

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 61-72.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020048
伍浩天1( ), 聂蛟1, 杨文娟1, 张智勇1, 吴康红1, 李晓瑜1, 方小梅1,2, 阮仁武1,2, 易泽林1,2(
), 聂蛟1, 杨文娟1, 张智勇1, 吴康红1, 李晓瑜1, 方小梅1,2, 阮仁武1,2, 易泽林1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-02-05
修回日期:2020-04-30
出版日期:2020-12-28
发布日期:2020-12-28
通讯作者:
易泽林
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: yzlin1969@126.com基金资助:
Hao-tian WU1( ), Jiao NIE1, Wen-juan YANG1, Zhi-yong ZHANG1, Kang-hong WU1, Xiao-yu LI1, Xiao-mei FANG1,2, Ren-wu RUAN1,2, Ze-lin YI1,2(
), Jiao NIE1, Wen-juan YANG1, Zhi-yong ZHANG1, Kang-hong WU1, Xiao-yu LI1, Xiao-mei FANG1,2, Ren-wu RUAN1,2, Ze-lin YI1,2( )
)
Received:2020-02-05
Revised:2020-04-30
Online:2020-12-28
Published:2020-12-28
Contact:
Ze-lin YI
摘要:
为探明小型机械在丘陵山区播种苦荞的农机农技配套技术,以酉荞5号(中抗倒伏苦荞品种)为试验材料,于2016和2017年秋季,利用播种深度2(A1)、3(A2)和4 cm(A3),播种量16.8(B1)、33.6(B2)和50.4 kg·hm-2(B3),施肥量150(C1)、300(C2)和450 kg·hm-2(C3)三因素三水平设计L934正交试验,研究9个处理水平对苦荞倒伏和产量的影响。结果表明:对苦荞倒伏影响表现为播种深度>播种量>施肥量,随播种深度的增加,倒伏时期后移,3 cm播种深度苦荞倒伏级别和倒伏率最小;随播种量、施肥量的增加倒伏级别和倒伏率都增大。茎秆基部第二节间长度、茎粗、鲜重和抗折力从盛花期到成熟期逐渐增加,对茎秆基部第二节间茎粗、鲜重和抗折力的影响表现为播种量>播种深度>施肥量,随播种量的增加,第二节间茎粗、鲜重和抗折力逐渐减小,第二节间长度先减后增;播深对茎秆第二节间长度影响大于播量和施肥量,随播深的增加,第二节间茎粗、鲜重和抗折力先增后减,第二节间长度先减后增;随施肥量的增加,第二节间长度、直径、鲜重和抗折力逐渐增加。从盛花期到成熟期茎秆基部第二节间4-香豆酸辅酶A连接酶(4-coumarate:CoA ligase, 4CL)、苯丙氨酸解氨酶(phenylalanine ammonia-lyase,PAL)、肉桂醇脱氢酶(cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase,CAD)活性先升后降,木质素含量逐渐增加,对木质素含量、4CL、PAL、CAD酶活性的影响表现为播种量>播种深度>施肥量。对产量、单株粒数和总株数的影响表现为播种量>播种深度>施肥量,对千粒重的影响表现为播种量>施肥量>播种深度。随播种量的增加,总株数增加,单株粒数和千粒重减少,产量先增后减;随播种深度的增加,产量、单株粒数和总株数先升后降,千粒重先减后增;随施肥量的增加,总株数和产量差异不显著,单株粒数和千粒重显著增加。本试验条件下,丘陵山区苦荞小型机械播种A2B2C3处理(3 cm播种深度、33.6 kg·hm-2播种量和450 kg·hm-2施肥量)最佳。
伍浩天, 聂蛟, 杨文娟, 张智勇, 吴康红, 李晓瑜, 方小梅, 阮仁武, 易泽林. 机播深度、播种量和施肥量对苦荞倒伏及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 61-72.
Hao-tian WU, Jiao NIE, Wen-juan YANG, Zhi-yong ZHANG, Kang-hong WU, Xiao-yu LI, Xiao-mei FANG, Ren-wu RUAN, Ze-lin YI. Effects of machine sowing depth and amounts of seeds and fertilizer on lodging and yield of Tartary buckwheat[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 61-72.
处理 Treatment | 因素 Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
播种深度 Sowing depth (A, cm) | 播种量 Sowing rates (B, kg·hm-2) | 施肥量 Fertilizing amount (C, kg·hm-2) | |
| 1 | 1 (2) | 1 (16.8) | 1 (150) |
| 2 | 1 (2) | 2 (33.6) | 2 (300) |
| 3 | 1 (2) | 3 (50.4) | 3 (450) |
| 4 | 2 (3) | 1 (16.8) | 2 (300) |
| 5 | 2 (3) | 2 (33.6) | 3 (450) |
| 6 | 2 (3) | 3 (50.4) | 1 (150) |
| 7 | 3 (4) | 1 (16.8) | 3 (450) |
| 8 | 3 (4) | 2 (33.6) | 1 (150) |
| 9 | 3 (4) | 3 (50.4) | 2 (300) |
表1 L934正交试验设计
Table 1 L934 orthogonal design
处理 Treatment | 因素 Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
播种深度 Sowing depth (A, cm) | 播种量 Sowing rates (B, kg·hm-2) | 施肥量 Fertilizing amount (C, kg·hm-2) | |
| 1 | 1 (2) | 1 (16.8) | 1 (150) |
| 2 | 1 (2) | 2 (33.6) | 2 (300) |
| 3 | 1 (2) | 3 (50.4) | 3 (450) |
| 4 | 2 (3) | 1 (16.8) | 2 (300) |
| 5 | 2 (3) | 2 (33.6) | 3 (450) |
| 6 | 2 (3) | 3 (50.4) | 1 (150) |
| 7 | 3 (4) | 1 (16.8) | 3 (450) |
| 8 | 3 (4) | 2 (33.6) | 1 (150) |
| 9 | 3 (4) | 3 (50.4) | 2 (300) |
处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) | 单株粒数 Grain number per plant | 千粒重 Thousand grains weight (g) | 总株数Number of plants (×104 plant·hm-2 ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 1 | 1647.00±16.17f | 1636.86±17.94e | 111.33±4.04d | 113.67±4.93d | 31.16±0.97c | 31.83±0.81b | 43.45±0.68h | 43.32±0.37e |
| 2 | 1674.71±8.58ef | 1664.38±9.49de | 103.33±2.52e | 107.33±1.53de | 29.31±0.18d | 30.03±0.28cd | 88.65±0.54e | 87.50±0.62d |
| 3 | 1726.01±14.49cd | 1721.15±10.64c | 99.33±2.52e | 105.00±2.65e | 28.28±0.15e | 28.98±0.14de | 132.95±0.68b | 131.07±0.38b |
| 4 | 1699.66±18.81de | 1687.66±18.81d | 135.00±8.89a | 139.67±8.74a | 32.22±0.68b | 32.86±0.68ab | 44.25±0.52g | 42.63±0.97f |
| 5 | 1823.36±17.47a | 1816.78±18.28a | 121.67±4.04bc | 127.00±3.00bc | 30.42±0.29c | 30.42±0.89c | 89.45±0.18d | 88.84±0.62c |
| 6 | 1774.12±22.10b | 1764.12±22.08b | 100.00±6.00e | 106.33±6.03de | 22.36±0.74g | 22.88±0.80g | 133.30±0.38a | 132.53±0.13a |
| 7 | 1669.73±14.49f | 1659.73±14.49de | 127.00±6.56b | 132.67±6.03ab | 33.50±0.19a | 33.90±0.07a | 43.15±0.97i | 41.71±0.08g |
| 8 | 1742.73±11.59c | 1733.05±11.47c | 115.67±3.06cd | 121.67±3.06c | 28.38±0.49e | 28.57±0.54e | 88.25±0.86f | 87.31±0.17d |
| 9 | 1782.77±11.18b | 1776.17±9.48b | 98.00±1.00e | 105.00±1.00e | 24.73±0.20f | 25.23±0.40f | 132.25±0.67c | 131.01±0.47b |
表2 不同处理下苦荞产量及产量构成因素
Table 2 Yield and yield components of tartary buckwheat under different treatment
处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) | 单株粒数 Grain number per plant | 千粒重 Thousand grains weight (g) | 总株数Number of plants (×104 plant·hm-2 ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 1 | 1647.00±16.17f | 1636.86±17.94e | 111.33±4.04d | 113.67±4.93d | 31.16±0.97c | 31.83±0.81b | 43.45±0.68h | 43.32±0.37e |
| 2 | 1674.71±8.58ef | 1664.38±9.49de | 103.33±2.52e | 107.33±1.53de | 29.31±0.18d | 30.03±0.28cd | 88.65±0.54e | 87.50±0.62d |
| 3 | 1726.01±14.49cd | 1721.15±10.64c | 99.33±2.52e | 105.00±2.65e | 28.28±0.15e | 28.98±0.14de | 132.95±0.68b | 131.07±0.38b |
| 4 | 1699.66±18.81de | 1687.66±18.81d | 135.00±8.89a | 139.67±8.74a | 32.22±0.68b | 32.86±0.68ab | 44.25±0.52g | 42.63±0.97f |
| 5 | 1823.36±17.47a | 1816.78±18.28a | 121.67±4.04bc | 127.00±3.00bc | 30.42±0.29c | 30.42±0.89c | 89.45±0.18d | 88.84±0.62c |
| 6 | 1774.12±22.10b | 1764.12±22.08b | 100.00±6.00e | 106.33±6.03de | 22.36±0.74g | 22.88±0.80g | 133.30±0.38a | 132.53±0.13a |
| 7 | 1669.73±14.49f | 1659.73±14.49de | 127.00±6.56b | 132.67±6.03ab | 33.50±0.19a | 33.90±0.07a | 43.15±0.97i | 41.71±0.08g |
| 8 | 1742.73±11.59c | 1733.05±11.47c | 115.67±3.06cd | 121.67±3.06c | 28.38±0.49e | 28.57±0.54e | 88.25±0.86f | 87.31±0.17d |
| 9 | 1782.77±11.18b | 1776.17±9.48b | 98.00±1.00e | 105.00±1.00e | 24.73±0.20f | 25.23±0.40f | 132.25±0.67c | 131.01±0.47b |
处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) | 单株粒数 Grain number per plant | 千粒重 Thousand grains weight (g) | 总株数Number of plants (×104 plant·hm-2 ) | 倒伏率 Lodging percentage (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| A1 | 1682.57c | 1674.13c | 104.67c | 108.67c | 29.58a | 30.28a | 88.35b | 87.29b | 33.11a | 33.89a |
| A2 | 1765.71a | 1756.19a | 118.89a | 124.33a | 28.33b | 28.72b | 89.00a | 88.00a | 17.14c | 18.14c |
| A3 | 1731.74b | 1722.98b | 113.56b | 119.78b | 28.87b | 29.23b | 87.88c | 86.68c | 25.08b | 26.09b |
| B1 | 1672.13c | 1661.42c | 124.44a | 128.67a | 32.29a | 32.86a | 43.62c | 42.56c | 19.11c | 20.11c |
| B2 | 1777.38a | 1771.37a | 113.56b | 118.67b | 29.37b | 29.67b | 88.78b | 87.88b | 22.43b | 23.44b |
| B3 | 1730.52b | 1720.52b | 99.11c | 105.44c | 25.12c | 25.70c | 132.83a | 131.54a | 33.80a | 34.58a |
| C1 | 1737.70a | 1728.90a | 109.00b | 113.89b | 27.30c | 27.76c | 88.33b | 87.05b | 23.41b | 24.41b |
| C2 | 1719.05ab | 1709.40ab | 112.11ab | 117.33ab | 28.75b | 29.37b | 88.38ab | 87.21ab | 23.77b | 24.77b |
| C3 | 1723.29ab | 1714.99ab | 116.00a | 121.55a | 30.74a | 31.10a | 88.52a | 87.72a | 28.16a | 28.94a |
| RA | 83.14** | 82.06** | 14.22** | 15.67** | 1.25* | 1.56* | 1.12* | 1.32* | 15.97** | 15.75** |
| RB | 105.25** | 109.95** | 25.33** | 23.22** | 7.17** | 7.17** | 89.22** | 88.98** | 14.69** | 14.47** |
| RC | 18.65 | 19.49 | 7.00* | 7.67* | 3.44* | 3.34* | 0.12 | 0.35 | 4.75* | 4.52* |
表3 不同处理因素对苦荞产量及产量构成、倒伏率的多重比较
Table 3 The multiple comparisons of yield and yield compositions, lodging percentage of tartary buckwheat under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) | 单株粒数 Grain number per plant | 千粒重 Thousand grains weight (g) | 总株数Number of plants (×104 plant·hm-2 ) | 倒伏率 Lodging percentage (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| A1 | 1682.57c | 1674.13c | 104.67c | 108.67c | 29.58a | 30.28a | 88.35b | 87.29b | 33.11a | 33.89a |
| A2 | 1765.71a | 1756.19a | 118.89a | 124.33a | 28.33b | 28.72b | 89.00a | 88.00a | 17.14c | 18.14c |
| A3 | 1731.74b | 1722.98b | 113.56b | 119.78b | 28.87b | 29.23b | 87.88c | 86.68c | 25.08b | 26.09b |
| B1 | 1672.13c | 1661.42c | 124.44a | 128.67a | 32.29a | 32.86a | 43.62c | 42.56c | 19.11c | 20.11c |
| B2 | 1777.38a | 1771.37a | 113.56b | 118.67b | 29.37b | 29.67b | 88.78b | 87.88b | 22.43b | 23.44b |
| B3 | 1730.52b | 1720.52b | 99.11c | 105.44c | 25.12c | 25.70c | 132.83a | 131.54a | 33.80a | 34.58a |
| C1 | 1737.70a | 1728.90a | 109.00b | 113.89b | 27.30c | 27.76c | 88.33b | 87.05b | 23.41b | 24.41b |
| C2 | 1719.05ab | 1709.40ab | 112.11ab | 117.33ab | 28.75b | 29.37b | 88.38ab | 87.21ab | 23.77b | 24.77b |
| C3 | 1723.29ab | 1714.99ab | 116.00a | 121.55a | 30.74a | 31.10a | 88.52a | 87.72a | 28.16a | 28.94a |
| RA | 83.14** | 82.06** | 14.22** | 15.67** | 1.25* | 1.56* | 1.12* | 1.32* | 15.97** | 15.75** |
| RB | 105.25** | 109.95** | 25.33** | 23.22** | 7.17** | 7.17** | 89.22** | 88.98** | 14.69** | 14.47** |
| RC | 18.65 | 19.49 | 7.00* | 7.67* | 3.44* | 3.34* | 0.12 | 0.35 | 4.75* | 4.52* |
处理 Treatment | 倒伏时期Lodging stage | 倒伏级别Lodging degree | 倒伏率Lodging percentage (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 1 | FS | FS | 2 | 2 | 24.12±1.36c | 25.52±1.05c |
| 2 | FBS | FBS | 2 | 3 | 28.70±2.62b | 29.36±1.12b |
| 3 | FBS | FBS | 3 | 3 | 46.50±0.61a | 46.84±1.05a |
| 4 | MS | MS | 1 | 1 | 11.45±1.05e | 13.15±0.80e |
| 5 | MS | MS | 1 | 2 | 16.23±0.91d | 17.62±0.85d |
| 6 | MS | FS | 1 | 1 | 23.74±0.14c | 24.18±0.37c |
| 7 | MS | FS | 2 | 2 | 21.74±0.37c | 21.93±0.73c |
| 8 | FS | FS | 1 | 1 | 22.36±2.50c | 23.74±1.73c |
| 9 | FS | FS | 2 | 2 | 31.14±1.02b | 32.08±1.93b |
表4 不同处理下苦荞倒伏特性
Table 4 Lodging characteristics of tartary buckwheat under different treatment
处理 Treatment | 倒伏时期Lodging stage | 倒伏级别Lodging degree | 倒伏率Lodging percentage (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 1 | FS | FS | 2 | 2 | 24.12±1.36c | 25.52±1.05c |
| 2 | FBS | FBS | 2 | 3 | 28.70±2.62b | 29.36±1.12b |
| 3 | FBS | FBS | 3 | 3 | 46.50±0.61a | 46.84±1.05a |
| 4 | MS | MS | 1 | 1 | 11.45±1.05e | 13.15±0.80e |
| 5 | MS | MS | 1 | 2 | 16.23±0.91d | 17.62±0.85d |
| 6 | MS | FS | 1 | 1 | 23.74±0.14c | 24.18±0.37c |
| 7 | MS | FS | 2 | 2 | 21.74±0.37c | 21.93±0.73c |
| 8 | FS | FS | 1 | 1 | 22.36±2.50c | 23.74±1.73c |
| 9 | FS | FS | 2 | 2 | 31.14±1.02b | 32.08±1.93b |
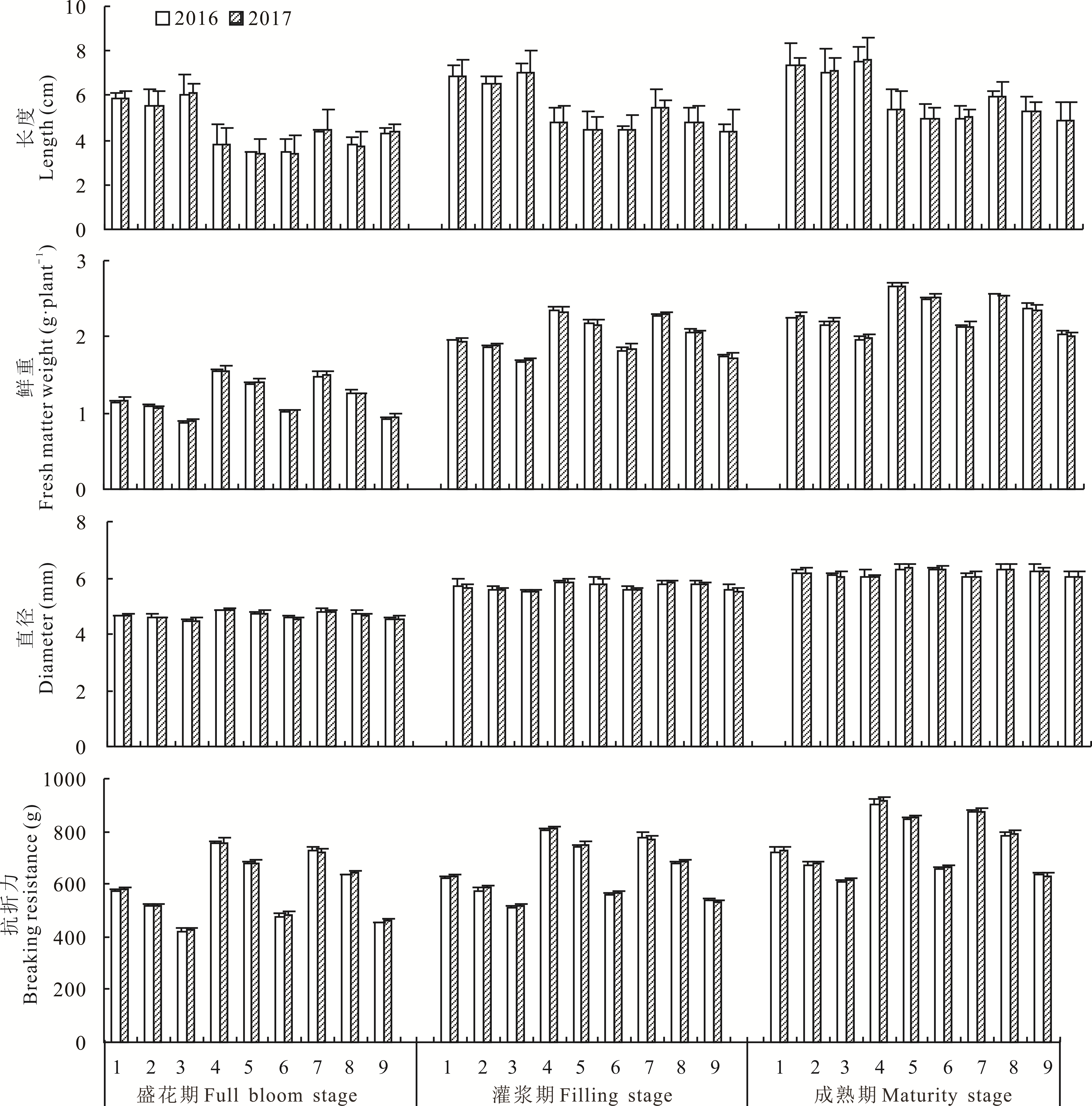
图1 不同处理下茎秆基部第二节间形态指标不同字母表示不同处理间显著性差异(P<0.05)。下同。Different letters indicate significantly difference (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Morphological indexes of second internode of stem base under different treatments
| 性状Trait | 产量Yield | 倒伏率Lodging percentage | 茎秆抗折力Culm breaking resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 倒伏率 Lodging percentage | -0.726* | ||
| 茎秆抗折力 Culm breaking resistance | 0.428 | -0.963** | |
| 第二节间长 Length of the 2nd internode | -0.473 | 0.784* | -0.935** |
| 第二节间粗 Diameter of the 2nd internode | 0.932** | -0.989** | 0.945** |
| 第二节间鲜重 Fresh weight of the 2nd internode | -0.868** | -0.878** | 0.982** |
| 木质素含量 Lignin content in culm | 0.943** | -0.914** | 0.987** |
| 4CL活性 4CL activity | 0.378 | -0.618* | 0.867** |
| PAL活性 PAL activity | 0.403 | -0.647* | 0.809** |
| CAD活性 CAD activity | 0.358 | -0.608* | 0.795* |
表5 苦荞茎秆第二节间形态特性和生理特性与抗倒伏能力的相关系数
Table 5 Correlation coefficient between morphological and physiological characteristics of second internode and lodging resistance of tartary buckwheat
| 性状Trait | 产量Yield | 倒伏率Lodging percentage | 茎秆抗折力Culm breaking resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 倒伏率 Lodging percentage | -0.726* | ||
| 茎秆抗折力 Culm breaking resistance | 0.428 | -0.963** | |
| 第二节间长 Length of the 2nd internode | -0.473 | 0.784* | -0.935** |
| 第二节间粗 Diameter of the 2nd internode | 0.932** | -0.989** | 0.945** |
| 第二节间鲜重 Fresh weight of the 2nd internode | -0.868** | -0.878** | 0.982** |
| 木质素含量 Lignin content in culm | 0.943** | -0.914** | 0.987** |
| 4CL活性 4CL activity | 0.378 | -0.618* | 0.867** |
| PAL活性 PAL activity | 0.403 | -0.647* | 0.809** |
| CAD活性 CAD activity | 0.358 | -0.608* | 0.795* |
| 1 | Zhou M L, Ivan K, Galina S, et al. Buckwheat germplasm in the world. London: Academic Press, 2018. |
| 2 | Susan S. Advances in food and nutrition research. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, 2018, 50(2): 213. |
| 3 | Zhao G, Shan F. Tartary buckwheat. Beijing: Science Press, 2009 |
| 赵钢, 陕方. 中国苦荞. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. | |
| 4 | Ohmi O, Mitsuyuki T. Distribution of cultivated and wild buckwheat species in the Nu river valley of Southwestern China. Fagopyrum, 2005(22): 1-5. |
| 5 | Feng B L, Yao A H, Gao J F, et al. Study on the regional layout and development of buckwheat in China. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 21(3): 375-377. |
| 冯佰利, 姚爱华, 高金峰, 等. 中国荞麦优势区域布局与发展研究. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(3): 375-377. | |
| 6 | Ding M Q, Wu Y M, Wei L, et al. Progress of research on buckwheat forage and its application in the livestock and poultry industries. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(1): 176-185. |
| 丁梦琦, 吴燕民, 未丽, 等. 饲用荞麦在畜牧业中的应用与研究. 草业科学, 2018, 35(1): 176-185. | |
| 7 | Xiang D B, Peng L X, Zhao G, et al. Advances in the cultivation of buckwheat. Crops, 2013(3): 1-6. |
| 向达兵, 彭镰心, 赵钢, 等. 荞麦栽培研究进展. 作物杂志, 2013(3): 1-6. | |
| 8 | Zhao G, Zou L. Nutrition and function of buckwheat. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. |
| 赵钢, 邹亮. 荞麦的营养与功能. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. | |
| 9 | Zhao G, Zhao J L, Peng L X, et al. Effects of yeast polysaccharide on growth and flavonoid accumulation in Fagopyrum tataricum sprout cultures. Molecules, 2012, 17(10): 11335-11345. |
| 10 | Zuo G M, Tan B, Wang J H, et al. Evaluation and utilization of nutrient function components in tartary buckwheat rice and tartary buckwheat powder processing. Food Science, 2009, 30(14): 183-187. |
| 左光明, 谭斌, 王金华, 等. 苦荞米与苦荞粉加工中营养功能成分的评价及利用. 食品科学, 2009, 30(14): 183-187. | |
| 11 | Gao W Y. Research on the development status and promotion strategy of small agricultural machinery. Times Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 45(1): 23-24. |
| 高文勇. 小型农业机械的发展状况及推广策略研究. 时代农机, 2018, 45(1): 23-24. | |
| 12 | Ding X Y. Study on mechanized cultivation technology of buckwheat. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013(9): 9-12. |
| 丁孝义. 荞麦机械化栽培技术研究. 现代农业科技, 2013(9): 9-12. | |
| 13 | Yang M J, Yang Y, Guo Z X, et al. Comprehensive high yield cultivation techniques of tartary buckwheat. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2010(3): 129. |
| 杨明君, 杨媛, 郭忠贤, 等. 苦荞麦综合高产栽培技术. 内蒙古农业科技, 2010(3): 129. | |
| 14 | Zheng T, Fan G Q, Wang X F, et al. Effect of tillage management, sowing depth and soil-covering on the seedlings quality of mechanical sowing wheat under intercropping condition. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(5): 164-168. |
| 郑亭, 樊高琼, 王秀芳, 等. 耕作方式、播深及覆土对机播套作小麦麦苗素质的影响. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(5): 164-168. | |
| 15 | Li H M, Jiang L H, Gu Z X. Influence factors and improvement measures of maize machine planting quality. Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 2(9): 14-16. |
| 李慧敏, 姜连花, 谷在兴. 玉米机播质量影响因素及改进措施. 农业工程, 2012, 2(9): 14-16. | |
| 16 | Wang X C, Yang W Y. The mechanization of maize soybean strip intercropping has stepped to a new level. Soybean Science and Technology, 2012(6): 48-50 |
| 王小春, 杨文钰. 玉米-大豆带状间套作全程机械化迈上新台阶. 大豆科技, 2012(6): 48-50. | |
| 17 | Wu W X, Ma R C, Fan G Q, et al. Mechanized farming system of wheat/maize/bean//The 11th annual conference of China association for science and technology. Beijing: China Association for Science and Technology, 2009: 189-192. |
| 吴维雄, 马荣朝, 樊高琼, 等. “麦/玉/豆”配套机械化生产体系研究// 第十一届中国科学技术协会年会论文集. 北京: 中国科学技术协会, 2009: 189-192. | |
| 18 | Kong E, Liu D C, Guo X L, et al. Anatomical and chemical characteristics associated with lodging resistance in wheat. The Crop Journal, 2013(1): 43-49. |
| 19 | Jones L, Ennos A R, Turner S R. Cloning and characterization of irregular xylem4 (irx4): A severely lignin-deficient mutant of Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 2001, 26(2): 205-216. |
| 20 | Gao Z N, Guo L Z, Li L, et al. Effects of nitrogen on oilseed flax stem lignin and relative enzyme and lodging resistance. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2014, 36(5): 610-615. |
| 高珍妮, 郭丽琢, 李丽, 等. 氮肥对胡麻茎秆木质素合成酶活性及其抗倒性的影响. 中国油料作物学报, 2014, 36(5): 610-615. | |
| 21 | Xiang D B, Li J, Fan Y, et al. Effect of planting density on lodging resistance and yield of tartary buckwheat. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(6): 242-247. |
| 向达兵, 李静, 范昱, 等. 种植密度对苦荞麦抗倒伏特性及产量的影响. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(6): 242-247. | |
| 22 | Liu X B, Wu D Q, Wang C, et al. Effects of spraying uniconazole on lodging resistance of culm and yield in common buckwheat. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(24): 4903-4915. |
| 刘星贝, 吴东倩, 汪灿, 等. 喷施烯效唑对甜荞茎秆抗倒性能及产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(24): 4903-4915. | |
| 23 | Wang C, Li M, Wang S X, et al. Effects of different sowing date, seeding rate and fertilization on yield and agronomic traits of Fagopyrum esculentum Xinnong 1 planted spring. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(3): 52-55. |
| 汪灿, 李曼, 王诗雪, 等. 不同播期、播种量和施肥量对甜荞信农1号春播产量及农艺性状的影响. 贵州农业科学, 2014, 42(3): 52-55. | |
| 24 | Wang C, Ruan R W, Yuan X H, et al. Relationship of anatomical structure and lignin metabolism with lodging resistance of culm in buckwheat. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(10): 1846-1856. |
| 汪灿, 阮仁武, 袁晓辉, 等. 荞麦茎秆解剖结构和木质素代谢及其与抗倒性的关系. 作物学报, 2014, 40(10): 1846-1856. | |
| 25 | Qiao C G. Lodging index-a synthetic indication of lodging-resistance. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 1988, 10(1): 7-10. |
| 乔春贵. 作物抗倒伏性的综合指标——倒伏指数. 吉林农业大学学报, 1988, 10(1): 7-10. | |
| 26 | Xiang D B, Zou L, Peng L X, et al. Appropriate mechanical sowing depth and soil-covering thickness improving seedling quality of tartary buckwheat. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(12): 26-33. |
| 向达兵, 邹亮, 彭镰心, 等. 适宜机播深度及覆土厚度提高苦荞幼苗素质. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(12): 26-33. | |
| 27 | Fan G Q, Zheng T, Chen Y,et al. Effects of tillage managements, sowing depth and soil-covering on population quality and yield of mechanical sowing wheat under relay intercropping condition. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27: 20-25. |
| 樊高琼, 郑亭, 陈溢, 等. 耕作方式、播深及覆土对机播套作小麦群体质量和产量的影响. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(S2): 20-25. | |
| 28 | Molatudi R L, Mariga I K. The effect of maize seed size and depth of planting on seedling emergence and seedling vigor. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 2009, 5(12): 2234-2237. |
| 29 | Liu X, Yin C M, Li H, et al. Sowing depth and waterlogging time after wheat sowing affect on germination rate and seedling quality before winter. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(3): 189-194. |
| 刘鑫, 尹承苗, 李慧, 等. 播种深度和播后淹水时间对冬小麦出苗率及冬前幼苗质量的影响. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(3): 189-194. | |
| 30 | Zhang Y L, Xiao K, Li Y M. Effects and physiological mechanism of planting densities on photosynthesis characteristics of flag leaf and grain yield in wheat hybrid C6-38/Py85-1. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2005, 31 (4): 498-505. |
| 张永丽, 肖凯, 李雁鸣. 种植密度对杂种小麦C6-38/Py85-1旗叶光合特性和产量的调控效应及其生理机制. 作物学报, 2005, 31 (4): 498-505. | |
| 31 | Wang X, Li Z Y, Ma W Q, et al. Effects of fertilization on yield increase of wheat in different agro-ecological regions of China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(12): 2469-2476. |
| 王旭, 李贞宇, 马文奇, 等. 中国主要生态区小麦施肥增产效应分析. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(12): 2469-2476. | |
| 32 | Berry P M, Spink J. Predicting yield losses caused by lodging in wheat. Field Crops Research, 2012, 137: 19-26. |
| 33 | Acreche M M, Slafer G A. Lodging yield penalties as affected by breeding in Mediterranean wheats. Field Crops Research, 2011, 122: 40-48. |
| 34 | Lang Y Z, Yang X D, Wang M E, et al. Effects of lodging at different filling stages on rice grain yield and quality. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(4): 407-412. |
| 郎有忠, 杨晓东, 王美娥, 等. 结实阶段不同时期倒伏对水稻产量及稻米品质的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(4): 407-412. | |
| 35 | Cao P W, Zhao M L, Wang J H, et al. Effect of lodging on maize yield in different stages. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2014(4): 38-39. |
| 曹品伟, 赵美玲, 王建华, 等. 不同时期的倒伏对玉米产量的影响. 黑龙江农业科学, 2014(4): 38-39. | |
| 36 | Huang Y G, Zheng Y H, Yuan Y S, et al. Effects of lodging period and degree on wheat yield. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 46(6): 51-53, 58. |
| 黄迎光, 郑以宏, 袁永胜, 等. 倒伏时期和倒伏程度对小麦产量的影响. 山东农业科学, 2014, 46(6): 51-53, 58. | |
| 37 | Yang Y H, Zhu Z, Zhang Y D, et al. Relationship between lodging resistance and stem morphological traits in different rice varieties (lines). Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 27(2): 231-235. |
| 杨艳华, 朱镇, 张亚东, 等. 不同水稻品种(系)抗倒伏能力与茎秆形态性状的关系. 江苏农业学报, 2011, 27(2): 231-235. | |
| 38 | Ma N, Li L, Xu J, et al. Researches on the lodging resistance and agronomic traits of winter rape (Brassica napus L.). Crops, 2010(6): 36-41. |
| 马霓, 李玲, 徐军, 等. 甘蓝型油菜抗倒伏性及农艺性状研究. 作物杂志, 2010(6): 36-41. | |
| 39 | Dong Q, Wang A P, Liang S M. Study on the architectural characteristics of wheat stalks. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University, 2003, 23(3): 188-191. |
| 董琦, 王爱萍, 梁素明. 小麦基部茎节形态结构特征与抗倒性的研究. 山西农业大学学报, 2003, 23(3): 188-191. | |
| 40 | Wang C, Ruan R W, Yuan X H, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and planting density on the lignin synthesis in the culm in relation to lodging resistance of buckwheat. Plant Production Science, 2015, 18(2): 218-227. |
| 41 | Hu D, Liu X B, Wang C, et al. Expression analysis of key enzyme genes in lignin synthesis of culm among different lodging resistances of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(9): 1864-1872. |
| 胡丹, 刘星贝, 汪灿, 等. 不同抗倒性甜荞茎秆木质素合成关键酶基因的表达分析. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(9): 1864-1872. |
| [1] | 林慧龙, 蒲彦妃, 王丹妮, 马海丽. 草原指数保险:评述与中国方案设计[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 171-185. |
| [2] | 徐强, 田新会, 杜文华. 高寒牧区黑麦和箭筈豌豆混播对草产量和营养品质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 49-59. |
| [3] | 王玉霞, 柴锦隆, 周洋洋, 徐长林, 王琳, 鱼小军. 种植方式对陇中干旱区扁蓿豆种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 60-72. |
| [4] | 王辛有, 曹文侠, 王小军, 刘玉祯, 高瑞, 王世林, 安海涛, 邓秀霞, 王文虎. 河西地区豆禾混播草地生产性能对刈割高度与施肥的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 99-110. |
| [5] | 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 梁国玲, 马祥. 干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦产量及干物质积累与分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 177-188. |
| [6] | 肖婉君, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 刘兰兰, 陈永中, 焦旭升, 张碧全, 白刚, 金建琴. 施用有机肥对当归药材性状、产量及抗病性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 189-199. |
| [7] | 贾雨雷, 廖真, 汪丽芳, 卜建超, 林标声, 林辉, 苏德伟, 鲁国东, 林占熺. 化肥减量配施菌草固氮菌肥对巨菌草生长、营养品质及土壤养分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 215-223. |
| [8] | 沙栢平, 谢应忠, 高雪芹, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲. 地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 102-114. |
| [9] | 王红林, 左艳春, 严旭, 周晓康, 寇晶, 杨希智, 郭俊英, 蒲军, 张浩仁, 杜周和. 刈割高度与施氮量对饲料桑全株产量及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 203-211. |
| [10] | 旦增塔庆, Chapagain Purna Bhadra, Pant Shankar Raj, 杰布, 格桑顿珠, 陈少锋. 不同燕麦品种在尼泊尔北部山区的生长特性及其营养品质的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 73-82. |
| [11] | 王乐政, 华方静, 曹鹏鹏, 高凤菊, 夏文荣. 不同播期夏播小豆产量性能动态指标与光温水效应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 116-129. |
| [12] | 姜慧新, 柏杉杉, 吴波, 宋静怡, 王国良. 22个燕麦品种在黄淮海地区的农艺性状与饲草品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 140-149. |
| [13] | 于晓波, 梁建秋, 何泽民, 周全卢, 吴海英, 张明荣. 撒播量对大豆茎秆特性和产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 117-124. |
| [14] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 于铁峰. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| [15] | 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 吐尔逊·吐尔洪, 涂振东, 王卉, 山其米克, 艾克拜尔·伊拉洪. 长期不同施肥处理对连作高粱生长规律及产量的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 81-92. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||