

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 176-185.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022369
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
韩丹1,3( ), 龙凤1, 陈胜1, 户萌菲1, 王栋2, 陈水红1(
), 龙凤1, 陈胜1, 户萌菲1, 王栋2, 陈水红1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-15
修回日期:2022-10-17
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-06-16
通讯作者:
陈水红
作者简介:E-mail: cshdky@126.com基金资助:
Dan HAN1,3( ), Feng LONG1, Sheng CHEN1, Meng-fei HU1, Dong WANG2, Shui-hong CHEN1(
), Feng LONG1, Sheng CHEN1, Meng-fei HU1, Dong WANG2, Shui-hong CHEN1( )
)
Received:2022-09-15
Revised:2022-10-17
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-06-16
Contact:
Shui-hong CHEN
摘要:
分蘖生长在茎基部不伸长的节间,有不定根,能独立于主茎存活,禾本科作物布顿大麦主要通过分蘖来提高产量;内生真菌和基因均能调控布顿大麦分蘖,为了探究内生真菌对宿主植物分蘖相关基因TB1的影响,本研究利用RT-PCR法对布顿大麦TB1基因进行克隆并测序,采用生物信息学方法对该基因的序列结果进行分析,用SYBR Green荧光染料法对新疆温宿县和青海柴达木盆地带内生真菌(E+)和不带内生真菌(E-)的布顿大麦TB1基因进行q-PCR相对表达量分析。结果显示,克隆的TB1基因蛋白质编码区(CDS)全长为804 bp,编码267个氨基酸残基;TB1基因无启动子和PolyA位点;经亚细胞定位,TB1蛋白预计在液泡,TB1蛋白无跨膜结构域、无信号肽、不属于跨膜蛋白、存在于TCP家族;推测TB1蛋白为不稳定蛋白质。布顿大麦TB1基因与大麦亚种的TB1同源性最高,为96.72%,且与大麦亚种的TB1处于同一支系。温宿县和柴达木盆地布顿大麦根、茎、叶中TB1基因表达量趋势一致,内生真菌显著降低了植株分蘖发生部位茎基部的TB1基因表达量,表明内生真菌侵染影响了宿主TB1基因表达进而调控宿主植物分蘖。研究结果为后续布顿大麦分蘖机制研究奠定了理论基础。
韩丹, 龙凤, 陈胜, 户萌菲, 王栋, 陈水红. 布顿大麦TB1基因的克隆及内生真菌对其表达量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 176-185.
Dan HAN, Feng LONG, Sheng CHEN, Meng-fei HU, Dong WANG, Shui-hong CHEN. Cloning of TB1 from Hordeum bogdanii and the effect of endophytic fungi on its expression[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 176-185.

图 2 回接内生真菌的布顿大麦菌丝镜检箭头所指的蓝色细条表示菌丝体Blue stripes indicated by arrows indicate mycelium.
Fig.2 Microscopic examination of H.bogdanii hyphae with endophytic fungi

图3 tef、tub、act测序结果与接菌前序列比对A: tef;B: tub; C: act; 1: 接入前序列The pre-access sequence; 2~4: 温宿县Wensu County; 5~7: 柴达木盆地Tsaidam Basin.
Fig. 3 tef, tub and act sequencing results and sequence comparison before inoculation
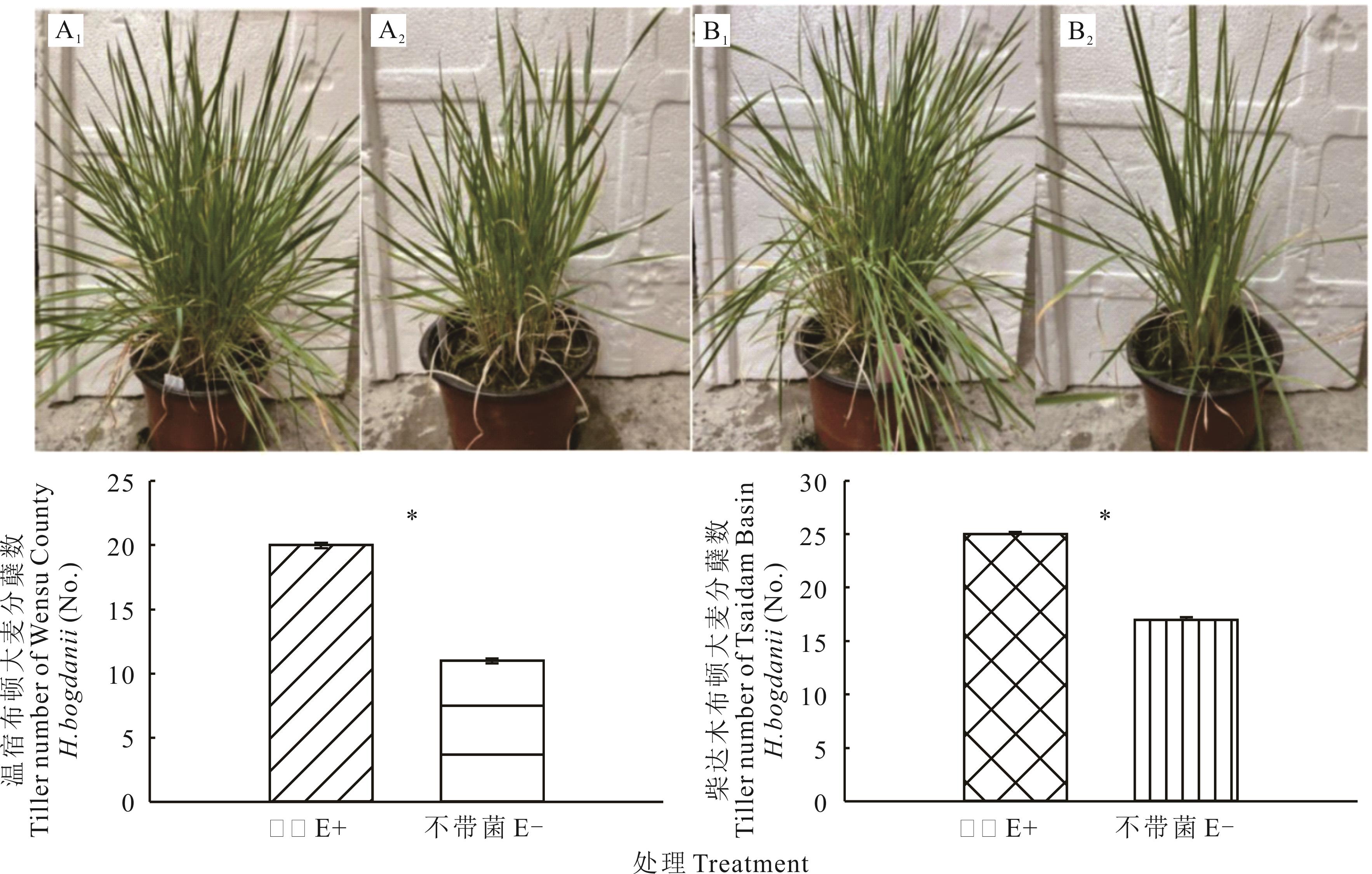
图4 温宿县和柴达木盆地植株分蘖数统计A1: 温宿县E+ Wensu County E+ plants; A2: 温宿县E-Wensu County E- plants; B1: 柴达木盆地Tsaidam Basin E+ plants; B2: 柴达木盆地E- Tsaidam Basin E- plants; *表示P<0.05水平下E+、E-间差异显著 * indicates significant differences between E+ and E- at P<0.05 level.
Fig.4 Statistics on the tillers of H.bogdanii plants in Wensu County and Tsaidam Basin
| 生态型Ecotype | 根Root | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf |
|---|---|---|---|
| 温宿县E+ Wensu County E+ | 0.678±0.056bA | 0.328±0.060cA | 3.480±0.097aB* |
| 温宿县E- Wensu County E- | 1.000±0.003aA* | 1.034±0.086aA* | 1.006±0.067aA |
| 柴达木盆地E+ Tsaidam Basin E+ | 0.547±0.067bA | 0.382±0.135bA | 13.427±0.088aA* |
| 柴达木盆地E- Tsaidam Basin E- | 1.008±0.299aA* | 1.010±0.164aAA* | 1.082±0.222aA |
表1 两种生态型布顿大麦TB1基因相对表达量
Table 1 Relative expression of TB1 gene in two ecotypes of H. bogdanii
| 生态型Ecotype | 根Root | 茎Stem | 叶Leaf |
|---|---|---|---|
| 温宿县E+ Wensu County E+ | 0.678±0.056bA | 0.328±0.060cA | 3.480±0.097aB* |
| 温宿县E- Wensu County E- | 1.000±0.003aA* | 1.034±0.086aA* | 1.006±0.067aA |
| 柴达木盆地E+ Tsaidam Basin E+ | 0.547±0.067bA | 0.382±0.135bA | 13.427±0.088aA* |
| 柴达木盆地E- Tsaidam Basin E- | 1.008±0.299aA* | 1.010±0.164aAA* | 1.082±0.222aA |
项目 Item | 自由度 df | 温宿县 Wensu County | 柴达木盆地Tsaidam Basin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | ||
| 内生真菌Endophytic fungi (E) | 1 | 49.821 | 0.001 | 1128.868 | 0.001 |
| 部位Site (S) | 2 | 211.398 | 0.001 | 1522.982 | 0.001 |
| 内生真菌×部位E×S | 2 | 215.233 | 0.001 | 1488.700 | 0.001 |
表2 内生真菌在不同部位对温宿县和柴达木盆地布顿大麦TB1基因表达量双因素方差分析
Table 2 Two-way ANOVA of TB1 gene expression of H. bogdanii in Wensu County and Tsaidam Basin by endophytic fungi in different parts
项目 Item | 自由度 df | 温宿县 Wensu County | 柴达木盆地Tsaidam Basin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | ||
| 内生真菌Endophytic fungi (E) | 1 | 49.821 | 0.001 | 1128.868 | 0.001 |
| 部位Site (S) | 2 | 211.398 | 0.001 | 1522.982 | 0.001 |
| 内生真菌×部位E×S | 2 | 215.233 | 0.001 | 1488.700 | 0.001 |
| 1 | Jia S Z. Forage plants of China: Volume 1. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1987. |
| 贾慎修. 中国饲用植物志: 第1卷. 北京: 农业出版社, 1987. | |
| 2 | Ma R C, Zhang H S, Mu L T, et al. Regional test of Hordeum bogdanii grass. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 1998, 21(4): 35-38. |
| 马瑞昌, 张鸿书, 木拉提, 等. 布顿大麦草区域试验. 新疆农业大学学报, 1998, 21(4): 35-38. | |
| 3 | Han D, Chen S H. Effects of diesel oil contaminated soil on reproductive growth of Hordeum bogdanii. Journal of Tarim University, 2021, 33(1): 106-112. |
| 韩丹, 陈水红. 柴油污染土壤对布顿大麦生殖生长的影响. 塔里木大学学报, 2021, 33(1): 106-112. | |
| 4 | Gao J H, Nan Z B. A review of bioprotective alkaloids of grass-fungal endophyte symbioses. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(6): 2531-2546. |
| 高嘉卉, 南志标. 禾草内生真菌生物碱的研究进展. 生态学报, 2007, 27(6): 2531-2546. | |
| 5 | Bongiorno V A, Rhoden S A, Garcia A, et al. Genetic diversity of endophytic fungi from Coffea arabica cv. IAPAR-59 in organic crops. Annals of Microbiology, 2016, 66(2): 855-865. |
| 6 | Chen S H, Cao Y, Chen T X, et al. Research process on the endophyte improving the grass’s salt and alkali resistance. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2018, 34(4): 35-42. |
| 陈水红, 曹莹, 陈泰祥, 等. 内生真菌提高禾草抗盐碱性研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34(4): 35-42. | |
| 7 | Tanaka A, Takemoto D, Chujo T, et al. Fungal endophytes of grasses. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2012, 15(4): 462-468. |
| 8 | Nan Z B. Incidence and distribution of endophytic fungi in seeds of some native and introduced grasses in China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 1996, 5(2): 1-8. |
| 南志标. 内生真菌在我国部分国产和引进禾草品种种子中的分布. 草业学报, 1996, 5(2): 1-8. | |
| 9 | Xu W L, Zhong H J, Liu X Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of tree architectures related CYC/TB1 family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiology Journal, 2021, 57(11): 2179-2191. |
| 徐文鸾, 钟函江, 刘杏月, 等. 茶树树型相关CYC/TB1家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 植物生理学报, 2021, 57(11): 2179-2191. | |
| 10 | Xiao Y L. Identification analysis and functional verification of TCP gene family in Chenopodium quinoa. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2021. |
| 肖玉林. 藜麦TCP基因家族鉴定分析与功能验证. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2021. | |
| 11 | Lan J Q, Qin G J. The molecular function and regulation of Class II TCP transcription factors. Chinese Science: Life Science, 2021, 51(11): 1542-1557. |
| 兰婧秋, 秦跟基. ClassⅡ TCP转录因子的主要功能和分子调控机制. 中国科学:生命科学, 2021, 51(11): 1542-1557. | |
| 12 | Bi C Y, Huang X F, Wang H S, et al. Identification of TCP transcription factors in Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. genome and expression analysis under stress. Plant Science Journal, 2021, 39(2): 163-172. |
| 毕楚韵, 黄小芳, 王和寿, 等. 甘薯基因组TCP转录因子鉴定与逆境胁迫表达分析. 植物科学学报, 2021, 39(2): 163-172. | |
| 13 | Wang M, Le Moigne M A, Bertheloot J, et al. BRANCHED1: A key hub of shoot branching. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 76. |
| 14 | Zhang S, Zhou Q, Chen F, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of TCP transcription factors in petunia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(18): 6594. |
| 15 | Doebley J, Stec A, Hubbard L. The evolution of apical dominance in maize. Nature, 1997, 386(6624): 485-488. |
| 16 | Finlayson S A. Arabidopsis teosinte branched 1-like 1 regulates axillary bud outgrowth and is homologous to monocot teosinte branched1. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2007, 48(5): 667-677. |
| 17 | Choi M S, Woo M O, Koh E B, et al. Teosinte branched 1 modulates tillering in rice plants. Plant Cell Reports, 2012, 31(1): 57-65. |
| 18 | Takeda T, Suwa Y, Suzuki M, et al. The OsTB1 gene negatively regulates lateral branching in rice. The Plant Journal, 2003, 33: 513-520. |
| 19 | Kebrom T H, Burson B L, Finlayson S A. Phytochrome B represses teosinte branched 1 expression and induces sorghum axillary bud outgrowth in response to light signals. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(3): 1109-1117. |
| 20 | Aguilar-Martínez J A, Poza-Carrión C, Cubas P. Arabidopsis BRANCHED1 acts as an integrator of branching signals within axillary buds. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(2): 458-472. |
| 21 | Li X J, Lin X Q, Liu H B, et al. Cloning and bioinformatics analysis of the TB1 gene in sugarcane. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2015, 36(11): 1978-1985. |
| 李旭娟, 林秀琴, 刘洪博, 等. 甘蔗TB1基因的克隆与生物信息学分析. 热带作物学报, 2015, 36(11): 1978-1985. | |
| 22 | Wang X J, Xiao R, Jiang L L, et al. Theory and medical application of real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Disease Surveillance and Control, 2013, 7(5): 284-286. |
| 王秀娟, 肖瑞, 姜丽丽, 等. 实时荧光定量PCR的原理及其医学应用. 疾病监测与控制, 2013, 7(5): 284-286. | |
| 23 | Li M, Li X, Zheng Z Q. Application and research progress of real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR technology. Feed Review, 2018(7): 94. |
| 李萌, 李雪, 郑志强. 实时荧光定量PCR技术的应用及研究进展. 饲料博览, 2018(7): 94. | |
| 24 | Li J Y, Zhao J N, Qin T, et al. Establishment of SYBR Green I real-time fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR for detection of vesicular stomatitis virus. Veterinary Science in China, 2022, 52(2): 152-161. |
| 李嘉阳, 赵佳男, 秦彤, 等. SYBR GreenⅠ实时荧光定量RT-PCR检测水泡性口炎病毒方法的建立. 中国兽医科学, 2022, 52(2): 152-161. | |
| 25 | Wang D T, Guo Q Q, Zhu H W, et al. Compare relative and absolute quantity PCR through sika deer P21 gene detection// Progress of Deer Scientific Research in ‘Twelfth Five-Year’. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2016: 672-676. |
| 王大涛, 郭倩倩, 朱宏伟, 等. 通过梅花鹿P21基因的检测比较相对和绝对荧光定量PCR//“十二五” 鹿科学研究进展. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2016: 672-676. | |
| 26 | Gong X H, Li Q, Tang J Y, et al. Establishment of quantitative real-time fluorescence PCR method for duck BMP4 gene. Proceedings of the 8th National Symposium on Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Young Scientific and Technological Workers. 2016, DOI:10.26914/c.cnkihy.2016.006524. |
| 宫晓华, 李琦, 唐井玉, 等. 鸭BMP4基因相对实时荧光定量PCR方法的建立. 第八届全国畜牧兽医青年科技工作者学术研讨会论文集.2016, DOI:10.26914/c.cnkihy.2016.006524. | |
| 27 | Liu J H. The expression level of active efflux system related genes and mechanism of multidrug resistance in E.coli isolated from ducks. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 刘建华. 鸭源大肠杆菌主动外排基因及其调控基因的表达水平与多重耐药机制. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2011. | |
| 28 | Wang T, Chen T X, Li C J. Advance on symbiosis mechanism of endophytic fungi and host grasses. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(12): 78-89. |
| 王添, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 内生真菌与宿主禾草共生机制的研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(12): 78-89. | |
| 29 | Han D, Mi J Y, Li X X, et al. Research progress on multi-factor regulation of crop tillering mechanism. Journal of Bohai University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 42(4): 325-332. |
| 韩丹, 米璟钰, 李晓霞, 等. 多因素调控作物促分蘖机理研究进展. 渤海大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(4): 325-332. | |
| 30 | He G H. Molecular regulatory mechanisms of wheat spike domestication traits and tillering. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2021. |
| 何冠华. 小麦穗部驯化性状与分蘖的分子调控机理. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. | |
| 31 | Liu Y, Wang Q S, Ding Y F, et al. Advances in mechanisms of tiller occurs in rice. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(3): 1-5. |
| 刘杨, 王强盛, 丁艳锋, 等. 水稻分蘖发生机理的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(3): 1-5. | |
| 32 | Liu Y, Ding Y F, Wang Q S, et al. Effect of hormones on the growth of rice tiller bud and the expression of the genes related to tiller growth. Plant Physiology Journal, 2011, 47(4): 367-372. |
| 刘杨, 丁艳锋, 王强盛, 等. 激素对水稻分蘖芽生长和分蘖相关基因表达的调控效应. 植物生理学报, 2011, 47(4): 367-372. | |
| 33 | Khush G S. Green revolution: Preparing for the 21st century. Genome, 1999, 42(4): 646-655. |
| 34 | Jin Q Y, Lin E P, Peng H Z, et al. Cloning and expression analyzing of TB1 homologous gene in Phyllostachys violascens. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2007, 43(8): 41-47. |
| 金群英, 林二培, 彭华正, 等. 早竹TB1同源基因的克隆和表达分析. 林业科学, 2007, 43(8): 41-47. | |
| 35 | Wang T, Zhao X D, Zhen P P, et al. Genome-wide identification and characteristic analyzation of the TCP transcription factors family in peanut. Crops, 2021, 37(2): 35-44. |
| 王通, 赵孝东, 甄萍萍, 等. 花生TCP转录因子的全基因组鉴定及组织表达特性分析. 作物杂志, 2021, 37(2): 35-44. | |
| 36 | Zhao Z R, Zhong R, Zhang X X. Effects of interaction of Epichloë gansuensis and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the seedling growth and cadmium (Cd) tolerance of Achnatherum inebrians. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(3): 432-443. |
| 赵振锐, 钟睿, 张兴旭. 内生真菌和丛枝菌根真菌互作对醉马草幼苗生长和镉耐性的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(3): 432-443. | |
| 37 | Shi C, Huang W, Wang C L. Effects of endophytic fungi on salt tolerance of Elymus dahuricus. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2016, 39(4): 277-280. |
| 施宠, 黄炜, 王纯利. 内生真菌对披碱草耐盐性的影响. 新疆农业大学学报, 2016, 39(4): 277-280. | |
| 38 | Nan Z B. Effects of Acremonium endophyte on the growth of Hordeum bodganii. Pratacultural Science, 1996, 13(1): 16-18. |
| 南志标. 内生真菌对布顿大麦草生长的影响. 草业科学, 1996, 13(1): 16-18. | |
| 39 | Li H Q, Wang J J, Zhang G M, et al. Effects of fungal endophytes on the growth of perennial ryegrass under drought condition. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(4): 599-607. |
| 李会强, 汪建军, 张光明, 等. 干旱条件下内生真菌对多年生黑麦草生长的影响. 草业科学, 2016, 33(4): 599-607. |
| [1] | 金媛媛, 陈振江, 王添, 李春杰. 内生真菌和田间管理措施对土壤真菌群落丰度和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 142-152. |
| [2] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 刘静, 金媛媛, 魏学凯. Epichloë内生真菌对禾草种子萌发影响研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 192-206. |
| [3] | 张鹏, 任茜, 孟思宇, 魏小星, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对盐胁迫下紫花针茅种子萌发和幼苗生长的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 110-121. |
| [4] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 王宏生, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对高寒草地紫花针茅凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 150-158. |
| [5] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 王正凤, 陈泰祥. 禾草-内生真菌人工接种技术研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 179-189. |
| [6] | 李淑琴, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 李秀璋, 慕彪彪, 李春杰. 基于CNKI数据库的禾草与非禾草内生真菌文献计量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 121-132. |
| [7] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [8] | 张若晨, 李涛, 姚祥, 陈振江, 李春杰. 基于Web of Science数据库禾草内生真菌生物碱论文计量统计分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 180-190. |
| [9] | 崔雪莲, 夏超. 外源脱落酸对醉马草内生真菌共生体幼苗建植过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 70-80. |
| [10] | 李秀璋, 宋辉, 张宗豪, 徐海峰, 刘欣, 李玉玲, 李春杰. 甘肃内生真菌基因组密码子使用的偏好性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 67-77. |
| [11] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 刘静, 王宏生. 不同密度甘肃马先蒿寄生和内生真菌互作对紫花针茅内源激素及生物碱含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 147-156. |
| [12] | 李柯, 施宠, 何飞焱, 李昊宇. Pb胁迫下内生真菌侵染对德兰臭草生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 112-120. |
| [13] | 何雅丽, 陈振江, 魏学凯, 张海娟, 刘阳, 刘辉, 李春杰. 喷施茉莉酮酸甲酯及感染内生真菌促进醉马草抗虫性的生理作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 121-129. |
| [14] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 李春杰. 甘肃马先蒿寄生对禾草内生真菌共生体共生关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 42-51. |
| [15] | 马碧花, 蔺伟虎, 高敏, 王兴迪, 田沛. 干旱胁迫下水杨酸和内生真菌对多年生黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 135-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||