

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 67-79.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022132
李春艳1,2( ), 王艳2(
), 王艳2( ), 李欣瑞1,3(
), 李欣瑞1,3( ), 李英主1, 李明峰1,2, 陈丽丽1, 雷雄1, 闫利军1, 游明鸿1, 季晓菲1, 张昌兵1, 吴婍1, 苟文龙1, 李达旭1(
), 李英主1, 李明峰1,2, 陈丽丽1, 雷雄1, 闫利军1, 游明鸿1, 季晓菲1, 张昌兵1, 吴婍1, 苟文龙1, 李达旭1( ), 鄢家俊1(
), 鄢家俊1( ), 白史且1(
), 白史且1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-25
修回日期:2022-05-30
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2022-12-30
通讯作者:
李达旭,鄢家俊,白史且
作者简介:E-mail: baishiqie@126.com基金资助:
Chun-yan LI1,2( ), Yan WANG2(
), Yan WANG2( ), Xin-rui LI1,3(
), Xin-rui LI1,3( ), Ying-zhu LI1, Ming-feng LI1,2, Li-li CHEN1, Xiong LEI1, Li-jun YAN1, Ming-hong YOU1, Xiao-fei JI1, Chang-bing ZHANG1, Qi WU1, Wen-long GOU1, Da-xu LI1(
), Ying-zhu LI1, Ming-feng LI1,2, Li-li CHEN1, Xiong LEI1, Li-jun YAN1, Ming-hong YOU1, Xiao-fei JI1, Chang-bing ZHANG1, Qi WU1, Wen-long GOU1, Da-xu LI1( ), Jia-jun YAN1(
), Jia-jun YAN1( ), Shi-qie BAI1(
), Shi-qie BAI1( )
)
Received:2022-03-25
Revised:2022-05-30
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2022-12-30
Contact:
Da-xu LI,Jia-jun YAN,Shi-qie BAI
摘要:
为揭示野生老芒麦形态变异特征和遗传背景,对我国野生老芒麦主要分布区域不同生态类型的104个居群520份野生老芒麦种质进行了23个形态指标测定和遗传多样性分析。结果表明:不同生境老芒麦材料的形态特征存在显著差异,数量性状变异系数为9.49%~49.56%;聚类分析将104个居群分为具有各自明显特征和开发利用潜力的4类;形态特征与地理环境因子的相关性分析发现,野生老芒麦抽穗早晚及茎秆叶鞘基部小刺等特殊性状与其海拔呈显著相关;主成分分析发现,株高、抽穗、茎节数、单株干鲜重、旗叶长宽等指标代表了老芒麦67.79%形态多样性,是造成老芒麦形态特征变异的主要因素,可作为老芒麦形态分化的重要参考指标。
李春艳, 王艳, 李欣瑞, 李英主, 李明峰, 陈丽丽, 雷雄, 闫利军, 游明鸿, 季晓菲, 张昌兵, 吴婍, 苟文龙, 李达旭, 鄢家俊, 白史且. 中国野生老芒麦形态多样性研究与种质利用潜力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 67-79.
Chun-yan LI, Yan WANG, Xin-rui LI, Ying-zhu LI, Ming-feng LI, Li-li CHEN, Xiong LEI, Li-jun YAN, Ming-hong YOU, Xiao-fei JI, Chang-bing ZHANG, Qi WU, Wen-long GOU, Da-xu LI, Jia-jun YAN, Shi-qie BAI. Morphological diversity and germplasm utilization potential of wild Elymus sibiricus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 67-79.
性状 Traits | 最大值 Maximum | 最小值 Minimum | 均值 Mean | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation(%) | 香农-维纳多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 124.0 | 8.9 | 69.4 | 29.4 | 42.31 | 1.907 |
| 旗叶长Flag leaf length (cm) | 24.5 | 9.8 | 18.2 | 2.8 | 15.35 | 2.079 |
| 旗叶宽Flag leaf width (cm) | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 14.67 | 2.029 |
| 倒二叶长Penultimate leaf length (cm) | 27.0 | 12.3 | 20.4 | 2.5 | 12.19 | 1.966 |
| 倒二叶宽Penultimate leaf width (cm) | 1.5 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 16.84 | 2.014 |
| 分蘖数Number of tillers | 628.4 | 129.5 | 310.0 | 106.2 | 34.25 | 1.971 |
| 茎节数Number of stem nodes | 5.0 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 31.41 | 1.811 |
| 单株穗数Panicle number per hill | 264.2 | 19.0 | 132.2 | 65.5 | 49.56 | 1.924 |
| 穗长Panicle length (cm) | 30.1 | 16.2 | 25.5 | 2.4 | 9.49 | 1.807 |
| 穗宽Panicle width (cm) | 2.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 3.9 | 31.78 | 1.807 |
| 小穗数Panicle number | 72.0 | 29.8 | 56.1 | 8.6 | 15.27 | 2.035 |
| 芒长Awn length (mm) | 23.6 | 10.8 | 15.5 | 2.3 | 14.98 | 1.893 |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 4.6 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 0.3 | 9.77 | 2.039 |
| 单株干重Single plant dry weight (g) | 943.3 | 89.3 | 427.8 | 184.8 | 43.21 | 2.038 |
| 单株鲜重Single plant fresh weight (g) | 446.7 | 35.9 | 210.2 | 101.5 | 48.28 | 2.084 |
| 植株被粉Leaves with powder | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 53.52 | 1.421 |
| 锈病Rust disease | 2.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 33.10 | 1.828 |
| 叶片被毛Leaves with tomentum | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 76.14 | 1.870 |
| 叶色Leaf color | 3.6 | 1.0 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 20.00 | 1.895 |
| 茎秆叶鞘小刺Stem leaf sheaths small spines | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 36.35 | 0.450 |
| 穗色Panicle color | 4.8 | 0.6 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 34.53 | 1.800 |
| 茎秆基部叶鞘有无绒毛Leaf sheaths at the base of the stalk with or without tomentum | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 97.44 | 1.626 |
| 抽穗Heading | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 51.90 | 0.516 |
| 总计Total | 1.774 |
表1 供试老芒麦23个形态性状变异分析
Table 1 Variation analys is of 23 morphological characteristics of E. sibiricus germplasm
性状 Traits | 最大值 Maximum | 最小值 Minimum | 均值 Mean | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation(%) | 香农-维纳多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 124.0 | 8.9 | 69.4 | 29.4 | 42.31 | 1.907 |
| 旗叶长Flag leaf length (cm) | 24.5 | 9.8 | 18.2 | 2.8 | 15.35 | 2.079 |
| 旗叶宽Flag leaf width (cm) | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 14.67 | 2.029 |
| 倒二叶长Penultimate leaf length (cm) | 27.0 | 12.3 | 20.4 | 2.5 | 12.19 | 1.966 |
| 倒二叶宽Penultimate leaf width (cm) | 1.5 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 16.84 | 2.014 |
| 分蘖数Number of tillers | 628.4 | 129.5 | 310.0 | 106.2 | 34.25 | 1.971 |
| 茎节数Number of stem nodes | 5.0 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 31.41 | 1.811 |
| 单株穗数Panicle number per hill | 264.2 | 19.0 | 132.2 | 65.5 | 49.56 | 1.924 |
| 穗长Panicle length (cm) | 30.1 | 16.2 | 25.5 | 2.4 | 9.49 | 1.807 |
| 穗宽Panicle width (cm) | 2.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 3.9 | 31.78 | 1.807 |
| 小穗数Panicle number | 72.0 | 29.8 | 56.1 | 8.6 | 15.27 | 2.035 |
| 芒长Awn length (mm) | 23.6 | 10.8 | 15.5 | 2.3 | 14.98 | 1.893 |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 4.6 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 0.3 | 9.77 | 2.039 |
| 单株干重Single plant dry weight (g) | 943.3 | 89.3 | 427.8 | 184.8 | 43.21 | 2.038 |
| 单株鲜重Single plant fresh weight (g) | 446.7 | 35.9 | 210.2 | 101.5 | 48.28 | 2.084 |
| 植株被粉Leaves with powder | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 53.52 | 1.421 |
| 锈病Rust disease | 2.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 33.10 | 1.828 |
| 叶片被毛Leaves with tomentum | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 76.14 | 1.870 |
| 叶色Leaf color | 3.6 | 1.0 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 20.00 | 1.895 |
| 茎秆叶鞘小刺Stem leaf sheaths small spines | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 36.35 | 0.450 |
| 穗色Panicle color | 4.8 | 0.6 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 34.53 | 1.800 |
| 茎秆基部叶鞘有无绒毛Leaf sheaths at the base of the stalk with or without tomentum | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 97.44 | 1.626 |
| 抽穗Heading | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 51.90 | 0.516 |
| 总计Total | 1.774 |
区域 Area | 香农-维纳多样性指数Shannon wiener diversity index (H) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | X17 | X18 | X19 | X20 | X21 | X22 | X23 | * | |
| 东北地区Northeast China | 1.311 | 1.294 | 1.096 | 1.030 | 1.162 | 1.166 | 0.694 | 1.117 | 1.107 | 1.166 | 1.339 | 1.079 | 0.638 | 1.013 | 1.100 | 0.050 | 0.373 | 0.753 | 0.385 | 0.000 | 0.733 | 0.000 | 0.285 | 0.821 |
| 华北地区Northern China | 1.305 | 1.236 | 1.077 | 1.031 | 1.022 | 1.225 | 0.597 | 1.168 | 1.145 | 1.293 | 1.450 | 1.134 | 0.708 | 0.976 | 1.008 | 0.208 | 0.415 | 0.547 | 0.459 | 0.083 | 0.652 | 0.052 | 0.292 | 0.830 |
| 西北地区Northwest China | 1.277 | 1.244 | 1.059 | 1.069 | 1.025 | 1.219 | 0.561 | 1.118 | 1.120 | 1.189 | 1.312 | 1.041 | 0.706 | 1.044 | 1.078 | 0.110 | 0.309 | 0.643 | 0.421 | 0.007 | 0.691 | 0.006 | 0.285 | 0.806 |
| 青藏高原地区Qinghai-Tibetan plateau area | 1.313 | 1.219 | 1.072 | 1.002 | 1.039 | 1.220 | 0.576 | 1.182 | 1.181 | 1.319 | 1.413 | 1.135 | 0.709 | 1.043 | 1.078 | 0.150 | 0.360 | 0.669 | 0.471 | 0.052 | 0.758 | 0.059 | 0.315 | 0.841 |
| 总计Total | 0.824 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
表2 老芒麦各居群23个表型性状遗传多样性指数
Table 2 Genetic diversity index of 23 phenotypic traits in E. sibiricus populations
区域 Area | 香农-维纳多样性指数Shannon wiener diversity index (H) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | X17 | X18 | X19 | X20 | X21 | X22 | X23 | * | |
| 东北地区Northeast China | 1.311 | 1.294 | 1.096 | 1.030 | 1.162 | 1.166 | 0.694 | 1.117 | 1.107 | 1.166 | 1.339 | 1.079 | 0.638 | 1.013 | 1.100 | 0.050 | 0.373 | 0.753 | 0.385 | 0.000 | 0.733 | 0.000 | 0.285 | 0.821 |
| 华北地区Northern China | 1.305 | 1.236 | 1.077 | 1.031 | 1.022 | 1.225 | 0.597 | 1.168 | 1.145 | 1.293 | 1.450 | 1.134 | 0.708 | 0.976 | 1.008 | 0.208 | 0.415 | 0.547 | 0.459 | 0.083 | 0.652 | 0.052 | 0.292 | 0.830 |
| 西北地区Northwest China | 1.277 | 1.244 | 1.059 | 1.069 | 1.025 | 1.219 | 0.561 | 1.118 | 1.120 | 1.189 | 1.312 | 1.041 | 0.706 | 1.044 | 1.078 | 0.110 | 0.309 | 0.643 | 0.421 | 0.007 | 0.691 | 0.006 | 0.285 | 0.806 |
| 青藏高原地区Qinghai-Tibetan plateau area | 1.313 | 1.219 | 1.072 | 1.002 | 1.039 | 1.220 | 0.576 | 1.182 | 1.181 | 1.319 | 1.413 | 1.135 | 0.709 | 1.043 | 1.078 | 0.150 | 0.360 | 0.669 | 0.471 | 0.052 | 0.758 | 0.059 | 0.315 | 0.841 |
| 总计Total | 0.824 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
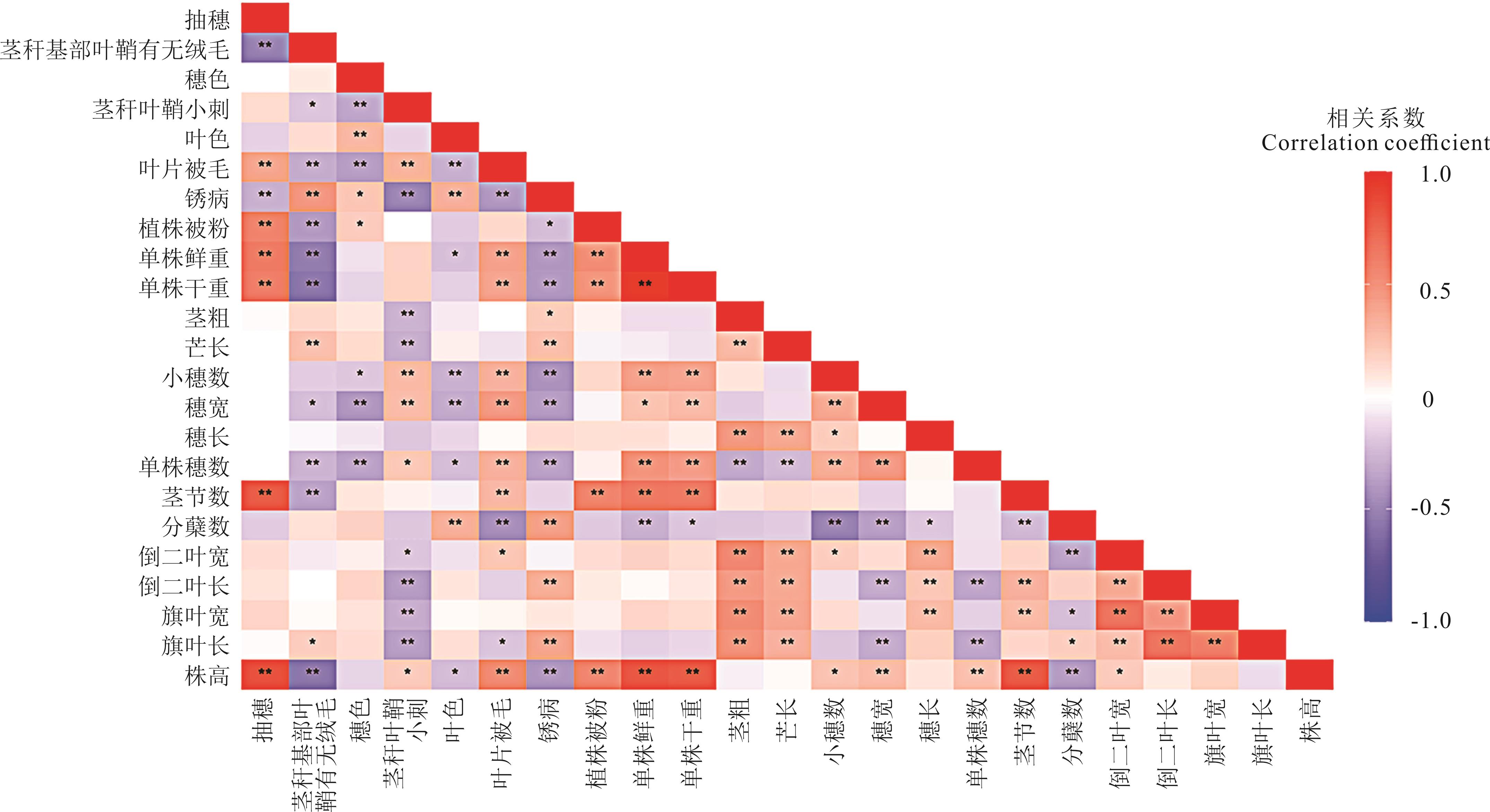
图2 520份老芒麦种质资源表型性状相关性分析矩阵图*:表示老芒麦不同表型性状之间存在显著差异(P<0.05),**:表示老芒麦不同表型性状之间存在极显著差异(P<0.01)。*: Indicates significant differences between phenotypic traits in E. sibiricus (P<0.05), **: Indicates highly significant differences between phenotypic traits in E. sibiricus (P<0.01).株高:Plant height;旗叶长:Flag leaf length;旗叶宽:Flag leaf width;倒二叶长:Penultimate leaf length;倒二叶宽:Penultimate leaf width;分蘖数:Number of tillers;茎节数:Number of stem nodes;单株穗数:Panicle number per hill;穗长:Panicle length;穗宽:Panicle width;小穗数:Panicle number;芒长:Awn length;茎粗:Stem diameter;单株干重:Single plant dry weight;单株鲜重:Single plant fresh weight;植株被粉:Leaves with powder;锈病:Rust disease;叶片被毛:Leaves with tomentum;叶色:Leaf color;茎秆叶鞘小刺:Stem leaf sheaths small spines;穗色:Panicle color;茎秆基部叶鞘有无绒毛:Leaf sheaths at the base of the stalk with or without tomentum;抽穗:Heading.下同The same below.
Fig.2 Matrix of correlation analysis of phenotypic traits in 520 E. sibiricus germplasm resources

图3 老芒麦23个表型性状与地理因子的相关性分析矩阵图*:表示老芒麦表型性状与地理因子呈显著差异(P<0.05),**:表示老芒麦表型性状与地理因子呈极显著差异(P<0.01)。*: Indicates significant differences between phenotypic traits and geographical factors in E. sibiricus (P<0.05), **: Indicates a highly significant difference between phenotypic traits and geographical factors in E. sibiricus (P<0.01).
Fig.3 Matrix of correlation analysis of 23 phenotypic traits of E. sibiricus with geographical factors
抽穗特性 Heading characteristics | 编号 No. | 居群名称 Population name | 来源地 Source | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 编号 No. | 居群名称 Population name | 来源地 Source | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
抽穗期早 Early heading stage | 1 | SAG-GS18001 | 甘肃Gansu | 2550 | 18 | SAG-SC18012 | 四川Sichuan | 3571 |
| 2 | SAG-GS18002 | 甘肃Gansu | 2550 | 19 | SAG-SC18013 | 四川Sichuan | 3261 | |
| 3 | SAG-GS18003 | 甘肃Gansu | 2770 | 20 | SAG-SC18015 | 四川Sichuan | 3061 | |
| 4 | SAG-GS18011 | 甘肃Gansu | 3010 | 21 | SAG-XJ18001 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2376 | |
| 5 | SAG-GS18012 | 甘肃Gansu | 3380 | 22 | SAG-XJ18002 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2237 | |
| 6 | SAG-QH18003 | 青海Qinghai | 3640 | 23 | SAG-XJ18003 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2038 | |
| 7 | SAG-QH18015 | 青海Qinghai | 3310 | 24 | SAG-XJ18016 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1171 | |
| 8 | SAG-QH18016 | 青海Qinghai | 3270 | 25 | SAG-XJ18025 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1465 | |
| 9 | SAG-SC18002 | 四川Sichuan | 3343 | 26 | SAG-XJ18026 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1417 | |
| 10 | SAG-SC18003 | 四川Sichuan | 3325 | 27 | SAG-XZ18002 | 西藏Xizang | 3909 | |
| 11 | SAG-SC18004 | 四川Sichuan | 3335 | 28 | SAG-XZ18004 | 西藏Xizang | 4118 | |
| 12 | SAG-SC18006 | 四川Sichuan | 2951 | 29 | SAG-XZ18005 | 西藏Xizang | 3969 | |
| 13 | SAG-SC18007 | 四川Sichuan | 3224 | 30 | SAG-XZ18006 | 西藏Xizang | 3646 | |
| 14 | SAG-SC18008 | 四川Sichuan | 2831 | 31 | SAG-XZ18007 | 西藏Xizang | 4025 | |
| 15 | SAG-SC18009 | 四川Sichuan | 2816 | 32 | SAG-XZ18014 | 西藏Xizang | 3786 | |
| 16 | SAG-SC18010 | 四川Sichuan | 2677 | 33 | SAG-XZ18015 | 西藏Xizang | 3340 | |
| 17 | SAG-SC18011 | 四川Sichuan | 2792 | 34 | SAG-XZ18018 | 西藏Xizang | 3736 | |
抽穗期晚 Late heading stage | 1 | SAG-HB18001 | 河北Hebei | 1394 | 25 | SAG-NM18035 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1340 |
| 2 | SAG-HB18002 | 河北Hebei | 1427 | 26 | SAG-NM18038 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1306 | |
| 3 | SAG-HB18003 | 河北Hebei | 1369 | 27 | SAG-NM18041 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1277 | |
| 4 | SAG-HB18004 | 河北Hebei | 1371 | 28 | SAG-NM18042 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1515 | |
| 5 | SAG-HB18005 | 河北Hebei | 1413 | 29 | SAG-NM18043 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1683 | |
| 6 | SAG-HB18006 | 河北Hebei | 1434 | 30 | SAG-NM18046 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1677 | |
| 7 | SAG-HB18007 | 河北Hebei | 1494 | 31 | SAG-NM18050 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1214 | |
| 8 | SAG-HB18008 | 河北Hebei | 1490 | 32 | SAG-XJ18004 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1877 | |
| 9 | SAG-HB18009 | 河北Hebei | 1479 | 33 | SAG-XJ18005 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1837 | |
| 10 | SAG-HB18010 | 河北Hebei | 1487 | 34 | SAG-XJ18007 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1841 | |
| 11 | SAG-HB18011 | 河北Hebei | 1633 | 35 | SAG-XJ18010 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1169 | |
| 12 | SAG-HB18012 | 河北Hebei | 1671 | 36 | SAG-XJ18012 | 新疆Xinjiang | 130 | |
| 13 | SAG-HB18013 | 河北Hebei | 1673 | 37 | SAG-XJ18013 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1056 | |
| 14 | SAG-NM18001 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 583 | 38 | SAG-XJ18015 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1169 | |
| 15 | SAG-NM18004 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 745 | 39 | SAG-XJ18017 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1191 | |
| 16 | SAG-NM18006 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 468 | 40 | SAG-XJ18018 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1435 | |
| 17 | SAG-NM18017 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 800 | 41 | SAG-XJ18021 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1449 | |
| 18 | SAG-NM18021 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 839 | 42 | SAG-XJ18022 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1432 | |
| 19 | SAG-NM18027 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1238 | 43 | SAG-XJ18023 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1530 | |
| 20 | SAG-NM18030 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 963 | 44 | SAG-XJ18024 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1421 | |
| 21 | SAG-NM18031 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1140 | 45 | SAG-XJ18027 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1689 | |
| 22 | SAG-NM18032 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1302 | 46 | SAG-XJ18028 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1725 | |
| 23 | SAG-NM18033 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1085 | 47 | SAG-XJ18029 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1921 | |
| 24 | SAG-NM18034 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1407 | 48 | SAG-XJ18030 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2039 | |
| 不抽穗No heading | 1 | SAG-NM18003 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 684 | 12 | SAG-NM18022 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 827 |
| 2 | SAG-NM18005 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 746 | 13 | SAG-NM18023 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 818 | |
| 3 | SAG-NM18007 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 300 | 14 | SAG-NM18024 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 817 | |
| 4 | SAG-NM18008 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 272 | 15 | SAG-NM18025 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 880 | |
| 5 | SAG-NM18009 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 189 | 16 | SAG-NM18026 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1088 | |
| 6 | SAG-NM18010 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 229 | 17 | SAG-NM18028 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 548 | |
| 7 | SAG-NM18014 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 789 | 18 | SAG-NM18029 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1112 | |
| 8 | SAG-NM18015 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 988 | 19 | SAG-NM18040 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1155 | |
| 9 | SAG-NM18016 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 812 | 20 | SAG-NM18044 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1750 | |
| 10 | SAG-NM18018 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 714 | 21 | SAG-NM18045 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1509 | |
| 11 | SAG-NM18019 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 668 | 22 | SAG-XJ18011 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1139 |
表3 不同抽穗特性的野生老芒麦原生地海拔信息
Table 3 Altitude information of wild E. sibiricus native sites with different heading characteristics
抽穗特性 Heading characteristics | 编号 No. | 居群名称 Population name | 来源地 Source | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 编号 No. | 居群名称 Population name | 来源地 Source | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
抽穗期早 Early heading stage | 1 | SAG-GS18001 | 甘肃Gansu | 2550 | 18 | SAG-SC18012 | 四川Sichuan | 3571 |
| 2 | SAG-GS18002 | 甘肃Gansu | 2550 | 19 | SAG-SC18013 | 四川Sichuan | 3261 | |
| 3 | SAG-GS18003 | 甘肃Gansu | 2770 | 20 | SAG-SC18015 | 四川Sichuan | 3061 | |
| 4 | SAG-GS18011 | 甘肃Gansu | 3010 | 21 | SAG-XJ18001 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2376 | |
| 5 | SAG-GS18012 | 甘肃Gansu | 3380 | 22 | SAG-XJ18002 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2237 | |
| 6 | SAG-QH18003 | 青海Qinghai | 3640 | 23 | SAG-XJ18003 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2038 | |
| 7 | SAG-QH18015 | 青海Qinghai | 3310 | 24 | SAG-XJ18016 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1171 | |
| 8 | SAG-QH18016 | 青海Qinghai | 3270 | 25 | SAG-XJ18025 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1465 | |
| 9 | SAG-SC18002 | 四川Sichuan | 3343 | 26 | SAG-XJ18026 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1417 | |
| 10 | SAG-SC18003 | 四川Sichuan | 3325 | 27 | SAG-XZ18002 | 西藏Xizang | 3909 | |
| 11 | SAG-SC18004 | 四川Sichuan | 3335 | 28 | SAG-XZ18004 | 西藏Xizang | 4118 | |
| 12 | SAG-SC18006 | 四川Sichuan | 2951 | 29 | SAG-XZ18005 | 西藏Xizang | 3969 | |
| 13 | SAG-SC18007 | 四川Sichuan | 3224 | 30 | SAG-XZ18006 | 西藏Xizang | 3646 | |
| 14 | SAG-SC18008 | 四川Sichuan | 2831 | 31 | SAG-XZ18007 | 西藏Xizang | 4025 | |
| 15 | SAG-SC18009 | 四川Sichuan | 2816 | 32 | SAG-XZ18014 | 西藏Xizang | 3786 | |
| 16 | SAG-SC18010 | 四川Sichuan | 2677 | 33 | SAG-XZ18015 | 西藏Xizang | 3340 | |
| 17 | SAG-SC18011 | 四川Sichuan | 2792 | 34 | SAG-XZ18018 | 西藏Xizang | 3736 | |
抽穗期晚 Late heading stage | 1 | SAG-HB18001 | 河北Hebei | 1394 | 25 | SAG-NM18035 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1340 |
| 2 | SAG-HB18002 | 河北Hebei | 1427 | 26 | SAG-NM18038 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1306 | |
| 3 | SAG-HB18003 | 河北Hebei | 1369 | 27 | SAG-NM18041 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1277 | |
| 4 | SAG-HB18004 | 河北Hebei | 1371 | 28 | SAG-NM18042 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1515 | |
| 5 | SAG-HB18005 | 河北Hebei | 1413 | 29 | SAG-NM18043 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1683 | |
| 6 | SAG-HB18006 | 河北Hebei | 1434 | 30 | SAG-NM18046 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1677 | |
| 7 | SAG-HB18007 | 河北Hebei | 1494 | 31 | SAG-NM18050 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1214 | |
| 8 | SAG-HB18008 | 河北Hebei | 1490 | 32 | SAG-XJ18004 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1877 | |
| 9 | SAG-HB18009 | 河北Hebei | 1479 | 33 | SAG-XJ18005 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1837 | |
| 10 | SAG-HB18010 | 河北Hebei | 1487 | 34 | SAG-XJ18007 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1841 | |
| 11 | SAG-HB18011 | 河北Hebei | 1633 | 35 | SAG-XJ18010 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1169 | |
| 12 | SAG-HB18012 | 河北Hebei | 1671 | 36 | SAG-XJ18012 | 新疆Xinjiang | 130 | |
| 13 | SAG-HB18013 | 河北Hebei | 1673 | 37 | SAG-XJ18013 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1056 | |
| 14 | SAG-NM18001 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 583 | 38 | SAG-XJ18015 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1169 | |
| 15 | SAG-NM18004 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 745 | 39 | SAG-XJ18017 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1191 | |
| 16 | SAG-NM18006 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 468 | 40 | SAG-XJ18018 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1435 | |
| 17 | SAG-NM18017 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 800 | 41 | SAG-XJ18021 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1449 | |
| 18 | SAG-NM18021 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 839 | 42 | SAG-XJ18022 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1432 | |
| 19 | SAG-NM18027 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1238 | 43 | SAG-XJ18023 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1530 | |
| 20 | SAG-NM18030 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 963 | 44 | SAG-XJ18024 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1421 | |
| 21 | SAG-NM18031 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1140 | 45 | SAG-XJ18027 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1689 | |
| 22 | SAG-NM18032 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1302 | 46 | SAG-XJ18028 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1725 | |
| 23 | SAG-NM18033 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1085 | 47 | SAG-XJ18029 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1921 | |
| 24 | SAG-NM18034 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1407 | 48 | SAG-XJ18030 | 新疆Xinjiang | 2039 | |
| 不抽穗No heading | 1 | SAG-NM18003 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 684 | 12 | SAG-NM18022 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 827 |
| 2 | SAG-NM18005 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 746 | 13 | SAG-NM18023 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 818 | |
| 3 | SAG-NM18007 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 300 | 14 | SAG-NM18024 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 817 | |
| 4 | SAG-NM18008 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 272 | 15 | SAG-NM18025 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 880 | |
| 5 | SAG-NM18009 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 189 | 16 | SAG-NM18026 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1088 | |
| 6 | SAG-NM18010 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 229 | 17 | SAG-NM18028 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 548 | |
| 7 | SAG-NM18014 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 789 | 18 | SAG-NM18029 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1112 | |
| 8 | SAG-NM18015 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 988 | 19 | SAG-NM18040 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1155 | |
| 9 | SAG-NM18016 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 812 | 20 | SAG-NM18044 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1750 | |
| 10 | SAG-NM18018 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 714 | 21 | SAG-NM18045 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 1509 | |
| 11 | SAG-NM18019 | 内蒙古Inner Mongolia | 668 | 22 | SAG-XJ18011 | 新疆Xinjiang | 1139 |
主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Accumulative rate of contribution (%) | 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Accumulative rate of contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.277 | 27.289 | 27.289 | 13 | 0.379 | 1.649 | 91.544 |
| 2 | 4.263 | 18.534 | 45.823 | 14 | 0.365 | 1.587 | 93.131 |
| 3 | 2.613 | 11.362 | 57.185 | 15 | 0.341 | 1.484 | 94.615 |
| 4 | 1.262 | 5.489 | 62.674 | 16 | 0.298 | 1.294 | 95.908 |
| 5 | 1.176 | 5.115 | 67.789 | 17 | 0.277 | 1.205 | 97.113 |
| 6 | 0.993 | 4.316 | 72.105 | 18 | 0.218 | 0.946 | 98.059 |
| 7 | 0.941 | 4.092 | 76.197 | 19 | 0.155 | 0.674 | 98.734 |
| 8 | 0.778 | 3.384 | 79.581 | 20 | 0.133 | 0.579 | 99.313 |
| 9 | 0.731 | 3.177 | 82.758 | 21 | 0.081 | 0.351 | 99.664 |
| 10 | 0.652 | 2.836 | 85.594 | 22 | 0.047 | 0.206 | 99.871 |
| 11 | 0.531 | 2.310 | 87.904 | 23 | 0.030 | 0.129 | 100.000 |
| 12 | 0.458 | 1.990 | 89.895 |
表4 主成分分析的特征向量和贡献率
Table 4 Eigenvector and contribution rate of principal component analysis
主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Accumulative rate of contribution (%) | 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Accumulative rate of contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.277 | 27.289 | 27.289 | 13 | 0.379 | 1.649 | 91.544 |
| 2 | 4.263 | 18.534 | 45.823 | 14 | 0.365 | 1.587 | 93.131 |
| 3 | 2.613 | 11.362 | 57.185 | 15 | 0.341 | 1.484 | 94.615 |
| 4 | 1.262 | 5.489 | 62.674 | 16 | 0.298 | 1.294 | 95.908 |
| 5 | 1.176 | 5.115 | 67.789 | 17 | 0.277 | 1.205 | 97.113 |
| 6 | 0.993 | 4.316 | 72.105 | 18 | 0.218 | 0.946 | 98.059 |
| 7 | 0.941 | 4.092 | 76.197 | 19 | 0.155 | 0.674 | 98.734 |
| 8 | 0.778 | 3.384 | 79.581 | 20 | 0.133 | 0.579 | 99.313 |
| 9 | 0.731 | 3.177 | 82.758 | 21 | 0.081 | 0.351 | 99.664 |
| 10 | 0.652 | 2.836 | 85.594 | 22 | 0.047 | 0.206 | 99.871 |
| 11 | 0.531 | 2.310 | 87.904 | 23 | 0.030 | 0.129 | 100.000 |
| 12 | 0.458 | 1.990 | 89.895 |
| 性状 Traits | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height | 0.901 | 0.085 | -0.185 | 0.146 | -0.170 |
| 抽穗Heading | 0.895 | 0.024 | -0.031 | -0.167 | -0.121 |
| 茎节数Number of stem nodes | 0.882 | 0.205 | 0.032 | -0.210 | -0.029 |
| 单株鲜重Single plant fresh weight | 0.825 | 0.042 | -0.122 | 0.454 | 0.003 |
| 单株干重Single plant dry weight | 0.823 | 0.018 | -0.030 | 0.462 | -0.044 |
| 植株被粉Leaves with powder | 0.717 | 0.009 | -0.233 | -0.119 | 0.232 |
| 茎秆基部叶鞘有无绒毛Leaf sheaths at the base of the stalk with or without tomentum | -0.648 | 0.153 | 0.054 | -0.230 | 0.117 |
| 旗叶宽Flag leaf width | 0.163 | 0.801 | 0.062 | -0.061 | -0.083 |
| 茎粗Stem diameter | -0.081 | 0.778 | -0.064 | -0.183 | -0.017 |
| 倒二叶宽Penultimate leaf width | 0.117 | 0.766 | -0.254 | 0.066 | 0.012 |
| 旗叶长Flag leaf length | -0.037 | 0.668 | 0.535 | -0.201 | -0.085 |
| 倒二叶长Penultimate leaf length | 0.180 | 0.660 | 0.493 | -0.126 | 0.065 |
| 芒长Awn length | -0.064 | 0.620 | -0.033 | -0.101 | 0.243 |
| 穗长Panicle length | -0.030 | 0.600 | -0.162 | 0.251 | 0.131 |
| 分蘖数Number of tillers | -0.177 | -0.281 | 0.797 | -0.028 | 0.182 |
| 锈病Rust disease | -0.350 | 0.246 | 0.547 | -0.195 | 0.302 |
| 小穗数Panicle number | 0.142 | 0.166 | -0.521 | 0.471 | -0.105 |
| 单株穗数Panicle number per hill | 0.144 | -0.247 | -0.082 | 0.824 | -0.137 |
| 穗宽Panicle width | 0.008 | -0.064 | -0.399 | 0.585 | -0.299 |
| 穗色Panicle color | 0.078 | 0.042 | 0.013 | -0.355 | 0.784 |
| 茎秆叶鞘小刺Stem leaf sheaths small spines | 0.116 | -0.242 | -0.271 | -0.107 | -0.677 |
| 叶色Leaf color | -0.104 | -0.078 | 0.412 | -0.115 | 0.431 |
| 叶片被毛Leaves with tomentum | 0.372 | 0.058 | -0.351 | 0.285 | -0.414 |
表5 老芒麦23个性状对前5个主成分的负荷量
Table 5 The load of 23 characters of E. sibiricus on the first five principal components
| 性状 Traits | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height | 0.901 | 0.085 | -0.185 | 0.146 | -0.170 |
| 抽穗Heading | 0.895 | 0.024 | -0.031 | -0.167 | -0.121 |
| 茎节数Number of stem nodes | 0.882 | 0.205 | 0.032 | -0.210 | -0.029 |
| 单株鲜重Single plant fresh weight | 0.825 | 0.042 | -0.122 | 0.454 | 0.003 |
| 单株干重Single plant dry weight | 0.823 | 0.018 | -0.030 | 0.462 | -0.044 |
| 植株被粉Leaves with powder | 0.717 | 0.009 | -0.233 | -0.119 | 0.232 |
| 茎秆基部叶鞘有无绒毛Leaf sheaths at the base of the stalk with or without tomentum | -0.648 | 0.153 | 0.054 | -0.230 | 0.117 |
| 旗叶宽Flag leaf width | 0.163 | 0.801 | 0.062 | -0.061 | -0.083 |
| 茎粗Stem diameter | -0.081 | 0.778 | -0.064 | -0.183 | -0.017 |
| 倒二叶宽Penultimate leaf width | 0.117 | 0.766 | -0.254 | 0.066 | 0.012 |
| 旗叶长Flag leaf length | -0.037 | 0.668 | 0.535 | -0.201 | -0.085 |
| 倒二叶长Penultimate leaf length | 0.180 | 0.660 | 0.493 | -0.126 | 0.065 |
| 芒长Awn length | -0.064 | 0.620 | -0.033 | -0.101 | 0.243 |
| 穗长Panicle length | -0.030 | 0.600 | -0.162 | 0.251 | 0.131 |
| 分蘖数Number of tillers | -0.177 | -0.281 | 0.797 | -0.028 | 0.182 |
| 锈病Rust disease | -0.350 | 0.246 | 0.547 | -0.195 | 0.302 |
| 小穗数Panicle number | 0.142 | 0.166 | -0.521 | 0.471 | -0.105 |
| 单株穗数Panicle number per hill | 0.144 | -0.247 | -0.082 | 0.824 | -0.137 |
| 穗宽Panicle width | 0.008 | -0.064 | -0.399 | 0.585 | -0.299 |
| 穗色Panicle color | 0.078 | 0.042 | 0.013 | -0.355 | 0.784 |
| 茎秆叶鞘小刺Stem leaf sheaths small spines | 0.116 | -0.242 | -0.271 | -0.107 | -0.677 |
| 叶色Leaf color | -0.104 | -0.078 | 0.412 | -0.115 | 0.431 |
| 叶片被毛Leaves with tomentum | 0.372 | 0.058 | -0.351 | 0.285 | -0.414 |
| 1 | Zhou G D, Li Z Y, Li H Y, et al. Research advances in germplasm resource of Elymus sibiricus. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(11): 2026-2031. |
| 周国栋, 李志勇, 李鸿雁, 等. 老芒麦种质资源的研究进展. 草业科学, 2011, 28(11): 2026-2031. | |
| 2 | Yan W H, Ma Y B, Zhang J R, et al. The analysis of genetic diversity and the construction of core collection for Elymus sibiricus L. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2017(1): 1-12. |
| 闫伟红, 马玉宝, 张晶然, 等. 老芒麦遗传多样性分析及核心种质构建. 草学, 2017(1): 1-12. | |
| 3 | Chen G, He L F. Evaluation of ecological adaptability and productivity of two species of Elymus in alpine region. Pratacultural Science, 2004, 21(9): 39-42. |
| 陈功, 贺兰芳. 高寒地区两种老芒麦生态适应性和生产性能评价. 草业科学, 2004, 21(9): 39-42. | |
| 4 | Su H J, Zhuo Y P, Wang L K, et al. Progress in breeding of Elymus sibiricus. China Herbivore Science, 2016, 36(1): 53-56. |
| 苏红锦, 卓玉璞, 王历宽, 等. 我国老芒麦育种研究进展. 中国草食动物科学, 2016, 36(1): 53-56. | |
| 5 | Yuan Q H, Zhang J Y, Zhang W S, et al. Biodiversity of native populations of Elymus dahuricus and Elymus sibircus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2003, 12(5): 44-49. |
| 袁庆华, 张吉宇, 张文淑, 等. 披碱草和老芒麦野生居群生物多样性研究. 草业学报, 2003, 12(5): 44-49. | |
| 6 | Liu X L, De Y, Zhao L X. Morpholoical characteristics about wild Elymus sibiricus L. Shanghai: Youth Academic Seminar of China Grass Society, 2010: 214-222. |
| 刘新亮, 德英, 赵来喜. 我国野生老芒麦种质资源形态特征比较. 上海: 中国草学会青年学术研讨会, 2010: 214-222. | |
| 7 | Yan J J. Genetic diversity and potential germplasm selection of Elymus sibiricus L. in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2009. |
| 鄢家俊. 青藏高原老芒麦种质资源遗传多样性及优异种质筛选. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2009. | |
| 8 | Li X R, Chen S X, Yan J J, et al. Research progress on Elymus sibiricus Linn. germplasm resources. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2021(1): 6-17. |
| 李欣瑞, 陈淑娴, 鄢家俊, 等. 老芒麦种质资源研究进展. 草学, 2021(1): 6-17. | |
| 9 | Xie W G, Zhang X Q, Cai H W, et al. Genetic diversity analysis and transferability of cereal EST-SSR markers to orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 2010, 38: 740-749. |
| 10 | Shehzad T, Okuizumi H, Kawase M, et al. Development of SSR-based sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) diversity research set of germplasm and its evaluation by morphological traits. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 2009, 56: 809-827. |
| 11 | Yin T T, Gu L L, Yan F, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of 59 Elymus sibiricus germplasm resources. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(11): 2307-2317. |
| 尹婷婷, 谷丽丽, 闫锋, 等. 59份老芒麦种质资源的表型多样性分析. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(11): 2307-2317. | |
| 12 | Jia Z Y. Creation of new germplasm and association analysis of main agronomic traits in Elymus sibiricus L. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 贾振宇. 老芒麦新种质创制及主要农艺性状关联分析. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021. | |
| 13 | Zheng Y Y. Analysis of flowering time variation and development and application of molecular markers based on flowering candidate genes in Elymus sibiricus. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. |
| 郑玉莹. 老芒麦开花时间变异分析及开花候选基因分子标记开发与应用. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. | |
| 14 | Wang Z L, Zhao L X. Description specifications and data standards for Elymus sibiricus germplasm resources. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2007. |
| 王照兰, 赵来喜. 老芒麦种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007. | |
| 15 | Chang Y F, Liu B W, Liu W L, et al. Study on morphological diversity and classification and identification methods of different species of Vicia seedling. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(7): 28-36, 53. |
| 常媛飞, 刘博文, 刘万良, 等. 野豌豆属14个种牧草幼苗形态多样性与分类鉴定方法的研究. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(7): 28-36, 53. | |
| 16 | Yun J F, Wang Y, Xu C B, et al. The biological characters and production performance of a new Russian wildrye strain. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2006, 28(5): 1-7. |
| 云锦凤, 王勇, 徐春波, 等. 新麦草新品系生物学特性及生产性能研究. 中国草地学报, 2006, 28(5): 1-7. | |
| 17 | Yang Y F, Li J D. The ecological plasticity of the quantitative characters for ear heads of Leymus chinensis population in natural meadow in Northeast China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(5): 752-758. |
| 杨允菲, 李建东. 东北草原羊草种群单穗数量性状的生态可塑性. 生态学报, 2001, 21(5): 752-758. | |
| 18 | Hao F, Xu Z, Li P, et al. Morphological genetic diversity of Bromus L. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2011, 33(2): 17-24. |
| 郝峰, 徐柱, 李平, 等. 雀麦属13种植物形态遗传多样性研究. 中国草地学报, 2011, 33(2): 17-24. | |
| 19 | Huang F, Li Z Y, Li H Y, et al. Analysis of morphological diversity of Elymus sibiricus L. germplasm resources.Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2015, 37(3): 111-115. |
| 黄帆, 李志勇, 李鸿雁, 等. 老芒麦种质资源形态多样性分析. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(3): 111-115. | |
| 20 | Zhang H H, Liang W W, Zhang X Z, et al. Analysis on morphology and growth characteristics of wild Elymus sibiricus L. germplasm resources in Xinjiang. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(4): 701-708. |
| 张荟荟, 梁维维, 张学洲, 等. 新疆野生老芒麦种质资源形态及生长特性分析. 草地学报, 2021, 29(4): 701-708. | |
| 21 | Li Y, Li L H, Wang Y Q, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of 39 germplasm resources of Elymus sibiricus L. Seed, 2021, 40(9): 57-63, 71. |
| 李瑶, 李露红, 王永琪, 等. 39份老芒麦种质资源表型多样性分析. 种子, 2021, 40(9): 57-63, 71. | |
| 22 | Xiao L, Jiang J X, Yi Z L, et al. A study on phenotypic diversity of Miscanthus sinensis natural population in Guangxi Province.Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(4): 43-50. |
| 肖亮, 蒋建雄, 易自力, 等. 广西省芒野生居群表型多样性研究. 草业学报, 2013, 22(4): 43-50. | |
| 23 | Qi J, Cao W X, Yan W H. Phenotypic diversity and environment relations of wild Elymus populations. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(5): 1027-1033. |
| 祁娟, 曹文侠, 闫伟红. 披碱草属野生居群表型多样性及其与环境关系研究. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(5): 1027-1033. | |
| 24 | Yan X B, Guo Y X, Zhou H, et al. Effects of geographical factors on genetic variation of Elymus nutans indigenous in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2007, 27(2): 328-333. |
| 严学兵, 郭玉霞, 周禾, 等. 青藏高原垂穗披碱草遗传变异的地理因素分析. 西北植物学报, 2007, 27(2): 328-333. | |
| 25 | Chen Z, Guan Y Z, Liang X P, et al. Effects of altitude on the morphological traits of Elymus species.Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(5): 897-904. |
| 陈钊, 管永卓, 梁新平, 等. 海拔高度对披碱草属植物形态特征的可塑性. 草地学报, 2015, 23(5): 897-904. | |
| 26 | Yan J J, Bai S Q, Zhang C B, et al. Production performance diversity of Elymus sibiricus germplasm from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in China. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 49(9): 2193-2198. |
| 鄢家俊, 白史且, 张昌兵, 等. 青藏高原野生老芒麦种质牧草生产性能多样性评价. 湖北农业科学, 2010, 49(9): 2193-2198. | |
| 27 | Yan J J, Bai S Q, Ma X, et al. Ear character diversity of native populations of Elymus sibiricus in the northwest Plateau of Sichuan Province. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2007, 16(6): 99-106. |
| 鄢家俊, 白史且, 马啸, 等. 川西北高原野生老芒麦居群穗部形态多样性研究. 草业学报, 2007, 16(6): 99-106. | |
| 28 | Slatkin M. Isolation by distance in equilibrium and nonequilibrium populations. Evolution, 1993, 47(1): 264-279. |
| 29 | Xie W G, Zhao X H, Zhang J Q, et al. Assessment of genetic diversity of Siberian wild rye (Elymus sibiricus L.) germplasms with variation of seed shattering and implication for future genetic improvement. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 2015, 58: 211-218. |
| [1] | 王珊珊, 谷海涛, 谢慧芳, 何绍冬, 甘长波, 卫小勇, 孔广超. 113份饲草型六倍体小黑麦种质饲草产量与品质性状的评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 192-202. |
| [2] | 李瑞强, 王玉祥, 孙玉兰, 张磊, 陈爱萍. 盐胁迫对5份无芒雀麦苗期生长和生理生化的影响及综合性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-111. |
| [3] | 孙禄娟, 何建军, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 司二静, 杨轲, 李葆春, 马小乐, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄, 王化俊. 基于全长转录组测序的盐生草SSR标记开发及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 199-210. |
| [4] | 张永超, 魏小星, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程形态特征变化规律及对养分添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 101-111. |
| [5] | 任文静, 吕玉虎, 周国朋, 常单娜, 向春阳, 曹卫东. 一个紫云英F4重组自交系群体的农艺性状与养分吸收评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 101-110. |
| [6] | 陈子英, 常单娜, 韩梅, 李正鹏, 严清彪, 张久东, 周国朋, 孙小凤, 曹卫东. 47份箭筈豌豆品种(系)在青海作秋绿肥的能力评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 39-51. |
| [7] | 张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. |
| [8] | 吴廷美, 林慧龙, 范迪, 籍常婷, 赵玉婷, 魏靖琼. 冻原高山草地牧户家畜养殖规模影响因素分析——以青海省为例[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 117-126. |
| [9] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生老芒麦苗期耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 127-136. |
| [10] | 王吉祥, 宫焕宇, 屠祥建, 郭侲洐, 赵嘉楠, 沈健, 栗振义, 孙娟. 耐亚磷酸盐紫花苜蓿品种筛选及评价指标的鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 186-199. |
| [11] | 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 秦燕, 魏小星, 刘敏洁. 青藏高原老芒麦落粒性及农艺性状相关性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 130-139. |
| [12] | 蔺豆豆, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 宫文龙. 15份燕麦材料苗期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. |
| [13] | 郭剑波, 赵国强, 贾书刚, 董俊夫, 陈龙, 王淑平. 施肥对高寒草原草地质量指数及土壤性质影响的综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 85-93. |
| [14] | 王苗苗, 周向睿, 梁国玲, 赵桂琴, 焦润安, 柴继宽, 高雪梅, 李娟宁. 5份燕麦材料苗期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 143-154. |
| [15] | 雷雄, 游明鸿, 白史且, 陈丽丽, 邓培华, 熊毅, 熊艳丽, 余青青, 马啸, 杨建, 张昌兵. 川西北高原50份燕麦种质农艺性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 131-142. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||