

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 41-55.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022084
王志婷1( ), 刘廷玺1,2,3(
), 刘廷玺1,2,3( ), 童新1,2,3, 段利民1,2,3, 李东方1,2, 刘小勇4
), 童新1,2,3, 段利民1,2,3, 李东方1,2, 刘小勇4
收稿日期:2022-02-19
修回日期:2022-05-23
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2022-12-30
通讯作者:
刘廷玺
作者简介:E-mail: txliu1966@163.com基金资助:
Zhi-ting WANG1( ), Ting-xi LIU1,2,3(
), Ting-xi LIU1,2,3( ), Xin TONG1,2,3, Li-min DUAN1,2,3, Dong-fang LI1,2, Xiao-yong LIU4
), Xin TONG1,2,3, Li-min DUAN1,2,3, Dong-fang LI1,2, Xiao-yong LIU4
Received:2022-02-19
Revised:2022-05-23
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2022-12-30
Contact:
Ting-xi LIU
摘要:
不同草地处理措施对植被和土壤会产生重要的影响。为探究不同草地处理措施对草甸草地的影响,以科尔沁草甸草地不同点为研究对象,设置围封(UNM)、围封+刈割(M)、围封+火烧(F)、放牧(G)4种处理,针对生长季土壤脲酶(S-UE)、碱性磷酸酶(S-AKP)、蔗糖酶(S-SC)活性和植被特征等开展研究,以探究草甸草地的最佳处理方式。结果显示:1)土壤酶活性随着土层深度的增加而降低,不同处理间的差异随着土层深度增加逐渐降低。2)放牧较围封处理,不同点植被高度、盖度、地上生物量和酶活性均降低,而丰富度指数增加。3)刈割较围封处理,不同功能群物种的补偿能力不同,禾本科的补偿能力大于菊科。4)火烧较围封处理,不同点植被高度、盖度、地上生物量、丰富度指数和3种水解酶活性均增加。5)多年刈割较放牧处理,植被高度、盖度和地上生物量和蔗糖酶、碱性磷酸酶活性均增加,丰富度指数和土壤脲酶活性均降低。综上所述,控制性火烧是半干旱地区草甸草地的最佳处理方式。
王志婷, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 李东方, 刘小勇. 半干旱草甸草地不同处理下植被特征与土壤酶活性的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 41-55.
Zhi-ting WANG, Ting-xi LIU, Xin TONG, Li-min DUAN, Dong-fang LI, Xiao-yong LIU. Changes in vegetation characteristics and soil enzyme activities under different treatments in semi-arid meadow grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 41-55.
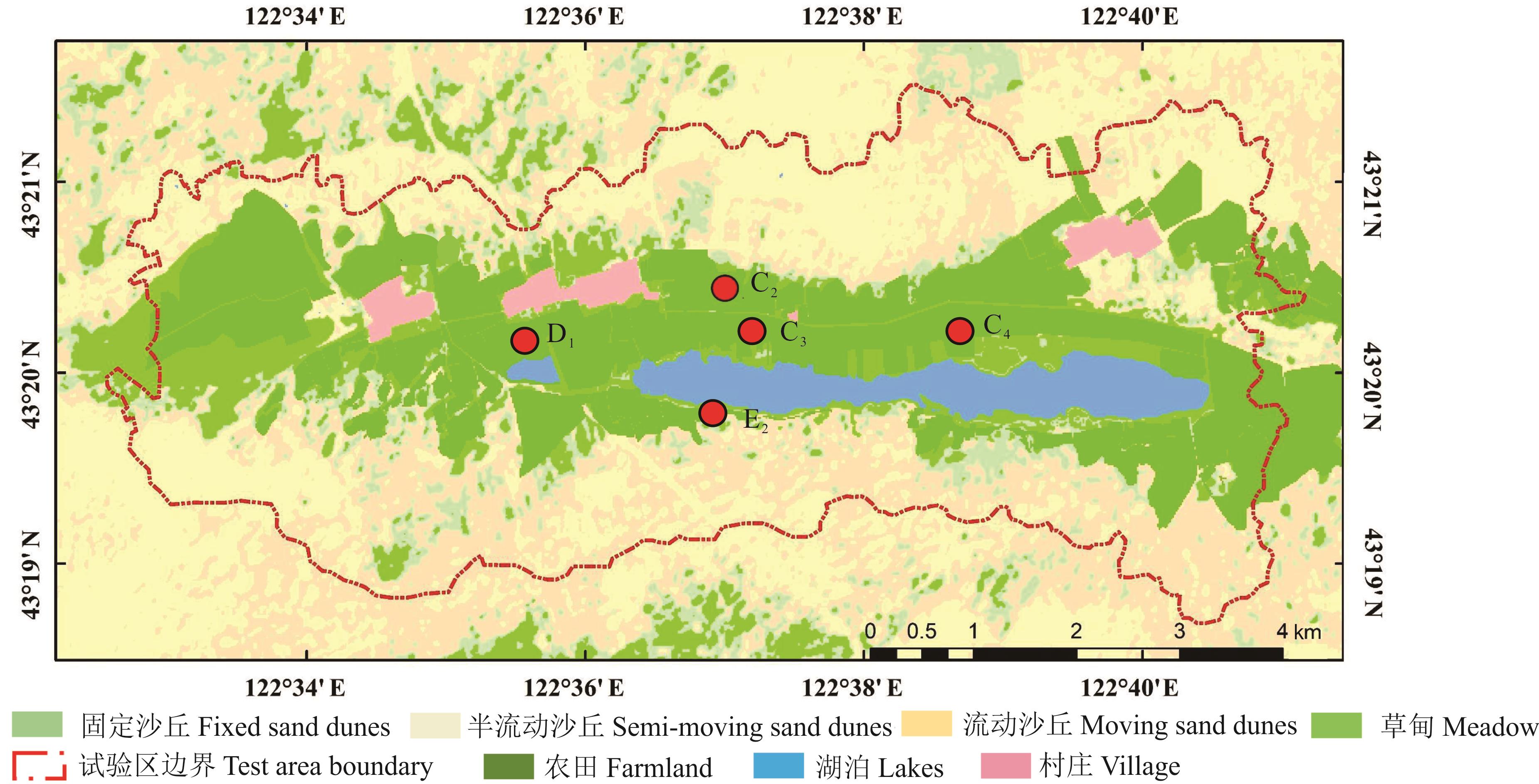
图1 研究区试验点布设及草地处理方式示意图D1、C2、C3、E2和C4分别代表草甸地样地名称。D1, C2, C3, E2 and C4 represent the names of meadow grassland sites, respectively.
Fig.1 Layout of test points and grassland treatment mode in the study area
草甸草地点 Meadow grassland site | 草地处理方式 Grassland treatment |
|---|---|
| C2 | UNM、M1、F、G |
| C3 | UNM、M1、G |
| D1 | UNM、F、G |
| C4 | ML、G |
| E2 | ML、G |
表1 不同样地草地处理方式
Table 1 Different ways of dealing with grass
草甸草地点 Meadow grassland site | 草地处理方式 Grassland treatment |
|---|---|
| C2 | UNM、M1、F、G |
| C3 | UNM、M1、G |
| D1 | UNM、F、G |
| C4 | ML、G |
| E2 | ML、G |
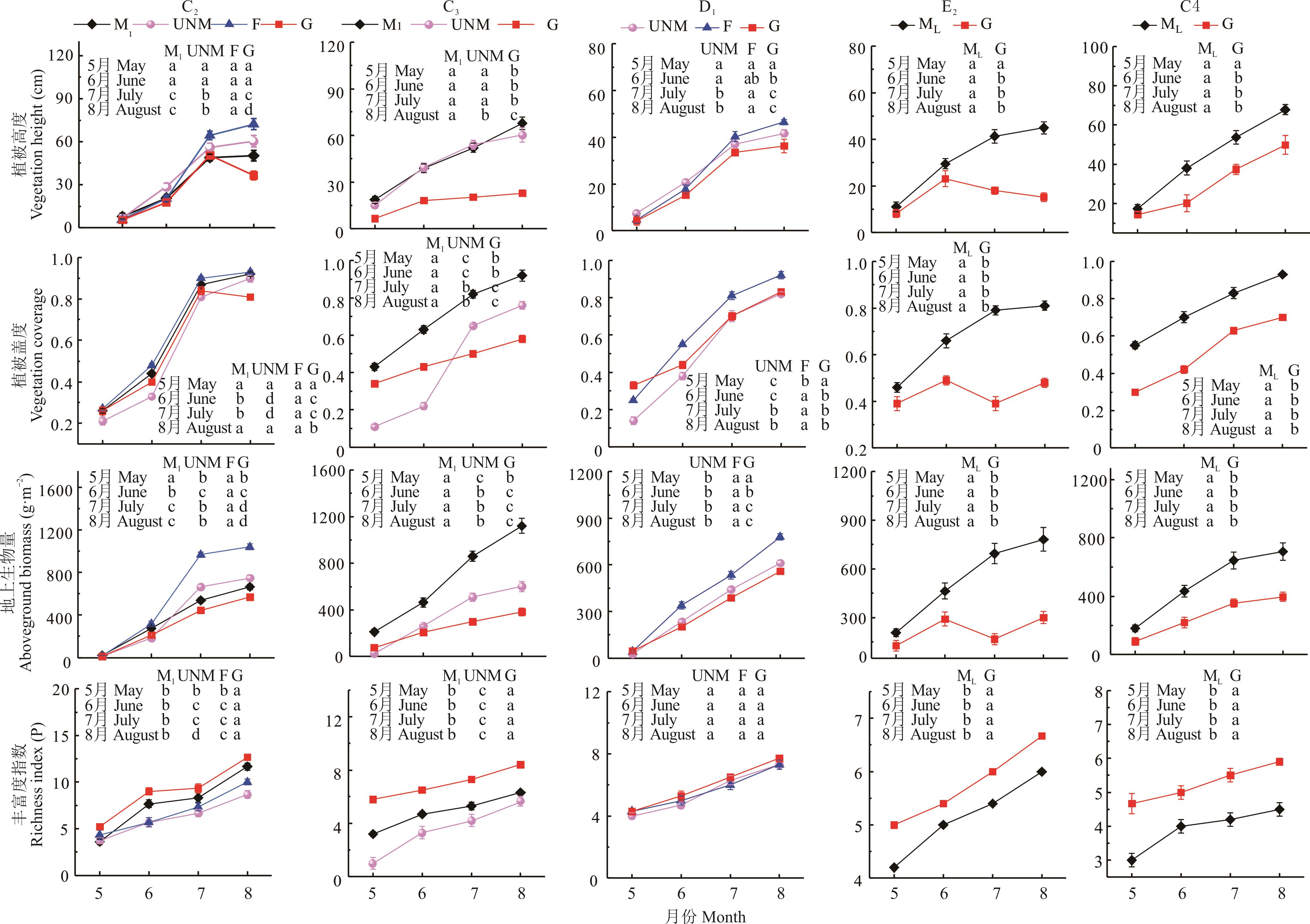
图3 各试验点草地不同处理植被群落特征的月变化同行不同小写字母代表该指标在不同处理下差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences at the 0.05 level.
Fig.3 Monthly variation of vegetation community characteristics in different treatments of grassland in different experimental sites

图4 不同处理方式草地生长季土壤温度的月变化相同字母代表不同草地处理下差异不显著(P>0.05),不同字母代表不同草地处理下差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Same letters mean no significant differences at the 0.05 level among different grassland treatments; Different letters mean significant differences at the 0.05 level among different grassland treatments, the same below.
Fig.4 Monthly variation of soil temperature in growing season of grassland under different treatments

图9 植被特征与土壤酶活性的相关性H: 植被高度Vegetation height; C: 植被盖度Vegetation coverage; B: 地上生物量Aboveground biomass; R: 丰富度指数 Richness index; W: 土壤水分Soil moisture content; T: 土壤温度 Soil temperature; S-AKP: 土壤碱性磷酸酶活性 Soil alkaline phosphatase activity; S-UE: 土壤脲酶活性 Soil urease activity; S-SC: 土壤蔗糖酶活性 Soil sucrase activity. “**”“*”分别表示在0.01、0.05水平上显著相关。“**”“*”indicates significant correlation at 0.01, 0.05 levels. “”表示正相关,“”表示负相关,颜色越深,表示其相关性越强。“”indicates positive correlation,“”indicates negative correlation,the darker the color, the stronger the correlation.
Fig.9 Correlation between vegetation characteristics and soil enzyme activities
| 1 | Shen H H, Zhu Y K, Zhao X, et al. Analysis of current grassland resources in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(2): 139-154. |
| 沈海花, 朱言坤, 赵霞, 等. 中国草地资源的现状分析. 科学通报, 2016, 61(2): 139-154. | |
| 2 | Li B. The rangeland degradation in North China and its preventive strategy. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1997, 30(6): 2-10. |
| 李博. 中国北方草地退化及其防治对策. 中国农业科学, 1997, 30(6): 2-10. | |
| 3 | Shang Z H, Dong S K, Zhou H K, et al. Synthesis-review for research cases of grassland ecological restoration: Years, effect and method. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(24): 8148-8160. |
| 尚占环, 董世魁, 周华坤, 等. 退化草地生态恢复研究案例综合分析:年限、效果和方法. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24): 8148-8160. | |
| 4 | Yue X Y, Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, et al. Desertification risk assessment in Horqin sandy land. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(1): 8-16. |
| 岳喜元, 左小安, 赵学勇, 等. 科尔沁沙地沙漠化风险评价. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 8-16. | |
| 5 | Zhao L Y, Zhong H S, Qi K, et al. Effects of enclosure and grazing on interspecific association of plant communities in Horqin Sandy Land, Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(9): 3724-3733. |
| 赵丽娅, 钟韩珊, 齐开, 等. 围封和放牧对科尔沁沙地植物群落种间关联的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(9): 3724-3733. | |
| 6 | Zhu M L, Gong L, Zhang L L. Soil enzyme activities and their relationships to environmental factors in a typical oasis in the upper reaches of the Tarim River. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(7): 2678-2685. |
| 朱美玲, 贡璐, 张龙龙. 塔里木河上游典型绿洲土壤酶活性与环境因子相关分析. 环境科学, 2015, 36(7): 2678-2685. | |
| 7 | Yang G J, Wang S P. Vegetation and soil characteristics of degraded alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(6): 2109-2118. |
| 杨国靖, 王少平. 青藏高原区退化高寒草甸植被和土壤特征. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(6): 2109-2118 . | |
| 8 | Wang Y Q, Wang H S, Song M L, et al. Effects of autumn clipping on vegetation and soil ecological properties of degraded alpine grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(3): 61-69. |
| 王玉琴, 王宏生, 宋梅玲, 等. 秋季刈割对高寒退化草地植被和土壤生态属性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(3): 61-69. | |
| 9 | Wang M, Fu X Q, Shi F S, et al. Compensatory growth responding to clipping: A case study in a subtropical grassland northeast of Chongqing. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2014, 20(3): 474-483. |
| 王梅, 付秀琴, 石福孙, 等. 刈割对南方草地植物补偿性生长的影响-以渝东北部岐山草场为例. 应用与环境生物学报, 2014, 20(3): 474-483. | |
| 10 | Jiang L M, Yang X D, Yang J J, et al. Effects of different management strategies on soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools in arid areas and their influencing factors. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(12): 22-33. |
| 蒋腊梅, 杨晓东, 杨建军, 等. 不同管理模式对干旱区草地土壤有机碳氮库的影响及其影响因素探究. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 22-33. | |
| 11 | Wei Y L, Cao W X, Li J H, et al. Phospholipidfatty acid (PLFA) analysis of soil microbial community structure with different intensities of grazing and fencing in alpine shrubland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4897-4908. |
| 韦应莉, 曹文侠, 李建宏, 等. 不同放牧与围封高寒灌丛草地土壤微生物群落结构PLFA分析. 生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4897-4908. | |
| 12 | Li Q, Sun Y N, Lin L, et al. Changes of soil enzyme activities and nutrients across different succession stages of grazing alpine Kobresia grassland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 35(7): 2022-2028. |
| 李茜, 孙亚男, 林丽, 等. 放牧高寒嵩草草地不同演替阶段土壤酶活性及养分演变特征. 应用生态学报, 2019, 35(7): 2022-2028. | |
| 13 | Liu J H, Zhang T. Response of plant characteristics and soil nutrients on grazing disturbance in typical grassland in Xilinguole. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(12): 2016-2023. |
| 刘佳慧, 张韬. 放牧扰动对锡林郭勒典型草原植被特征及土壤养分的影响. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(12): 2016-2023. | |
| 14 | Yin G M, Wang M Y, Xue Y L, et al. Effect of different grazing patterns on vegetation characteristics of meadow steppe. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2013, 35(2): 89-93. |
| 殷国梅, 王明盈, 薛艳林, 等. 草甸草原区不同放牧方式对植被群落特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 2013, 35(2): 89-93. | |
| 15 | Yang X H, Zhang K B, Hou R P. Impacts of exclusion on vegetative features and aboveground biomass in semiarid degraded rangeland. Ecology and Enviroment, 2005, 14(5): 730-734. |
| 16 | Li B, Shibuya T, Yogo Y, et al. Effects of ramet clipping and nutrient availability on growth and biomass allocation of yellow nutsedge. Ecological Research, 2004, 12(19): 603-612. |
| 17 | Pan S Y, Kong B B, Yao T H, et al. Effects of clipping and fertilizing on the relationship between functional diversity and above-ground net primary productivity in an alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(9): 867-877. |
| 潘石玉, 孔彬彬, 姚天华, 等. 刈割和施肥对高寒草甸功能多样性与地上净初级生产力关系的影响. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(9): 867-877. | |
| 18 | Li S Y, Sun Y L, Zhao J W, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on microbial quantity, enzyme activity in rhizosphere soil and alfalfa hay yield. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(4): 113-120. |
| 李生仪, 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 等. 施氮对苜蓿根际土壤微生物数量、酶活性及干草产量的影响. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(4): 113-120. | |
| 19 | Wu X D, Zhang X J, Xie Y Z, et al. Vertical distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and soil enzyme activities in alfalfa artificial field with different growing years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 23(1): 245-251. |
| 吴旭东, 张晓娟, 谢应忠, 等. 不同种植年限紫花苜蓿人工草地土壤有机碳及土壤酶活性垂直分布特征. 草业学报, 2013, 23(1): 245-251. | |
| 20 | Hechmi S, Hamdi H, Mokni-tlili S, et al. Variation of soil properties with sampling depth in two different light-textured soils after repeated applications of urban sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 297(20): 1-8. |
| 21 | Luo D, Wang M J, Zheng S L, et al. Effects of enclosure on soil microbial and enzyme activity in desert steppe. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(5): 760-767. |
| 罗冬, 王明玖, 郑少龙, 等. 围封对荒漠草原土壤微生物数量及其酶活性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(5): 760-767. | |
| 22 | Fterich A, Mahdhi M, Mars M. Impact of grazing on soil microbial communities along a chronosequence of Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana in arid soils in Tunisia. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2012, 50(1): 56-63. |
| 23 | Monokrousos N, Boutsis G, Diamantopoulos J D. Development of soil chemical and biological properties in the initial stages of post-mining deposition sites. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 186(12): 9065-9074. |
| 24 | Panayiotou E, Dimou M, Monokrousos N. The effects of grazing intensity on soil processes in a Mediterranean protected area. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2017, 189(9): 441-447. |
| 25 | Xu X F, Niu D K, Guo X M, et al. Effects of grazing on soil microbial and enzyme activities in Wugong Mountain, China. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(7): 1634-1640. |
| 徐晓凤, 牛德奎, 郭晓敏, 等. 放牧对武功山草甸土壤微生物生物量及酶活性的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(7): 1634-1640. | |
| 26 | Northup B K, Brown J R, Holt J A. Grazing impacts on the spatial distribution of soil microbial biomass around tussock grasses in a tropical grassland. Applied Soil Ecology, 1999, 13(1): 259-270. |
| 27 | Niu D C, Jiang S G, Qin Y, et al. Effects of grazing and fencing on soil microorganisms and enzymes activities. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(4): 528-534. |
| 牛得草, 江世高, 秦燕, 等. 围封与放牧对土壤微生物和酶活性的影响. 草业科学, 2013, 30(4): 528-534. | |
| 28 | Khomutova T E, Fornasier F, Yeltsov M V, et al. Influence of grazing on the structure and biological activity of dry steppe soils of the southern Russian Plain. Land Degradation and Development, 2021, 32(17): 4832-4844. |
| 29 | Tarchen T, Gaweng B, Dunzhu D, et al. Effect of livestock exclusion duration years on plant and soil properties in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(1): 10-17. |
| 30 | Ficken C D, Wright J P. Effects of fire frequency on litter decomposition as mediated by changes to litter chemistry and soil environmental conditions. Applied Soil Ecology, 2017, 12(10): 1-19. |
| 31 | Biggs T H. The effects of fire events on soil geochemistry in semi-arid grasslands. USDA Forest Service-Research Papers RMRS, 2005, 36(5): 503-507. |
| 32 | Fultz L M, Moore-Kucera J, Dathe J, et al. Forest wildfire and grassland prescribed fire effects on soil biogeochemical processes and microbial communities: Two case studies in the semi-arid Southwest. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 99(2): 118-128. |
| 33 | Xue L, Li Q J, Chen H Y. Effects of a wildfire on selected physical, chemical and biochemical soil properties in a Pinus massoniana forest in south China. Forests, 2014, 5(12): 2947-2966. |
| 34 | Lin Y J, Wu N, Zhang Y M. Effect of fire on soil nutrient content and enzyme activity in Gurbantunggut desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(17): 6156-6162. |
| 林亚军, 吴楠, 张元明. 火烧对古尔班通古特沙漠土壤养分和土壤酶活性的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(17): 6156-6162. | |
| 35 | Wang L H, Xin Y, Zhao Y S, et al. Soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in the process of vegetation restoration in burned area of Great Xing’an Mountains. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(3): 184-189. |
| 王丽红, 辛颖, 赵雨森, 等. 大兴安岭火烧迹地植被恢复中土壤微生物量及酶活性. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(3): 184-189. | |
| 36 | René G, Gros R. Soil microbial functions after forest fires affected by the compost quality. Land Degradation & Development, 2016, 27(5): 1391-1402. |
| 37 | Zhou D W, Yue X Q, Sun G, et al. Changes in soil microorganisms following grassland burning. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 1999, 1(1): 118-124. |
| 周道玮, 岳秀泉, 孙刚, 等. 草原火烧后土壤微生物的变化. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 1999, 1(1): 118-124. | |
| 38 | Zibilske L M, Makus D J. Black oat cover crop management effects on soil temperature and biological properties on a Mollisol in Texas, USA. Geoderma, 2009, 149(3): 379-384. |
| 39 | Qin Y, He F, Tong Z Y, et al. Influence of cutting interval on soil enzyme activity and nutrients in Leymus chinensis meadow. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(4): 55-62. |
| 秦燕, 何峰, 仝宗永, 等. 刈割对羊草草原土壤酶活性和养分含量的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 55-62. | |
| 40 | Ji C, Luo Y, Jan V, et al. A keystone microbial enzyme for nitrogen control of soil carbon storage. Science Advances, 2018, 4(8): 1689-1694. |
| 41 | Fujisaki K, Chevallier T, Chapuis-Lardy L, et al. Soil carbon stock changes in tropical croplands are mainly driven by carbon inputs: A synthesis. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2018, 259(3): 147-158. |
| 42 | Gilmullina A, Rumpel C, Blagodatskaya E, et al. Management of grasslands by mowing versus grazing-impacts on soil organic matter quality and microbial functioning. Applied Soil Ecology, 2020, 156(2): 103-107. |
| 43 | Chu H Y, Lin X G, Takeshi F J, et al. Soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, bacterial community structure in response to long-term fertilizer management. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2007, 39(11): 2971-2976. |
| 44 | He N P, Han X G, Yu G R. Soil carbon sequestration rates and potential in the grazing grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(3): 844-851. |
| 何念鹏, 韩兴国, 于贵瑞. 内蒙古放牧草地土壤碳固持速率和潜力. 生态学报, 2012, 32(3): 844-851. | |
| 45 | Chen D M, Zhang N N, Liu L, et al. The effect of different restoration measures on the desert field alpine grassland in Zoigê. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2016, 22(4): 573-578. |
| 陈冬明, 张楠楠, 刘琳, 等. 不同恢复措施对若尔盖沙化草地的恢复效果比较. 应用与环境生物学报, 2016, 22(4): 573-578. | |
| 46 | Zhang Y, Asiya M, Xin X P, et al. Effects of fencing and grazing on the community structure, biomass and forage quality of temperate steppe in Xinjiang. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 23(3): 815-821. |
| 张宇, 阿斯娅·曼力克, 辛晓平, 等. 禁牧与放牧对新疆温性草原群落结构、生物量及牧草品质的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 23(3): 815-821. | |
| 47 | Yan R, Xin X, Yan Y, et al. Impacts of differing grazing rates on canopy structure and species composition in Hulunber meadow steppe. Rangeland Ecology & Management, 2015, 68(1): 54-64. |
| 48 | Chaichi M R, Saravi M M, Malekian A. Effects of livestock trampling on soil physical properties and vegetation cover (case study: Lar rangeland, Iran). International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2005, 7(6): 903-908. |
| 49 | Marty J T. Society for conservation biology effects of cattle grazing on diversity in ephemeral wetlands. Plant & Soil, 2005, 19(5): 1626-1632. |
| 50 | Semmartin M, Garibaldi L A, Chaneton E J. Grazing history effects on above- and below-ground litter decomposition and nutrient cycling in two co-occurring grasses. Plant and Soil, 2008, 303(1): 177-189. |
| 51 | Loreau M. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 2001, 294(5543): 804-808. |
| 52 | Holdo R M, Holt R D, Ritchie C. Plant productivity and soil nitrogen as a function of grazing, migration and fire in an African savanna. Journal of Ecology, 2007, 95(1): 115-128. |
| 53 | Peeder J D, Schuman G E. Influence of livestock grazing on C sequestration in semi-arid mixed-grass and short-grass rangelands. Environmental Pollution, 2002, 116(2): 457-463. |
| 54 | Antonsen H, Olsson P A. Relative importance of burning, mowing and species translocation in the restoration of a former boreal hayfield: Responses of plant diversity and the microbial community. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 42(2): 337-347. |
| 55 | Kotas P, Choma M, Hana Š, et al. Linking above- and belowground responses to 16 years of fertilization, mowing, and removal of the dominant species in a temperate grassland. Ecosystems, 2016, 20(2): 354-367. |
| 56 | Julieta C, Roxana A, Diego E, et al. Fire and grazing differentially affect aerial biomass and species composition in Andean grasslands. Acta Oecologica, 2011, 37(4): 337-345. |
| 57 | Chang M. Study on the species composition and community characteristics of subalpine meadow during restoration after a fire. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(6): 1286-1293. |
| 常明. 火烧后亚高山草甸恢复过程中物种组成和群落特征变化规律的研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(6): 1286-1293. | |
| 58 | Flematti G R, Merritt D J, Piggott M J, et al. Burning vegetation produces cyanohydrins that liberate cyanide and stimulate seed germination. Nature Communications, 2011, 27(10): 1-6. |
| [1] | 马文明, 刘超文, 周青平, 邓增卓玛, 唐思洪, 迪力亚尔·莫合塔尔null, 侯晨. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体生态化学计量学及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 57-68. |
| [2] | 程分生, 尤龙辉, 余锦林, 徐惠昌, 游惠明, 聂森, 李建民, 叶功富. 冷季型绿肥对锥栗园土壤生化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 62-75. |
| [3] | 周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72. |
| [4] | 宗文贞, 郭家昊, 贾云龙, 郑永兴, 杨旭, 胡芳弟, 王静. 单宁在植物-土壤氮循环中作用的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 174-183. |
| [5] | 冯军, 石超, 门胜男, Hafiz Athar Hussain, 柯剑鸿, Linna Cholidah, 陈锦芬, 郭欣, 武海燕, 冉泰霖, 向信华, 王龙昌. 不同降雨下旱地油菜节水节肥技术对土壤养分及酶活性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 51-62. |
| [6] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [7] | 李争艳, 徐智明, 师尚礼, 贺春贵. 江淮地区不同轮茬作物对苜蓿产量及根际土壤质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 28-39. |
| [8] | 李国旗, 赵盼盼, 邵文山, 靳长青. 围封条件下荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤理化性状与酶活性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. |
| [9] | 秦燕, 刘文辉, 何峰, 仝宗永, 李向林. 施肥与切根对退化羊草草原土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 5-14. |
| [10] | 刘明, 陈远学, 陈强, 彭丹, 喻晓, 杨军伟, 徐开未. 翻压接种根瘤菌的紫花苕子对植烟土壤肥力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 162-169. |
| [11] | 申小云, 霍宾, 闽小莹, 吴婷, 廖建军, 蔡平, 张毓, 何玉邦, 孙建青, 吴永林. 普氏原羚自然栖息地草地矿物质营养的评价[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 108-115. |
| [12] | 赛牙热木·哈力甫, 艾克拜尔·伊拉洪, 宋瑞清, 阿不都赛买提·乃合买提, 米日尼沙·买买提明, 迪里努尔·艾力. 察布查尔草原土壤酶活性垂直分布及土壤理化性质相关性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 116-125. |
| [13] | 苏鑫,卢嫚,冯程程,郭迎岚,岳中辉. 松嫩平原盐碱草地土壤酶活性与植物群落特征的关系初探[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 69-78. |
| [14] | 李文彬, 宁楚涵, 徐孟, 刘润进, 郭绍霞. 丛枝菌根真菌和高羊茅对压实土壤的改良效应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 131-141. |
| [15] | 张旭辉, 李治玲, 李勇, 王洋清. 施用生物炭对西南地区紫色土和黄壤的作用效果[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 63-72. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||