

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 1-16.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021458
• 研究论文 •
收稿日期:2021-12-10
修回日期:2022-03-14
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2022-10-17
通讯作者:
许玉凤
作者简介:E-mail: 1546246929@qq.com基金资助:
Chen CHEN1,2( ), Chang-qing JING1, Wei-kang ZHAO1, Yu-feng XU2(
), Chang-qing JING1, Wei-kang ZHAO1, Yu-feng XU2( )
)
Received:2021-12-10
Revised:2022-03-14
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2022-10-17
Contact:
Yu-feng XU
摘要:
草地是新疆重要的植被类型,是碳源/汇的重要研究对象之一,研究其质量变化驱动力并预估其未来变化趋势具有重要的生态意义。本研究利用归一化植被指数(NDVI)、植被净初级生产力(NPP)和气象资料等数据,应用地理信息图谱确定1980-2020年变化和稳定草地的范围,排除人类活动干扰,分析草地质量变化及其对气候变化的响应;使用Thornthwaite Memorial等模型估算新疆草地质量并预测其2021-2040年变化趋势。研究发现:1)新疆草地质量总体呈上升趋势,高覆盖度草地上升趋势显著;山地草地覆盖度和质量高,沙漠边缘草地覆盖度和质量低;2)新疆草地质量变化的主要驱动力为气温和降水,与降水呈正相关;而超过一定限度的气温会抑制草地质量,且覆盖度越低对气温和降水越敏感;3)通过模型计算的气候生产力能够反映新疆草地质量及其时空变化特征,且草地覆盖度越低,反映越准确;4)在气候变化背景下,未来新疆低覆盖度草地质量提升,其他类型草地质量呈下降趋势。研究新疆草地质量的变化并预估其未来变化趋势,可为其制定生态保护措施、研究碳储量变化等提供参考。
陈宸, 井长青, 赵苇康, 许玉凤. 新疆草地质量对气候变化的响应及其变化趋势[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 1-16.
Chen CHEN, Chang-qing JING, Wei-kang ZHAO, Yu-feng XU. Grassland quality response to climate change in Xinjiang and predicted future trends[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 1-16.
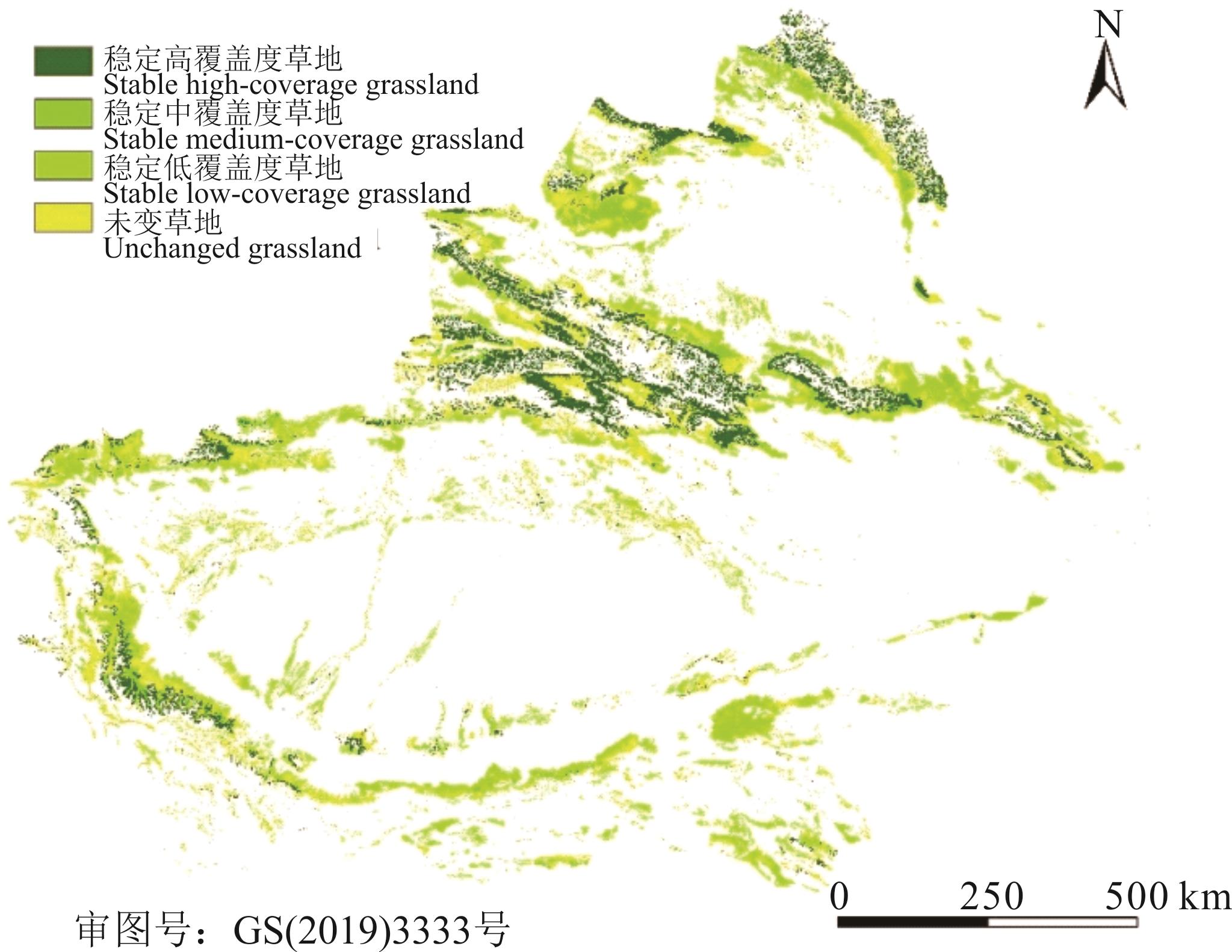
图1 1980-2020年新疆草地分布其中稳定高覆盖度草地、稳定中覆盖度草地、稳定低覆盖度草地是指该区域1980-2020年间始终是该覆盖度草地;未变草地包括稳定各覆盖度草地及研究期间其覆盖度已发生变化,但分类始终为草地大类的草地。Among them, stable high-coverage grassland, stable medium-coverage grassland, and stable low-coverage grassland refer to the grassland in the region where the coverage has not changed from 1980 to 2020; Unchanged grassland includes stable coverage grassland, and grassland whose coverage has changed during the study period, but is always classified as grassland.
Fig.1 Grassland distribution in Xinjiang from 1980 to 2020
| 1 | Wu N T, Liu G X, Liu A J, et al. Monitoring and driving force analysis of net primary productivity in native grassland: A case study in Xilingol steppe, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(4): 1233-1240. |
| 乌尼图, 刘桂香, 刘爱军, 等. 天然草原净初级生产力变化监测与驱动力分析——以锡林郭勒草原为例. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(4): 1233-1240. | |
| 2 | Liu X Y, Mu Y T. Research progress in the ecosystem services function and value of grasslands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(6): 286-295. |
| 刘兴元, 牟月亭. 草地生态系统服务功能及其价值评估研究进展. 草业学报, 2012, 21(6): 286-295. | |
| 3 | Du J Q, Jiaerheng·Ahati, Zhao C X, et al. Dynamic changes in vegetation NDVI from 1982 to 2012 and its responses to climate change and human activities in Xinjiang, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(12): 3567-3578. |
| 杜加强, 贾尔恒·阿哈提, 赵晨曦, 等. 1982-2012年新疆植被NDVI的动态变化及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(12): 3567-3578. | |
| 4 | Zheng W, Zhu J Z. Analysis of desertification process and driving force factors in grassland ecosystem of Xinjiang. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(9): 1340-1351. |
| 郑伟, 朱进忠. 新疆草地荒漠化过程及驱动因素分析. 草业科学, 2012, 29(9): 1340-1351. | |
| 5 | Zhang G P, Xu H L, Du Q, et al. Response of ecosystem service value to land use/cover change in the Yarkant River Basin in recent 20 years. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(6): 1303-1310. |
| 张广朋, 徐海量, 杜清, 等. 近20a叶尔羌河流域生态服务价值对土地利用/覆被变化的响应. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(6): 1303-1310. | |
| 6 | Tian L, Xu Y Q, Sun P L. Impact of conversion cropland to forest and grassland project on land use/cover change and landscape pattern: A case study of Zhangjiakou City. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2015, 20(4): 205-213. |
| 田璐, 许月卿, 孙丕苓. 退耕还林还草工程对土地利用/覆被变化及景观格局的影响——以张家口市为例. 中国农业大学学报, 2015, 20(4): 205-213. | |
| 7 | Zhu Y, Li J X, Meng C, et al. Land use change in the eastern part of Chongming Island in Shanghai in recent two decades. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007(9): 2040-2044. |
| 朱颖, 李俊祥, 孟陈, 等. 上海崇明岛东部近20年土地利用变化. 应用生态学报, 2007(9): 2040-2044. | |
| 8 | Shao H Y, Xian W, Yang W N, et al. Land use/cover change during lately 50 years in Three Gorges Reservoir area. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008(2): 453-458. |
| 邵怀勇, 仙巍, 杨武年, 等. 三峡库区近50年间土地利用/覆被变化. 应用生态学报, 2008(2): 453-458. | |
| 9 | Li Y J, Ding J L, Zhang J Y, et al. Response of vegetation cover to drought in the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains during 2001-2015 based on the land-use and land-cover change. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(17): 6206-6217. |
| 李艳菊, 丁建丽, 张钧泳, 等. 2001-2015年天山北坡植被覆盖对干旱的响应——基于土地利用/土地覆盖分析. 生态学报, 2019, 39(17): 6206-6217. | |
| 10 | Mu Z X, Yu Y M. The spatial-temporal variation characteristics of LUCC in the west of Tianshan Mountain areas. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2016(6): 112-118. |
| 穆振侠, 于宴民. 天山西部山区土地利用/土地覆被时空变化特性研究. 中国农村水利水电, 2016(6): 112-118. | |
| 11 | Zhang H Y, Fan J W, Shao Q Q. Land use/land cover change in the grassland restoration program areas in China, 2000-2010. Progress in Geography, 2015, 34(7): 840-853. |
| 张海燕, 樊江文, 邵全琴. 2000-2010年中国退牧还草工程区土地利用/覆被变化. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(7): 840-853. | |
| 12 | Hou X Y, Zhang D F, Yu X F. Grassland change and its spatial patterns in Xinjiang in 1990s. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2004(3): 409-417. |
| 侯西勇, 庄大方, 于信芳. 20世纪90年代新疆草地资源的空间格局演变. 地理学报, 2004(3): 409-417. | |
| 13 | Liu J Y, Liu M L, Zhuang D F, et al. Analysis of the spatial pattern of recent land use changes in China. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 2002, 32(12): 1031-1040, 1058-1060. |
| 刘纪远, 刘明亮, 庄大方, 等. 中国近期土地利用变化的空间格局分析. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2002, 32(12): 1031-1040, 1058-1060. | |
| 14 | Liu J Y, Zhang Z X, Xu X L, et al. Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China in the early 21st century. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2009, 64(12): 1411-1420. |
| 刘纪远, 张增祥, 徐新良, 等. 21世纪初中国土地利用变化的空间格局与驱动力分析. 地理学报, 2009, 64(12): 1411-1420. | |
| 15 | Liu J Y, Kuang W H, Zhang Z X, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(1): 3-14. |
| 刘纪远, 匡文慧, 张增祥, 等. 20世纪80年代以来中国土地利用变化的基本特征与空间格局. 地理学报, 2014, 69(1): 3-14. | |
| 16 | Li H M, Li W Q, Yuan Y, et al. A study on the urban land use/cover change and its driving factors in eastern Qinghai Province. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2021(27): 118-121. |
| 李洪梅, 李文奇, 袁媛, 等. 青海省东部城镇土地利用/覆盖变化及其驱动因素研究. 科学技术创新, 2021(27): 118-121. | |
| 17 | Pu L M, Zhang S W, Li F, et al. Responses of land use changes to human activities in the northeast Agro-pastoral zone in the past 40 years-Take the western region of Jilin Province as an example. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(6): 522-525. |
| 蒲罗曼, 张树文, 李飞, 等. 近40年东北农牧交错带土地利用变化对人类活动的响应: 以吉林省西部地区为例. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(6): 522-525. | |
| 18 | Huang X Y, Wang J A, Yin W X, et al. Impact of human activities on land use in Dafang County, Guizhou Province. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(4): 470-477. |
| 黄晓云, 王静爱, 尹卫霞, 等. 贵州省大方县人类活动对土地利用的影响. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(4): 470-477. | |
| 19 | Li Y G, He D M. The spatial and temporal variation of NDVI and its relationships to the climatic factors in Red River Basin. Mountain Research, 2009, 27(3): 333-340. |
| 李运刚, 何大明. 红河流域NDVI时空变化及其与气候因子的关系. 山地学报, 2009, 27(3): 333-340. | |
| 20 | Jiang L G, Liu Y, Wu S, et al. Analyzing ecological environment change and associated driving factors in China based on NDVI time series data. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 129: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107933. |
| 21 | Li F, Zhou W Z, Shao Z L, et al. Effects of ecological projects on vegetation in the Three Gorges Area of Chongqing, China. Journal of Mountain Science, 2022, 19(1): 121-135. |
| 22 | Ding M J, Zhang Y L, Liu L S, et al. Seasonal time lag response of NDVI to temperature and precipitation change and its spatial characteristics in Tibetan Plateau. Progress in Geography, 2010, 29(4): 507-512. |
| 丁明军, 张镱锂, 刘林山, 等. 青藏高原植被覆盖对水热条件年内变化的响应及其空间特征. 地理科学进展, 2010, 29(4): 507-512. | |
| 23 | Jiao W, Cheng Y N, Li Z. Remote sensing estimation and the reasons for temporal-spatial differences of vegetation net primary productivity in arid region of Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(1): 181-189. |
| 焦伟, 陈亚宁, 李稚. 西北干旱区植被净初级生产力的遥感估算及时空差异原因. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(1): 181-189. | |
| 24 | Tong L J, Liu Y Y, Wang Q, et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics of net primary productivity and its driving factors in Northwest China. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(4): 367-374. |
| 同琳静, 刘洋洋, 王倩, 等. 西北植被净初级生产力时空变化及其驱动因素. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(4): 367-374. | |
| 25 | Sun L X, Yu Y, Gao Y T, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of net primary productivity and its response to groundwater of a typical oasis in the Tarim Basin, China. Journal of Arid Land, 2021, 13(11): 1142-1154. |
| 26 | Li Y Y, Kang G H, Zhang P Y, et al. Analysis of spatial-temporal change of agricultural climatic productivity in Henan Province in recent 54 years based on Thornthwaite Memorial model. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(7): 287-293. |
| 李颜颜, 康国华, 张鹏岩, 等. 基于Thornthwaite Memorial模型的近54年河南省农业气候生产力时空变化特征分析. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(7): 287-293. | |
| 27 | Lu F Y, Yang B, Pei Z J, et al. Spatial and temporal evolution of climatic productivity potential in Heilongjiang Province. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(10): 1659-1664. |
| 卢玢宇, 杨波, 裴占江, 等. 黑龙江省气候生产潜力时空演变特征研究. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(10): 1659-1664. | |
| 28 | Sun C M, Chen Y Y, Wu W, et al. The spatial distribution patterns of grassland NPP in South China based on climate productivity models. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 2013, 34(4): 56-61. |
| 孙成明, 陈瑛瑛, 武威, 等. 基于气候生产力模型的中国南方草地NPP空间分布格局研究. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2013, 34(4): 56-61. | |
| 29 | Xu X K, Chen H, Zhang F. Temporal and spatial change of vegetation cover in the Northwest of China and factors analysis influencing on vegetations variation. Environmental Science, 2007(1): 41-47. |
| 徐兴奎, 陈红, 张凤. 中国西北地区地表植被覆盖特征的时空变化及影响因子分析. 环境科学, 2007(1): 41-47. | |
| 30 | Chen C, Jing C Q, Xing W Y, et al. Desert grassland dynamics in the last 20 years and its response to climate change in Xinjiang. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 1-14. |
| 陈宸, 井长青, 邢文渊, 等. 近20年新疆荒漠草地动态变化及其对气候变化的响应. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 1-14. | |
| 31 | Zhang W H, Lv X, Shi Y Y, et al. Graphic characteristics of land use transition in the Yellow River Basin. China Land Science, 2020, 34(8): 80-88. |
| 张文慧, 吕晓, 史洋洋, 等. 黄河流域土地利用转型图谱特征. 中国土地科学, 2020, 34(8): 80-88. | |
| 32 | Wan H X, Qin Z H, Xu Y M. Variation of vegetation cover and its relationship with climatic factors in the Bosten Lake Basin using MODIS data. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(5): 1429-1437. |
| 万洪秀, 覃志豪, 徐永明. 基于MODIS数据的博斯腾湖流域植被变化及其与气候因子的关系. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(5): 1429-1437. | |
| 33 | Wang Z, Li D K. Spatial-temporal distribution of vegetation net primary productivity and its driving factors from 2000 to 2015 in Shaanxi, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(6): 1876-1884. |
| 王钊, 李登科. 2000-2015年陕西植被净初级生产力时空分布特征及其驱动因素. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(6): 1876-1884. | |
| 34 | Jiang P, Ding W G, Xiao J, et al. Altitudinal difference of vegetation NPP and its response to climate change in Xinjiang. Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(3): 849-857. |
| 姜萍, 丁文广, 肖静, 等. 新疆植被NPP及其对气候变化响应的海拔分异. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(3): 849-857. | |
| 35 | Chen D H, Li H, Ma J L. The monitoring of forest resources in west Tianshan Mountain based on CBERS-2. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2007(2): 86-89. |
| 陈冬花, 李虎, 马江林. 基于CBERS-2数据的新疆天山西部森林资源监测研究. 国土资源遥感, 2007(2): 86-89. | |
| 36 | Liu H Y, Mi Z R, Lin L, et al. Shifting plant species composition in response to climate change stabilizes grassland primary production. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(16): 4051-4056. |
| 37 | Wu X L, Zhang T X, Wang H, et al. Characteristics of temperature and precipitation change in Xinjiang during 1961-2017. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2020, 14(4): 27-34. |
| 吴秀兰, 张太西, 王慧, 等. 1961-2017年新疆区域气候变化特征分析. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2020, 14(4): 27-34. | |
| 38 | Zhao Y P, Zhang X Z, Wang J S, et al. Correlation analysis between NDVI and climatic factors of grassland ecosystems in the northern Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2003. Resources Science, 2009, 31(11): 1988-1998. |
| 赵玉萍, 张宪洲, 王景升, 等. 1982年至2003年藏北高原草地生态系统NDVI与气候因子的相关分析. 资源科学, 2009, 31(11): 1988-1998. | |
| 39 | Sun M, Xu Z, Liu J L. Response of grassland climate productivity to climate change in farming-pastoral area of Inner Mongolia. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(6): 1085-1090. |
| 孙淼, 徐柱, 柳剑丽. 内蒙古农牧交错区草地气候生产力对气候变化的响应. 草业科学, 2011, 28(6): 1085-1090. | |
| 40 | Yao J Q, Mao W F, Chen J, et al. Signal and impact of wet-to-dry shift over Xinjiang, China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(1): 57-72. |
| 姚俊强, 毛炜峄, 陈静, 等. 新疆气候“湿干转折”的信号和影响探讨. 地理学报, 2021, 76(1): 57-72. |
| [1] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [2] | 张仁平, 郭靖, 马晓芳, 郭伟勇. 基于MODIS数据的新疆草地物候提取方法及变化趋势分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 1-12. |
| [3] | 马婧婧, 刘耘华, 盛建东, 李宁, 武红旗, 贾宏涛, 孙宗玖, 程军回. 新疆草地优势种植物相对生物量沿海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 25-35. |
| [4] | 陈宸, 井长青, 邢文渊, 邓小进, 付皓宇, 郭文章. 近20年新疆荒漠草地动态变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 1-14. |
| [5] | 付东青, 贾春英, 连晓春, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 玉米秸秆与番茄皮渣裹包混贮发酵品质及瘤胃降解特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 147-158. |
| [6] | 王乐政, 华方静, 曹鹏鹏, 高凤菊, 夏文荣. 不同播期夏播小豆产量性能动态指标与光温水效应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 116-129. |
| [7] | 郭剑波, 赵国强, 贾书刚, 董俊夫, 陈龙, 王淑平. 施肥对高寒草原草地质量指数及土壤性质影响的综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 85-93. |
| [8] | 荀其蕾,董乙强,安沙舟,闫凯. 基于MOD 09GA数据的新疆草地生长状况遥感监测研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 10-26. |
| [9] | 周天阳, 高景, 王金牛, 孙建, 徐波, 薛晶月, 贺俊东, 谢雨, 吴彦. 基于群落结构及土壤理化性质对围封7年青藏高原东南缘高山草地的综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 1-11. |
| [10] | 张仁平, 郭靖, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 新疆地区草地植被物候时空变化[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 66-75. |
| [11] | 柴艳, 孙宗玖, 李培英, 巴德木其其格, 张向向, 杨静. 新疆狗牙根种质芽期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 154-167. |
| [12] | 李莉, 张一弓, 贾纳提, 李学森. 盐碱胁迫下新疆野豌豆种子萌发及幼苗生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 46-53. |
| [13] | 覃凤飞, 沈益新, 李兰海, 胡增运, 程亮, 马旭龙, 陈青青, 王凌越. 干旱胁迫对新疆三个优势牧草种的光合特性与水分利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10): 86-94. |
| [14] | 周李磊, 朱华忠, 钟华平, 杨华, 索菲娅, 邵小明, 周星杰. 新疆伊犁地区草地土壤容重空间格局分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 64-75. |
| [15] | 郑江坤, 宫渊波, 刘金鑫, 刘剑波. 岷江上游山地牧道对林下草本群落分布特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||