

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 221-232.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024146
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
贾蕴欢1( ), 胡雯颖1, 邓健1,2(
), 胡雯颖1, 邓健1,2( ), 赵雪3, 陈子玥1, 王亚楠1, 李江文1,2, 张晓曦1,2
), 赵雪3, 陈子玥1, 王亚楠1, 李江文1,2, 张晓曦1,2
收稿日期:2024-04-29
修回日期:2024-07-01
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
邓健
作者简介:E-mail: deng050702@126.com基金资助:
Yun-huan JIA1( ), Wen-ying HU1, Jian DENG1,2(
), Wen-ying HU1, Jian DENG1,2( ), Xue ZHAO3, Zi-yue CHEN1, Ya-nan WANG1, Jiang-wen LI1,2, Xiao-xi ZHANG1,2
), Xue ZHAO3, Zi-yue CHEN1, Ya-nan WANG1, Jiang-wen LI1,2, Xiao-xi ZHANG1,2
Received:2024-04-29
Revised:2024-07-01
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Jian DENG
摘要:
不断加剧的大气氮沉降会改变土壤养分平衡,进而引起土壤微生物养分限制,但目前关于氮沉降对黄土丘陵区草地土壤微生物养分限制特征的影响还不清楚。研究基于野外模拟氮沉降控制试验,通过测定土壤微生物生物量和养分转化酶活性,结合土壤理化性质分析,揭示了不同氮添加水平下草地土壤微生物养分限制特征及其影响因素。结果表明:氮添加导致土壤pH下降,并引起土壤养分平衡特征变化,具体表现为土壤有机碳、全氮含量的增加,而全磷无显著变化;氮添加导致了土壤速效养分含量增加,且速效磷含量增加速率大于可溶性碳和矿质氮,引起速效养分碳氮的相对不足。草地土壤微生物生物量和胞外酶活性在低浓度氮添加下降低,在高浓度氮添加下升高。随着氮添加浓度的增加,草地土壤微生物氮限制加剧而碳限制缓解;微生物碳限制同时还影响着微生物碳利用效率特征;氮添加引起的土壤全量和速效养分不平衡变化通过调控微生物生物量和酶活性共同决定着土壤微生物的养分限制特征。研究为理解氮沉降背景下草地土壤养分循环特征提供了进一步的认识。
贾蕴欢, 胡雯颖, 邓健, 赵雪, 陈子玥, 王亚楠, 李江文, 张晓曦. 氮添加对黄土丘陵区草地土壤微生物养分限制特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 221-232.
Yun-huan JIA, Wen-ying HU, Jian DENG, Xue ZHAO, Zi-yue CHEN, Ya-nan WANG, Jiang-wen LI, Xiao-xi ZHANG. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil microbial nutrient limitation characteristics in grassland in the Loess Hilly Region[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 221-232.
| 指标 Index | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 | N4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.57±0.02a | 8.51±0.03ab | 8.43±0.05bc | 8.44±0.02bc | 8.35±0.02c |
| 有机碳Soil organic carbon (SOC, g·kg-1) | 3.82±0.29ab | 3.24±0.26bc | 2.49±0.06c | 3.05±0.18bc | 4.08±0.12a |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 0.52±0.01b | 0.46±0.01bc | 0.40±0.01c | 0.51±0.01b | 0.66±0.03a |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 0.58±0.01a | 0.58±0.01a | 0.57±0.01a | 0.55±0.02a | 0.61±0.03a |
| 微生物生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon (MBC, mg·kg-1) | 102.43±8.44ab | 76.90±3.14b | 49.82±4.11c | 99.87±5.96ab | 120.98±8.90a |
| 微生物生物量氮Microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN, mg·kg-1) | 20.07±1.67bc | 15.21±0.59cd | 14.08±0.68d | 24.99±1.69ab | 27.75±1.60a |
| 微生物生物量磷Microbial biomass phosphorus (MBP, mg·kg-1) | 3.93±0.38b | 3.21±0.12b | 3.30±0.16b | 5.17±0.10a | 5.57±0.12a |
| β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶β-1,4-glucosidase (BG, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 23.83±2.33ab | 19.73±1.06b | 13.42±0.87c | 20.12±0.84b | 28.51±0.47a |
| β-1,4-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶β-1,4-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAG, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 4.16±0.67b | 4.17±0.58b | 3.90±0.70b | 7.22±0.93ab | 10.30±1.07a |
| 亮氨酸氨基肽酶L-leucine aminopeptidase (LAP, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 18.24±0.93b | 17.58±0.13b | 12.89±0.85c | 16.97±1.18b | 27.48±0.45a |
| 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase (ALP, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 41.92±4.13ab | 39.30±2.29ab | 32.98±2.65b | 39.73±4.19ab | 46.72±1.38a |
| 可溶性有机碳Soluble organic carbon (DOC, mg·kg-1) | 220.41±5.82a | 227.23±9.03a | 227.76±5.89a | 242.25±10.78a | 240.86±2.88a |
| 铵态氮Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N, mg·kg-1) | 4.27±0.45a | 3.94±0.29a | 5.97±1.23a | 5.12±1.06a | 5.03±1.45a |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen (NO3--N, mg·kg-1) | 4.57±0.14a | 3.48±0.26bc | 2.82±0.19c | 3.71±0.24ab | 4.30±0.22ab |
| 速效磷Available phosphorus (AP, mg·kg-1) | 4.89±0.47b | 5.75±0.11ab | 6.53±1.01ab | 7.52±0.78a | 7.75±0.40a |
| 土壤碳氮比Soil C∶N | 8.56±1.60a | 8.29±1.91a | 7.21±0.45a | 7.00±0.81a | 7.23±1.08a |
| 土壤碳磷比 Soil C∶P | 17.13±3.21a | 14.52±2.80ab | 11.30±0.68b | 14.33±2.66ab | 17.49±2.61a |
| 土壤氮磷比Soil N∶P | 2.00±0.09b | 1.76±0.09c | 1.57±0.17c | 2.04±0.17b | 2.42±0.12a |
| 速效碳氮比Soil AC∶N | 25.35±4.59a | 30.61±1.42a | 27.75±9.02a | 27.85±3.34a | 27.92±8.48a |
| 速效碳磷比Soil AC∶P | 46.67±11.62a | 39.61±4.74a | 37.41±12.27a | 33.36±8.68a | 31.39±4.00a |
| 速效氮磷比Soil AN∶P | 1.83±0.13a | 1.29±0.13a | 1.53±0.88a | 1.21±0.38a | 1.24±0.60a |
表1 不同浓度氮添加处理下的土壤理化性质特征
Table 1 Soil physicochemical properties under different nitrogen addition concentration
| 指标 Index | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 | N4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.57±0.02a | 8.51±0.03ab | 8.43±0.05bc | 8.44±0.02bc | 8.35±0.02c |
| 有机碳Soil organic carbon (SOC, g·kg-1) | 3.82±0.29ab | 3.24±0.26bc | 2.49±0.06c | 3.05±0.18bc | 4.08±0.12a |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 0.52±0.01b | 0.46±0.01bc | 0.40±0.01c | 0.51±0.01b | 0.66±0.03a |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 0.58±0.01a | 0.58±0.01a | 0.57±0.01a | 0.55±0.02a | 0.61±0.03a |
| 微生物生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon (MBC, mg·kg-1) | 102.43±8.44ab | 76.90±3.14b | 49.82±4.11c | 99.87±5.96ab | 120.98±8.90a |
| 微生物生物量氮Microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN, mg·kg-1) | 20.07±1.67bc | 15.21±0.59cd | 14.08±0.68d | 24.99±1.69ab | 27.75±1.60a |
| 微生物生物量磷Microbial biomass phosphorus (MBP, mg·kg-1) | 3.93±0.38b | 3.21±0.12b | 3.30±0.16b | 5.17±0.10a | 5.57±0.12a |
| β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶β-1,4-glucosidase (BG, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 23.83±2.33ab | 19.73±1.06b | 13.42±0.87c | 20.12±0.84b | 28.51±0.47a |
| β-1,4-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶β-1,4-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAG, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 4.16±0.67b | 4.17±0.58b | 3.90±0.70b | 7.22±0.93ab | 10.30±1.07a |
| 亮氨酸氨基肽酶L-leucine aminopeptidase (LAP, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 18.24±0.93b | 17.58±0.13b | 12.89±0.85c | 16.97±1.18b | 27.48±0.45a |
| 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase (ALP, nmol·g-1·h-1) | 41.92±4.13ab | 39.30±2.29ab | 32.98±2.65b | 39.73±4.19ab | 46.72±1.38a |
| 可溶性有机碳Soluble organic carbon (DOC, mg·kg-1) | 220.41±5.82a | 227.23±9.03a | 227.76±5.89a | 242.25±10.78a | 240.86±2.88a |
| 铵态氮Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N, mg·kg-1) | 4.27±0.45a | 3.94±0.29a | 5.97±1.23a | 5.12±1.06a | 5.03±1.45a |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen (NO3--N, mg·kg-1) | 4.57±0.14a | 3.48±0.26bc | 2.82±0.19c | 3.71±0.24ab | 4.30±0.22ab |
| 速效磷Available phosphorus (AP, mg·kg-1) | 4.89±0.47b | 5.75±0.11ab | 6.53±1.01ab | 7.52±0.78a | 7.75±0.40a |
| 土壤碳氮比Soil C∶N | 8.56±1.60a | 8.29±1.91a | 7.21±0.45a | 7.00±0.81a | 7.23±1.08a |
| 土壤碳磷比 Soil C∶P | 17.13±3.21a | 14.52±2.80ab | 11.30±0.68b | 14.33±2.66ab | 17.49±2.61a |
| 土壤氮磷比Soil N∶P | 2.00±0.09b | 1.76±0.09c | 1.57±0.17c | 2.04±0.17b | 2.42±0.12a |
| 速效碳氮比Soil AC∶N | 25.35±4.59a | 30.61±1.42a | 27.75±9.02a | 27.85±3.34a | 27.92±8.48a |
| 速效碳磷比Soil AC∶P | 46.67±11.62a | 39.61±4.74a | 37.41±12.27a | 33.36±8.68a | 31.39±4.00a |
| 速效氮磷比Soil AN∶P | 1.83±0.13a | 1.29±0.13a | 1.53±0.88a | 1.21±0.38a | 1.24±0.60a |
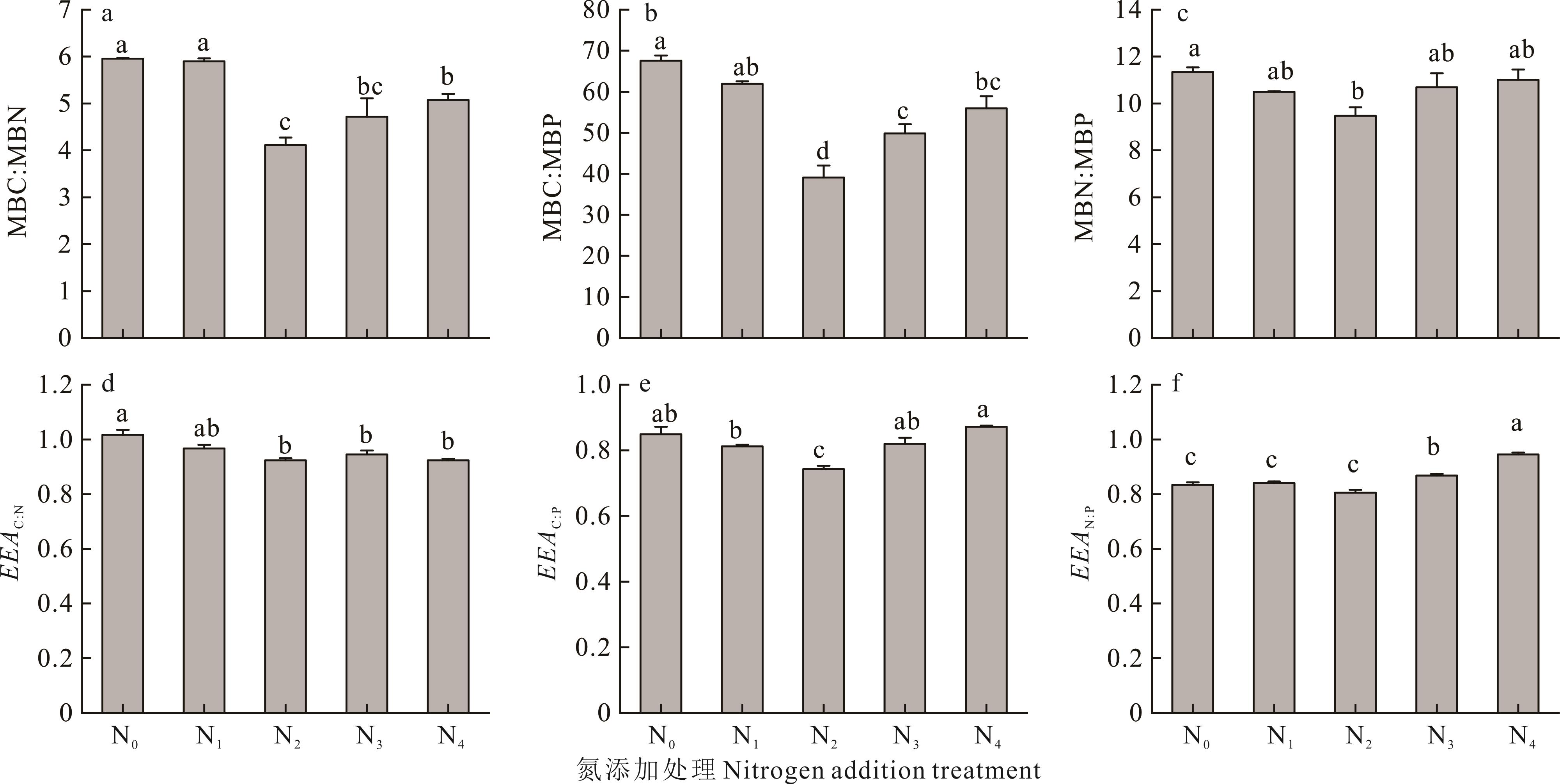
图1 氮添加处理对土壤微生物生物量计量比和胞外酶活性计量比的影响MBC:微生物生物量碳;MBN:微生物生物量氮;MBP:微生物生物量磷;EEAC∶N:酶活性碳氮比;EEAC∶P:酶活性碳磷比;EEAN∶P:酶活性氮磷比,下同。MBC: Microbial biomass carbon; MBN: Microbial biomass nitrogen; MBP: Microbial biomass phosphorus; EEAC∶N: Enzyme activity carbon∶nitrogen; EEAC∶P: Enzyme activity carbon∶phosphorus; EEAN∶P: Enzyme activity nitrogen∶phosphorus, the same below.不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05).
Fig.1 Effects of nitrogen addition on soil microbial biomass and extracellular enzyme activity stoichiometric ratio
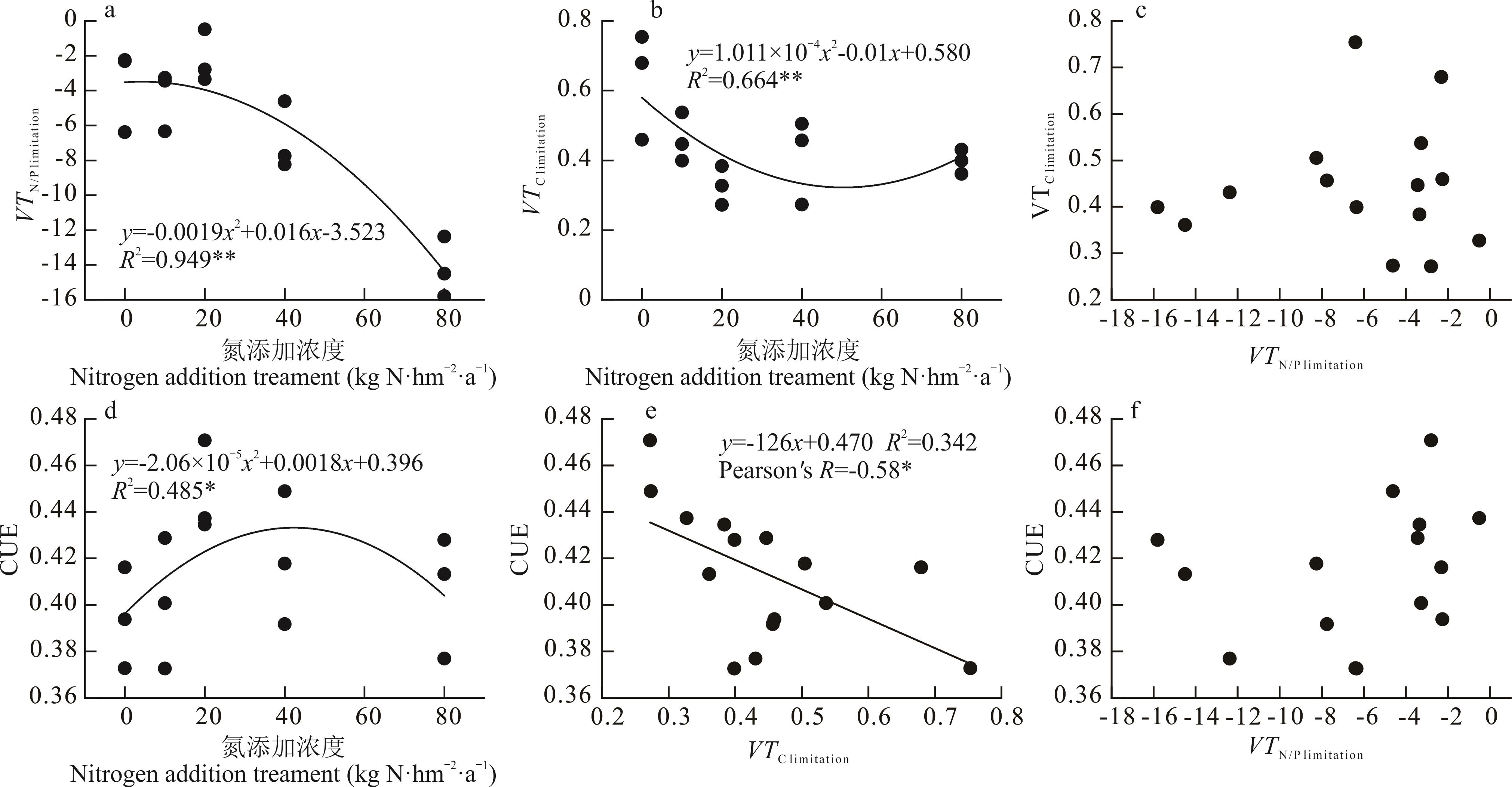
图2 氮添加处理下的土壤微生物养分限制特征、碳利用效率及其关系a:不同氮添加水平下的土壤氮/磷限制指标VTN/P limitation;b:不同氮添加水平下的土壤碳限制指标VTC limitation;d:不同氮添加水平下的土壤微生物碳利用效率;VTC limitation:碳限制,VTN/P limitation:氮磷限制,CUE:碳利用率;*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平上显著相关,没有标记表示相关性不显著,下同。a: Soil nitrogen/phosphorus limitation under different nitrogen addition levels; b: Soil carbon limitation under different nitrogen addition levels; d: Soil microbial carbon use efficiency under different nitrogen addition levels; VTC limitation: Carbon limitation, VTN/P limitation: Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation, CUE: Carbon use efficiency; * and ** indicate significant correlation at the P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively, and no marker indicates that the correlation is not significant, the same below.
Fig.2 Characteristics of soil microbial nutrient limitation, carbon use efficiency and their relationship under nitrogen addition treatment
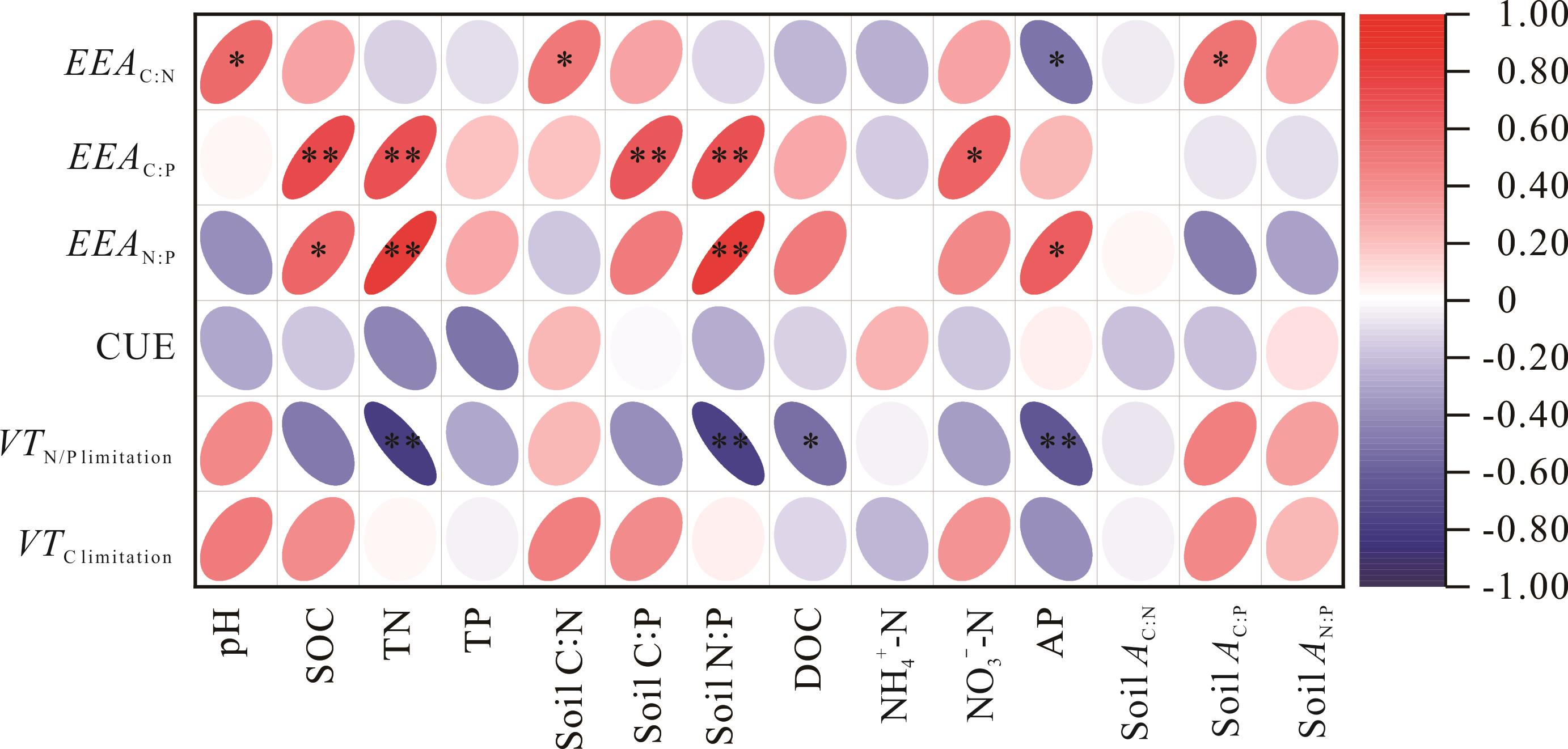
图3 土壤理化性质与微生物养分限制特征和碳利用效率的关系椭圆方向顺时针表示正相关,逆时针表示负相关;椭圆颜色越深表示相关系数越高;pH:酸碱度;SOC:有机碳;TN:全氮;TP:全磷;Soil C∶N:土壤碳氮比;Soil C∶P:土壤碳磷比;Soil N∶P:土壤氮磷比;DOC:可溶性有机碳;NH4+-N:铵态氮;NO3—-N:硝态氮;AP:速效磷;Soil AC∶N:速效碳氮比;Soil AC∶P:速效碳磷比;Soil AN∶P:速效氮磷比,下同。The elliptic direction indicates a positive correlation clockwise, and the counterclockwise indicates a negative correlation, and the darker the ellipse, the higher the correlation coefficient; SOC: Soil organic carbon; TN: Total nitrogen; TP: Total phosphorus; Soil C∶N: Soil carbon∶nitrogen; Soil C∶P: Soil carbon∶phosphorus; Soil N∶P: Soil nitrogen∶phosphorus; DOC: Soluble organic carbon; NH4+-N: Ammonium nitrogen; NO3—-N: Nitrate nitrogen; AP: Available phosphorus; Soil AC∶N: Available carbon∶nitrogen; Soil AC∶P: Available carbon∶phosphorus; Soil AN∶P: Available nitrogen∶phosphorus, the same below.
Fig.3 Relationship between soil physicochemical properties and microbial nutrient limitation characteristics and carbon use efficiency
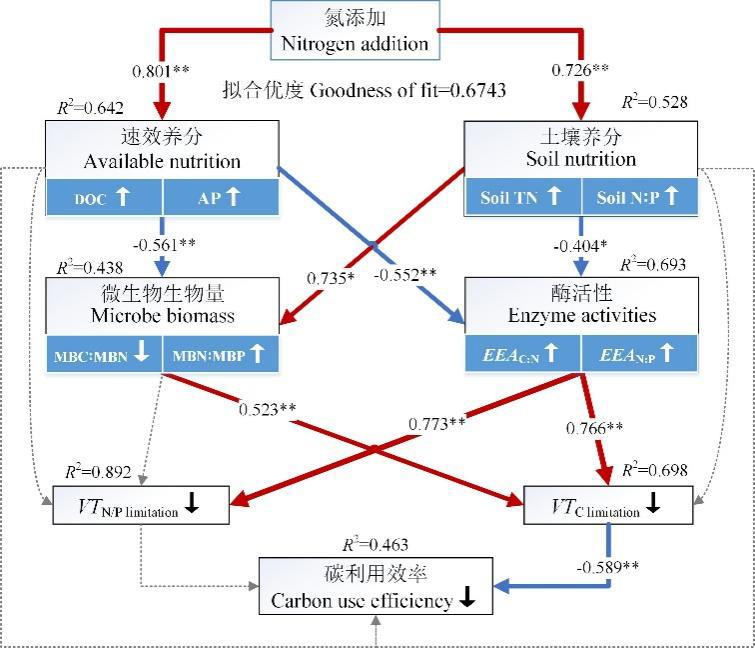
图4 氮添加调控土壤养分限制和碳利用效率的偏最小二乘回归分析图中实线表示影响路径显著(P<0.05),虚线表示不显著,显著的路径箭头上标注了标准化路径系数和显著性水平,潜变量附近的R2表示由模型解释的因变量方差;潜变量下部的指标为模型分析使用的观测变量,指标名称旁边的箭头表示该指标随着氮添加浓度增加总体呈现增加(↑)或降低(↓)趋势。The solid line indicates that the influence path is significant (P<0.05), the dotted line indicates that it is not significant, and the significant path arrows indicate the normalized path coefficient and significance level, R2 near the latent variable represents the variance of the dependent variable explained by the model, and the indicator in the lower part of the latent variable is the observed variable used in the model analysis, and the arrow next to the indicator name indicates that the index shows an overall increasing (↑) or decreasing (↓) trend with the increase of nitrogen addition concentration.
Fig.4 Partial least squares regression analysis of nitrogen addition regulating soil nutrient limitation and carbon use efficiency
| 1 | Bao P A, Qiu K Y, Huang Y Y, et al. Leaf functional trait characteristics and plasticity of desert steppe plants under nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 97-106. |
| 鲍平安, 邱开阳, 黄业芸, 等. 荒漠草原植物在氮磷添加下叶功能性状特征及其可塑性. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 97-106. | |
| 2 | Zhang Y, Zhang C H, Wang Q T, et al. Difference of soil carbon sequestration between rhizosphere and bulk soil in a mountain coniferous forest in southwestern China under nitrogen deposition. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(4): 473-483. |
| 张英, 张常洪, 汪其同, 等. 氮沉降下西南山地针叶林根际和非根际土壤微生物养分限制特征差异. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(4): 473-483. | |
| 3 | Fu W, Wu H, Zhao A H, et al. Ecological impacts of nitrogen deposition on terrestrial ecosystems: research progresses and prospects. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(5): 475-493. |
| 付伟, 武慧, 赵爱花, 等. 陆地生态系统氮沉降的生态效应:研究进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(5): 475-493. | |
| 4 | Zhang X, Zhao W B, Liu Y X, et al. The relationships between grasslands and soil moisture on the Loess Plateau of China: A review. Catena, 2016, 145: 56-67. |
| 5 | Zhu R F, Tang F L, Liu J L, et al. Response of soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen on a short-term fertilizing N in Leymus chinensis meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(3): 553-558. |
| 朱瑞芬, 唐凤兰, 刘杰淋, 等. 羊草草甸草原土壤微生物生物量碳氮对短期施氮的响应. 草地学报, 2016, 24(3): 553-558. | |
| 6 | Zhang T A, Chen Y H, Ruan H H, et al. Global negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil microbes. Multidisciplinary Journal of Microbial Ecology, 2018, 12(7): 1817-1825. |
| 7 | Xu Q M, Gu X M, Wang Y Y, et al. Simulated nitrogen deposition significantly increases nitrous oxide emission rate from alpine grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(12): 3785-3792. |
| 许庆民, 顾晓梦, 王云英, 等. 模拟氮沉降显著提高青藏高原高寒草地氧化亚氮排放速率. 草地学报, 2023, 31(12): 3785-3792. | |
| 8 | Wang X Y, Li Y Q, Wang L L, et al. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects microbial metabolic limitations in different desert types of northwestern China. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 874: 162504. |
| 9 | Shen F Y, Liu N, Chen F S, et al. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reveals the increased P limitation of microbial metabolism after the mixed cultivation of Korean pine and Manchurian walnut in Northeast China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2023, 118: 103539. |
| 10 | Guo Y H, Zhao H T, Gao Y, et al. Effect of inorganic nitrogen addition on soil microbial nutrient requirement strategy in the Pinus tabuliformis forest in Taiyue Mountain, Shanxi Province. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(1): 137-144. |
| 郭银花, 赵洪涛, 高雨, 等. 山西太岳山油松林无机氮添加对土壤微生物养分限制类型的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(1): 137-144. | |
| 11 | Moorhead D L, Rinkes Z L, Sinsabaugh R L, et al. Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: informing enzyme-based decomposition models. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2013, 4: 223. |
| 12 | Cui Y X, Wang X, Zhang X C, et al. Soil moisture mediates microbial carbon and phosphorus metabolism during vegetation succession in a semiarid region. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2020, 147: 107814. |
| 13 | Cui Y X, Moorhead D L, Guo X B, et al. Stoichiometric models of microbial metabolic limitation in soil systems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2021, 30(11): 2297-2311. |
| 14 | Xu M P, Li W J, Wang J Y, et al. Soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815: 152918. |
| 15 | Cao Y Y, Su X M, Zhou Z C, et al. Spatial differences in, and factors influencing, the shear strength of typical herb root-soil complexes in the Loess Plateau of China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(5): 94-105. |
| 曹玉莹, 苏雪萌, 周正朝, 等. 黄土高原典型草本植物根-土复合体抗剪性能的空间差异性及其影响因素研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 94-105. | |
| 16 | Yao N, Liu G Q, Yao S B, et al. Evaluating on effect of conversion from farmland to forest and grassland project on ecosystem carbon storage in loess hilly-gully region based on InVEST model. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 42(5): 329-336. |
| 姚楠, 刘广全, 姚顺波,等. 基于InVEST模型的黄土丘陵沟壑区退耕还林还草工程对生态系统碳储量的影响评估. 水土保持通报, 2022, 42(5): 329-336. | |
| 17 | Yao Y W, Ren H R. Estimation of grassland aboveground biomass in northern China based on topography-climate-remote sensing data. Ecological Indicators, 2024, 165: 112230. |
| 18 | Deng J, Zhao X, Lu X Y, et al. Different responses of enzymes activities related to nitrogen and phosphorus transformation to nitrogen addition in different sized soil aggregates in semi-arid grassland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(16): 6539-6549. |
| 邓健, 赵雪, 卢笑玥, 等. 半干旱草地土壤团聚体氮磷转化相关酶活性对氮添加的响应. 生态学报, 2023, 43(16): 6539-6549. | |
| 19 | Han Y H, Dong S K, Zhao Z Z, et al. Response of soil nutrients and stoichiometry to elevated nitrogen deposition in alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma, 2019, 343: 263-268. |
| 20 | Wei Y, Tong Y A, Qiao L, et al. Preliminary estimate of the atmospheric nitrogen deposition in different ecological regions of Shaanxi province. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(4): 795-800. |
| 魏样, 同延安, 乔丽, 等. 陕西省不同生态区大气氮沉降量的初步估算. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(4): 795-800. | |
| 21 | Zheng H, Xue J B, Hao J, et al. Effects of short-term different N addition levels on phosphorus components in a saline-alkaline grassland in North China. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(3): 712-720. |
| 郑慧, 薛江博, 郝杰, 等. 短期不同水平氮添加对华北盐渍化草地土壤磷组分的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(3): 712-720. | |
| 22 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (3rd edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 23 | Zhang W, Xu Y D, Gao D X, et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient dynamics along a revegetation chronosequence in the soils of abandoned land and Robinia pseudoacacia plantation on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 134: 1-14. |
| 24 | Geng J, Cheng S L, Fang H J, et al. The effects of types and doses of nitrogen addition on soil N2O flux in a cold-temperate coniferous forest, northern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(2): 395-404. |
| 耿静, 程淑兰, 方华军, 等. 氮素类型和剂量对寒温带针叶林土壤N2O排放的影响. 生态学报, 2017, 37(2): 395-404. | |
| 25 | Guo J Y, Wang Y X, Li J L, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on plant-soil carbon dynamics in terrestrial ecosystems of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(12): 4823-4833. |
| 郭洁芸, 王雅歆, 李建龙, 等. 氮添加对中国陆地生态系统植物-土壤碳动态的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(12): 4823-4833. | |
| 26 | Liu Y W, Bai W, Yin P S, et al. Effects of exogenous nitrogen addition on soil nutrients and plant community biomass in alpine swamp meadow in the headwaters region of the Yangtze River. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 483-491. |
| 刘永万, 白炜, 尹鹏松, 等. 外源氮素添加对长江源区高寒沼泽草甸土壤养分及植物群落生物量的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 483-491. | |
| 27 | Reay D S, Dentener F, Smith P, et al. Global nitrogen deposition and carbon sinks. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1: 430-437. |
| 28 | Liu S W, Yin M, Chu G, et al. Research progress of soil nitrogen priming effect and its microbial mechanisms. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 303-312. |
| 刘少文, 殷敏, 褚光, 等. 土壤氮激发效应及其微生物机理研究进展. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 303-312. | |
| 29 | Huang J, Wang G F, An S Z, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the vegetation structure and biomass of degraded meadow and soil fertility. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(3): 75-78. |
| 黄军, 王高峰, 安沙舟, 等. 施氮对退化草甸植被结构和生物量及土壤肥力的影响. 草业科学, 2009, 26(3): 75-78. | |
| 30 | Li R, Chang R Y. Effects of external nitrogen additions on soil organic carbon dynamics and the mechanism. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(10): 1012-1020. |
| 李嵘, 常瑞英. 土壤有机碳对外源氮添加的响应及其机制. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(10): 1012-1020. | |
| 31 | Fang Y, Xun F, Bai W M, et al. Long-term nitrogen addition leads to loss of species richness due to litter accumulation and soil acidification in a temperate steppe. PLoS One, 2012, 7(10): e47369. |
| 32 | Yang J Q, Diao H J, Hu S Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition at different levels on soil microorganisms in saline-alkaline grassland of northern China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2021, 45(7): 780-789. |
| 杨建强, 刁华杰, 胡姝娅, 等. 不同水平氮添加对盐渍化草地土壤微生物特征的影响. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(7): 780-789. | |
| 33 | Zhao M Z. Desorption of phosphate on some soils and clay minera. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1988, 25(2): 156-163. |
| 赵美芝. 几种土壤和粘土矿物上磷的解吸. 土壤学报, 1988, 25(2): 156-163. | |
| 34 | Ma Y J, Xu F L, Wang W L, et al. Increase of soil nutrients and enzymatic activity by adding nitrogen and phosphorus to Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2015, 21(3): 664-674. |
| 马亚娟, 徐福利, 王渭玲, 等. 氮磷提高华北落叶松人工林地土壤养分和酶活性的作用. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(3): 664-674. | |
| 35 | Sinsabaugh R L, Lauber C L, Weintraub M N, et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecology Letters, 2008,11: 1252-1264. |
| 36 | Ma W J, Li J, Gao Y, et al. Responses of soil extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community properties to interaction between nitrogen addition and increased precipitation in a semi-arid grassland ecosystem. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 703: 134691. |
| 37 | Claudia M B, Ed K H, Karolien D, et al. Long-term reactive nitrogen loading alters soil carbon and microbial community properties in a subalpine forest ecosystem. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2016, 92: 211-220. |
| 38 | Chang E H, Chung R S, Trai Y H, et al. Effect of different application rates of organic fertilizer on soil enzyme activity and microbial population. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2007, 53(2): 132-140. |
| 39 | Lu X K, Mo J M, Zhang W, et al. Effects of simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition on forest ecosystems in China: An overview. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2019, 27(5): 500-522. |
| 鲁显楷, 莫江明, 张炜, 等. 模拟大气氮沉降对中国森林生态系统影响的研究进展. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2019, 27(5): 500-522. | |
| 40 | Zhang X B, Zhang Z H, Lu X K. Responses of soil microbial carbon use efficiency to elevated nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystem. Advances in Earth Science, 2023, 38(10): 999-1014. |
| 张雪冰, 张泽和, 鲁显楷. 森林生态系统土壤微生物碳利用效率对氮沉降增加的响应及其机制. 地球科学进展, 2023, 38(10): 999-1014. | |
| 41 | Liu J B, Kathleen M R, Chen J H, et al. Aerosol-weakened summer monsoons decrease lake fertilization on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Nature Climate Change, 2017, 7(3): 190-194. |
| 42 | Zak D R, Holmes W, Burton A J, et al. Simulated atmospheric NO3 - deposition increases soil organic matter by slowing decomposition. Ecological Applications, 2008, 18(8): 2016-2027. |
| 43 | Wu J P, Wang S M, Cai M T, et al. Review on carbon use efficiency of plants and microbes and its influencing factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20): 7771-7779. |
| 吴建平, 王思敏, 蔡慕天, 等. 植物与微生物碳利用效率及影响因子研究进展. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20): 7771-7779. | |
| 44 | Cleveland C C, Liptzin D. C∶N∶P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry, 2007, 85(3): 235-252. |
| 45 | Keiblinger K M, Hall E K, Wanek W, et al. The effect of resource quantity and resource stoichiometry on microbial carbon-use-efficiency. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2010, 73(3): 430-440. |
| 46 | Li J, Sang C P, Yang J Y, et al. Stoichiometric imbalance and microbial community regulate microbial elements use efficiencies under nitrogen addition. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2021, 156(1): 108207. |
| 47 | Sun X Q, Dai H, Zeng Q X, et al. The influence of soil microbial community structure on microbial carbon use efficiency under nitrogen addition. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(4): 1737-1746. |
| 孙雪琦, 戴辉, 曾泉鑫, 等. 氮添加土壤微生物群落结构影响微生物碳利用效率. 生态学报, 2024, 44(4): 1737-1746. |
| [1] | 吕娜, 高吉喜, 李政海, 尤春赫, 刘晓曼, 张彪, 莫宇, 朱萨宁, 彭阳, 杨雪. 植物生长中期施肥对草甸草原群落特征与物种多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 109-122. |
| [2] | 张振豪, 贾子玉, 李鑫宇, 程云湘. 荒漠草原混牧牛羊的放牧行为特征[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 226-237. |
| [3] | 阿斯太肯·居力海提null, 孙宗玖, 于冰洁, 迪达尔·比苏力旦null, 李美莎, 敬一胜. 封育对蒿类荒漠草地土壤微生物碳源利用特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 29-40. |
| [4] | 贺世龙, 叶贺, 李静, 张雅玲, 德海山, 红梅. 不同时限氮沉降和降水变化对荒漠草原中小型土壤节肢动物群落结构与多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 140-154. |
| [5] | 徐玲玲, 牛犇, 张宪洲, 何永涛, 石培礼, 宗宁, 武建双, 王向涛. 藏北两个临近不同高寒草地碳通量对气候条件的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 1-16. |
| [6] | 黄琳曦, 陈倩, 张先言, 闫顺, 杨云, 辛培尧, 汪琼. 两种乔木凋落叶浸提液处理对地毯草土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 35-46. |
| [7] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [8] | 马源, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 张德罡. 高寒草甸退化程度对优势物种根际土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 125-137. |
| [9] | 石昊, 杨彩红, 夏菲, 王军强, 魏巍, 王敬龙, 薛云尹, 郑晒坤, 吴皓阳, 冉林灵, 严双, 姜晓敏. 短期增温对修复过程中藏北高寒退化草地生产力的初期影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 30-45. |
| [10] | 田晴华, 刘丹, 廖小琴, 宋小艳, 胡雷, 王长庭. 施氮对高寒草地土壤团聚体生物胶结物质及稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 46-57. |
| [11] | 赵文军, 刘蕊, 王正旭, 冯瑜, 薛开政, 刘魁, 徐梓荷, 曹卫东, 付利波, 尹梅, 陈华. 烤烟-绿肥轮作对云南烟田土壤质量与微生物养分限制的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 147-158. |
| [12] | 余万洋, 陈怡帆, 方发永, 张金鑫, 李舟, 赵龙山. 1980-2020年贵州省草地空间分布格局演变及驱动力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-18. |
| [13] | 杨志贵, 张建国, 李锦荣, 于红妍, 常丽, 宜树华, 吕燕燕, 张玉琢, 孟宝平. 内蒙古温性草原草地类型近20年时空动态变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 1-16. |
| [14] | 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| [15] | 张慧龙, 杨秀春, 杨东, 陈昂, 张敏. 2000-2020年内蒙古草地植被覆盖度时空变化及趋势预测[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 1-13. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||