
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 22-33.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020271
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gulnazar Ali, Hai-ning TAO, Zi-kui WANG( ), Yu-ying SHEN
), Yu-ying SHEN
Received:2020-06-15
Revised:2020-07-15
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-06-03
Contact:
Zi-kui WANG
Gulnazar Ali, Hai-ning TAO, Zi-kui WANG, Yu-ying SHEN. Evaluating the deep-horizon soil water content and water use efficiency in the alfalfa-wheat rotation system on the dryland of Loess Plateau using APSIM[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 22-33.
试验地点 Experiment site | 试验类型 Experiment design | 试验年限 Experiment period | 主要获取的数据Main extracted data | 水分测定深度Soil water depth (cm) | 数据用途 Data application in this study | 数据来源 Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 玉米-小麦-大豆轮作及苜蓿连作Zea mays-T. aestivum-Glycine max rotation and M. sativa continuous | 2001-2010 | 产量,土壤水分Biomass, soil water | 0~200 | 验证产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water | 杨轩[ Yang[ |
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 苜蓿-小麦轮作M. sativa-T. aestivum rotation | 1997-2003 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~300 | 验证短期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for short-term rotation | Shen et al.[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2006-2007 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | 万素梅[ Wan[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿-作物轮作M. sativa-crops rotation | 2005,2008 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | 方新宇[ Fang[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 1985-2001 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量和土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | Li et al.[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2007-2012 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | Cheng et al.[ |
Table 1 Information about the continuous alfalfa and alfalfa-wheat rotation experiment
试验地点 Experiment site | 试验类型 Experiment design | 试验年限 Experiment period | 主要获取的数据Main extracted data | 水分测定深度Soil water depth (cm) | 数据用途 Data application in this study | 数据来源 Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 玉米-小麦-大豆轮作及苜蓿连作Zea mays-T. aestivum-Glycine max rotation and M. sativa continuous | 2001-2010 | 产量,土壤水分Biomass, soil water | 0~200 | 验证产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water | 杨轩[ Yang[ |
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 苜蓿-小麦轮作M. sativa-T. aestivum rotation | 1997-2003 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~300 | 验证短期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for short-term rotation | Shen et al.[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2006-2007 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | 万素梅[ Wan[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿-作物轮作M. sativa-crops rotation | 2005,2008 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | 方新宇[ Fang[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 1985-2001 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量和土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | Li et al.[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2007-2012 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | Cheng et al.[ |
苜蓿生长年限 Phase of alfalfa in rotation (years) | 轮作小麦年限 Phase of wheat in rotation (year) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | |
| 2 | L2W2 | L2W4 | L2W6 | L2W8 | L2W10 | L2W12 | L2W14 | L2W16 | L2W18 |
| 4 | L4W2 | L4W4 | L4W6 | L4W8 | L4W10 | L4W12 | L4W14 | L4W16 | L4W18 |
| 6 | L6W2 | L6W4 | L6W6 | L6W8 | L6W10 | L6W12 | L6W14 | L6W16 | L6W18 |
| 8 | L8W2 | L8W4 | L8W6 | L8W8 | L8W10 | L8W12 | L8W14 | L8W16 | L8W18 |
| 10 | L10W2 | L10W4 | L10W6 | L10W8 | L10W10 | L10W12 | L10W14 | L10W16 | L10W18 |
| 12 | L12W2 | L12W4 | L12W6 | L12W8 | L12W10 | L12W12 | L12W14 | L12W16 | L12W18 |
| 14 | L14W2 | L14W4 | L14W6 | L14W8 | L14W10 | L14W12 | L14W14 | L14W16 | L14W18 |
| 16 | L16W2 | L16W4 | L16W6 | L16W8 | L16W10 | L16W12 | L16W14 | L16W16 | L16W18 |
| 18 | L18W2 | L18W4 | L18W6 | L18W8 | L18W10 | L18W12 | L18W14 | L18W16 | L18W18 |
Table 2 Scenarios of rotation phases in the alfalfa and wheat rotation systems
苜蓿生长年限 Phase of alfalfa in rotation (years) | 轮作小麦年限 Phase of wheat in rotation (year) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | |
| 2 | L2W2 | L2W4 | L2W6 | L2W8 | L2W10 | L2W12 | L2W14 | L2W16 | L2W18 |
| 4 | L4W2 | L4W4 | L4W6 | L4W8 | L4W10 | L4W12 | L4W14 | L4W16 | L4W18 |
| 6 | L6W2 | L6W4 | L6W6 | L6W8 | L6W10 | L6W12 | L6W14 | L6W16 | L6W18 |
| 8 | L8W2 | L8W4 | L8W6 | L8W8 | L8W10 | L8W12 | L8W14 | L8W16 | L8W18 |
| 10 | L10W2 | L10W4 | L10W6 | L10W8 | L10W10 | L10W12 | L10W14 | L10W16 | L10W18 |
| 12 | L12W2 | L12W4 | L12W6 | L12W8 | L12W10 | L12W12 | L12W14 | L12W16 | L12W18 |
| 14 | L14W2 | L14W4 | L14W6 | L14W8 | L14W10 | L14W12 | L14W14 | L14W16 | L14W18 |
| 16 | L16W2 | L16W4 | L16W6 | L16W8 | L16W10 | L16W12 | L16W14 | L16W16 | L16W18 |
| 18 | L18W2 | L18W4 | L18W6 | L18W8 | L18W10 | L18W12 | L18W14 | L18W16 | L18W18 |
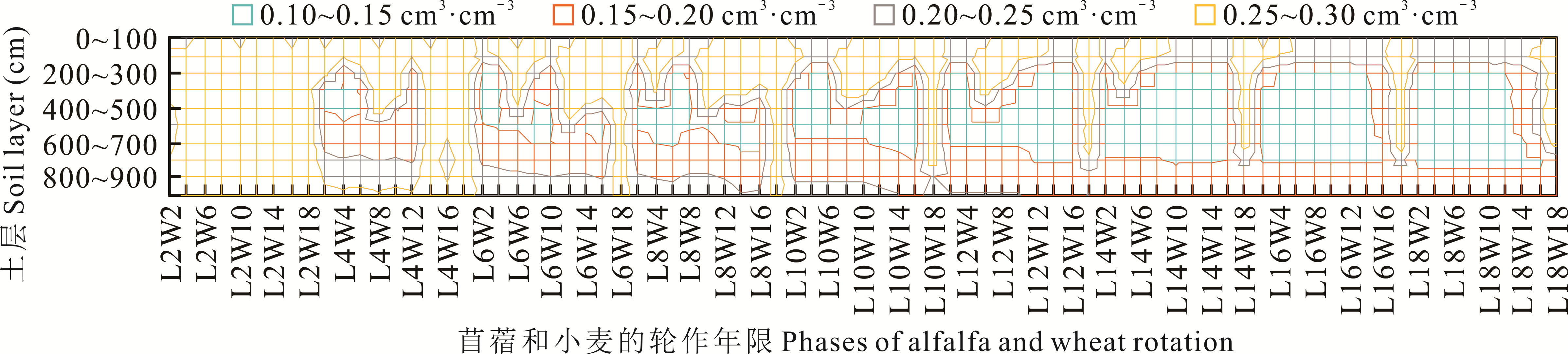
Fig.7 Soil water content distribution in the 0-1000 cm soil layer in alfalfa-wheat rotation field with different rotation patterns on the dryland of Loess Plateau
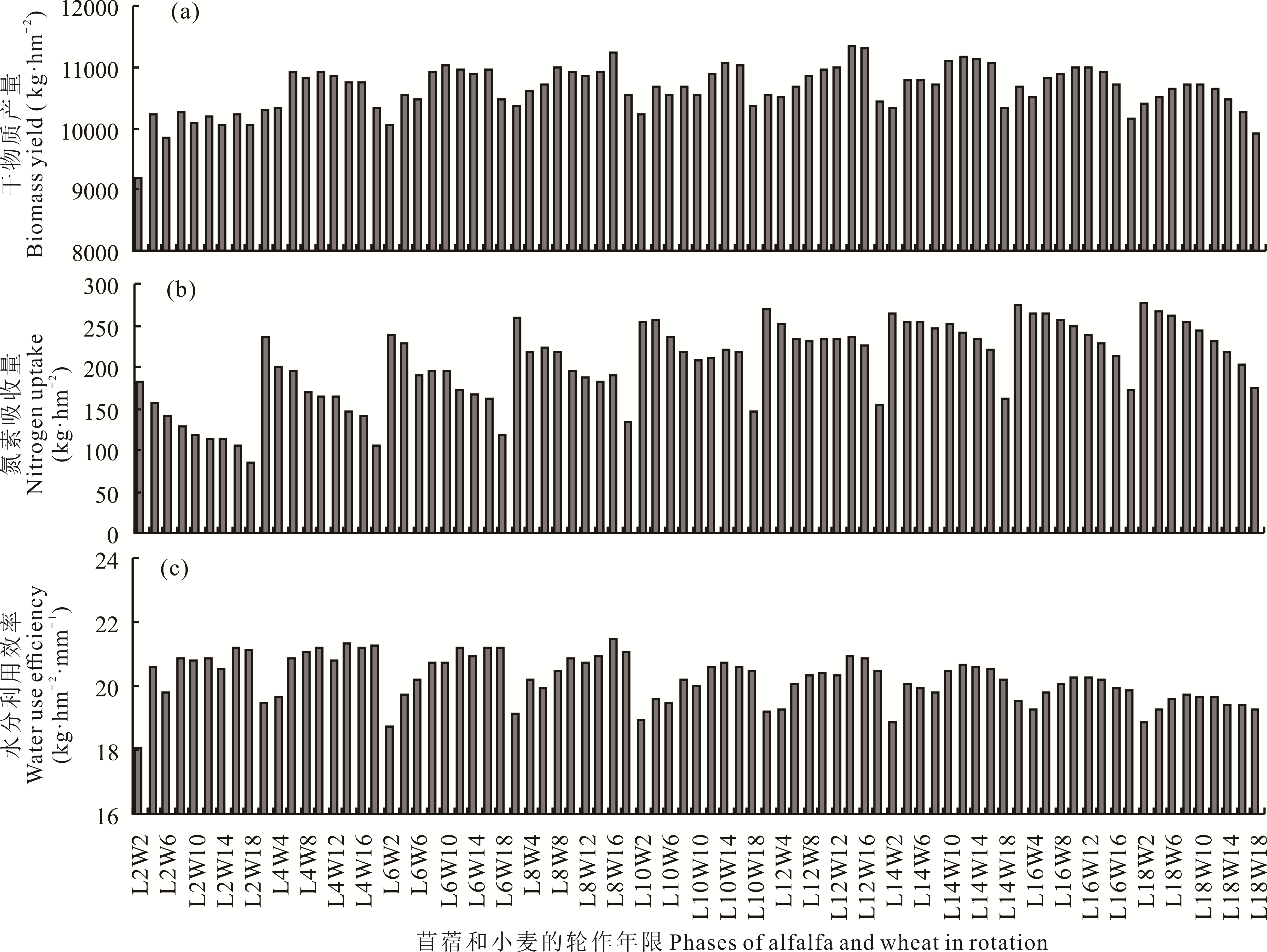
Fig.8 Biomass yield, nitrogen uptake and soil water content in alfalfa-wheat rotation field with different rotation patterns on the dryland of Loess Plateau
| 1 | Yang X, Li Z, Cui S, et al. Cropping system productivity and evapotranspiration in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China under future temperature and precipitation changes: An APSIM-based analysis of rotational vs. continuous systems. Agricultural Water Management, 2020, 229: 105959. |
| 2 | Fang X Y. Simulation of alfalfa-grain crop potation effects semi-humid areas of the loess plateau. Yangling: North West Agriculture and Forestry University, 2010. |
| 方新宇. 黄土高原半湿润区苜蓿—粮食作物轮作效应模拟研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. | |
| 3 | Jiang X J, Liu S, Zhang H. Effects of different management practices on vertical soil water flow patterns in the Loess Plateau. Soil and Tillage Research, 2017, 166: 33-42. |
| 4 | Wan S M. Study on alfalfa production performance and ifs ecological effects soil environment in the loess plateau. Yangling: North West Agriculture and Forestry University, 2008. |
| 万素梅. 黄土高原地区不同生长年限苜蓿生产性能及对土壤环境效应研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2008. | |
| 5 | Luo Z Z, Niu Y N, Li L L, et al. Response of soil physical properties to alfalfa growth years in the Western Loess Plateau. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(11): 1500-1507. |
| 罗珠珠, 牛伊宁, 李玲玲, 等. 黄土高原丘陵沟壑区土壤物理性质对苜蓿种植年限的响应. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(11): 1500-1507. | |
| 6 | Chen K. Dry soil layer formation and soil water recharging of alfalfa field on the Loess Plateau of Central Gansu. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 陈凯. 陇中黄土高原紫花苜蓿地土壤干层形成及其恢复效应研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013. | |
| 7 | Wang M Y, Li J, Sun J, et al. Soil desiccation characteristics of alfalfa grasslands and soil water restoration effects in alfalfa-grain crop rotations on the semi-arid areas of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(8): 4526-4534. |
| 王美艳, 李军, 孙剑, 等. 黄土高原半干旱区苜蓿草地土壤干燥化特征与粮草轮作土壤水分恢复效应. 生态学报, 2009, 29(8): 4526-4534. | |
| 8 | Li Y S. Productivity dynamic of alfalfa and its effects on water eco-environment. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002(3): 404-411. |
| 李玉山. 苜蓿生产力动态及其水分生态环境效应. 土壤学报, 2002(3): 404-411. | |
| 9 | Shan L, Liu Z M, Xin Y Q, et al. A study on the grass and field crops potation in mountain region of southern Ningxia. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 1992(4): 60-68. |
| 山仑, 刘忠民, 辛业全, 等. 宁夏山区草田轮作研究——不同轮作方式的生产力及效益. 水土保持学报, 1992(4): 60-68. | |
| 10 | Wang X C, Li J, Fang X Y, et al. Restoration of soil water in alfalfa-grain crop rotation fields on semi-arid region. Transactions of the CSAE, 2011, 27(1): 81-88. |
| 王学春, 李军, 方新宇, 等. 半干旱区草粮轮作田土壤水分恢复效应.农业工程学报, 2011, 27(1): 81-88. | |
| 11 | Shen Y Y, Nan Z B, Gao C Y, et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of soil water dynamics and crop yield response from a 4-year of lucerne and winter wheat rotation system in the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004(3): 640-647. |
| 沈禹颖, 南志标, 高崇岳, 等. 黄土高原苜蓿-冬小麦轮作系统土壤水分时空动态及产量响应. 生态学报, 2004(3): 640-647. | |
| 12 | Luo Y, Guo W. Development and problems of crop models. Transactions of the CSAE, 2008, 24(5): 307-312. |
| 13 | Shen Y Y, Nan Z B, Bill B, et al. Development of APSIM (agricultural production systems simulator) and its application. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(8): 1027-1032. |
| 沈禹颖, 南志标, Bill Bellotti, 等. APSIM 模型的发展与应用. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(8): 1027-1032. | |
| 14 | Yang X, Wang Z K, Cao Q, et al. Effects of precipitation and air temperature changes on yield of winter wheat, maize and lucerne in Eastern Gansu of China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(9): 106-114. |
| 杨轩, 王自奎, 曹铨, 等. 陇东地区几种旱作作物产量对降水与气温变化的响应. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(9): 106-114. | |
| 15 | Yang X. Effects of climate change on yield, water use and soil nutrients of the crop production systems on the Loess Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 杨轩. 气候变化对黄土高原作物生产系统产量、水分利用及土壤养分的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 16 | Shen Y Y, Li L L, Chen W, et al. Soil water, soil nitrogen and productivity of lucerne-wheat sequences on deep silt loams in a summer dominant rainfall environment. Field Crops Research, 2009, 111: 97-108. |
| 17 | Li Y S, Huang M B. Pasture yield and soil water depletion of continuous growing alfalfa in the Loess Plateau of China. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2008, 124: 24-32. |
| 18 | Cheng L P, Liu W Z. Long term effects of farming system on soil water content and dry soil layer in deep loess profile of loess tableland in China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2014, 13(6): 1382-1392. |
| 19 | Shen Y Y. Soil and crop composition dynamics of alfalfa-wheat rotation system on the Loess Plateau. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2004. |
| 沈禹颖. 黄土高原苜蓿-小麦轮作系统土壤与作物的组分动态. 广州: 中山大学, 2004. | |
| 20 | Chen W, Shen Y Y, Robertson M J, et al. Simulation analysis of Lucerne-wheat crop rotation on the Loess Plateau of Northern China. Field Crops Research, 2008, 108: 179-187. |
| 21 | Keating B A, Carberry P S, Hammer G L, et al. An overview of APSIM, a model designed for farming systems simulation. European Journal of Agronomy, 2003, 18(3): 267-288. |
| 22 | Wang L. Study on crop potential productivity and optimal irrigation technique in the north China plain by agricultural production system simulator. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2007. |
| 王琳. APSIM模型应用于华北平原作物生产潜力和节水优化模式. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2007. | |
| 23 | Dai T, Wang J, He D, et al. Adaptability of APSIM model in Southwestern China: A case study of winter wheat in Chongqing City.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(4): 1237-1243. |
| 戴彤, 王靖, 赫迪, 等. APSIM模型在西南地区的适应性评价——以重庆冬小麦为例. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(4): 1237-1243. | |
| 24 | Yang X. Analysis of the production potential of winter wheat, maize and lucerne based on the APSIM model. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013. |
| 杨轩. 基于APSIM模型的冬小麦、玉米和紫花苜蓿的生产潜力分析. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013. | |
| 25 | Liu P S, Li J, Jia Z K, et al. Effect of different alfalfa-rotation patterns on soil nutrient dynamic. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 32(3): 81-85. |
| 刘沛松, 李军, 贾志宽, 等. 不同草田轮作模式对土壤养分动态的影响. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(3): 81-85. | |
| 26 | Mao G L, Hu D Y, Xu X, et al. Effects of alfalfa post-harvest rotation on water use efficiency and crop yield in arid andy area. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(3): 219-224. |
| 毛桂莲, 虎德钰, 许兴, 等. 干旱风沙区苜蓿后茬不同轮作方式对水分利用效率和产量的影响. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(3): 219-224. | |
| 27 | Fan J, Hao M D, Shao M A. Water consumption of deep soil layers and eco-environmental effects of agricultural ecosystem in the Loess Plateau. Transactions of the CSAE, 2004(1): 61-64. |
| 樊军, 郝明德, 邵明安. 黄土旱塬农业生态系统土壤深层水分消耗与水分生态环境效应. 农业工程学报, 2004(1): 61-64. | |
| 28 | Cheng J M, Wan H E, Wang J. Alfalfa growth and its relation with soil water status in loess hilly and gully region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005(3): 435-438. |
| 程积民, 万惠娥, 王静. 黄土丘陵区紫花苜蓿生长与土壤水分变化. 应用生态学报, 2005(3): 435-438. |
| [1] | Dan-dan ZHANG, Yuan-qing ZHANG, Jing CHENG, Guang JIN, Bo LI, Dong-cai WANG, Fang XU, Rui-feng SUN. Effects of different roughage combinations on in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics of Jinnan cattle [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 93-100. |
| [2] | Zhen-feng ZANG, Jie BAI, Cong LIU, Kan-zhuo ZAN, Ming-xiu LONG, Shu-bin HE. Variety specificity of alfalfa morphological and physiological characteristics in response to drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [3] | Xiao-jun SUO, Nian ZHANG, Qian-ping YANG, Hu TAO, Qi XIONG, Xiao-feng LI, Feng ZHANG, Ming-xin CHEN. Effects of peanut vine and alfalfa meal on weight gain performance, internal organ development, and blood indexes of Boer×Macheng crossbred goats [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 146-154. |
| [4] | Zhan XIE, Lin MU, Zhi-fei ZHANG, Gui-hua CHEN, Yang LIU, Shuai GAO, Zhong-shan WEI. Effects on fermentation in alfalfa mixed silage of added lactic acid bacteria or organic acid salt combined with urea [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [5] | Ji-xiang WANG, Huan-yu GONG, Xiang-jian TU, Zhen-xing GUO, Jia-nan ZHAO, Jian SHEN, Zhen-yi LI, Juan SUN. Screening of phosphite-tolerant alfalfa varieties and identification of phosphite tolerance indicators [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 186-199. |
| [6] | Yi-yao HOU, Xiao LI, Rui-cai LONG, Qing-chuan YANG, Jun-mei KANG, Chang-hong GUO. Effect of overexpression of the alfalfa MsHB7 gene on drought tolerance of Arabidopsis [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [7] | Di ZHANG, Li-fei REN, Guang-bin LIU, Fu-qing LUO, Wen-hao ZHANG, Tian-zuo WANG. Comparative metabolite profiling of alfalfa seeds dried at different temperatures [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 158-166. |
| [8] | Bai-ping SHA, Ying-zhong XIE, Xue-qin GAO, Wei CAI, Bing-zhe FU. Effects of coupling of drip irrigation water and fertilizer on yield and quality of alfalfa in the yellow river irrigation district [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(2): 102-114. |
| [9] | Shuang LIU, Fu-ping HUI. Distribution of alfalfa in the Ming and Qing Dynasties and the underlying driving factors [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(2): 178-189. |
| [10] | Zhen-song LI, Li-qiang WAN, Shuo LI, Xiang-lin LI. Response of alfalfa root architecture and physiological characteristics to drought and rehydration [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [11] | WU Yong, LIU Xiao-jing, LIN Fang, TONG Chang-chun. A data envelopment analysis study of alfalfa fertilization responses and economic return in the desert irrigation area of Hexi [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(9): 94-105. |
| [12] | XING Yi-mei, DONG Li, ZHAN Li-feng, CAI Hua, YANG Sheng-qiu, SUN Na. Effect of mixed inoculation of Glomus mosseae and Sinorhizobium melilotion alkali resistance of alfalfa [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [13] | QIN Feng-fei, LI Zhi-hua, LIU Xin-bao, QU Hui, PINGCUO Zhuo-ma, LUOSONG Qun-cuo, SU Meng-han. Effects of exogenous 2, 4-epibrassinolide on the growth and photosynthesis of alfalfa under high temperature and low light stress in summer [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(9): 146-160. |
| [14] | TONG Chang-chun, LIU Xiao-jing, LIN Fang, YU Tie-feng. Yield effect of optimisation of photosynthetic characteristics of alfalfa through balanced fertilization [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| [15] | XIE De-jin, LI Jing-wen, YE You-jie, YIN Biao, REN Ke, CHEN Ling-yan, RONG Jun-dong, ZHENG Yu-shan. Effects of light quality on growth, and physiological and biochemical traits of Sarcandra glaba seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 104-115. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||