

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 28-38.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023133
收稿日期:2023-04-24
修回日期:2023-05-29
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2023-12-12
通讯作者:
刘锦春
作者简介:E-mail: jinchun@swu.edu.cn基金资助:
Ying LEI( ), Jie LUO, Xu-man GUO, Er-ting BI, Jin-chun LIU(
), Jie LUO, Xu-man GUO, Er-ting BI, Jin-chun LIU( )
)
Received:2023-04-24
Revised:2023-05-29
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2023-12-12
Contact:
Jin-chun LIU
摘要:
深入探讨小生境尺度下物种多样性及其影响因素,可以为弃耕地演替早期群落恢复提供理论依据。本研究以重庆喀斯特典型弃耕地(弃耕年限为4~6年)为研究对象,根据地下特征选出均质浅土、均质深土、异质梯型和异质漏斗型4种小生境并对其进行植物群落调查,分析不同小生境的土壤理化性质、生物量和物种多样性变化及其之间的关系。结果表明:1) 4种小生境中土壤含水量随着土壤深度的增加呈增加趋势,但总氮含量和碳氮比随着土壤深度的增加呈降低趋势;在2种异质生境中,土壤深度、土壤含水率的变异系数相差不大,均属于高等变异强度。2) 不同小生境之间的物种丰富度指数、香农-维纳指数和均匀度指数无显著差异。3) 各小生境的地上生物量之间无显著差异,异质性生境的地下生物量和总生物量均高于均质性生境。4) 不同小生境中仅异质漏斗型的生物量与多样性存在显著负相关关系(P<0.05)。资源异质性对喀斯特弃耕地演替早期群落生物量产生了积极影响,但物种多样性在该阶段受生境的影响不大。中等厚度土壤促进了植物的生长、有利于生产力的维持。因此在植被恢复的早期阶段,应充分利用各生境类型特点,维持植物的多样性及其生长。
雷颖, 罗杰, 郭旭曼, 秘二停, 刘锦春. 小生境尺度下喀斯特弃耕地植物多样性、生物量及其影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 28-38.
Ying LEI, Jie LUO, Xu-man GUO, Er-ting BI, Jin-chun LIU. Microhabitat plant diversity and biomass differences in abandoned karst farmland and their driving factors[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(2): 28-38.
土壤理化性质 Soil physicochemical properties | 小生境类型 Niche type | 平均值 Average | 变异系数 CV |
|---|---|---|---|
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 均质浅土HoS | 5.00±0.00b | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 18.18±3.20ab | 0.79 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 25.80±2.67a | 0.55 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 30.00±0.00a | - | |
土壤含水量 Soil water content (%) | 均质浅土HoS | 9.89±1.84b | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 17.69±1.26a | 0.38 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 18.54±1.44a | 0.42 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 19.80±0.78a | - | |
土壤C含量 Total carbon content (mg·g-1) | 均质浅土HoS | 37.68±10.16a | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 17.33±0.94a | 0.20 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 15.11±0.55ab | 0.13 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 13.79±0.43b | - | |
土壤N含量 Total nitrogen content (mg·g-1) | 均质浅土HoS | 3.91±0.93a | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 2.26±0.07a | 0.12 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 2.04±0.05ab | 0.09 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 1.90±0.03b | - | |
碳氮比 Carbon nitrogen ratio | 均质浅土HoS | 9.57±0.59a | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 8.14±0.40b | 0.30 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 7.54±0.23bc | 0.26 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 7.29±0.18c | - |
表1 小生境的土壤有效性(平均值)和异质性(变异系数)(平均值±标准误)
Table 1 Soil availability (average) and heterogeneity (coefficient of variation) of different microhabitat (mean±SE)
土壤理化性质 Soil physicochemical properties | 小生境类型 Niche type | 平均值 Average | 变异系数 CV |
|---|---|---|---|
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 均质浅土HoS | 5.00±0.00b | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 18.18±3.20ab | 0.79 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 25.80±2.67a | 0.55 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 30.00±0.00a | - | |
土壤含水量 Soil water content (%) | 均质浅土HoS | 9.89±1.84b | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 17.69±1.26a | 0.38 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 18.54±1.44a | 0.42 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 19.80±0.78a | - | |
土壤C含量 Total carbon content (mg·g-1) | 均质浅土HoS | 37.68±10.16a | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 17.33±0.94a | 0.20 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 15.11±0.55ab | 0.13 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 13.79±0.43b | - | |
土壤N含量 Total nitrogen content (mg·g-1) | 均质浅土HoS | 3.91±0.93a | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 2.26±0.07a | 0.12 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 2.04±0.05ab | 0.09 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 1.90±0.03b | - | |
碳氮比 Carbon nitrogen ratio | 均质浅土HoS | 9.57±0.59a | - |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 8.14±0.40b | 0.30 | |
| 异质梯型HeT | 7.54±0.23bc | 0.26 | |
| 均质深土HoD | 7.29±0.18c | - |
| 土壤小生境Soil niche | 物种Species | 科Family | 重要值Important value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均质浅土 HoS | 千里光S. scandens | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.52 |
| 乌蔹莓C. japonica | 葡萄科Vitaceae | 0.40 | |
| 黄花蒿A. annua | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.36 | |
| 覆盆子Rubus idaeus | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 0.33 | |
| 土人参Talinum paniculatum | 马齿苋科Portulacaceae | 0.26 | |
| 异质漏斗型 HeF | 小蓬草C. canadensis | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.32 |
| 白茅I. cylindrica | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.29 | |
| 鸭跖草C. communis | 鸭跖草科Commelinaceae | 0.28 | |
| 酢浆草O. corniculata | 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 0.22 | |
| 乌蔹莓C. japonica | 葡萄科Vitaceae | 0.16 | |
| 异质梯型 HeT | 小蓬草C. canadensis | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.46 |
| 垂盆草S. sarmentosum | 景天科Crassulaceae | 0.24 | |
| 狗尾草S. viridis | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.23 | |
| 升马唐D. ciliaris | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.21 | |
| 艾Artemisia argyi | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.20 | |
| 均质深土 HoD | 小蓬草C. canadensis | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.40 |
| 升马唐D. ciliaris | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.36 | |
| 酢浆草O. corniculata | 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 0.24 | |
| 垂盆草S. sarmentosum | 景天科Crassulaceae | 0.14 | |
| 金色狗尾草Setaria pumila | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.12 |
表2 不同小生境中物种重要值排序(前5位)
Table 2 Order of important value of species in different microhabitats (top 5)
| 土壤小生境Soil niche | 物种Species | 科Family | 重要值Important value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均质浅土 HoS | 千里光S. scandens | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.52 |
| 乌蔹莓C. japonica | 葡萄科Vitaceae | 0.40 | |
| 黄花蒿A. annua | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.36 | |
| 覆盆子Rubus idaeus | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 0.33 | |
| 土人参Talinum paniculatum | 马齿苋科Portulacaceae | 0.26 | |
| 异质漏斗型 HeF | 小蓬草C. canadensis | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.32 |
| 白茅I. cylindrica | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.29 | |
| 鸭跖草C. communis | 鸭跖草科Commelinaceae | 0.28 | |
| 酢浆草O. corniculata | 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 0.22 | |
| 乌蔹莓C. japonica | 葡萄科Vitaceae | 0.16 | |
| 异质梯型 HeT | 小蓬草C. canadensis | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.46 |
| 垂盆草S. sarmentosum | 景天科Crassulaceae | 0.24 | |
| 狗尾草S. viridis | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.23 | |
| 升马唐D. ciliaris | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.21 | |
| 艾Artemisia argyi | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.20 | |
| 均质深土 HoD | 小蓬草C. canadensis | 菊科Asteraceae | 0.40 |
| 升马唐D. ciliaris | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.36 | |
| 酢浆草O. corniculata | 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 0.24 | |
| 垂盆草S. sarmentosum | 景天科Crassulaceae | 0.14 | |
| 金色狗尾草Setaria pumila | 禾本科Gramineae | 0.12 |
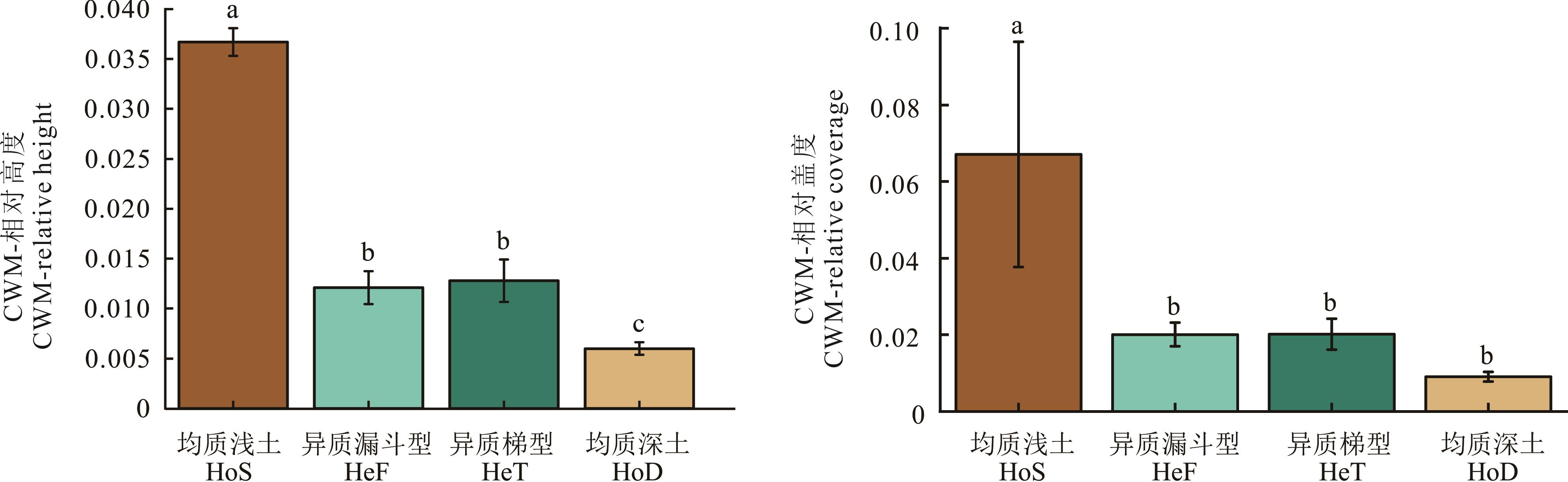
图4 不同小生境的群落加权功能性状均值(平均值±标准误)不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.4 The community-weighted mean traits of different microhabitats (mean±SE)
小生境类型 Soil niche type | 丰富度指数 Richness index | 香农-维纳指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 均匀度指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均质浅土HoS | 5.20±0.49a | 1.83±0.22a | 1.12±0.14a |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 6.50±0.68a | 1.96±0.16a | 1.08±0.06a |
| 异质梯型HeT | 7.15±0.60a | 1.99±0.18a | 1.02±0.06a |
| 均质深土HoD | 6.86±0.47a | 1.98±0.11a | 1.08±0.04a |
表3 不同小生境物种多样性指数(平均值±标准误)
Table 3 Species diversity indices in different microhabitats (mean±SE)
小生境类型 Soil niche type | 丰富度指数 Richness index | 香农-维纳指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 均匀度指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均质浅土HoS | 5.20±0.49a | 1.83±0.22a | 1.12±0.14a |
| 异质漏斗型HeF | 6.50±0.68a | 1.96±0.16a | 1.08±0.06a |
| 异质梯型HeT | 7.15±0.60a | 1.99±0.18a | 1.02±0.06a |
| 均质深土HoD | 6.86±0.47a | 1.98±0.11a | 1.08±0.04a |
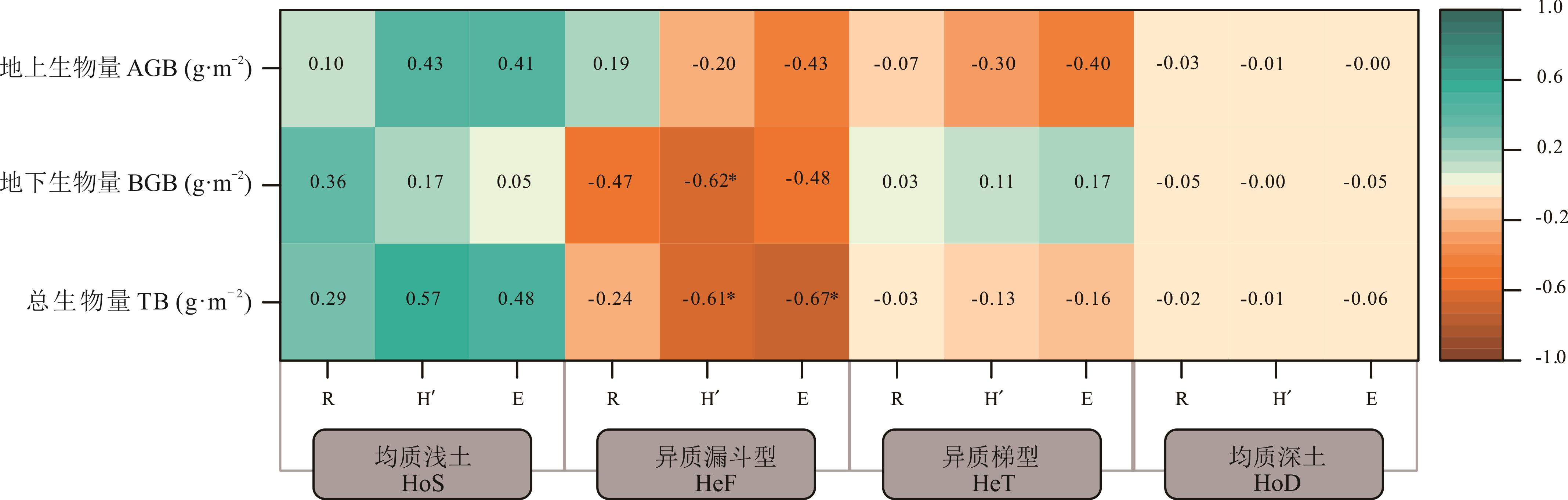
图6 不同小生境中生物量与多样性的相关性TB:总生物量, BGB:地下生物量,AGB:地上生物量;R:丰富度指数, H':香农-维纳指数, E:均匀度指数,*:P<0.05。TB: Total biomass, BGB: Belowground biomass, AGB: Above ground biomass, R: Richness index, H': Shannon-Wiener index, E: Pielou index, *:P<0.05.
Fig.6 The correlation of biomass and diversity under different microhabitats
| 1 | Zhang J Y, Zhao H L, Zhang T H, et al. Dynamics of species diversity of communities in restoration processes in Horqin sandy land. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2004, 28(1): 86-92. |
| 张继义, 赵哈林, 张铜会, 等. 科尔沁沙地植被恢复系列上群落演替与物种多样性的恢复动态. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(1): 86-92. | |
| 2 | Li L X, Wang R J, Gu B, et al. Changes in biodiversity during the succession of plant communities on the rocky slopes of mine in islands. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(7): 1741-1747. |
| 李林霞, 王瑞君, 辜彬, 等. 海岛矿区岩质边坡植物群落演替中物种多样性的变化. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(7): 1741-1747. | |
| 3 | Li Y Y, Shao M A. The change of plant diversity during natural recovery process of vegetation in Ziwuling area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004(2): 252-260. |
| 李裕元, 邵明安. 子午岭植被自然恢复过程中植物多样性的变化. 生态学报, 2004(2): 252-260. | |
| 4 | Li Z, Zhao Y J, Song H Y, et al. Effects of karst soil thickness heterogeneity on the leaf anatomical structure and photosynthetic traits of two grasses under different water treatments. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(2): 721-732. |
| 李周, 赵雅洁, 宋海燕, 等. 不同水分处理下喀斯特土层厚度异质性对两种草本叶片解剖结构和光合特性的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(2): 721-732. | |
| 5 | Yan X, Cai Y L. Multi-scale anthropogenic driving forces of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China. Land Degradation & Development, 2012, 26(2): 193-200. |
| 6 | Ma H Y, Zhang L L, Wei X Q, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of land use and vegetation cover in Southwest China from 2000 to 2015. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(2): 618-628. |
| 马海云, 张林林, 魏学琼, 等. 2000-2015年西南地区土地利用与植被覆盖的时空变化. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(2): 618-628. | |
| 7 | Chen Y, Wang S, Wang Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of cultivated land non-agriculturalization and its drivers in typical areas of Southwest China from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(13): 3211. |
| 8 | Zhang J, Li S H, Song H Y, et al. Growth and photosynthetic physiological responses of Lolium perenne L. to water stress in the simulated karst soil habitats. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 1240-1248. |
| 张静, 李素慧, 宋海燕, 等. 模拟喀斯特不同土壤生境下黑麦草对水分胁迫的生长和光合生理响应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1240-1248. | |
| 9 | Zhu S Q, Zhu X K, Yu L Z. Theory and practice of vegetation restoration in karst areas of Guizhou. Environmental Protection and Technology, 2000, 6(1): 31-35. |
| 朱守谦, 祝小科, 喻理正. 贵州喀斯特区植被恢复的理论和实践. 贵州环保科技, 2000, 6(1): 31-35. | |
| 10 | An M T. Studies on maintenance mechanism of plant species diversity and soil moisture and nutrient pattern in karst forest. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2019. |
| 安明态. 喀斯特森林土壤水分和养分格局及其植物物种多样性维持机制研究. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019. | |
| 11 | Li Y B, Wang S J, Tan Q, et al. Research development and problems of karst rocky desertification. Earth and Environment, 2006, 34(3): 9-14. |
| 李阳兵, 王世杰, 谭秋, 等. 喀斯特石漠化的研究现状与存在的问题. 地球与环境, 2006, 34(3): 9-14. | |
| 12 | Yang M D. On the fragility of karst environment. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 1990, 2(1): 21-29. |
| 杨明德. 论喀斯特环境的脆弱性. 云南地理环境研究, 1990, 2(1): 21-29. | |
| 13 | Zheng L, Long C L. Differences of plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties in Maolan karst forest under different topographic conditions. Guihaia, 2020, 40(6): 792-801. |
| 郑鸾, 龙翠玲. 茂兰喀斯特森林不同地形植物多样性与土壤理化特征研究. 广西植物, 2020, 40(6): 792-801. | |
| 14 | Du X L, Wang S J. Micro-habitat characteristics in the karst desertification area: A case study of the Wangjiazhai catchment in Guizhou Province. Earth and Environment, 2010, 38(3): 255-261. |
| 杜雪莲, 王世杰. 喀斯特石漠化区小生境特征研究——以贵州清镇王家寨小流域为例. 地球与环境, 2010, 38(3): 255-261. | |
| 15 | Tang Q, Ding F J, Zhu S X, et al. Effects of different vegetative succession stages on soil chemical properties and enzyme activities in karst region of Maolan. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(10): 1943-1952. |
| 汤茜, 丁访军, 朱四喜, 等. 茂兰喀斯特地区不同植被演替阶段对土壤化学性质与酶活性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(10): 1943-1952. | |
| 16 | Li S, Xue L, Wang J, et al. The dynamics of bare rock surface temperature, air temperature and relative humidity in karst rocky desertification area. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(2): 436-442. |
| 李生, 薛亮, 王佳, 等. 石漠化地区裸岩表面温度和空气温湿度动态变化. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(2): 436-442. | |
| 17 | Medinski T V, Mills A J, Esler K J, et al. Do soil properties constrain species richness? Insights from boundary line analysis across several biomes in south western Africa. Journal of Arid Environments, 2010, 74(9): 1052-1060. |
| 18 | Liu J T, Li S H, Song H Y, et al. Seed and fruiting phenology plasticity and offspring seed germination rate in two Asteraceae herbs growing in karst soils with varying thickness and water availability. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2022, 13(2): 319-327. |
| 19 | Zhang J, Wang J M, Chen J Y, et al. Soil moisture determines horizontal and vertical root extension in the perennial grass Lolium perenne L. growing in karst soil. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 629. |
| 20 | Heidrich L, Bae S, Levick S, et al. Heterogeneity-diversity relationships differ between and within trophic levels in temperate forests. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2020, 4(9): 1204-1212. |
| 21 | Šímová I, Li Y M, Storch D. Relationship between species richness and productivity in plants: the role of sampling effect, heterogeneity and species pool. Journal of Ecology, 2013, 101(1): 161-170. |
| 22 | Wang L, Liu C, Alves D G, et al. Plant diversity is associated with the amount and spatial structure of soil heterogeneity in meadow steppe of China. Landscape Ecology, 2015, 30(9): 1713-1721. |
| 23 | Baer S G, Adams T, Scott D A, et al. Soil heterogeneity increases plant diversity after 20 years of manipulation during grassland restoration. Ecological Applications, 2020, 30(1): e2014. |
| 24 | Rybicki J, Abrego N, Ovaskainen O. Habitat fragmentation and species diversity in competitive communities. Ecology Letters, 2020, 23(3): 506-517. |
| 25 | Phoutthavong K, Nakamura A, Cheng X, et al. Differences in pteridophyte diversity between limestone forests and non-limestone forests in the monsoonal tropics of southwestern China. Plant Ecology, 2019, 220(10): 917-934. |
| 26 | Wu J, Liu Z, Qian J. Non-linear effect of habitat fragmentation on plant diversity: Evidence from a sand dune field in a desertified grassland in northeastern China. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 54: 90-96. |
| 27 | Liu Y, Qi W C, He D N, et al. Soil resource availability is much more important than soil resource heterogeneity in determining the species diversity and abundance of karst plant communities. Ecology and Evolution, 2021, 11(23): 16680-16692. |
| 28 | Yu Y H, Zhong X P, Zheng W, et al. Species diversity, functional traits, stoichiometry and correlation of plant community in different succession stages of karst forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(6): 2408-2417. |
| 喻阳华, 钟欣平, 郑维, 等. 喀斯特森林不同演替阶段植物群落物种多样性、功能性状、化学计量及其关联. 生态学报, 2021, 41(6): 2408-2417. | |
| 29 | Li Z, Zhao Y J, Song H Y, et al. The effects of soil thickness heterogeneity on grassland plant community structure and growth of dominant species in karst area. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(10): 2023-2032. |
| 李周, 赵雅洁, 宋海燕, 等. 喀斯特土层厚度异质性对草地群落结构和优势种生长的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(10): 2023-2032. | |
| 30 | Filibeck G, Sperandii M G, Bazzichetto M, et al. Exploring the drivers of vascular plant richness at very fine spatial scale in sub-Mediterranean limestone grasslands (Central Apennines, Italy). Biodiversity and Conservation, 2019, 28(10): 2701-2725. |
| 31 | Zhang Y H, Xu X L, Li Z W, et al. Modelling soil thickness using environmental attributes in karst watersheds. Catena, 2022, 212: 106053. |
| 32 | Wei X, Bezemer T M, Berendse F. Soil heterogeneity and plant species diversity in experimental grassland communities: contrasting effects of soil nutrients and pH at different spatial scales. Plant Soil, 2019, 442(1/2): 497-509. |
| 33 | Ren X M. Quantitative classification of main plant communities and environmental explanation of species composition and richness in Taibai mountain, China. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2012. |
| 任学敏. 太白山主要植物群落数量分类及其物种组成和丰富度的环境解释. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. | |
| 34 | Jiang L, Wei C S, He Z S, et al. Functional trait variation of plant communities in canopy gaps of Castanopsis kawakamii natural forest. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(3): 267-279. |
| 江蓝, 魏晨思, 何中声, 等. 格氏栲天然林林窗植物群落功能性状的变异. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(3): 267-279. | |
| 35 | Ou Z Y, Zhu J Y, Peng Y H, et al. Relationship between plant diversity and environmental factors of Excentrodendron hsienmu community in karst mountatins in Pinguo County, Guangxi. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(2): 204-211. |
| 欧芷阳, 朱积余, 彭玉华, 等. 广西平果县喀斯特山地蚬木生存群落物种多样性与环境的关系. 植物研究, 2014, 34(2): 204-211. | |
| 36 | Guan X Y, Wang S L, Gao Z Y, et al. Spatio-temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(4): 1202-1210. |
| 管孝艳, 王少丽, 高占义, 等. 盐渍化灌区土壤盐分的时空变异特征及其与地下水埋深的关系. 生态学报, 2012, 32(4): 1202-1210. | |
| 37 | Zhao Y J, Zhang J, Song H Y, et al. Effects of different soil thickness, water and planting patterns on the litter mass loss and stoichiometry characteristics of two herbs in the karst regions. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(18): 6549-6558. |
| 赵雅洁, 张静, 宋海燕, 等. 不同土壤厚度、水分和种植方式对喀斯特两种草本凋落物分解质量损失和化学计量特征的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(18): 6549-6558. | |
| 38 | Yan Y J, Dai H Q, Li J, et al. Geometric morphology and soil properties of shallow karst fissures in an area of karst rocky desertification in SW China. Catena, 2019, 174: 48-58. |
| 39 | Tang Y Q, Zhang X H, Zhou J, et al. The mechanism of underground leakage of soil in karst rocky desertification areas-A case in Chenqi small watershed, Puding, Guizhou Province. Carsologica Sinica, 2010, 29(2): 121-127. |
| 唐益群, 张晓晖, 周洁, 等. 喀斯特石漠化地区土壤地下漏失的机理研究——以贵州普定县陈旗小流域为例.中国岩溶, 2010, 29(2): 121-127. | |
| 40 | Zhang L W, Mi X C, Harrison R D, et al. Resource heterogeneity, not resource quantity, plays an important role in determining tree species diversity in two species-rich forests. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 8: 224. |
| 41 | Peng X, Jin G Z. Effects of plant characteristics and environmental factors on the dark diversity in a broadleaved Korean pine forest. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(6): 656-666. |
| 彭鑫, 金光泽. 植物特性和环境因子对阔叶红松林暗多样性的影响. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(6): 656-666. | |
| 42 | Zhang W, Zhang J L, Mo B T, et al. The plant community species quantity trait and diversity analysis of the karst mountain grassland. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(5): 849-854. |
| 张文, 张建利, 莫本田, 等. 喀斯特山地草地植物群落物种数量特征及多样性分析. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(5): 849-854. | |
| 43 | Wang Z T. Study on characteristic of artificial vegetation on rocky side-slope in karst area of mid-Guizhou Province. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 王志泰. 黔中岩溶地区高速公路石质边坡人工植被特征研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2012. | |
| 44 | Zhang C, Zhang W, Chen H S, et al. Temporal and spatial variation in surface soil moisture content of karst slopes in the dry season. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(19): 6326-6334. |
| 张川, 张伟, 陈洪松, 等. 喀斯特典型坡地旱季表层土壤水分时空变异性. 生态学报, 2015, 35(19): 6326-6334. | |
| 45 | Tamme R, Hiiesalu I, Laanisto L, et al. Environmental heterogeneity, species diversity and co-existence at different spatial scales. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2010, 24(4): 796-801. |
| 46 | Craven D, Isbell F, Manning P, et al. Plant diversity effects on grassland productivity are robust to both nutrient enrichment and drought. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2016, 371(1694): 20150277. |
| 47 | He J S, Fang J Y, Ma K P, et al. Biodiversity and ecosystem productivity: Why is there a discrepancy in the relationship between experimental and natural ecosystems? Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2003(6): 835-843. |
| 贺金生, 方精云, 马克平, 等. 生物多样性与生态系统生产力: 为什么野外观测和受控实验结果不一致? 植物生态学报, 2003(6): 835-843. | |
| 48 | Xi N X, Zhang C H, Bloor J M G. Species richness alters spatial nutrient heterogeneity effects on above-ground plant biomass. Biology Letters, 2017, 13(12): 20170510. |
| 49 | Liu Y J, Li G E, Wang M X, et al. Effects of three-dimensional soil heterogeneity and species composition on plant biomass and biomass allocation of grass-mixtures. AOB Plants, 2021, 13(4): 33. |
| 50 | Loreau M. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: recent theoretical advances. Oikos, 2000, 91(1): 3-17. |
| 51 | Stevens M H H, Carson W P. Resource quantity, not resource heterogeneity, maintains plant diversity. Ecology Letters, 2002, 5(3): 420-426. |
| [1] | 张欢, 牟怡晓, 张桂杰. 添加枸杞副产物对紫花苜蓿青贮发酵品质及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 136-144. |
| [2] | 蒋翔, 马建霞. 我国草地生态恢复对不同因素响应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 14-31. |
| [3] | 罗楠, 舒英格, 陈梦军, 肖盛杨. 喀斯特山区不同草地土壤结构及分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 11-22. |
| [4] | 赵娜, 杨雪海, 陈芳, 郭万正, 李晓峰, 魏金涛, 陈明新, 周广生, 傅廷栋, 谭志平. 青贮饲用油菜对育肥期山羊瘤胃发酵参数及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 146-154. |
| [5] | 商振达, 谭占坤, 李家奎, 卓嘎, 王宏辉, 巴桑, 谢国平, 刘锁珠. 西藏地区荞麦与玉米混合青贮对发酵品质和微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 95-105. |
| [6] | 伍文宪, 张蕾, 黄小琴, 杨潇湘, 薛龙海, 刘勇. 川西北高寒牧区不同人工草地对土壤微生物多样性影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 29-41. |
| [7] | 任海伟, 刘菲菲, 王莉, 李志忠, 王昱, 孙安琪, 沈佳莉, 孙文斌, 余倩倩. 添加纤维素酶对干玉米秸秆与白菜废弃物混贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 158-167. |
| [8] | 曹铨, 沈禹颖, 王自奎, 张小明, 杨轩. 生草对果园土壤理化性状的影响研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 180-188. |
| [9] | 王静,胡靖,杜国祯. 施氮磷肥对青藏高原高寒草甸土壤线虫群落组成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(12): 20-28. |
| [10] | 苟燕妮, 南志标. 放牧对草地土壤微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 194-205. |
| [11] | 杨阳, 刘秉儒. 宁夏荒漠草原不同群落生物多样性与生物量关系及影响因子分析[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 48-57. |
| [12] | 蒲正宇,史军义,姚俊,杨玲,周德群. 昆明金殿国家森林公园蝶类多样性季节性变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(2): 109-116. |
| [13] | 赵彦光,洪琼花,谢萍,陈官平,王文华,李太荣,杨兴成,马宁. 云贵高原石漠化地区人工草场营养价值评价研究[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | 皇甫江云,毛凤显,卢欣石. 中国西南地区的草地资源分析[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1): 75-82. |
| [15] | 李馨,熊康宁,龚进宏,陈永毕. 人工草地在喀斯特石漠化治理中的作用及其研究现状[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(6): 279-286. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||