

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 112-120.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020068
王桔红1( ), 史生晶2, 陈文3(
), 史生晶2, 陈文3( ), 甘桂媚1, 陈赛娜1, 李张伟4
), 甘桂媚1, 陈赛娜1, 李张伟4
收稿日期:2020-02-21
修回日期:2020-03-23
出版日期:2020-12-28
发布日期:2020-12-28
通讯作者:
陈文
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: cyw1018@sina.com基金资助:
Ju-hong WANG1( ), Sheng-jing SHI2, Wen CHEN3(
), Sheng-jing SHI2, Wen CHEN3( ), Gui-mei GAN1, Sai-na CHEN1, Zhang-wei LI4
), Gui-mei GAN1, Sai-na CHEN1, Zhang-wei LI4
Received:2020-02-21
Revised:2020-03-23
Online:2020-12-28
Published:2020-12-28
Contact:
Wen CHEN
摘要:
为探查枯草芽孢杆菌和放线菌对植物抗盐性的影响,采用培养皿法研究枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌(粉孢类群2-5、淡紫灰类群6-3和烬灰类群1-6)对盐胁迫下鬼针草和鳢肠种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响。结果表明:1)枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌在25~75 mmol·L-1盐浓度下提高鬼针草种子发芽率,而4种菌液对盐胁迫下鳢肠种子发芽率影响较小。2)枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对盐胁迫下鬼针草根长作用较小,对鳢肠根长具有不同程度的促生作用。3)4种菌液对盐胁迫下鬼针草茎长作用较小,对鳢肠茎长具有显著的促生作用,100 mmol·L-1盐浓度下鳢肠茎长分别增加了30.56%、28.57%、26.47%和24.24%。4)枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对盐胁迫下鬼针草干重影响较小,但能不同程度地提高鳢肠干重。枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对盐胁迫下鬼针草种子发芽率和鳢肠根长、茎长及干重具有较显著的促生作用,有利于鬼针草和鳢肠幼苗适应盐逆境。
王桔红, 史生晶, 陈文, 甘桂媚, 陈赛娜, 李张伟. 枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对盐胁迫下鬼针草和鳢肠种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 112-120.
Ju-hong WANG, Sheng-jing SHI, Wen CHEN, Gui-mei GAN, Sai-na CHEN, Zhang-wei LI. Effects of Bacillus subtilis and three actinomycetes on seed germination and seedling growth of Bidens pilosa and Eclipta prostrata under salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 112-120.
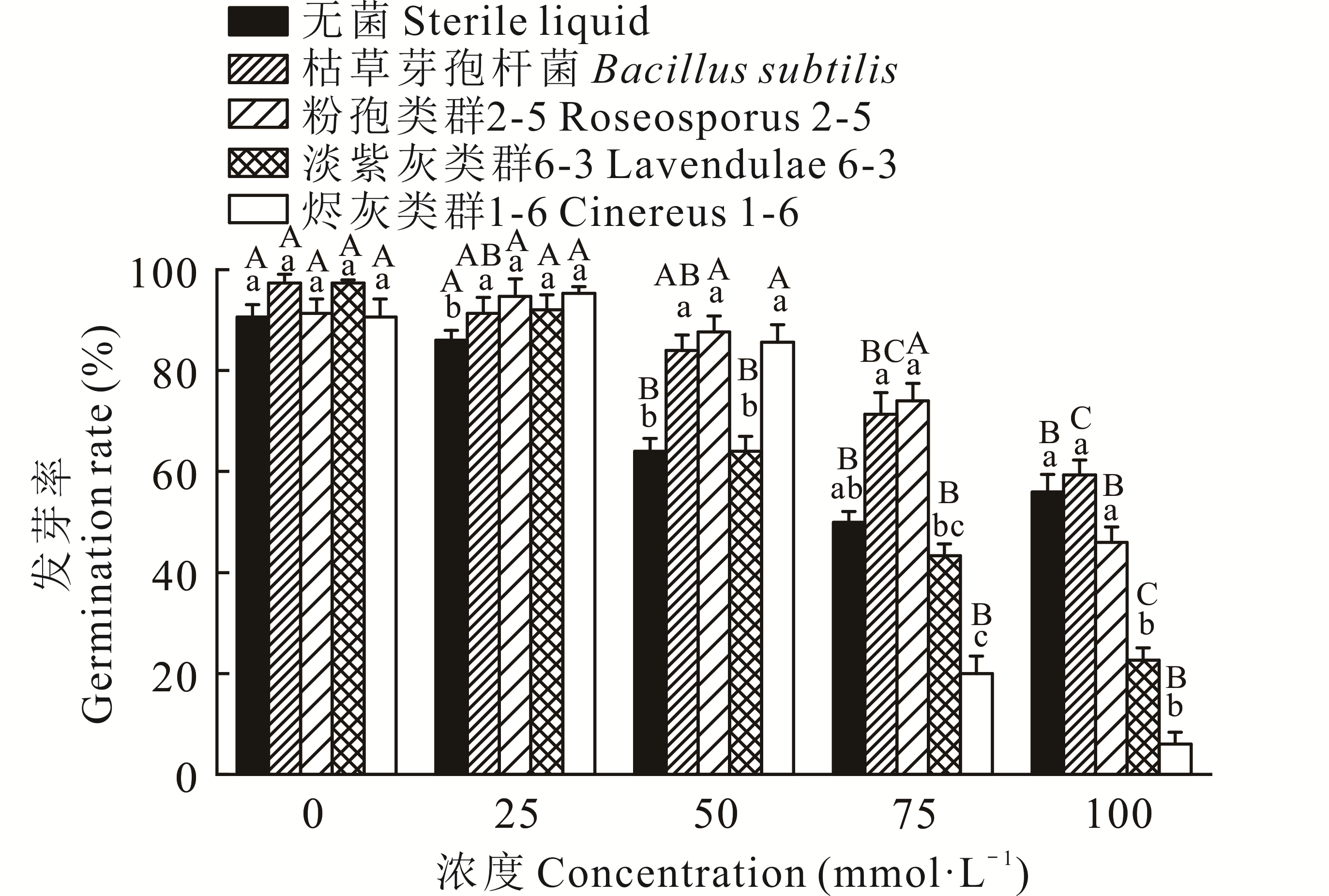
图1 不同盐浓度下枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对鬼针草种子萌发的影响不同大写字母表示同一菌液不同盐浓度间的显著性,不同小写字母表示同一盐浓度不同菌液间的显著性(P<0.05),下同。Different capital letters indicate the significance between different salt concentrations in the same bacterial solution, and different lowercase letters indicate the significance between different bacterial solutions with the same salt concentration (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Effect of B. subtilis and three actinomycetes on seed germination of B. pilosa under different salt concentrations
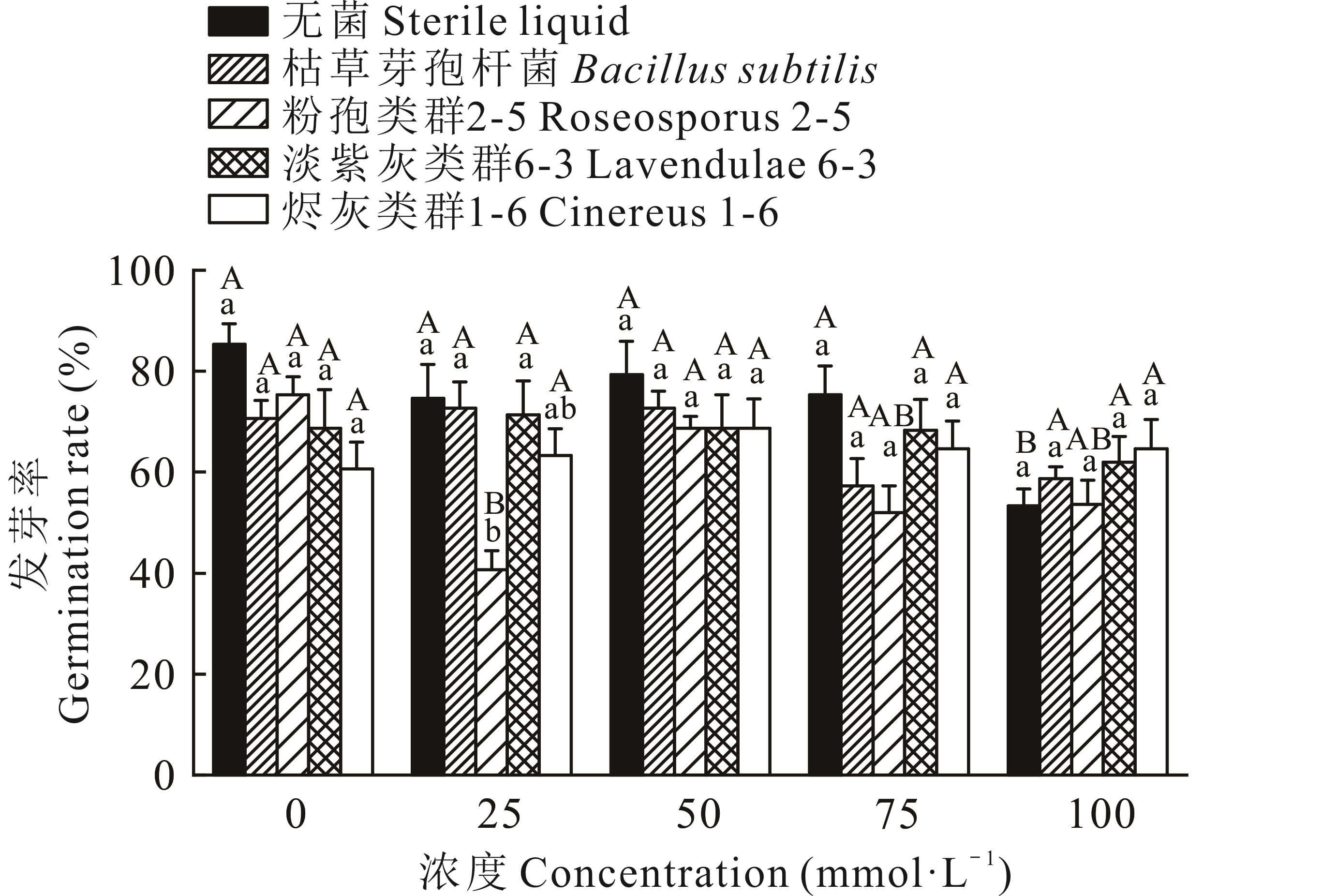
图2 不同盐浓度下枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对鳢肠种子萌发的影响
Fig.2 Effect of B. subtilis and three actinomycetes on seed germination of E. prostrata under different salt concentrations
指标 Index | 浓度 Concentration (mmol·L-1) | 无菌液 Sterile liquid | 枯草芽孢杆菌 B. subtilis | 粉孢类群2-5 Roseosporus 2-5 | 淡紫灰类群6-3 Lavendulae 6-3 | 烬灰类群1-6 Cinereus 1-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
鬼针草干重 Dry weight of B. pilosa | 0 | 0.1037±0.001Ba | 0.1071±0.003Aa | 0.0699±0.007Ab | 0.0845±0.004ABb | 0.0757±0.007Bb |
| 25 | 0.1304±0.003Aa | 0.0990±0.002ABb | 0.0745±0.007Ac | 0.0973±0.005Ab | 0.1019±0.002Ab | |
| 50 | 0.1233±0.002Aa | 0.0872±0.004Bb | 0.0729±0.006Ab | 0.0717±0.009Bb | 0.0782±0.002Bb | |
| 75 | 0.0870±0.010Ca | 0.0748±0.005Cab | 0.0645±0.002Abc | 0.0715±0.004Bab | 0.0495±0.003Cc | |
| 100 | 0.0551±0.005Da | 0.0512±0.004Da | 0.0356±0.004Bb | 0.0483±0.006Cab | 0.0119±0.001Dc | |
鳢肠干重 Dry weight of E. prostrata | 0 | 0.0299±0.001Ab | 0.0225±0.002Bd | 0.0364±0.001Aa | 0.0244±0.001Acd | 0.0274±0.001Abc |
| 25 | 0.0249±0.005Ab | 0.0320±0.002Aa | 0.0273±0.001Cb | 0.0267±0.001Ab | 0.0238±0.001ABb | |
| 50 | 0.0262±0.005Aa | 0.0341±0.003Aa | 0.0353±0.001Aa | 0.0255±0.002Aa | 0.0261±0.002ABa | |
| 75 | 0.0231±0.003Ab | 0.0298±0.002Aa | 0.0315±0.001Ba | 0.0241±0.000Ab | 0.0233±0.001ABb | |
| 100 | 0.0193±0.002Bbc | 0.0208±0.001Bbc | 0.0266±0.002Ca | 0.0162±0.002Bc | 0.0228±0.000Bab |
表1 不同盐浓度的枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对鬼针草和鳢肠干重的影响
Table 1 Effect of B. subtilis and three actinomycetes on dry weight of B. pilosa and E. prostrata underdifferent salt concentrations (g·plant-1)
指标 Index | 浓度 Concentration (mmol·L-1) | 无菌液 Sterile liquid | 枯草芽孢杆菌 B. subtilis | 粉孢类群2-5 Roseosporus 2-5 | 淡紫灰类群6-3 Lavendulae 6-3 | 烬灰类群1-6 Cinereus 1-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
鬼针草干重 Dry weight of B. pilosa | 0 | 0.1037±0.001Ba | 0.1071±0.003Aa | 0.0699±0.007Ab | 0.0845±0.004ABb | 0.0757±0.007Bb |
| 25 | 0.1304±0.003Aa | 0.0990±0.002ABb | 0.0745±0.007Ac | 0.0973±0.005Ab | 0.1019±0.002Ab | |
| 50 | 0.1233±0.002Aa | 0.0872±0.004Bb | 0.0729±0.006Ab | 0.0717±0.009Bb | 0.0782±0.002Bb | |
| 75 | 0.0870±0.010Ca | 0.0748±0.005Cab | 0.0645±0.002Abc | 0.0715±0.004Bab | 0.0495±0.003Cc | |
| 100 | 0.0551±0.005Da | 0.0512±0.004Da | 0.0356±0.004Bb | 0.0483±0.006Cab | 0.0119±0.001Dc | |
鳢肠干重 Dry weight of E. prostrata | 0 | 0.0299±0.001Ab | 0.0225±0.002Bd | 0.0364±0.001Aa | 0.0244±0.001Acd | 0.0274±0.001Abc |
| 25 | 0.0249±0.005Ab | 0.0320±0.002Aa | 0.0273±0.001Cb | 0.0267±0.001Ab | 0.0238±0.001ABb | |
| 50 | 0.0262±0.005Aa | 0.0341±0.003Aa | 0.0353±0.001Aa | 0.0255±0.002Aa | 0.0261±0.002ABa | |
| 75 | 0.0231±0.003Ab | 0.0298±0.002Aa | 0.0315±0.001Ba | 0.0241±0.000Ab | 0.0233±0.001ABb | |
| 100 | 0.0193±0.002Bbc | 0.0208±0.001Bbc | 0.0266±0.002Ca | 0.0162±0.002Bc | 0.0228±0.000Bab |
| 1 | Yuan Y, Wang S. Research progress and specific measures of saline-alkali land treatment. Modern Agricultural Sciences and Technology, 2020(3): 260-261. |
| 袁永, 王胜. 盐碱地治理研究进展及具体措施. 现代农业科技, 2020(3): 260-261. | |
| 2 | Niu S Q, He A L, Ding X Y, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis GB03 and water retaining agent on growth and salt tolerance in Puccinellia tenuiflflora. Plant Physiology Journal, 2016, 52(3): 285-292. |
| 牛舒琪, 何傲蕾, 丁新宇, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌GB03与保水剂互作对小花碱茅生长和耐盐性的影响. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(3): 285-292. | |
| 3 | Cao C X, Long T, Cheng X L, et al. Field efficacy trials of Bacillus subtilis against powdery mildew of Strawberry. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 50(20): 4188-4189. |
| 曹春霞, 龙同, 程贤亮, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌防治草莓白粉病田间药效试验. 湖北农业科学, 2011, 50(20): 4188-4189. | |
| 4 | Stein T, Borchert S, Conrad B, et al. Two different lantibiotic-like peptides originate from the ericin gene cluster of Bacillus subtilis A1/ 3. Journal of Bacteriology, 2002, 184(6): 1703-1711. |
| 5 | Xing Z Y, Xu H X, Chen X R. Effects of Bacillus subtilis B1 and B2 strains on prevention and growth of Angelica sinensis and Astragalus membranaceus. Plant Protection, 2008, 34(6): 142-144. |
| 辛中尧, 徐红霞, 陈秀蓉. 枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)B1、B2菌株对当归、黄芪的防病促进生长效果. 植物保护, 2008, 34(6): 142-144. | |
| 6 | Zhang X, Tang W H, Zhang L Q. Biological control of plant diseases and plant growth promotion by Bacillus subtilis B931. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2007, 33(2): 236-241. |
| 张霞, 唐文华, 张力群. 枯草芽孢杆菌B931防治植物病害和促进植物生长的作用. 作物学报, 2007, 33(2): 236-241. | |
| 7 | Cai X Q, Lin C P, He H, et al. Effects of endophytic bacterial strain BS-2 on rice seeding growth. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 34(2): 189-194. |
| 蔡学清, 林彩萍, 何红, 等. 内生枯草芽孢杆菌BS-2对水稻苗生长的效应. 福建农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 34(2): 189-194. | |
| 8 | Zhang J, Zhu R S, Wang C F, et al. Research progress on application of Bacillus subtilis in agriculture. Modern Agricultural Sciences and Technology, 2019(13): 163-170. |
| 张洁, 朱仁胜, 王春芳, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌在农业领域的应用研究进展. 现代农业科技, 2019(13): 163-170. | |
| 9 | Zhang C X, Kong F Y, Liu C K, et al. Tobacco growth enhancement and disease protection by the volatile-producing Bacillus subtilis Tpb55. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2009, 25(3): 245-249. |
| 张成省, 孔凡玉, 刘朝科, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌Tpb55挥发物对烟草的防病促生效应. 中国生物防治学报, 2009, 25(3): 245-249. | |
| 10 | Ruan Y F. Antibacterial effect of F24 actionmycetes fermentation broth of different formula and its influence on growth of tomato seedling. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2008. |
| 阮云飞. F24放线菌不同配方发酵液抑菌效果及对番茄种苗生长的影响. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2008. | |
| 11 | Sun J R. Preliminary study on mechanisms of growth promoting and cold & salt-tolerance improving of Streptomyces S506 in tomato seedling. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University, 2012. |
| 孙佳瑞. 链霉菌S506促生和提高番茄耐寒耐盐机制的初步研究. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2012. | |
| 12 | Yi H W. Studies on improving the capacity of salt-tolerance of cucumber by Bacillus subtilis. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2006. |
| 尹汉文. 枯草芽孢杆菌提高黄瓜耐盐性的研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2006. | |
| 13 | Yin H W, Guo S R, Liu W, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on salt tolerance of cucumber. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2006, 29(3): 18-22. |
| 尹汉文, 郭世荣, 刘伟, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌对黄瓜耐盐性的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 2006, 29(3): 18-22. | |
| 14 | Yi Y J, Xiao L T, Wang R Z, et al. Growth effect of endophyte B-001 (Bacillus subtilis) on tobacco seedling and its fluctuation. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 2007, 34(6): 619-623. |
| 易有金, 肖浪涛, 王若仲, 等. 内生枯草芽孢杆菌B-001对烟草幼苗的促生作用及其生长动态. 植物保护学报, 2007, 34(6): 619-623. | |
| 15 | Hu Y J, Wei J Y, Zhang J L, et al. Effect of Bacillus subtilis on soil nutrients content and enzymes activity. Crop Research, 2019, 33(6): 561-566. |
| 胡亚杰, 韦建玉, 张纪利, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌对植烟土壤养分含量与酶活性的影响. 作物研究, 2019, 33(6): 561-566. | |
| 16 | Jia Y, Jia L Y, Huang J X. The bio-control and application of actinomycetes against plant diseases. Journal of Xi'an University of Arts & Science (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 15(3): 6-10. |
| 贾雨, 贾丽苑, 黄建新. 放线菌对植物病害的防治作用及应用. 西安文理学院学报(自然科学版), 2012, 15(3): 6-10. | |
| 17 | Hao J H, Liu Q Q, Qiang S. Reproductive traits associated with invasiveness in Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae). Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2009, 44(6): 656-665. |
| 郝建华, 刘倩倩, 强胜. 菊科入侵植物鬼针草的繁殖特征及其与入侵性的关系. 植物学报, 2009, 44(6): 656-665. | |
| 18 | Wang J H, Chen W. Comparative study of biomass of modules and morphological plasticity of four Asteraceae species at the flowering stage. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(8): 2031-2037. |
| 王桔红, 陈文. 四种菊科植物开花期构件生物量及表型可塑性比较. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(8): 2031-2037. | |
| 19 | Yang J Y, Ma X Y, Jiang W L, et al. Research progress on noxious weed-Eclipta prostrata L. in cotton. Weed Science, 2015, 33(4): 14-17. |
| 杨晋燕, 马小艳, 姜伟丽, 等. 棉田恶性杂草鳢肠的研究进展. 杂草科学, 2015, 33(4): 14-17. | |
| 20 | Gao Y. Management status and solutions of landscaping project in coastal saline-alkali land. Xiandai Horticulture, 2017(22): 183. |
| 高杨. 滨海盐碱地园林绿化工程管理现状及解决措施. 现代园艺, 2017(22): 183. | |
| 21 | Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Streptomyces identification manual. Beijing: Science Press, 1975. |
| 中国科学院微生物研究所. 链霉菌鉴定手册. 北京: 科学出版社, 1975. | |
| 22 | Dai F P. Identification and the study on antibacterial activity of halotolerant Streptomyces isolated from the soils of reed rhizosphere in Hexi corridor. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2014. |
| 代芳平. 河西走廊芦苇根际土壤耐盐链霉菌的分离, 鉴定及抗菌活性研究. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2014. | |
| 23 | Hong L, Shen H, Yang Q H, et al. Studies on seed germination and storage of the invasive alien species Bidens pilosa L.. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 2004, 22(5): 433-437. |
| 洪岚, 沈浩, 杨期和, 等. 外来入侵植物三叶鬼针草种子萌发与贮藏特性研究. 武汉植物学研究, 2004, 22(5): 433-437. | |
| 24 | Zhou D Q. Microbiology experimental course (2nd Edition). Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 周德庆. 微生物学实验教程(第二版). 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 25 | Wei S J, Wang S Q, Li K T, et al. Effects of Streptomyces 702 on seed germination and seedling growth of rice and soil microbes. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(5): 853-861. |
| 魏赛金, 王世强, 李昆太, 等. 链霉菌702对水稻种子萌发、幼苗生长及土壤微生物的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(5): 853-861. | |
| 26 | Kuang Y, Nan Z B, Tian P. Effects of Epichloë endophyte and seed hydro-priming on the germination of Festuca sinensis under NaCl stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 160-168. |
| 旷宇, 南志标, 田沛. 内生真菌和水引发对NaCl胁迫条件下中华羊茅种子萌发的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 160-168. | |
| 27 | Yang Y. Study on seed germination and seedling salt tolerance of Hemiptelea davidii. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 杨颖. 刺榆种子萌发及幼苗耐盐性研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. | |
| 28 | Li Z, Yun L, Shi Z Y, et al. Physiological characteristics of Psathyrostachys juncea at seed germination and seedling growth stages under salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(8): 119-129. |
| 李珍, 云岚, 石子英, 等. 盐胁迫对新麦草种子萌发及幼苗期生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 119-129. | |
| 29 | Miao S, Xia Z P, Li Z Q. Effect of NaCl on growth and physiological characteristics of three Pennisetum species. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019(6): 132-136. |
| 缪珊, 夏振平, 李志强. NaCl胁迫对三种狼尾草生长及生理特性的影响. 黑龙江农业科学, 2019(6): 132-136. | |
| 30 | Du L X, Dong K H, Xia F S, et al. Effects of salt stress on germination and physiological characteristics of Psath yrostachys seeds. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2009, 17(6): 789-794. |
| 杜丽霞, 董宽虎, 夏方山, 等. 盐胁迫对新麦草种子萌发特性和生理特性的影响. 草地学报, 2009, 17(6): 789-794. | |
| 31 | Xu M, Wang X, Wang Y X, et al. Effects of different salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Elytrigia elongata. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(1): 15-20. |
| 徐曼, 王茜, 王奕骁, 等. 不同盐胁迫对长穗偃麦草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(1): 15-20. | |
| 32 | Yang H W, Liu W Y, Shen B Y, et al. Seed germination and physiological characteristics of Chenopodium quinoa under salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(8): 146-153. |
| 杨宏伟, 刘文瑜, 沈宝云, 等. NaCl胁迫对藜麦种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 146-153. | |
| 33 | Yan H X, Guo S R, Liu W. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on rhizosphere enzyme activities of cucumber under salt-stress. Journal of North China Agriculture, 2010, 25(4): 209-212. |
| 闫海霞, 郭世荣, 刘伟. 枯草芽孢杆菌对盐胁迫条件下黄瓜根际酶活性的影响. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(4): 209-212. | |
| 34 | Zhang H, Kim M S, Sun Y, et al. Soil bacteria confer plant salt tolerance by tissue-specific regulation of the sodium transporter HKT1. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2008, 21(6): 737-744. |
| 35 | Qu F B, Yu M L, Zhang Z Q, et al. Effect of salt tolerant bacteria on the germination of tomato seeds. Northern Horticulture, 2014(18): 35-38. |
| 曲发斌, 于明礼, 张柱岐, 等. 耐盐细菌对番茄种子萌发的影响. 北方园艺, 2014(18): 35-38. | |
| 36 | Xin S Q, Wang G, Gao Y. Effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on the rice germination and seedling development under salt stress. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 51(3): 490-492, 496. |
| 辛树权, 王贵, 高扬. 植物生长促生菌对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2012, 51(3): 490-492, 496. | |
| 37 | Han Q Q, Jia T T, Lü X P, et al. Effect of Bacillus subtilis GB03 on salt tolerance of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Plant Physiology Journal, 2014, 50(9): 1423-1428. |
| 韩庆庆, 贾婷婷, 吕昕培, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌GB03对紫花苜蓿耐盐性的影响. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(9): 1423-1428. | |
| 38 | Cui X H, Lin Z H, Yang S P. Osmotolerant mechanism of a halophilic purple sulfur bacterium 283-1. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 32(3): 228-231. |
| 崔小华, 林志华, 杨素萍. 嗜盐紫色硫细菌283-1的耐盐机制. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 32(3): 228-231. |
| [1] | 赵欣桐, 陈晓东, 李子吉, 张巨明, 刘天增. 植物内生肠杆菌对狗牙根耐盐性的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 127-136. |
| [2] | 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 王学琴, 姚姗. 盐胁迫对湖南稷子苗期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| [3] | 汪芳珍, 杨成行, 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清. 盐处理下旱生植物沙芥蛋白激酶相关基因的差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 116-124. |
| [4] | 田甜, 王海江, 王金刚, 朱永琪, 史晓艳, 李维弟, 李文瑞玉. 盐胁迫下施加氮素对饲用油菜有机渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 125-136. |
| [5] | 高玉莲, 常静, 王贻卉, 李锋, 李海平, 马崇勇. 瑞香狼毒根提取物对3种作物种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 83-91. |
| [6] | 牛欢欢, 王森森, 贾宏定, 陈桂华. 光叶紫花苕子浸提液对4种牧草种子萌发过程的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 161-168. |
| [7] | 李凤兰, 武佳文, 姚树宽, 赵梓颐, 赵潇璨, 贺付蒙, 朱元芳, 石奇海, 周磊, 徐永清. 假苍耳不同部位水浸提液对5种土著植物化感作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 169-178. |
| [8] | 王苗苗, 周向睿, 梁国玲, 赵桂琴, 焦润安, 柴继宽, 高雪梅, 李娟宁. 5份燕麦材料苗期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 143-154. |
| [9] | 崔雪莲, 夏超. 外源脱落酸对醉马草内生真菌共生体幼苗建植过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 70-80. |
| [10] | 梁军, 全小龙, 张杰雪, 史惠兰, 段中华, 乔有明. 3种禾草水提取液对其种子发芽和幼苗生长的潜在化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 81-89. |
| [11] | 黄勇, 郭猛, 张红瑞, 周艳, 李贺敏, 高致明, 王盼盼. 盐胁迫对石竹种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 105-111. |
| [12] | 马婷燕, 李彦忠. 32个紫花苜蓿品种的种带真菌种类及致病性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 131-139. |
| [13] | 何建军, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 边秀秀, 司二静, 杨轲, 王化俊, 马小乐, 李葆春, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄. 干旱和盐胁迫对盐生植物盐生草种子萌发特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 129-140. |
| [14] | 李珍, 云岚, 石子英, 王俊, 张晨, 郭宏宇, 盛誉. 盐胁迫对新麦草种子萌发及幼苗期生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 119-129. |
| [15] | 伍国强, 李辉, 雷彩荣, 蔺丽媛, 金娟, 李善家. 添加KCl对高盐胁迫下红豆草生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 45-55. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||