
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1-14.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020398
Xin YANG1( ), Wen-xia CAO1, Xiao-jun YU1, Hai-bin WANG2, Yuan-yuan HAO1(
), Wen-xia CAO1, Xiao-jun YU1, Hai-bin WANG2, Yuan-yuan HAO1( )
)
Received:2020-08-24
Revised:2020-12-14
Online:2021-08-30
Published:2021-08-30
Contact:
Yuan-yuan HAO
Xin YANG, Wen-xia CAO, Xiao-jun YU, Hai-bin WANG, Yuan-yuan HAO. Dynamic monitoring of grassland resources and their responses to environmental factors in Qinghai Province based on analyses of daily MODIS NDVI data from the past 20 years[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 1-14.
| 类别Class | 类型Type | NDVI值NDVI value |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 冰雪覆盖 Cryoconite cover | -1.0~0 |
| Ⅱ | 无植被区No vegetation area | 0~0.1 |
| Ⅲ | 退化草地Depleted grassland | 0.1~0.4 |
| Ⅳ | 普通草地Ordinary grassland | 0.4~0.7 |
| Ⅴ | 优质草地High quality grassland | 0.7~1.0 |
Table 1 Growth status of grassland vegetation in Qinghai Province
| 类别Class | 类型Type | NDVI值NDVI value |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 冰雪覆盖 Cryoconite cover | -1.0~0 |
| Ⅱ | 无植被区No vegetation area | 0~0.1 |
| Ⅲ | 退化草地Depleted grassland | 0.1~0.4 |
| Ⅳ | 普通草地Ordinary grassland | 0.4~0.7 |
| Ⅴ | 优质草地High quality grassland | 0.7~1.0 |
区名 District name | 退化 Deterioration | 轻度退化 Mild deterioration | 稳定 Stablilzation | 轻度改善 Mild improvement | 改善 Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青海省Qinghai Province | 15.79 | 28.54 | 12.97 | 29.94 | 12.75 |
| 环湖及祁连山区Around the lake and Qilian Mountains | 9.91 | 29.19 | 13.31 | 34.49 | 13.10 |
| 柴达木盆地Qaidam Basin | 27.84 | 24.17 | 5.92 | 22.68 | 19.39 |
| 青南高原Southern Qinghai Plateau | 11.09 | 30.88 | 15.66 | 32.80 | 9.57 |
| 东部农业区The eastern agricultural region | 3.28 | 29.93 | 27.88 | 35.02 | 3.89 |
Table 2 Grassland change trends in various regions of Qinghai Province from 2000 to 2019 (%)
区名 District name | 退化 Deterioration | 轻度退化 Mild deterioration | 稳定 Stablilzation | 轻度改善 Mild improvement | 改善 Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青海省Qinghai Province | 15.79 | 28.54 | 12.97 | 29.94 | 12.75 |
| 环湖及祁连山区Around the lake and Qilian Mountains | 9.91 | 29.19 | 13.31 | 34.49 | 13.10 |
| 柴达木盆地Qaidam Basin | 27.84 | 24.17 | 5.92 | 22.68 | 19.39 |
| 青南高原Southern Qinghai Plateau | 11.09 | 30.88 | 15.66 | 32.80 | 9.57 |
| 东部农业区The eastern agricultural region | 3.28 | 29.93 | 27.88 | 35.02 | 3.89 |
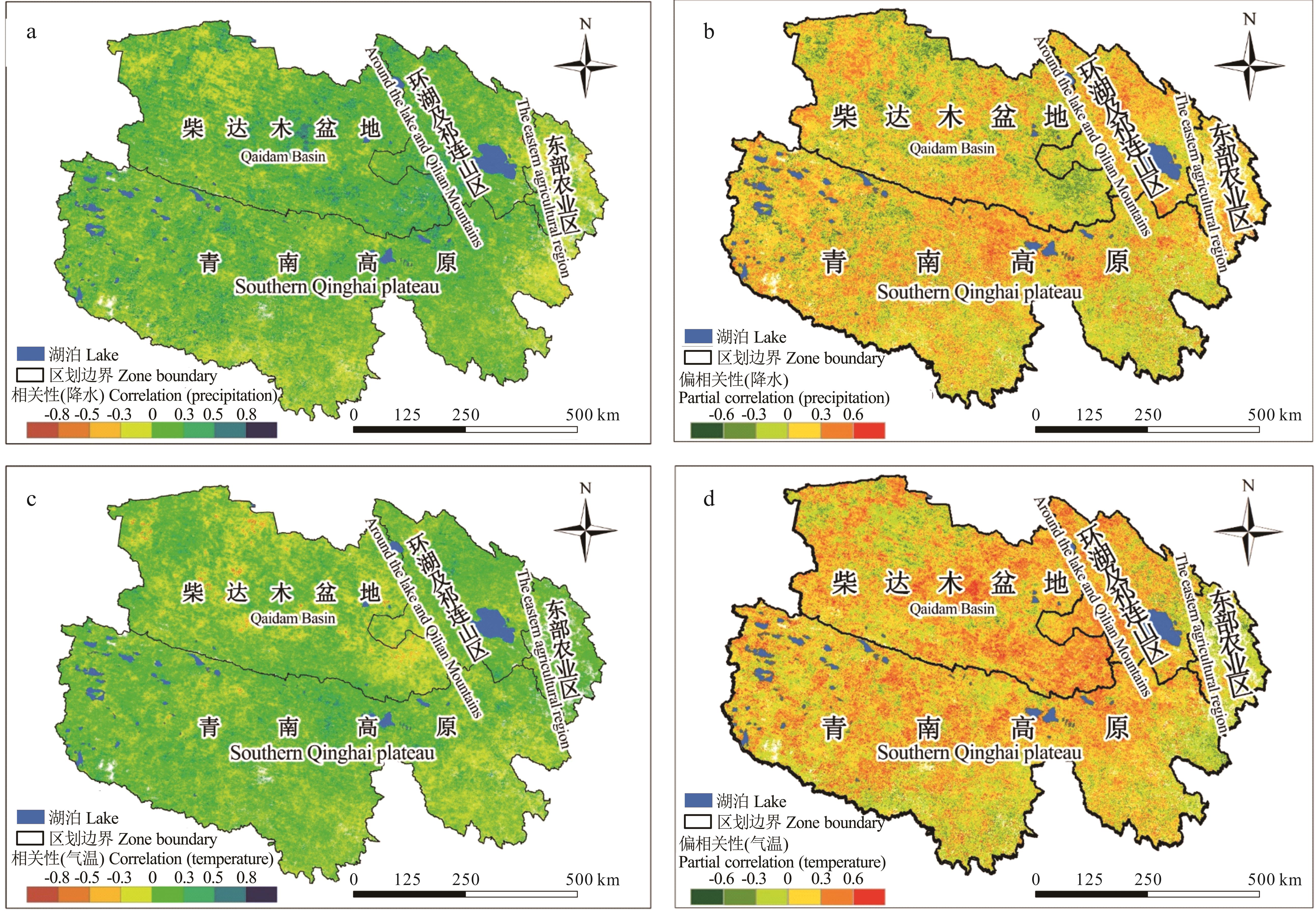
Fig.11 Correlation and partial correlation coefficients between grassland vegetation NDVI and precipitation or temperature in Qinghai Province from 2000 to 2015
| 1 | Li B. The rangeland degradation in North China and it’s preventive strategy. Chinese Agricultural Sciences, 1997(6): 2-10. |
| 李博. 中国北方草地退化及其防治对策. 中国农业科学, 1997(6): 2-10. | |
| 2 | Lv X, Wang J L, Kang H J, et al. Grass-stock balance analysis in Guoluo and Yushu areas of Qinghai Province from 2006 to 2015 based on estimation of yield by remote sensing. Journal of Natural Resources, 2018, 33(10): 1821-1832. |
| 吕鑫, 王卷乐, 康海军, 等. 基于遥感估产的2006-2015年青海果洛与玉树地区草畜平衡分析. 自然资源学报, 2018, 33(10): 1821-1832. | |
| 3 | Zhang G S, Fu Y, Yang Q, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and climate zoning of natural grassland types in Qinghai Province. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(1): 23-29. |
| 张国胜, 伏洋, 杨琼, 等. 青海省天然草地类型空间分布特征及气候分区. 草业科学, 2009, 26(1): 23-29. | |
| 4 | Qing D H. Highlights of the report of the first working group of the IPCC fifth assessment report. Progress in Climate Change Research, 2014, 10(1): 1-6. |
| 秦大河. IPCC第五次评估报告第一工作组报告的亮点结论. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(1): 1-6. | |
| 5 | Gottfried M, Pauli H, Futschik A, et al. Continent-wide response of mountain vegetation to climate change. Nature Climate Change, 2012, 2(2): 111-115. |
| 6 | Wu D H, Zhao X, Liang S L, et al. Time-lag effects of global vegetation responses to climate change. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21(9): 3520-3531. |
| 7 | Zhang J, Yuan M S, Zhang J, et al. The response of the NDVI dynamic changes of the alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau to natural and human factors in the past 30 years. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(18): 6269-6281. |
| 张江, 袁旻舒, 张婧, 等. 近30年来青藏高原高寒草地NDVI动态变化对自然及人为因子的响应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(18): 6269-6281. | |
| 8 | Cui B C, Zheng J H, Turxun H, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics of grassland net primary productivity (NPP) in the Tarim River basin. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. |
| 崔博超, 郑江华, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 等. 塔里木河流域草地净初级生产力时空分异特征研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. | |
| 9 | Wang T, Zhao Y Z, Wang H, et al. Temporal and spatial changes of the vegetation index of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on GIMMS NDVI and its response to temperature and precipitation. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2020, 42(2): 641-652. |
| 王涛, 赵元真, 王慧, 等. 基于GIMMS NDVI的青藏高原植被指数时空变化及其气温降水响应. 冰川冻土, 2020, 42(2): 641-652. | |
| 10 | Liu T, Jiang T, Guo L J. Remote sensing monitoring of grass yields of different types of grassland in the Three River Source Region based on MODIS. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 37(5): 18-26. |
| 刘唐, 江涛, 郭连杰. 基于MODIS的三江源地区不同类型草地草产量的遥感监测. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 37(5): 18-26. | |
| 11 | Liu S L, Zhao H D, Dong S K, et al. Research on vegetation dynamic changes in Altun Mountain Nature Reserve based on SPOT NDVI. Arid Zone Research, 2014, 31(5): 832-837. |
| 刘世梁, 赵海迪, 董世魁, 等. 基于SPOT NDVI的阿尔金山自然保护区植被动态变化研究. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31(5): 832-837. | |
| 12 | Zhao J Y, Peng J H. Analysis on the characteristics of temporal and spatial changes of vegetation cover in Qinghai Plateau based on MODIS NDVI. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(4): 67-73. |
| 赵健赟, 彭军还. 基于MODIS NDVI的青海高原植被覆盖时空变化特征分析. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(4): 67-73. | |
| 13 | Zhang J H, Feng Z M, Jiang L G, et al. Analysis of the correlation between vegetation NDVI and climate factors in the Lancang River Basin. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015, 30(9): 1425-1435. |
| 张景华, 封志明, 姜鲁光, 等. 澜沧江流域植被NDVI与气候因子的相关性分析. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(9): 1425-1435. | |
| 14 | Xu H R. Analysis of vegetation cover changes in Qinghai Province based on MODIS images. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2016. |
| 徐浩然. 基于MODIS影像的青海省植被覆盖变化分析. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2016. | |
| 15 | Wang J. Drought monitoring in Qinghai Province based on MODIS products. Changsha: Central South University, 2014. |
| 王君. 基于MODIS产品的青海省干旱监测. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014. | |
| 16 | Wang F K, Lei Y H, Du Z L, et al. The impact of climate change on the output of main crops in the Qaidam Basin. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(14): 107-112. |
| 王发科, 雷玉红, 都占良, 等. 气候变化对柴达木盆地主要农作物产量的影响. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(14): 107-112. | |
| 17 | Dou Y H. Vulnerability assessment of alpine grassland in Qingnan Plateau based on AHP. Qinghai Environment, 2018, 28(3): 145-150. |
| 窦永红. 基于AHP的青南高原高寒草地脆弱性评估. 青海环境, 2018, 28(3): 145-150. | |
| 18 | Suo L Z G, Yi X Z M. Response of vegetation index (NDVI) of Qingnan Plateau to climatic factors. Farm Staff, 2019(19): 150-151. |
| 索朗卓嘎, 益西卓玛. 青南高原植被指数(NDVI)对气候因子的响应. 农家参谋, 2019(19): 150-151. | |
| 19 | Liu F, Zeng Y N. Changes in the temporal and spatial patterns of vegetation NPP on the Qinghai Plateau in the past 16 years and the effects of climate and human factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(5): 1528-1540. |
| 刘凤, 曾永年. 近16年青海高原植被NPP时空格局变化及气候与人为因素的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(5): 1528-1540. | |
| 20 | Zhang X P, He W, Fang T. Emergy analysis of agricultural eco-economic system in Huangshui Valley-Taking Xining City as an example. Arid Land Geography, 2011, 34(2): 344-354. |
| 张小平, 何伟, 方婷. 湟水谷地农业生态经济系统的能值分析——以西宁市为例. 干旱区地理, 2011, 34(2): 344-354. | |
| 21 | Lu L P, Zhao C Y. Study on the spatial change of different desert vegetation indexes based on MODIS Data-Taking Sangong River Basin in Xinjiang as an example. Arid Land Geography, 2005, 28(3): 381-385. |
| 卢丽萍, 赵成义. 基于MODIS数据不同荒漠植被指数的空间变化研究——以新疆三工河流域为例. 干旱区地理, 2005, 28(3): 381-385. | |
| 22 | Liu Y, Li Y, Cui C X, et al. Application evaluation of MODIS MOD13Q1 data in desertification monitoring in Northern Xinjiang. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(3): 14-21. |
| 刘艳, 李杨, 崔彩霞, 等. MODIS MOD13Q1数据在北疆荒漠化监测中的应用评价. 草业学报, 2010, 19(3): 14-21. | |
| 23 | Wei Y X, Wang L W, Liu C. Grassland classification in Qinghai Province based on MODIS NDVI time series data. Resources Science, 2008, 30(5): 688-693. |
| 卫亚星, 王莉雯, 刘闯. 基于MODIS NDVI时序数据的青海省草地分级. 资源科学, 2008, 30(5): 688-693. | |
| 24 | Yang S X, Zhang W J, Feng Q S, et al. Remote sensing monitoring of grassland growth in Qingnan area based on MODIS daily surface reflectance data. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(8): 14-26. |
| 杨淑霞, 张文娟, 冯琦胜, 等. 基于MODIS逐日地表反射率数据的青南地区草地生长状况遥感监测研究. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 14-26. | |
| 25 | Sun L G, Liu J F, Xu Q H. Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation cover changes in Hebei Bashang area. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 2014, 26(1): 167-172. |
| 孙雷刚, 刘剑锋, 徐全洪. 河北坝上地区植被覆盖变化遥感时空分析. 国土资源遥感, 2014, 26(1): 167-172. | |
| 26 | Christian K. Mountain Ecosystems: Studies in treeline ecology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005, 86(42): 401. |
| 27 | Dai Z J, Zhao X, Li G W, et al. Based on GIMMS NDVI 3g.v1, the characteristics of spatial and temporal changes of NDVI in the vegetation growing season in Qinghai Province in recent 34 years. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(4): 713-725. |
| 代子俊, 赵霞, 李冠稳, 等. 基于GIMMS NDVI 3g.v1的近34年青海省植被生长季NDVI时空变化特征. 草业科学, 2018, 35(4): 713-725. | |
| 28 | Zhao W L, Luo T X, Zhang L. The relative influence of climate change and grazing on the vegetation index of typical alpine desert grassland in Tibet. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(22): 8494-8503. |
| 赵旺林, 罗天祥, 张林. 气候变化与放牧对西藏典型高寒荒漠草地植被指数变化的相对影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(22): 8494-8503. | |
| 29 | Zhao X Y, Wan W Y, Wang W J. The impact of climate change in the past 50 years on the production potential and phenological period of forages on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(4): 532-543. |
| 赵雪雁, 万文玉, 王伟军. 近50年气候变化对青藏高原牧草生产潜力及物候期的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(4): 532-543. | |
| 30 | Yang Y H. Carbon and nitrogen storage in alpine grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. Beijing: Peking University, 2008. |
| 杨元合. 青藏高原高寒草地生态系统碳氮储量. 北京: 北京大学, 2008. | |
| 31 | Chen J J, Yi S H, Qin Y, et al. The response of alpine grassland landscape to topographical factors and frozen soil types in the source area of the Shule River. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(6): 1599-1606. |
| 陈建军, 宜树华, 秦彧, 等. 疏勒河源区高寒草地景观对地形因子和冻土类型的响应. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(6): 1599-1606. | |
| 32 | Wang P L, Tang G L, Cao L J, et al. Surface air temperature variability and its relationship with altitude & latitude over the Tibetan Plateau in 1981-2010. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2012, 8(5): 313-319. |
| 33 | Zhang T R, Yan L D, Zhang F, et al. The impacts of climate on the natural pasture grass in Qinghai Province. Plateau Meteorology, 2007, 26(4): 724-731. |
| 34 | Lv X R, Lv X Y. Climate tendency analysis warming and drying in grassland of Northeast Qingzang Plateau of China. Grassland of China, 2002, 24(4): 8-13. |
| 35 | Yang Y H, Fang J Y, Pan Y D, et al. Aboveground biomass in Tibetan grasslands. Journal of Arid Environments, 2009, 73(1): 91-95. |
| [1] | Xiao-ding LIN, Le CHANG, Dan FENG. Remote-sensing estimation of vegetation gross primary productivity and its spatiotemporal changes in Qinghai Province from 2000 to 2019 [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 16-27. |
| [2] | Chen CHEN, Chang-qing JING, Wen-yuan XING, Xiao-jin DENG, Hao-yu FU, Wen-zhang GUO. Desert grassland dynamics in the last 20 years and its response to climate change in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 1-14. |
| [3] | SUN Si-si, WU Zhan-ping, XIAO Qi-tao, YU Fei, GU Shu-hong, FANG Di, LI Lang, ZHAO Xing-bing. Factors influencing CO2 fluxes of a grassland ecosystem on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 184-191. |
| [4] | Hui-fang ZHAO, Xiao-dong LI, Dong ZHANG, Rui-xiang XIAO. Aboveground biomass in grasslands in Qinghai Province estimated from MODIS data and its influencing factors [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 5-16. |
| [5] | WU Ni-tu, LIU Gui-xiang, YANG Yong, SONG Xiang-yang, BAI Hai-hua. Dynamic monitoring of net primary productivity and its response to climate factors in native grassland in Inner Mongolia using a light-use efficiency model [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 1-10. |
| [6] | LU Feng-shuai, ADE Lu-ji, CHENG Yun-xiang, HOU Fu-jiang. Relationship between soil moisture and vegetation cover in Qilian Mountain alpine steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 23-32. |
| [7] | NI Lu, WU Jing, LI Chun-bin, QIN Ge-xia, LI Zheng, KONG Jie. Temporal and spatial variations in natural grassland phenology in China over the last 30 years [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1): 1-12. |
| [8] | SHEN Bei-bei, DING Lei, LI Zhen-wang, XIN Xiao-ping, XU Da-wei, ZHU Xiao-yu, WANG Xu, CHEN Bao-rui. Analysis of spatio-temporal changes and climate-response of net primary production in Hulunbuir grassland [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(5): 1-14. |
| [9] | LI Chong-yang, FAN Wen-tao, LI Guo-mei, GAO Jing, TANG Zeng, SONG Ren-de. Driving force analysis of changes in grassland coverage on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on NDVI in 2000-2016 [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 25-32. |
| [10] | SUN Li-kun, LIU Guang-xiu, ZHANG Bao-gui, ZHANG Gao-sen. Effects of environmental factors on population genetic diversity of Tamarix chinensis [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 178-186. |
| [11] | LI Hong-mei. Analysis on the impact of climate change on vegetation in the Qaidam Basin [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(3): 13-23. |
| [12] | GE Jing, MENG Bao-Ping, YANG Shu-Xia, GAO Jin-Long, YIN Jian-Peng, ZHANG Ren-Ping, FENG Qi-Sheng, LIANG Tian-Gang. Monitoring of above-ground biomass in alpine grassland based on agricultural digital camera and MODIS remote sensing data: A case study in the Yellow River Headwater Region [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(7): 23-34. |
| [13] | GE Zhao-Xuan, SUN Guo-Long, YUAN Ye, HUANG Xuan-Rui, ZHANG Zhi-Dong. Herbaceous plant species diversity and functional diversity in the forest-steppe zone of Hebei, China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(7): 35-44. |
| [14] | LI Hai-Xia, YANG Jing, CHEN Ya-Ning, HAO Xing-Ming. Retrieval of soil moisture information in Xinjiang using MODIS [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(6): 16-27. |
| [15] | GE Jing, MENG Bao-Ping, YANG Shu-Xia, GAO Jin-Long, FENG Qi-Sheng, LIANG Tian-Gang, HUANG Xiao-Dong, GAO Xin-Hua, LI Wen-Long, ZHANG Ren-Ping, WANG Yun-Long. Dynamic monitoring of alpine grassland coverage based on UAV technology and MODIS remote sensing data-A case study in the headwaters of the Yellow River [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(3): 1-12. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||