

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 155-167.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021382
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-10-28
修回日期:2021-11-29
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
张敬
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: nauzj@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Jia-ming YAO( ), Yue HE, Huan-huan HAO, Xin-ru HUANG, Jing ZHANG(
), Yue HE, Huan-huan HAO, Xin-ru HUANG, Jing ZHANG( ), Bin XU
), Bin XU
Received:2021-10-28
Revised:2021-11-29
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Jing ZHANG
摘要:
光敏色素互作因子(PIFs)属于bHLH家族的一个亚家族,在植物光信号、激素信号传导和调控植物耐逆性等方面发挥重要作用。本研究从多年生黑麦草中克隆出一个PIF基因,其与拟南芥AtPIF5的亲缘关系最近,因此命名为LpPIL5-like(LpPIL5)。LpPIL5基因编码区序列(CDS)全长为1410 bp,具有5个外显子,编码470个氨基酸,具有典型的bHLH结构域和APB功能域,且其蛋白定位于细胞核。LpPIL5的启动子区域(1500 bp)具有ABRE、MBS和G-box等多种光、激素和逆境响应顺式作用元件。表达模式分析结果显示LpPIL5在叶片中表达量较高,而在根、茎、叶鞘等部位表达量较低。LpPIL5基因的表达受昼夜节律调控,且在光下的表达量显著高于黑暗。此外,聚乙二醇(PEG)、NaCl、CdCl2和高温逆境及6-苄基腺嘌呤(6-BA)和脱落酸(ABA)等激素处理显著抑制了叶片中LpPIL5基因表达,而在根中,LpPIL5基因的相对表达量在处理的12 h后明显增加,处理24 h时,显著高于对照。
姚佳明, 何悦, 郝欢欢, 黄心如, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草LpPIL5基因特征分析及转录调控[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 155-167.
Jia-ming YAO, Yue HE, Huan-huan HAO, Xin-ru HUANG, Jing ZHANG, Bin XU. Characterization and transcriptional regulation analysis of the LpPIL5 gene in perennial ryegrass[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 155-167.
| 引物名称Primer name | 上游引物序列Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| LpPIL5-CDS | CGCggatccATGAACCAATTCGTGCCT | CCCaagcttTCTCTTGTTCGGATGCG |
| LpPIL5-qPCR | CCGACTCGCTCGACAAGGAC | GGAAGACGTCCGACAGCTCG |
| LpeLF4A | AACTCAACTTGAAGTGTTGGAGTG | AGATCTGGTCCTGGAAAGAATATG |
表1 试验所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in the study
| 引物名称Primer name | 上游引物序列Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| LpPIL5-CDS | CGCggatccATGAACCAATTCGTGCCT | CCCaagcttTCTCTTGTTCGGATGCG |
| LpPIL5-qPCR | CCGACTCGCTCGACAAGGAC | GGAAGACGTCCGACAGCTCG |
| LpeLF4A | AACTCAACTTGAAGTGTTGGAGTG | AGATCTGGTCCTGGAAAGAATATG |
| 溶液名称Solution name | 成分Ingredient |
|---|---|
| 酶解液Enzyme solution | 10 mmol·L-1 MES,1.5%纤维素酶R10(Cellulase R10),0.75%离析酶R10(Macerozyme R10), 20 mmol·L-1 KCl,10 mmol·L-1 CaCl2,0.1% BSA,0.6 mol·L-1甘露醇Mannitol |
| W5 溶液W5 solution | 154 mmol·L-1 NaCl,125 mmol·L-1 CaCl2,5 mmol·L-1 KCl,2 mmol·L-1 MES |
| MMg溶液MMg solution | 0.4 mol·L-1甘露醇Mannitol,15 mmol·L-1 MgCl2,4 mmol·L-1 MES |
| PEG 4000溶液PEG 4000 solution | 20% PEG 4000,10 mmol·L-1 CaCl2,0.3 mol·L-1甘露醇Mannitol |
表2 提取并转化原生质体所用溶液
Table 2 The solution used to extract and transform protoplasts
| 溶液名称Solution name | 成分Ingredient |
|---|---|
| 酶解液Enzyme solution | 10 mmol·L-1 MES,1.5%纤维素酶R10(Cellulase R10),0.75%离析酶R10(Macerozyme R10), 20 mmol·L-1 KCl,10 mmol·L-1 CaCl2,0.1% BSA,0.6 mol·L-1甘露醇Mannitol |
| W5 溶液W5 solution | 154 mmol·L-1 NaCl,125 mmol·L-1 CaCl2,5 mmol·L-1 KCl,2 mmol·L-1 MES |
| MMg溶液MMg solution | 0.4 mol·L-1甘露醇Mannitol,15 mmol·L-1 MgCl2,4 mmol·L-1 MES |
| PEG 4000溶液PEG 4000 solution | 20% PEG 4000,10 mmol·L-1 CaCl2,0.3 mol·L-1甘露醇Mannitol |
图2 部分样品的mRNA(a)及LpPIL5基因(b)全长克隆的电泳图1~4、5~8、9~12、13~16和17~19分别为0、4、8、12和16 h叶片mRNA。1-4, 5-8, 9-12, 13-16 and 17-19 lanes are mRNA extracted from leaf samples at 0, 4, 8, 12 and 16 h of treatment, respectively.
Fig.2 Electrophoretogram of some samples’ mRNA (a) and full length of LpPIL5 gene (b)

图3 LpPIL5的基因结构(a)和氨基酸序列(b)分析a为LpPIL5基因结构,黑色为外显子,灰色为内含子;b为多年生黑麦草LpPIL5蛋白与大麦HvPIL1、二穗短柄草BdPIF1、小米SiPIL1、柳枝稷PvPIL13、高粱SbPIF1、玉米ZmPIL5以及水稻OsPIL13的蛋白对比。红色标记为APB功能域和碱性螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白具有的保守bHLH结构域。a: LpPIL5 gene structure, black is exon, gray is intron; b: Comparison of L. perenne LpPIL5 protein with H. vulgare HvPIL1, B. distachyon BdPIF1, S. italica SiPIL1, P. virgatum PvPIL13, S. bicolor SbPIF1, Z. mays ZmPIL5, and O. sativa OsPIL13. The APB motif and conserved bHLH domain of basic helix-loop-helix protein were marked in red.
Fig.3 Gene structure (a) and amino acid sequence (b) analysis of LpPIL5

图4 LpPIL5及其同源蛋白的系统进化树分析各基因的NCBI登录号为:大麦HvPIL1(KAE8800015.1)、二穗短柄草BdPIF1(XP_003559649.1)、小米SiPIL1(XP_004982351.1)、柳枝稷PvPIL13(XP_039830032.1)、高粱SbPIF1(XP_021306930)、玉米ZmPIL5(ACG28763.1)、水稻OsPIL13(XP_025880141.1)以及拟南芥PIFs家族蛋白AtPIF1(AT2G20180)、AtPIF3(AT1G09530)、AtPIF4(AT2G43010)、AtPIF5(AT3G59060)、AtPIF6(AT3G62090)、AtPIF7(AT5G61270)、AtPIF8(AT4G00050)和AtPIL1(AT2G46970)。NCBI accession numbers of each gene: H. vulgare HvPIL1 (KAE8800015.1), B. distachyon BdPIF1 (XP_003559649.1), S. italica SiPIL1 (XP_004982351.1), P. virgatum PvPIL13 (XP_039830032.1), S. bicolor SbPIF1 (XP_0213 06930), Z. mays ZmPIL5 (ACG28763.1), O. sativa OsPIL13 (XP_025880141.1) and A. thaliana PIFs family proteins, including AtPIF1 (AT2G20180), AtPIF3 (AT1G09530), AtPIF4 (AT2G43010), AtPIF5 (AT3G59060), AtPIF6 (AT3G62090), AtPIF7 (AT5G61270), AtPIF8 (AT4G00050) and AtPIL1 (AT2G46970).
Fig.4 Phylogenetic analysis of LpPIL5 and its homologous proteins
名称 Name | 序列 Sequence | 功能 Function | 个数Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-box | CCGTCC | 顺式调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element | 1 |
| ABRE | TACGGTC | 脱落酸响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | 2 |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | 2 |
| MBS | CAACTG | MYB结合位点参与干旱诱导MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | 1 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 茉莉酸甲酯顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the methyl jasmonate-responsiveness | 1 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸甲酯顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the methyl jasmonate-responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | CACGAC | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | TAACACGTAG | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | CACGTC | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | TACGTG | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| CAAT-box | CAAT | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 9 |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 6 |
| CAAT-box | CCAAT | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 5 |
| CAAT-box | TGCCAAC | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 1 |
| I-box | cCATATCCAAT | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| BoxⅡ | ACACGTAGA | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| TCCC-motif | TCTCCCT | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 2 |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 2 |
| TATA-box | ATATAT | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 1 |
| TATA-box | TATAA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 2 |
| TATA-box | TATAAAA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 2 |
| TATA-box | TATAAA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 2 |
| TATA-box | TATA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 3 |
表3 LpPIL5启动子顺式作用元件分析
Table 3 The analysis of cis-acting regulatory elements in the LpPIL5 promoter
名称 Name | 序列 Sequence | 功能 Function | 个数Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-box | CCGTCC | 顺式调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element | 1 |
| ABRE | TACGGTC | 脱落酸响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | 2 |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | 2 |
| MBS | CAACTG | MYB结合位点参与干旱诱导MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | 1 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 茉莉酸甲酯顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the methyl jasmonate-responsiveness | 1 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸甲酯顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in the methyl jasmonate-responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | CACGAC | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | TAACACGTAG | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | CACGTC | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| G-box | TACGTG | 光响应顺式作用元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| CAAT-box | CAAT | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 9 |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 6 |
| CAAT-box | CCAAT | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 5 |
| CAAT-box | TGCCAAC | 启动子和增强子区域的共同顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 1 |
| I-box | cCATATCCAAT | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| BoxⅡ | ACACGTAGA | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| TCCC-motif | TCTCCCT | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 2 |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 部分光响应元件Part of a light responsive element | 2 |
| TATA-box | ATATAT | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 1 |
| TATA-box | TATAA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 2 |
| TATA-box | TATAAAA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 2 |
| TATA-box | TATAAA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 2 |
| TATA-box | TATA | 转录开始的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | 3 |

图7 LpPIL5在不同组织(a)和光照条件(b)下的相对表达量不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05).
Fig.7 Relative expression of LpPIL5 gene in different tissues (a) and light or dark conditions (b)
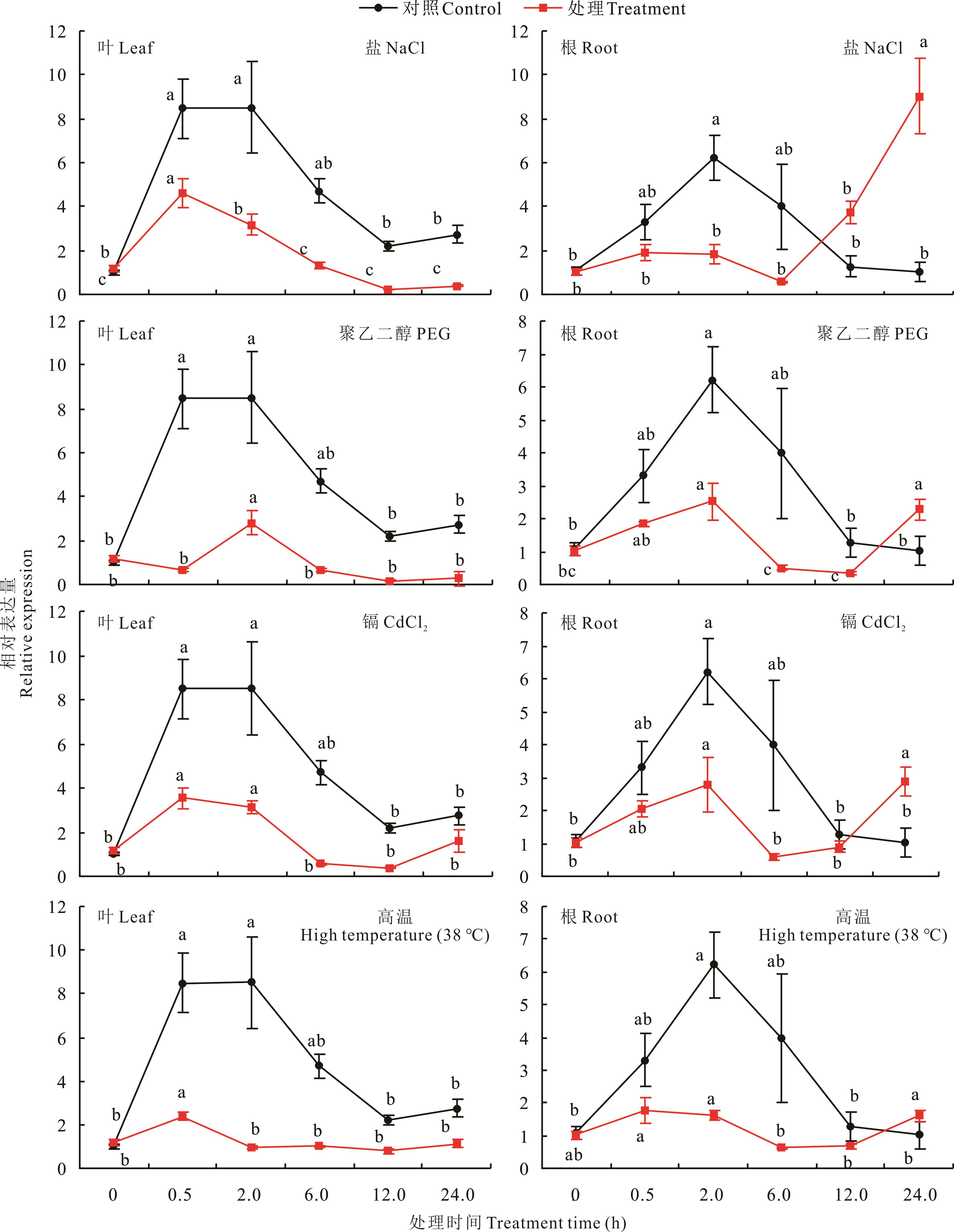
图8 4种非生物胁迫处理下多年生黑麦草叶片和根中LpPIL5的相对表达量不同小写字母表示相同处理不同处理时间之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatment time of the same treatment (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.8 The relative expression of LpPIL5 in leaves and roots in response to four different abiotic stresses
| 1 | Li H M, Lu X M, Gao Q H, et al. Effects of different light qualities on the growth, photosynthetic pigments and stomatal characteristics of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(6): 62-70. |
| 李慧敏, 陆晓民, 高清海, 等. 不同光质对黄秋葵幼苗生长、光合色素和气孔特征的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 62-70. | |
| 2 | Inoue K, Nishihama R, Kohchi T. Evolutionary origin of phytochrome responses and signaling in land plants. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2017, 40(11): 2502-2508. |
| 3 | Ulijasz A T, Cornilescu G, Cornilescu C C, et al. Structural basis for the photoconversion of a phytochrome to the activated Pfr form. Nature, 2010, 463(7278): 250-254. |
| 4 | Tong Z, Zhao Y J, Wang T, et al. Photoreceptors and light-regulated development in plants. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2000, 42(2): 111-115. |
| 童哲, 赵玉锦, 王台, 等. 植物的光受体和光控发育研究. 植物学报, 2000, 42(2): 111-115. | |
| 5 | Toledo-Ortiz G, Enamul H, Quail P H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. The Plant Cell, 2003, 15(8): 1749-1770. |
| 6 | Leivar P, Quail P H. PIFs: Pivotal components in a cellular signaling hub. Trends in Plant Science, 2011, 16(1): 19-28. |
| 7 | Huq E. PIF4, a phytochrome-interacting bHLH factor, functions as a negative regulator of phytochrome B signaling in Arabidopsis. The EMBO Journal, 2014, 21(10): 2441-2450. |
| 8 | Leivar P, Monte E, Al-Sady B, et al. The Arabidopsis phytochrome-interacting factor PIF7, together with PIF3 and PIF4, regulates responses to prolonged red light by modulating phyB levels. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(2): 337-352. |
| 9 | Lucas M D, Davière J M, Rodríguez-Falcón M, et al. A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature, 2008, 451(7177): 480-484. |
| 10 | Hornitschek P, Lorrain S, Zoete V, et al. Inhibition of the shade avoidance response by formation of non-DNA binding bHLH heterodimers. The EMBO Journal, 2009, 28(24): 3893-3902. |
| 11 | Martinez-Garcia J F, Huq E, Quail P H. Direct targeting of light signals to a promoter element-bound transcription factor. Science, 2000, 288(5467): 859-863. |
| 12 | Moon J, Zhu L, Shen H, et al. PIF1 directly and indirectly regulates chlorophyll biosynthesis to optimize the greening process in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2008, 105(27): 9433-9438. |
| 13 | Oh E, Kang H, Yamaguchi S, et al. Genome-wide analysis of genes targeted by phytochrome interacting factor 3-like 5 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2009, 21(2): 403-419. |
| 14 | Shin J, Park E, Choi G. PIF3 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in an HY5-dependent manner with both factors directly binding anthocyanin biosynthetic gene promoters in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 2007, 49(6): 981-994. |
| 15 | Schfer E, Nagy F. Photomorphogenesis in plants and bacteria. The Netherlands: Springer, 2006. |
| 16 | Alabadi B. Molecular interactions between light and hormone signaling to control plant growth. Plant Molecular Biology, 2009, 69(4): 409-417. |
| 17 | Paik I, Kathare P K, Kim J I, et al. Expanding roles of PIFs in signal integration from multiple processes. Molecular Plant, 2017, 8(10): 1035-1046. |
| 18 | Lee N, Choi G. Phytochrome-interacting factor from Arabidopsis to liverwort. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2017, 35:54-60. |
| 19 | Koini M A, Alvey L, Allen T, et al. High temperature-mediated adaptations in plant architecture require the bHLH transcription factor PIF4. Current Biology, 2009, 19(5): 408-413. |
| 20 | Stavang J A, Gallego-Bartolomé J, Gómez M D, et al. Hormonal regulation of temperature-induced growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 2010, 60(4): 589-601. |
| 21 | Al-Sady B, Kikis E A, Monte E, et al. Mechanistic duality of transcription factor function in phytochrome signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, 2008, 105(6): 2232-2237. |
| 22 | Sibbett B. The role of phytochrome-interacting factor 3 in regulating growth and development in hexaploid wheat. Southampton: University of Southampton, 2018. |
| 23 | Yong G, Wu M, Zhang M, et al. Roles of a maize phytochrome-interacting factors protein ZmPIF3 in regulation of drought stress responses by controlling stomatal closure in transgenic rice without yield penalty. Plant Molecular Biology, 2018, 97(4/5): 311-323. |
| 24 | Kudo M, Kidokoro S, Yoshida T, et al. Double overexpression of DREB and PIF transcription factors improves drought stress tolerance and cell elongation in transgenic plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(4): 458-471. |
| 25 | Zhang Y Q, Liu Z J, Chen Y D, et al. Phytochrome interacting factor 5 (PIF5) positively regulates dark-induced senescence and chlorophyll degradation in Arabidopsis. Plant Science, 2015, 237: 57-68. |
| 26 | Khanna R, Shen Y, Marion C M, et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor PIF5 acts on ethylene biosynthesis and phytochrome signaling by distinct mechanisms. The Plant Cell, 2007, 19(12): 3915-3929. |
| 27 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods, 2002, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 28 | Huang L, Yan H, Jiang X, et al. Identification of candidate reference genes in perennial ryegrass for quantitative RT-PCR under various abiotic stress conditions. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e93724. |
| 29 | Yu G, Cheng Q, Xie Z, et al. An efficient protocol for perennial ryegrass mesophyll protoplast isolation and transformation, and its application on interaction study between LpNOL and LpNYC1. Plant Methods, 2017, 13(1): 46. |
| 30 | Paik I, Huq E. Rapid examination of phytochrome-phytochrome interacting factor (PIF) interaction by in vitro coimmunoprecipitation assay. New York: Humana, 2019. |
| 31 | Nakamura Y, Kato T, Yamashino T, et al. Characterization of a set of phytochrome-interacting factor-like bHLH proteins in Oryza sativa. Journal of the Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan, 2007, 71(5): 1183-1191. |
| 32 | Rosado D, Gramegna G, Cruz A, et al. Phytochrome interacting factors (PIFs) in Solanum lycopersicum: Diversity, evolutionary history and expression profiling during different developmental processes. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0165929. |
| 33 | Pham V N, Kathare P K, Huq E. Phytochromes and phytochrome interacting factors. Plant Physiology, 2018, 176: 1025-1038. |
| 34 | Possart A, Xu T, Paik I, et al. Characterization of phytochrome interacting factors from the moss Physcomitrella patens illustrates conservation of phytochrome signaling modules in land plants. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(2): 310-330. |
| 35 | Gao Y, Ren X, Qian J, et al. The phytochrome-interacting family of transcription factors in maize (Zea mays L.): Identification, evolution, and expression analysis. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2019, 41(1): 1-7. |
| 36 | Wu G, Zhao Y, Shen R, et al. Characterization of maize phytochrome-interacting factors in light signaling and photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiology, 2019, 181(2): 789-803. |
| 37 | Yu H, Tepperman J M, Fairchild C D, et al. Phytochrome B binds with greater apparent affinity than phytochrome A to the basic helix-loop-helix factor PIF3 in a reaction requiring the PAS domain of PIF3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2000, 97(24): 13419-13424. |
| 38 | Ni M, Tepperman J M, Quail P H. PIF3, a phytochrome-interacting factor necessary for normal photoinduced signal transduction, is a novel basic helix-loop-helix protein. Cell, 1998, 95(5): 657-667. |
| 39 | Halliday K J, Hudson M, Min N, et al. Poc1: An Arabidopsis mutant perturbed in phytochrome signaling because of a T-DNA insertion in the promoter of PIF3, a gene encoding a phytochrome-interacting bHLH protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1999, 96(10): 5832-5837. |
| 40 | Wang X, Liu Y, Huai D, et al. Genome-wide identification of peanut PIF family genes and their potential roles in early pod development. Gene, 2021, 781(4): 145539. |
| 41 | Zhang K, Zheng T, Zhu X, et al. Genome-wide identification of PIFs in grapes (Vitis vinifera L.) and their transcriptional analysis under lighting/shading conditions. Genes, 2018, 9(9): 451. |
| 42 | Park E, Kim J, Lee Y, et al. Degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3 in phytochrome-mediated light signaling. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2004, 45(8): 968-975. |
| 43 | Kao C Y, Cocciolone S M, Vasil K, et al. Localization and interaction of the cis-acting elements for abscisic acid, viviparous1, and light activation of the c1 gene of maize. The Plant Cell, 1996, 8(7): 1171-1179. |
| 44 | Gao C, Sun J, Wang C, et al. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix gene family in peanut and assessment of its roles in pod development. PLoS One, 2017, 12(7): e0181843. |
| [1] | 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| [2] | 张晴, 邢静, 姚佳明, 殷庭超, 黄心如, 何悦, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草细胞分裂素信号通路B类ARR转录因子LpARR10的耐镉功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [3] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 黄书超, 杨琰珊, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 张银翠. 微生物肥料与化肥减量配施对多年生黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [4] | 高莉娟, 张正社, 文裕, 宗西方, 闫启, 卢丽燕, 易显凤, 张吉宇. 象草全基因组bHLH转录因子家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 47-59. |
| [5] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [6] | 赵利清, 彭向永, 刘俊祥, 毛金梅, 孙振元. GSH对铅胁迫下多年生黑麦草生长及光合生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 97-104. |
| [7] | 罗维, 舒健虹, 刘晓霞, 王子苑, 牟琼, 王小利, 吴佳海. 高羊茅FaRVE8基因的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 60-69. |
| [8] | 周瀚洋, 孙鹏越, 尉欣荣, 周雨, 张智伟, 高金柱, 赵东豪, 罗艺岚, 呼天明, 付娟娟. 琥珀酸黄杆菌缓解遮阴对多年生黑麦草胁迫的效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 137-143. |
| [9] | 杨婷, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 胡麻异质型ACCase亚基基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 111-120. |
| [10] | 魏勇, 王晓瑜, 李应德, 段廷玉. AM真菌在白三叶-黑麦草体系中对抗逆信号的传导作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 138-146. |
| [11] | 马碧花, 蔺伟虎, 高敏, 王兴迪, 田沛. 干旱胁迫下水杨酸和内生真菌对多年生黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 135-144. |
| [12] | 夏曾润, 王文颖, 刘亚琪, 王锁民. 罗布麻K+通道编码基因AvAKT1的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 180-189. |
| [13] | 滕珂, 张蕊, 檀鹏辉, 岳跃森, 范希峰, 武菊英. 日本结缕草ZjERF1的克隆、转录激活活性、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 56-65. |
| [14] | 王日明, 王志强, 向佐湘. γ-氨基丁酸对高温胁迫下黑麦草光合特性及碳水化合物代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 168-178. |
| [15] | 陆姗姗, 洪园淑, 刘萍. 苦豆子赖氨酸脱羧酶基因启动子在拟南芥中的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 159-167. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||