
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 139-154.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021499
Ying JIANG1( ), Chang WEI1(
), Chang WEI1( ), Qiu-juan JIAO1, Feng-min SHEN1, Ge-zi LI2, Xue-hai ZHANG2, Fang YANG3, Hai-tao LIU1(
), Qiu-juan JIAO1, Feng-min SHEN1, Ge-zi LI2, Xue-hai ZHANG2, Fang YANG3, Hai-tao LIU1( )
)
Received:2021-12-28
Revised:2022-03-09
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Hai-tao LIU
About author:First author contact:JIANG Ying、WEI Chang These authors contributed equally to this work.
Ying JIANG, Chang WEI, Qiu-juan JIAO, Feng-min SHEN, Ge-zi LI, Xue-hai ZHANG, Fang YANG, Hai-tao LIU. Effects of exogenous silicon application on physiological parameters, root architecture and diameter distribution of maize under cadmium stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 139-154.
生长指标 Growth index | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 47.00± 2.67a | 29.80± 0.79d | 33.50± 0.72c | 32.83± 2.19c | 38.73± 1.42b | 38.87± 1.07b | 33.53± 1.52c | 29.90± 1.06d |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 29.70± 1.30a | 21.37± 1.59cde | 18.67± 0.74e | 22.53± 1.47bcd | 22.07± 0.76bcd | 23.33± 3.13bc | 24.97± 1.88b | 19.97± 0.49de |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot weight (g) | 4.31± 0.46a | 1.78± 0.12b | 2.01± 0.33b | 1.83± 0.43b | 2.28± 0.29b | 2.45± 0.53b | 1.86± 0.31b | 0.92± 0.47c |
| 地下部鲜重Root weight (g) | 1.50± 0.21a | 0.95± 0.08bc | 1.13± 0.15abc | 1.19± 0.38abc | 1.22± 0.20abc | 1.49± 0.27a | 1.28± 0.10ab | 0.85± 0.22c |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight (g) | 0.31± 0.02a | 0.15± 0.01cd | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.16± 0.04cd | 0.20± 0.02bc | 0.22± 0.04b | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.12± 0.01d |
| 地下部干重Root dry weight (g) | 0.08± 0.01bc | 0.06± 0.00c | 0.07± 0.01bc | 0.09± 0.02bc | 0.10± 0.01ab | 0.11± 0.01a | 0.09± 0.01ab | 0.08± 0.02bc |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.26± 0.03d | 0.39± 0.05c | 0.45± 0.02bc | 0.53± 0.03b | 0.48± 0.03bc | 0.52± 0.04b | 0.53± 0.04b | 0.65± 0.13a |
| 茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 49.66± 4.52bc | 53.82± 9.55bc | 51.68± 12.18bc | 64.70± 7.22ab | 71.20± 12.36a | 53.89± 9.14bc | 39.93± 4.46c |
| 根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 73.68± 5.37c | 91.35± 11.38bc | 105.11± 27.94abc | 118.95± 16.89ab | 139.12± 13.63a | 108.98± 11.00ab | 99.55± 28.29bc |
Table 1 Effects of different Si treatment on the growth and tolerance index of maize seedlings under Cd stress (mean±SD)
生长指标 Growth index | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 47.00± 2.67a | 29.80± 0.79d | 33.50± 0.72c | 32.83± 2.19c | 38.73± 1.42b | 38.87± 1.07b | 33.53± 1.52c | 29.90± 1.06d |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 29.70± 1.30a | 21.37± 1.59cde | 18.67± 0.74e | 22.53± 1.47bcd | 22.07± 0.76bcd | 23.33± 3.13bc | 24.97± 1.88b | 19.97± 0.49de |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot weight (g) | 4.31± 0.46a | 1.78± 0.12b | 2.01± 0.33b | 1.83± 0.43b | 2.28± 0.29b | 2.45± 0.53b | 1.86± 0.31b | 0.92± 0.47c |
| 地下部鲜重Root weight (g) | 1.50± 0.21a | 0.95± 0.08bc | 1.13± 0.15abc | 1.19± 0.38abc | 1.22± 0.20abc | 1.49± 0.27a | 1.28± 0.10ab | 0.85± 0.22c |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight (g) | 0.31± 0.02a | 0.15± 0.01cd | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.16± 0.04cd | 0.20± 0.02bc | 0.22± 0.04b | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.12± 0.01d |
| 地下部干重Root dry weight (g) | 0.08± 0.01bc | 0.06± 0.00c | 0.07± 0.01bc | 0.09± 0.02bc | 0.10± 0.01ab | 0.11± 0.01a | 0.09± 0.01ab | 0.08± 0.02bc |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.26± 0.03d | 0.39± 0.05c | 0.45± 0.02bc | 0.53± 0.03b | 0.48± 0.03bc | 0.52± 0.04b | 0.53± 0.04b | 0.65± 0.13a |
| 茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 49.66± 4.52bc | 53.82± 9.55bc | 51.68± 12.18bc | 64.70± 7.22ab | 71.20± 12.36a | 53.89± 9.14bc | 39.93± 4.46c |
| 根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 73.68± 5.37c | 91.35± 11.38bc | 105.11± 27.94abc | 118.95± 16.89ab | 139.12± 13.63a | 108.98± 11.00ab | 99.55± 28.29bc |
项目 Item | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 总根长RL (cm) | 966.95±120.15a | 367.71±32.39b | 380.44±64.23b | 393.17±142.11b | 484.58±115.19b | 433.66±43.93b | 436.79±41.96b | 206.38±19.77c |
| 各分级总根长RL of each class (cm) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 794.09±104.54a | 266.37±14.84b | 290.32±43.70b | 290.55±129.39b | 358.25±98.33b | 297.63±39.49b | 284.08±28.68b | 115.60±17.26c |
| Ⅱ | 146.80±17.46a | 86.01±20.61bcd | 67.94±20.62d | 79.36±14.49bcd | 101.85±14.47b | 97.94±5.46bc | 130.00±15.51a | 71.24±5.93cd |
| Ⅲ | 16.10±2.26b | 9.43±1.67c | 11.83±2.01bc | 13.17±1.46bc | 15.30±2.37bc | 22.39±7.32a | 13.67±4.06bc | 10.61±1.19bc |
| Ⅳ | 9.60±3.06b | 5.85±1.59b | 10.31±0.66b | 10.02±2.99b | 9.13±2.70b | 15.49±5.20a | 8.93±3.13b | 8.83±0.89b |
| 根表面积SA (cm2) | 100.56±10.31a | 47.73±3.24de | 52.42±8.81cde | 56.09±14.61bcd | 68.12±13.74bc | 72.87±9.37b | 68.21±4.97bc | 36.29±4.09e |
| 各分级根表面积SA of each class (cm2) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 42.73±5.91a | 15.93±0.73b | 19.04±2.73b | 19.20±8.51b | 25.10±7.50b | 22.21±2.28b | 20.62±2.25b | 6.66±1.09c |
| Ⅱ | 32.49±3.91a | 18.75±4.14cd | 15.48±5.06d | 17.75±3.50cd | 23.11±3.12bc | 22.60±1.28bc | 28.80±3.31ab | 15.20±2.07d |
| Ⅲ | 6.05±0.87b | 3.57±0.59b | 4.45±0.78b | 4.93±0.53b | 5.69±0.82b | 8.62±2.93a | 5.15±1.56b | 4.08±0.48b |
| Ⅳ | 7.43±2.33b | 4.68±1.38b | 8.12±0.60b | 8.83±3.00ab | 7.27±2.23b | 12.82±4.35a | 7.38±2.04b | 7.24±1.03b |
| 根体积RV (cm3) | 0.83±0.07ab | 0.49±0.03d | 0.57±0.10cd | 0.65±0.11bcd | 0.76±0.13bc | 0.99±0.23a | 0.85±0.05ab | 0.51±0.07d |
| 各分级根体积RV of each class (cm3) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.23±0.04a | 0.09±0.01cd | 0.12±0.02bc | 0.12±0.05bc | 0.17±0.05b | 0.15±0.01b | 0.14±0.02bc | 0.04±0.01d |
| Ⅱ | 0.59±0.07a | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.29±0.10d | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.43±0.06bc | 0.43±0.03bc | 0.52±0.06ab | 0.27±0.05d |
| Ⅲ | 0.18±0.03b | 0.11±0.02b | 0.13±0.02b | 0.15±0.02b | 0.17±0.02b | 0.27±0.09a | 0.16±0.05b | 0.13±0.02b |
| Ⅳ | 0.54±0.17bc | 0.36±0.12c | 0.61±0.09bc | 0.84±0.36ab | 0.55±0.19bc | 1.03±0.33a | 0.61±0.13bc | 0.60±0.19bc |
| 平均直径RD (mm) | 0.33±0.01e | 0.41±0.01d | 0.44±0.00cd | 0.47±0.07bcd | 0.45±0.02cd | 0.54±0.07ab | 0.50±0.01abc | 0.56±0.03a |
| 根尖数RT | 1759.67±91.54a | 598.33±118.45bc | 513.33±74.57c | 564.00±190.84bc | 723.00±97.15bc | 603.33±147.55bc | 735.33±53.68b | 623.67±46.19bc |
| 分枝数RF | 3768.67±659.30a | 1111.67±62.77bc | 1225.67±282.53bc | 1313.67±507.38bc | 1578.67±391.95b | 1512.33±282.17b | 1451.00±178.10b | 641.00±142.45c |
Table 2 Effects of different Si treatment on root structure and root of different root diameters classes of maize seedlings under Cd stress (mean±SD)
项目 Item | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 总根长RL (cm) | 966.95±120.15a | 367.71±32.39b | 380.44±64.23b | 393.17±142.11b | 484.58±115.19b | 433.66±43.93b | 436.79±41.96b | 206.38±19.77c |
| 各分级总根长RL of each class (cm) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 794.09±104.54a | 266.37±14.84b | 290.32±43.70b | 290.55±129.39b | 358.25±98.33b | 297.63±39.49b | 284.08±28.68b | 115.60±17.26c |
| Ⅱ | 146.80±17.46a | 86.01±20.61bcd | 67.94±20.62d | 79.36±14.49bcd | 101.85±14.47b | 97.94±5.46bc | 130.00±15.51a | 71.24±5.93cd |
| Ⅲ | 16.10±2.26b | 9.43±1.67c | 11.83±2.01bc | 13.17±1.46bc | 15.30±2.37bc | 22.39±7.32a | 13.67±4.06bc | 10.61±1.19bc |
| Ⅳ | 9.60±3.06b | 5.85±1.59b | 10.31±0.66b | 10.02±2.99b | 9.13±2.70b | 15.49±5.20a | 8.93±3.13b | 8.83±0.89b |
| 根表面积SA (cm2) | 100.56±10.31a | 47.73±3.24de | 52.42±8.81cde | 56.09±14.61bcd | 68.12±13.74bc | 72.87±9.37b | 68.21±4.97bc | 36.29±4.09e |
| 各分级根表面积SA of each class (cm2) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 42.73±5.91a | 15.93±0.73b | 19.04±2.73b | 19.20±8.51b | 25.10±7.50b | 22.21±2.28b | 20.62±2.25b | 6.66±1.09c |
| Ⅱ | 32.49±3.91a | 18.75±4.14cd | 15.48±5.06d | 17.75±3.50cd | 23.11±3.12bc | 22.60±1.28bc | 28.80±3.31ab | 15.20±2.07d |
| Ⅲ | 6.05±0.87b | 3.57±0.59b | 4.45±0.78b | 4.93±0.53b | 5.69±0.82b | 8.62±2.93a | 5.15±1.56b | 4.08±0.48b |
| Ⅳ | 7.43±2.33b | 4.68±1.38b | 8.12±0.60b | 8.83±3.00ab | 7.27±2.23b | 12.82±4.35a | 7.38±2.04b | 7.24±1.03b |
| 根体积RV (cm3) | 0.83±0.07ab | 0.49±0.03d | 0.57±0.10cd | 0.65±0.11bcd | 0.76±0.13bc | 0.99±0.23a | 0.85±0.05ab | 0.51±0.07d |
| 各分级根体积RV of each class (cm3) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.23±0.04a | 0.09±0.01cd | 0.12±0.02bc | 0.12±0.05bc | 0.17±0.05b | 0.15±0.01b | 0.14±0.02bc | 0.04±0.01d |
| Ⅱ | 0.59±0.07a | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.29±0.10d | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.43±0.06bc | 0.43±0.03bc | 0.52±0.06ab | 0.27±0.05d |
| Ⅲ | 0.18±0.03b | 0.11±0.02b | 0.13±0.02b | 0.15±0.02b | 0.17±0.02b | 0.27±0.09a | 0.16±0.05b | 0.13±0.02b |
| Ⅳ | 0.54±0.17bc | 0.36±0.12c | 0.61±0.09bc | 0.84±0.36ab | 0.55±0.19bc | 1.03±0.33a | 0.61±0.13bc | 0.60±0.19bc |
| 平均直径RD (mm) | 0.33±0.01e | 0.41±0.01d | 0.44±0.00cd | 0.47±0.07bcd | 0.45±0.02cd | 0.54±0.07ab | 0.50±0.01abc | 0.56±0.03a |
| 根尖数RT | 1759.67±91.54a | 598.33±118.45bc | 513.33±74.57c | 564.00±190.84bc | 723.00±97.15bc | 603.33±147.55bc | 735.33±53.68b | 623.67±46.19bc |
| 分枝数RF | 3768.67±659.30a | 1111.67±62.77bc | 1225.67±282.53bc | 1313.67±507.38bc | 1578.67±391.95b | 1512.33±282.17b | 1451.00±178.10b | 641.00±142.45c |
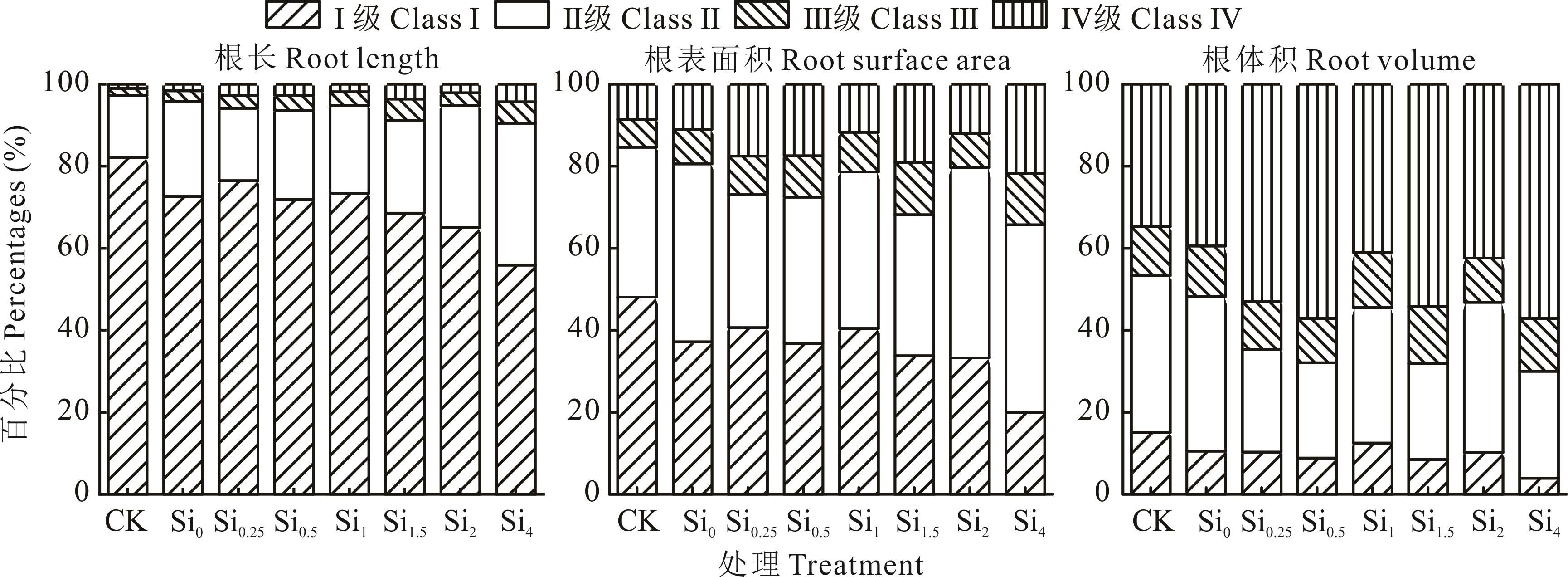
Fig.6 Effects of different Si treatment on maize seedling percentage of root length, root surface area and root volume in different root diameters under Cd stress
项目 Item | Cd处理 Cd treatment (μmol·L-1) | Si处理 Si treatment (mmol·L-1) | 平均值 Average value | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0.82 | 1 |
| Cd50Si0 | 50 | 0 | 0.31 | 7 |
| Cd50Si0.25 | 50 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 4 |
| Cd50Si0.5 | 50 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 5 |
| Cd50Si1 | 50 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 2 |
| Cd50Si1.5 | 50 | 1.50 | 0.49 | 3 |
| Cd5 Si2 | 50 | 2.00 | 0.36 | 6 |
| Cd50Si4 | 50 | 4.00 | 0.07 | 8 |
Table 3 Effects of different Si treatment on comprehensive evaluation of tolerance of maize seedlings under Cd stress
项目 Item | Cd处理 Cd treatment (μmol·L-1) | Si处理 Si treatment (mmol·L-1) | 平均值 Average value | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0.82 | 1 |
| Cd50Si0 | 50 | 0 | 0.31 | 7 |
| Cd50Si0.25 | 50 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 4 |
| Cd50Si0.5 | 50 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 5 |
| Cd50Si1 | 50 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 2 |
| Cd50Si1.5 | 50 | 1.50 | 0.49 | 3 |
| Cd5 Si2 | 50 | 2.00 | 0.36 | 6 |
| Cd50Si4 | 50 | 4.00 | 0.07 | 8 |
| 1 | Chen N C, Zheng Y J, He X F, et al. Analysis of the report on the national general survey of soil contamination. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692. |
| 陈能场, 郑煜基, 何晓峰, 等. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692. | |
| 2 | Liu C F, Shi G R, Yu R G, et al. Eco-physiological mechanisms of silicon-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in plants: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(23): 7799-7810. |
| 刘彩凤, 史刚荣, 余如刚, 等. 硅缓解植物镉毒害的生理生态机制. 生态学报, 2017, 37(23): 7799-7810. | |
| 3 | Satarug S, Garrett S H, Sens M A, et al. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2010, 118(2): 182-190. |
| 4 | Nishijo M, Nakagawa H, Suwazono Y, et al. Causes of death in patients with Itai-itai disease suffering from severe chronic cadmium poisoning: A nested case-control analysis of a follow-up study in Japan. BMJ Open, 2017, 7(7): e015694. |
| 5 | Malcovska S M, Ducaiova Z, Maslanakova I, et al. Effect of silicon on growth, photosynthesis, oxidative status and phenolic compounds of maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium excess. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2014, 225(8): 2056. |
| 6 | Chen J J, Yu W, Zu Y Q, et al. Variety difference of Cd accumulation and translocation in Zea mays. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(10): 1671-1676. |
| 陈建军, 于蔚, 祖艳群, 等. 玉米(Zea mays)对镉积累与转运的品种差异研究. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(10): 1671-1676. | |
| 7 | Qu D Y, Zhang L G, Gu W R, et al. Effects of chitosan on root growth and leaf photosynthesis of maize seedlings under cadmium stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(5): 1300-1309. |
| 曲丹阳, 张立国, 顾万荣, 等. 壳聚糖对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗根系生长及叶片光合的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(5): 1300-1309. | |
| 8 | Zhang C C, Chang J T, Gao S L, et al. Effects of silicon on yield and physiological characteristics of rice plants under cadmium and zinc stress. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 26(6): 936-941. |
| 张翠翠, 常介田, 高素玲, 等. 硅处理对镉锌胁迫下水稻产量及植株生理特性的影响. 核农学报, 2012, 26(6): 936-941. | |
| 9 | Wang H, Zhao S C, Xia W J, et al. Effect of cadmium stress on photosynthesis, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008(1): 36-42. |
| 汪洪, 赵士诚, 夏文建,等. 不同浓度镉胁迫对玉米幼苗光合作用、脂质过氧化和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008(1): 36-42. | |
| 10 | Qu D Y, Gu W R, Li L J, et al. Regulation of chitosan on the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in Zea mays seedling leaves under cadmium stress. Plant Science Journal, 2018, 36(2): 291-299. |
| 曲丹阳, 顾万荣, 李丽杰,等. 壳聚糖对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗叶片AsA-GSH循环的调控效应. 植物科学学报, 2018, 36(2): 291-299. | |
| 11 | Wu Z C, Zhao X H, Sun X C, et al. Antioxidant enzyme systems and the ascorbate-glutathione cycle as contributing factors to cadmium accumulation and tolerance in two oilseed rape cultivars (Brassica napus L.) under moderate cadmium stress. Chemosphere, 2015, 138(11): 526-536. |
| 12 | Yu K L, Zou J, Zou J H. Effects of cadmium stress on antioxidant enzyme system and absorption of mineral elements in maize seedlings. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(6): 1050-1056. |
| 宇克莉, 邹婧, 邹金华. 镉胁迫对玉米幼苗抗氧化酶系统及矿质元素吸收的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(6): 1050-1056. | |
| 13 | Xu H X, Weng X Y, Mao W H, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and excitation energy distribution in leaves of rice. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(4): 338-342. |
| 徐红霞, 翁晓燕, 毛伟华, 等. 镉胁迫对水稻光合、叶绿素荧光特性和能量分配的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(4): 338-342. | |
| 14 | Yu K L, Meng Q M, Zou J H. Effects of Cd2+ on seedling growth, chlorophyll contents and ultrastructures in maize. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010, 25(3): 118-123. |
| 宇克莉, 孟庆敏, 邹金华. 镉对玉米幼苗生长、叶绿素含量及细胞超微结构的影响. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(3): 118-123. | |
| 15 | Ge C L, Luo J F, Liu C, et al. Effect of heavy metals on the photosynthesis and photosynthates transformation in rice. Acta Agriculturae Nucleatae Sinica, 2005,19(3): 214-218. |
| 葛才林, 骆剑峰, 刘冲,等. 重金属对水稻光合作用和同化物输配的影响. 核农学报, 2005,19(3): 214-218. | |
| 16 | Ge C L. Molecular mechanism of heavy metals toxicity and tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2002. |
| 葛才林. 水稻 (Oryza sativa L.)和小麦(Triticum aestivum L.) 的重金属毒害与耐性的分子机理研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2002. | |
| 17 | Wei C, Jiao Q J, Liu H T, et al. Physiological effects of different Cd concentrations on maize root architecture and classification. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. |
| 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 柳海涛, 等. 镉暴露条件下玉米生长及根系构型分级特征研究. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. | |
| 18 | He J Y, Wang Y Y, Ren Y F, et al. Effect of cadmium on root morphology and physiological characteristics of rice seedlings. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(5): 1863-1868. |
| 何俊瑜, 王阳阳, 任艳芳, 等. 镉胁迫对不同水稻品种幼苗根系形态和生理特性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(5): 1863-1868. | |
| 19 | Ma J F. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2004, 50(1): 11-18. |
| 20 | Epstein E. Silicon: Its manifold roles in plants. Annals of Applied Biology, 2009, 155(2): 155-160. |
| 21 | Chen D M, Chen D Q, Xue R R, et al. Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 367: 447-455. |
| 22 | Zhang J L, Zhu C H, Dou P, et al. Effect of phosphorus and silicon application on the uptake and utilization of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium by maize seedlings. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(5): 677-688. |
| 张嘉莉, 朱从桦, 豆攀, 等. 硅、磷配施对玉米苗期生长及氮磷钾积累的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(5): 677-688. | |
| 23 | Shi Z Y, Yang S Q, Han D, et al. Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.) by reducing cadmium ion uptake and enhancing antioxidative capacity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(8): 7638-7646. |
| 24 | Wu J W, Geilfus C M, Pitann B, et al. Silicon-enhanced oxalate exudation contributes to alleviation of cadmium toxicity in wheat. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2016, 131: 10-18. |
| 25 | Zhu X F, Zheng C, Hu Y T, et al. Cadmium-induced oxalate secretion from root apex is associated with cadmium exclusion and resistance in Lycopersicon esculentum. Plant Cell and Environment, 2011, 34(7): 1055-1064. |
| 26 | Ma J, Cai H M, He C W, et al. A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon inhibits cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells. New Phytologist, 2015, 206(3): 1063-1074. |
| 27 | Vaculik M, Landberg T, Grege M, et al. Silicon modifies root anatomy, and uptake and subcellular distribution of cadmium in young maize plants. Annals of Botany, 2012, 110(2): 433-443. |
| 28 | Greger M, Kabir A H, Landberg T, et al. Silicate reduces cadmium uptake into cells of wheat. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 211: 90-97. |
| 29 | Wang X K, Huang J L. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015. |
| 王学奎, 黄见良. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015. | |
| 30 | Shi G R, Xia S L, Ye J, et al. PEG-simulated drought stress decreases cadmium accumulation in castor bean by altering root morphology. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2015, 111(3): 127-134. |
| 31 | Zadeh L A. Fuzzy sets. Information & Control, 1965, 8(3): 338-353. |
| 32 | Huang H L, Li M, Rizwan M, et al. Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 401: 123393. |
| 33 | Shi Y, Zhang Y, Han W H, et al. Silicon enhances water stress tolerance by improving root hydraulic conductance in Solanum lycopersicum L. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 196. |
| 34 | Feng J P, Shi Q H, Wang X F, et al. Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. Scientia Horticulturae, 2010, 123(4): 521-530. |
| 35 | Yang C G, Dou H, Liang Y C, et al. Influence of silicon on cadmium availability and cadmium uptake by maize in cadmium-contaminated soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(1): 116-121. |
| 杨超光, 豆虎, 梁永超, 等. 硅对土壤外源镉活性和玉米吸收镉的影响. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(1): 116-121. | |
| 36 | Ozyigit I I, Baktibekova D, Hocaoglu-Ozyigit A, et al. The effects of cadmium on growth, some anatomical and physiological parameters of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, 2021, 4(2): 235-253. |
| 37 | Shen C X, Yu Z L, Que Z Q. Physiological and morphological responses of the rice TP309 to short-term cadmium stress. Journal of Yichun University, 2019, 41(12): 5-9. |
| 沈春修, 於紫蕾, 却志群. 水稻品种台北309对短期镉胁迫的生理及形态响应. 宜春学院学报, 2019, 41(12): 5-9. | |
| 38 | Zhang L, Li J M, Wang H X. Physiological and ecological responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root to cadmium stress. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002, 33(1): 61-65. |
| 张玲, 李俊梅, 王焕校. 镉胁迫下小麦根系的生理生态变化. 土壤通报, 2002, 33(1): 61-65. | |
| 39 | Chen C F. The effect and mechanism of silicon on alleviating cadmium contamination of Chinese cabbage. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Soil Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry), 2007. |
| 陈翠芳. 硅对减轻黑叶白菜镉污染的效应及其机制. 北京: 中国科学院大学 (广州地球化学研究所), 2007. | |
| 40 | Dai Z, Wang C Y, Li N, et al. Effects of combined application of selenium and silicon on cadmium and mineral elements in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) under cadmium stress. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(1): 108-117. |
| 代邹, 王春雨, 李娜, 等. 硒、硅配施对镉胁迫下杂交稻中镉及矿质元素的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(1): 108-117. | |
| 41 | Nwugo C C, Huerta A J. Effects of silicon nutrition on cadmium uptake, growth and photosynthesis of rice plants exposed to low-level cadmium. Plant and Soil, 2008, 311(1/2): 73-86. |
| 42 | Wang P T, Zhao J, Yu H H. Reactive oxygen species signaling in stomata. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2014, 49(4): 490-503. |
| 王棚涛, 赵晶, 余欢欢. 气孔运动中的活性氧信号. 植物学报, 2014, 49(4): 490-503. | |
| 43 | Wang X M, Zhao X X, Huang L S, et al. The Na+ and K+ accumulative effect of four different salt tolerance genotypes in rice under salt stress. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(11): 2140-2146. |
| 王旭明, 赵夏夏, 黄露莎, 等. 盐胁迫下4个不同耐盐基因型水稻Na+、K+积累效应. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(11): 2140-2146. | |
| 44 | Israelsson M, Siegel R S, Young J, et al. Guard cell ABA and CO2 signaling network updates and Ca2+ sensor priming hypothesis. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2006, 9(6): 654-663. |
| 45 | Farooq M A, Ali S, Hameed A, et al. Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 96: 242-249. |
| 46 | Rahman S U, Qi X B, Kamran M, et al. Silicon elevated cadmium tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by endorsing nutrients uptake and antioxidative defense mechanisms in the leaves. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 166: 148-159. |
| 47 | Farquhar G D, Sharkey T D. Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Annual Reviews Plant Physiology, 1982, 33: 317-345. |
| 48 | Zhou Z, Zhang B, Liu H T, et al. Zinc effects on cadmium toxicity in two wheat varieties (Triticum aestivum L.) differing in grain cadmium accumulation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 183: 109562. |
| 49 | Hossain M T, Mori R, Soga K, et al. Growth promotion and an increase in cell wall extensibility by silicon in rice and some other Poaceae seedlings. Journal of Plant Research, 2002, 115(1117): 23-27. |
| 50 | Cunha K P V D, Nascimento C W A D. Silicon effects on metal tolerance and structural changes in maize (Zea mays L.) grown on a cadmium and zinc enriched soil. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2009, 197: 323-330. |
| 51 | Fan X Y, Wen X H, Huang F, et al. Effects of silicon on morphology, ultrastructure and exudates of rice root under heavy metal stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38(8): 197. |
| [1] | Ying-zheng LI, Yu-lin CHENG, Lu-lu XU, Wan-song LI, Xu YAN, Xiao-feng LI, Ru-yu HE, Yang ZHOU, Jun-jun ZHENG, Xing-yu WANG, De-long ZHANG, Ming-jun CHENG, Yun-hong XIA, Jian-mei HE, Qi-lin TANG. A comparative study of silage quality characteristics of whole-plant, whole-ear and whole-straw silage of different maize varieties (lines) [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [2] | Ji-peng TIAN, Bei-yi LIU, Hong-ru GU, Cheng-long DING, Yun-hui CHENG, Zhu YU. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and calcium propionate on fermentation quality and mycotoxin contents of whole plant maize and oat silages [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 157-166. |
| [3] | Qing ZHANG, Jing XING, Jia-ming YAO, Ting-chao YIN, Xin-ru HUANG, Yue HE, Jing ZHANG, Bin XU. The role of a cytokinin signaling pathway type-B ARR transcription factor, LpARR10, in cadmium tolerance of perennial ryegrass [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [4] | Chang WEI, Qiu-juan JIAO, Hai-tao LIU, Jing-jing ZHANG, Feng-min SHEN, Ying JIANG, Xue-hai ZHANG, Luan-zi SUN, Fang YANG, Zhen LIU. Physiological effects of different Cd concentrations on maize root architecture and classification [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. |
| [5] | Yu-huan WU, Zi-kui WANG, Ya-nan LIU, Qian-hu MA. Effects of row configuration on characteristics of the light environment and light use efficiency in maize/alfalfa intercropping [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 144-155. |
| [6] | Xin-ming WU, Zhi-hong FANG, Hui-wu CHI, Hui-li JIA, Jian-ning LIU, Yong-hong SHI, Xue-min WANG. Comparison of 30 maize (Zea mays) varieties for food and feed in the Yanmenguan area [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. |
| [7] | Hui-li WU, Wei TIAN, Yan-ling JI, Lai-qing LOU, Qing-sheng CAI. Screening for plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that promote cadmium absorption and accumulation and their effects on annual ryegrass [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 53-61. |
| [8] | Li-qin HUANG, Song-qiao LI, Zhen-zhong YUAN, Jing TANG, Jing-cai YAN, Qi-yuan TANG. Effects of feeding co-fermented whole plant rice and spent mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) substrate on slaughter performance, meat quality and organ size indexes of Liuyang black goats [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 133-140. |
| [9] | He-xing QI, Guang-xin LU, Zong-ren LI, Cheng-ti XU, Ke-jia DE, Xiao-juan ZHOU, Ying-cheng WANG, Gui-hua MA. Identification and pathogenicity of Alternaria leaf blight strains in silage maize in Qinghai Province [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 94-105. |
| [10] | Xiong-xiong LI, Ting JIAO, Sheng-guo ZHAO, Wei-na QIN, Xue-mei GAO, Zheng-wen WANG, Jian-ping WU, Zhao-min LEI. Synergistic effect of oregano essential oil and organic cobalt on degradation characteristics of silage maize stalks and rumen fermentation of sheep [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 191-202. |
| [11] | Zhen-song LI, Li-qiang WAN, Shuo LI, Xiang-lin LI. Response of alfalfa root architecture and physiological characteristics to drought and rehydration [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [12] | Jia-meng GUO, Ling-zhi HE, Dong-liang YAN, Zhuo LI, Yong-chao WANG, Rui-xin SHAO, Qing-hua YANG. Effects of controlled release nitrogen and urea ratio on nitrogen accumulation, transfer, and nitrogen-use efficiency of different summer maize varieties [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 81-95. |
| [13] | Peng QI, Xiao-jiao WANG, Yi-ming YAO, Xiao-long CHEN, Jun WU, Li-qun CAI. Effects of different tillage practices and nitrogen application rate on carbon dioxide emissions and carbon balance in rain-fed maize crops [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 96-106. |
| [14] | LEI En, SHAO Di, ZHU Tian-biao, SHU Xing, YANG Yong-bing, WANG Yue-dong, TANG Qi-yuan. Role of grain crushing resistance and grain threshing characteristics in determining suitability of feed maize cultivars for machine harvesting and effect of plant moisture content [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(9): 125-135. |
| [15] | LÜ Han-qiang, YU Ai-zhong, WANG Yu-long, SU Xiang-xiang, LÜ Yi-tong, CHAI Qiang. Effect of green manure retention practices on nitrogen absorption and utilization by maize crops in the arid oasis irrigation area [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 93-103. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||