

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 192-206.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020601
• 综合评述 • 上一篇
李春杰1,2( ), 郎鸣晓1, 陈振江1, 陈泰祥1, 刘静1, 金媛媛1, 魏学凯1
), 郎鸣晓1, 陈振江1, 陈泰祥1, 刘静1, 金媛媛1, 魏学凯1
收稿日期:2020-12-30
修回日期:2021-05-17
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-15
通讯作者:
李春杰
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: chunjie@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Chun-jie LI1,2( ), Ming-xiao LANG1, Zhen-jiang CHEN1, Tai-xiang CHEN1, Jing LIU1, Yuan-yuan JIN1, Xue-kai WEI1
), Ming-xiao LANG1, Zhen-jiang CHEN1, Tai-xiang CHEN1, Jing LIU1, Yuan-yuan JIN1, Xue-kai WEI1
Received:2020-12-30
Revised:2021-05-17
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-15
Contact:
Chun-jie LI
摘要:
种子是农业生产实践中最基本的生产资料,其萌发对植物物种的生存和繁衍起着决定性作用,但此过程易受到环境因素的影响,提高种子在胁迫环境下的萌发质量对禾草建植具有重要意义。Epichlo?内生真菌与禾草形成互惠共生关系,可促进共生体种子萌发并提高对环境胁迫抗性,使其在植物群落中占据优势生态位,因此对动植物及微生物生态系统产生广泛影响。将国内外关于Epichlo?属内生真菌在不同生境及处理下对宿主禾草种子萌发的影响进行综述,重点探讨Epichlo?属内生真菌对宿主禾草种子在正常生长条件和胁迫环境下的萌发及化感效应等方面的作用,发现内生真菌在正常萌发条件和胁迫环境中均能促进种子萌发,而在化感作用下萌发响应不一致,同时,内生真菌的侵染能显著缓解贮藏时间对种子萌发的负效应。通过对前人研究的总结,建议今后应加强对Epichlo?内生真菌促进禾草种子萌发及提高抗性生理生化等方面的研究,揭示内生真菌与禾草共生对种子萌发的影响机制,从而筛选出优良内生真菌菌株,以期利用内生真菌资源为禾草种质资源的创制开辟新途径。
李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 刘静, 金媛媛, 魏学凯. Epichloë内生真菌对禾草种子萌发影响研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 192-206.
Chun-jie LI, Ming-xiao LANG, Zhen-jiang CHEN, Tai-xiang CHEN, Jing LIU, Yuan-yuan JIN, Xue-kai WEI. Effects of Epichloë endophytic fungi on the germination of grass seeds[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 192-206.
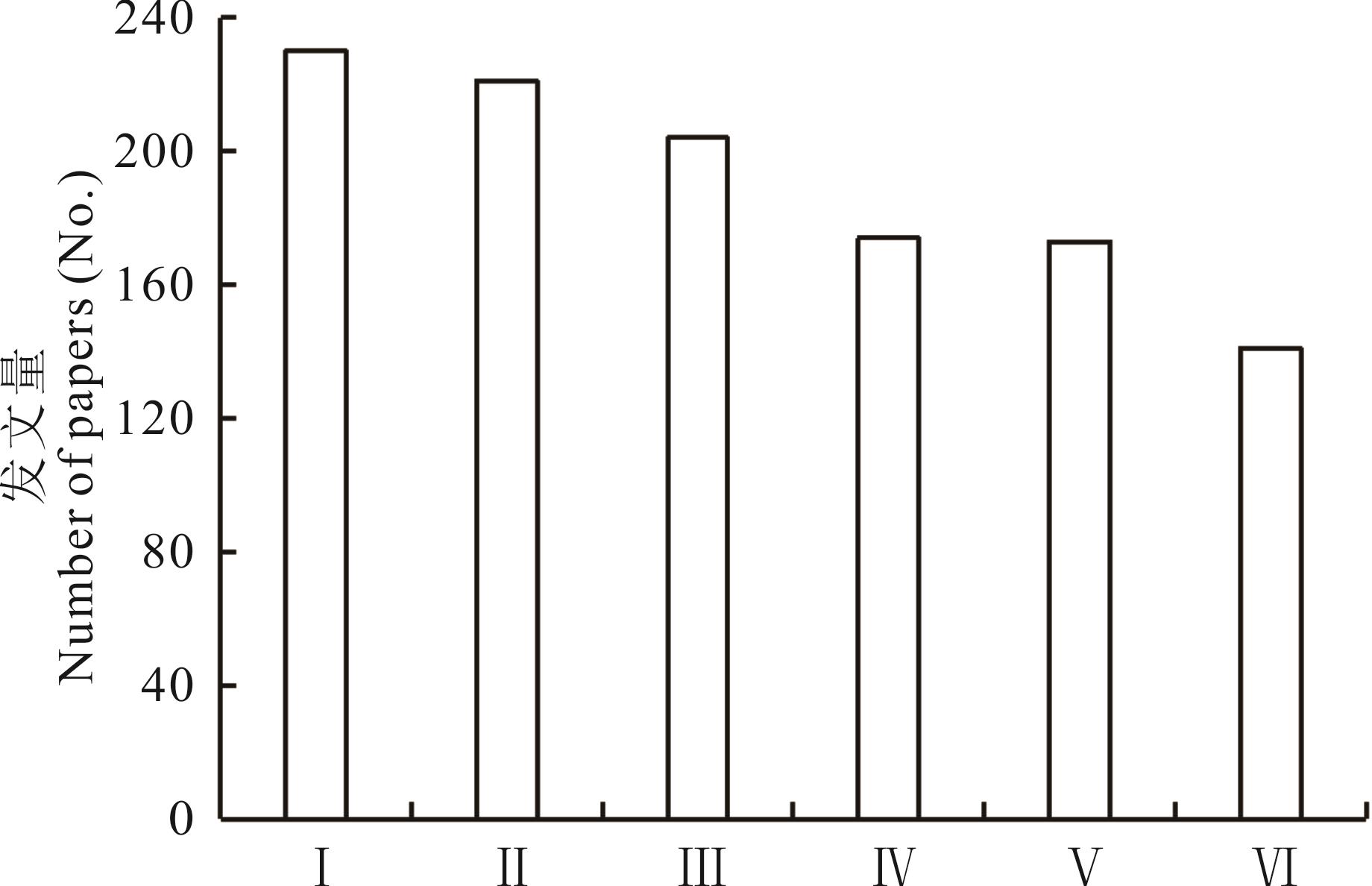
图1 国内外禾草内生真菌研究现状 (1977-2021年)Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ和Ⅵ分别表示共生体进化途径探索、对宿主抗性影响、分离鉴定及多样性研究、共生体产毒性的防控、对宿主生长影响和资源调查与群落影响。Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ and Ⅵ respectively indicate the exploration on the evolutionary pathway of symbionts, the influence on the resistance of the host, the separation and identification with the diversity, the improvement and control of toxicity, the influence on the growth of the host and the resource investigation with community influence.
Fig.1 Current research status of grass endophyte at China and abroad (1977-2021)
胁迫 Stress | 宿主 Host | 对宿主种子萌发的影响 Effect on seed germination of hosts | 参考文献 Reference | 备注 Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
渗透 Osmosis | 黑麦草L. perenne | E+相较于E-发芽率提高、发芽时间缩短。E+ has higher germination rate and shorter germination time than E-. | [ | |
| 鹅观草R. kamoji | E+相较于E-发芽率提高、发芽时间缩短。E+ has higher germination rate and shorter germination time than E-. | [ | ||
| 醉马草A. inebrians | E+发芽率和发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | E+发芽率低于E-。E+ germination rate is lower than E-. | [ | ||
酸碱 pH | 醉马草A.inebrians | E+发芽率、发芽势高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination potential are higher than E-. | [ | |
| 野大麦H. brevisubulatum | E+发芽势显著高于E-。E+ germination potential is significantly higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 中华羊茅F.sinensis | E+发芽率、发芽势高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination potential are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 黑麦草L. perenne | E+发芽率下降趋势更缓。E+ germination rate decreased more slowly. | [ | ||
盐分 Salt | 野大麦H. brevisubulatum | E+发芽率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | |
| 德兰臭草M. transsilvanica | E+与E-之间发芽率、相对萌发率与萌发指数差异显著。There are significant differences in germination rate, relative germination rate and germination index between E+ and E-. | [ | ||
| 醉马草A. inebrians | E+发芽率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 中华羊茅F.sinensis | E+萌发力及幼苗生长高于E-。E+ germination power and seedling growth are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 黑麦草L. perenne | E+萌发率、活力指数、苗长高于E-。E+ germination rate, vitality index and seedling length are higher than E-. | [ | ||
重金属 Heavy metal | 醉马草A.inebrians | E+种子对锰耐受力大于E-。E+ seeds are more resistant to Mn2+ than E-. | [ | 锰Mn |
| E+萌发率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | 镉Cd | ||
| 德兰臭草M.transsilvanica | 在高Pb浓度下,E+种子各项萌发指标高于E-。E+ germination parameters are higher than E- under high Pb concentration. | [ | 铅Pb | |
| E+发芽率、发芽势、活力指数高于E-。E+ germination rate, germination potential and vitality index are higher than E-. | [ | 镉Cd | ||
| 披碱草E. dahuricus | E+萌发率高于E-。E+ germination rate is higher than E-. | [ | 镉Cd | |
温度 Temperature | 野大麦H.brevisubulatum | 高温(30 ℃)和低温(10 ℃)胁迫下,E+发芽率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E- under high temperature (30 ℃) and low temperature (10 ℃) stress. | [ | |
| 中华羊茅F.sinensis | 5~30 ℃条件下E+发芽率、幼苗干重、胚芽生长高于E-,萌发时间小于E-。E+ germination rate, seedling dry weight, embryo growth are higher than E-, seed germination time is shorter than E- under 5-30 ℃. | [ | ||
| 醉马草A.inebrians | 10 ℃下E+发芽率高于E-。E+ germination rate is higher than E- under 10 ℃. | [ | ||
生物 Biology | 野大麦H.brevisubulatum | E+种子萌发指标高于E-。E+ germination parameters are higher than E-. | [ | # |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | E+萌发率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | ## |
表1 内生真菌对宿主在不同胁迫下种子萌发影响
Table 1 Effects of grass endophyte on seed germination of hosts under different stresses
胁迫 Stress | 宿主 Host | 对宿主种子萌发的影响 Effect on seed germination of hosts | 参考文献 Reference | 备注 Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
渗透 Osmosis | 黑麦草L. perenne | E+相较于E-发芽率提高、发芽时间缩短。E+ has higher germination rate and shorter germination time than E-. | [ | |
| 鹅观草R. kamoji | E+相较于E-发芽率提高、发芽时间缩短。E+ has higher germination rate and shorter germination time than E-. | [ | ||
| 醉马草A. inebrians | E+发芽率和发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | E+发芽率低于E-。E+ germination rate is lower than E-. | [ | ||
酸碱 pH | 醉马草A.inebrians | E+发芽率、发芽势高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination potential are higher than E-. | [ | |
| 野大麦H. brevisubulatum | E+发芽势显著高于E-。E+ germination potential is significantly higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 中华羊茅F.sinensis | E+发芽率、发芽势高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination potential are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 黑麦草L. perenne | E+发芽率下降趋势更缓。E+ germination rate decreased more slowly. | [ | ||
盐分 Salt | 野大麦H. brevisubulatum | E+发芽率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | |
| 德兰臭草M. transsilvanica | E+与E-之间发芽率、相对萌发率与萌发指数差异显著。There are significant differences in germination rate, relative germination rate and germination index between E+ and E-. | [ | ||
| 醉马草A. inebrians | E+发芽率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 中华羊茅F.sinensis | E+萌发力及幼苗生长高于E-。E+ germination power and seedling growth are higher than E-. | [ | ||
| 黑麦草L. perenne | E+萌发率、活力指数、苗长高于E-。E+ germination rate, vitality index and seedling length are higher than E-. | [ | ||
重金属 Heavy metal | 醉马草A.inebrians | E+种子对锰耐受力大于E-。E+ seeds are more resistant to Mn2+ than E-. | [ | 锰Mn |
| E+萌发率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | 镉Cd | ||
| 德兰臭草M.transsilvanica | 在高Pb浓度下,E+种子各项萌发指标高于E-。E+ germination parameters are higher than E- under high Pb concentration. | [ | 铅Pb | |
| E+发芽率、发芽势、活力指数高于E-。E+ germination rate, germination potential and vitality index are higher than E-. | [ | 镉Cd | ||
| 披碱草E. dahuricus | E+萌发率高于E-。E+ germination rate is higher than E-. | [ | 镉Cd | |
温度 Temperature | 野大麦H.brevisubulatum | 高温(30 ℃)和低温(10 ℃)胁迫下,E+发芽率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E- under high temperature (30 ℃) and low temperature (10 ℃) stress. | [ | |
| 中华羊茅F.sinensis | 5~30 ℃条件下E+发芽率、幼苗干重、胚芽生长高于E-,萌发时间小于E-。E+ germination rate, seedling dry weight, embryo growth are higher than E-, seed germination time is shorter than E- under 5-30 ℃. | [ | ||
| 醉马草A.inebrians | 10 ℃下E+发芽率高于E-。E+ germination rate is higher than E- under 10 ℃. | [ | ||
生物 Biology | 野大麦H.brevisubulatum | E+种子萌发指标高于E-。E+ germination parameters are higher than E-. | [ | # |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | E+萌发率、发芽指数高于E-。E+ germination rate and germination index are higher than E-. | [ | ## |
化感作用 Allelopathy | 宿主 Host | 作用作物 Acceptor | 影响 Effect | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
草粉及 浸提液 Forage powder and water extract | 披碱草 E.dahuricus | 高羊茅 F. arundinacea | E+草粉对高羊茅种子发芽率、发芽速度指数的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on germination rate and germination speed index of tall fescue seeds was higher than E-. | [ |
黑麦草 L. perenne | E+草粉对多年生黑麦草种子发芽率的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on germination rate of perennial ryegrass is higher than E-. | |||
草地早熟禾 P. pratensis | E+草粉对草地早熟禾种子发芽率的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on germination rate of Kentucky bluegrass seeds is higher than E-. | |||
羊草 L. chinensis | 克氏针茅 Stipa krylovii | 在低浓度下,E+绿叶和地下部分相较于E-显著促进克氏针茅的萌发,且草粉对克氏针茅种子萌发的抑制作用比浸提液处理更为显著。E+ green leaves and underground parts significantly promote germination of S. krylovii compare with E- under low concentration, and the inhibitory effect of grass powder on germination of S. krylovii seeds is more significant than extract treatment. | [ | |
醉马草 A.inebrians | 高羊茅 F. arundinacea | E+草粉相较于E-对高羊茅发芽率有促进作用。E+ grass meal promoted germination rate of tall fescue compared with E-. | [ | |
黑麦草 L. perenne | E+草粉对多年生黑麦草种子发芽率的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on the germination rate of perennial ryegrass is higher than E-. | |||
草地早熟禾 P. pratensis | E+草粉对草地早熟禾种子发芽率、芽长的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on the germination rate and bud length of P.pratensis seeds is higher than E-. | |||
中华羊茅 F.sinensis | 黑麦草 L. perenne | 不同地理种群E+与E-草粉对黑麦草的化感作用不同, 且不同受体植物对同一地理种群中华羊茅的表现不同。Different geographical populations of E+ and E- grass meal have different allelopathic effects on ryegrass, and different recipient plants have different performances on the same geographical population of F.sinensis. | [ | |
发酵液 Fermentation broth | 中华羊茅 F.sinensis | 中华羊茅 F. sinensis | 不同浓度的发酵液对种子萌发的各项指标起到不同程度的促进和抑制作用。Different concentrations of fermentation broth can promote and inhibit various indexes of germination to varying degrees. | [ |
挥发油 Volatile oil | 醉马草 A.inebrians | 黑麦草 L. perenne | E+挥发油对黑麦草种子萌发的抑制作用强于E-。E+ volatile oil has stronger inhibitory effect on ryegrass seed germination than E-. | [ |
伴生 Companion | 醉马草 A.inebrians | 针茅 S. capillata | E+伴生对针茅的发芽率、胚芽长的抑制作用显著大于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ on the germination rate and embryo length of S. capillata is higher than E-. | [ |
表2 内生真菌引起的不同化感作用对禾草种子萌发的影响
Table 2 Effects of different allelopathy caused by grass endophyte on germination of grass seeds
化感作用 Allelopathy | 宿主 Host | 作用作物 Acceptor | 影响 Effect | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
草粉及 浸提液 Forage powder and water extract | 披碱草 E.dahuricus | 高羊茅 F. arundinacea | E+草粉对高羊茅种子发芽率、发芽速度指数的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on germination rate and germination speed index of tall fescue seeds was higher than E-. | [ |
黑麦草 L. perenne | E+草粉对多年生黑麦草种子发芽率的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on germination rate of perennial ryegrass is higher than E-. | |||
草地早熟禾 P. pratensis | E+草粉对草地早熟禾种子发芽率的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on germination rate of Kentucky bluegrass seeds is higher than E-. | |||
羊草 L. chinensis | 克氏针茅 Stipa krylovii | 在低浓度下,E+绿叶和地下部分相较于E-显著促进克氏针茅的萌发,且草粉对克氏针茅种子萌发的抑制作用比浸提液处理更为显著。E+ green leaves and underground parts significantly promote germination of S. krylovii compare with E- under low concentration, and the inhibitory effect of grass powder on germination of S. krylovii seeds is more significant than extract treatment. | [ | |
醉马草 A.inebrians | 高羊茅 F. arundinacea | E+草粉相较于E-对高羊茅发芽率有促进作用。E+ grass meal promoted germination rate of tall fescue compared with E-. | [ | |
黑麦草 L. perenne | E+草粉对多年生黑麦草种子发芽率的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on the germination rate of perennial ryegrass is higher than E-. | |||
草地早熟禾 P. pratensis | E+草粉对草地早熟禾种子发芽率、芽长的抑制作用高于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ grass meal on the germination rate and bud length of P.pratensis seeds is higher than E-. | |||
中华羊茅 F.sinensis | 黑麦草 L. perenne | 不同地理种群E+与E-草粉对黑麦草的化感作用不同, 且不同受体植物对同一地理种群中华羊茅的表现不同。Different geographical populations of E+ and E- grass meal have different allelopathic effects on ryegrass, and different recipient plants have different performances on the same geographical population of F.sinensis. | [ | |
发酵液 Fermentation broth | 中华羊茅 F.sinensis | 中华羊茅 F. sinensis | 不同浓度的发酵液对种子萌发的各项指标起到不同程度的促进和抑制作用。Different concentrations of fermentation broth can promote and inhibit various indexes of germination to varying degrees. | [ |
挥发油 Volatile oil | 醉马草 A.inebrians | 黑麦草 L. perenne | E+挥发油对黑麦草种子萌发的抑制作用强于E-。E+ volatile oil has stronger inhibitory effect on ryegrass seed germination than E-. | [ |
伴生 Companion | 醉马草 A.inebrians | 针茅 S. capillata | E+伴生对针茅的发芽率、胚芽长的抑制作用显著大于E-。The inhibitory effect of E+ on the germination rate and embryo length of S. capillata is higher than E-. | [ |
| 1 | Schardl C L, Leuchtmann A, Spiering M J. Symbioses of grasses with seedborne fungal endophytes. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55(1): 315-340. |
| 2 | Schardl C L, Leuchtmann A, Chung K R, et al. Coevolution by common descent of fungal symbionts (Epichloë spp.) and grass hosts. Molecular, Biology and Evolution, 1997, 14(2): 133-143. |
| 3 | Clay K. Fungal endophytes of grasses: A defensive mutualism between plants and fungi. Ecology, 1998, 69(1): 10-16. |
| 4 | Li C J. Biological and ecological characteristics of Achnatherum inebrians/Neotyphodium endophyte symbiont. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2005. |
| 李春杰. 醉马草-内生真菌共生体生物学与生态学特性的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2005. | |
| 5 | Li H Q. Effects of endophyte on growth and drought resistance of perennial ryegrass. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2016. |
| 李会强.内生真菌对多年生黑麦草生长及抗旱性能的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016. | |
| 6 | Wang Z F, Li C J, White J. Effects of Epichloë endophyte infection on growth, physiological properties and seed germination of wild barley under saline conditions. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2020, 206(1): 43-51. |
| 7 | Chen Z J, Li C J, Nan Z B, et al. Segregation of Lolium perenne into a subpopulation with high infection by endophyte Epichloëfestucae var. lolii results in improved agronomic performance. Plant and Soil, 2020, 466: 595-612. |
| 8 | Chen N, He R L, Chai Q, et al. Transcriptomic analyses giving insights into molecular regulation mechanisms involved in cold tolerance by Epichloë endophyte in seed germination of Achnatherum inebrians.Plant Growth Regulation, 2016, 80(3): 367-375. |
| 9 | Zhang X X. Response of Achnatherum inebrians/Neotyphodium gansuense symbiont to stresses and secondary metabolites activities. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2012. |
| 张兴旭. 醉马草—内生真菌共生体对胁迫的响应及其次生代谢产物活性的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2012. | |
| 10 | Zhang X X. Effects of endophyte infection on pest resistance to drunken horse grass. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2008. |
| 张兴旭. 内生真菌对醉马草抗虫性影响的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2008. | |
| 11 | Xia C, Li N, Zhang X X, et al. An Epichloë, endophyte improves photosynthetic ability and dry matter production of its host Achnatherum inebrians, infected by Blumeria graminis, under various soil water conditions. Fungal Ecology, 2016, 22: 26-34. |
| 12 | Guo C H, Li X Z, Liu L, et al. Effect of the Epichloë endophyte on the soil nematode community in the rhizosphere of Achnatherum inebrians. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(4): 140-148. |
| 郭长辉, 李秀璋, 柳莉, 等. 内生真菌对醉马草根际土壤线虫群落的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 140-148. | |
| 13 | Xia C. Responses of Epichloё gansuensis-Achnatherum inebrians symbiont to drought stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2018. |
| 夏超. 醉马草-内生真菌共生体对干旱胁迫的响应. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018. | |
| 14 | Nan Z B, Li C J. Roles of the grass-Neotyphodium association in pastoral agriculture systems. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(3): 605-616. |
| 南志标, 李春杰. 禾草-内生真菌共生体在草地农业系统中的作用. 生态学报, 2004, 24(3): 605-616. | |
| 15 | Zhang J F. Effect of fungal endophyte on intraspecific competition of Elymus nutans under water stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013. |
| 张金锋.水分胁迫下内生真菌对垂穗披碱草种内竞争的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013. | |
| 16 | Bewley J D, Black M. Seed: Seed development and maturation. New York: Plenum Press, 1994. |
| 17 | Zhang H S, Hu J. Seed science. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. |
| 张红生, 胡晋. 种子学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. | |
| 18 | Ma H Y, Liang Z W. Effects of different soil pH and soil extracts on the germination and seedling growth of Leymus chinensis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(2): 181-188. |
| 马红媛, 梁正伟. 不同pH值土壤及其浸提液对羊草种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 植物学通报, 2007, 24(2): 181-188. | |
| 19 | Weitbrecht K, Muller K, Leubner M G. First off the mark: Early seed germination. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62: 3289-3309. |
| 20 | Liu H. Study on the resistance and utilization of Medicago sativa L. cv. “Zhongmu No.1”. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2004. |
| 刘华. 中苜一号紫花苜蓿抗逆性及其利用研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2004. | |
| 21 | Saikkonen K, Ahlholm J, Helander M, et al. Endophytic fungi in wild and cultivated grasses in Finland. Ecography, 2000, 23(3): 360-366. |
| 22 | Li C J, Lang M X, Chen Z J, et al. Advances in artificial inoculation technology for grass-endophytic fungi. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 179-189. |
| 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 等. 禾草-内生真菌人工接种技术研究进展. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 179-189. | |
| 23 | Philipson M N, Christey M C. The relationship of host and endophyte during flowering seed formation and germination of Lolium perenne. New Zealand Journal of Botany, 1986, 24: 125-134. |
| 24 | White J F, Morgen J G, Morrow A C. Taxonomy, life cycle, reproduction and detection of Acremonium endophytes. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 1993, 44(1/2/3/4): 13-37. |
| 25 | Pedroe E G, Pablo H M, Claudio M G. Effects of the Neotyphodium endophyte fungus on dormancy and germination rate of Lolium multiflorum seeds. Austral Ecology, 2006, 31(6): 767-775. |
| 26 | De Battista J P, Bouton J H, Bacon C W, et al. Rhizome and herbage production of endophyte-removed tall fescue clones and populations. Agronomy Journal, 1990, 82(4): 651-654. |
| 27 | Arachevaleta M, Bacon C W, Hoveland C S, et al. Effect of tall fescue endophyte on plant response to environmental stress. Agronomy Journal, 1989, 81(1): 83-90. |
| 28 | Ma B H, Lin W H, Gao M, et al. Effects of salicylic acid and Epichloë on perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1): 135-144. |
| 马碧花, 蔺伟虎, 高敏, 等. 干旱胁迫下水杨酸和内生真菌对多年生黑麦草的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 135-144. | |
| 29 | Malinowski D, Leuchtmann A, Schmidt D, et al. Growth and water status in meadow fescue is affected by Neotyphodium and Phialophora species endophytes. Journal of Agromedicine, 1997, 89: 673-678. |
| 30 | Ren A Z, Gao Y B, Gao W S. Effects of endophyte infection on seed germination, seeding growth and osmotic stress resistance of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2002(4): 420-426. |
| 任安芝, 高玉葆, 高文生. 内生真菌侵染对黑麦草种子萌发、幼苗生长及渗透胁迫抗性的影响. 植物生态学报, 2002(4): 420-426. | |
| 31 | White J R, Belanger F, Meyer W, et al. Clavicipitalean fungal epibionts and endophytes development of symbiotic interactions with plants. Symbiosis, 2002, 33: 201-213. |
| 32 | Clay K. Effects of fungal endophytes on the seed and seedling biology of Lolium perenne and Festuca arundinacea. Oecologia, 1987, 73(3): 358-362. |
| 33 | Zhou J L. Interaction of nitrogen and phosphorus supply and Epichloë bromicola on growth of wild barley. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 周景乐. 氮磷供应与内生真菌互作对野大麦生长的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 34 | Chen W, Liu H, Jiang N, et al. Physio-ecological effects of endophyte infection on tall fescue with elevated CO2 and nitrogen supply. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis, 2015, 48(4): 43-52. |
| 陈薇, 刘慧, 姜楠, 等. 不同CO2浓度和氮素处理下内生真菌感染对高羊茅的生理生态影响. 南开大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 48(4): 43-52. | |
| 35 | Pang M T. Effect on seed germination and proline metabolism of alfalfa seedlings under PEG stress. Taigu: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 庞妙甜. PEG胁迫对苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗脯氨酸代谢关键酶活性的影响. 太谷: 山西农业大学, 2016. | |
| 36 | Bu Y Y, Guo P, Ji Y L, et al. Effects of Epichloësinica on Roegneria kamoji seedling physiology under PEG-6000 simulated drought stress. Symbiosis, 2018, 77(2): 123-132. |
| 37 | Li X Z, Simpson W R, Song M L, et al. Effects of seed moisture content and Epichloë endophyte on germination and physiology of Achnatherum inebrians. South African Journal of Botany, 2020, 134(5): 407-414. |
| 38 | Ren A Z. Physiological-ecological mechanisms of endophyte effect on drought adaptation of Lolium perenne L. Tianjing: Nankai University, 2003. |
| 任安芝. 内生真菌对黑麦草抗旱性影响的生理生态机制研究. 天津: 南开大学, 2003. | |
| 39 | Bacon C W. Abiotic stress tolerances (moisture, nutrients) and photosynthesis in endophyte-infected tall fescue. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 1993, 44: 123-141. |
| 40 | Li C J, Yao X, Nan Z B. Advances in research of Achnatherum inebrians-Epichloë endophyte symboints. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 42(8): 793-805. |
| 李春杰, 姚祥, 南志标. 醉马草内生真菌共生体研究进展. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(8): 793-805. | |
| 41 | Song M L, Li C J, Peng Q Q, et al. Effects of Neotyphodium endophyte on germination of Hordeum brevisubulatum under temperature and water stress conditions. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(6): 833-837. |
| 宋梅玲, 李春杰, 彭清青, 等. 温度和水分胁迫下内生真菌对野大麦种子发芽的影响. 草地学报, 2010, 18(6): 833-837. | |
| 42 | Tang K, Zhu W W, Zhou W X, et al. Research progress on effects of soil pH on plant growth and development. Crop Research, 2013, 27(2): 207-212. |
| 唐琨, 朱伟文, 周文新, 等. 土壤pH对植物生长发育影响的研究进展. 作物研究, 2013, 27(2): 207-212. | |
| 43 | Zhao Y K, Zhang W S, Wang Y N, et al. Research progress in physiology and molecular biology of plant responses to high pH. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2008, 16(3): 783-787. |
| 赵彦坤, 张文胜, 王幼宁, 等. 高pH对植物生长发育的影响及其分子生物学研究进展.中国生态农业学报, 2008, 16(3): 783-787. | |
| 44 | Peng Q Q, Li C J, Song M L, et al. Effects of Neotyphodium endophytes on seed germination of three grass species under different pH conditions. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(5): 72-78. |
| 彭清青, 李春杰, 宋梅玲, 等. 不同酸碱条件下内生真菌对三种禾草种子萌发的影响. 草业学报, 2011, 20(5): 72-78. | |
| 45 | Chen Z J, Liu J, Wei X K, et al. Effects of latosols extracts with different pH and endophytic fungi on growth and physiology of Lolium perenne seedling. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2017, 37(7): 1348-1356. |
| 陈振江, 刘静, 魏学凯, 等. 不同pH砖红壤浸提液和内生真菌对黑麦草幼苗生长生理的影响. 西北植物学报, 2017, 37(7): 1348-1356. | |
| 46 | Wan Z W. Effect of temperature, illumination and pH factor on growth and contents of ergot alkaloids of Epichloë endophyte symbiotic Achnatherum inebrians. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 万志文. 温度、光照和pH对醉马草内生真菌共生体生长及麦角生物碱含量的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. | |
| 47 | Chen Z J, Jin Y Y, Yao X, et al. Fungal endophyte improves survival of Lolium perenne in low fertility soils by increasing root growth, metabolic activity and absorption of nutrients. Plant and Soil, 2020, 452(1/2): 185-206. |
| 48 | Cabot C, Sibole J V, Poschenrieder C. Lessons from crop plants struggling with salinity. Plant Science, 2014, 226(3): 2-13. |
| 49 | Shu K, Qi Y, Chen F, et al. Salt stress represses soybean seed germination by negatively regulating GA biosynthesis while positively mediating ABA biosynthesis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1-12. |
| 50 | Liu Y W, Yu Y, Fang J. Saline-alkali stress and molecular mechanism of saline-alkali tolerance in plants. Soils and Crops, 2018, 7(2): 201-211. |
| 刘奕媺, 于洋, 方军. 盐碱胁迫及植物耐盐碱分子机制研究. 土壤与作物, 2018, 7(2): 201-211. | |
| 51 | Zhang J J, An S Z, Shi C, et al. Effects of endophytic fungi on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of Melica transsilvanica under salt stress. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(2): 59-64. |
| 张晶晶, 安沙舟, 施宠, 等. 内生真菌侵染对盐胁迫下德兰臭草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(2): 59-64. | |
| 52 | Ahmad R Z, Khalid R, Aqeel M, et al. Fungal endophytes trigger Achnatherum inebrians germination ability against environmental stresses. South African Journal of Botany, 2020(134): 230-236. |
| 53 | Kuang Y, Nan Z B, Tian P. Effects of Epichloë endophyte and seed hydro-priming on the germination of Festuca sinensis under NaCl stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 160-168. |
| 旷宇, 南志标, 田沛. 内生真菌和水引发对NaCl胁迫条件下中华羊茅种子萌发的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 160-168. | |
| 54 | Zhang P P, Hu L X, Fu J M. Effects of endophytic fungi on seed germination of perennial ryegrass under salt stress. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(7): 1094-1099. |
| 张萍萍, 胡龙兴, 傅金民. 内生真菌侵染对盐胁迫下黑麦草种子萌发的影响. 草业科学, 2012, 29(7): 1094-1099. | |
| 55 | Zhang Y W. Effect of Epichloë endophyte on seed associated fungi and disease resistance of wild barley under salt stress conditions. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 张永雯. 内生真菌对野大麦种带真菌及其盐胁迫条件下抗病性的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 56 | Zhang X X, Nan Z B, Li C J. Research progress of improved resistance of the grass to the heavy metal stress by endophyte. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(8): 1466-1474. |
| 张兴旭, 南志标, 李春杰. 内生真菌提高禾草耐重金属胁迫的研究进展. 草业科学, 2014, 31(8): 1466-1474. | |
| 57 | Wan Z W, Wang P, Zhang X X, et al. Effect of manganese and SA on germination of Achnatherum inebrians seed containing or free of endophyte. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(1): 107-113. |
| 万志文, 王萍, 张兴旭, 等. 锰、水杨酸与内生真菌互作对醉马草种子萌发的影响. 草地学报, 2016, 24(1): 107-113. | |
| 58 | Li K, Shi C, Wang W Q, et al. Seed germination and growth effects of endophyte infection on Melica transsilvanica under Pb stress. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2020, 37(2): 280-286. |
| 李柯, 施宠, 王文全, 等. 重金属Pb胁迫下内生真菌侵染对德兰臭草种子萌发及生长的影响. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(2): 280-286. | |
| 59 | Li K, Shi C, Li H Y, et al. Seed germination and growth effects of endophyte infection on Melica transsilvanica under Cd stress. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(10): 1916-1926. |
| 李柯, 施宠, 李昊宇, 等. 重金属Cd胁迫下内生真菌感染对德兰臭草种子萌发及生长的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(10): 1916-1926. | |
| 60 | Yu H R, Li Q F, He Y M, et al. Effects of different temperature and light on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Clematis fruticosa Turcz. seed germination. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 549(9): 139-142, 146. |
| 于浩然, 李青丰, 贺一鸣, 等. 不同温度及光照对灌木铁线莲种子萌发生理生化特性的影响. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018, 549(9): 139-142, 146. | |
| 61 | Liu K, Baskin J M, Baskin C C, et al. Effect of diurnal fluctuating versus constant temperatures on germination of 445 species from the eastern Tibet Plateau. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e69364. |
| 62 | Peng Q Q. Effect of Neotyphodium endophyte on chilling tolerance to Festuca sinensis. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2012. |
| 彭清青. Neotyphodium内生真菌对中华羊茅耐寒性的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2012. | |
| 63 | Chen N. Molecular mechanism involved in low temperature resistance of endophyte infected drunken horse grass during seed germination. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2011. |
| 陈娜. 内生真菌提高醉马草低温萌发能力的分子机制. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2011. | |
| 64 | Li X Z, Yao X, Li C J, et al. Potential analysis of grass endophyte Neotyphodium as biocontrol agents. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(6): 621-634. |
| 李秀璋, 姚祥, 李春杰, 等. 禾草内生真菌作为生防因子的潜力分析. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(6): 621-634. | |
| 65 | Liu J. Studies on antifungal and insect-resistant activities and fermentation technology of Epichloë grass endophyte. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 刘静. 禾草内生真菌抑菌抗虫活性和发酵条件的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 66 | Ren A Z, Gao Y B. Plant endophytic fungi-a kind of resource microorganisms with broad application prospects. Microbiology China, 2001, 28(6): 90-93. |
| 任安芝, 高玉葆. 植物内生真菌-一类应用前景广阔的资源微生物. 微生物学通报, 2001, 28(6): 90-93. | |
| 67 | Li X Z, Song M L, Xiang Y, et al. The effect of seed-borne fungi and Epichloë endophyte on seed germination and biomass of Elymus sibiricus. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 2488. |
| 68 | Li C J, Gao J H, Nan Z B. Interactions of Neotyphodium ganauense, Achnatherum inebrians, and plant-pathogenic fungi. Mycological Research, 2007, 111(10): 1220-1227. |
| 69 | Li X Z. Study on the evolution and interactions of Epichloë gansuensis with host seed-borne fungi and rhizospheric microorganism. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 李秀璋. 醉马草内生真菌与宿主种带真菌、根际微生物的互作及其进化研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. | |
| 70 | Malinowski D P, Belesky D P. Adaptations of endophyte-infected cool-season grasses to environmental stresses: Mechanisms of drought and mineral stress tolerance. Crop Science, 2000, 40: 923-940. |
| 71 | Ma M Z, Christensen M J, Nan Z B. Effects of the endophyte Epichloëfestucae var. lolii of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) on indicators of oxidative stress from pathogenic fungi during seed germination and seedling growth. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2015, 141(3): 571-583. |
| 72 | Chen F, Meng Y J, Shuai H W, et al. Effect of plant allelochemicals on seed germination and its ecological significance. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(1): 36-46. |
| 陈锋, 孟永杰, 帅海威, 等. 植物化感物质对种子萌发的影响及其生态学意义. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(1): 36-46. | |
| 73 | Sun W H, Yu S W. Allelopathy and its potential application. Plant Physiology Communication, 1992, 28(2): 81-87. |
| 孙文浩, 余叔文. 相生相克效应及其应用. 植物生理学通讯, 1992, 28(2): 81-87. | |
| 74 | Farooq M, Jabran K, Cheema Z A, et al. The role of allelopathy in agricultural pest management. Pest Management Science, 2011, 67(5): 493-506. |
| 75 | Yang S, Li C J, Chai Q, et al. Allelopathic effects of Neotyphodium endophytes of Elymus dahuricus on seeds and seedlings of three turf grass species. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(4): 33-40. |
| 杨松, 李春杰, 柴青, 等. 披碱草内生真菌对三种草坪草种子与种苗的化感效应. 草业学报, 2010, 19(4): 33-40. | |
| 76 | Wu L J, Jing Y F, Ren A Z, et al. Effects of endophyte-infected Leymus chinensis on seed germination of Stipa krylovii. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(6): 669-674. |
| 吴连杰, 荆元芳, 任安芝, 等. 感染内生真菌的羊草对克氏针茅种子萌发的影响. 植物研究, 2012, 32(6): 669-674. | |
| 77 | Yang S, Huang X, Chai Q, et al. Allelopathic effects of endophytic fungi of Achnatherum inebrians Keng on the seed and seedling of three turf grasses. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(1): 78-83, 88. |
| 杨松, 黄玺, 柴青, 等. 醉马草内生真菌对3种草坪草种子与种苗的化感效应. 草地学报, 2010, 18(1): 78-83, 88. | |
| 78 | Li M M, Gu L J, Ma B H, et al. Effects of Festuca sinensis-endophyte symbiont on germination and seedling growth of Lolium perenne. Grassland and Turf, 2019, 39(1): 35-42. |
| 李苗苗, 古丽君, 马碧花, 等. 中华羊茅内生真菌共生体对多年生黑麦草种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 草原与草坪, 2019, 39(1): 35-42. | |
| 79 | Liu J, Zhou J L, Chen Z J, et al. Effect of seed soaking with Epichloë fermentation broth on germination characteristics in perennial ryegrass under drought stress. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(4): 839-847. |
| 刘静, 周景乐, 陈振江, 等. 内生真菌发酵液浸种对干旱胁迫下黑麦草种子萌发的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(4): 839-847. | |
| 80 | Wang Q Y. Effects of fermentation filtrate of Coniothyrium minitans on sunflower and the changes of SOD activity. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(12): 1274-1275, 1282. |
| 王庆云. 盾壳霉发酵物对向日葵的促生作用及SOD活性的影响. 山西农业科学, 2014, 42(12): 1274-1275, 1282. | |
| 81 | Zhong S, Wang W N, Zhou L Y, et al. Effect of fermentation liquid of Epichloë isolated from Festuca sinensis on seed germination. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(5): 736-739. |
| 钟松, 王文妮, 周连玉, 等. 中华羊茅内生真菌发酵液对种子萌发特性的影响.山西农业科学, 2017, 45(5): 736-739. | |
| 82 | Xia C, Zhong R, Zhang X X, et al. Allelopathic effects of volatile compounds from endophyte-free and infected Achnatherum inebrians on Lolium perenne. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 32(5): 658-666. |
| 夏超, 钟睿, 张兴旭, 等. 醉马草挥发油对多年生黑麦草种子萌发及幼苗生理变化的影响. 草业科学, 2015, 32(5): 658-666. | |
| 83 | Huang X, Li C J, Nan Z B, et al. Effects of Achnatherum inebrians infected with Neotyphodium endophyte on accompanying species of Stipa capillata and Poa sphondylodes. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(5): 87-93. |
| 黄玺, 李春杰, 南志标, 等. 醉马草内生真菌对其伴生种硬质早熟禾和针茅生长的影响. 草业学报, 2010, 19(5): 87-93. | |
| 84 | Peng S L, Shao H. Research significance and foreground of allelopathy. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001, 12(5): 780-786. |
| 彭少麟, 邵华. 化感作用的研究意义及发展前景. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(5): 780-786. | |
| 85 | Kong C H, Xu T, Hu F S. Study on interactions among allelochemicals of Ageratum conyzoides. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 1998, 22(5): 403-408. |
| 孔垂华, 徐涛, 胡飞胜. 胜红蓟化感物质之间相互作用的研究. 植物生态学报, 1998, 22(5): 403-408. | |
| 86 | Garbutt K, Williams W E, Bazzaz F A. Analysis of the differential response of five annuals to elevated CO2 during growth. Ecology, 1990, 71(3): 1185-1194. |
| 87 | Shi Z B, Zhou Y, Li X, et al. Physio-ecological effects of endophyte infection on the host grass with elevated CO2. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(19): 6135-6141. |
| 师志冰, 周勇, 李夏, 等. CO2浓度升高条件下内生真菌感染对宿主植物的生理生态影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(19): 6135-6141. | |
| 88 | Zhang X X, Li C J, Nan Z B. Interactive effect of storage time and endophytic fungi on seed physiology of Achnatherum inebrians (Hance) Ken. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(2): 252-257. |
| 张兴旭, 李春杰, 南志标. 内生真菌和保存时间互作对醉马草种子的生理影响. 草地学报, 2010, 18(2): 252-257. | |
| 89 | Jin W J, Li C J. Effect of storage time on the activity of endophytic fungi of Festuca sinensis. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2015, 31(6): 930-935. |
| 金文进, 李春杰. 保存时间对中华羊茅种子内生真菌活力的影响.中国生物防治学报, 2015, 31(6): 930-935. | |
| 90 | Hume D E, Card S D, Bylin A G, et al. Endophyte storage and seed germination of Epichloe-infected meadow fescue. Seed Science & Technology, 2016, 44(1): 138-155. |
| 91 | Li J L. Research progress in physiology and ecology of turfgrass resistance. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 2017. |
| 李建龙. 草坪草抗性生理与生态研究进展. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 2017. | |
| 92 | Shi Y. Effects of endophytic fungi on growth and development of plants. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2010(6): 36-38. |
| 石瑛. 内生真菌对植物生长发育的影响. 现代农业科技, 2010(6): 36-38. | |
| 93 | Dai M L, Wang P, Sun J K, et al. Research progress of saline-alkali stress effect on seeds’ germination and its physiological and biochemical mechanism. Northern Horticulture, 2015(10): 176-179. |
| 代明龙, 王平, 孙吉康, 等. 盐碱胁迫对植物种子萌发的影响及生理生化机制研究进展. 北方园艺, 2015(10): 176-179. | |
| 94 | Cai M F, Li K M, Xie D P, et al. The status and protection strategy of farmland soils polluted by heavy metals. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 37(120): 223-230. |
| 蔡美芳, 李开明, 谢丹平, 等. 我国耕地土壤重金属污染现状与防治对策研究. 环境科学与技术, 2014, 37(120): 223-230. | |
| 95 | Nancy V, Aleta M. Testing native species with deep dormancy. Seed and Technology, 2002, 24(1): 43-51. |
| 96 | Li C J, Wang Z F, Chen T X, et al. Creation of novel barley germplasm using an Epichloë endophyte. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(20): 2608-2617. |
| 李春杰, 王正凤, 陈泰祥, 等. 利用禾草内生真菌创制大麦新种质. 科学通报, 2021, 66(20): 2608-2617. | |
| 97 | Chen L. Molecular detection, genotypes and chemotypes of Epichloë endophytes in Achnatherum inebrians. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 陈丽. 醉马草内生真菌分子检测、基因型及产碱多样性的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015. |
| [1] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [2] | 白婕, 臧真凤, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 王可珍, 屈洋, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿叶片和根系膜脂过氧化及C、N特征对水分和N添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 213-220. |
| [3] | 陈金慧, 马慧燕, 陈煜, 何禾. 五爪金龙两种化感作用途径释放的化学成分分析及其效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 88-100. |
| [4] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [5] | 张家驹, 于洁, 李明娜, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才. 蒺藜苜蓿lncRNA167及其剪切产物miR167c的鉴定和功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 164-180. |
| [6] | 赵欣桐, 陈晓东, 李子吉, 张巨明, 刘天增. 植物内生肠杆菌对狗牙根耐盐性的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 127-136. |
| [7] | 吴路遥, 张建国, 常闻谦, 张少磊, 常青. 三种荒漠植物叶绿素荧光参数日变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 203-213. |
| [8] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [9] | 李欣航, 肖泽华, 匡雪韶, 王悟敏, 罗亮宇, 刘文胜. 锰胁迫下鸡眼草的富集特征及生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 139-147. |
| [10] | 柳福智, 张迎芳, 陈垣. 外源海藻糖对NaHCO3胁迫下甘草幼苗生长调节及总黄酮含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 148-156. |
| [11] | 王诗雅, 郑殿峰, 冯乃杰, 梁喜龙, 项洪涛, 冯胜杰, 王新欣, 左官强. 鼓粒期淹水胁迫对大豆叶片AsA-GSH循环的损伤及烯效唑的缓解效应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 157-166. |
| [12] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [13] | 包赛很那, 王向涛, 武俊喜, 苗彦军, 贾祥, 田彦婷. 苗期劲直黄芪根浸提液对8种西藏野生植物化感作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 211-220. |
| [14] | 彭磊, 张力, 周小龙, 万彦博, 师庆东. 水分胁迫对新疆准东地区钠猪毛菜的生活史对策的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 65-74. |
| [15] | 罗巧玉, 王彦龙, 陈志, 马永贵, 任启梅, 马玉寿. 水分逆境对发草脯氨酸及其代谢途径的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 75-83. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||