

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 91-106.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022094
李雯1,2( ), 赵丽蓉1,2, 张建平1,2(
), 赵丽蓉1,2, 张建平1,2( ), 刘自刚1(
), 刘自刚1( ), 齐燕妮2, 李闻娟2, 谢亚萍2
), 齐燕妮2, 李闻娟2, 谢亚萍2
收稿日期:2022-02-23
修回日期:2022-04-06
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2022-12-30
通讯作者:
张建平,刘自刚
作者简介:E-mail: 739015868@qq.com基金资助:
Wen LI1,2( ), Li-rong ZHAO1,2, Jian-ping ZHANG1,2(
), Li-rong ZHAO1,2, Jian-ping ZHANG1,2( ), Zi-gang LIU1(
), Zi-gang LIU1( ), Yan-ni QI2, Wen-juan LI2, Ya-ping XIE2
), Yan-ni QI2, Wen-juan LI2, Ya-ping XIE2
Received:2022-02-23
Revised:2022-04-06
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2022-12-30
Contact:
Jian-ping ZHANG,Zi-gang LIU
摘要:
DMP家族成员是植物特有的膜蛋白,在植物生殖发育及衰老过程中发挥重要作用。亚麻是我国重要的油料及经济作物,目前关于DMP基因家族在亚麻中的分布及功能研究尚未有报道。本研究利用生物信息学方法对亚麻DMP基因家族进行鉴定,对其序列特征、系统进化、复制事件进行了分析,并利用转录组数据和qRT-PCR分析其在不同组织器官及胁迫处理下的表达模式。本研究以陇亚10号基因组为参照,利用同源性分析共鉴定到17个LuDMP成员,命名为LuDMP-1~LuDMP-17,不均匀分布在9条染色体上。序列特征分析结果表明,除LuDMP-9、LuDMP-16和LuDMP-17 外,其余成员均不含内含子;基因启动子区含有大量激素与逆境胁迫相关响应元件;编码的蛋白氨基酸长度为195~240 aa,分子量为20946~25830 Da,等电点为4.76~9.71;所有蛋白均为疏水性蛋白,含有2~5个跨膜结构域及4~8个motif,其中有4个motif存在于所有LuDMP蛋白;绝大多数蛋白定位于细胞膜。LuDMP家族共有3对串联复制事件和8对片段复制事件,进化过程中经历了强烈的纯化选择。转录组分析结果表明,大多数LuDMP成员在果实和茎中呈现特异性表达模式。系统进化分析将 DMP蛋白分为5个亚族,第III亚族DMP数量最多,含有11个LuDMP成员,各亚族中DMP蛋白具有单子叶或双子叶特异性聚类模式。第IV亚族中的LuDMP-1和LuDMP-7与拟南芥及玉米单倍体诱导基因具有很近的亲缘关系,位于同一进化分支,序列同源性达到67%以上,而且该基因在成熟花药中的表达量明显高于其他组织,推测其为亚麻单倍体诱导的候选基因。本研究在陇亚10号中克隆到了LuDMP-1,全长为699 bp。LuDMP-1/7启动子区域含有激素响应及逆境胁迫相关作用元件,吲哚乙酸、赤霉素、萘乙酸、聚乙二醇、高温及低温处理下, LuDMP-1/7基因表达量均有不同程度的提高,其中对低温和高温的响应最明显,分别较对照提高了约260和600倍。本研究为阐明亚麻DMP蛋白的功能奠定了基础,并为亚麻单倍体育种提供了基因资源。
李雯, 赵丽蓉, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 亚麻DMP基因家族的全基因组鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 91-106.
Wen LI, Li-rong ZHAO, Jian-ping ZHANG, Zi-gang LIU, Yan-ni QI, Wen-juan LI, Ya-ping XIE. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the DMP gene family in flax (Linum usitatissimum)[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 91-106.
| 引物名称Primer name | 序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 用途Usage |
|---|---|---|
| DMP-F | ATGGAGGAAGACGACTATGGAATCA | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| DMP-R | CTAACTAGCACTGCACCCAATCCC | |
| qDMP-F | CACTTCACGGACAGTTTCAAGGATC | 定量反转录聚合酶连锁反应Quantificational RT-PCR |
| qDMP-R | CAAGCCACTACAAACAACACCAACC | |
| GAPDH-F | CTTTACCCTCAGCAAATCCG | 内参Reference gene |
| GAPDH-R | AGGTTCTTCCCGCTCTCAAT |
表1 本研究所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in this research
| 引物名称Primer name | 序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 用途Usage |
|---|---|---|
| DMP-F | ATGGAGGAAGACGACTATGGAATCA | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| DMP-R | CTAACTAGCACTGCACCCAATCCC | |
| qDMP-F | CACTTCACGGACAGTTTCAAGGATC | 定量反转录聚合酶连锁反应Quantificational RT-PCR |
| qDMP-R | CAAGCCACTACAAACAACACCAACC | |
| GAPDH-F | CTTTACCCTCAGCAAATCCG | 内参Reference gene |
| GAPDH-R | AGGTTCTTCCCGCTCTCAAT |
| 基因名Gene name | 基因号 Gene-ID | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 外显子数 No. of exons | 蛋白 长度 Protein length (aa) | 总平均亲水性Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular location | 跨膜结 构域 Transmembrane domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LuDMP-1 | L.us.o.g.scaffold34.203 | Chr1:885721-886419(+) | 1 | 232 | 0.107 | 8.08 | 25392.66 | CM,Nucleus | 5 |
| LuDMP-2 | L.us.o.g.scaffold0.456 | Chr2:21280161-21280973(+) | 1 | 198 | 0.231 | 8.63 | 21293.48 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-3 | L.us.o.g.scaffold0.36 | Chr2:21635014-21637816(-) | 1 | 195 | 0.244 | 8.28 | 20946.10 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-4 | L.us.o.g.scaffold30.59 | Chr4:20534605-20535300(+) | 1 | 231 | 0.202 | 4.89 | 25126.95 | CM | 2 |
| LuDMP-5 | L.us.o.g.scaffold30.58 | Chr4:20536021-20536638(+) | 1 | 205 | 0.364 | 6.93 | 22745.70 | CP | 3 |
| LuDMP-6 | L.us.o.g.scaffold30.57 | Chr4:20537649-20538317(+) | 1 | 222 | 0.310 | 6.18 | 23847.58 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-7 | L.us.o.g.scaffold70.212 | Chr7:9831303-9832001(+) | 1 | 232 | 0.057 | 8.08 | 25375.63 | CM,Nucleus | 4 |
| LuDMP-8 | L.us.o.g.scaffold136.194 | Chr8:1238120-1238776(+) | 1 | 218 | 0.064 | 9.19 | 23883.09 | CP | 2 |
| LuDMP-9 | L.us.o.g.scaffold69.277 | Chr10:17296812-17298353(-) | 2 | 229 | 0.093 | 9.71 | 25372.99 | CM | 5 |
| LuDMP-10 | L.us.o.g.scaffold305.10 | Chr12:5379664-5380827(-) | 1 | 217 | 0.313 | 9.06 | 23577.41 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-11 | L.us.o.g.scaffold48.30 | Chr14:1446411-1447221(+) | 1 | 237 | 0.061 | 9.19 | 23746.92 | CM,CP | 4 |
| LuDMP-12 | L.us.o.g.scaffold28.148 | Chr15:5929885-5930780(-) | 1 | 226 | 0.283 | 9.28 | 24020.92 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-13 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.51 | Chr15:7942536-7943540(+) | 1 | 233 | 0.184 | 4.76 | 25373.19 | CM | 2 |
| LuDMP-14 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.50 | Chr15:7944336-7945076(+) | 1 | 205 | 0.582 | 6.50 | 22782.72 | CM,Nucleus | 3 |
| LuDMP-15 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.49 | Chr15:7946004-7946771(+) | 1 | 222 | 0.252 | 6.18 | 23865.56 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-16 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.46 | Chr15:7954525-7955820(+) | 2 | 230 | 0.275 | 5.28 | 24596.32 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-17 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.45 | Chr15: 7957608-7959009(+) | 2 | 240 | 0.256 | 5.01 | 25829.65 | CM | 2 |
表2 亚麻LuDMP成员基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of flax LuDMP members
| 基因名Gene name | 基因号 Gene-ID | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 外显子数 No. of exons | 蛋白 长度 Protein length (aa) | 总平均亲水性Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular location | 跨膜结 构域 Transmembrane domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LuDMP-1 | L.us.o.g.scaffold34.203 | Chr1:885721-886419(+) | 1 | 232 | 0.107 | 8.08 | 25392.66 | CM,Nucleus | 5 |
| LuDMP-2 | L.us.o.g.scaffold0.456 | Chr2:21280161-21280973(+) | 1 | 198 | 0.231 | 8.63 | 21293.48 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-3 | L.us.o.g.scaffold0.36 | Chr2:21635014-21637816(-) | 1 | 195 | 0.244 | 8.28 | 20946.10 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-4 | L.us.o.g.scaffold30.59 | Chr4:20534605-20535300(+) | 1 | 231 | 0.202 | 4.89 | 25126.95 | CM | 2 |
| LuDMP-5 | L.us.o.g.scaffold30.58 | Chr4:20536021-20536638(+) | 1 | 205 | 0.364 | 6.93 | 22745.70 | CP | 3 |
| LuDMP-6 | L.us.o.g.scaffold30.57 | Chr4:20537649-20538317(+) | 1 | 222 | 0.310 | 6.18 | 23847.58 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-7 | L.us.o.g.scaffold70.212 | Chr7:9831303-9832001(+) | 1 | 232 | 0.057 | 8.08 | 25375.63 | CM,Nucleus | 4 |
| LuDMP-8 | L.us.o.g.scaffold136.194 | Chr8:1238120-1238776(+) | 1 | 218 | 0.064 | 9.19 | 23883.09 | CP | 2 |
| LuDMP-9 | L.us.o.g.scaffold69.277 | Chr10:17296812-17298353(-) | 2 | 229 | 0.093 | 9.71 | 25372.99 | CM | 5 |
| LuDMP-10 | L.us.o.g.scaffold305.10 | Chr12:5379664-5380827(-) | 1 | 217 | 0.313 | 9.06 | 23577.41 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-11 | L.us.o.g.scaffold48.30 | Chr14:1446411-1447221(+) | 1 | 237 | 0.061 | 9.19 | 23746.92 | CM,CP | 4 |
| LuDMP-12 | L.us.o.g.scaffold28.148 | Chr15:5929885-5930780(-) | 1 | 226 | 0.283 | 9.28 | 24020.92 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-13 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.51 | Chr15:7942536-7943540(+) | 1 | 233 | 0.184 | 4.76 | 25373.19 | CM | 2 |
| LuDMP-14 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.50 | Chr15:7944336-7945076(+) | 1 | 205 | 0.582 | 6.50 | 22782.72 | CM,Nucleus | 3 |
| LuDMP-15 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.49 | Chr15:7946004-7946771(+) | 1 | 222 | 0.252 | 6.18 | 23865.56 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-16 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.46 | Chr15:7954525-7955820(+) | 2 | 230 | 0.275 | 5.28 | 24596.32 | CM | 4 |
| LuDMP-17 | L.us.o.g.scaffold107.45 | Chr15: 7957608-7959009(+) | 2 | 240 | 0.256 | 5.01 | 25829.65 | CM | 2 |
基因ID Gene ID | AtDMP8 | AtDMP9 | ZmDMP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E值 E value | 同源性Per ident (%) | E值 E value | 同源性 Per ident (%) | E值 E value | 同源性 Per ident (%) | |
| LuDMP-1 | 1×1086 | 57.55 | 3×1086 | 67.39 | 2×1090 | 67.98 |
| LuDMP-2 | 2×1034 | 33.15 | 9×1033 | 32.58 | 9×1028 | 36.05 |
| LuDMP-3 | 9×1036 | 33.71 | 2×1033 | 32.58 | 3×1029 | 35.80 |
| LuDMP-4 | 2×1047 | 33.76 | 6×1046 | 38.71 | 4×1045 | 44.94 |
| LuDMP-5 | 7×1043 | 35.68 | 4×1041 | 35.14 | 6×1041 | 39.33 |
| LuDMP-6 | 1×1042 | 34.76 | 1×1042 | 36.22 | 3×1040 | 39.11 |
| LuDMP-7 | 1×1088 | 57.96 | 4×1086 | 67.39 | 1×1090 | 67.98 |
| LuDMP-8 | 6×1041 | 39.56 | 2×1038 | 38.46 | 1×1036 | 39.33 |
| LuDMP-9 | 7×1028 | 33.88 | 8×1026 | 32.07 | 5×1025 | 33.88 |
| LuDMP-10 | 7×1046 | 36.94 | 6×1043 | 39.13 | 5×1044 | 43.58 |
| LuDMP-11 | 4×1040 | 37.50 | 1×1037 | 36.41 | 1×1035 | 37.64 |
| LuDMP-12 | 2×1041 | 36.02 | 8×1040 | 36.56 | 1×1039 | 44.89 |
| LuDMP-13 | 3×1047 | 33.47 | 7×1046 | 38.71 | 1×1045 | 45.51 |
| LuDMP-14 | 5×1041 | 34.59 | 7×1040 | 33.51 | 6×1040 | 38.76 |
| LuDMP-15 | 2×1042 | 35.11 | 9×1044 | 36.76 | 8×1040 | 40.56 |
| LuDMP-16 | 1×1040 | 35.48 | 3×1042 | 37.30 | 7×1041 | 40.45 |
| LuDMP-17 | 4×1044 | 37.63 | 2×1045 | 38.38 | 9×1043 | 42.46 |
表3 LuDMP基因同源性比对
Table 3 LuDMP gene homology comparison
基因ID Gene ID | AtDMP8 | AtDMP9 | ZmDMP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E值 E value | 同源性Per ident (%) | E值 E value | 同源性 Per ident (%) | E值 E value | 同源性 Per ident (%) | |
| LuDMP-1 | 1×1086 | 57.55 | 3×1086 | 67.39 | 2×1090 | 67.98 |
| LuDMP-2 | 2×1034 | 33.15 | 9×1033 | 32.58 | 9×1028 | 36.05 |
| LuDMP-3 | 9×1036 | 33.71 | 2×1033 | 32.58 | 3×1029 | 35.80 |
| LuDMP-4 | 2×1047 | 33.76 | 6×1046 | 38.71 | 4×1045 | 44.94 |
| LuDMP-5 | 7×1043 | 35.68 | 4×1041 | 35.14 | 6×1041 | 39.33 |
| LuDMP-6 | 1×1042 | 34.76 | 1×1042 | 36.22 | 3×1040 | 39.11 |
| LuDMP-7 | 1×1088 | 57.96 | 4×1086 | 67.39 | 1×1090 | 67.98 |
| LuDMP-8 | 6×1041 | 39.56 | 2×1038 | 38.46 | 1×1036 | 39.33 |
| LuDMP-9 | 7×1028 | 33.88 | 8×1026 | 32.07 | 5×1025 | 33.88 |
| LuDMP-10 | 7×1046 | 36.94 | 6×1043 | 39.13 | 5×1044 | 43.58 |
| LuDMP-11 | 4×1040 | 37.50 | 1×1037 | 36.41 | 1×1035 | 37.64 |
| LuDMP-12 | 2×1041 | 36.02 | 8×1040 | 36.56 | 1×1039 | 44.89 |
| LuDMP-13 | 3×1047 | 33.47 | 7×1046 | 38.71 | 1×1045 | 45.51 |
| LuDMP-14 | 5×1041 | 34.59 | 7×1040 | 33.51 | 6×1040 | 38.76 |
| LuDMP-15 | 2×1042 | 35.11 | 9×1044 | 36.76 | 8×1040 | 40.56 |
| LuDMP-16 | 1×1040 | 35.48 | 3×1042 | 37.30 | 7×1041 | 40.45 |
| LuDMP-17 | 4×1044 | 37.63 | 2×1045 | 38.38 | 9×1043 | 42.46 |

图2 LuDMP-1基因全长扩增M:DL1000 marker;1:阴性对照;2:DNA扩增;3:cDNA扩增。1: Negative control; 2: DNA amplification; 3: cDNA amplification.
Fig.2 Full-length amplification of LuDMP-1
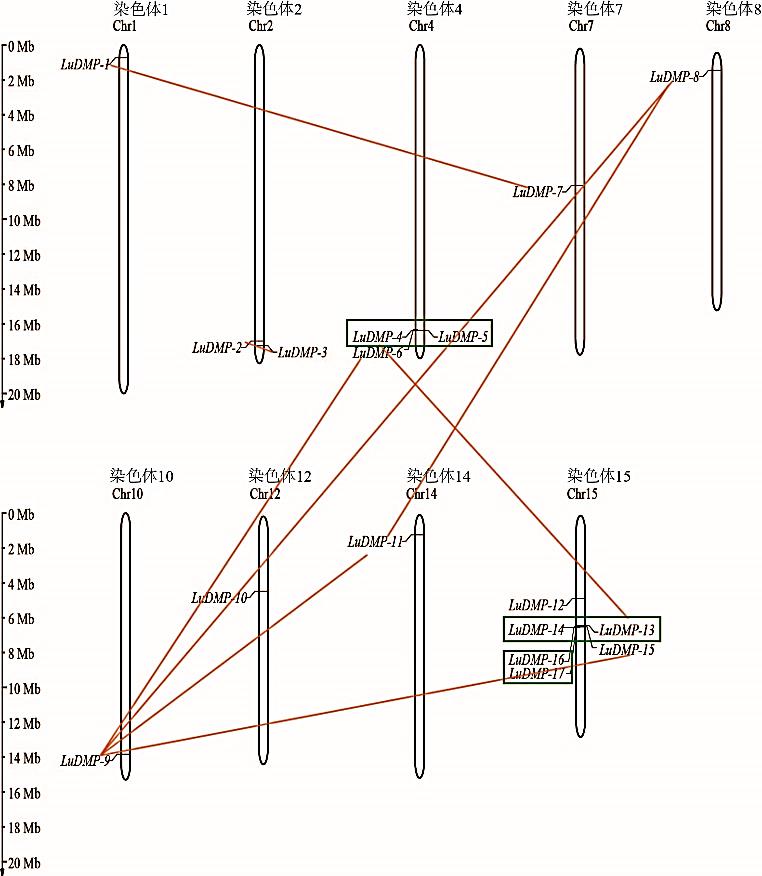
图6 LuDMP基因染色体定位横线代表片段复制,方框代表串联复制。The horizontal line represents segmental duplication, and the box represents tandem duplication. Chr: 染色体Chromosome.
Fig.6 Chromosomal locations of LuDMP genes
基因对 Gene pair | 复制事件 Duplication events | 同义替换率 Ks | 非同义替换率 Ka | Ka/Ks | 选择类型 Select type | 分歧时间 Divergence Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LuDMP-4/LuDMP-5 | 串联复制 Tandem duplication | 1.6616 | 0.2819 | 0.169656 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 136.19670 |
| LuDMP-13/LuDMP-14 | 串联复制 Tandem duplication | 2.0752 | 0.2957 | 0.142492 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 170.09840 |
| LuDMP-16/LuDMP-17 | 串联复制 Tandem duplication | 0.8487 | 0.6472 | 0.762578 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 69.56557 |
| LuDMP-1/LuDMP-7 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.2499 | 0.0097 | 0.038816 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 20.48361 |
| LuDMP-2/LuDMP-3 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.1296 | 0.0278 | 0.214506 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 10.62295 |
| LuDMP-4/LuDMP-13 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.2225 | 0.0025 | 0.011236 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 18.23770 |
| LuDMP-6/LuDMP-9 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | n.a. | 0.4789 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| LuDMP-8/LuDMP-9 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 1.6678 | 0.2323 | 0.139285 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 136.70490 |
| LuDMP-8/LuDMP-11 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.2826 | 0.0484 | 0.171267 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 23.16393 |
| LuDMP-9/LuDMP-11 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 1.6134 | 0.2380 | 0.147515 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 132.24590 |
| LuDMP-9/LuDMP-15 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | n.a. | 0.4402 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
表4 LuDMP基因复制分析
Table 4 Duplication analysis of LuDMP genes
基因对 Gene pair | 复制事件 Duplication events | 同义替换率 Ks | 非同义替换率 Ka | Ka/Ks | 选择类型 Select type | 分歧时间 Divergence Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LuDMP-4/LuDMP-5 | 串联复制 Tandem duplication | 1.6616 | 0.2819 | 0.169656 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 136.19670 |
| LuDMP-13/LuDMP-14 | 串联复制 Tandem duplication | 2.0752 | 0.2957 | 0.142492 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 170.09840 |
| LuDMP-16/LuDMP-17 | 串联复制 Tandem duplication | 0.8487 | 0.6472 | 0.762578 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 69.56557 |
| LuDMP-1/LuDMP-7 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.2499 | 0.0097 | 0.038816 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 20.48361 |
| LuDMP-2/LuDMP-3 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.1296 | 0.0278 | 0.214506 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 10.62295 |
| LuDMP-4/LuDMP-13 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.2225 | 0.0025 | 0.011236 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 18.23770 |
| LuDMP-6/LuDMP-9 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | n.a. | 0.4789 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| LuDMP-8/LuDMP-9 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 1.6678 | 0.2323 | 0.139285 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 136.70490 |
| LuDMP-8/LuDMP-11 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 0.2826 | 0.0484 | 0.171267 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 23.16393 |
| LuDMP-9/LuDMP-11 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | 1.6134 | 0.2380 | 0.147515 | 纯化选择 Purifying selection | 132.24590 |
| LuDMP-9/LuDMP-15 | 片段复制 Segmental duplication | n.a. | 0.4402 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
顺式元件 Cis-element | 典型序列 Typical sequence | 特性 Characteristic | 基因Gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| TATA-box | TATA | 转录开始的-30左右的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcript-ion start | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导所必需的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| Sp1 | GGGCGG | 光响应元件Light responsive element | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-8 |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 参与脱落酸反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in the abcisic acid responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-16 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 参与甲基茉莉酸(MeJA)反应的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 参与甲基茉莉酸(MeJA)反应的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| GCN4_motif | TGAGTCA | 参与胚乳表达的顺式调控元件Cis-regulatory elements involved in endosperm expression | LuDMP-2、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-15 |
| O2-site | GATGATGTGG | 参与玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控的顺式调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| MBS | CAACTG | 与干旱诱导相关的MYB结合位点MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-14 |
| SARE | TTCGACCATCTT | 水杨酸响应元件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-7 |
| TC-rich repeats | GTTTTCTTAC | 防御和应激响应元件Cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16 |
| CAT-box | GCCACT | 与分生组织表达相关的顺式作用调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression | LuDMP-3、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-15 |
| P-box | CCTTTTG | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | LuDMP-6、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14 |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 生长素响应元件Auxin-responsive element | LuDMP-6、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-14 |
| TATC-box | TATCCCA | 赤霉素响应元件Cis-acting element involved in gibberellin-responsiveness | LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-15 |
| GC-motif | CCCCCG | 参与缺氧特异性诱导的增强剂样元件Enhancer-like element involved in anoxic specific inducibility | LuDMP-9、LuDMP-15、LuDMP-17 |
| DRE | TACCGACAT | 脱水、低温及盐胁迫响应元件Cis-acting element involved in dehydration, low-temperature, salt stresses | LuDMP-3 |
| RY-element | CATGCATG | 参与种子特异性调控的顺式调控元件Cis-regulatory elements involved in seed-specific regulation | LuDMP-2 |
| GARE-motif | TCTGTTG | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-12 |
| TCA-element | CCATTTTTT | 水杨酸响应元件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | LuDMP-2、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-14、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 低温响应元件Cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14 |
表5 亚麻LuDMP启动子顺式元件分析
Table 5 Analysis of cis-elements of flax LuDMP promoters
顺式元件 Cis-element | 典型序列 Typical sequence | 特性 Characteristic | 基因Gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| TATA-box | TATA | 转录开始的-30左右的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcript-ion start | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导所必需的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| Sp1 | GGGCGG | 光响应元件Light responsive element | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-8 |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 参与脱落酸反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in the abcisic acid responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-16 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 参与甲基茉莉酸(MeJA)反应的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 参与甲基茉莉酸(MeJA)反应的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14、 LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| GCN4_motif | TGAGTCA | 参与胚乳表达的顺式调控元件Cis-regulatory elements involved in endosperm expression | LuDMP-2、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-15 |
| O2-site | GATGATGTGG | 参与玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控的顺式调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-4、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| MBS | CAACTG | 与干旱诱导相关的MYB结合位点MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-3、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-14 |
| SARE | TTCGACCATCTT | 水杨酸响应元件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-7 |
| TC-rich repeats | GTTTTCTTAC | 防御和应激响应元件Cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-15、LuDMP-16 |
| CAT-box | GCCACT | 与分生组织表达相关的顺式作用调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression | LuDMP-3、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-15 |
| P-box | CCTTTTG | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | LuDMP-6、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14 |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 生长素响应元件Auxin-responsive element | LuDMP-6、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-14 |
| TATC-box | TATCCCA | 赤霉素响应元件Cis-acting element involved in gibberellin-responsiveness | LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-15 |
| GC-motif | CCCCCG | 参与缺氧特异性诱导的增强剂样元件Enhancer-like element involved in anoxic specific inducibility | LuDMP-9、LuDMP-15、LuDMP-17 |
| DRE | TACCGACAT | 脱水、低温及盐胁迫响应元件Cis-acting element involved in dehydration, low-temperature, salt stresses | LuDMP-3 |
| RY-element | CATGCATG | 参与种子特异性调控的顺式调控元件Cis-regulatory elements involved in seed-specific regulation | LuDMP-2 |
| GARE-motif | TCTGTTG | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-12 |
| TCA-element | CCATTTTTT | 水杨酸响应元件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | LuDMP-2、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-14、LuDMP-16、LuDMP-17 |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 低温响应元件Cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | LuDMP-1、LuDMP-2、LuDMP-5、LuDMP-6、LuDMP-7、LuDMP-8、LuDMP-9、LuDMP-10、LuDMP-11、LuDMP-12、LuDMP-13、LuDMP-14 |
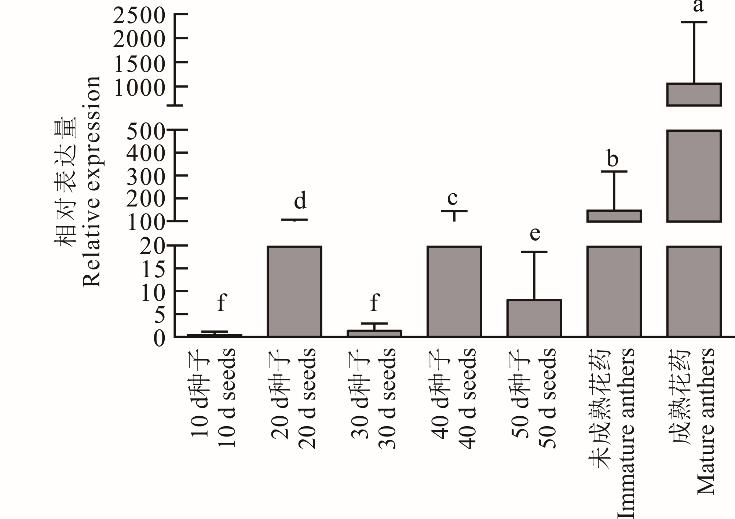
图8 LuDMP-1/7基因在种子及花药中的表达模式不同小写字母表示在0.05水平具有显著性差异。下同。Different small letters mean significant differences at the 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.8 Expression patterns of LuDMP-1/7 in seeds and anther
| 1 | Yamada K, Osakabe Y, Mizoi J, et al. Functional analysis of an Arabidopsis thaliana abiotic stress-inducible facilitated diffusion transporter for monosaccharides. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(2): 1138-1146. |
| 2 | Xicluna J, Lacombe B, Dreyer I, et al. Increased functional diversity of plant K+ channels by preferential heteromerization of the shakerlike subunits AKT2 and KAT2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(1): 486-494. |
| 3 | Chen Y, Heazlewood J. Organellar proteomic profiling to analyze membrane traf-ficking pathways. Trends in Plant Science, 2020, 26(3): 299-300. |
| 4 | Chen Y, Weckwerth W. Mass spectrometry untangles plant membrane protein sig-naling networks. Trends in Plant Science, 2020, 25(9): 930-944. |
| 5 | Mori T, Igawa T, Tamiya G, et al. Gamete attachment re-quires GEX2 for successful fertilization in Arabidopsis. Current Biology, 2014, 24(2): 170-175. |
| 6 | Kasaras A, Melzer M, Kunze R. Arabidopsis senescence-associated protein DMP1 is involved in membrane remodeling of the ER and tonoplast. BMC Plant Biology, 2012, 12: 54. |
| 7 | Kasaras A, Kunze R. Expression, localisation and phylogeny of a novel family of plant-specific membrane proteins. Plant Biology, 2010, 12(Supple 1): 140-152. |
| 8 | Zhong Y, Liu C X, Qi X L, et al. Mutation of ZmDMP enhances haploid induction in maize. Nature Plants, 2019, 5(6): 575-580. |
| 9 | Zhong Y, Chen B J, Mengran L, et al. A DMP-triggered in vivo maternal haploid induction system in the dicotyledonous Arabidopsis. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(5): 466-467. |
| 10 | Zhu S, Wang X, Chen W, et al. Cotton DMP gene family: Characterization, evolution, and expression profiles during development and stress. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021, 183(2): 1257-1269. |
| 11 | Wei Y H, Kong J P, Zhang Y H, et al. Development status, research and development trend and countermeasures of flax at home and abroad. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 44(Supple 2): 70-75. |
| 魏彦宏, 孔建平, 张彦红, 等. 国内外亚麻发展现状、研发趋势与对策. 新疆农业科学, 2007, 44(增刊2): 70-75. | |
| 12 | Huis R, Hawkins S, Neutelings G. Selection of reference genes for quantitative gene expression normalization in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). BMC Plant Biology, 2010, 10(1): 71. |
| 13 | Chytilova M, Mudronova D, Nemcova R, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of flax-seed oil and Lactobacillus plantarum-BiocenolTM LP96 in gnotobiotic pigs challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Research in Veterinary Science, 2013, 95(1): 103-109. |
| 14 | Heller K, Sheng Q C, Guan F, et al. A comparative study between Europe and China in crop management of two types of flax: Linseed and fibre flax. Industrial Crops and Products, 2015, 68: 24-31. |
| 15 | Liu Q, Talboot M, Llewellyn D J. Pectin methylesterase and pectin remodelling differ in the fibre walls of two Gossypium species with very different fibre properties. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e65131. |
| 16 | Guo D, Du M, Zhou B Y, et al. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of CCT gene family in maize. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2019, 20(4): 1001-1010. |
| 郭栋, 杜媚, 周宝元, 等. 玉米CCT基因家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(4): 1001-1010. | |
| 17 | Zheng L, Bai X T, Li H Y. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of TCP gene family in Sorghum bicolor. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 48(10): 30-36. |
| 郑玲, 白雪婷, 李会云. 高粱TCP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(10): 30-36. | |
| 18 | Yuan H, Guo W, Zhao L, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY transcription factor family in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). BMC Genomics, 2021, 22(1): 375. |
| 19 | Cai X X, Shen Y, Zhou W H, et al. Genome-wide identification and bioinformatics analysis of soybean CHX gene family. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2018, 37(12): 5360-5369. |
| 才晓溪, 沈阳, 周伍红, 等. 大豆CHX基因家族全基因组鉴定与生物信息学分析. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2018, 37(12): 5360-5369. | |
| 20 | Wang X H, Xu N L, Yao M M, et al. Identification and evolution analysis of LBD gene family in Lophopyrum elongatum. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 202-216. |
| 王新华, 许娜丽, 姚明明, 等. 长穗偃麦草LBD基因家族的鉴定与进化分析. 西北农业学报, 2022, 31(2): 202-216. | |
| 21 | Huang C, Liang X M, Dai C, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of BnAPs gene family members in Brassica napus. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 597-607. |
| 黄成, 梁晓梅, 戴成, 等. 甘蓝型油菜BnAPs基因家族成员全基因组鉴定及分析. 作物学报, 2022, 48(3): 597-607. | |
| 22 | Chen D F, Wei X Q, Xu L, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of wax apple PG gene family. Journal of Fruit Science, 2022, 39(4): 16. |
| 陈迪飞, 魏秀清, 许玲, 等. 莲雾PG基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 果树学报, 2022, 39(4): 16. | |
| 23 | Dang Z, Zhang J P, Wang L M, et al. Breeding technology report on new flax variety Longya-15. Plant Fiber Sciences in China, 2020, 42(4): 145-149. |
| 党照, 张建平, 王利民, 等. 胡麻新品种陇亚15号选育技术报告.中国麻业科学, 2020, 42(4): 145-149. | |
| 24 | Lynch M, Conery J S. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science, 2000, 290(5494): 1151-1155. |
| 25 | Tang Y K, Jia Y Y. Method of processing real time PCR data. Biotechnology, 2008, 18(3): 89-91. |
| 唐永凯, 贾永义. 荧光定量PCR数据处理方法的探讨. 生物技术, 2008, 18(3): 89-91. | |
| 26 | Ren R, Wang H, Guo C, et al. Widespread whole genome duplications contribute to genome complexity and species diversity in angiosperms. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(3): 414-428. |
| 27 | Zhang L, Jian H J, Yang B, et al. Identification and expression analysis of sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) gene family members in Brassica napus. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(2): 197-207. |
| 张莉, 荐红举, 杨博, 等. 甘蓝型油菜蔗糖磷酸合酶(SPS)基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析. 作物学报, 2018, 44(2): 197-207. | |
| 28 | Soltis P S, Soltis D E. Ancient WGD events as drivers of key innovations in angiosperms. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2016, 30: 159-165. |
| 29 | Kelliher T, Starr D, Su X, et al. One-step genome editing of elite crop germplasm during haploid induction. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(3): 287-292. |
| 30 | Jacquier N M A, Gilles L M, Pyott D E, et al. Puzzling out plant reproduction by haploid induction for innovations in plant breeding. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(6): 610-619. |
| 31 | Gilles L M, Khaled A, Laffaire J B, et al. Loss of pollen-specific phospholipase not like dad triggers gynogenesis in maize. The EMBO Journal, 2017, 36(6): 707-717. |
| 32 | Kelliher T, Starr D, Richbourg L, et al. MATRILINEAL, a sperm-specific phospholipase, triggers maize haploid induction. Nature, 2017, 542(7639): 105-109. |
| 33 | Liu C X, Li X, Meng D X, et al. A 4-bp insertion at ZmPLA1 encoding a putative phospholipase a generates haploid induction in maize. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(3): 520-522. |
| 34 | Yao L, Zhang Y, Liu C, et al. OsMATL mutation induces haploid seed formation in indica rice. Nature Plants, 2018, 4(8): 530-533. |
| 35 | Liu H Y, Wang K, Jia Z M, et al. Efficient induction of haploid plants in wheat by editing of TaMTL using an optimized Agrobacterium-mediated CRISPR system. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(4): 1337-1349. |
| [1] | 姚佳明, 何悦, 郝欢欢, 黄心如, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草LpPIL5基因特征分析及转录调控[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 155-167. |
| [2] | 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| [3] | 高莉娟, 张正社, 文裕, 宗西方, 闫启, 卢丽燕, 易显凤, 张吉宇. 象草全基因组bHLH转录因子家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 47-59. |
| [4] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [5] | 罗维, 舒健虹, 刘晓霞, 王子苑, 牟琼, 王小利, 吴佳海. 高羊茅FaRVE8基因的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 60-69. |
| [6] | 杨婷, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 胡麻异质型ACCase亚基基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 111-120. |
| [7] | 夏曾润, 王文颖, 刘亚琪, 王锁民. 罗布麻K+通道编码基因AvAKT1的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 180-189. |
| [8] | 滕珂, 张蕊, 檀鹏辉, 岳跃森, 范希峰, 武菊英. 日本结缕草ZjERF1的克隆、转录激活活性、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 56-65. |
| [9] | 陆姗姗, 洪园淑, 刘萍. 苦豆子赖氨酸脱羧酶基因启动子在拟南芥中的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 159-167. |
| [10] | 李闻娟, 齐燕妮, 王利民, 党照, 赵利, 赵玮, 谢亚萍, 王斌, 张建平, 李淑洁. 不同胡麻品种TAG合成途径关键基因表达与含油量、脂肪酸组分的相关性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 138-149. |
| [11] | 贾俊婷, 赵品苍, 刘祝江, 袁光孝, 杨伟光, 刘书, 陈双燕, 李晓霞, 刘公社. 羊草LcMADS12基因的克隆及原核表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 64-72. |
| [12] | 董笛, 滕珂, 于安东, 檀鹏辉, 梁小红, 韩烈保. 沟叶结缕草八氢番茄红素基因ZmPSY的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 69-76. |
| [13] | 邵麟惠, 郑兴卫, 李聪. 蒺藜苜蓿E3泛素连接酶U-box基因克隆及表达分[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(7): 62-72. |
| [14] | 张胤冰, 孙鑫博, 樊波, 韩烈保, 张雪, 袁建波, 许立新. 结缕草ZjNAC基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 239-245. |
| [15] | 李小冬, 舒健虹, 于二汝, 吴佳海, 蔡一鸣, 王小利. 高羊茅在低氮胁迫下的蛋白组学分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 67-76. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||