

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 110-121.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021492
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-12-28
修回日期:2022-03-21
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-09-14
通讯作者:
鲍根生
作者简介:E-mail: baogensheng2008@hotmail.com基金资助:
Peng ZHANG( ), Xi REN, Si-yu MENG, Xiao-xing WEI, Gen-sheng BAO(
), Xi REN, Si-yu MENG, Xiao-xing WEI, Gen-sheng BAO( )
)
Received:2021-12-28
Revised:2022-03-21
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-09-14
Contact:
Gen-sheng BAO
摘要:
紫花针茅是青海湖流域盐渍化危害严重的高寒草地优势禾草之一,天然草地中紫花针茅保持较高的内生真菌侵染率,内生真菌侵染能提高禾草耐盐能力,然而有关盐胁迫下,内生真菌提高紫花针茅种子萌发和幼苗生长的研究鲜有报道。以带菌(E+)和不带菌(E-)的紫花针茅种子为研究对象,研究不同浓度的单盐(NaCl、Na2SO4、Na2CO3、NaHCO3)和复合盐(NaCl+Na2CO3)胁迫对E+和E-种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响。结果表明:随盐浓度增加,紫花针茅种子发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数不断降低,而内生真菌的存在抑制了其下降趋势;幼苗和胚根生长抑制强度随盐浓度增加,且种子萌发相对盐害率也持续增加。Na2CO3和Na2SO4对紫花针茅种子萌发和幼苗生长产生的盐害较强。由此可见,内生真菌侵染是紫花针茅适应青海湖流域盐渍化土壤且成为高寒草原优势禾草的原因之一,这将为利用内生真菌-紫花针茅共生体进行盐碱地改良和耐盐禾草种质创新奠定了理论基础。
张鹏, 任茜, 孟思宇, 魏小星, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对盐胁迫下紫花针茅种子萌发和幼苗生长的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 110-121.
Peng ZHANG, Xi REN, Si-yu MENG, Xiao-xing WEI, Gen-sheng BAO. Effects of Epichloё endophyte on seed germination and seedling growth of Stipa purpurea under salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 110-121.
处理 Treatment | df | 发芽率Germination rate | 发芽势Germination power | 发芽指数Germination index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F (%) | P | F (%) | P | F | P | ||
| 带菌状态 Endophyte status (E) | 1 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 盐类型 Salt type (ST) | 5 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 盐浓度 Salt concentration (SC) | 2 | 1161.22 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||
| 带菌状态×盐类型 E×ST | 5 | 0.62 | 0.28 | <0.01 | |||
| 带菌状态×盐浓度 E×SC | 2 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 盐类型×盐浓度ST×SC | 10 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 带菌状态×盐浓度×盐类型E×SC×ST | 10 | <0.05 | 0.22 | <0.01 | |||
表1 内生真菌侵染、盐类型和盐浓度对紫花针茅种子发芽率、发芽势、发芽指数影响的三因素方差分析
Table 1 Results of three-way ANOVA for endophyte infection status (E), salt type (ST) and salt concentration (SC) on seed germination rate, germination power, germination index of S. purpurea
处理 Treatment | df | 发芽率Germination rate | 发芽势Germination power | 发芽指数Germination index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F (%) | P | F (%) | P | F | P | ||
| 带菌状态 Endophyte status (E) | 1 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 盐类型 Salt type (ST) | 5 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 盐浓度 Salt concentration (SC) | 2 | 1161.22 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||
| 带菌状态×盐类型 E×ST | 5 | 0.62 | 0.28 | <0.01 | |||
| 带菌状态×盐浓度 E×SC | 2 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 盐类型×盐浓度ST×SC | 10 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
| 带菌状态×盐浓度×盐类型E×SC×ST | 10 | <0.05 | 0.22 | <0.01 | |||
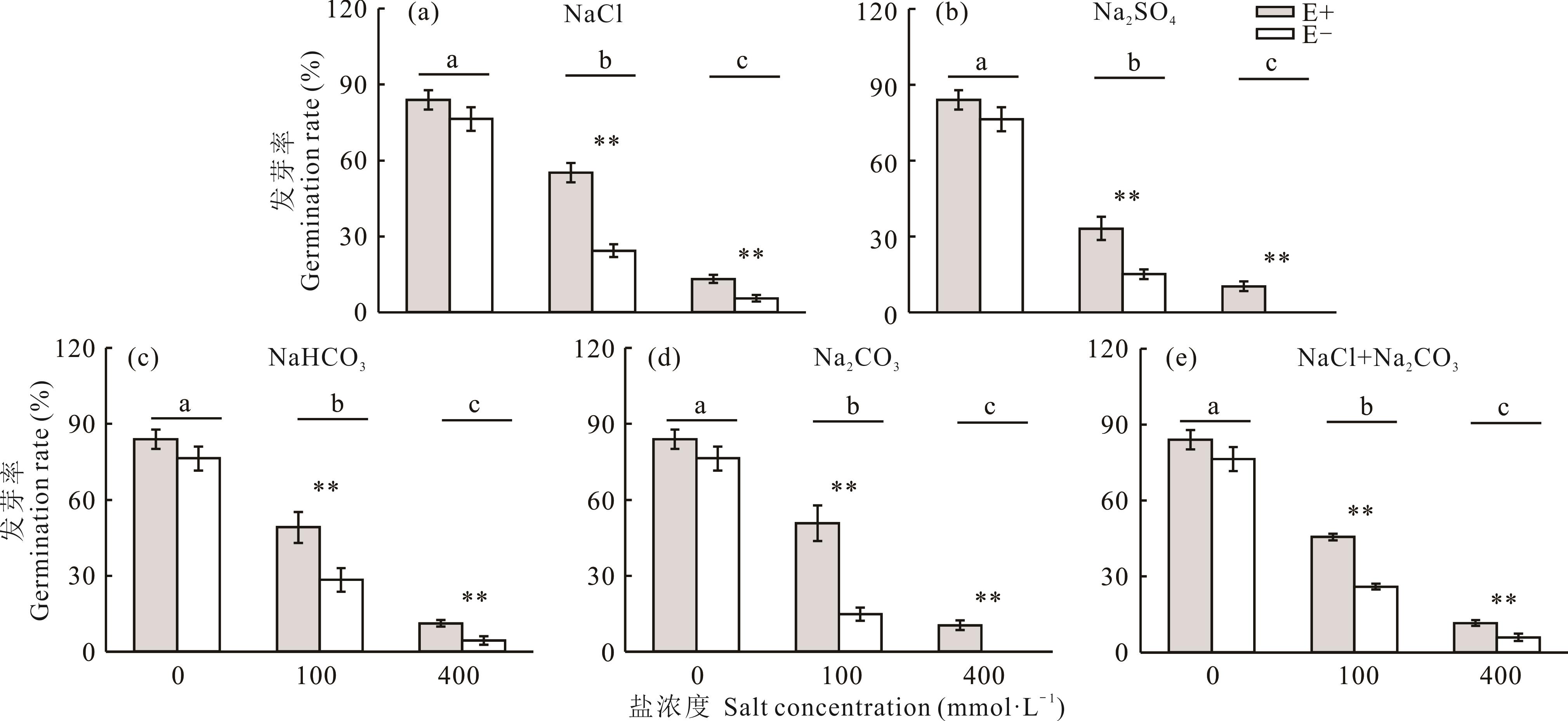
图1 单盐或复合盐对E+、E-紫花针茅种子发芽率的影响*和**表示紫花针茅E+、E-种子发芽率在相同盐浓度下差异分别达到显著(P<0.05)和极显著(P<0.01)水平。小写字母表示不同盐浓度下紫花针茅种子发芽率差异显著(P<0.05)。数据为平均值±标准误。下同。The lowercase letters indicate seed germination rate of E+ or E- S. purpurea was significant difference at P<0.05 level among the different salt concentration. * and ** indicate seed germination rate of S. purpurea significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 level, respectively (independent T-test), between E+ and E- under the same salt stress. The data presented are the mean±standard error. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of single or compound salts on seed germination rate of E+ and E- S. purpurea
处理 Treatment | df | 相对盐害率Relative salt damage rate | 幼苗高度Seedling height | 胚根长度Radicle length | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F (%) | P | F (mm) | P | F (mm) | P | ||
| 带菌状态 Endophyte status (E) | 1 | 184.23 | <0.01 | 82.03 | <0.01 | 365.87 | <0.01 |
| 盐类型 Salt type (ST) | 5 | 210.12 | <0.01 | 213.84 | <0.01 | 83.97 | <0.01 |
| 盐浓度 Salt concentration (SC) | 2 | 1309.83 | <0.01 | 1349.33 | <0.01 | 522.09 | <0.01 |
| 带菌状态×盐类型 E×ST | 5 | 14.90 | <0.01 | 1.32 | 0.26 | 19.55 | <0.01 |
| 带菌状态×盐浓度 E×SC | 2 | 48.70 | <0.01 | 13.55 | <0.01 | 122.02 | <0.01 |
| 盐类型×盐浓度ST×SC | 10 | 64.43 | <0.01 | 61.53 | <0.01 | 21.69 | <0.01 |
| 带菌状态×盐浓度×盐类型E× SC×ST | 10 | 14.48 | <0.01 | 1.67 | 0.09 | 4.99 | <0.01 |
表2 内生真菌侵染、盐类型和盐浓度对紫花针茅幼苗生长(幼苗高度和胚根长度)特性及相对盐害率影响的三因素方差分析
Table 2 Results of three-way ANOVA for endophyte infection status (E), salt type (ST) and salt concentration (SC) on relative salt damage rate, seedling height and radicle length of S. purpurea
处理 Treatment | df | 相对盐害率Relative salt damage rate | 幼苗高度Seedling height | 胚根长度Radicle length | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F (%) | P | F (mm) | P | F (mm) | P | ||
| 带菌状态 Endophyte status (E) | 1 | 184.23 | <0.01 | 82.03 | <0.01 | 365.87 | <0.01 |
| 盐类型 Salt type (ST) | 5 | 210.12 | <0.01 | 213.84 | <0.01 | 83.97 | <0.01 |
| 盐浓度 Salt concentration (SC) | 2 | 1309.83 | <0.01 | 1349.33 | <0.01 | 522.09 | <0.01 |
| 带菌状态×盐类型 E×ST | 5 | 14.90 | <0.01 | 1.32 | 0.26 | 19.55 | <0.01 |
| 带菌状态×盐浓度 E×SC | 2 | 48.70 | <0.01 | 13.55 | <0.01 | 122.02 | <0.01 |
| 盐类型×盐浓度ST×SC | 10 | 64.43 | <0.01 | 61.53 | <0.01 | 21.69 | <0.01 |
| 带菌状态×盐浓度×盐类型E× SC×ST | 10 | 14.48 | <0.01 | 1.67 | 0.09 | 4.99 | <0.01 |
| 1 | Wang Q Z, Liu Q, Gao Y N, et al. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. |
| 王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 等. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. | |
| 2 | Yang S, Zhang H X, Zhang L. Physiological and biochemical indices of salt tolerance and scanning of salt-tolerance plants: A Review. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2010, 25(3): 59-65. |
| 杨升, 张华新, 张丽. 植物耐盐生理生化指标及耐盐植物筛选综述. 西北林学院学报, 2010, 25(3): 59-65. | |
| 3 | Gong B. Study about the mechanism of nitrogen signal regulating salinity-alkalinity adaption and the function of SAMS and GSNOR in Solanum lycopersicum. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 巩彪. 氮信号调控番茄盐碱适应机理及SAMS和GSNOR基因的功能研究. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2014. | |
| 4 | Xu J, Chen Y J, Liu J Z. Research progress of the effects of halophyte shrubs on spatial distribution of soil nutrients and salts and their mechanisms. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(1): 19-23, 69. |
| 许婕, 陈永金, 刘加珍. 盐生植物灌丛对土壤养分和盐分空间分布的影响及其机制研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 2020, 48(1): 19-23, 69. | |
| 5 | Tang X Y, Zhang W Y, Gao Y T, et al. Comparative experiment on the shear strength of typical saline soil in eastern and western Qinghai. Journal of Qinghai University (Natural Science), 2021, 39(4): 58-65. |
| 唐雄宇, 张吾渝, 高义婷, 等. 青海东西部典型盐渍土抗剪强度对比试验研究. 青海大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 39(4): 58-65. | |
| 6 | Zhan Z Y, Xia Q X. Analysis of physicochemical properties and improvement methods of salinized soil in irrigation area along the Yellow River in Gansu Province. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 25(1): 85-86. |
| 展争艳, 夏庆鑫. 甘肃沿黄灌区盐渍化土壤理化性质分析及改良方法初探. 安徽农学通报, 2019, 25(1): 85-86. | |
| 7 | Porcel R, Aroca R, Ruiz-Lozano J M. Salinity stress alleviation using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2012, 32(1): 181-200. |
| 8 | Hui F Q. Preliminary study on effects and mechanisms of salt and drought resistance and heavy metals in Nicotiana tobacum conferred by Piriformospora indica. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014. |
| 惠非琼. 印度梨形孢对烟草耐盐、抗旱及重金属作用及机理的初步研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014. | |
| 9 | Li L, Wu H Q, Ma Z Y, et al. Growth promotion and salt tolerance induction by Piriformospora indica colonization in Medicago truncatula. Microbiology China, 2015, 42(8): 1492-1500. |
| 李亮, 武洪庆, 马朝阳, 等. 印度梨形孢促进蒺藜苜蓿生长及其提高耐盐性研究. 微生物学通报, 2015, 42(8): 1492-1500. | |
| 10 | Wang Y Y, Tong H Y, Zhou X X, et al. Effect of Piriformospora indica on salt resistance of Salvia leucantha seedlings. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 40(3): 54-59. |
| 汪云叶, 童虹宇, 周小雪, 等. 印度梨形孢对墨西哥鼠尾草抗盐性的影响. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(3): 54-59. | |
| 11 | Xu Y J, Zhao L F, Xing H F, et al. Effects of endophytic bacteria on proline and malondialdehyde of wheat seedlings under salt stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(11): 3726-3737. |
| 徐亚军, 赵龙飞, 邢鸿福, 等. 内生细菌对盐胁迫下小麦幼苗脯氨酸和丙二醛的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(11): 3726-3737. | |
| 12 | Huang L, Bao W K, Li F L, et al. Effects of soil structure and vegetation on microbial community. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2021. https://doi.org/10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2020.08001. |
| 黄龙, 包维楷, 李芳兰, 等. 土壤结构和植被对土壤微生物群落的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2021. https://doi.org/10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2020.08001. | |
| 13 | White J F, Kingsley K L, Zhang Q, et al. Endophytic microbes and their potential applications in crop management. Pest Management Science, 2019, 75(10): 2558-2565. |
| 14 | Riedell W E, Kieckhefer R E, Petroski R J, et al. Naturally-occurring and synthetic loline alkaloid derivatives: Insect feeding behavior modification and toxicity. Journal of Entomological Science, 1991, 26(1): 122-129. |
| 15 | Vignale M V, Astiz-Gassó M M, Novas M V, et al. Epichloid endophytes confer resistance to the smut Ustilago bullata in the wild grass Bromus auleticus (Trin.). Biological Control, 2013, 67(1): 1-7. |
| 16 | Gundel P E, Pérez L I, Helander M, et al. Symbiotically modified organisms: Nontoxic fungal endophytes in grasses. Trends in Plant Science, 2013, 18(8): 420-427. |
| 17 | Peng Q Q, Li C J, Song M L, et al. Effects of seed hydropriming on growth of Festuca sinensis infected with Neotyphodium endophyte. Fungal Ecology, 2013, 6(1): 83-91. |
| 18 | Siegel M R, Latch G C M, Johnson M C. Fungal endophytes of grasses. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1987, 25(1): 293-315. |
| 19 | Pereira S I A, Moreira H, Argyras K, et al. Promotion of sunflower growth under saline water irrigation by the inoculation of beneficial microorganisms. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 105: 36-47. |
| 20 | Al-Garni S M S. Increasing NaCl-salt tolerance of a halophytic plant Phragmites australis by mycorrhizal symbiosis. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Science, 2006, 1(2): 119-126. |
| 21 | Azad K, Kaminskyj S. A fungal endophyte strategy for mitigating the effect of salt and drought stress on plant growth. Symbiosis, 2016, 68: 73-78. |
| 22 | Ghaffari M R, Ghabooli M, Khatabi B, et al. Metabolic and transcriptional response of central metabolism affected by root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica under salinity in barley. Plant Molecular Biology, 2016, 90(6): 699-717. |
| 23 | Ouziad F, Wilde P, Schmelzer E, et al. Analysis of expression of aquaporins and Na+/H+ transporters in tomato colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and affected by salt stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(1/2): 177-186. |
| 24 | Vaishnav A, Shukla A K, Sharma A, et al. Endophytic bacteria in plant salt stress tolerance: Current and future prospects. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2019, 38(2): 650-668. |
| 25 | Chen Y Q, Su K Q, Chen T X, et al. Effects of complex saline-alkali stress on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of Achnatherum inebrians. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 等. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. | |
| 26 | Christensen M J, Bennett R J, Ansari H A, et al. Epichloë endophytes grow by intercalary hyphal extension in elongating grass leaves. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2008, 45(2): 84-93. |
| 27 | Wang X, Hu Y K, A D L, et al. Niche characteristics of Festuca ovina community in alpine meadow of Bayanbulak. Arid Land Geography, 2009, 32(2): 255-260. |
| 王鑫, 胡玉昆, 阿迪拉, 等. 巴音布鲁克高寒草原羊茅(Festuca ovina)群落生态位特征. 干旱区地理, 2009, 32(2): 255-260. | |
| 28 | Fan J P, Du J H, Liu W H, et al. The study on water soluble salt content of the surface soils horizon and main rivers in Qinghai Lake. Journal of Qinghai Normal University (Natural Science), 2001(3): 67-69. |
| 范建平, 杜军华, 刘文惠, 等. 青海湖湖滨土壤地表盐分总量及主要河流盐分含量的研究. 青海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2001(3): 67-69. | |
| 29 | Bao G S, Zhang X X, Li X Z, et al. Incidence and isolation of endophyte in native grasses of Qinghai Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 269(12): 1997-2007. |
| 鲍根生, 张兴旭, 李秀璋, 等. 青海高原禾草内生真菌资源的调查和分离. 草业科学, 2015, 269(12): 1997-2007. | |
| 30 | Li C J, Nan Z B, Liu Y, et al. Methodology of endophyte detection of drunken horse grass (Achnatherum inebrians)//Proceedings of Hangzhou Joint Annual Meeting of Chinese Society of Plant Diseases and Fungi. Hangzhou: Chinese Society of Plant Pathology, 2008: 21-24. |
| 李春杰, 南志标, 刘勇, 等. 醉马草内生真菌检测方法的研究//中国植病、菌物学会杭州联合年会论文集. 杭州: 中国植物病理学会, 2008: 21-24. | |
| 31 | Bao G S, Li C J. Isolation and identification of endophytes infecting Stipa purpurea, a dominant grass in meadows of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 128(3): 32-42. |
| 鲍根生, 李春杰. 青藏高原高寒草地优势禾草—紫花针茅内生真菌分离和鉴定. 草业学报, 2016, 128(3): 32-42. | |
| 32 | Bao G S, Wang Y Q, Song M L, et al. Effects of Pedicularis kansuensis parasitism on physiological characteristics of grass-Epichloë symbiont under different hemiparasite density. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2020, 60(3): 590-600. |
| 鲍根生, 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 等. 甘肃马先蒿不同寄生密度对紫花针茅内生真菌共生体生理特性的影响. 微生物学报, 2020, 60(3): 590-600. | |
| 33 | Diao Y M. Situation of water environment of Qinghai Lake andprotection measures. Yangtze River, 2014, 45(18): 33-36. |
| 刁玉美. 青海湖流域水环境状况分析及保护对策. 人民长江, 2014, 45(18): 33-36. | |
| 34 | Li Y M. Saline characteristics of soil salt and its components in Qaidam Basin. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2019(11): 72-75, 80. |
| 李月梅. 柴达木盆地细土平原带土壤盐分及其组成的盐渍特征. 中国农村水利水电, 2019(11): 72-75, 80. | |
| 35 | Wang Z F. Effects of endophyte infection on salt tolerance of wild barely (Hordeum brevisubulatum). Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2009. |
| 王正凤. 内生真菌对野大麦耐盐性影响的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2009. | |
| 36 | Li Q F, Yi J. Germination testing standardiaztion and seedling evaluation for twelve herbage seeds. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 1995(6): 39-43. |
| 李青丰, 易津. 牧草种子萌发检验标准化的研究. 中国草地, 1995(6): 39-43. | |
| 37 | Zhang L X, Chang Q S, Hou X G, et al. Effects of different sodium salt stress on seed germination of Prunella vulgaris. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(3): 177-186. |
| 张利霞, 常青山, 侯小改, 等. 不同钠盐胁迫对夏枯草种子萌发特性的影响. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 177-186. | |
| 38 | Li S J, Han D H, Wang E J, et al. Effects of exogenous betaine on seed germination and antioxidase activities of of Lycium ruthenium seedlings under NaCl stress. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(4): 674-680. |
| 李善家, 韩多红, 王恩军, 等. 外源甜菜碱对盐胁迫下黑果枸杞种子萌发和幼苗保护酶活性的影响. 草业科学, 2016, 33(4): 674-680. | |
| 39 | Dissanayaka D M S B, Nishida S, Tawaraya K, et al. Organ-specific allocation pattern of acquired phosphorus and dry matter in two rice genotypes with contrasting tolerance to phosphorus deficiency. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2018, 64(3): 282-290. |
| 40 | Yang Y Z, Yan H X, Zhao S W, et al. Effects of PEG-6000 mediated simulated drought on seed germination of Dianthus plumarius. Seed, 2020, 39(2): 11-14, 20. |
| 杨永志, 闫海霞, 赵淑文, 等. PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫对常夏石竹种子萌发的影响. 种子, 2020, 39(2): 11-14, 20. | |
| 41 | Jiang Y H, Liu Y, Xing B D, et al. Effects of salt stress on biological characters of potato seedling emergence and seedling stage. Chinese Potato Journal, 2021, 35(4): 326-333. |
| 江应红, 刘易, 邢斌德, 等. 盐胁迫对马铃薯出苗及苗期生物学性状的影响. 中国马铃薯, 2021, 35(4): 326-333. | |
| 42 | Blumwald E. Engineering salt tolerance in plants. Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews, 2003, 20(1): 261-276. |
| 43 | Zhang Z, Liu M, Liang Y, et al. The effects of salt stress on the growth of three cold-season turfgrass. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(5): 1877-1880. |
| 张志, 刘敏, 梁艳, 等. 盐胁迫对3种冷季型草坪草生长的影响. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(5): 1877-1880. | |
| 44 | Ma H, Xu X H, Jiang X W, et al. Effect of PEG priming on seed germination and vigor of turfgrass. Seed, 2006(11): 20-25, 30. |
| 马卉, 徐秀红, 江绪文, 等. PEG引发对草坪草种子萌发及活力的影响. 种子, 2006(11): 20-25, 30. | |
| 45 | Di G L, Wang J L, Shen Z B, et al. Effects of evaluation of alkali stress on Japonica rice growth in cold region. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021(8): 23-26. |
| 邸桂俐, 王建丽, 申忠宝, 等. 钠盐胁迫对锁链稗种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 黑龙江农业科学, 2021(8): 23-26. | |
| 46 | Lei C Y, Ji X M, Peng M Z, et al. Effects of sodium salinity stress types on the germination of Kalidium foliatum seeds and its young seedling growth. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(5): 1436-1441. |
| 雷春英, 吉小敏, 彭钼植, 等. 不同类型盐分对盐爪爪种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(5): 1436-1441. | |
| 47 | Di G L,Gao C, Han W B, et al. Effects of three kinds of salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Echinochloa crusgalli. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2021(18): 103-108. |
| 邸桂俐, 高超, 韩微波, 等. 三种盐胁迫对稗草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2021(18): 103-108. | |
| 48 | Xu M, Wang Q, Wang Y X, et al. Effects of different salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Elytrigia elongate. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(1): 15-20. |
| 徐曼, 王茜, 王奕骁, 等. 不同盐胁迫对长穗偃麦草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(1): 15-20. | |
| 49 | Yang Y H, Jian J J, Qiu X D, et al. Effects of combined saline-alkali stress on physiological and biochemical characteristics of lily. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2021: 1-11. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1161.S.20211206.1401.002.html. |
| 杨雨华, 鉴晶晶, 邱小蝶, 等. 复合盐碱胁迫对百合生长和生理特性的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021: 1-11. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1161.S.20211206.1401.002.html. | |
| 50 | Lu Y M, Su C Q, Li H F. Effects of different salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Trifolium repens. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(4): 123-129. |
| 卢艳敏, 苏长青, 李会芬. 不同盐胁迫对白三叶种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(4): 123-129. | |
| 51 | Yang J, An S Z, Dong Y Q, et al. Effects of degradation degree on modules growth and biomass allocation of Stipa purpurea population at flowering stage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2018, 40(4): 75-81. |
| 杨娇, 安沙舟, 董乙强, 等. 退化程度对紫花针茅花期种群构件生长及生物量分配的影响. 中国草地学报, 2018, 40(4): 75-81. | |
| 52 | Zhou Y L, Sun X D, Yang Y Q, et al. Expression of Stipa purpurea SpCIPK26 in Arabidopsis thaliana enhances salt and drought tolerance and regulates abscisic acid signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2016, 17(6): 966. |
| 53 | Zhang W, Zhang W H. Study on salt content characteristics and distribution law of saline soil in Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Geotechnical Engineering World, 2004, 7(10): 74-76. |
| 张文, 张卫红. 青藏高原盐渍土的含盐特征及分布规律研究. 岩土工程界, 2004, 7(10): 74-76. | |
| 54 | Zhai Y R, Chen Z J, Wei X K, et al. Potential analysis of wild barley endophytic fungal symbiont as an ecological grass. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(9): 1715-1725. |
| 翟纡润, 陈振江, 魏学凯, 等. 野大麦-内生真菌共生体作为生态草的潜力浅析. 草业科学, 2021, 38(9): 1715-1725. | |
| 55 | Chen Y Q, Su K Q, Li C J. Effects of NaCl stress on seed germination and seedling growth of two cold-season grasses. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(5): 870-879. |
| 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 李春杰. 盐胁迫对醉马草和高羊茅种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(5): 870-879. | |
| 56 | Gao M. Effects of Epichloё endophyte on salt tolerance of Festuca sinensis. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. |
| 高敏. 内生真菌对中华羊茅耐盐胁迫影响的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. | |
| 57 | Shi C, Huang W, Wang C L. Effects of endophytic fungi on salt tolerance of Elymus dahuricus. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2016, 39(4): 277-280. |
| 施宠, 黄炜, 王纯利. 内生真菌对披碱草耐盐性的影响. 新疆农业大学学报, 2016, 39(4): 277-280. | |
| 58 | Chen Z J. Study of low nitrogen stress tolerance on new breeding material of Lolium perenne Epichloё endophyte symbiont. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. |
| 陈振江. 多年生黑麦草内生真菌共生体新品系耐低氮胁迫的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. | |
| 59 | Zhang X X, Guo Q S, Shen X L. Effects of seed priming on salt tolerance in Prunella vulgaris seed germination under saline conditions. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2009, 34(8): 944-947. |
| 张贤秀, 郭巧生, 沈雪莲. 种子引发对夏枯草种子耐盐性的影响. 中国中药杂志, 2009, 34(8): 944-947. | |
| 60 | Foyer C H, Noctor G. Ascorbate and glutathione: The heart of the redox hub. Plant Physiology, 2011, 155(1): 2-18. |
| 61 | Song M L. Mechanisms of salt tolerance improved by Epichloё endophyte in wild barley. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2015. |
| 宋梅玲. 野大麦内生真菌共生体耐盐性的生理机制研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015. | |
| 62 | Christensen M J, Bennett R J, Ansari H A, et al. Epichloë endophytes grow by intercalary hyphal extension in elongating grass leaves. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2008, 45(2): 84-93. |
| 63 | Chen T X, White J F, Li C J. Fungal endophyte Epichloë bromicola infection regulates anatomical changes to account for salt stress tolerance in wild barley (Hordeum brevisubulatum). Plant Soil, 2021, 461(1): 533-546. |
| [1] | 谢文辉, 黄莉娟, 赵丽丽, 王雷挺, 赵文武. 钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 220-233. |
| [2] | 刘亚男, 于人杰, 高燕丽, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 武志海, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白MtANN2基因的表达模式及盐胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 124-134. |
| [3] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 刘静, 金媛媛, 魏学凯. Epichloë内生真菌对禾草种子萌发影响研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 192-206. |
| [4] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [5] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 王宏生, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对高寒草地紫花针茅凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 150-158. |
| [6] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生垂穗披碱草成苗期间的耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 76-85. |
| [7] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 王正凤, 陈泰祥. 禾草-内生真菌人工接种技术研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 179-189. |
| [8] | 李淑琴, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 李秀璋, 慕彪彪, 李春杰. 基于CNKI数据库的禾草与非禾草内生真菌文献计量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 121-132. |
| [9] | 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 王学琴, 姚姗. 盐胁迫对湖南稷子苗期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| [10] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [11] | 闫慧芳, 孙娟. 含水量和劣变时间对高丹草种子活力及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 152-160. |
| [12] | 汪芳珍, 杨成行, 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清. 盐处理下旱生植物沙芥蛋白激酶相关基因的差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 116-124. |
| [13] | 田甜, 王海江, 王金刚, 朱永琪, 史晓艳, 李维弟, 李文瑞玉. 盐胁迫下施加氮素对饲用油菜有机渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 125-136. |
| [14] | 张若晨, 李涛, 姚祥, 陈振江, 李春杰. 基于Web of Science数据库禾草内生真菌生物碱论文计量统计分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 180-190. |
| [15] | 高玉莲, 常静, 王贻卉, 李锋, 李海平, 马崇勇. 瑞香狼毒根提取物对3种作物种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 83-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||