

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 159-169.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023338
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
魏娜1,3( ), 敬文茂1,3, 许尔文1,3, 王荣新1,3, 赵晶忠1,3, 马雪娥1,3, 张吉宇2, 刘文献2(
), 敬文茂1,3, 许尔文1,3, 王荣新1,3, 赵晶忠1,3, 马雪娥1,3, 张吉宇2, 刘文献2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-14
修回日期:2023-11-01
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-05-13
通讯作者:
刘文献
作者简介:E-mail: liuwx@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Na WEI1,3( ), Wen-mao JING1,3, Er-wen XU1,3, Rong-xin WANG1,3, Jing-zhong ZHAO1,3, Xue-e MA1,3, Ji-yu ZHANG2, Wen-xian LIU2(
), Wen-mao JING1,3, Er-wen XU1,3, Rong-xin WANG1,3, Jing-zhong ZHAO1,3, Xue-e MA1,3, Ji-yu ZHANG2, Wen-xian LIU2( )
)
Received:2023-09-14
Revised:2023-11-01
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
Wen-xian LIU
摘要:
干旱是农业生产中最常见的逆境胁迫之一,对植物的生长发育、光合作用、气孔开闭、渗透功能和激素调节等方面都会产生不良影响。白花草木樨在我国北方干旱地区广泛种植,是具有耐旱、耐盐碱、耐贫瘠和粗蛋白含量高等特点的优质牧草。转录因子(TF)作为调控基因表达的重要蛋白分子,可作用于其下游启动子区的特定顺式元件以激活或抑制基因的转录,进而调控植物生长发育及响应逆境。植物ERF转录因子家族基因参与植物对非生物胁迫的抗性,是作物抗逆性改良的理想候选基因。本研究对白花草木樨关键耐旱基因MaERF058进行烟草亚细胞定位分析,发现该基因表达蛋白定位于细胞核。干旱胁迫下,过表达MaERF058的拟南芥长势明显优于野生型。干旱条件下转MaERF058基因白花草木樨毛状根脯氨酸含量较对照显著(P<0.01)增加;丙二醛含量显著(P<0.01)降低;过氧化氢酶活性显著(P<0.05)增加;单胺氧化酶染色(NBT法)结果显示转基因毛状根的活性氧含量低于对照。以上结果表明白花草木樨MaERF058基因编码的转录因子对调控白花草木樨响应干旱胁迫具有积极作用。研究结果为解析白花草木樨耐旱分子机制提供了新思路,同时也能够为加快耐旱牧草分子育种提供优异基因资源。
魏娜, 敬文茂, 许尔文, 王荣新, 赵晶忠, 马雪娥, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 白花草木樨MaERF058基因耐旱功能验证[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 159-169.
Na WEI, Wen-mao JING, Er-wen XU, Rong-xin WANG, Jing-zhong ZHAO, Xue-e MA, Ji-yu ZHANG, Wen-xian LIU. Functional analysis of the MaERF058 gene in response to drought stress in Melilotus albus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(8): 159-169.
| 引物Primer | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MsERF058-F | AACCAATGCATTGGATGTACGGAAATAGTAAT |
| MsERF058-R | GGATCCCGTTAGGAAACCAATAACTGTCC |
| 35S-F | CTATCCTTCGCAAGACCCTTC |
| MsERF058-R1 | GGATCCCGTTAGGAAACCAATAACTGTCC |
| HPT-F | GGTCGCGGAGGCTATGGATGC |
| HPT-R | GCTTCTGCGGGCGATTTGTGT |
表1 试验中所用到的PCR引物
Table 1 PCR primers used in the experiment
| 引物Primer | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MsERF058-F | AACCAATGCATTGGATGTACGGAAATAGTAAT |
| MsERF058-R | GGATCCCGTTAGGAAACCAATAACTGTCC |
| 35S-F | CTATCCTTCGCAAGACCCTTC |
| MsERF058-R1 | GGATCCCGTTAGGAAACCAATAACTGTCC |
| HPT-F | GGTCGCGGAGGCTATGGATGC |
| HPT-R | GCTTCTGCGGGCGATTTGTGT |
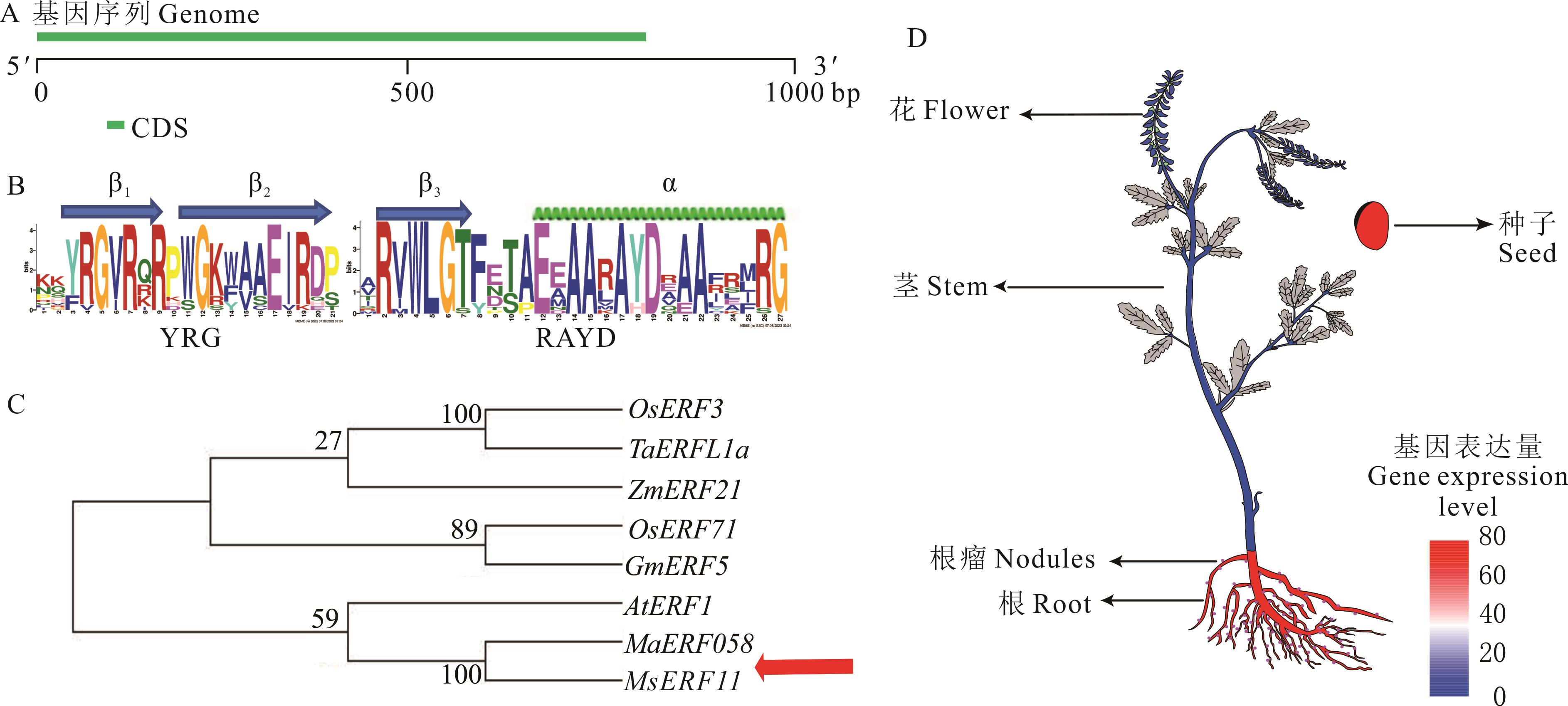
图 1 MaERF058序列和组织表达模式分析A: MaERF058 基因的结构分析Structural analysis of the MaERF058 gene; B: 草木樨ERF蛋白中AP2重复序列The AP2 repeat sequence in the ERF protein of M. albus; C: MaERF058及其他植物同源ERF基因的系统发育树Phylogenetic tree of MaERF058 and other plant homologous ERF genes; D: MaERF058组织表达模式分析The analysis of MaERF058 tissue expression pattern.
Fig. 1 Sequence and tissue expression pattern analysis of MaERF058

图2 MaERF058蛋白烟草表皮亚细胞定位GFP: 绿色荧光蛋白Green fluorescent protein; mCherry: 细胞核定位标记蛋白Nuclear localization protein; Merge: GFP, mCherry和明场叠加Merged images of GFP, mCherry, and bright field; 下同The same below.
Fig. 2 Subcellular localization of MaERF058 protein in tobacco epidermis

图3 MaERF058转基因拟南芥表达量鉴定Col-0: 野生型株系Wild-type; OE#1~13: 转基因拟南芥不同株系Different strains of transgenic Arabidopsis. 下同The same below.
Fig. 3 Identification of the expression level of MaERF058 transgenic Arabidopsis
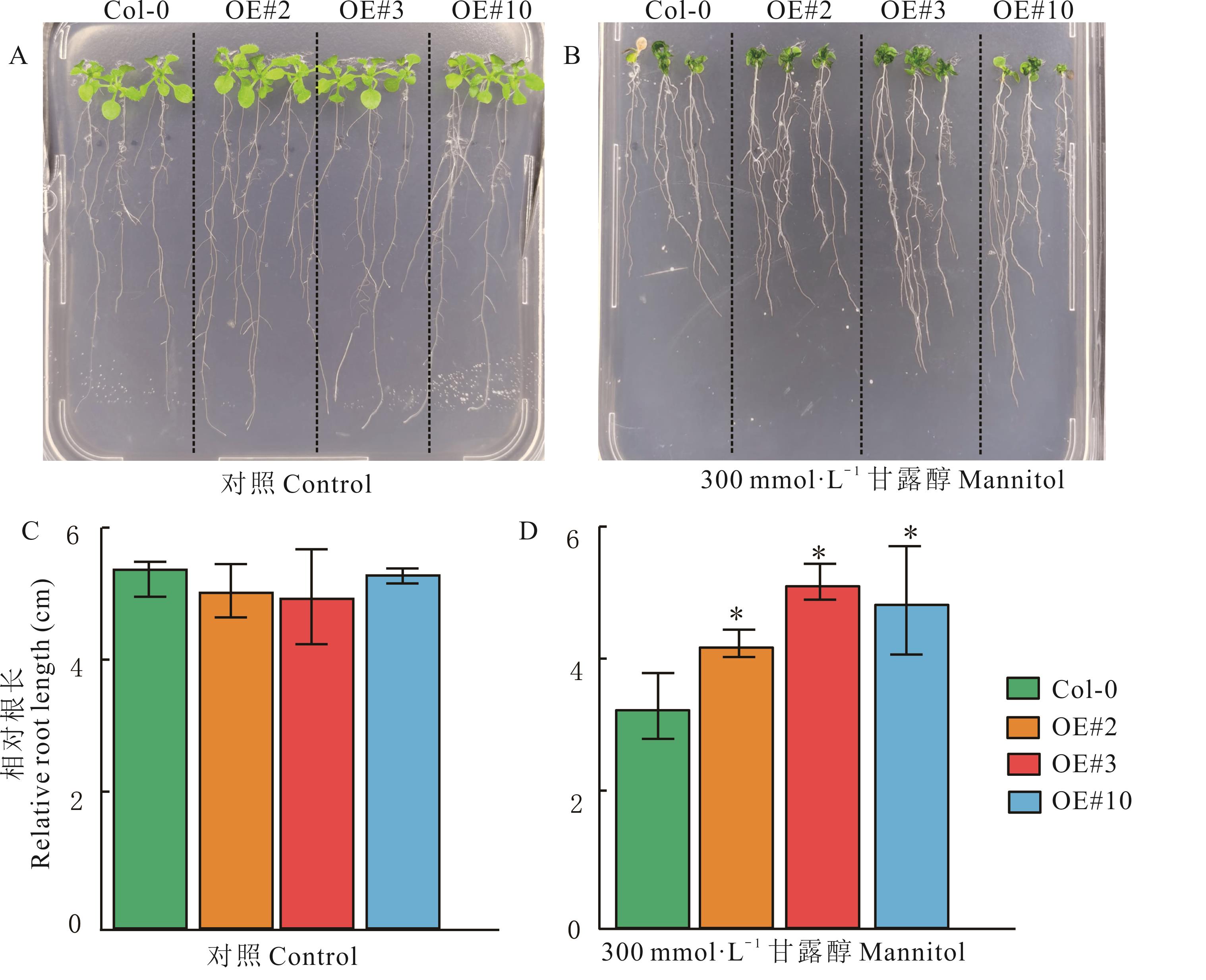
图4 干旱胁迫下MaERF058转基因拟南芥平板根长表型评价误差为3个生物学重复的标准误3 biological repeated standard errors; *: P<0.05; 下同The same below.
Fig. 4 Evaluation of plate root length phenotype of Arabidopsis transgenic MaERF058 under drought stress

图5 MaERF058瞬时转化毛状根PCR检测及绿色荧光蛋白检测A: 毛状根生长表型Hairy root growth phenotype; B:阳性毛状根检测The detection of positive hairy roots; M: Marker; -: 空白对照Blank control; +: PHG-MaERF058-EGFP载体质粒Vector plasmid; WT: 野生型Col-0; 1~8: 不同的阳性毛状根株系Different positive hairy root strains; C: 野生型和转基因毛状根绿色荧光蛋白检测The detection of green fluorescent protein in Col-0 and transgenic hairy roots. 下同The same below.
Fig. 5 PCR detection of MaERF058 transient transformation hairy root and green fluorescent protein detection
| 1 | Licausi F, Ohme-Takagi M, Perata P. APETALA 2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytologist, 2013, 199(3): 639-649. |
| 2 | Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(2): 411-432. |
| 3 | Riechmann J L, Heard J, Martin G, et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science, 2000, 290: 2105-2110. |
| 4 | Ohme-Takagi M, Shinshi H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. The Plant Cell, 1995, 7(2): 173-182. |
| 5 | Wei N, Zhai Q Y, Li H, et al. Genome-wide identification of ERF transcription factor family and functional analysis of the drought stress-responsive genes in Melilotus albus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(19): 12023. |
| 6 | Zhou Q, Li Y, Wang X, et al. Effects of different drought degrees on physiological characteristics and endogenous hormones of soybean. Plants, 2022, 11(17): 2282. |
| 7 | Cheng M, Liao P, Kuo W, et al. The Arabidopsis ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 regulates abiotic stress responsive gene expression by binding to different cis-acting elements in response to different stress signals. Plant Physiology, 2013, 162(3): 1566-1582. |
| 8 | Xu Z, Xia L, Chen M, et al. Isolation and molecular characterization of the Triticum aestivum L. ethylene-responsive factor 1 (TaERF1) that increases multiple stress tolerance. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(6): 719-732. |
| 9 | Quan R, Hu S, Zhang Z, et al. Overexpression of an ERF transcription factor TSRF1 improves rice drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2010, 8(4): 476-488. |
| 10 | Yang D, Zhou S, Quan R, et al. Mechanism of plant response to abiotic stresses regulated by AP2/ERF proteins. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2012, 14(6): 23-29. |
| 11 | Li Q, Jiang W, Jiang Z, et al. Transcriptome and functional analyses reveal ERF053 from Medicago falcata as key regulator in drought resistances. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 11(13): 995754. |
| 12 | Zhao M J, Yin L J, Liu Y, et al. The ABA-induced soybean ERF transcription factor gene GmERF75 plays a role in enhancing osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis and soybean. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 1-14. |
| 13 | Wang H, Ni D, Shen J, et al. Genome-wide identification of the AP2/ERF gene family and functional analysis of GmAP2/ERF144 for drought tolerance in soybean. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 28(13): 848766. |
| 14 | Stickler F C, Johnson I J. Dry matter and nitrogen production of legumes and legume associations in the fall of the seeding year 1. Agronomy Journal, 1959, 51(3): 135-137. |
| 15 | Ma Q D, Xu P, Li W J, et al. Method, effect and water-salt dynamics by furrow-ridge to emprove high salinized grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 1997, 5(2): 85-92. |
| 马其东, 许鹏, 李卫军, 等. 沟垄作种植牧草改良重盐渍草地的效果及其水盐动态. 草地学报, 1997, 5(2): 85-92. | |
| 16 | Cong J M, Chen F Q, Sun C L. Study on comprehensive development of Metlilotus suaverolens L. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(5): 2962-2963. |
| 丛建民, 陈凤清, 孙春玲. 草木樨综合开发研究. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(5): 2962-2963. | |
| 17 | Wu F. Study on whole genome sequencing and functional genes of key traits in Cleistogenes songorica and Melilotus albus. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. |
| 吴凡. 无芒隐子草和白花草木樨全基因组及其关键性状相关功能基因研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. | |
| 18 | Wu F, Duan Z, Xu P, et al. Genome and systems biology of Melilotus albus provides insights into coumarins biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(3): 592-609. |
| 19 | Hu L F, Liu S Q. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of the ERF gene family in cucumbers. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 2011, 34(4): 624-634. |
| 20 | Zhang Z S, Jin X Y, Liu Z P, et al. Genome-wide identification of FAD gene family and functional analysis of MsFAD3.1 involved in the accumulation of α-linolenic acid in alfalfa. Crop Science, 2021, 61(4): 566-579. |
| 21 | Bailey T L, Boden M, Buske F A, et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37: W202-W208. |
| 22 | Zong X, Wang S, Han Y, et al. Genome-wide profiling of the potential regulatory network of lncRNA and mRNA in Melilotus albus under salt stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2021, 189: 104548. |
| 23 | Chen J H, Liu W X. Construction and application of a graphic visualization tool for important forage omics data. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(2): 57-67. |
| 陈嘉慧, 刘文献. 重要牧草组学数据图形可视化展示工具的构建及应用. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 57-67. | |
| 24 | Wang Q X. Functional analysis of alfalfa SAP22 gene in response to drought stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. |
| 王秋霞. 紫花苜蓿SAP22的鉴定及响应干旱胁迫功能分析. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. | |
| 25 | Ma Y T. Identification of alfalfa-specific gene MsASG166 and analysis of its function in response to drought stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. |
| 马艺桐. 紫花苜蓿特有基因MsASG166的鉴定及响应干旱胁迫功能分析. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. | |
| 26 | Edwards D J, Grodevant N W, Lee P J, et al. DNA-MAN: dynamic natural attributes for synthetic military forces//IEEE systems and information engineering design symposium. IEEE, 2007, 1(1): 246-250. |
| 27 | Mao P. Identification of the WRKY gene family in Medicago sativa and functional analysis of MsWRKY100 gene in response to drought stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. |
| 毛培. 紫花苜蓿WRKY基因家族鉴定及MsWRKY100基因耐旱功能研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. | |
| 28 | Wang S S, Duan Z, Zhang J Y. Establishment of hairy root transformation system of Melilotus albus induced by Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2591-2599. |
| 王升升, 段珍, 张吉宇. 发根农杆菌介导的白花草木樨毛状根转化体系的建立.草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2591-2599. | |
| 29 | Luo K, Jahufer M Z Z, Wu F, et al. Genotypic variation in a breeding population of yellow sweet clover (Melilotus officinalis). Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 00972. |
| 30 | Duan Z, Wang S, Zhang Z, et al. The MabHLH11 transcription factor interacting with MaMYB4 acts additively in increasing plant scopolin biosynthesis. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(6): 1675-1685. |
| 31 | Okamuro J K, Caster B, Villarroel R, et al. The AP2 domain of APETALA2 defines a large new family of DNA binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1997, 94(13): 7076-7081. |
| 32 | Faraji S, Filiz E, Kazemitabar S K, et al. The AP2/ERF gene family in Triticum durum: genome-wide identification and expression analysis under drought and salinity stresses. Genes, 2020, 11(12): 1464. |
| 33 | Ohama N, Sato H, Shinozaki K, et al. Transcriptional regulatory network of plant heat stress response. Trends in Plant Science, 2017, 22(1): 53-65. |
| 34 | Ding S, Cai Z, Du H, et al. Genome-wide analysis of TCP family genes in Zea mays L. identified a role for ZmTCP42 in drought tolerance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(11): 2762. |
| 35 | Lou X, Yao S, Chen P, et al. Transcriptome identification of R2R3-MYB gene family members in Pinus massoniana and PmMYB4 response to drought stress. Forests, 2023, 14(2): 410. |
| 36 | Yang S, Zhu H, Huang L, et al. Transcriptome-wide and expression analysis of the NAC gene family in pepino (Solanum muricatum) during drought stress. PeerJ, 2021, 9: e10966. |
| 37 | Jin Y, Pan W Y, Zheng X F, et al. OsERF101, an ERF family transcription factor, regulates drought stress response in reproductive tissues. Plant Molecular Biology, 2018, 98: 51-65. |
| 38 | Long H Y, Deng L X. Response and adaptation of plant morphology to drought stress. Hubei Agricultural Science, 2019, 58(8): 5-7. |
| 龙海燕, 邓伦秀. 植物形态对干旱胁迫的反应与适应性研究. 湖北农业科学, 2019, 58(8): 5-7. | |
| 39 | Song C P, Agarwal M, Onta M, et al. Role of an Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP-type transcriptional repressor in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. The Plant Cell, 2005, 17(8): 2384-2396. |
| 40 | Zhang H B, Li W Z, Chen J, et al. Transcriptional activator TSRF1 reversely regulates pathogen resistance and osmotic stress tolerance in tobacco. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 63(1): 63-71. |
| 41 | Shen H Y, Xiong H C, Guo X T, et al. A new method of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation in peanut plants. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2012, 18(2): 518-522. |
| 申红芸, 熊宏春, 郭笑彤, 等. 一种发根农杆菌介导的花生遗传转化新方法. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(2): 518-522. | |
| 42 | Du L, Huang X, Ding L, et al. TaERF87 and TaAKS1 synergistically regulate TaP5CS1/TaP5CR1-mediated proline biosynthesis to enhance drought tolerance in wheat. New Phytologist, 2023, 237(1): 232-250. |
| 43 | Luo D, Liu J, Wu Y, et al. NUCLEAR TRANSPORT FACTOR 2‐LIKE improves drought tolerance by modulating leaf water loss in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). The Plant Journal, 2022, 112(2): 429-450. |
| [1] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [2] | 曾露婧, 王国华. 干旱及复水对荒漠绿洲过渡带一年生草本植物生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 41-57. |
| [3] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [4] | 李玉珠, 余江弟, 丁菲菲, 苗佳敏, 白小明, 师尚礼. 植物遗传转化中体细胞再生的分子机制及应用研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 198-211. |
| [5] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [6] | 王宝强, 马文静, 王贤, 朱晓林, 赵颖, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗次生代谢产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 141-151. |
| [7] | 张一龙, 李雯, 喻启坤, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶与根氮代谢对不同干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [8] | 张浩, 胡海英, 李惠霞, 贺海明, 马霜, 马风华, 宋柯辰. 荒漠草原优势植物牛枝子对干旱胁迫的生理响应与转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| [9] | 梁佳, 胡朝阳, 谢志明, 马刘峰, 陈芸, 方志刚. 外源褪黑素缓解甜高粱幼苗干旱胁迫的生理效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 206-215. |
| [10] | 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 李杭, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [11] | 张一龙, 喻启坤, 李雯, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根地上地下表型特征及内源激素对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 163-178. |
| [12] | 王占军, 季波, 纪童, 蒋齐. 5种豆科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 187-199. |
| [13] | 王升升, 段珍, 周培, 张吉宇. 白花草木樨结瘤缺失型突变体的结瘤表型及生物量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 247-256. |
| [14] | 刘牧野, 郭丽珠, 岳跃森, 武菊英, 范希峰, 肖国增, 滕珂. 干旱胁迫下不同性别野牛草生理及抗氧化酶基因表达差异[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 93-103. |
| [15] | 刘福, 陈诚, 张凯旋, 周美亮, 张新全. 日本百脉根LjbHLH34基因克隆及耐旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||