

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 63-72.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020393
周诗晶1( ), 罗佳宁1, 刘仲淼1, 董超1, 秦燕2, 吴淑娟1, 甘红军3, 谢菲3, 庄光辉3, 伏兵哲4, 牛得草1(
), 罗佳宁1, 刘仲淼1, 董超1, 秦燕2, 吴淑娟1, 甘红军3, 谢菲3, 庄光辉3, 伏兵哲4, 牛得草1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-08-19
修回日期:2020-12-02
出版日期:2021-09-16
发布日期:2021-09-16
通讯作者:
牛得草
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: xiaocao0373@163.com基金资助:
Shi-jing ZHOU1( ), Jia-ning LUO1, Zhong-miao LIU1, Chao DONG1, Yan QIN2, Shu-juan WU1, Hong-jun GAN3, Fei XIE3, Guang-hui ZHUANG3, Bing-zhe FU4, De-cao NIU1(
), Jia-ning LUO1, Zhong-miao LIU1, Chao DONG1, Yan QIN2, Shu-juan WU1, Hong-jun GAN3, Fei XIE3, Guang-hui ZHUANG3, Bing-zhe FU4, De-cao NIU1( )
)
Received:2020-08-19
Revised:2020-12-02
Online:2021-09-16
Published:2021-09-16
Contact:
De-cao NIU
摘要:
箭筈豌豆是一种优良的绿肥作物,具有固氮、改善土壤结构等功能,在农业生产中使用十分普遍,但目前关于种植箭筈豌豆对土壤微生物养分代谢特征影响的研究还鲜有报道。本研究基于盆栽试验,设置了不同种植密度的箭筈豌豆处理,包括低密度组(19株·盆-1)与高密度组(40株·盆-1),同时设置空白土壤作为对照,研究上述处理对土壤养分和微生物特性的影响。结果显示:1)高密度组箭筈豌豆生物量和养分积累量均高于低密度组,从土壤获得的有效养分增加,植物生长受P的限制性增强;2)种植箭筈豌豆高密度组处理显著降低了土壤可溶性无机磷含量,尽管对可溶性有机碳和总氮的影响不显著,但可溶性总氮较对照明显有降低的趋势,最终对土壤可溶性养分计量比RC:N、RC:P、RN:P的影响不显著;3)种植箭筈豌豆增加了SMBC、SMBN含量和SMBC∶SMBP、SMBN∶SMBP,降低了SMBP含量和SMBC∶SMBN,表明微生物生长对N的需求量增加;4)种植箭筈豌豆降低了土壤BG(C-获取酶)酶活性而增加了(NAG+LAP)(N-获取酶)和AP(P-获取酶)酶活性,降低了BG∶(NAG+LAP)、BG∶AP和 (NAG+LAP)∶AP,表明土壤微生物通过增加N和P获取的酶活性以增加对短缺养分的获取。因此,种植不同密度的箭筈豌豆在改变土壤养分特征的同时,还改变了土壤微生物养分代谢特征,微生物通过调整体内养分含量及胞外酶的分泌量及计量比以适应新的资源供应特征。
周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72.
Shi-jing ZHOU, Jia-ning LUO, Zhong-miao LIU, Chao DONG, Yan QIN, Shu-juan WU, Hong-jun GAN, Fei XIE, Guang-hui ZHUANG, Bing-zhe FU, De-cao NIU. The effects of Vicia sativa planting density on soil microbial nutrient metabolism[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 63-72.
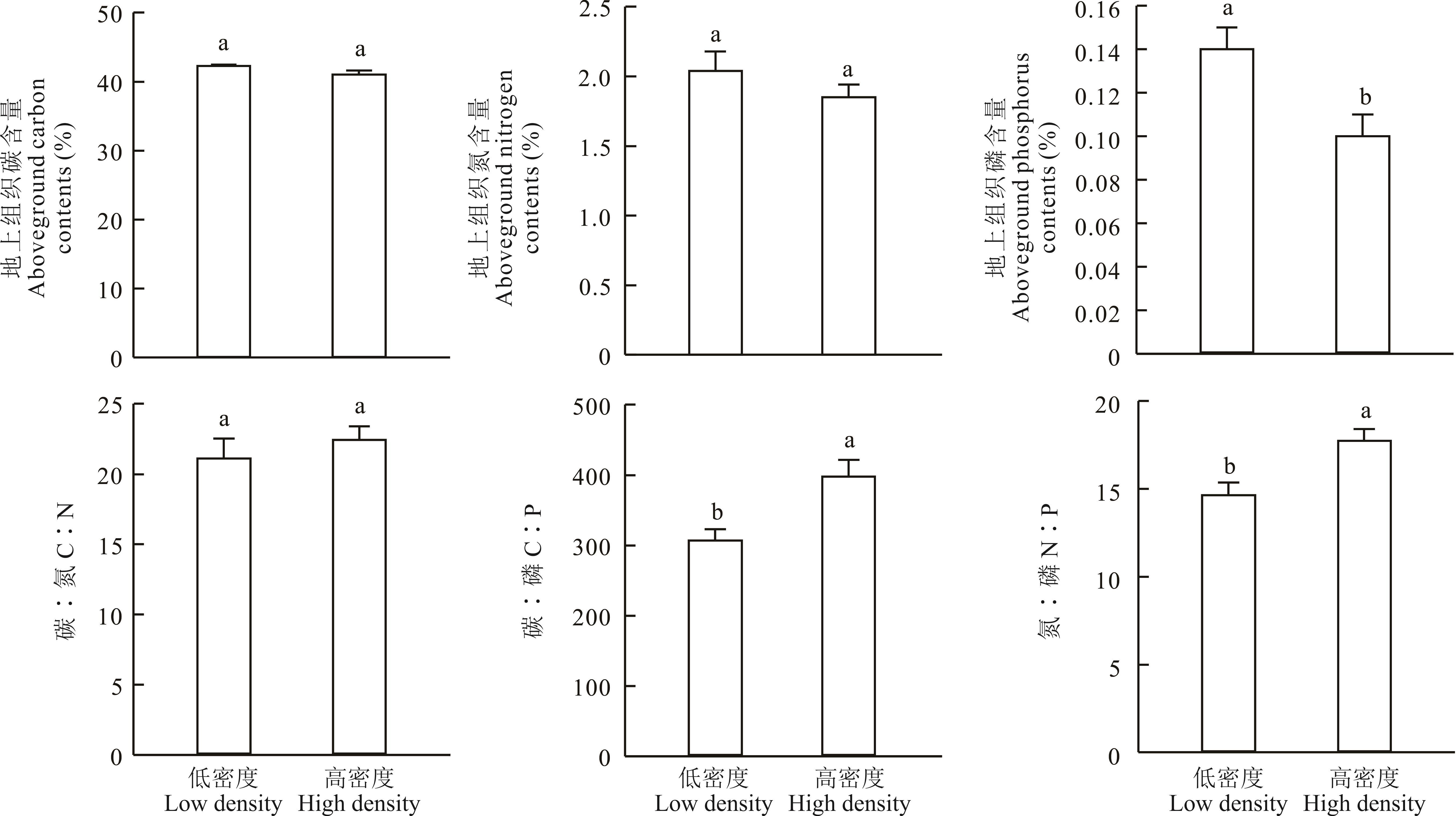
图1 不同种植密度箭筈豌豆地上组织碳氮磷养分含量及计量比特征不同字母表示在P<0.05水平存在显著性差异。下同。Different letters represent significant difference at P<0.05 level. The same below.
Fig. 1 Contents of C, N and P and their mass ratios in the above ground biomass of V. sativa planted with different densities
项目 Item | 指标 Index | 低密度组 Low density | 高密度组 High density |
|---|---|---|---|
生物量 Biomass | 整体植物地上生物量Above ground biomass of each pot (g·盆Pot-1) | 3.32±0.21b | 7.86±0.40a |
| 整体植物地下生物量Under ground biomass of each pot (g·pot-1) | 2.08±0.37b | 6.43±1.16a | |
| 整体植物总生物量Total biomass of each pot (g·pot -1) | 5.40±0.48b | 14.29±0.98a | |
| 单株植物地上生物量Above ground biomass of each plant (mg·株Plant-1) | 174.63±11.20a | 196.60±9.96a | |
| 单株植物地下生物量Under ground biomass of each plant (mg·plant-1) | 109.58±19.65a | 160.70±28.96a | |
| 单株植物总生物量Total biomass of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 284.21±25.30a | 357.30±24.52a | |
养分积累量 Nutrient accumulation | 整体植物碳积累量Content of C accumulation of each pots (mg·pot -1) | 2091.90±169.55b | 5125.18±244.05a |
| 整体植物氮积累量Content of N accumulation of each pot (mg·pot -1) | 104.71±6.23b | 265.42±21.11a | |
| 整体植物磷积累量Content of P accumulation of each pot (mg·pot -1) | 7.34±0.54b | 16.69±1.61a | |
| 单株植物碳积累量Content of C accumulation of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 110.10±8.92a | 128.13±6.10a | |
| 单株植物氮积累量Content of N accumulation of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 5.51±0.33a | 6.64±0.53a | |
| 单株植物磷积累量Content of P accumulation of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 0.39±0.03a | 0.42±0.04a | |
养分积累计量比 Nutrient accumulation ratio | 植物养分积累总量C∶N。C∶N ratio of total plant nutrient accumulation. | 19.92±0.88a | 19.55±0.89a |
| 植物养分积累总量C∶P。C∶P ratio of total plant nutrient accumulation. | 285.22±13.58a | 315.29±24.38a | |
| 植物养分积累总量N∶P。N∶P ratio of total plant nutrient accumulation. | 14.38±0.68a | 16.13±1.00a |
表1 不同种植密度箭筈豌豆的生物量与养分积累量
Table 1 Biomass and C, N and P accumulation in V. sativa planted with different densities
项目 Item | 指标 Index | 低密度组 Low density | 高密度组 High density |
|---|---|---|---|
生物量 Biomass | 整体植物地上生物量Above ground biomass of each pot (g·盆Pot-1) | 3.32±0.21b | 7.86±0.40a |
| 整体植物地下生物量Under ground biomass of each pot (g·pot-1) | 2.08±0.37b | 6.43±1.16a | |
| 整体植物总生物量Total biomass of each pot (g·pot -1) | 5.40±0.48b | 14.29±0.98a | |
| 单株植物地上生物量Above ground biomass of each plant (mg·株Plant-1) | 174.63±11.20a | 196.60±9.96a | |
| 单株植物地下生物量Under ground biomass of each plant (mg·plant-1) | 109.58±19.65a | 160.70±28.96a | |
| 单株植物总生物量Total biomass of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 284.21±25.30a | 357.30±24.52a | |
养分积累量 Nutrient accumulation | 整体植物碳积累量Content of C accumulation of each pots (mg·pot -1) | 2091.90±169.55b | 5125.18±244.05a |
| 整体植物氮积累量Content of N accumulation of each pot (mg·pot -1) | 104.71±6.23b | 265.42±21.11a | |
| 整体植物磷积累量Content of P accumulation of each pot (mg·pot -1) | 7.34±0.54b | 16.69±1.61a | |
| 单株植物碳积累量Content of C accumulation of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 110.10±8.92a | 128.13±6.10a | |
| 单株植物氮积累量Content of N accumulation of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 5.51±0.33a | 6.64±0.53a | |
| 单株植物磷积累量Content of P accumulation of each plant (mg·plant -1) | 0.39±0.03a | 0.42±0.04a | |
养分积累计量比 Nutrient accumulation ratio | 植物养分积累总量C∶N。C∶N ratio of total plant nutrient accumulation. | 19.92±0.88a | 19.55±0.89a |
| 植物养分积累总量C∶P。C∶P ratio of total plant nutrient accumulation. | 285.22±13.58a | 315.29±24.38a | |
| 植物养分积累总量N∶P。N∶P ratio of total plant nutrient accumulation. | 14.38±0.68a | 16.13±1.00a |
| 指标 Index | 对照组 CK | 低密度组 Low density | 高密度组 High density |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (SOC, g·kg-1) | 4.78±0.37b | 5.98±0.10a | 5.78±0.13a |
| 土壤全氮Soil total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 0.37±0.04a | 0.45±0.04a | 0.34±0.07a |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 0.76±0.01a | 0.78±0.02a | 0.71±0.01b |
| 可溶性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon (DOC, mg·kg-1) | 106.70±8.18a | 117.33±8.54a | 91.60±6.53a |
| 可溶性总氮Dissolved total nitrogen (DTN, mg·kg-1) | 13.11±1.85a | 11.37±1.28a | 9.61±0.78a |
| 可溶性无机磷 Dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP, mg·kg-1) | 4.91±0.19a | 4.42±0.35a | 3.39±0.14b |
| RC∶N | 8.44±0.57a | 10.62±0.89a | 9.61±0.45a |
| RC∶P | 21.83±1.73a | 27.83±3.24a | 27.35±2.69a |
| RN∶P | 2.68±0.37a | 2.70±0.47a | 2.88±0.32a |
表2 不同种植密度土壤的养分含量
Table 2 Nutrient content of soil under different planting densities
| 指标 Index | 对照组 CK | 低密度组 Low density | 高密度组 High density |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (SOC, g·kg-1) | 4.78±0.37b | 5.98±0.10a | 5.78±0.13a |
| 土壤全氮Soil total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 0.37±0.04a | 0.45±0.04a | 0.34±0.07a |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 0.76±0.01a | 0.78±0.02a | 0.71±0.01b |
| 可溶性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon (DOC, mg·kg-1) | 106.70±8.18a | 117.33±8.54a | 91.60±6.53a |
| 可溶性总氮Dissolved total nitrogen (DTN, mg·kg-1) | 13.11±1.85a | 11.37±1.28a | 9.61±0.78a |
| 可溶性无机磷 Dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP, mg·kg-1) | 4.91±0.19a | 4.42±0.35a | 3.39±0.14b |
| RC∶N | 8.44±0.57a | 10.62±0.89a | 9.61±0.45a |
| RC∶P | 21.83±1.73a | 27.83±3.24a | 27.35±2.69a |
| RN∶P | 2.68±0.37a | 2.70±0.47a | 2.88±0.32a |
| 指标Index | 对照组 CK | 低密度组 Low density | 高密度组 High density |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤微生物生物量碳Soil microbial biomass carbon (SMBC, mg·kg-1) | 118.67±14.64b | 119.50±23.90b | 194.42±8.03a |
| 土壤微生物生物量氮Soil microbial biomass nitrogen (SMBN, mg·kg-1) | 19.27±2.04c | 33.12±2.62b | 51.01±5.24a |
| 土壤微生物生物量磷 Soil microbial biomass phosphorus (SMBP, mg·kg-1) | 31.78±12.79a | 12.49±2.90a | 22.80±3.17a |
| SMBC∶SMBN | 6.25±0.59a | 3.58±0.57b | 3.96±0.37b |
| SMBC∶SMBP | 5.84±1.64a | 15.81±7.70a | 9.62±2.03a |
| SMBN∶SMBP | 1.06±0.42a | 3.67±1.24a | 2.52±0.56a |
表3 不同种植密度下土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷含量及其计量比
Table 3 Soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and stoichiometric ratios under different planting densities
| 指标Index | 对照组 CK | 低密度组 Low density | 高密度组 High density |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤微生物生物量碳Soil microbial biomass carbon (SMBC, mg·kg-1) | 118.67±14.64b | 119.50±23.90b | 194.42±8.03a |
| 土壤微生物生物量氮Soil microbial biomass nitrogen (SMBN, mg·kg-1) | 19.27±2.04c | 33.12±2.62b | 51.01±5.24a |
| 土壤微生物生物量磷 Soil microbial biomass phosphorus (SMBP, mg·kg-1) | 31.78±12.79a | 12.49±2.90a | 22.80±3.17a |
| SMBC∶SMBN | 6.25±0.59a | 3.58±0.57b | 3.96±0.37b |
| SMBC∶SMBP | 5.84±1.64a | 15.81±7.70a | 9.62±2.03a |
| SMBN∶SMBP | 1.06±0.42a | 3.67±1.24a | 2.52±0.56a |

图2 不同种植密度土壤酶活性及其计量比的变化BG:β-1,4-葡糖苷酶β-1,4-glucosidase;NAG: β-1,4-N-乙酰葡糖胺糖苷酶β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase;LAP: 亮氨酸氨基肽酶Leucine aminopeptidase;AP: 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase.
Fig. 2 Changes of the soil enzymatic activities and stoichiometric ratios on different planting densities
| 1 | Jia G M. Effects of vegetation succession and land management on soil nutrients, microbial activity and community structure in the Loess Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2006. |
| 贾国梅.黄土高原地区植被演替和土地管理对土壤养分、微生物活性和群落结构的影响.兰州: 兰州大学, 2006. | |
| 2 | Liu S J, Xia X, Chen G M, et al. Study progress on functions and affecting factors of soil enzymes. Chinese Agricutural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(21): 1-7. |
| 刘善江, 夏雪, 陈桂梅, 等. 土壤酶的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(21): 1-7. | |
| 3 | Zak D R, Pregitzer K S, King J S, et al. Elevated atmospheric CO2, fine roots and the response of soil microorganisms: a review and hypothesis. New Phytologist, 2000, 147(1): 201-222. |
| 4 | Cao W D, Huang H X. Thoughts on several issues of restoration and development of green manure in China. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2009(4): 1-3. |
| 曹卫东, 黄鸿翔. 关于我国恢复和发展绿肥若干问题的思考. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009(4): 1-3. | |
| 5 | Guo Y D, Cheng M, Zhao X F, et al. Effects of green manure rotation on soil properties and yield and quality of silage maize in saline-alkali soils. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(6): 856-864. |
| 郭耀东, 程曼, 赵秀峰, 等. 轮作绿肥对盐碱地土壤性质、后作青贮玉米产量及品质的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(6): 856-864. | |
| 6 | Gao J S, Cao W D, Li D C, et al. Effects of long-term double-rice and green manure rotation on rice yield and soil organic matter in paddy field. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(16): 4542-4548. |
| 高菊生, 曹卫东, 李冬初, 等. 长期双季稻绿肥轮作对水稻产量及稻田土壤有机质的影响. 生态学报, 2011, 31(16): 4542-4548. | |
| 7 | Song L, Liao W Y, Wang Y J, et al. Effects of interplanting green manure on physical and chemical properties on tea soil. Soils, 2016, 48(4): 675-679. |
| 宋莉, 廖万有, 王烨军, 等. 套种绿肥对茶园土壤理化性状的影响. 土壤, 2016, 48(4): 675-679. | |
| 8 | Wang Q, Geng Z C, Xu C Y, et al. Effects of biochar application on soil microbial nutrient limitations and carbon use efficiency in Lou soil. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(5): 2425-2433. |
| 王强, 耿增超, 许晨阳, 等. 施用生物炭对塿土土壤微生物代谢养分限制和碳利用效率的影响. 环境科学, 2020, 41(5): 2425-2433. | |
| 9 | Niu D C, Jiang S G, Qin Y, et al. Effects of enclosure and grazing on soil microbes and enzyme activities. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(4): 528-534. |
| 牛得草, 江世高, 秦燕, 等. 围封与放牧对土壤微生物和酶活性的影响. 草业科学, 2013, 30(4): 528-534. | |
| 10 | Mooshammer M, Wanek W, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, et al. Stoichiometric imbalances between terrestrial decomposer communities and their resources: Mechanisms and implications of microbial adaptations to their resources. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2014, 5(22): 22. |
| 11 | Yuan X B, Niu D C, Gherardi L A, et al. Linkages of stoichiometric imbalances to soil microbial respiration with increasing nitrogen addition: Evidence from a long-term grassland experiment. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2019, 138: 107580. |
| 12 | Sinsabaugh R L, Shah J J F, Hill B H, et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of stream sediments with comparison to terrestrial soils. Biogeochemistry, 2012, 111(1/2/3): 455-467. |
| 13 | Liu J X. Study on the correlation between soil enzyme activities and soil nutrients in different farmlands. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004(4): 523-525. |
| 刘建新. 不同农田土壤酶活性与土壤养分相关关系研究. 土壤通报, 2004(4): 523-525. | |
| 14 | Zhu Y Q, Jian D W, Zheng W, et al. Effects of improving soil fertility by planting different leguminous green manure plants under different mixed cropping patterns. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(5): 889-900. |
| 朱亚琼, 简大为, 郑伟, 等. 不同种植模式下豆科绿肥对土壤改良效果的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(5): 889-900. | |
| 15 | Yang W H, Ren Q S, Qin H, et al. Characteristics of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, and phosphrus under Cynodon dactylon vegetation at different altitudes in the hydro-fluctuation belt of the Three Gorges Dam Reservoir. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(2): 57-68. |
| 杨文航, 任庆水, 秦红, 等. 三峡库区消落带不同海拔狗牙根草地土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷含量特征. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 57-68. | |
| 16 | Dong R. Genetic diversity analysis and pod shattering biological characteristics study of common vetch (Vicia sativa L.). Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 董瑞. 箭筈豌豆遗传多样性及裂荚生物学特性研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. | |
| 17 | Lu B L, Bao X G, Zhang J D, et al. Evaluation of Vicia sativa germplasm resources in Gansu. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 32(8): 1296-1302. |
| 卢秉林, 包兴国, 张久东, 等. 甘肃箭筈豌豆种质资源评价. 草业科学, 2015, 32(8): 1296-1302. | |
| 18 | Lin C, Yang Y S, Guo J F, et al. Fine root decomposition of evergreen broadleaved and coniferous tree species in mid-subtropical China: Dynamics of dry mass, nutrient and organic fractions. Plant and Soil, 2011, 338(1/2): 311-327. |
| 19 | Nelson D W. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. Methods of Soil Analysis, 1982, 9: 961-1010. |
| 20 | Yang Y L, Lu M Y. Methods of soil total nitrogen analysis. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1991(4): 191-193, 190. |
| 杨玉兰, 卢明远. 土壤总氮的分析方法. 土壤通报, 1991(4): 191-193, 190. | |
| 21 | Li Z W, Xiao H B, Tang Z H, et al. Microbial responses to erosion-induced soil physico-chemical property changes in the hilly red soil region of southern China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2015, 71: 37-44. |
| 22 | Vance E D, Brookes P C, Jenkinson D S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1987, 19(6): 703-707. |
| 23 | Joergensen R G, Mueller T. The fumigation-extraction method to estimate soil microbial biomass: Calibration of the KEC value. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1996, 28(1): 33-37. |
| 24 | Verchot L V, Borelli T. Application of para-nitrophenol (pNP) enzyme assays in degraded tropical soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2004, 37(4): 625-633. |
| 25 | Yuan Z L, Li L H, Han X G, et al. Foliar nitrogen dynamics and nitrogen resorption of a sandy shrub Salix gordejevii in northern China. Plant and Soil, 2005, 278(1): 183-193. |
| 26 | Lu X T, Rees S, Yu Q, et al. Convergent responses of nitrogen and phosphorus resorption to nitrogen inputs in a semiarid grassland. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(9): 2775-2784. |
| 27 | Huang J Y. Nutrient resorption patterns of species along N, P and water gradients in a typical temperate steppe. Beijing: Institute of Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008. |
| 黄菊莹. 典型草原优势植物养分回收特性对养分和水分梯度变化的响应. 北京: 中国科学院植物研究所, 2008. | |
| 28 | Koerselman W, Meuleman A F M. The vegetation N∶P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. Journal of Applied Ecoloy, 1996, 33: 1441-1450. |
| 29 | Liu W H, Qin Y, Liang G L, et al. Effect of different agronomy treatments on the carbon and nitrogen stock and allocation of the oat cultivation grassland on alpine meadow. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(3): 565-573. |
| 刘文辉, 秦燕, 梁国玲, 等. 高寒区栽培措施对燕麦人工草地系统碳氮储量及分配机制的影响. 核农学报, 2019, 33(3): 565-573. | |
| 30 | Liu Z P. Spatial distribution of soil nutrients and the impact factors across the Loess Plateau of China. Xianyang: Institue of Soil and Water Conservation of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013. |
| 刘志鹏. 黄土高原地区土壤养分的空间分布及其影响因素. 咸阳: 中国科学院研究生院(教育部水土保持与生态环境研究中心), 2013. | |
| 31 | Zhou M, Xiao H B, Nie X D, et al. Analysis and prospect of soil organic carbon research process in recent 30 years at home and abroad. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(3): 391-400. |
| 周咪, 肖海兵, 聂小东, 等. 近30年国内外土壤有机碳研究进程解析与展望. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(3): 391-400. | |
| 32 | Qi Y C, Dong Y S, Geng Y B, et al. Research progress on carbon cycle of grassland ecosystem in China. Progress in Geography, 2003(4): 342-352. |
| 齐玉春, 董云社, 耿元波, 等. 我国草地生态系统碳循环研究进展. 地理科学进展, 2003(4): 342-352. | |
| 33 | Moreau D, Bardgett R D, Finlay R D, et al. A plant perspective on nitrogen cycling in the rhizosphere. Functional Ecology, 2019, 33(4): 540-552. |
| 34 | Tian L M, Zhao L, Wu X D, et al. Soil moisture and texture primarily control the soil nutrient stoichiometry across the Tibetan grassland. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622/623: 192-202. |
| 35 | Chen A Q, Fu B, Lu Y, et al. Exogenous organic materials applied to paddy field improving soil microbial biomass C, N and dissolved organic C, N. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(21): 160-167. |
| 陈安强, 付斌, 鲁耀, 等. 有机物料输入稻田提高土壤微生物碳氮及可溶性有机碳氮. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(21): 160-167. | |
| 36 | Han X F. Study on dynamic changes of soil inorganic phosphorus and their migration characteristics of farmland in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016. |
| 韩晓飞. 三峡库区农田土壤无机磷动态变化及其迁移特征. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016. | |
| 37 | Wang S Q, Yu G R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008(8): 3937-3947. |
| 王绍强, 于贵瑞. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征. 生态学报, 2008(8): 3937-3947. | |
| 38 | Zhang Y J. The research on the change of plant-soil characteristics and allelopathic mechanism in the process of degradation succession in the typical grassland northern China. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 张玉娟. 典型草原退化演替中植被-土壤特征变化及化感影响机制研究. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. | |
| 39 | Jenkinson D S, Ladd J N. Microbial biomass in soil: measurement and turnover. Soil Biochemistry, 1981, 5: 415-471. |
| 40 | Ken E G, Ernst W, Steve P M. Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 1998, 30(10): 1389-1414. |
| 41 | Zhao C Y. Study on soil respiration and soil carbon cycle of different terrestrial ecosystem. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2004. |
| 赵成义. 陆地不同生态系统土壤呼吸及土壤碳循环研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2004. | |
| 42 | Sterner R W, Elser J J. Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 2003. |
| 43 | Li L X. Effect of NPK fertilization on dry matter production, nutrient uptake and soil enzyme activity of winter wheat in lime concretion black soil. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 李刘霞. 氮磷钾配施对砂姜黑土冬小麦干物质生产、养分吸收利用及土壤酶活性的影响. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2014. | |
| 44 | Hessen D O, Ågren G I, Anderson T R, et al. Carbon sequestration in ecosystems: the role of stoichiometry. Ecology, 2004, 85(5): 1179-1192. |
| 45 | Steven D A, Peter M V. Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2004, 37(5): 937-944. |
| 46 | Sinsabaugh R L, Hill B H, F Shah J J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature, 2009, 462(7274): 795-798. |
| 47 | Sinsabaugh R L, Lauber C L, Weintraub M N, et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol Lett, 2008, 11(11): 1252-1264. |
| [1] | 徐强, 田新会, 杜文华. 高寒牧区黑麦和箭筈豌豆混播对草产量和营养品质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 49-59. |
| [2] | 南志标, 王彦荣, 聂斌, 李春杰, 张卫国, 夏超. 春箭筈豌豆新品种“兰箭3号”选育与特性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 111-120. |
| [3] | 顾继雄, 郭天斗, 王红梅, 李雪颖, 梁丹妮, 杨青莲, 高锦月. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地转变过程土壤微生物响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 46-57. |
| [4] | 韩福贵, 满多清, 郑庆钟, 赵艳丽, 张裕年, 肖斌, 付贵全, 杜娟. 青土湖典型湿地白刺灌丛沙堆群落物种多样性及土壤养分变化特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 36-45. |
| [5] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 王宏生. 围封和防除狼毒对狼毒斑块土壤理化性质和微生物量影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 63-72. |
| [6] | 宗文贞, 郭家昊, 贾云龙, 郑永兴, 杨旭, 胡芳弟, 王静. 单宁在植物-土壤氮循环中作用的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 174-183. |
| [7] | 黄玙璠, 舒英格, 肖盛杨, 陈梦军. 喀斯特山区不同草地土壤养分与酶活性特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 93-104. |
| [8] | 王琼, 段廷玉, 南志标. 箭筈豌豆炭疽病病原菌分离鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 127-136. |
| [9] | 魏鹏, 安沙舟, 董乙强, 孙宗玖, 别尔达吾列提·希哈依, 李超. 基于高通量测序的准噶尔盆地荒漠土壤细菌多样性及群落结构特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 182-190. |
| [10] | 王婷, 张永超, 赵之重. 青藏高原退化高寒湿地植被群落结构和土壤养分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 9-18. |
| [11] | 冯军, 石超, 门胜男, Hafiz Athar Hussain, 柯剑鸿, Linna Cholidah, 陈锦芬, 郭欣, 武海燕, 冉泰霖, 向信华, 王龙昌. 不同降雨下旱地油菜节水节肥技术对土壤养分及酶活性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 51-62. |
| [12] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [13] | 柳书俊, 姚新转, 赵德刚, 吕立堂. 湄潭茶园土壤养分特征及肥力质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 33-45. |
| [14] | 施颖, 胡廷花, 高红娟, 罗巧玉, 于应文. 两种放牧模式下高寒草甸群落植被构成及稳定性特征[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 1-10. |
| [15] | 帅林林, 周青平, 陈有军, 苟小林, 周蓉. 高寒半湿润沙地草本修复期土壤微生物变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 11-22. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||