

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 1-14.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022142
• 研究论文 •
胡宇霞( ), 龚吉蕊(
), 龚吉蕊( ), 朱趁趁, 矢佳昱, 张子荷, 宋靓苑, 张魏圆
), 朱趁趁, 矢佳昱, 张子荷, 宋靓苑, 张魏圆
收稿日期:2022-03-31
修回日期:2022-05-18
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-01-29
通讯作者:
龚吉蕊
作者简介:E-mail: jrgong@bnu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yu-xia HU( ), Ji-rui GONG(
), Ji-rui GONG( ), Chen-chen ZHU, Jia-yu SHI, Zi-he ZHANG, Liang-yuan SONG, Wei-yuan ZHANG
), Chen-chen ZHU, Jia-yu SHI, Zi-he ZHANG, Liang-yuan SONG, Wei-yuan ZHANG
Received:2022-03-31
Revised:2022-05-18
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-01-29
Contact:
Ji-rui GONG
摘要:
生态系统服务在维持生态安全、可持续发展和人类福祉方面发挥着重要作用。本研究以内蒙古荒漠草原为研究区,分别对2000、2017年水源涵养、土壤保持、生境质量、游憩潜力进行定量评估,分析其时空分布特征,探讨服务间的权衡/协同关系,并识别不同服务簇的主导服务类型和空间格局。结果表明:从2000-2017年,各项生态系统服务的空间异质性显著,水源涵养服务的高值区域主要集中在东南部和西南部,土壤保持高值位于西南部,生境质量和游憩潜力的分布都较随机。各项生态系统服务主要呈现降低趋势;大部分服务对间表现为协同关系,而土壤保持和生境质量服务对表现为权衡关系,服务对间的相关性程度有所降低;生态系统服务簇分为土壤保持、人居环境、水源涵养三个功能区,具有明显的空间异质性。土壤保持区,主要土地利用类型为未利用地,未来的管理要限制放牧数量,通过改变地表植被覆盖来影响土壤可侵蚀性。人居环境区,草地覆盖度高,为人类活动提供优良场所,促进生态旅游等多产业协同发展。水源涵养区,土地利用类型主要为中覆盖度草地和低覆盖度草地,未来管理以蓄水保水为主,坚持生态优先,实现该区域生态可持续发展。
胡宇霞, 龚吉蕊, 朱趁趁, 矢佳昱, 张子荷, 宋靓苑, 张魏圆. 基于生态系统服务簇的内蒙古荒漠草原生态系统服务的空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 1-14.
Yu-xia HU, Ji-rui GONG, Chen-chen ZHU, Jia-yu SHI, Zi-he ZHANG, Liang-yuan SONG, Wei-yuan ZHANG. Spatial distribution of ecosystem services in the desert steppe, Inner Mongolia based on ecosystem service bundles[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 1-14.
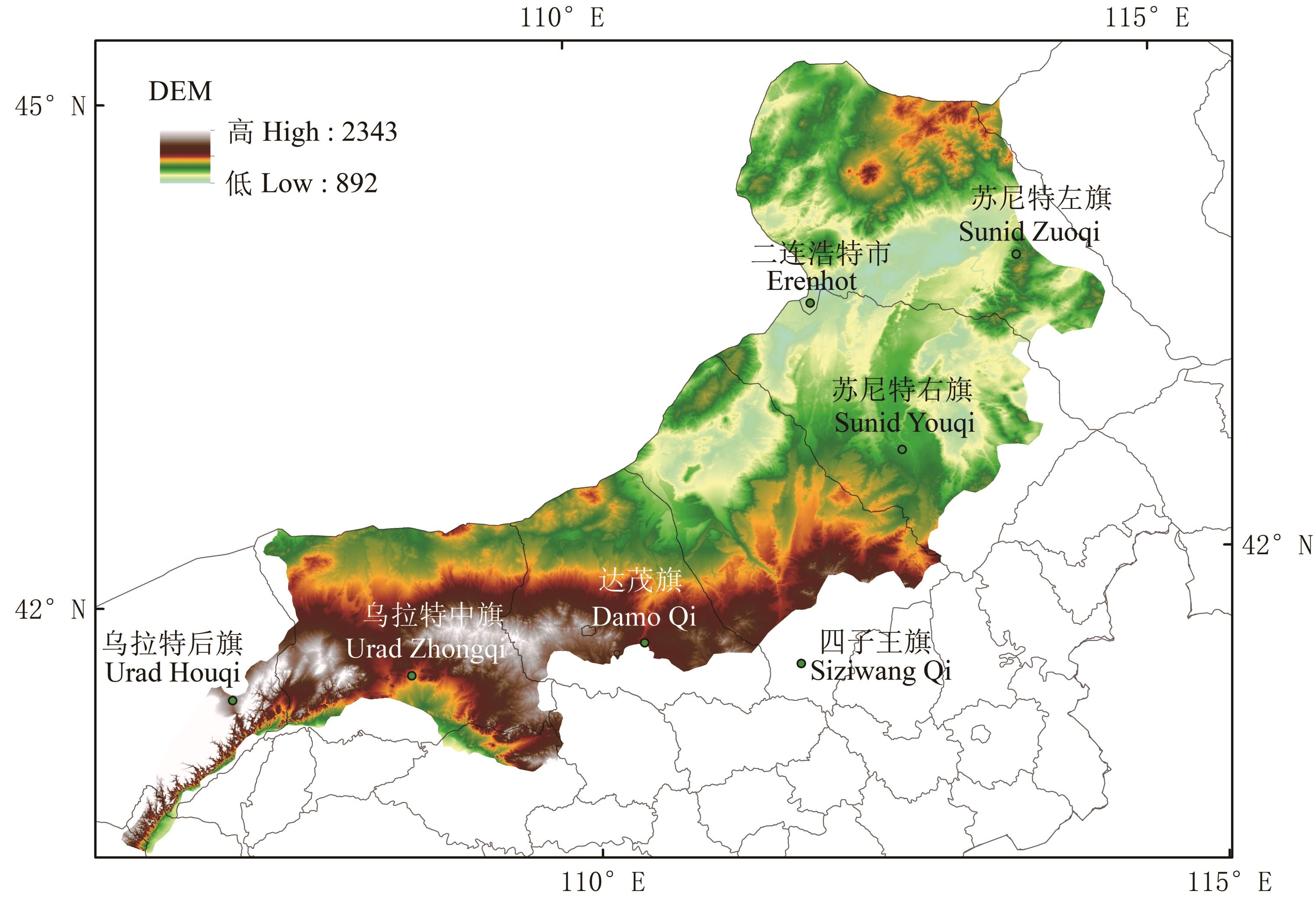
图1 研究区地理位置基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1822号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS(2019)1822 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.1 Location of the study area
| 参数Parameter | 分类Classification | 得分Score | 描述Describe |
|---|---|---|---|
地形糙度指数 Terrain roughness index ( | 水平 Level | 1 | 采用Riley等 |
| 近水平 Near horizontal | 2 | ||
| 稍微粗糙Slightly rough | 3 | ||
| 中度粗糙Moderately rough | 4 | ||
| 适度粗糙Modest rough | 5 | ||
| 高度粗糙Highly rough | 6 | ||
| 极度粗糙Extremely rough | 7 | ||
水体面积 Water area ( | 无 none | 0 | 参照Swetnam等 |
| 0~1000 | 1 | ||
| 1000~2500 | 2 | ||
| 2500~5000 | 3 | ||
| 5000~10000 | 4 | ||
| >10000 | 5 | ||
土地覆盖类型 Land use type ( | 未利用地Unused land | 0 | 参考Swetnam等 |
| 居民点Settlement | 1 | ||
| 农田Cropland | 2 | ||
| 水体Water | 3 | ||
| 草地Grassland | 4 | ||
| 灌木Shrub | 5 | ||
景区级别 Scenic level ( | 无景区No scenic spots | 0 | 具有景区的地区具有较高的游憩潜力,且认为景区级别越高,游憩潜力越大。Areas with scenic spots have higher recreational potential, and it is believed that the higher the level of scenic spots, the greater the recreational potential. |
| 1A | 1 | ||
| 2A | 2 | ||
| 3A | 3 | ||
| 4A | 4 | ||
与道路的距离 Distance from road ( | >10 km | 1 | 参照Paracchini等 |
| 5~10 km | 2 | ||
| 1~5 km | 3 | ||
| <1 km | 4 |
表 1 视觉质量指数各参数分类方案
Table 1 Classification scheme of each parameter of visual quality index
| 参数Parameter | 分类Classification | 得分Score | 描述Describe |
|---|---|---|---|
地形糙度指数 Terrain roughness index ( | 水平 Level | 1 | 采用Riley等 |
| 近水平 Near horizontal | 2 | ||
| 稍微粗糙Slightly rough | 3 | ||
| 中度粗糙Moderately rough | 4 | ||
| 适度粗糙Modest rough | 5 | ||
| 高度粗糙Highly rough | 6 | ||
| 极度粗糙Extremely rough | 7 | ||
水体面积 Water area ( | 无 none | 0 | 参照Swetnam等 |
| 0~1000 | 1 | ||
| 1000~2500 | 2 | ||
| 2500~5000 | 3 | ||
| 5000~10000 | 4 | ||
| >10000 | 5 | ||
土地覆盖类型 Land use type ( | 未利用地Unused land | 0 | 参考Swetnam等 |
| 居民点Settlement | 1 | ||
| 农田Cropland | 2 | ||
| 水体Water | 3 | ||
| 草地Grassland | 4 | ||
| 灌木Shrub | 5 | ||
景区级别 Scenic level ( | 无景区No scenic spots | 0 | 具有景区的地区具有较高的游憩潜力,且认为景区级别越高,游憩潜力越大。Areas with scenic spots have higher recreational potential, and it is believed that the higher the level of scenic spots, the greater the recreational potential. |
| 1A | 1 | ||
| 2A | 2 | ||
| 3A | 3 | ||
| 4A | 4 | ||
与道路的距离 Distance from road ( | >10 km | 1 | 参照Paracchini等 |
| 5~10 km | 2 | ||
| 1~5 km | 3 | ||
| <1 km | 4 |
年份 Year | 水源涵养 Water conservation (WC, mm) | 土壤保持 Soil conservation (SC, t·hm-2) | 生境质量 Habitat quality (HQ) | 游憩潜力 Recreation potential (RP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.80 | 11.68 | 0.66 | 0.26 |
| 2017 | 0.67 | 7.30 | 0.59 | 0.24 |
表2 2000、2017年荒漠草原各项生态系统服务均值
Table 2 Mean value of various ecosystem services in desert steppe in 2000 and 2017
年份 Year | 水源涵养 Water conservation (WC, mm) | 土壤保持 Soil conservation (SC, t·hm-2) | 生境质量 Habitat quality (HQ) | 游憩潜力 Recreation potential (RP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.80 | 11.68 | 0.66 | 0.26 |
| 2017 | 0.67 | 7.30 | 0.59 | 0.24 |
项目 Item | 供给服务 Providing services (水源涵养WC) | 调节服务 Regulating services (土壤保持SC) | 支持服务 Supporting services (生境质量HQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤保持SC | 0.089*** | ||
| 生境质量HQ | 0.273*** | -0.188*** | |
| 游憩潜力RP | 0.144*** | 0.253*** | 0.331*** |
表3 2000年荒漠草原生态系统服务Spearman相关系数
Table 3 Spearman correlation coefficients between ecosystem services of desert steppe in 2000
项目 Item | 供给服务 Providing services (水源涵养WC) | 调节服务 Regulating services (土壤保持SC) | 支持服务 Supporting services (生境质量HQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤保持SC | 0.089*** | ||
| 生境质量HQ | 0.273*** | -0.188*** | |
| 游憩潜力RP | 0.144*** | 0.253*** | 0.331*** |
项目 Item | 供给服务 Providing services (水源涵养WC) | 调节服务 Regulating services (土壤保持SC) | 支持服务 Supporting services (生境质量HQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤保持SC | 0.029*** | ||
| 生境质量HQ | 0.102*** | -0.135*** | |
| 游憩潜力RP | 0.133*** | 0.232*** | 0.279*** |
表 4 2017年荒漠草原生态系统服务Spearman相关系数
Table 4 Spearman correlation coefficients between ecosystem services of desert steppe in 2017
项目 Item | 供给服务 Providing services (水源涵养WC) | 调节服务 Regulating services (土壤保持SC) | 支持服务 Supporting services (生境质量HQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤保持SC | 0.029*** | ||
| 生境质量HQ | 0.102*** | -0.135*** | |
| 游憩潜力RP | 0.133*** | 0.232*** | 0.279*** |
| 1 | Costanza R, D’Arge R, de Groot R, et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Ecological Economics, 1998, 25(1): 3-15. |
| 2 | Costanza R, de Groot R, Braat L, et al. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosystem Services, 2017, 28: 1-16. |
| 3 | Li H L, Peng J, Hu Y N, et al. Ecological function zoning in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region based on ecosystem service bundles. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(8): 2657-2666. |
| 李慧蕾, 彭建, 胡熠娜, 等. 基于生态系统服务簇的内蒙古自治区生态功能分区. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(8): 2657-2666. | |
| 4 | Renard D, Rhemtulla J M, Bennett E M. Historical dynamics in ecosystem service bundles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112(43): 13411-13416. |
| 5 | Yang Y Y, Zheng H, Kong L Q, et al. Mapping ecosystem services bundles to detect high- and low-value ecosystem services areas for land use management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 225: 11-17. |
| 6 | Raudsepp-Hearne C, Peterson G D, Bennett E M. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107(11): 5242-5247. |
| 7 | Qi N, Zhao J, Yang Y Z, et al. Quantifying ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies in Northeast China based on ecosystem service bundles. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 2827-2837. |
| 祁宁, 赵君, 杨延征, 等. 基于服务簇的东北地区生态系统服务权衡与协同. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9): 2827-2837. | |
| 8 | Peng L, Deng W, Huang P, et al. Evaluation of multiple ecosystem services landscape index and identification of ecosystem services bundles in Sichuan Basin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(23): 9328-9340. |
| 彭立, 邓伟, 黄佩, 等. 四川盆地多重生态系统服务景观指数评价与服务簇识别. 生态学报, 2021, 41(23): 9328-9340. | |
| 9 | Ren Y J, Lv Y H, Fu B J. Quantifying the impacts of grassland restoration on biodiversity and ecosystem services in China: A meta-analysis. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 95: 542-550. |
| 10 | Xie G D, Liu J Y, Xu J, et al. A spatio-temporal delineation of trans-boundary ecosystem service flows from Inner Mongolia. Environmental Research Letters, 2019, 14(6): 65002. |
| 11 | Bai Y F, Zhao Y J, Wang Y, et al. Assessment of grassland ecosystem services and functional zoning in Northern China helped build ecological security barriers. Proceedings of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(6): 675-689. |
| 白永飞, 赵玉金, 王扬, 等. 中国北方草地生态系统服务评估和功能区划助力生态安全屏障建设. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(6): 675-689. | |
| 12 | Batunacun, Wieland R, Lakes T, et al. Identifying drivers of land degradation in Xilingol, China, between 1975 and 2015. Land Use Policy, 2019, 83: 543-559. |
| 13 | Wang S X, Qin J, Li W J, et al. Evaluation of ecosystem service value of Stipa brevifolia desert steppe under different loading rates. Grassland and Prataculture, 2018, 30(2): 38-44. |
| 王舒新, 秦洁, 李江文, 等. 不同放牧强度下短花针茅荒漠草原生态系统服务价值评估. 草原与草业, 2018, 30(2): 38-44. | |
| 14 | Mu S L, Guo Q. Ecosystem service value assessment and its spatial patterns in temperate grassland of Inner Mongolia. Northern Horticulture, 2018(18): 94-101. |
| 穆松林, 郭群. 内蒙古自治区温带草原生态系统服务价值评估及空间特征. 北方园艺, 2018(18): 94-101. | |
| 15 | Zhang G, Zhou G S, Chen F, et al. Analysis of the variability of canopy resistance over a desert steppe site in Inner Mongolia, China. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2014, 31(3): 681-692. |
| 16 | Sha Y Y, Shi Z G, Liu X D, et al. Distinct impacts of the Mongolian and Tibetan Plateaus on the evolution of the East Asian monsoon. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2015, 120(10): 4764-4782. |
| 17 | Pan T, Wu S H, Dai E F, et al. Spatiotemporal variation of water source supply service in Three Rivers Source Area of China based on InVEST model. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(1): 183-189. |
| 潘韬, 吴绍洪, 戴尔阜, 等. 基于InVEST模型的三江源区生态系统水源供给服务时空变化. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(1): 183-189. | |
| 18 | Zhou W Z, Liu G H, Pan J J, et al. Distribution of available soil water capacity in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2005, 15(1): 3-12. |
| 19 | Yang F, Hua D F, Huang P P, et al. Analysis of soil conservation service and its dynamic change in time and space in Xiamen. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2019, 42(3): 8-11, 18. |
| 杨帆, 滑东飞, 黄盼盼, 等. 厦门市土壤保持服务及其时空动态变化分析. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2019, 42(3): 8-11, 18. | |
| 20 | Yu B W, Rao E M, Chao X L, et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of nature reserves in soil conservation Hainan Island. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(12): 3694-3702. |
| 于博威, 饶恩明, 晁雪林, 等. 海南岛自然保护区对土壤保持服务功能的保护效果. 生态学报, 2016, 36(12): 3694-3702. | |
| 21 | Rao E M, Xiao Y, Ouyang Z Y, et al. Spatial characteristics of soil conservation service and its impact factors in Hainan Island. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(3): 746-755. |
| 饶恩明, 肖燚, 欧阳志云, 等. 海南岛生态系统土壤保持功能空间特征及影响因素. 生态学报, 2013, 33(3): 746-755. | |
| 22 | Li Y Q, Feng Z K, Han L B, et al. Evaluation of soil conservation benefits in Danjiangkou Reservoir area and upstream ecosystem. China Population, Resource and Environment, 2010, 20(5): 64-69. |
| 李亦秋, 冯仲科, 韩烈保, 等. 丹江口库区及上游生态系统土壤保持效益价值评估. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2010, 20(5): 64-69. | |
| 23 | Huang T, Yu D Y, Qiao J M, et al. Landscape pattern change and soil conservation in Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia. Resources Science, 2018, 40(6): 1256-1266. |
| 黄婷, 于德永, 乔建民, 等. 内蒙古锡林郭勒盟景观格局变化对土壤保持能力的影响. 资源科学, 2018, 40(6): 1256-1266. | |
| 24 | Lufafa A, Tenywa M M, Isabirye M, et al. Prediction of soil erosion in a Lake Victoria basin catchment using a GIS-based Universal Soil Loss model. Agricultural Systems, 2003, 76(3): 883-894. |
| 25 | Chen Y, Qiao F, Jiang L. Effects of land use pattern change on regional scale habitat quality based on InVEST Model-A case study in Beijing. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2016, 52(3): 553-562. |
| 陈妍, 乔飞, 江磊. 基于InVEST模型的土地利用格局变化对区域尺度生境质量的影响研究——以北京为例. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(3): 553-562. | |
| 26 | Zhong L N, Wang J. Evalution on effect of land consolidation on habitat quality based on InVEST model. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(1): 250-255. |
| 钟莉娜, 王军. 基于InVEST模型评估土地整治对生境质量的影响. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(1): 250-255. | |
| 27 | Swetnam R D, Harrison-Curran S K, Smith G R. Quantifying visual landscape quality in rural Wales: A GIS-enabled method for extensive monitoring of a valued cultural ecosystem service. Ecosystem Services, 2017, 26: 451-464. |
| 28 | Paracchini M L, Zulian G, Kopperoinen L, et al. Mapping cultural ecosystem services: A framework to assess the potential for outdoor recreation across the EU. Ecological Indicators, 2014, 45: 371-385. |
| 29 | Riley S J, DeGloria S D, Elliot R. A terrain ruggedness index that quantifies topographic heterogeneity. Intermountain Journal of Sciences, 1999(5): 1-4. |
| 30 | Jing H C, Liu Y H, He P, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services and it’s influencing factors in typical areas of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A case study of Nagqu City. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(7): 2657-2673. |
| 景海超, 刘颖慧, 贺佩, 等. 青藏高原典型区生态系统服务空间异质性及其影响因素——以那曲市为例. 生态学报, 2022, 42(7): 2657-2673. | |
| 31 | Brauman K A, Daily G C, Ka’Eo Duarte T, et al. The nature and value of ecosystem services: An overview highlighting hydrologic services. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 2007, 32(1): 67-98. |
| 32 | Zhang X F, Niu J M, Buyantuev A, et al. Understanding grassland degradation and restoration from the perspective of ecosystem services: A case study of the Xilin River Basin in Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability, 2016, 8(7): 594. |
| 33 | Kang T T, Yang S, Bu J Y, et al. Quantitative assessment for the dynamics of the main ecosystem services and their interactions in the Northwestern arid area, China. Sustainability, 2020, 12(3): 803. |
| 34 | Tong C, Wu J, Yong S, et al. A landscape-scale assessment of steppe degradation in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Arid Environments, 2004, 59(1): 133-149. |
| 35 | Dai H Y, Li D, Na R S, et al. Dry and wet environment evolution and climatic background analysis of regional ecological construction in Inner Mongolia. Arid Land Geography, 2019, 42(4): 745-752. |
| 代海燕, 李丹, 娜日苏, 等. 内蒙古干湿环境演变与地区生态建设优势气候背景分析. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(4): 745-752. | |
| 36 | Liu Y, Li Y S, Shan S Y, et al. Spatiotemporal variability in the water conservation amount in Gansu Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(8): 1420-1431. |
| 刘越, 李雨珊, 单姝瑶, 等. 甘肃祁连山国家级自然保护区水源涵养量的时空变化. 草业科学, 2021, 38(8): 1420-1431. | |
| 37 | Liu X D, Ma Q H, Yu H Y, et al. Climate warming-induced drought constrains vegetation productivity by weakening the temporal stability of the plant community in an arid grassland ecosystem. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2021, 307: 108526. |
| 38 | Yang B, Gong J R, Zhang Z H, et al. Stabilization of carbon sequestration in a Chinese desert steppe benefits from increased temperatures and from precipitation outside the growing season. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 691: 263-277. |
| 39 | Steinhoff-Knopp B, Kuhn T K, Burkhard B. The impact of soil erosion on soil-related ecosystem services: Development and testing a scenario-based assessment approach. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2021, 193(S1): 274. |
| 40 | Rao E M, Xiao Y. Spatial characteristics and effects of soil conservation service in Sichuan Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(24): 8741-8749. |
| 饶恩明, 肖燚. 四川省生态系统土壤保持功能空间特征及其影响因素. 生态学报, 2018, 38(24): 8741-8749. | |
| 41 | Feng X M, Wang Y F, Chen L D, et al. Modeling soil erosion and its response to land-use change in hilly catchments of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geomorphology, 2010, 118(3/4): 239-248. |
| 42 | Li M Y, Zhou Y, Xiao P N, et al. Evolution of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effect in Northwest Hubei Province from 2000 to 2020 based on the InVEST Model. Land, 2021, 10(8): 857. |
| 43 | Wu J S, Cao Q W, Shi S Q, et al. Spatio-temporal variability of habitat quality in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Area based on land use change. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(11): 3457-3466. |
| 吴健生, 曹祺文, 石淑芹, 等. 基于土地利用变化的京津冀生境质量时空演变. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(11): 3457-3466. | |
| 44 | Zeng Y X, Zhong L X, Wang L E. Spatiotemporal changes in recreation potential of ecosystem services in Sanjiangyuan, China. Journal of Spatial Science, 2018, 63(2): 359-377. |
| 45 | Mea. Millennium ecosystem assessment: Living beyond our means-natural assets and Human Well-being. Washington, DC, USA: World Resources Institute, 2005. |
| 46 | Peng J, Hu X X, Zhao M Y, et al. Research progress on ecosystem service trade-offs: From cognition to decision-making. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(6): 960-973. |
| 彭建, 胡晓旭, 赵明月, 等. 生态系统服务权衡研究进展: 从认知到决策, 地理学报, 2017, 72(6): 960-973. | |
| 47 | Jafarzadeh A A, Mahdavi A, Shamsi S R F, et al. Assessing synergies and trade-offs between ecosystem services in forest landscape management. Land Use Policy, 2021, 111: 105741. |
| 48 | Wang Y H, Dai E F. Spatial-temporal changes in ecosystem services and the trade-off relationship in mountain regions: A case study of Hengduan Mountain region in Southwest China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 264: 121573. |
| [1] | 牛伟玲, 陈辉, 侯慧新, 郭晨睿, 马娇林, 武建双. 10年禁牧未改变藏西北高寒荒漠植物水氮利用效率[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 35-48. |
| [2] | 刘万龙, 许冬梅, 史佳梅, 许爱云. 不同群落生境蒙古冰草种群株丛结构和叶片功能性状的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 72-80. |
| [3] | 张晓宁, 李晓丹, 年丽丽, 杨莹博, 刘学录. 基于文献计量的草地生态系统水源涵养功能研究现状[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 35-49. |
| [4] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| [5] | 金玲, 陆颖, 马红彬, 谢应忠, 沈艳. 内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原植物群落的数量分类与排序[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 12-21. |
| [6] | 倪芳芳, 吕世杰, 屈志强, 白璐, 孟彪, 张博涵, 李治国. 不同载畜率下荒漠草原非生长季植物群落特征对近地面风沙通量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 26-33. |
| [7] | 程燕明, 马红彬, 马菁, 马子元, 刘进娣, 周瑶, 彭文栋. 不同放牧方式对荒漠草原土壤碳氮储量及固持的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 18-27. |
| [8] | 陈林, 陈高路, 宋乃平, 李学斌, 万红云, 何文强. 宁夏东部荒漠草原猪毛蒿光合特征和水分利用效率对降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 87-98. |
| [9] | 张峰, 孙嘉伟, 孙宇, 郑佳华, 乔荠瑢, 赵萌莉. 不同载畜率对短花针茅荒漠草原优势物种间关系及其空间分布特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 1-11. |
| [10] | 吴旭东, 蒋齐, 任小玢, 俞鸿千, 王占军, 何建龙, 季波, 杜建民. 降水水平对荒漠草原生物土壤结皮碳、氮和微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 34-43. |
| [11] | 孙忠超, 郭天斗, 于露, 马彦平, 赵亚楠, 李雪颖, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地人为转变过程土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 34-45. |
| [12] | 蒙仲举, 陈颜洁, 包斯琴. 苏尼特右旗荒漠草原三种放牧方式下群落斑块特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 13-23. |
| [13] | 顾继雄, 郭天斗, 王红梅, 李雪颖, 梁丹妮, 杨青莲, 高锦月. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地转变过程土壤微生物响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 46-57. |
| [14] | 熊梅, 乔荠瑢, 杨阳, 张峰, 郑佳华, 吴建新, 赵萌莉. 不同载畜率下短花针茅和土壤生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 212-219. |
| [15] | 张静静, 刘尊驰, 鄢创, 王云霞, 刘凯, 时新荣, 袁志友. 土壤pH值变化对3种草原类型土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 69-81. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||