

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 40-51.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020401
车昭碧( ), 徐鹏飞, 郭亚亚, 曹佳敏, 黄星宇, 杨寒珺, 鲁为华(
), 徐鹏飞, 郭亚亚, 曹佳敏, 黄星宇, 杨寒珺, 鲁为华( )
)
收稿日期:2020-08-31
修回日期:2020-09-27
出版日期:2021-10-19
发布日期:2021-10-19
通讯作者:
鲁为华
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: winnerlwh@sina.com基金资助:
Zhao-bi CHE( ), Peng-fei XU, Ya-ya GUO, Jia-min CAO, Xing-yu HUANG, Han-jun YANG, Wei-hua LU(
), Peng-fei XU, Ya-ya GUO, Jia-min CAO, Xing-yu HUANG, Han-jun YANG, Wei-hua LU( )
)
Received:2020-08-31
Revised:2020-09-27
Online:2021-10-19
Published:2021-10-19
Contact:
Wei-hua LU
摘要:
为明确北方蚁影响下蚁巢及其周围土壤种子库变化特征,以山地草甸中广泛分布的北方蚁为研究对象,探究距蚁巢不同距离、不同深度下土壤种子库的特征,以及土壤环境对种子库物种分布的影响。结果表明:蚁巢中心及周围土壤种子库中共出现28个物种,隶属12科28属,其中禾本科植物居多,蚁巢中心0~10 cm、10~20 cm深度下,土壤中平车前、北疆剪股颖、无芒雀麦、鸭茅、草地早熟禾萌发数量均显著高于其他样点(P<0.05);土壤种子库物种生活型组成以多年生草本植物为主,蚁巢中心0~10 cm、10~20 cm深度下多年生草本植物数量均显著高于其他样点(P<0.05);蚁巢中心0~10 cm、10~20 cm深度土壤种子库种子数量和物种数均显著高于蚁巢周围区域(P<0.05)。相同距离下,0~10 cm深度土壤种子库种子数量及物种数均高于10~20 cm深度;蚁巢大小与蚁巢中心土壤种子库种子数量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);随着距离的增加,同深度下土壤种子库丰富度指数、多样性指数、优势度指数、均匀度指数大致呈现出“V”字型变化趋势,并在距蚁巢100 cm处物种多样性指数降至最低;RDA分析表明,土壤速效磷是影响该区土壤种子库分布的主要因子。北方蚁能对周围环境中的种子进行收集与搬运,增加了蚁巢内种子的数量,影响了周围环境中土壤种子库的空间分布,在小尺度范围内进行了种子再分配,改变了土壤种子库内的物种分布。
车昭碧, 徐鹏飞, 郭亚亚, 曹佳敏, 黄星宇, 杨寒珺, 鲁为华. 北方蚁(Formica aquilonia)对山地草甸土壤种子库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 40-51.
Zhao-bi CHE, Peng-fei XU, Ya-ya GUO, Jia-min CAO, Xing-yu HUANG, Han-jun YANG, Wei-hua LU. Effects of the ant species Formica aquilonia on soil seed banks in mountain meadows[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 40-51.
采样地点 Sampling position | 蚁巢样编号 Nest number | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 蚁巢直径 Nest size (cm) | 蚁巢高度 Nest height (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
大石湾 Da Shiwan | 1 | 43°51.406' N, 86°1.623' E | 1607 | 60 | 46 |
| 2 | 43°51.247' N, 86°1.632' E | 1623 | 55 | 40 | |
| 3 | 43°51.230' N, 86°1.632' E | 1630 | 40 | 35 | |
| 4 | 43°51.210' N, 86°1.626' E | 1638 | 30 | 26 | |
| 5 | 43°51.268' N, 86°1.637' E | 1639 | 45 | 37 |
表1 各蚁巢基本概况
Table 1 Basic situation of each ant nest
采样地点 Sampling position | 蚁巢样编号 Nest number | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 蚁巢直径 Nest size (cm) | 蚁巢高度 Nest height (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
大石湾 Da Shiwan | 1 | 43°51.406' N, 86°1.623' E | 1607 | 60 | 46 |
| 2 | 43°51.247' N, 86°1.632' E | 1623 | 55 | 40 | |
| 3 | 43°51.230' N, 86°1.632' E | 1630 | 40 | 35 | |
| 4 | 43°51.210' N, 86°1.626' E | 1638 | 30 | 26 | |
| 5 | 43°51.268' N, 86°1.637' E | 1639 | 45 | 37 |
科名 Family | 属名 Genus | 种名 Species | 萌发幼苗数量Germination seedlings number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 cm | 50 cm | 100 cm | 150 cm | 200 cm | CK | |||
| 0~10 cm | ||||||||
| 车前科Plantaginaceae | 车前属 Plantago | 平车前Plantago depressa | 7.60±2.70a | 1.40±3.13b | 1.20±1.64b | 2.40±3.78b | 2.20±3.90b | - |
| 唇形科Labiatae | 薄荷属 Mentha | 野薄荷M. canadensis | - | 0.60±1.34 | - | - | - | - |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 车轴草属 Trifolium | 白车轴草Trifolium repens | - | - | - | 0.40±0.89 | - | - |
| 苜蓿属Medicago | 黄花苜蓿M. falcata | - | - | 0.60±1.34 | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.40±0.55 | |
| 天蓝苜蓿Medicago lupulina | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | ||
| 禾本科Gramineae | 剪股颖属 Agrostis | 北疆剪股颖A. turkestanica | 22.00±4.42a | 7.20±6.46b | 5.60±5.60b | 5.60±4.83b | 2.00±2.12b | 3.00±2.45b |
| 雀麦属 Bromus | 无芒雀麦B. inermis | 16.00±2.35a | 6.80±6.30b | 4.80±3.27bc | 2.20±2.59c | 1.00±1.23c | 1.00±1.00c | |
| 梯牧草属 Phleum | 假梯牧草P. phleoides | 0.60±1.34 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 鸭茅属 Dactylis | 鸭茅D. glomerata | 6.80±2.17a | 1.80±2.17b | 0.60±1.34b | 0.40±0.55b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.40±0.55b | |
| 早熟禾属 Poa | 草地早熟禾P. pratensis | 30.40±8.23a | 11.40±6.58b | 7.40±4.93b | 6.20±5.02b | 4.20±4.09b | 3.60±1.82b | |
| 菊科Compositae | 蒿属 Artemisia | 细裂叶莲蒿Artemisia gmelinii | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - |
| 蓟属 Cephalanoplos | 刺儿菜Cirsium arvense | 1.80±1.92a | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | - | 0.20±0.45b | |
| 大蓟Cirsium japonicum | 0.20±0.44 | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | 0.40±0.89 | - | ||
| 牛蒡属 Arctium | 牛蒡Arctium lappa | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | |
| 蒲公英属 Taraxacum | 蒲公英Taraxacum mongolicum | 0.40±0.89 | - | - | - | 0.80±1.10 | - | |
| 蓍草属 Achillea | 千叶蓍A. millefolium | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | - | - | |
| 蓼科Polygonaceae | 蓼属 Polygonum | 萹蓄Polygonum aviculare | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.40±0.89 |
| 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 水毛茛属 Batrachium | 水毛茛Batrachium bungei | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.20±0.44 | 0.80±1.10 | 0.20±0.44 | 0.40±0.89 |
| 唐松草属 Thalictrum | 唐松草T. aquilegiifolium | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | - | 1.20±1.79 | 0.20±0.44 | |
| 茜草科Rubiaceae | 拉拉藤属 Galium | 拉拉藤G. aparine | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | - | - | - | - |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 草莓属 Fragaria | 森林草莓Fragaria vesca | 3.60±2.61 | 5.00±8.49 | 3.20±4.38 | 4.60±5.94 | 2.60±2.07 | 0.60±0.89 |
| 委陵菜属 Potentilla | 委陵菜Potentilla chinensis | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | |
| 十字花科 Cruciferae | 大蒜芥属 Sisymbrium | 大蒜芥Sisymbrium altissimum | 0.80±1.10 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 涩荠属 Malcolmia | 涩荠Malcolmia africana | 1.40±3.13 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 石竹科Caryophyllaceae | 石竹属 Dianthus | 长萼石竹Dianthus kuschakewiczii | - | - | - | - | 0.60±0.89 | - |
| 荨麻科Urticaceae | 荨麻属 Urtica | 荨麻Urtica fissa | 1.20±2.68 | 0.20±0.45 | 0.20±0.48 | - | 0.20±0.48 | 0.40±0.89 |
| 10~20 cm | ||||||||
| 车前科Plantaginaceae | 车前属 Plantago | 平车前P. depressa | 4.20±4.92a | 0.80±1.79b | 0.40±0.89b | - | 0.40±0.55b | - |
| 唇形科Labiatae | 薄荷属 Mentha | 野薄荷M. canadensis | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 黄芪属 Astragalus | 天山黄耆Astragalus lepsensis | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - |
| 苜蓿属Medicago | 黄花苜蓿M. falcata | - | - | 0.40±0.89b | 0.60±0.89a | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | |
| 禾本科Gramineae | 剪股颖属 Agrostis | 北疆剪股颖A. turkestanica | 23.60±17.17a | 1.40±1.52b | 0.80±1.30b | 0.40±0.89b | 1.80±2.68b | 0.40±0.89b |
| 雀麦属 Bromus | 无芒雀麦B. inermis | 19.40±7.86a | 0.40±0.55b | - | - | 0.60±0.89b | 0.20±0.45b | |
| 鸭茅属 Dactylis | 鸭茅D. glomerata | 6.40±4.39a | 0.20±0.45b | - | - | 0.40±0.55b | - | |
| 羊茅属 Festuca | 羊茅F. ovina | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - | 0.2±0.45 | - | |
| 早熟禾属 Poa | 草地早熟禾P. pratensis | 25.20±8.93a | 1.60±1.14b | 1.00±1.00b | 1.20±0.84b | 2.20±1.10b | 0.60±0.89b | |
| 菊科Compositae | 蒿属 Artemisia | 细裂叶莲蒿A. gmelinii | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 蓟属 Cephalanoplos | 刺儿菜C. arvense | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | 0.20±0.45 | |
| 蒲公英属 Taraxacum | 蒲公英T. mongolicum | 0.80±1.10 | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | |
| 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 水毛茛属 Batrachium | 水毛茛B. bungei | 0.20±0.45b | - | - | 0.20±0.45b | 0.60±1.34a | 1.00±1.23a |
| 唐松草属 Thalictrum | 唐松草T. aquilegiifolium | 0.40±0.59 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 茜草科Rubiaceae | 拉拉藤属 Galium | 拉拉藤G. aparine | 0.40±0.89 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 草莓属 Fragaria | 森林草莓F. vesca | 3.00±2.74a | 0.80±1.79b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.80±1.30b | 1.60±0.55a |
| 十字花科Cruciferae | 大蒜芥属 Sisymbrium | 大蒜芥S. altissimum | - | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.45 |
| 石竹科Caryophyllaceae | 石竹属 Dianthus | 长萼石竹D. kuschakewiczii | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | - |
| 荨麻科Urticaceae | 荨麻属 Urtica | 荨麻U. fissa | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - | 0.40±0.89 | - |
表2 各蚁巢土壤种子库数量及物种组成
Table 2 Number and species composition of soil seed banks in each ant nest
科名 Family | 属名 Genus | 种名 Species | 萌发幼苗数量Germination seedlings number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 cm | 50 cm | 100 cm | 150 cm | 200 cm | CK | |||
| 0~10 cm | ||||||||
| 车前科Plantaginaceae | 车前属 Plantago | 平车前Plantago depressa | 7.60±2.70a | 1.40±3.13b | 1.20±1.64b | 2.40±3.78b | 2.20±3.90b | - |
| 唇形科Labiatae | 薄荷属 Mentha | 野薄荷M. canadensis | - | 0.60±1.34 | - | - | - | - |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 车轴草属 Trifolium | 白车轴草Trifolium repens | - | - | - | 0.40±0.89 | - | - |
| 苜蓿属Medicago | 黄花苜蓿M. falcata | - | - | 0.60±1.34 | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.40±0.55 | |
| 天蓝苜蓿Medicago lupulina | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | ||
| 禾本科Gramineae | 剪股颖属 Agrostis | 北疆剪股颖A. turkestanica | 22.00±4.42a | 7.20±6.46b | 5.60±5.60b | 5.60±4.83b | 2.00±2.12b | 3.00±2.45b |
| 雀麦属 Bromus | 无芒雀麦B. inermis | 16.00±2.35a | 6.80±6.30b | 4.80±3.27bc | 2.20±2.59c | 1.00±1.23c | 1.00±1.00c | |
| 梯牧草属 Phleum | 假梯牧草P. phleoides | 0.60±1.34 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 鸭茅属 Dactylis | 鸭茅D. glomerata | 6.80±2.17a | 1.80±2.17b | 0.60±1.34b | 0.40±0.55b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.40±0.55b | |
| 早熟禾属 Poa | 草地早熟禾P. pratensis | 30.40±8.23a | 11.40±6.58b | 7.40±4.93b | 6.20±5.02b | 4.20±4.09b | 3.60±1.82b | |
| 菊科Compositae | 蒿属 Artemisia | 细裂叶莲蒿Artemisia gmelinii | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - |
| 蓟属 Cephalanoplos | 刺儿菜Cirsium arvense | 1.80±1.92a | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | - | 0.20±0.45b | |
| 大蓟Cirsium japonicum | 0.20±0.44 | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | 0.40±0.89 | - | ||
| 牛蒡属 Arctium | 牛蒡Arctium lappa | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | |
| 蒲公英属 Taraxacum | 蒲公英Taraxacum mongolicum | 0.40±0.89 | - | - | - | 0.80±1.10 | - | |
| 蓍草属 Achillea | 千叶蓍A. millefolium | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | - | - | |
| 蓼科Polygonaceae | 蓼属 Polygonum | 萹蓄Polygonum aviculare | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.40±0.89 |
| 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 水毛茛属 Batrachium | 水毛茛Batrachium bungei | 0.20±0.44 | - | 0.20±0.44 | 0.80±1.10 | 0.20±0.44 | 0.40±0.89 |
| 唐松草属 Thalictrum | 唐松草T. aquilegiifolium | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | - | 1.20±1.79 | 0.20±0.44 | |
| 茜草科Rubiaceae | 拉拉藤属 Galium | 拉拉藤G. aparine | 0.20±0.44 | 0.20±0.44 | - | - | - | - |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 草莓属 Fragaria | 森林草莓Fragaria vesca | 3.60±2.61 | 5.00±8.49 | 3.20±4.38 | 4.60±5.94 | 2.60±2.07 | 0.60±0.89 |
| 委陵菜属 Potentilla | 委陵菜Potentilla chinensis | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.44 | - | |
| 十字花科 Cruciferae | 大蒜芥属 Sisymbrium | 大蒜芥Sisymbrium altissimum | 0.80±1.10 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 涩荠属 Malcolmia | 涩荠Malcolmia africana | 1.40±3.13 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 石竹科Caryophyllaceae | 石竹属 Dianthus | 长萼石竹Dianthus kuschakewiczii | - | - | - | - | 0.60±0.89 | - |
| 荨麻科Urticaceae | 荨麻属 Urtica | 荨麻Urtica fissa | 1.20±2.68 | 0.20±0.45 | 0.20±0.48 | - | 0.20±0.48 | 0.40±0.89 |
| 10~20 cm | ||||||||
| 车前科Plantaginaceae | 车前属 Plantago | 平车前P. depressa | 4.20±4.92a | 0.80±1.79b | 0.40±0.89b | - | 0.40±0.55b | - |
| 唇形科Labiatae | 薄荷属 Mentha | 野薄荷M. canadensis | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 黄芪属 Astragalus | 天山黄耆Astragalus lepsensis | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - |
| 苜蓿属Medicago | 黄花苜蓿M. falcata | - | - | 0.40±0.89b | 0.60±0.89a | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | |
| 禾本科Gramineae | 剪股颖属 Agrostis | 北疆剪股颖A. turkestanica | 23.60±17.17a | 1.40±1.52b | 0.80±1.30b | 0.40±0.89b | 1.80±2.68b | 0.40±0.89b |
| 雀麦属 Bromus | 无芒雀麦B. inermis | 19.40±7.86a | 0.40±0.55b | - | - | 0.60±0.89b | 0.20±0.45b | |
| 鸭茅属 Dactylis | 鸭茅D. glomerata | 6.40±4.39a | 0.20±0.45b | - | - | 0.40±0.55b | - | |
| 羊茅属 Festuca | 羊茅F. ovina | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - | 0.2±0.45 | - | |
| 早熟禾属 Poa | 草地早熟禾P. pratensis | 25.20±8.93a | 1.60±1.14b | 1.00±1.00b | 1.20±0.84b | 2.20±1.10b | 0.60±0.89b | |
| 菊科Compositae | 蒿属 Artemisia | 细裂叶莲蒿A. gmelinii | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 蓟属 Cephalanoplos | 刺儿菜C. arvense | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | 0.20±0.45 | |
| 蒲公英属 Taraxacum | 蒲公英T. mongolicum | 0.80±1.10 | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | |
| 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 水毛茛属 Batrachium | 水毛茛B. bungei | 0.20±0.45b | - | - | 0.20±0.45b | 0.60±1.34a | 1.00±1.23a |
| 唐松草属 Thalictrum | 唐松草T. aquilegiifolium | 0.40±0.59 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 茜草科Rubiaceae | 拉拉藤属 Galium | 拉拉藤G. aparine | 0.40±0.89 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 草莓属 Fragaria | 森林草莓F. vesca | 3.00±2.74a | 0.80±1.79b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.20±0.45b | 0.80±1.30b | 1.60±0.55a |
| 十字花科Cruciferae | 大蒜芥属 Sisymbrium | 大蒜芥S. altissimum | - | - | - | - | - | 0.20±0.45 |
| 石竹科Caryophyllaceae | 石竹属 Dianthus | 长萼石竹D. kuschakewiczii | - | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | 0.20±0.45 | - |
| 荨麻科Urticaceae | 荨麻属 Urtica | 荨麻U. fissa | 0.20±0.45 | - | - | - | 0.40±0.89 | - |
距离 Distance (cm) | 深度 Depth (cm) | 土壤种子库内各生活型萌发数量Germination number of each life type in the soil seed bank | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 半灌木Subshrub | 多年生草本Perennial herbs | 一年生草本Annual herb | ||
| 0 | 0~10 | - | 92.80±15.01a | - |
| 10~20 | 0.20±0.40 | 84.00±37.49A | - | |
| 50 | 0~10 | - | 35.00±20.87b | - |
| 10~20 | - | 5.60±3.05B | - | |
| 100 | 0~10 | - | 24.80±13.66bc | - |
| 10~20 | - | 3.20±2.77B | - | |
| 150 | 0~10 | - | 23.20±10.33bc | 0.20±0.40 |
| 10~20 | - | 2.40±0.55B | - | |
| 200 | 0~10 | 0.20±0.40 | 16.20±5.45c | - |
| 10~20 | - | 8.00±5.29B | - | |
| CK | 0~10 | - | 10.20±4.87c | 0.20±0.40 |
| 10~20 | - | 4.80±2.95B | - | |
表3 土壤种子库物种生活型组成
Table 3 Life type composition of soil seed bank species
距离 Distance (cm) | 深度 Depth (cm) | 土壤种子库内各生活型萌发数量Germination number of each life type in the soil seed bank | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 半灌木Subshrub | 多年生草本Perennial herbs | 一年生草本Annual herb | ||
| 0 | 0~10 | - | 92.80±15.01a | - |
| 10~20 | 0.20±0.40 | 84.00±37.49A | - | |
| 50 | 0~10 | - | 35.00±20.87b | - |
| 10~20 | - | 5.60±3.05B | - | |
| 100 | 0~10 | - | 24.80±13.66bc | - |
| 10~20 | - | 3.20±2.77B | - | |
| 150 | 0~10 | - | 23.20±10.33bc | 0.20±0.40 |
| 10~20 | - | 2.40±0.55B | - | |
| 200 | 0~10 | 0.20±0.40 | 16.20±5.45c | - |
| 10~20 | - | 8.00±5.29B | - | |
| CK | 0~10 | - | 10.20±4.87c | 0.20±0.40 |
| 10~20 | - | 4.80±2.95B | - | |
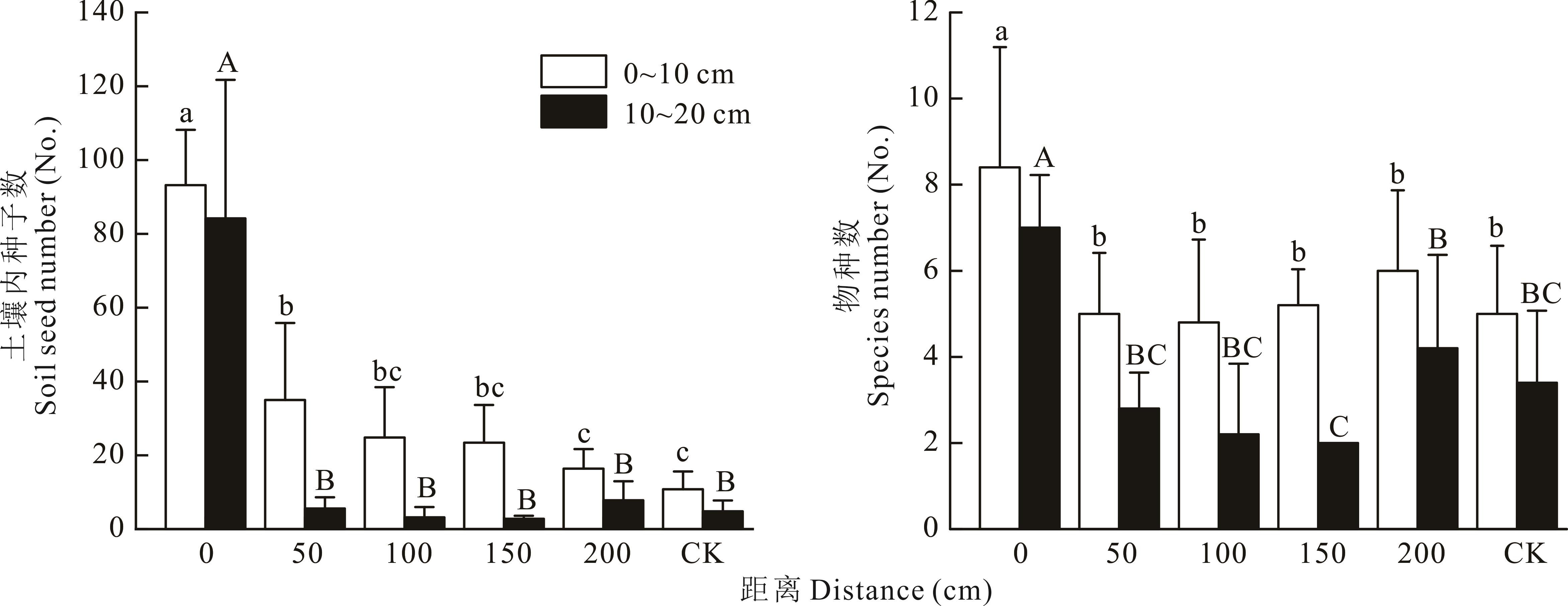
图1 蚁巢中心及周围土壤种子库的分布特征不同小写字母(0~10 cm土壤深度)和不同大写字母(10~20 cm土壤深度)表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters (soil depth of 0-10 cm) and different capital letters (soil depth of 10-20 cm) indicate significant differences at P<0.05. The same below.
Fig.1 Distribution characteristics of seed banks in the center and surrounding soil of ant nests
项目 Item | 离巢距离 Distance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 cm | 50 cm | 100 cm | 150 cm | 200 cm | CK | |
| 种子数Seed number | 0.965** | 0.216 | 0.379 | 0.263 | -0.678 | 0.043 |
| 物种数Species number | 0.542 | -0.305 | 0.819 | 0.726 | -0.247 | -0.625 |
表4 蚁巢大小与土壤种子数、物种数的Pearson相关分析
Table 4 Pearson correlation analysis among nest size and soil seed number, species number
项目 Item | 离巢距离 Distance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 cm | 50 cm | 100 cm | 150 cm | 200 cm | CK | |
| 种子数Seed number | 0.965** | 0.216 | 0.379 | 0.263 | -0.678 | 0.043 |
| 物种数Species number | 0.542 | -0.305 | 0.819 | 0.726 | -0.247 | -0.625 |
| 项目Item | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigen values | 0.692 | 0.026 | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.875 | 0.727 | 0.530 | 0.659 |
| 变量积累百分比物种数据 Cumulation percentage variance species date | 69.2 | 71.8 | 72.6 | 72.8 |
| 物种-环境关系 Species-environment relationship | 95.0 | 98.5 | 99.6 | 99.8 |
| 所有特征值之和 Sum of all eigenvalue | 1.000 | - | - | - |
| 所有典范特征值之和 Sum of all canonical eigenvalue | 0.729 | - | - | - |
| 蒙特卡罗检验Summary of Monte Carlo test | - | - | - | - |
| 第一典范轴P值Significance of first canonical axis | 0.036 | - | - | - |
| 所有典范轴P值Test of significance of all canonical axis | 0.038 | - | - | - |
表5 土壤种子库物种与土壤理化因子的RDA排序分析
Table 5 RDA sorting analysis of soil seed bank species and soil physical and chemical factors
| 项目Item | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigen values | 0.692 | 0.026 | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.875 | 0.727 | 0.530 | 0.659 |
| 变量积累百分比物种数据 Cumulation percentage variance species date | 69.2 | 71.8 | 72.6 | 72.8 |
| 物种-环境关系 Species-environment relationship | 95.0 | 98.5 | 99.6 | 99.8 |
| 所有特征值之和 Sum of all eigenvalue | 1.000 | - | - | - |
| 所有典范特征值之和 Sum of all canonical eigenvalue | 0.729 | - | - | - |
| 蒙特卡罗检验Summary of Monte Carlo test | - | - | - | - |
| 第一典范轴P值Significance of first canonical axis | 0.036 | - | - | - |
| 所有典范轴P值Test of significance of all canonical axis | 0.038 | - | - | - |
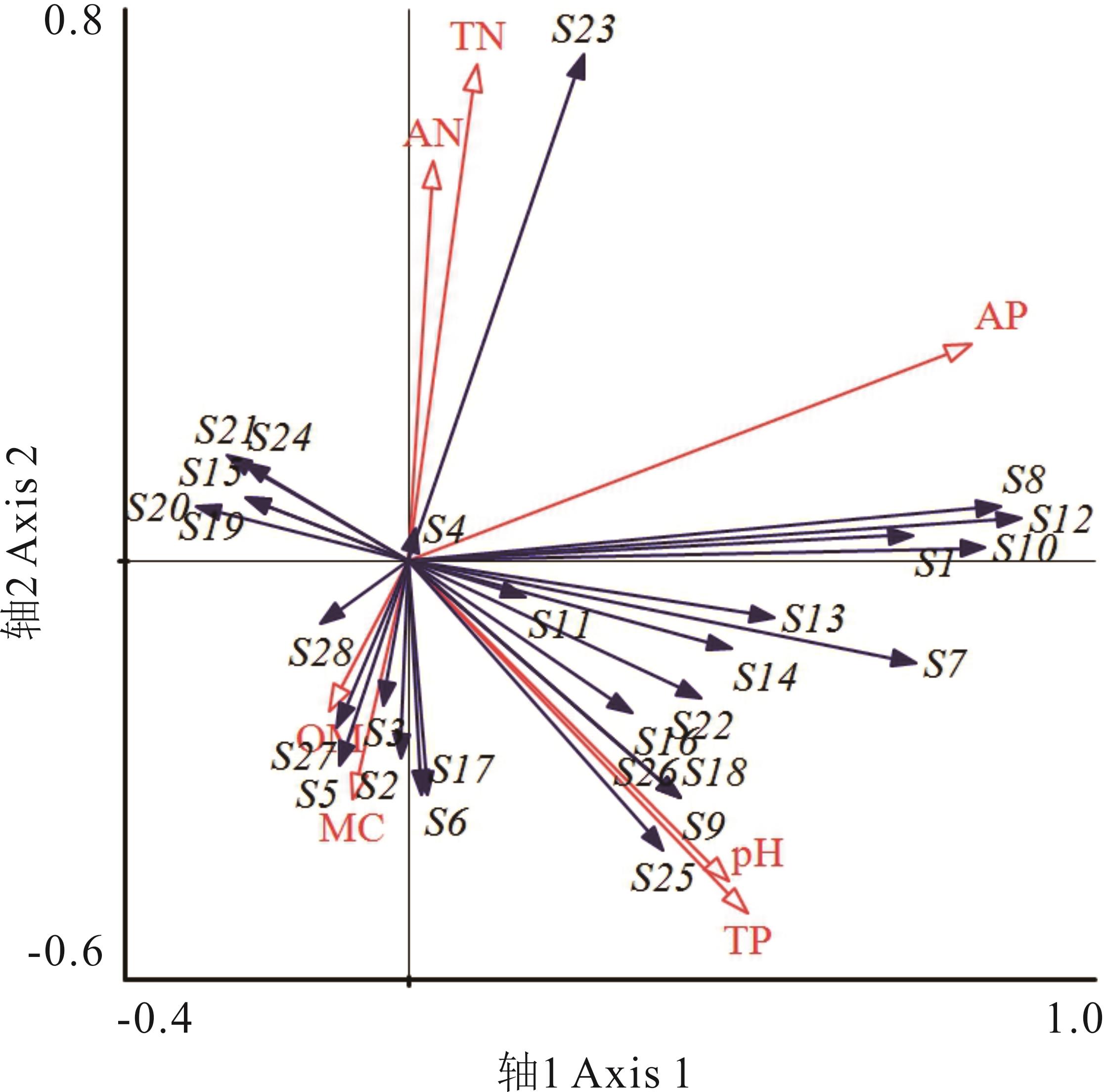
图3 土壤种子库物种数量分布与土壤理化因子的RDA排序MC: 含水率Moisture content; OM: 有机质Organic matter; pH: pH值 pH value; TN: 全氮Total nitrogen; TP: 全磷Total phosphorus; AN: 速效氮Available nitrogen; AP: 速效磷Available phosphorus.S1: 平车前P. depressa; S2: 野薄荷M. canadensis; S3: 白花三叶草T. repens; S4: 天山黄耆A. lepsensis; S5: 黄花苜蓿M. falcata; S6: 天蓝苜蓿M. lupulina; S7: 北疆剪股颖A. turkestanica; S8: 无芒雀麦B. inermis; S9: 假梯牧草P. phleoides; S10: 鸭茅D. glomerata; S11: 羊茅F. ovina; S12: 草地早熟禾P. pratensis; S13: 细裂叶莲蒿A. gmelinii; S14: 小蓟C. setosum; S15: 牛蒡A. lappa; S16: 蒲公英T. mongolicum; S17: 千叶蓍A. millefolium; S18: 大蓟C. japonicum; S19: 萹蓄P. aviculare; S20: 水毛茛B. bungei; S21: 唐松草T. aquilegiifolium; S22: 拉拉藤G. aparine; S23: 森林草莓F. vesca; S24: 委陵菜P. chinensis; S25: 大蒜芥S. altissimum; S26: 涩芥M. africana; S27: 长萼石竹D. kuschakewiczii; S28: 荨麻U. fissa.
Fig.3 RDA sequence of soil seed bank species quantity distribution and soil physicochemical factors
| 1 | Thompson K, Grime J P. Seasonal variation in the seed banks of herbaceous species in ten contrasting habitats. Journal of Ecology, 1979, 67(3): 893-921. |
| 2 | Li G Q, Shao W S, Zhao P P, et al. Analysis of soil seed bank characteristics and soil physical and chemical properties of four plant communities in a desert steppe region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(17): 6282-6292. |
| 李国旗, 邵文山, 赵盼盼, 等. 荒漠草原区4种植物群落土壤种子库特征及其土壤理化性质. 生态学报, 2019, 39(17): 6282-6292. | |
| 3 | Yu L, Zhou Y R, Zhao Y N, et al, Responses of the soil seed bank to simulated rainfall levels and anthropogenically introduced shrub encroachment in the desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. |
| 于露, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 等. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对灌丛引入和降水梯度的响应特征. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. | |
| 4 | Kelt D A, Meserve P L, Forister M L, et al. Seed predation by birds and small mammals in semiarid Chile. Oikos, 2004, 104(1): 133-141. |
| 5 | Bates M. The origin of species: By means of natural selection or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life. American Anthropologist, 2010, 61(1): 176-177. |
| 6 | Wills B D, Landis D A. The role of ants in north temperate grasslands: A review. Oecologia, 2017, 186(2): 323-338. |
| 7 | Schupp E W, Pedro J, José M G. Seed dispersal effectiveness revisited: A conceptual review. New Phytologist, 2010, 188(2): 333-353. |
| 8 | Beattie A J, Culver D C. Interactions between ants and the diaspores of some common spring flowering herbs in West Virginia. Castanea, 1979, 44(3): 177-186. |
| 9 | Handel S N, Beattie A J. Seed dispersal by ants. Scientific American, 1990, 263(2): 76-83. |
| 10 | Hughes L, Westoby M, Jurado E. Convergence of elaiosomes and insect prey: Evidence from ant foraging behaviour and fatty acid composition. Functional Ecology, 1994, 8(3): 358-365. |
| 11 | Dostal P. Effect of three mound-building ant species on the formation of soil seed bank in mountain grassland, Flora, 2004, 200(2): 148-158. |
| 12 | Wu H T, Batzer D P, Yan X M, et al. Contributions of ant mounds to soil carbon and nitrogen pools in a marsh wetland of Northeastern China. Applied Soil Ecology, 2013, 70(4): 9-15. |
| 13 | Dai J. Influence of ants on plant diversity in different degraded Songnen grassland. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2016. |
| 代军. 松嫩草地不同退化程度下蚂蚁对植物多样性的影响. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2016. | |
| 14 | Yu X J, Pu X P, Huang S J, et al. Effects of ants (Tetramorium sp.) on eastern Qilian Mountains alpine grassland ecosystem. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(2): 140-145. |
| 鱼小军, 蒲小鹏, 黄世杰, 等. 蚂蚁对东祁连山高寒草地生态系统的影响. 草业学报, 2010, 19(2): 140-145. | |
| 15 | Yin X Y. Formica aquilonia yarrow principalconstituent content determination. Natural Sciences Journal of Harbin University, 2011, 27(5): 86-87. |
| 尹相壹. 北方蚁主要成分含量测定. 哈尔滨师范大学自然科学学报, 2011, 27(5): 86-87. | |
| 16 | Li R, Ye Y. Progressesin seed dormancy and dormancy-breaking mechanisms. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2005, 25(11): 212-217. |
| 李蓉, 叶勇. 种子休眠与破眠机理研究进展. 西北植物学报, 2005, 25(11): 212-217. | |
| 17 | Zhang T, Chen Z P, Chen K J, et al. Characteristics of soil seed banks of different site types in arid mining area. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(1): 51-58. |
| 张涛, 陈智平, 车克钧, 等. 干旱区矿区不同立地类型土壤种子库特征. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(1): 51-58. | |
| 18 | Briese D T, Macauley B J. Food collection within an ant community in semi-arid Australia with spatial reference to seed harvesters. Australian Journal of Ecology, 1985, 6: 1-19. |
| 19 | Crist T O, James A M. Harvester ant foraging and shrub-steppe seeds: Interaction of seed resources and seed use. Ecology, 1992, 73: 1768-1779. |
| 20 | Huang M. The role of elaiosome to seed dispersal of ant-dispersed herbaceous plants. Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2014. |
| 黄曼. 油质体在蚁播植物种子散布中的作用研究. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2014. | |
| 21 | Wang S L, Peng F, Lu W H, et al. Seed morphology and effects of sheep rumen digestion on seed germination of 28 gramineae plants. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(12): 97-105. |
| 王树林, 彭峰, 鲁为华, 等. 28种禾本科植物种子形态学特征及其萌发对绵羊瘤胃消化的反应. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(12): 97-105. | |
| 22 | Niu C J. Foundations in ecology (The Third Edition). Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015. |
| 牛翠娟. 基础生态学(第三版). 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015. | |
| 23 | Pan S W, Yuan X, Lei Z H, et al. Effect of life form composition of indigenous plant species on soil and water conservation on slopes in Sichuan-Chongqing region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(15): 4654-4663. |
| 潘声旺, 袁馨, 雷志华, 等.乡土植物生活型构成对川渝地区边坡植被水土保持效益的影响. 生态学报, 2016, 36(15): 4654-4663. | |
| 24 | Chen Y W, Li X R, Su Y G, et al. Study on the eco-functions of Fomica cunicularia (Hymenoptera: Fomicidae) in a revegetated area on the southeast fringe of Tengger Desert North China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(4): 1508-1514. |
| 陈应武, 李新荣, 苏延桂, 等. 腾格里沙漠人工植被区掘穴蚁(Formica cunicularia)的生态功能. 生态学报, 2007, 27(4): 1508-1514. | |
| 25 | Dauber J, Rommeler A, Wolters V. The ant Lasius flavus alters the viable seed bank in pastures. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2006, 42: 157-163. |
| 26 | Whitford W G, Dimarco R. Variability in soils and vegetation associated with harvester ant (Pogonomyrmex rugosus) nests on a Chihuahuan Desert watershed. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 1995, 20(3): 169-173. |
| 27 | Donath T W, Eckstein R L. Effects of bryophytes and grass litter on seedling emergence vary by vertical seed position and seed size. Plant Ecology, 2010, 207(2): 257-268. |
| 28 | Chen Y W, Li X R. Spatio-temporal distribution of nests and influence of ant (Formica cunicularia Lat.) activity on soil property and seed bank after revegetation in the Tengger Desert. Arid Soil Research & Rehabilitation, 2012, 26(4): 365-378. |
| 29 | Li Y J, Bao W K, Wu F Z. Soil seed bank and natural regeneration potential of shrubland in dry valleys of Minjiang River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(2): 399-407. |
| 李彦娇, 包维楷, 吴福忠. 岷江干旱河谷灌丛土壤种子库及其自然更新潜力评估. 生态学报, 2010, 30(2): 399-407. | |
| 30 | Beattie A J, Culver D C. Effects of the mound nests of the ant, Formica obscuripes, on the surrounding vegetation. The American Midland Naturalist, 1977, 97: 391-399. |
| 31 | Carlson S R, Whitford W G. Ant mound influence on vegetation and soils in a semiarid mountain ecosystem. The American Midland Naturalist, 1991, 126: 125-139. |
| 32 | Gad M R M, Kelan S S. Soil seed bank and seed germination of sand dunes vegetation in North Sinai-Egypt. Annals of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 57(1): 63-72. |
| 33 | Chen Y Y, Wu Z R, Pan P, et al. The germination characteristies of soil seed bank and its relationship with soil properties in aerially-seeded Pinus massoiana plantations. Chinese Jounal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(1): 92-97. |
| 陈颖颖, 吴自荣, 潘萍, 等.飞播马尾松林土壤种子库的萌发特征及其与土壤理化性质的关系. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(1): 92-97. | |
| 34 | Ma Z. The study of soil seed bank in the alpineareas on the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2014. |
| 马真. 青藏高原东部高寒地区土壤种子库研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2014. | |
| 35 | Zhang H Y, Liu B. Quantitative classification and ordination of plant vegetation in the Bosten Lake wetlands. Plant Science Journal, 2015, 33(1): 36-43. |
| 张海燕, 刘彬. 博斯腾湖湖滨湿地植被数量分类与排序. 植物科学学报, 2015, 33(1): 36-43. | |
| 36 | Zhao N, He M X, Li H Y. Influences of peat and perlite on germination characteristics of soil seed bank. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 36(6): 92-96. |
| 赵娜, 贺梦璇, 李洪远. 草炭与珍珠岩对土壤种子库种子萌发特征的影响. 水土保持通报, 2016, 36(6): 92-96. | |
| 37 | Ha W X. Plant and soil communities of different restoration years in Karst fault basin area of Yunnan Province. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2019. |
| 哈文秀. 云南喀斯特断陷盆地区不同恢复年限植被与土壤特征研究. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. | |
| 38 | Westoby H M. Fate of seeds adapted for dispersal by ants in Australian Sclerophyll vegetation. Ecology, 1992, 73(4): 1285-1299. |
| 39 | Giladi I. Choosing benefits or partners: A review of the evidence for the evolution of myrmecochory. Oikos, 2006, 112(3): 481-492. |
| 40 | Ness J H, Bressmer K. Abiotic influences on the behaviour of rodents, ants, and plants affect an ant-seed mutualism. Ecoscience, 2005, 12(1): 76-81. |
| 41 | Bond W J, Stock W D. The costs of leaving home: Ants disperse myrmecochorous seeds to low nutrient sites. Oecologia, 1989, 81(3): 412-417. |
| 42 | Ness J H, Morin D F. Forest edges and landscape history shape interactions between plants, seed-dispersing ants and seed predators. Biological Conservation, 2008, 141(3): 838-847. |
| [1] | 唐立涛, 毛睿, 王长庭, 李洁, 胡雷, 字洪标. 氮磷添加对高寒草甸植物群落根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 105-116. |
| [2] | 贺翔, 白梅梅, 徐长林, 宋美娟, 汪鹏斌, 鱼小军. 东祁连山小叶金露梅+杯腺柳灌丛草地植被和土壤对其自然恢复演替的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 12-24. |
| [3] | 孙忠超, 郭天斗, 于露, 马彦平, 赵亚楠, 李雪颖, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地人为转变过程土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 34-45. |
| [4] | 张丽星, 海春兴, 常耀文, 高晓媚, 高文邦, 解云虎. 羊草及芨芨草草原和西北针茅草原土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 68-79. |
| [5] | 张超, 闫瑞瑞, 梁庆伟, 娜日苏, 李彤, 杨秀芳, 包玉海, 辛晓平. 不同利用方式下草地土壤理化性质及碳、氮固持研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 90-98. |
| [6] | 侯金伟, 陈焘, 南志标. 不同埋藏方式及杀菌剂处理对黄土高原3种植物种子存活的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 129-136. |
| [7] | 李洁, 潘攀, 王长庭, 胡雷, 陈科宇, 杨文高. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地根系动态特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. |
| [8] | 刘斯莉, 王长庭, 张昌兵, 胡雷, 唐立涛, 潘攀. 川西北高原3种禾本科牧草根系特征比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 41-53. |
| [9] | 罗超, 郭小平, 冯昶栋, 叶金鹏, 薛东明. 乌海周边土壤种子库特征及其与地上植被和土壤因子的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 13-28. |
| [10] | 王琇瑜, 黄晓霞, 和克俭, 孙晓能, 吕曾哲舟, 张勇, 朱湄, 曾睿钦. 滇西北高寒草甸植物群落功能性状与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 6-17. |
| [11] | 车力木格, 刘新平, 何玉惠, 孙姗姗, 王明明. 半干旱沙地草本植物群落特征对短期降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 19-28. |
| [12] | 于露, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 郭天斗, 孙忠超, 王红梅. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对灌丛引入和降水梯度的响应特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. |
| [13] | 施颖, 胡廷花, 高红娟, 罗巧玉, 于应文. 两种放牧模式下高寒草甸群落植被构成及稳定性特征[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 1-10. |
| [14] | 常海涛, 赵娟, 刘佳楠, 刘任涛, 罗雅曦, 张静. 退耕还林与还草对土壤理化性质及分形特征的影响——以宁夏荒漠草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 14-25. |
| [15] | 宿婷婷, 马红彬, 周瑶, 贾希洋, 张蕊, 张双乔, 胡艳莉. 黄土丘陵典型草原土壤理化性质对生态恢复措施的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 34-46. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||