2021, 23(4): 680-691. |
| 李宇君, 张磊. 基于沙地指数模型的沙地监测方法. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(4): 680-691. | |
| [13] | Zhang Q, Zhou H K, Wang X L, et al. Research on comprehensive definition and classification of degraded grassland of black soil beach cased on morphology-vegetation-soil characteristics. Qinghai Science and Technology, 2023, 30(5): 19-26. |
| 张强, 周华坤, 王晓丽, 等. 基于形态-植被-土壤特征的黑土滩退化草地综合定义与分类方法研究. 青海科技, 2023, 30(5): 19-26. | |
| [14] | Chen G M. The status of the degraded pasture and its strategyes of management in black beach of the headwater region of the Three River. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2005(10): 37-39, 44. |
| 陈国明. 三江源地区“黑土滩”退化草地现状及治理对策. 四川草原, 2005(10): 37-39, 44. | |
| [15] | Ma Y S, Lang B N, Wang Q J. Review and prospect of the study on ‘black soil type’ deteriorated grassland. Pratacultural Science, 1999(2): 5-9. |
| 马玉寿, 郎百宁, 王启基. “黑土型”退化草地研究工作的回顾与展望. 草业科学, 1999(2): 5-9. | |
| [16] | Dang X P, Dong Y. Study on the dynamic changes of desertification land in the Three Rivers Source region of Qinghai Province. Inner Mongolia Forestry Investigation and Design, 2017, 40(6): 20-26. |
| 党晓鹏, 东雨. 青海省三江源地区沙化土地变化动态研究. 内蒙古林业调查设计, 2017, 40(6): 20-26. | |
| [17] | Shang Z H, Long R J. Formation reason and recovering problem of the‘black soil type’degraded alpine grassland in Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005(6): 652-656. |
| 尚占环, 龙瑞军. 青藏高原“黑土型”退化草地成因与恢复. 生态学杂志, 2005(6): 652-656. | |
| [18] | Shang Z H, Dong Q M, Shi J J, et al. Research progress in recent ten years of ecological restoration for “black soil land” degraded grassland on Tibetan Plateau-Concurrently discuss of ecological restoration in Sanjiangyuan region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. |
| 尚占环, 董全民, 施建军, 等. 青藏高原“黑土滩”退化草地及其生态恢复近10年研究进展——兼论三江源生态恢复问题. 草地学报, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. | |
| [19] | Yu Z R, Wang J W. Land salinization in China and the prevention countermeasures. Rural Eco-Environment, 1997, 13(3): 2-6. |
| 宇振荣, 王建武. 中国土地盐碱化及其防治对策研究. 农村生态环境, 1997, 13(3): 2-6. | |
| [20] | Ma H W, Wang Y F, Guo E L. Remote sensing monitoring of aeolian desertification in Ongniud Banner based on GEE. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(3): 504-516. |
| 马浩文, 王永芳, 郭恩亮. 基于GEE的翁牛特旗土地沙漠化遥感监测. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(3): 504-516. | |
| [21] | Xia L, Song X N, Cai S H, et al. Role of surface hydrothermal elements in grassland degradation over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 4618-4631. |
| 夏龙, 宋小宁, 蔡硕豪, 等. 地表水热要素在青藏高原草地退化中的作用. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11): 4618-4631. | |
| [22] | He H X, Yan J N, Liang D, et al. Time-series land cover change detection using deep learning-based temporal semantic segmentation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 305: 114101. |
| [23] | Li Z M, Chen B, Wu S B, et al. Deep learning for urban land use category classification: A review and experimental assessment. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 311: 114290. |
| [24] | Gao G Y, Liang Y, Liu J B, et al. A modified RUSLE model to simulate soil erosion under different ecological restoration types in the loess hilly area. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 2024, 12(2): 258-266. |
| [25] | Qiu H H, Hu B Q, Zhang Z. Impacts of land use change on ecosystem service value based on SDGs report-Taking Guangxi as an example. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 133: 108366. |
| [26] | Misuk K, KyuBaek H. An empirical evaluation of sampling methods for the classification of imbalanced data. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e0271260. |
| [27] | Millard K, Richardson M. On the importance of training data sample selection in random forest image classification: A case study in peatland ecosystem mapping. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(7): 8489-8515. |
| [28] | Wang F, Ding J L, Wu M C. Remote sensing monitoring models of soil salinization based on NDVI-SI feature space. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26(8): 168-173, 8. |
| 王飞, 丁建丽, 伍漫春. 基于NDVI-SI特征空间的土壤盐渍化遥感模型. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(8): 168-173, 8. | |
| [29] | Breiman L. Bagging predictors. Machine Learning, 1996, 24: 123-140. |
| [30] | Cortes C, Vapnik V. Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 1995, 20: 273-297. |
| [31] | Breiman L, Friedman J, Olshen R A, et al. Classification and regression trees. Routledge, 2017.https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315139470. |
| [32] | National Technical Committee on Desertification Control Standardization (SAC/TC 365). Specification for types and classification of land degradation: LY/T 3354-2023. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2023. |
| 全国荒漠化防治标准化技术委员会(SAC/TC 365). 土地退化类型与分级规范: LY/T 3354-2023. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2023. | |
| [33] | Liu K Y, Zhao Z Y, Li L. Research progress in the application of SAR data in soil salinity monitoring. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2024, 26(8): 1893-1910. |
| 刘康怡, 赵振宇, 李俐. SAR数据在土壤盐渍化监测中的应用研究进展.地球信息科学学报, 2024, 26(8): 1893-1910. | |
| [34] | Chen A, Xu C, Zhang M, et al. Cross-scale mapping of above-ground biomass and shrub dominance by integrating UAV and satellite data in temperate grassland. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 304: 114024. |
| [35] | Li W K, Zhao Q H, Jia S H, et al. Multi-feature and multi-level Sentinel-2 image extraction of lake and reservoir water bodies on Liaoning Province. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2024(3): 37-42, 106. |
| 李文康, 赵泉华, 贾淑涵, 等. 多特征多层次Sentinel-2影像辽宁省湖库水体提取. 测绘通报, 2024(3): 37-42, 106. |
| [1] | 王喆, 王镜, 颉耀文, 赵慧芳, 校瑞香, 宗萨才文求藏. 三江源地区草地地上生物量时空变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 1-12. |
| [2] | 佘洁, 沈爱红, 石云, 赵娜, 张风红, 何洪源, 吴涛, 李红霞, 马益婷, 朱晓雯. 基于无人机遥感影像和面向对象技术的荒漠草原植被分类[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 1-14. |
| [3] | 白宇飞, 尹航, 杨海波, 冯振华, 李斐. 无人机多光谱和RGB影像融合的苜蓿产量估测[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 45-58. |
| [4] | 李芳, 王广军, 杜海波, 李萌, 梁四海, 彭红明. 融合MODIS和Landsat数据的青海湖流域典型区NDVI重构与年内最大值变化分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 28-39. |
| [5] | 花蕊, 包达尔罕, 董瑞, 唐庄生, 楚彬, 郝媛媛, 花立民. 基于无人机遥感的天然草原鼠害发生面积调查方法研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 71-82. |
| [6] | 苗春丽, 李仲贤, 赵志成, 伏帅, 高金龙, 刘洁, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 栽培苜蓿草地智能感知系统关键生物物理指标实时监测及分析算法研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 90-103. |
| [7] | 赵翊含, 侯蒙京, 冯琦胜, 高宏元, 梁天刚, 贺金生, 钱大文. 基于Landsat 8和随机森林的青海门源天然草地地上生物量遥感估算[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 1-14. |
| [8] | 张玉琢, 杨志贵, 于红妍, 张强, 杨淑霞, 赵婷, 许画画, 孟宝平, 吕燕燕. 基于STARFM的草地地上生物量遥感估测研究——以甘肃省夏河县桑科草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 23-34. |
| [9] | 花蕊, 周睿, 包达尔罕, 董克池, 唐庄生, 花立民. 基于旋翼无人机低空遥感的高原鼠兔危害等级划分技术研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 165-176. |
| [10] | 张伟, 宜树华, 秦彧, 上官冬辉, 秦炎. 基于无人机的高寒草甸地表温度监测及影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 15-27. |
| [11] | 杨帆, 邵全琴, 郭兴健, 李愈哲, 王东亮, 张雅娴, 汪阳春, 刘纪远, 樊江文. 玛多县大型野生食草动物种群数量对草畜平衡的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 1-13. |
| [12] | 张永, 杨自辉, 郭树江, 王强强, 詹科杰, 张剑挥, 魏怀东. 基于遥感分析20年来民勤绿洲防护林带植被变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 14-24. |
| [13] | 荀其蕾,董乙强,安沙舟,闫凯. 基于MOD 09GA数据的新疆草地生长状况遥感监测研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 10-26. |
| [14] | 葛静, 孟宝平, 杨淑霞, 高金龙, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚, 黄晓东, 高新华, 李文龙, 张仁平, 王云龙. 基于UAV技术和MODIS遥感数据的高寒草地盖度动态变化监测研究—以黄河源东部地区为例[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(3): 1-12. |
| [15] | 杨淑霞, 张文娟, 冯琦胜, 孟宝平, 高金龙, 梁天刚. 基于MODIS逐日地表反射率数据的青南地区草地生长状况遥感监测研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 14-26. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||