

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 121-130.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020026
收稿日期:2020-01-20
修回日期:2020-03-03
出版日期:2020-12-28
发布日期:2020-12-28
通讯作者:
冯伟
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: fwnpw@163.com基金资助:
Bo-wen XIAO1( ), Wei FENG2(
), Wei FENG2( ), Ting-yu DUAN1
), Ting-yu DUAN1
Received:2020-01-20
Revised:2020-03-03
Online:2020-12-28
Published:2020-12-28
Contact:
Wei FENG
摘要:
二月兰是重要的地被、景观和绿肥作物。通过种子、离体叶片和温室盆栽试验,对分离自二月兰种子的链格孢菌,芸薹生链格孢,细极链格孢,黑附球菌,变红镰刀菌,顶孢哈氏霉,细基格孢属等5属7种可培养真菌进行了致病性测定。结果表明,7种真菌可致二月兰种子萌发后烂种烂芽率16.50%~68.50%,其中芸薹生链格孢、顶孢哈氏霉可引致种子发芽率降低18.18%~27.27%。7种种带真菌分别引致二月兰离体叶片出现褪绿和坏死腐烂等症状,发病率100%,病斑面积8.84%~99.38%,病情指数22.50~95.00。盆栽条件下,种带真菌均可致植物出现萎蔫褪绿和坏死叶斑等症状,病株率100%,叶片发病率41.56%~79.88%,病情指数16.22~56.93。与对照(不接种带真菌)相比,种带真菌侵染二月兰植株后第9天植物丙二醛(MDA)含量增加30.40%~204.15%,过氧化物酶(POD)活性变幅为-1.81%~82.87%,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性升高18.78%~86.14%,叶绿素含量(SPAD值)降低13.24%~37.85%。致病性试验表明,芸薹生链格孢致病性最强,顶孢哈氏霉致病性最弱。
肖博文, 冯伟, 段廷玉. 二月兰种带真菌致病性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 121-130.
Bo-wen XIAO, Wei FENG, Ting-yu DUAN. Pathogenicity ofseed-borne fungi of Orychophragmus violaceus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 121-130.
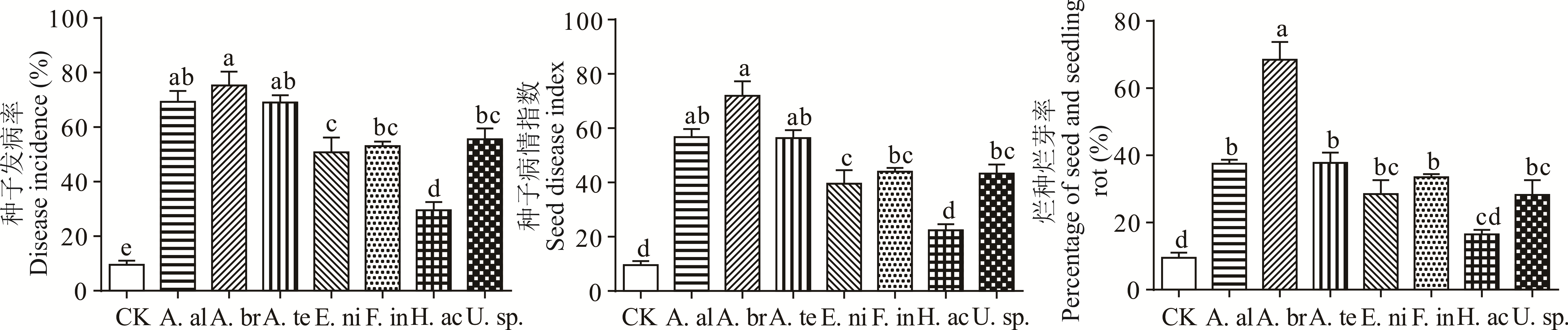
图4 种带真菌处理下二月兰种子发病率、病情指数和烂种烂芽率
Fig.4 Seed disease incidence, disease index and percentage of seed and seedling rot of O. violaceus after inoculation with various seed borne fungi

图7 种带真菌处理下二月兰种子(A)、离体叶片(B)和盆栽(C)发病照片a: 对照CK; b: 链格孢菌A. alternata; c: 芸薹生链格孢A. brassicicola; d: 细极链格孢A. tenuissima; e: 黑附球菌E. nigrum; f: 变红镰刀菌F. incarnatum; g: 顶孢哈氏霉H. acremonioides; h: 细基格孢属Ulocladium sp..
Fig.7 Photos of the seeds, in vitro leaf and potted plant of O. violaceus after inoculation with various seed borne fungi
| 1 | Zhao Q, Gao X B, Ning X G, et al. Carbon-nitrogen fixation and effects on the physical and chemical properties in winter cover crop in north China. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(4): 750-753. |
| 赵秋, 高贤彪, 宁晓光, 等. 华北地区几种冬闲覆盖作物碳氮蓄积及其对土壤理化性质的影响. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(4): 750-753. | |
| 2 | Yang L, Cao W D, Bai J S, et al. Effects of february orchid application on dry matter accumulation and nutrient uptake in maize and soil nutrient status. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2014, 29(1): 183-189. |
| 杨璐, 曹卫东, 白金顺, 等. 翻压二月兰对玉米干物质积累和养分吸收及土壤养分的影响. 华北农学报, 2014, 29(1): 183-189. | |
| 3 | Zhao Q, Gao X B, Ning X G, et al. Effects of spring maize and winter cover crop rotation on accumulation of carbon and nitrogen and soil nutrition and microbe in north China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2013, 19(4): 1005-1011. |
| 赵秋, 高贤彪, 宁晓光, 等. 华北地区春玉米-冬绿肥轮作对碳、氮蓄积和土壤养分以及微生物的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(4): 1005-1011. | |
| 4 | Li Y Q, Sun W Y, Xu J X, et al. Influence of combined application of green manure and inorganic fertilizerson cotton growth and fertilizer use efficiency in Huanghuaihai Area. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2012, 18(6): 1398-1403. |
| 李燕青, 孙文彦, 许建新, 等. 黄淮海地区绿肥与化肥配施对棉花生长和肥料利用率的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(6): 1397-1403. | |
| 5 | Zhao Q, Gao X B, Ning X G, et al. Effect of Orychophragmus violaceus cover on growing environment of a peach orchard and quality of peach. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2013(1): 93-96. |
| 赵秋, 高贤彪, 宁晓光, 等. 冬绿肥二月兰间作及翻压对北方桃园生长环境及果实品质的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2013(1): 93-96. | |
| 6 | Liu J. Study on nutrition characteristics and green manure effect of Orychophragmus violaceus. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2010. |
| 刘佳. 二月兰的营养特性及其绿肥效应研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2010. | |
| 7 | Zhang L J, Dai S L. Development value and garden application of Orychophragmus violaceus. Journal of Beijing Garden, 2005, 21(4): 43-45. |
| 张莉俊, 戴思兰. 二月兰的开发价值与园林应用. 北京园林, 2005, 21(4): 43-45. | |
| 8 | Xiong J, Wang G L, Cao W D, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of soil NO3--N in Orychophragmus violaceus/spring maize rotation system in North China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(2): 467-473. |
| 熊静, 王改兰, 曹卫东, 等. 华北二月兰-春玉米轮作体系中土壤硝态氮的时空变化特征. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(2): 467-473. | |
| 9 | Yang L, Cao W, Thorup-Kristensen K, et al. Effect of Orychophragmus violaceus incorporation on nitrogen uptake in succeeding maize. Plant Soil and Environment, 2015, 61(6): 260-265. |
| 10 | Bai J S, Cao W D, Xiong J, et al. Integrated application of February orchid (Orychophragmus violaceus) as green manure with chemical fertilizer for improving grain yield and reducing nitrogen losses in spring maize system in northern China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(12): 2490-2499. |
| 11 | Yang L, Cao W D, Bai J S, et al. Effect of combined application of February orchid (Orychophragmus violaceus L.) and chemical fertilizer on nutrient uptake and utilization of spring maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2013, 19(4): 799-807. |
| 杨璐, 曹卫东, 白金顺, 等. 种植翻压二月兰配施化肥对春玉米养分吸收利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(4): 799-807. | |
| 12 | Cao W D, Huang H X. Ideas on restoration and development of green manures in China. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2009(4): 1-3. |
| 曹卫东, 黄鸿翔. 关于我国恢复和发展绿肥若干问题的思考. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009(4): 1-3. | |
| 13 | Cao W D, Bao X G, Xu C X, et al. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| 14 | Guo C, Wang C M, Zhou T W, et al. First report of leaf blight caused by Alternaria brassicicola on Orychophragmus violaceus in China. Plant Disease, 2019, 103(5): 1032. |
| 15 | Xiao B W, Yu S Y, Feng W, et al. Isolation and identification of seed borne fungi on Orychophragmus violaceus. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 338-349. |
| 肖博文, 于丝雨, 冯伟, 等. 二月兰种带真菌分离与鉴定. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 338-349. | |
| 16 | Farr D F, Rossman, Fungal Databases , U.S.A. Y.National Fungus Collections, ARS, USDA. . |
| 17 | Chen T, Nan Z B. Seed-borne fungi infection of siberian wildrye: Effects on seed germination and seedling growth. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(2): 96-103. |
| 陈焘, 南志标. 不同储存年限老芒麦种子种带真菌检测及致病性测定. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 96-103. | |
| 18 | Yang Y X, Han J G, Li S T, et al. Effects of seed-borne fungi on germination and vigor of Zoysia japonica seed. Seed, 2006, 25(10): 16-19. |
| 杨颜霞, 韩建国, 李寿田, 等. 种带真菌对结缕草种子发芽和活力的影响. 种子, 2006, 25(10): 16-19. | |
| 19 | Yamamoto A, Nakamura T, Adu-Gyamfi J J, et al. Relationship between chlorophyll content in leaves of sorghum and pigeonpea determined by extraction method and by chlorophyll meter (SPAD-502). Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2002, 25(10): 2295-2301. |
| 20 | Uddling J, Gelang-Alfredsson J, Piikki K, et al. Evaluating the relationship between leaf chlorophyll concentration and SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter readings. Photosynthesis Research, 2007, 91(1): 37-46. |
| 21 | Zhang H, Jiang Y, He Z, et al. Cadmium accumulation and oxidative burst in garlic (Allium sativum). Journal of Plant Physiology, 2005, 162(9): 977-984. |
| 22 | Millanes A M, Fontaniella B, Legaz M E, et al. Glycoproteins from sugarcane plants regulate cell polarity of Ustilago scitaminea teliospores. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2005, 162(3): 253-265. |
| 23 | Dieterich S, Bieligk U, Beulich K, et al. Gene expression of antioxidative enzymes in the human heart: Increased expression of catalase in the end-stage failing heart. Circulation, 2000, 101(1): 33-39. |
| 24 | Arias M M D, Munkvold G P, Ellis M L, et al. Distribution and frequency of Fusarium species associated with soybean roots in Iowa. Plant Disease, 2013, 97(12): 1557-1562. |
| 25 | Li M, Murray G M, Ash G J. New root diseases of canola in Australia. Australasian Plant Disease Notes, 2007, 2(1): 93-94. |
| 26 | Qü T, Nan Z B. Research progress on responses and mechanisms of crop and grass under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 17(2): 126-135. |
| 曲涛, 南志标. 作物和牧草对干旱胁迫的响应及机理研究进展. 草业学报, 2008, 17(2): 126-135. | |
| 27 | Wang B L, Yang C, Qü D. Effect of different environmental factors on SOD activity, MDA and soluble protein contents of wheat leaves. The Journal of Northwest Agricultural University, 2000, 28(6): 72-77. |
| 王保莉, 杨春, 曲东. 环境因素对小麦苗期SOD、MDA及可溶性蛋白的影响. 西北农业大学学报, 2000, 28(6): 72-77. | |
| 28 | Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Analytical Biochemistry, 1979, 95(2): 351-358. |
| 29 | Bowler C, Montagu M V, Inze D. Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 1992, 43(1): 83-116. |
| 30 | Beyer W, Imlay J, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. Progress in nucleic acid research and molecular biology. Academic Press, 1991, 40: 221-253. |
| 31 | Gai X T, Yang R X, Pan X J, et al. First report of Fusarium incarnatum causing stalk rot on maize in China. Plant Disease, 2016, 100(5): 1010. |
| 32 | Li L, Pan H, Deng L, et al. First report of Alternaria tenuissima causing brown spot disease of kiwifruit foliage in China. Plant Disease, 2019, 103(3): 582. |
| 33 | Wang X F, Li Z A, Tang K Z, et al. First report of Alternaria brown spot of citrus caused by Alternaria alternata in Yunnan Province, China. Plant Disease, 2010, 94(3): 375. |
| 34 | Peres N A R, Agostini J P, Timmer L W. Outbreaks of Alternaria brown spot of citrus in Brazil and Argentina. Plant Disease, 2003, 87(6): 750. |
| 35 | Wu D, Zhang D H, Timko M P, et al. First report of Epicoccum nigrum causing brown leaf spot of loquat in Southwestern China. Plant Disease, 2017, 101(8): 1553. |
| [1] | 聂秀美, 慕平, 赵桂琴, 何海鹏, 吴文斌, 蔺豆豆, 苏伟娟, 张丽睿. 贮藏年限对裸燕麦种带真菌和真菌毒素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 106-120. |
| [2] | 张学良, 张宇亭, 刘瑞, 谢军, 张建伟, 徐文静, 石孝均. 绿肥不同还田方式对土壤温室气体排放的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 25-33. |
| [3] | 古丽君, 段廷玉. 光叶紫花苕研究状况的文献分析——基于CNKI数据库的文献计量[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 221-228. |
| [4] | 陈晓芬, 张路平, 秦文婧, 陈静蕊, 徐样庚, 刘明, 李忠佩, 徐昌旭, 刘佳. 红壤旱地上4种冬绿肥适宜播种量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 137-146. |
| [5] | 吕汉强, 于爱忠, 王玉珑, 苏向向, 吕奕彤, 柴强. 干旱绿洲灌区玉米氮素吸收利用对绿肥还田利用方式的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 93-103. |
| [6] | 杨叶华, 张松, 王帅, 刘正兰, 方林发, 张学良, 刘瑞, 张建伟, 张宇亭, 石孝均. 中国不同区域常见绿肥产量和养分含量特征及替代氮肥潜力评估[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 39-55. |
| [7] | 王春明, 元维伟, 张小杰, 周天旺, 郭成, 金社林. 二月兰叶斑病病原甘蓝链格孢的分离鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 88-97. |
| [8] | 马婷燕, 李彦忠. 32个紫花苜蓿品种的种带真菌种类及致病性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 131-139. |
| [9] | 方香玲, 张彩霞, 南志标. 紫花苜蓿镰刀菌根腐病研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 169-183. |
| [10] | 张振粉, 苏静, 杨成德, 师尚礼, 花立民, WALAAMohamaden. 紫花苜蓿种带阪崎克罗诺杆菌的分离鉴定及其致病性初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 130-141. |
| [11] | 王爱军, 王娜, 顾思思, 赵文娟, 李平, 郑爱萍. 我国水稻纹枯病菌的融合类群及致病性差异[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 55-63. |
| [12] | 王登科, 于翔宇, 张学风, 黄蕾, 李晓婷, 贺治斌, 康林, 王党军, 姚露花, 郭彦军. 酸、铝和盐胁迫对夏季豆科绿肥作物种子萌发及根瘤菌抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 35-44. |
| [13] | 李春杰, 陈泰祥, 赵桂琴, 南志标. 燕麦病害研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 203-222. |
| [14] | 杜青峰, 王党军, 于翔宇, 姚露花, 和玉吉, 王瑞, 马生兰, 郭彦军. 玉米间作夏季绿肥对当季植物养分吸收和土壤养分有效性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 225-233. |
| [15] | 陈国军, 闫慧峰, 吴凯, 杨举田, 田雷, 谭效磊, 宗浩, 陈秀斋, 张永春, 孙延国, 刘海伟, 石屹. 不同收获期的籽粒苋绿肥还田对土壤养分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 215-224. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||